glove box CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2001, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001Pages: 4284, PDF Size: 83.53 MB
Page 1814 of 4284
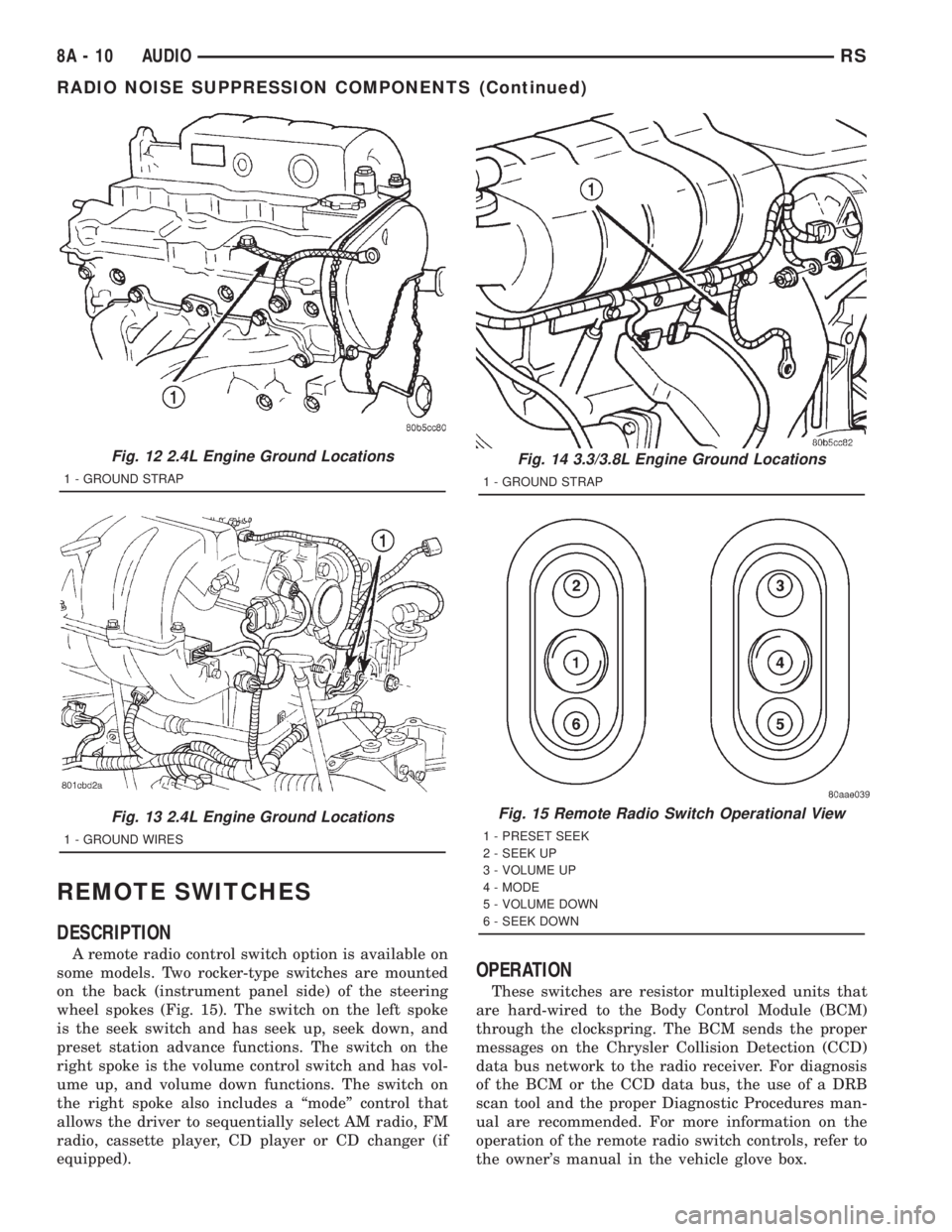
REMOTE SWITCHES
DESCRIPTION
A remote radio control switch option is available on
some models. Two rocker-type switches are mounted
on the back (instrument panel side) of the steering
wheel spokes (Fig. 15). The switch on the left spoke
is the seek switch and has seek up, seek down, and
preset station advance functions. The switch on the
right spoke is the volume control switch and has vol-
ume up, and volume down functions. The switch on
the right spoke also includes a ªmodeº control that
allows the driver to sequentially select AM radio, FM
radio, cassette player, CD player or CD changer (if
equipped).
OPERATION
These switches are resistor multiplexed units that
are hard-wired to the Body Control Module (BCM)
through the clockspring. The BCM sends the proper
messages on the Chrysler Collision Detection (CCD)
data bus network to the radio receiver. For diagnosis
of the BCM or the CCD data bus, the use of a DRB
scan tool and the proper Diagnostic Procedures man-
ual are recommended. For more information on the
operation of the remote radio switch controls, refer to
the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box.
Fig. 12 2.4L Engine Ground Locations
1 - GROUND STRAP
Fig. 13 2.4L Engine Ground Locations
1 - GROUND WIRES
Fig. 14 3.3/3.8L Engine Ground Locations
1 - GROUND STRAP
Fig. 15 Remote Radio Switch Operational View
1 - PRESET SEEK
2 - SEEK UP
3 - VOLUME UP
4 - MODE
5 - VOLUME DOWN
6 - SEEK DOWN
8A - 10 AUDIORS
RADIO NOISE SUPPRESSION COMPONENTS (Continued)
Page 1856 of 4284

BATTERY SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
A single 12-volt battery system is standard factory-
installed equipment on this model. All of the compo-
nents of the battery system are located within the
engine compartment of the vehicle. The service infor-
mation for the battery system in this vehicle covers
the following related components, which are covered
in further detail elsewhere in this service manual:
²Battery- The storage battery provides a reli-
able means of storing a renewable source of electrical
energy within the vehicle.
²Battery Cable- The battery cables connect the
battery terminal posts to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem.
²Battery Holddown- The battery holddown
hardware secures the battery in the battery tray in
the engine compartment.
²Battery Thermoguard- The battery thermo-
guard insulates the battery to protect it from engine
compartment temperature extremes.
²Battery Tray- The battery tray provides a
secure mounting location in the vehicle for the bat-
tery and an anchor point for the battery holddown
hardware.
For battery system maintenance schedules and
jump starting procedures, see the owner's manual in
the vehicle glove box. Optionally, refer to Lubrication
and Maintanance for the recommended battery main-
tenance schedules and for the proper battery jump
starting procedures. While battery charging can be
considered a maintenance procedure, the battery
charging procedures and related information are
located in the standard procedures section of this ser-
vice manual. This was done because the battery must
be fully-charged before any battery system diagnosis
or testing procedures can be performed. Refer to
Standard procedures for the proper battery charging
procedures.
OPERATION
The battery system is designed to provide a safe,
efficient, reliable and mobile means of delivering and
storing electrical energy. This electrical energy is
required to operate the engine starting system, as
well as to operate many of the other vehicle acces-sory systems for limited durations while the engine
and/or the charging system are not operating. The
battery system is also designed to provide a reserve
of electrical energy to supplement the charging sys-
tem for short durations while the engine is running
and the electrical current demands of the vehicle
exceed the output of the charging system. In addition
to delivering, and storing electrical energy for the
vehicle, the battery system serves as a capacitor and
voltage stabilizer for the vehicle electrical system. It
absorbs most abnormal or transient voltages caused
by the switching of any of the electrical components
or circuits in the vehicle.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY SYSTEM
The battery, starting, and charging systems in the
vehicle operate with one another and must be tested
as a single complete system. In order for the engine
to start and the battery to charge properly, all of the
components that are used in these systems must per-
form within specifications. It is important that the
battery, starting, and charging systems be thoroughly
tested and inspected any time a battery needs to be
charged or replaced. The cause of abnormal battery
discharge, overcharging or early battery failure must
be diagnosed and corrected before a battery is
replaced and before a vehicle is returned to service.
The service information for these systems has been
separated within this service manual to make it eas-
ier to locate the specific information you are seeking.
However, when attempting to diagnose any of these
systems, it is important that you keep their interde-
pendency in mind.
The diagnostic procedures used for the battery,
starting, and charging systems include the most
basic conventional diagnostic methods, to the more
sophisticated On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) built into
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Use of an
induction-type milliampere ammeter, a volt/ohmme-
ter, a battery charger, a carbon pile rheostat (load
tester) and a 12-volt test lamp may be required. All
OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in elec-
tronic memory for any failure it detects. Refer to
Charging System for the proper charging system on-
board diagnostic test procedures.
8F - 2 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
Page 1904 of 4284

²Remote Keyless Entry Module (RKE)- Refer
toRemote Keyless Entry Modulein Power Locks
for more information.
²Electronic Vehicle Information Center
(EVIC)- Refer toElectronic Vehicle Information
Centerin Overhead Console for more information.
²Heated Seat Module (HSM)- Refer toHeated
Seat Modulein Electronic Control Modules for more
information.
²Memory Heated Seat Module (MHSM)-If
the vehicle is equipped with the Memory System,
refer toMemory Seat Mirror Module (MSMM)in
Electronic Control Modules for more information.
Refer toWiring Diagramsfor complete circuit
diagrams. Following are general descriptions of the
major components in the heated seat system.
OPERATION
The heated seat system will only operate when the
ignition switch is in the On position, and the surface
temperature at the front seat heating element sen-
sors is below the designed temperature set points of
the system. The heated seat system will not operate
in ambient temperatures greater than about 41É C
(105É F). The front seat heating elements and sensors
are hard wired to the Heated Seat Module (HSM) or
the Memory Heated Seat Module (MHSM).
The heated seat switches are hard wired to the
Body Control Module (BCM). The BCM monitors the
heated seat switch inputs, then sends heated seat
switch status messages to the HSM or MHSM over
the Programmable Communications Interface J1850
(PCI) data bus. The HSM or MHSM contains the con-
trol logic for the heated seat system. The HSM or
MHSM responds to the heated seat switch status
messages, ignition switch status messages, and the
front seat heating element sensor inputs by control-
ling the output to the front seat heating elements
through integral solid-state relays.
When a seat heater is turned on, the sensor
located on the seat cushion electric heater element
provides the HSM or MHSM with an input indicating
the surface temperature of the seat cushion. If the
surface temperature input is below the temperature
set point for the selected Low or High heated seat
switch position, the HSM or MHSM energizes the
integral solid-state relay, which supplies battery cur-
rent to the heating elements in the seat cushion and
back. When the sensor input indicates the correct
temperature set point has been achieved, the HSM or
MHSM de-energizes the solid-state relay. The HSM
or MHSM will continue to cycle the solid-state relay
as needed to maintain the temperature set point.
The HSM or MHSM and the seat heater elements
operate on non-switched battery current supplied
through the power seat fuse in the intelligent powermodule. However, the HSM or MHSM will automati-
cally turn off the heating elements if it detects an
open in the sensor circuit, a short in the heating ele-
ment circuit causing an excessive current draw, or
when the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion.
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the features, use and operation
of the heated seat system.
DRIVER HEATED SEAT
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The heated seat switches are mounted in the
instrument panel center bezel (Fig. 2). The two three-
position rocker-type switches, one switch for each
front seat, are incorporated into one large switch
assembly that also includes the hazzard, rear window
wiper and washer switches. The heated seat switches
provide a resistor multiplexed signal to the Body
Control Module (BCM) through separate hard wired
circuits. Each switch has an Off, Low, and High posi-
tion so that both the driver and the front seat pas-
senger can select a preferred seat heating mode.
Each switch has two Light-Emitting Diodes (LED)
which light to indicate that the heater for the seat is
turned on.
The heated seat switches and their LEDs cannot
be repaired. If either switch or LED is faulty or dam-
aged, the entire switch assembly must be replaced.
Fig. 2 HEATED SEAT SWITCHES
8G - 8 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMRS
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1957 of 4284

LAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
LAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR
SPECIFICATIONS........................17
CENTER CONSOLE LAMP SWITCH
REMOVAL..............................18
INSTALLATION...........................18
CLUSTER ILLUMINATION LAMPS
REMOVAL..............................18
INSTALLATION...........................18
COURTESY LAMP
REMOVAL..............................18
INSTALLATION...........................18
DOME LAMP
REMOVAL..............................18INSTALLATION...........................18
GLOVE BOX LAMP SWITCH
REMOVAL..............................18
INSTALLATION...........................19
LIFTGATE LAMP
REMOVAL..............................19
INSTALLATION...........................19
READING LAMP
REMOVAL..............................19
INSTALLATION...........................20
VANITY LAMP
REMOVAL..............................20
INSTALLATION...........................20
LAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR
SPECIFICATIONS
BULB APPLICATION TABLE
LAMP BULB
ABS LED
AIRBAG LED
ALARM SET PC74
AUTOSTICK VFD*
BRAKE SYSTEM WARNING LED
CONSOLE 194
CRUISE INDICATOR VFD*
DOME/RAIL LAMPS 578
DOOR AJAR INDICATOR LED
DOOR COURTESY LAMP 578
FRONT DOOR COURTESY 567
GLOVE BOX 194
HIGH BEAM INDICATOR
(BASE CLUSTER)LED
HIGH BEAM INDICATOR PC74
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER PC74
LIFTGATE 578
LIFTGATE AJAR LED
LAMP BULB
LOW FUEL INDICATOR LED
LOW WASHER FLUID
INDICATORLED
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR
(BASE CLUSTER)LED
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR PC74
OIL INDICATOR (BASE
CLUSTER)LED
OIL INDICATOR PC74
OVERHEAD CONSOLE
READINGPC579
OVERDRIVE OFF
INDICATORVFD*
READING 578
SEAT BELT INDICATOR LED
TEMPERATURE INDICATOR LED
TRAC OFF INDICATOR VFD*
TURN SIGNAL INDICATOR
(BASE CLUSTER)LED
TURN SIGNAL INDICATOR PC74
VISOR VANITY 6501966
VOLTAGE INDICATOR LED
* VACUUM
FLUORESCENT
DISPLAY
RSLAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR8L-17
Page 1958 of 4284

CENTER CONSOLE LAMP
SWITCH
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Open console lid and remove tray.
(3) Using a flat bladed tool, pry up on the switch.
(4) Remove bulb from switch.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install bulb into switch.
(2) Push switch into console opening.
(3) Install tray and close lid.
(4) Connect battery negative cable.
CLUSTER ILLUMINATION
LAMPS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the Instrument Cluster. Refer to Elec-
trical, Instrument Cluster, Removal.
(2) Turn over cluster and expose the illumination
bulb sockets.
(3) Identify which bulb is defective and twist it out
of the cluster using a counterclockwise motion.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the new bulb socket into the cluster
using a clockwise motion.
(2) Install the Instrument Cluster. Refer to Electri-
cal, Instrument Cluster, Installation.
COURTESY LAMP
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Using a trim stick, pry lamp from door panel
(Fig. 1).
(3) Disconnect wire harness from the lamp.
(4) Remove lens from the lamp and remove bulb.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install bulb and lens to lamp.
(2) Reconnect wire harness to lamp.
(3) Press lamp into the door panel.
(4) Reconnect battery negative cable.
DOME LAMP
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Using a flat bladed tool, pry off the lamp lens.
(3) Remove bulb from lamp.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install bulb to lamp.
(2) Press lens into place.
(3) Connect battery negative cable.
GLOVE BOX LAMP SWITCH
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Open glove box door.
(3) Push switch through from behind (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1 COURTESY LAMP
1 - WIRE HARNESS
2 - COURTESY LAMP
Fig. 2 GLOVE BOX LAMP/SWITCH
1 - GLOVE BOX BULB
2 - GLOVE BOX LAMP SWITCH
8L - 18 LAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIORRS
Page 1959 of 4284
(4) Disconnect wire harness from switch.
(5) Pull bulb from switch.
INSTALLATION
(1) Push bulb into switch.
(2) Connect wire harness to switch.
(3) Push switch into instrument panel.
(4) Close glove box door.
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
LIFTGATE LAMP
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Using a flat bladed tool, pry lamp from trim
panel (Fig. 3).
(3) Disconnect wire harness connector from lamp.
(4) Pry off lens and remove bulb.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install bulb and snap lens into place.
(2) Reconnect wire harness connector to lamp.
(3) Position lamp onto trim panel and snap into
place.
(4) Reconnect battery negative cable.
READING LAMP
REMOVAL
The front reading lamps are incorporated into the
overhead console. If the reading lamps require replace-
ment, the overhead console must be replaced. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CONSOLE - REMOV-
AL). The rear reading lamps are incorporated into the
assist handle. If the rear reading lamps require
replacement, the assist handle must be replaced.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/ASSIST HANDLE -
REMOVAL). The bulbs can be serviced separately.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Using a flat bladed tool, pry off the lamp lens
(Fig. 4), (Fig. 5).
(3) Remove bulb from lamp (Fig. 6), (Fig. 7).
Fig. 3 LIFTGATE LAMP
1 - LIFTGATE LAMP
2 - WIRE HARNESSFig. 4 OVERHEAD CONSOLE
1 - LAMP LENS
2 - OVERHEAD CONSOLE
Fig. 5 COURTESY/READING LAMP
1 - HVAC LOUVER
2 - ASSIST HANDLE
3 - LAMP LENS
RSLAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR8L-19
GLOVE BOX LAMP SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1975 of 4284

The EVIC module contains a central processing
unit and interfaces with other electronic modules in
the vehicle over the Programmable Communications
Interface (PCI) J1850 data bus circuit. The PCI data
bus circuit allows the sharing of sensor information.
This helps to reduce wire harness complexity, reduce
internal controller hardware, and reduce component
sensor current loads. At the same time, this system
provides increased reliability, enhanced diagnostics,
and allows the addition of many new feature capabil-
ities.
The EVIC ªMenuº push button provides the vehicle
operator with a user interface, which allows the
selection of several optional customer programmable
electronic features to suit individual preferences.
Refer toELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFORMA-
TION CENTER PROGRAMMINGin the Service
Procedures section of this group for more information
on the customer programmable feature options.
If the vehicle is equipped with the optional
Homelinkttransceiver, the EVIC will also display
messages and an icon indicating when the
Homelinkttransceiver is being trained, which of the
three transmitter buttons is transmitting, and when
the transceiver is cleared.
Data input for all EVIC functions, including VFD
dimming level, is received through the J1850 PCI
data bus circuit. The EVIC module uses its internal
programming and all of its data inputs to calculate
and display the requested data. If the data displayed
is incorrect, perform the self-diagnostic tests as
described in this group. If these tests prove inconclu-
sive, the use of a DRBIIItscan tool and the proper
Diagnostic Procedures manual are recommended for
further testing of the EVIC module and the J1850
PCI data bus circuit.
The EVIC module cannot be repaired, and is avail-
able for service only as a unit. This unit includes the
plastic module and display lens. If any of these com-
ponents is faulty or damaged, the complete EVIC
module must be replaced.
OPERATION
The EVIC has access to both non-switched and
ignition switched sources of battery current so that
some of its features remain operational at any time,
while others may only operate with the ignition
switch in the On position. When the ignition switch
is turned to the On position, the EVIC module VFD
will return to the last function being displayed before
the ignition was turned to the Off position.
The compass/thermometer display is the normal
EVIC display. With the ignition switch in the Onposition, momentarily depressing and releasing the
C/T (compass/thermometer) push button switch will
cause the EVIC to return to the compass/thermome-
ter/trip computer display mode from any other mode.
While in the compass/thermometer/trip computer dis-
play mode, momentarily depressing and releasing the
Step push button will step through the available trip
computer display options.
The EVIC trip computer features several functions
that can be reset. The functions that can be reset
are: average fuel economy, trip odometer and elapsed
time. With the ignition switch in the On position and
with one of the functions of the trip computer that
can be reset currently displayed, depressing the
Reset push button twice within three seconds will
perform a global reset, and all of the trip computer
information that can be reset will be reset to zero.
With the ignition switch in the On position and the
function that is to be reset currently displayed,
momentarily depressing and releasing the Reset
push button once will perform a local reset, and only
the value of the displayed function will be reset to
zero. A global or local reset will only occur if the
function currently displayed is a function that can be
reset. The distance to service function can also be
reset using the local reset method, but it will reset
back to the Service Interval distance that is set in
the EVIC programmable features mode. Refer to
ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFORMATION CEN-
TER PROGRAMMINGin the Service Procedures
section of this group for more information on setting
the Service Interval.
For more information on the features, control func-
tions and setting procedures for the EVIC module,
see the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - ELECTRONIC
VEHICLE INFORMATION CENTER
Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC) data
is obtained from the Body Control Module (BCM) on
the J1850 Data Bus circuit. The EVIC will display
dashes (- -) for any of the screens it did not receive
the bus messages. The label corresponding to the
missing information will be lit. If no EVIC data is
displayed, check the J1850 Data Bus circuit commu-
nications and the BCM. If the brightness level is
improper check the J1850 Data Bus circuit.
The DRB IIItis recommended for checking the
J1850 Data Bus circuit and the BCM. Perform the
EVIC self diagnosis before replacing the EVIC mod-
ule.
RSOVERHEAD CONSOLE8M-7
ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFO CENTER (Continued)
Page 1978 of 4284

OPERATION
The Compass Mini-Trip Computer (CMTC), Com-
pass Temperature (CT) module in the overhead con-
sole has buttons used to select various functions. The
CMTC, CT selector buttons will not operate until the
ignition is in the RUN position.
When the ignition switch is first turned to the
RUN position the CMTC, CT display;
²Blanks momentarily
²
All segments of the VFD will light for one second
²Blanks momentarily
²Returns to the last mode setting selected before
the ignition was last switched OFF.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - COMPASS MINI-TRIP
COMPUTER
Compass Mini-Trip Computer (CMTC) and Com-
pass Temperature (CT) data is obtained from the
Body Control Module (BCM) on the J1850 Data Bus
circuit. The CMTC and CT will display dashes (- -)
for any of the screens it did not receive the bus mes-
sages. The label corresponding to the missing infor-
mation will be lit. If no compass mini-trip computer
data is displayed, check the J1850 Data Bus circuit
communications and the BCM. If the brightness level
is improper check the J1850 Data Bus circuit.
The DRB IIItis recommended for checking the
J1850 Data Bus circuit and the BCM. Perform the
CMTC, CT self diagnosis before replacing the CMTC
or CT module.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove overhead console. Refer to Overhead
Console Removal and Installation in this section(Re-
fer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CONSOLE -
REMOVAL) .
(3) Remove the screws holding Compass Mini-Trip
Computer module in the overhead console.
(4) Remove CMTC module from console assembly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the compass mini-trip computer mod-
ule in the overhead console.
(2) Install the ten screws holding the compass
mini-trip computer module in the overhead console.
(3) Install the overhead console. Refer to Overhead
Console Removal and Installation in this section.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
NOTE: If a new module has been installed, the com-
pass will have to be calibrated and the variance set.
Refer to Compass Variation Adjustment and Com-
pass Calibration in the Service Procedures section
of this group for the procedures.
UNIVERSAL TRANSMITTER
DESCRIPTION
On some RS models a Homelinkttransceiver is
standard factory-installed equipment. The Homelinkt
transceiver is integral to the Electronic Vehicle Infor-
mation Center (EVIC) and the Compass Mini-Trip
Computer (CMTC), which is located in the overhead
console. The only visible component of the Homelinkt
are the three transmitter push buttons centered
between the modules push buttons located just rear-
ward of the display screen in the overhead console.
The three Homelinkttransmitter push buttons are
identified with one, two or three light indicators so
that they be easily identified by sight or by feel.
Each of the three Homelinkttransmitter push but-
tons controls an independent radio transmitter chan-
nel. Each of these three channels can be trained to
transmit a different radio frequency signal for the
remote operation of garage door openers, motorized
gate openers, home or office lighting, security sys-
tems or just about any other device that can be
equipped with a radio receiver in the 286 to 399
MegaHertz (MHz) frequency range for remote opera-
tion. The Homelinktis capable of operating systems
using either rolling code or non-rolling code technol-
ogy.
The electronics module displays messages and a
small house-shaped icon with one, two or three dots
corresponding to the three transmitter buttons to
indicate the status of the Homelinkt. The EVIC mes-
sages are:
²Cleared Channels- Indicates that all of the
transmitter codes stored in the Homelinkthave been
successfully cleared.
²Training- Indicates that the Homelinktis in
its transmitter learning mode.
²Trained- Indicates that the Homelinkthas
successfully acquired a new transmitter code.
²Transmit- Indicates that a trained Homelinkt
transmitter button has been depressed and that the
Homelinktis transmitting.
The Homelinktcannot be repaired, and is avail-
able for service only as a unit with the EVIC or
CMTC modules. If any of these components is faulty
or damaged, the complete EVIC or CMTC module
must be replaced.
OPERATION
The Homelinktoperates on a non-switched source
of battery current so the unit will remain functional,
regardless of the ignition switch position. For more
information on the features, programming procedures
and operation of the Homelinkt, see the owner's
manual in the vehicle glove box.
8M - 10 OVERHEAD CONSOLERS
COMPASS/MINI-TRIP COMPUTER (Continued)
Page 1979 of 4284

DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - HOMELINKT
If the Homelinktis inoperative, but the Electronic
Vehicle Information Center (EVIC) or Compass Mini-
Trip Computer is operating normally, see the owner's
manual in the vehicle glove box for instructions on
training the Homelinkt. Retrain the Homelinktwith
a known good transmitter as instructed in the own-
er's manual and test the Homelinktoperation again.
If the unit is still inoperative, replace the faulty
Homelinktand EVIC/CMTC module as a unit. If
both the Homelinktand the EVIC/CMTC module are
inoperative, refer toOverhead Console Diagnosis
and Testingearlier in this group for further diagno-
sis. For complete circuit diagrams, refer toOver-
head Consolein Wiring Diagrams.
AMBIENT TEMP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Ambient air temperature is monitored by the over-
head console through ambient temperature messages
received from the Front Control Module (FCM) over
the Programmable Communications Interface (PCI)
J1850 data bus circuit. The FCM receives a hard
wired input from the ambient temperature sensor.
The ambient temperature sensor is a variable resis-
tor mounted to a bracket that is secured with a screw
to the right side of the headlamp mounting module
grille opening, behind the radiator grille and in front
of the engine compartment.
Refer toFront Control Modulein Electronic
Control Modules. For complete circuit diagrams, refer
to the appropriate wiring information. The ambient
temperature sensor cannot be adjusted or repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ambient temperature sensor is a variable
resistor that operates on a five-volt reference signal
sent to it by the Front Control Module. The resis-
tance in the sensor changes as temperature changes,
changing the temperature sensor signal circuit volt-
age to the Front Control Module. Based upon the
resistance in the sensor, the Front Control Module
senses a specific voltage on the temperature sensor
signal circuit, which it is programmed to correspond
to a specific temperature. The Front Control Module
then sends the proper ambient temperature mes-
sages to the EVIC, CMTC over the PCI J1850 data
bus.
The thermometer function is supported by the
ambient temperature sensor, a wiring circuit, the
Front Control Module, the Programmable Communi-
cations Interface (PCI) data bus, and a portion of the
Electronics module. If any portion of the ambienttemperature sensor circuit fails, the Front Control
Module will self-diagnose the circuit.
The ambient temperature sensor circuit can also be
diagnosed by referring toDiagnosis and Testing -
Ambient Temperature Sensor, and Diagnosis
and Testing - Ambient Temperature Sensor Cir-
cuit. If the temperature sensor and circuit are con-
firmed to be OK, but the temperature display is
inoperative or incorrect, refer toDiagnosis and
Testing - Overhead Consolein this group. For
complete circuit diagrams, refer to the appropriate
wiring information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Disconnect the ambient temperature sensor wire har-
ness connector.
(2) Measure the resistance of the ambient temper-
ature sensor. At ±40É C (±40É F), the sensor resis-
tance is 336 kilohms. At 55É C (140É F), the sensor
resistance is 2.488 kilohms. The sensor resistance
should read between these two values. If OK, refer to
Diagnosis and Testing - Ambient Temperature
Sensor Circuitin this group. If not OK, replace the
faulty ambient temperature sensor.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Disconnect the ambient temperature sensor wire har-
ness connector and the Front Control Module wire
harness connector.
(2) Connect a jumper wire between the two termi-
nals in the body half of the ambient temperature sen-
sor wire harness connector.
(3) Check for continuity between the sensor return
circuit and the ambient temperature sensor signal
circuit cavities of the Front Control Module wire har-
ness connector. There should be continuity. If OK, go
to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open sensor return
circuit or ambient temperature sensor signal circuit
to the ambient temperature sensor as required.
(4) Remove the jumper wire from the body half of
the ambient temperature sensor wire harness con-
nector. Check for continuity between the sensor
return circuit cavity of the Front Control Module
wire harness connector and a good ground. There
should be no continuity. If OK, go to Step 5. If not
OK, repair the shorted sensor return circuit as
required.
(5) Check for continuity between the ambient tem-
perature sensor signal circuit cavity of the Front
Control Module wire harness connector and a good
RSOVERHEAD CONSOLE8M-11
UNIVERSAL TRANSMITTER (Continued)
Page 2031 of 4284

trically and independently using the separate power
seat switches found on the outboard seat cushion
side shield of each front seat. See the owner's manual
in the vehicle glove box for more information on the
features, use and operation of the power seat system.
OPERATION - MEMORY SYSTEM
The Memory Seat/Mirror Module (MSMM) will
drive a maximum of 2 motors at a time in a given
direction. If conflicting directions are requested, the
priority for response will be as follows:
²Seat Track Rearward
²Seat Front Down
²Seat Rear Down
²Recliner Rearward
²Seat Track Forward
²Seat Front Up
²Seat Rear Up
²Recliner Forward
The inputs from these switches to the MSMM is a
current limited battery source fed by the MSMM.
This protects the MSMM printed circuit board traces
from acting as fuses. All of these switch contact
inputs to the MSMM are normally closed to ground,
except when actuated.
Soft stops are incorporated to prevent the motor
from being driven into a stall. Should the seat have
restricted travel, refer to Resetting Soft Stops in this
section.
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the features, use and operation
of the memory system. For diagnosis of the MSM, the
PCI data bus, or the other electronic modules on the
PCI data bus that provide inputs and outputs for the
memory system, the use of a DRBtscan tool and the
proper Diagnostic Procedures manual are recom-
mended.
ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFORMATION CENTER
The Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC)
serves as the user interface for the memory system.
It displays memory system status messages and pro-
vides the user with the means for enabling and dis-
abling the many customer programmable features
available on the vehicle, including those for the mem-
ory system.
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the features, use and operation
of the EVIC. Refer toElectronic Vehicle Informa-
tion Centerin Overhead Console Systems for more
information on the EVIC.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER SEAT
SYSTEM
Following are tests that will help to diagnose the
hard wired components and circuits of the power seatsystem. However, if the vehicle is also equipped with
the optional memory system, these tests may not
prove conclusive in the diagnosis of the driver side
power seat. In order to obtain conclusive testing of
the driver side power seat with the memory system
option, the Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) data bus network and all of the electronic mod-
ules that provide inputs to, or receive outputs from
the memory system components must be checked.
The most reliable, efficient, and accurate means to
diagnose the driver side power seat with the memory
system option requires the use of a DRBtscan tool
and the proper Diagnostic Procedures manual. The
DRBtscan tool can provide confirmation that the
PCI data bus is functional, that all of the electronic
modules are sending and receiving the proper mes-
sages on the PCI data bus, and that the memory sys-
tem is receiving the proper hard wired inputs and
relaying the proper hard wired outputs to perform its
driver side power seat functions.
WARNING: SOME VEHICLES ARE EQUIPPED WITH
SEATBACK MOUNTED AIRBAGS (Fig. 1). BEFORE
ATTEMPTING TO DIAGNOSE OR SERVICE ANY
SEAT OR POWER SEAT SYSTEM COMPONENT
YOU MUST FIRST DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE
BATTERY NEGATIVE CABLE. THEN WAIT TWO MIN-
UTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DIS-
CHARGE BEFORE FURTHER SYSTEM SERVICE.
THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE
AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO DO SO COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT
AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
Before any testing of the power seat system is
attempted, the battery should be fully-charged and
all of the power seat system wire harness connections
and pins cleaned and tightened to ensure proper cir-
cuit continuity and ground paths. For complete cir-
cuit diagrams, refer toPower Seatin Wiring
Diagrams.
With the dome lamp on, apply the power seat
switch in the direction of the failure. If the dome
lamp dims, the seat may be jamming. Check under
and behind the seat for binding or obstructions. If
the dome lamp does not dim, proceed with testing of
the individual components and circuits.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MEMORY SYSTEM
CHECK AND RESET SOFT STOPS
To check and reset the power memory seat soft
stops, use the power seat control switches to move
the seat in one direction to the end of travel, allow a
couple of seconds before re-energizing the seat in the
same direction until it stops and for three additional
seconds after it stops. (The amount the seat moved
RSPOWER SEATS8N-51
POWER SEATS (Continued)