oil CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 101 of 1938

(5) With the aid of a helper, apply pressure to the
brake pedal until a pressure of 6895 kPa (1000 psi) is
obtained on the proportioning valve inlet gauge.
Then based on the type of brake system the vehicle is
equipped with and the pressure specification shown
on the following table, compare the pressure reading
on the outlet gauge to the specification. If outlet
pressure at the proportioning valve is not within
specification when required inlet pressure is
obtained, replace the proportioning valve.
(6) Remove the pressure test fittings and pressure
gauges from the proportioning valve.
(7) Install the chassis brake lines in the correct
ports of the proportioning valve.
(8) Install the pressure test fittings and pressure
gauges in the opposite inlet and outlet port of the
height sensing proportioning valve. Repeat steps 4
and 5 for the other proportioning valve.
(9) Remove the pressure test fittings and pressure
gauges from the proportioning valve.
(10) Install the chassis brake lines in the correct
ports of the proportioning valve.
(11) Install the actuator (Fig. 22) on the height
sensing proportioning valve. Adjust the proportioning
valve actuator. See Height Sensing Proportioning
Valve in the Adjustment Section in this group of the
service manual for the adjustment procedure.
(12) Bleed both rear hydraulic circuits at the rear
brakes.
(13) Road test vehicle.
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or deteri-
orated rubber parts.
Swollen rubber parts indicate the presence of
petroleum in the brake fluid.To test for contamination, put a small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If fluid sepa-
rates into layers, there is mineral oil or other fluid
contamination of the brake fluid.
If brake fluid is contaminated, drain and thor-
oughly flush system. Replace master cylinder, propor-
tioning valve, caliper seals, wheel cylinder seals,
Antilock Brakes hydraulic unit and all hydraulic
fluid hoses.
RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP TEST
For diagnosis of specific problems with the red
brake warning lamp system, refer to Brake System
Diagnostics Chart 2, located in the Diagnosis And
Testing section in this group of the service manual.
TRACTION CONTROL LAMP TEST
The traction control light is tested by cycling the
traction control switch on and off. The traction con-
trol switch used on this vehicle is a momentary con-
tact type switch. The test procedure for the traction
control light is performed as follows: Press the trac-
tion control switch once and the ªTrac Offº lamp will
illuminate. With the ªTrac Offº lamp illuminated,
press the traction control switch again and the ªTrac
Offº lamp will turn off.
If the traction control lamp does not function as
described in the test above, diagnosis of the traction
control switch, lamp, wiring and other related compo-
nents of the traction control system is required.
STOP LAMP SWITCH TEST PROCEDURE
The required procedure for testing the stop lamp
switch is covered in Group 8H, Vehicle Speed Control
System in this service manual. The electrical circuit
tests for stop lamps is covered in Group 8W Rear-
Lighting in this service manual.
WHEEL
BASEDRIVE
TRAINSALES CODEBRAKE SYS-
TEMSPLIT POINT SLOPEINLET PRES-
SURE PSIOUTLET
PRESSURE
PSI
SWB FWD BRA+BGF149DISC/DRUM
W/O ANTILOCKVAR. .30 1000 PSI 250-350 PSI
SWB FWDBRA+BGF
BRB+BGF
BRV+BGF149,159,159HD
DISC/DRUM
WITH ANTILOCK25 BAR .59 1000 PSI660-780
PSI
LWB FWD BRA+BGF149DISC/DRUM
W/O ANTILOCKVAR. .30 1000 PSI 250-350 PSI
LWB FWDBRA+BGF
BRB+BGF
BRV+BGF149,159,159HD
DISC/DRUM
WITH ANTILOCK25 BAR .59 1000 PSI 660-780 PSI
SWB AWD BRE+BGF159DISC/DISC
WITH ANTILOCK25 BAR .36 1000 PSI 525-640 PSI
LWB AWD BRE+BGF159DISC/DISC
WITH ANTILOCK41 BAR .36 1000 PSI 690-800 PSI
NSBRAKES 5 - 19
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 102 of 1938

SERVICE PROCEDURES
MASTER CYLINDER FLUID LEVEL CHECK
Check master cylinder reservoir fluid level a mini-
mum of twice annually.
Master cylinder reservoirs are marked with the
words FULL and ADD to indicate proper brake fluid
fill level of the master cylinder (Fig. 26).
If necessary, add brake fluid to bring the level to
the bottom of the FULL mark on the side of the mas-
ter cylinder fluid reservoir.When filling master
cylinder fluid reservoir do not fill the filler
neck of the fluid reservoir (Fig. 26) with brake
fluid.
Use only Mopartbrake fluid or an equivalent from
a sealed container. Brake fluid must conform to DOT
3, specifications.
DO NOTuse brake fluid with a lower boiling
point, as brake failure could result during prolonged
hard braking.
Use only brake fluid that was stored in a tightly-
sealed container.
DO NOTuse petroleum-based fluid because seal
damage will result. Petroleum based fluids would be
items such as engine oil, transmission fluid, power
steering fluid ect.
BLEEDING BASE BRAKE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
NOTE: This bleeding procedure is only for the vehi-
cle's base brakes hydraulic system. For bleeding
the antilock brakes hydraulic system, refer to the
ITT Teves Mark 20 Antilock Brake System bleeding
procedure in the antilock brakes section of this ser-
vice manual.
PRESSURE BLEEDING PROCEDURE
CAUTION: Before removing the master cylinder
cover, throughly clean the cover and master cylin-
der fluid reservoir to prevent dirt and other foreign
matter from dropping into the master cylinder fluid
reservoir.
CAUTION: Use bleeder tank Special Tool C-3496-B
with adapter Special Tool 6921 to pressurize the
hydraulic system for bleeding.
CAUTION: When pressure bleeding the brakes
hydraulic system the fluid reservoir filler neck must
be removed from the master cylinder fluid reservoir.
Failure to remove the filler neck from the fluid res-
ervoir, may result in the filler neck separating from
the fluid reservoir when the hydraulic system is
pressurized.
Follow pressure bleeder manufacturer's instruc-
tions, for use of pressure bleeding equipment.
When bleeding the brake system, some air may be
trapped in the brake lines or valves far upstream, as
much as ten feet from the bleeder screw (Fig. 27).
Therefore, it is essential to have a fast flow of a large
volume of brake fluid when bleeding the brakes to
ensure all the air gets out.
(1) Remove the filler neck from the master cylin-
der fluid reservoir.
(2) Install the Adapter Master Cylinder Pressure
Bleed Cap, Special Tool 6921 on the fluid reservoir of
the master cylinder (Fig. 28). Attach the fluid hose
from the pressure bleeder to the fitting on Special
Tool 6921.
(3) Attach a clear plastic hose to the bleeder screw
at one wheel and feed the hose into a clear jar con-
taining fresh brake fluid.
Fig. 26 Master Cylinder Fluid Level Marks
Fig. 27 Trapped Air In Brake Fluid Line
5 - 20 BRAKESNS
Page 109 of 1938

(4) Remove the locking pliers from the front park
brake cable. This will allow the adjuster in the park
brake pedal mechanism to rotate around to its stop.
This will remove the tension from the adjuster and
front park brake cable.
Use the following procedure to reset the auto
adjuster in the park brake pedal mechanism.
(5) Grasp the exposed section of the front park
brake cable and pull rearward on it. While holding
the park brake in this position, install a pair of lock-
ing pliers on the front park brake cable just rearward
of the second body outrigger bracket (Fig. 42).
(6) Install the equalizer on the front park brake
cable.
(7) Install the left rear and intermediate park
brake cable in the correct location on the park brake
cable equalizer (Fig. 43).
(8) Remove the locking pliers from the front park
brake cable. This will allow the adjuster in the park
brake pedal mechanism to tension the park brake
cables.
(9) Apply and release the park brake pedal one
time. This will seat the park brake cables and allow
the auto adjuster in the park brake pedal mechanism
to correctly tension the park brake cables.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
WHEEL AND TIRE INSTALLATION
To install the wheel and tire assembly, first posi-
tion it properly on the mounting surface using the
hub pilot as a guide. Then progressively tighten thelug nuts in the proper sequence to half of the
required torque. Finally tighten the lug nuts in the
proper sequence to 129 N´m (95 ft. lbs.). Never use
oil or grease on studs or nuts.
FRONT DISC BRAKE CALIPER
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
WARNING: ALTHOUGH FACTORY INSTALLED
BRAKE LININGS ARE MADE FROM ASBESTOS
FREE MATERIALS, SOME AFTER MARKET BRAKE
LINING MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS. THIS SHOULD
BE TAKEN INTO ACCOUNT WHEN SERVICING A
VEHICLE'S BRAKE SYSTEM, WHEN AFTERMARKET
BRAKE LININGS MAY HAVE BEEN INSTALLED ON
THE VEHICLE. ALWAYS WEAR A RESPIRATOR
WHEN CLEANING BRAKE COMPONENTS AS
ASBESTOS CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM
SUCH AS ASBESTOSIS AND OR CANCER. NEVER
CLEAN BRAKE COMPONENTS BY USING COM-
PRESSED AIR, USE ONLY A VACUUM CLEANER
SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR THE REMOVAL OF
BRAKE DUST. IF A VACUUM CLEANER IS NOT
AVAILABLE, CLEAN BRAKE PARTS USING ONLY
WATER±DAMPENED SHOP TOWELS. DO NOT CRE-
ATE BRAKELINING DUST BY SANDING BRAKE LIN-
INGS WHEN SERVICING A VEHICLE. DISPOSE OF
ALL DUST AND DIRT SUSPECTED OF CONTAINING
ASBESTOS FIBERS USING ONLY SEALED AIR-
TIGHT BAGS OR CONTAINERS. FOLLOW ALL REC-
OMMENDED SAFETY PRACTICES PRESCRIBED BY
THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMIN-
ISTRATION (OSHA) AND THE ENVIRONMENTAL
PROTECTION AGENCY (EPA), FOR HANDLING AND
DISPOSAL OF PRODUCTS CONTAINING ASBES-
TOS.
CAUTION: During service procedures, grease or
any other foreign material must be kept off brake
shoe assemblies, and braking surfaces of brake
drum and external surfaces of hub/bearing assem-
bly.
REMOVE
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
hoist. See Hoisting in the Lubrication and Mainte-
nance group of this service manual.
(2) Remove front wheel and tire assemblies.
Fig. 43 Park Brake Cable Attachment To Equalizer
NSBRAKES 5 - 27
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 160 of 1938

REAR DRUM BRAKE WHEEL CYLINDER
With brake drums removed, inspect the wheel cyl-
inder boots for evidence of a brake fluid leak. Visu-
ally check the boots for cuts, tears, or heat cracks. If
any of these conditions exist, the wheel cylinders
should be completely cleaned, inspected and new
parts installed.
If a wheel cylinder is leaking and the brake lining
material is saturated with brake fluid, the brake
shoes must be replaced.
BRAKE HOSE AND BRAKE LINES INSPECTION
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes
and at the rear axle. Inspection of brake hoses
should be performed whenever the brake system is
serviced and every 7,500 miles or 12 months, which-
ever comes first (every engine oil change). Inspect
hydraulic brake hoses for surface cracking, scuffing,
or worn spots. If the fabric casing of the rubber hose
becomes exposed due to cracks or abrasions in the
rubber hose cover, the hose should be replaced imme-
diately. Eventual deterioration of the hose can take
place with possible burst failure. Faulty installation
can cause twisting, resulting in wheel, tire, or chassis
interference.
The steel brake tubing should be inspected period-
ically for evidence of physical damage or contact with
moving or hot components.
The flexible brake tube sections used on this vehi-
cle in the primary and secondary tubes from the
master cylinder to the ABS hydraulic control unit
connections and the chassis brake tubes between the
hydraulic control unit and the proportioning valve
must also be inspected. This flexible tubing must be
inspected for kinks, fraying and its contact with
other components of the vehicle or contact with the
body of the vehicle.
REAR WHEEL HUB AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
The rear hub and bearing assembly is designed for
the life of the vehicle and should require no mainte-
nance. The following procedure may be used for eval-
uation of bearing condition.
With wheel and brake drum removed, rotate
flanged outer ring of hub. Excessive roughness, lat-
eral play or resistance to rotation may indicate dirt
intrusion or bearing failure. If the rear wheel bear-
ings exhibit these conditions during inspection, the
hub and bearing assembly should be replaced.
Damaged bearing seals and resulting excessive
grease loss may also require bearing replacement.
Moderate grease loss from bearing is considered nor-
mal and should not require replacement of the hub
and bearing assembly.
ADJUSTMENTS
STOP LAMP SWITCH
(1) Remove stop lamp switch from its bracket by
rotating it approximately 30É in a counter-clockwise
direction.
(2) Disconnect wiring harness connector from stop
lamp switch.
(3) Hold stop lamp switch firmly in one hand.
Then using other hand, pull outward on the plunger
of the stop lamp switch until it has ratcheted out to
its fully extended position.
(4) Install the stop lamp switch into the bracket
using the following procedure. Depress the brake
pedal as far down as possible. Then while keeping
the brake pedal depressed, install the stop lamp
switch into the bracket by aligning index key on
switch with slot at top of square hole in mounting
bracket. When switch is fully installed in the square
hole of the bracket, rotate switch clockwise approxi-
mately 30É to lock the switch into the bracket.
CAUTION: Do not use excessive force when pulling
back on brake pedal to adjust the stop lamp switch.
If too much force is used, damage to the vacuum
booster, stop lamp switch or striker (Fig. 195) can
result.
(5) Connect the wiring harness connector to the
stop lamp switch.
(6) Gently pull back on brake pedal until the pedal
stops moving. This will cause the switch plunger
(Fig. 195) to ratchet backward to the correct position.
Fig. 195 Stop Light Switch Location In Vehicle
5 - 78 BRAKESNS
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 164 of 1938

(13) Lower the vehicle to the ground.Be sure
that the suspension is supporting the full
weight of the vehicle.
(14) Tighten the spring to front hanger pivot bolts
to a torque of 156 N´m (115 ft. lbs.).
(15) Tighten the shock absorber mounting bolts to
a torque of 101 N´m (75 ft. lbs.).
(16) Tighten the track bar mounting bolt to a
torque of 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(17) Road test vehicle to ensure that the prema-
ture rear wheel lockup condition has been corrected.
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID
The brake fluid used in this vehicle must conform
to DOT 3 specifications and SAE J1703 standards.No other type of brake fluid is recommended or
approved for usage in the vehicle brake system. Use
only Mopar brake fluid or an equivalent from a
tightly sealed container.
CAUTION: Never use reclaimed brake fluid or fluid
from an container which has been left open. An
open container will absorb moisture from the air
and contaminate the fluid.
CAUTION: Never use any type of a petroleum-
based fluid in the brake hydraulic system. Use of
such type fluids will result in seal damage of the
vehicle brake hydraulic system causing a failure of
the vehicle brake system. Petroleum based fluids
would be items such as engine oil, transmission
fluid, power steering fluid ect.
VEHICLE BRAKE SYSTEM COMPONENT SPECIFICATIONS
Brake System Component Specifications
5 - 82 BRAKESNS
ADJUSTMENTS (Continued)
Page 173 of 1938

The primary functions of the (CAB) are:
(1) Detect wheel locking or wheel slipping tenden-
cies by monitoring the speed of all four wheels of the
vehicle.
(2) Illuminate the TRAC lamp in the message cen-
ter on the instrument panel when a traction control
event is occurring.
(3) Control fluid modulation to the wheel brakes
while the system is in an ABS mode or the traction
control system is activated.
(4) Monitor the system for proper operation.
(5) Provide communication to the DRB Scan Tool
while in diagnostic mode.
(6) Store diagnostic information.
(7)The CAB continuously communicates with
the body controller by sending out a message to
the body controller on the CCD Bus. This mes-
sage is used for illumination of the yellow
antilock warning lamp. This is used if the ABS
controller communication is lost in the hard
wire between the body controller and the yel-
low antilock warning lamp. If the body control-
ler does not receive this message from the CAB,
the body controller will illuminate the antilock
yellow warning lamp.
The CAB continuously monitors the speed of each
wheel through the signals generated by the wheel
speed sensors to determine if any wheel is beginning
to lock. When a wheel locking tendency is detected,
the CAB commands the CAB command coils to actu-
ate. The CAB command coils then open and close the
valves in the HCU which modulate brake fluid pres-
sure in some or all of the hydraulic circuits. The CAB
continues to control pressure in individual hydraulic
circuits until a locking tendency is no longer present.
The ABS system is constantly monitored by the
CAB for proper operation. If the CAB detects a fault,
it will turn on the Amber ABS Warning Lamp anddisable the ABS braking system. The normal base
braking system will remain operational.
The CAB contains a self-diagnostic program which
will turn on the Amber ABS Warning Lamp when a
ABS system fault is detected. Faults are then stored
in a diagnostic program memory. There are multiple
fault messages which may be stored in the CAB and
displayed through the DRB Scan Tool. These fault
messages will remain in the CAB memory even after
the ignition has been turned off. The fault messages
can be read and or cleared from the CAB memory by
a technician using the DRB Scan Tool. The fault
occurrence and the fault code will also be automati-
cally cleared from the CAB memory after the identi-
cal fault has not been seen during the next 3500
miles of vehicle operation. Mileage though of the last
fault occurrence will not be automatically cleared.CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE INPUTS
²Four wheel speed sensors.
²Stop lamp switch.
²Ignition switch.
²System relay voltage.
²Ground.
²Traction Control Switch (If Equipped).
²Diagnostics Communications (CCD)
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE OUTPUTS
²C2D Communication To Body Controller And
Instrument Cluster
²ABS warning lamp actuation.
²Traction Control Light (If Equipped).
²Diagnostic communication. (CCD)
ABS WARNING LAMP (YELLOW)
The ABS system uses a yellow colored ABS Warn-
ing Lamp. The ABS warning lamp is located on the
right side of the message center located at the top of
the instrument panel. The purpose of the warning
lamp is discussed in detail below.
The ABS warning lamp will turn on when the CAB
detects a condition which results in a shutdown of
ABS function or when the body controller does not
receive C2D messages from the CAB. When the igni-
tion key is turned to the on position, the ABS Warn-
ing Lamp is on until the CAB completes its self tests
and turns the lamp off (approximately 4 seconds
after the ignition switch is turned on). Under most
conditions, when the ABS warning lamp is on, only
the ABS function of the brake system is affected. The
standard brake system and the ability to stop the car
will not be affected when only the ABS warning lamp
is on.
The ABS warning lamp is controlled by the CAB
and the body controller through a diode located in
the wiring harness junction block. The junction block
is located under the instrument panel to the left of
Fig. 10 Controller Antilock Brake (CAB)
NSBRAKES 5 - 91
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 180 of 1938

these inputs to the CAB should be investigated if a
complaint of intermittent warning system operation
is encountered.
(12) Low system voltage. If Low System Voltage is
detected by the CAB, the CAB will turn on the ABS
Warning Lamp until normal system voltage is
achieved. Once normal voltage is seen at the CAB,
normal operation resumes.
(13) High system voltage. If high system voltage is
detected by the CAB, the CAB will turn on the
Amber ABS Warning Lamp until normal system volt-
age is achieved. Once normal voltage is again
detected by the CAB, normal ABS operation will be
resumed at the next key on cycle.
(14) Additionally, any condition which results in
interruption of electrical current to the CAB or mod-
ulator assembly may cause the ABS Warning Lamp
to turn on intermittently.
(15) The body controller can turn on the (yellow)
ABS warning lamp if CCD communication between
the body controller and the CAB is interupted.
TONEWHEEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: The tone wheels used on this vehicle
equipped with the Teves Mark 20 Antilock Brake
System are different then those used on past mod-
els of this vehicle equipped with antilock brakes.
Reduced braking performance will result if this part
is used on earlier model vehicles and an accident
could result. Do not use on pre-1998 model year
vehicles.
Carefully inspect tonewheel at the suspected faulty
wheel speed sensor for missing, chipped or broken
teeth, this can cause erratic speed sensor signals.
Tonewheels should show no evidence of contact
with the wheel speed sensors. If contact was made,
determine cause and correct before replacing the
wheel speed sensor.
Excessive runout of the tonewheel can cause
erratic wheel speed sensor signals. Refer to Tone-
wheel Runout in the Specification Section in this sec-
tion of the service manual for the tonewheel runout
specification. Replace drive shaft assembly or rear
hub/bearing assembly if tonewheel runout exceeds
the specification.
Inspect tonewheels for looseness on their mounting
surfaces. Tonewheels are pressed onto their mounting
surfaces and should not rotate independently from
the mounting surface.
Check the wheel speed sensor head alignment to
the tone wheel. Also check the gap between the speed
sensor head and the tone wheel to ensure it is at
specification. Refer to Wheel Speed Sensor Clearance
in the Specification Section in this section of the ser-
vice manual.
PROPORTIONING VALVE
CAUTION: Proportioning valves (Fig. 18) should
never be disassembled.
If premature rear wheel skid occurs on hard brake
application, it could be an indication that a malfunc-
tion has occurred with one of the proportioning
valves.
If a malfunctioning proportioning valve is sus-
pected on a vehicle, refer to Proportioning Valve Test
in the Proportioning Valves Section in this group of
the service manual for the required test procedure.
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts.
Swollen rubber parts indicate the presence of
petroleum in the brake fluid.
To test for contamination, put a small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If fluid sepa-
rates into layers, there is mineral oil or other fluid
contamination of the brake fluid.
If brake fluid is contaminated, drain and thor-
oughly flush system. Replace master cylinder, propor-
tioning valve, caliper seals, wheel cylinder seals,
Antilock Brakes hydraulic unit and all hydraulic
fluid hoses.
TEST DRIVING ABS COMPLAINT VEHICLE
Most ABS complaints will require a test drive as a
part of the diagnostic procedure. The purpose of the
test drive is to duplicate the condition.
NOTE: Remember conditions that result in the
turning on of the Red BRAKE Warning Lamp may
indicate reduced braking ability. The following pro-
cedure should be used to test drive an ABS com-
plaint vehicle.
Fig. 18 Brake Proportioning Valve Identification
5 - 98 BRAKESNS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 202 of 1938

DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
CLUTCH RELEASE SYSTEM
CLUTCH CABLE Ð LHD
The manual transaxle clutch release system has a
unique self-adjusting mechanism to compensate for
clutch disc wear (Fig. 7). This adjuster mechanism is
located within the clutch cable assembly. The preload
spring maintains tension on the cable. This tension
keeps the clutch release bearing continuously loaded
against the fingers of the clutch cover assembly.
HYDRAULIC CLUTCH Ð RHD
Leverage, clamping force, and friction are what
make the clutch work. The disc serves as the friction
element and a diaphragm spring and pressure plate
provide the clamping force. The clutch pedal, hydrau-
lic linkage, release lever and bearing provide the
leverage to disengage and engage the modular clutch
assembly.
The modular clutch assembly contains the cover,
diaphragm spring, pressure plate, disc and flywheel
in one unit. The modular clutch also uses a drive
plate and is bolted to and driven by the drive plate.
The clutch linkage uses hydraulic pressure to oper-
ate the clutch. The clutch master cylinder push rod is
connected to the clutch pedal and the slave cylinder
push rod is connected to the release lever in the
clutch housing.
Depressing the clutch pedal develops fluid pressure
in the clutch master cylinder. This pressure is trans-
mitted to the slave cylinder through a connecting
line. In turn, the slave cylinder operates the clutch
release lever.
The clutch release bearing is mounted on the
transmission front bearing retainer. The bearing is
attached to the release lever, which moves the bear-
ing into contact with the clutch cover diaphragm
spring.Slave cylinder force causes the release lever to
move the release bearing into contact with the dia-
phragm spring. As additional force is applied, the
bearing presses the diaphragm spring fingers inward
on the fulcrums. This action moves the pressure
plate rearward relieving clamp force on the disc. The
clutch disc is disengaged and not driven at this point.
The process of clutch engagement is simply the
reverse of what occurs during disengagement. Releas-
ing pedal pressure removes clutch linkage pressure.
The release bearing moves away from the diaphragm
spring which allows the pressure plate to exert
clamping force on the clutch disc.
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
The clutch pedal position switch functions as a
safety interlock device. It prevents possible engine
cranking with the clutch engaged.
The clutch pedal position switch is wired in series
between the starter relay coil and the ignition
switch.
The clutch pedal position switch is mounted to a
bracket located behind the clutch pedal. The switch
is held in place by four plastic wing tabs.
The clutch pedal position switch IS NOT adjust-
able. The pedal blade contacts the switch in the down
position (Fig. 8).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION
SWITCH±ELECTRICAL TEST
Disconnect clutch pedal position switch harness
from instrument panel wiring harness. Using an
ohmmeter, check for continuity between the two ter-
minals in the connector on the switch harness. There
should be no continuity between the terminals when
Fig. 7 Clutch Cable Ð LHD
Fig. 8 Clutch Pedal Position Switch and
Components Ð LHD Shown
6 - 4 CLUTCHNS/GS
Page 204 of 1938
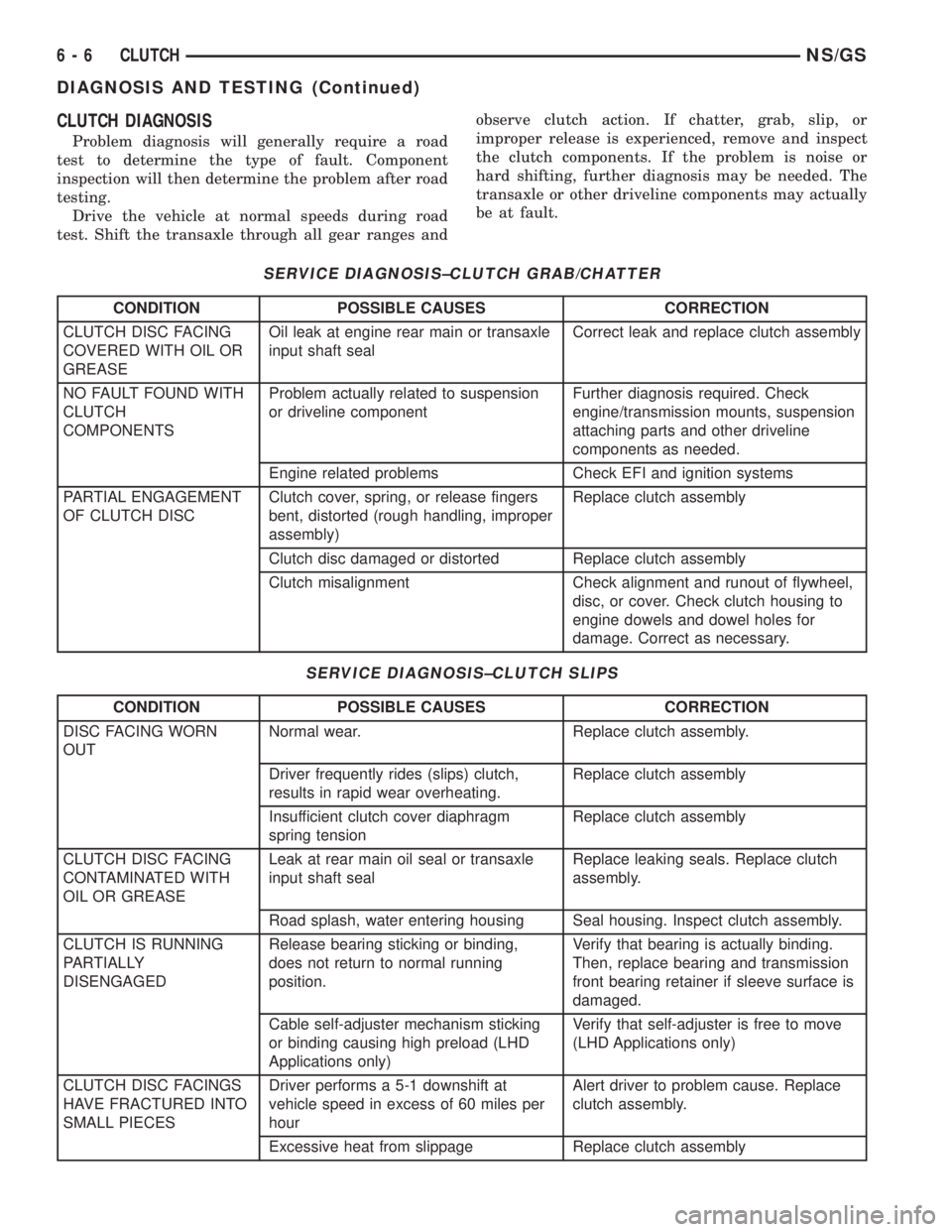
CLUTCH DIAGNOSIS
Problem diagnosis will generally require a road
test to determine the type of fault. Component
inspection will then determine the problem after road
testing.
Drive the vehicle at normal speeds during road
test. Shift the transaxle through all gear ranges andobserve clutch action. If chatter, grab, slip, or
improper release is experienced, remove and inspect
the clutch components. If the problem is noise or
hard shifting, further diagnosis may be needed. The
transaxle or other driveline components may actually
be at fault.
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS±CLUTCH GRAB/CHATTER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CLUTCH DISC FACING
COVERED WITH OIL OR
GREASEOil leak at engine rear main or transaxle
input shaft sealCorrect leak and replace clutch assembly
NO FAULT FOUND WITH
CLUTCH
COMPONENTSProblem actually related to suspension
or driveline componentFurther diagnosis required. Check
engine/transmission mounts, suspension
attaching parts and other driveline
components as needed.
Engine related problems Check EFI and ignition systems
PARTIAL ENGAGEMENT
OF CLUTCH DISCClutch cover, spring, or release fingers
bent, distorted (rough handling, improper
assembly)Replace clutch assembly
Clutch disc damaged or distorted Replace clutch assembly
Clutch misalignment Check alignment and runout of flywheel,
disc, or cover. Check clutch housing to
engine dowels and dowel holes for
damage. Correct as necessary.
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS±CLUTCH SLIPS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
DISC FACING WORN
OUTNormal wear. Replace clutch assembly.
Driver frequently rides (slips) clutch,
results in rapid wear overheating.Replace clutch assembly
Insufficient clutch cover diaphragm
spring tensionReplace clutch assembly
CLUTCH DISC FACING
CONTAMINATED WITH
OIL OR GREASELeak at rear main oil seal or transaxle
input shaft sealReplace leaking seals. Replace clutch
assembly.
Road splash, water entering housing Seal housing. Inspect clutch assembly.
CLUTCH IS RUNNING
PARTIALLY
DISENGAGEDRelease bearing sticking or binding,
does not return to normal running
position.Verify that bearing is actually binding.
Then, replace bearing and transmission
front bearing retainer if sleeve surface is
damaged.
Cable self-adjuster mechanism sticking
or binding causing high preload (LHD
Applications only)Verify that self-adjuster is free to move
(LHD Applications only)
CLUTCH DISC FACINGS
HAVE FRACTURED INTO
SMALL PIECESDriver performs a 5-1 downshift at
vehicle speed in excess of 60 miles per
hourAlert driver to problem cause. Replace
clutch assembly.
Excessive heat from slippage Replace clutch assembly
6 - 6 CLUTCHNS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 206 of 1938

CLUTCH COVER AND DISC RUNOUT
Check condition of the clutch cover before installa-
tion. A warped cover or diaphragm spring will cause
grab and/or incomplete release or engagement. Use
care when handling the clutch assembly. Impact can
distort the cover, diaphragm spring, and release fin-
gers.
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS
For all clutch chatter complaints, do the following:
(1) Check for loose, misaligned, or broken engine
and transmission mounts. If present, they should be
corrected at this time. Test vehicle for chatter. If
chatter is gone, there is no need to go any further. If
chatter persists:
(2) Check to see if clutch cable routing is correct
and operates smoothly (LHD applications).
(3) Check for loose connections in drivetrain. Cor-
rect any problems and determine if clutch chatter
complaints have been satisfied. If not:
(4) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle for procedure.
(5) Check to see if the release bearing is sticky or
binding. Replace bearing, if needed.
(6) Check linkage for excessive wear on the pivot
shaft, fork, and bushings. Replace all worn parts.
(7) Check clutch assembly for contamination (dirt,
oil). Replace clutch assembly, if required.
(8) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged. Replace with new clutch assembly, if nec-
essary.
(9) Check input shaft splines for damage. Replace,
if necessary.
(10) Check for uneven wear on clutch fingers.
(11) Check for broken clutch cover diaphragm
spring fingers. Replace with new clutch assembly, if
necessary.
CLASH±INTO±REVERSE COMPLAINTS
(1) Depress clutch pedal to floor and hold. After
three seconds, shift to reverse. If clash is present,
clutch has excessive spin time.
NOTE: Verify that nothing is obstructing pedal
travel. Floormats or other articles located under-
neath the clutch pedal could prevent the clutch
from disengaging fully.
(2) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle for procedure.
(3) Check the input shaft spline, clutch disc
splines, and release bearing for dry rust. If present,
clean rust off and apply a light coat of bearing grease
to the input shaft splines. Apply grease on the input
shaft splines only where the clutch disc slides. Verify
that the clutch disc slides freely along the input shaft
spline.(4) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged, and replace with new clutch assembly if
required.
(5) Check the input shaft for damaged splines.
Replace as necessary.
(6) Check for broken clutch cover diaphragm
spring fingers.
(7) Install clutch assembly and transaxle.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CLUTCH CABLE SYSTEM Ð LHD
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist vehicle
(2) Using a pair of pliers, grasp end of clutch cable
and pull downward.
(3) Remove clutch cable retaining clip from clutch
release lever (Fig. 9).
(4) Guide cable through slot in transaxle and dis-
connect (Fig. 10).
(5) Unsnap cable from the cable guide located at
the left shock tower (Fig. 10).
(6) Inside the vehicle, remove the driver side lower
dash cover and steel support plate. This provides
access to the top of the clutch pedal.
(7) Disconnect clutch cable upstop/spacer with
cable strand from clutch pedal (Fig. 11) (Fig. 12).
Fig. 9 Clutch Cable Retaining Clip Ð LHD
6 - 8 CLUTCHNS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)