fuse diagram CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2002 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2002Pages: 2399, PDF Size: 57.96 MB
Page 669 of 2399

STANDARD PROCEDURE - TESTING FOR A
SHORT TO GROUND ON FUSES POWERING
SEVERAL LOADS
(1) Refer to the wiring diagrams and disconnect or
isolate all items on the suspected fused circuits.
(2) Replace the blown fuse.
(3) Supply power to the fuse by turning ON the
ignition switch or re-connecting the battery.
(4) Start connecting or energizing the items in the
fuse circuit one at a time. When the fuse blows the
circuit with the short to ground has been isolated.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TESTING FOR A
VOLTAGE DROP
(1) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to
the side of the circuit closest to the battery (Fig. 9).
(2) Connect the other lead of the voltmeter to the
other side of the switch, component or circuit.
(3) Operate the item.
(4) The voltmeter will show the difference in volt-
age between the two points.
SPECIAL TOOLS
WIRING/TERMINAL
Fig. 9 TESTING FOR VOLTAGE DROP
PROBING TOOL PACKAGE 6807
TERMINAL PICK TOOL SET 6680
TERMINAL REMOVING TOOLS 6932 AND 8638
TERMINAL REMOVING TOOL 6934
8W - 01 - 10 8W-01 WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATIONRS
WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1196 of 2399

8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS.........2
ACCESSORY RELAY
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - ACCESSORY
RELAY...............................2
REMOVAL.............................3
INSTALLATION..........................3
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
DESCRIPTION..........................3OPERATION............................3
REMOVAL.............................4
INSTALLATION..........................4
IOD FUSE
DESCRIPTION..........................4
OPERATION............................5
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................5
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION..........................5
OPERATION............................5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - POWER OUTLET . . 5
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................6
POWER DISTRIBUTION
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
This group covers the various standard and
optional power distribution components used on this
model. The power distribution system for this vehicle
consists of the following components:
²Integrated Power Module (IPM)
²Front Control Module (FCM)
²Power Outlets
Refer to Wiring Diagrams for complete circuit sche-
matics.
The power distribution system also incorporates
various types of circuit control and protection fea-
tures, including:
²Automatic resetting circuit breakers
²Blade-type fuses
²Bus bars
²Cartridge fuses
²Circuit splice blocks
²Flashers
²Fusible links
²Relays
Following are general descriptions of the major
components in the power distribution system. See the
owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for more
information on the features and use of all of the
power distribution system components.
OPERATION
The power distribution system for this vehicle is
designed to provide safe, reliable, and centralized dis-
tribution points for the electrical current required to
operate all of the many standard and optional facto-
ry-installed electrical and electronic powertrain,
chassis, safety, security, comfort and convenience sys-
tems. At the same time, the power distribution sys-
tem was designed to provide ready access to these
electrical distribution points for the vehicle techni-
cian to use when conducting diagnosis and repair of
faulty circuits. The power distribution system can
also prove useful for the sourcing of additional elec-
trical circuits that may be required to provide the
electrical current needed to operate many accessories
that the vehicle owner may choose to have installed
in the aftermarket.
RS8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM8W-97-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1197 of 2399

SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
ACCESSORY RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The accessory relay is an electromechanical device
that switches fused battery current to the accessory
powered vehicle circuits when the ignition switch is
turned to the Accessory or On positions. The delay
feature will maintain power to the accessories for 45
seconds after the ignition is shut off or until a door is
opened. This allows sufficient time to close windows
and park the windshield wipers. The accessory relay
is located in the Integrated Power Module (IPM) in
the engine compartment.
The accessory relay is a International Standards
Organization (ISO) relay. Relays conforming to the
ISO specifications have common physical dimensions,
current capacities, terminal patterns, and terminal
functions.
The accessory relay cannot be repaired or adjusted
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor or diode, and three (two fixed and one movable)
electrical contacts. The movable (common feed) relay
contact is held against one of the fixed contacts (normal-
ly closed) by spring pressure. When the electromagnetic
coil is energized, it draws the movable contact away
from the normally closed fixed contact, and holds it
against the other (normally open) fixed contact.
When the electromagnetic coil is de-energized,
spring pressure returns the movable contact to the
normally closed position. The resistor or diode is con-
nected in parallel with the electromagnetic coil in the
relay, and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that are
produced when the coil is de-energized.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - ACCESSORY RELAY
The accessory relay (Fig. 1) is located in the Inte-
grated Power Module (IPM), in the engine compart-
ment. For complete circuit diagrams, refer toWiring
Diagrams.
(1) Remove the accessory relay from the IPM.
Refer toAccessory Relayin the Removal and
Installation section of this group for the procedure.
(2) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 5 ohms. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(4) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, perform the Relay Circuit Test that
follows. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) of
the IPM is connected to battery voltage and should
be hot at all times. Check for battery voltage at the
fused B(+) circuit cavity in the IPM receptacle for the
accessory relay. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair
the fused B(+) circuit to the IPM fuse as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to the common feed terminal (30) in the ener-
gized position. This terminal supplies battery voltage
to the fused B(+) fuse in the IPM that feeds the
accessories when the relay is energized by the igni-
tion switch. There should be continuity between the
IPM cavity for relay terminal 87 and the fused B(+)
fuse in the IPM at all times. If OK, go to Step 4. If
not OK, repair the open fused B(+) circuit to the IPM
fuse as required.
Terminal Pick Kit 6680
Fig. 1 Accessory Relay
8W - 97 - 2 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMRS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1200 of 2399

tion. The IOD fuse is a 15 ampere blade-type car-
tridge fuse and, when removed, it is stored in a fuse
cavity adjacent to the washer fuse within the IPM.
OPERATION
The term ignition-off draw identifies a normal con-
dition where power is being drained from the battery
with the ignition switch in the Off position. The IOD
fuse feeds the memory and sleep mode functions for
some of the electronic modules in the vehicle as well
as various other accessories that require battery cur-
rent when the ignition switch is in the Off position,
including the clock. The only reason the IOD fuse is
removed is to reduce the normal IOD of the vehicle
electrical system during new vehicle transportation
and pre-delivery storage to reduce battery depletion,
while still allowing vehicle operation so that the
vehicle can be loaded, unloaded and moved as needed
by both vehicle transportation company and dealer
personnel.
The IOD fuse is removed from the IPM fuse cavity
when the vehicle is shipped from the assembly plant.
Dealer personnel must install the IOD fuse when the
vehicle is being prepared for delivery in order to
restore full electrical system operation. Once the
vehicle is prepared for delivery, the IOD function of
this fuse becomes transparent and the fuse that has
been assigned the IOD designation becomes only
another Fused B(+) circuit fuse. The IOD fuse serves
no useful purpose to the dealer technician in the ser-
vice or diagnosis of any vehicle system or condition,
other than the same purpose as that of any other
standard circuit protection device.
The IOD fuse can be used by the vehicle owner as
a convenient means of reducing battery depletion
when a vehicle is to be stored for periods not to
exceed about thirty days. However, it must be
remembered that removing the IOD fuse will not
eliminate IOD, but only reduce this normal condition.
If a vehicle will be stored for more than about thirty
days, the battery negative cable should be discon-
nected to eliminate normal IOD; and, the battery
should be tested and recharged at regular intervals
during the vehicle storage period to prevent the bat-
tery from becoming discharged or damaged. Refer to
Battery Systemfor additional service information.
REMOVAL
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
(2) Unlatch and open the cover of the intelligent
power module.
(3) Remove the IOD fuse from fuse location
markedIODof the Integrated Power Module (IPM).
(4) Store the removed IOD fuse by installing it in
the unused fuse storage markedSPAREof the IPM.
(5) Close and latch the IPM.
INSTALLATION
(1) Be certain the ignition switch is in the Off posi-
tion.
(2) Unlatch and open the cover of the Integrated
Power Module (IPM).
(3) Remove the stored 15 amp IOD fuse from fuse
storage markedSPAREof the IPM.
(4) Use a thumb to press the IOD fuse firmly down
into IPM fuse cavity markedIOD.
(5) Close and latch the IPM cover.
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION
Accessory power outlets are standard equipment on
this model. Two power outlets are installed in the
instrument panel center lower bezel, which is located
near the bottom of the instrument panel center stack
area. Two additional power outlets are also incorpo-
rated into the vehicle, one on the left rear C-pillar
trim and the other in the center console, if equipped.
The power outlets bases are secured by a snap fit in
the appropriate bezels. A hinged plug flips closed to
conceal and protect the power outlet base when the
power outlet is not being used.
The power outlet receptacle unit and the power
outlet plugs are each available for service replace-
ment.
OPERATION
The power outlet base or receptacle shell is con-
nected to ground, and an insulated contact in the
bottom of the shell is connected to battery current.
The power outlet on the instrument panel marked
with a battery receives battery voltage from a fuse in
the Integrated Power Module (IPM) at all times. The
other power outlet on the instrument panel marked
with a key receives battery voltage only when the
key is in the on position.
The power outlet located in the center console
receives battery voltage all the time when positioned
between thefront seatsand key-on voltage when
positioned between therear seats. The power outlet
located on the C-pillar receives battery voltage only
when the key is in the on position.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - POWER OUTLET
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toCigar
Lighter/Power Outletin Wiring Diagrams.
RS8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM8W-97-5
IOD FUSE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1478 of 2399

FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pump relay is located in the PDC. The
inside top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay
and fuse location.
OPERATION
The fuel pump relay supplies battery voltage to the
fuel pump. A buss bar in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) supplies voltage to the solenoid side and
contact side of the relay. The fuel pump relay power
circuit contains a fuse between the buss bar in the
PDC and the relay. The fuse is located in the PDC.
Refer to the Wiring Diagrams for circuit information.
The PCM controls the fuel pump relay by switch-
ing the ground path for the solenoid side of the relay
on and off. The PCM turns the ground path off when
the ignition switch is in the Off position. When the
ignition switch is in the On position, the PCM ener-
gizes the fuel pump. If the crankshaft position sensor
does not detect engine rotation, the PCM de-ener-
gizes the relay after approximately one second.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The idle air control motor is mounted on the throt-
tle body. The PCM operates the idle air control motor
(Fig. 14) or (Fig. 15).
OPERATION
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the
idle air control motor to compensate for engine load,
coolant temperature or barometric pressure changes.
The throttle body has an air bypass passage that
provides air for the engine during closed throttle idle.
The idle air control motor pintle protrudes into the
air bypass passage and regulates air flow through it.
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed by moving the
IAC motor pintle in and out of the bypass passage. The
adjustments are based on inputs the PCM receives.
The inputs are from the throttle position sensor, crank-
shaft position sensor, coolant temperature sensor, MAP
sensor, vehicle speed sensor and various switch opera-
tions (brake, park/neutral, air conditioning).
When engine rpm is above idle speed, the IAC is
used for the following functions:
²Off-idle dashpot
²Deceleration air flow control
²A/C compressor load control (also opens the pas-
sage slightly before the compressor is engaged so
that the engine rpm does not dip down when the
compressor engages)
Target Idle
Target idle is determined by the following inputs:
²Gear position
²ECT Sensor
²Battery voltage
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensor
²VSS
²TPS
²MAP Sensor
Fig. 14 TPS/IAC 2.4L
1 - Idle Air Control Motor
2 - Throttle Position Sensor
Fig. 15 TPS/IAC 3.3/3.8L
1 - Idle Air Control Motor
2 - Throttle Position Sensor
RSFUEL INJECTION14-27
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2257 of 2399
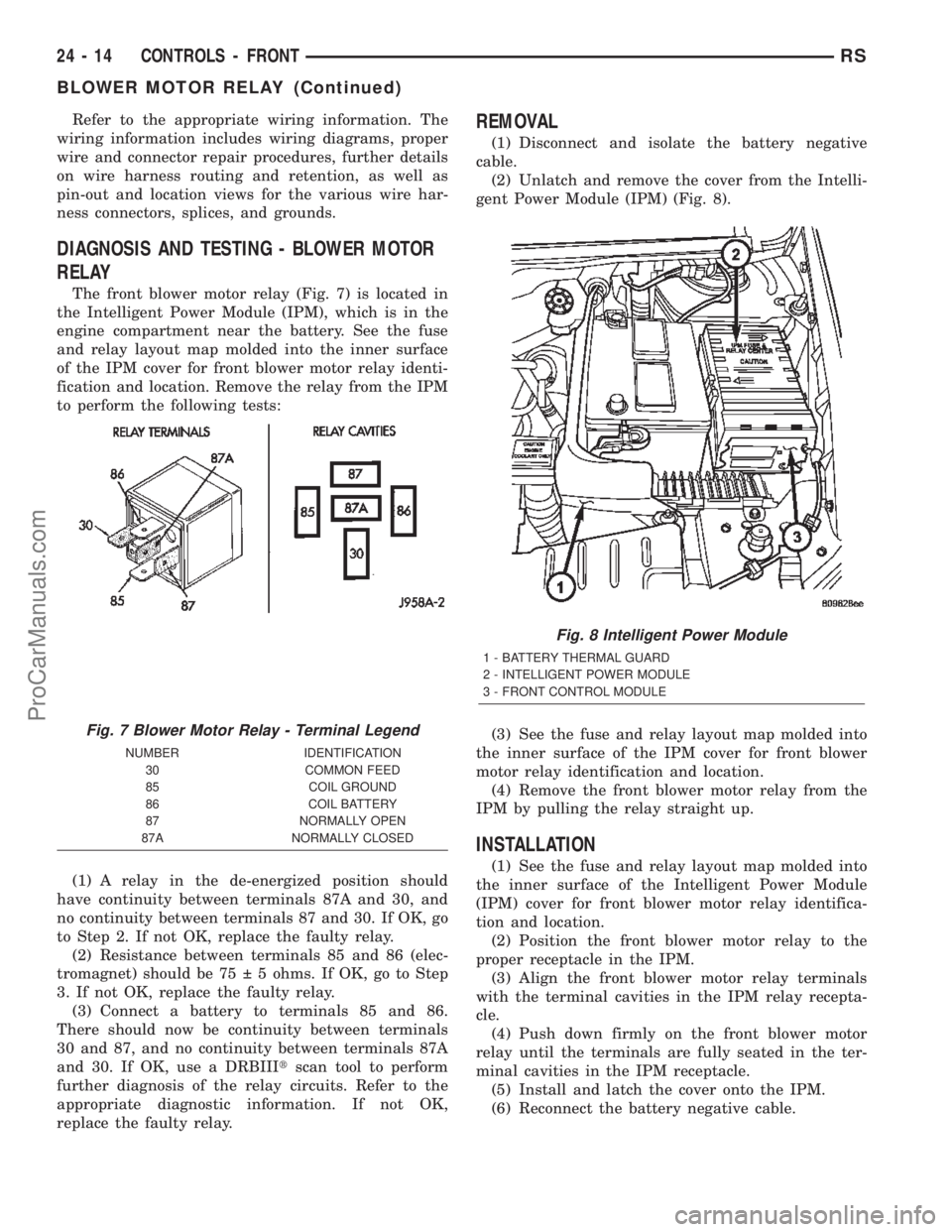
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices, and grounds.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER MOTOR
RELAY
The front blower motor relay (Fig. 7) is located in
the Intelligent Power Module (IPM), which is in the
engine compartment near the battery. See the fuse
and relay layout map molded into the inner surface
of the IPM cover for front blower motor relay identi-
fication and location. Remove the relay from the IPM
to perform the following tests:
(1) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 2. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(2) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 5 ohms. If OK, go to Step
3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, use a DRBIIItscan tool to perform
further diagnosis of the relay circuits. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information. If not OK,
replace the faulty relay.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unlatch and remove the cover from the Intelli-
gent Power Module (IPM) (Fig. 8).
(3) See the fuse and relay layout map molded into
the inner surface of the IPM cover for front blower
motor relay identification and location.
(4) Remove the front blower motor relay from the
IPM by pulling the relay straight up.
INSTALLATION
(1) See the fuse and relay layout map molded into
the inner surface of the Intelligent Power Module
(IPM) cover for front blower motor relay identifica-
tion and location.
(2) Position the front blower motor relay to the
proper receptacle in the IPM.
(3) Align the front blower motor relay terminals
with the terminal cavities in the IPM relay recepta-
cle.
(4) Push down firmly on the front blower motor
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(5) Install and latch the cover onto the IPM.
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
Fig. 7 Blower Motor Relay - Terminal Legend
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
Fig. 8 Intelligent Power Module
1 - BATTERY THERMAL GUARD
2 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
24 - 14 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2265 of 2399

a battery current output only when the compressor
clutch relay coil is de-energized.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices, and grounds.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH RELAY
The compressor clutch relay (Fig. 17) is located in
the Intelligent Power Module (IPM), which is in the
engine compartment near the battery. See the fuse
and relay layout map molded into the inner surface
of the IPM cover for compressor clutch relay identifi-
cation and location. Remove the relay from the IPM
to perform the following tests:
(1) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 2. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(2) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 5 ohms. If OK, go to Step
3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, use a DRBIIItscan tool to perform
further diagnosis of the relay circuits. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information. If not OK,
replace the faulty relay.
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unlatch and remove the cover from the Intelli-
gent Power Module (IPM).
(3) See the fuse and relay layout map molded into
the inner surface of the IPM cover for compressor
clutch relay identification and location.
(4) Remove the compressor clutch relay from the
IPM by pulling it straight up.
INSTALLATION
(1) See the fuse and relay layout map molded into
the inner surface of the Intelligent Power Module
(IPM) cover for compressor clutch relay identification
and location.
(2) Position the compressor clutch relay to the
proper receptacle in the IPM.
(3) Align the compressor clutch relay terminals
with the terminal cavities in the IPM relay recepta-
cle.
(4) Push down firmly on the compressor clutch
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(5) Install and latch the cover onto the IPM.
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The evaporator temperature sensor is a switch that
is installed on the top of the expansion valve in the
right rear corner of the engine compartment (Fig.
18). The sensor has a small probe that is inserted in
a small well in the body of the expansion valve that
is filled with a special silicone-based thermal grease.
A small molded plastic push-in retainer secures the
sensor to a threaded hole in the top surface of the
expansion valve. Two terminals within a molded
plastic connector receptacle on the sensor connect it
to the vehicle electrical system through a take out
and connector of the HVAC wire harness.
Fig. 17 Compressor Clutch Relay
24 - 22 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2276 of 2399

The blower motor relay terminals are connected to
the vehicle electrical system through a receptacle in
the Intelligent Power Module (IPM). The inputs and
outputs of the compressor clutch relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from the battery through a B(+)
circuit at all times.
²The coil ground terminal (85) receives a ground
input through the front/rear blower motor relay con-
trol circuit only when the FCM electronically pulls
the control circuit to ground.
²The coil battery terminal (86) receives a battery
current input from the battery through a B(+) circuit
at all times.
²The normally open terminal (87) provides a bat-
tery current output to the blower motor resistor
(manual heater-A/C control) or blower power module
(automatic heater-A/C control) through a fuse in the
IPM on the fused rear blower motor relay output cir-
cuit only when the blower motor relay coil is ener-
gized.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is not con-
nected to any circuit in this application, but provides
a battery current output only when the blower motor
relay coil is de-energized.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices, and grounds.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER MOTOR
RELAY
The rear blower motor relay (Fig. 6) is located in
the Intelligent Power Module (IPM), which is in the
engine compartment near the battery. See the fuse
and relay layout map molded into the inner surface
of the IPM cover for rear blower motor relay identi-
fication and location. Remove the relay from the IPM
to perform the following tests:
(1) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 2. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(2) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 5 ohms. If OK, go to Step
3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, use a DRBIIItscan tool to perform
further diagnosis of the relay circuits. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information. If not OK,
replace the faulty relay.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unlatch and remove the cover from the Intelli-
gent Power Module (IPM) (Fig. 7).
Fig. 6 Blower Motor Relay
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL GROUND
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
Fig. 7 Intelligent Power Module
1 - BATTERY THERMAL GUARD
2 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
RSCONTROLS - REAR24-33
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com