light CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 1965 of 2585
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
SERVICE
NOTE: Refer to the maintenance schedules in
LUBRICATION and MAINTENANCE, or the vehicle
owner's manual, for the recommended maintenance
(fluid/filter change) intervals for this transaxle.
NOTE: Only fluids of the type labeled MoparTATF+4
should be used. A filter change should be made at
the time of the transmission oil change. The magnet
(on the inside of the oil pan) should also be cleaned
with a clean, dry cloth.
NOTE: If the transaxle is disassembled for any rea-
son, the fluid and filter should be changed.
FLUID/FILTER SERVICE (RECOMMENDED)
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist. Refer to LUBRICA-
TION and MAINTENANCE for proper procedures.
Place a drain container with a large opening, under
transaxle oil pan. (2) Remove both engine mount-to-engine cross-
member cradle nuts. Using suitable screw jack and
wood block, raise engine and transmission slightly to
facilitate transaxle oil pan removal and installation. (3) Loosen pan bolts and tap the pan at one corner
to break it loose allowing fluid to drain, then remove
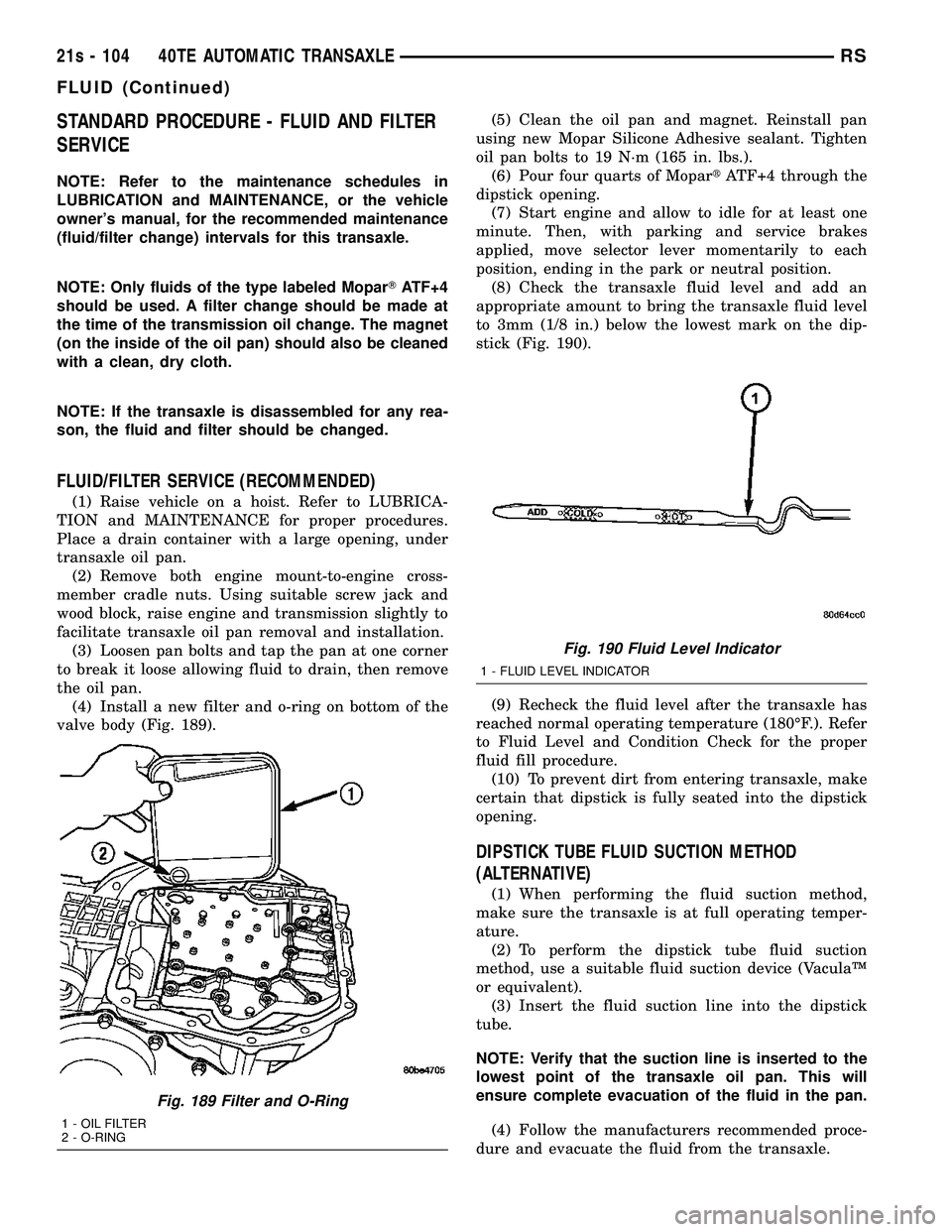
the oil pan. (4) Install a new filter and o-ring on bottom of the
valve body (Fig. 189). (5) Clean the oil pan and magnet. Reinstall pan
using new Mopar Silicone Adhesive sealant. Tighten
oil pan bolts to 19 N´m (165 in. lbs.). (6) Pour four quarts of Mopar tATF+4 through the
dipstick opening. (7) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position. (8) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the lowest mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 190).
(9) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.). Refer
to Fluid Level and Condition Check for the proper
fluid fill procedure. (10) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
DIPSTICK TUBE FLUID SUCTION METHOD
(ALTERNATIVE)
(1) When performing the fluid suction method,
make sure the transaxle is at full operating temper-
ature. (2) To perform the dipstick tube fluid suction
method, use a suitable fluid suction device (VaculaŸ
or equivalent). (3) Insert the fluid suction line into the dipstick
tube.
NOTE: Verify that the suction line is inserted to the
lowest point of the transaxle oil pan. This will
ensure complete evacuation of the fluid in the pan.
(4) Follow the manufacturers recommended proce-
dure and evacuate the fluid from the transaxle.
Fig. 189 Filter and O-Ring
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - O-RING
Fig. 190 Fluid Level Indicator
1 - FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
21s - 104 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
FLUID (Continued)
Page 2009 of 2585
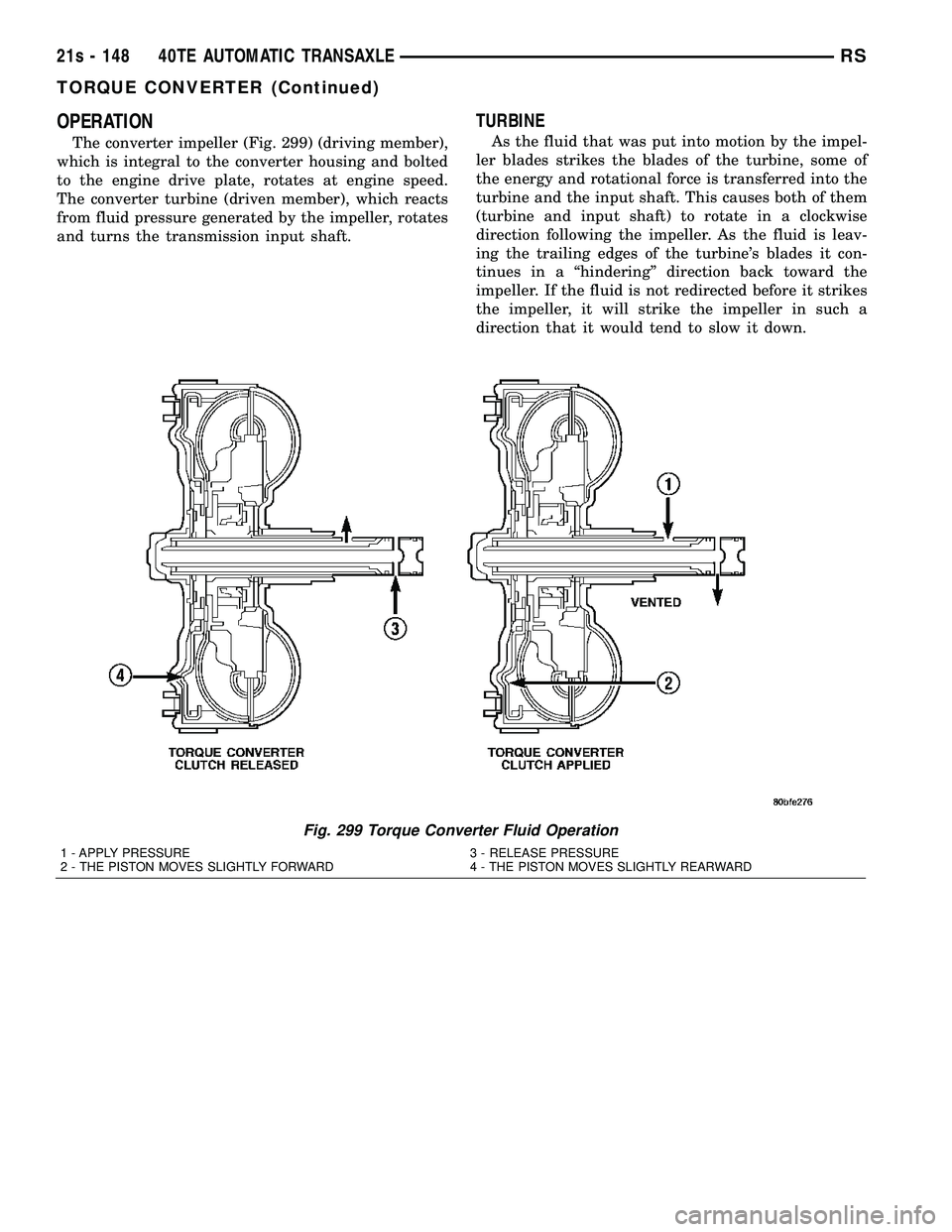
OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 299) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
Fig. 299 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
21s - 148 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2010 of 2585
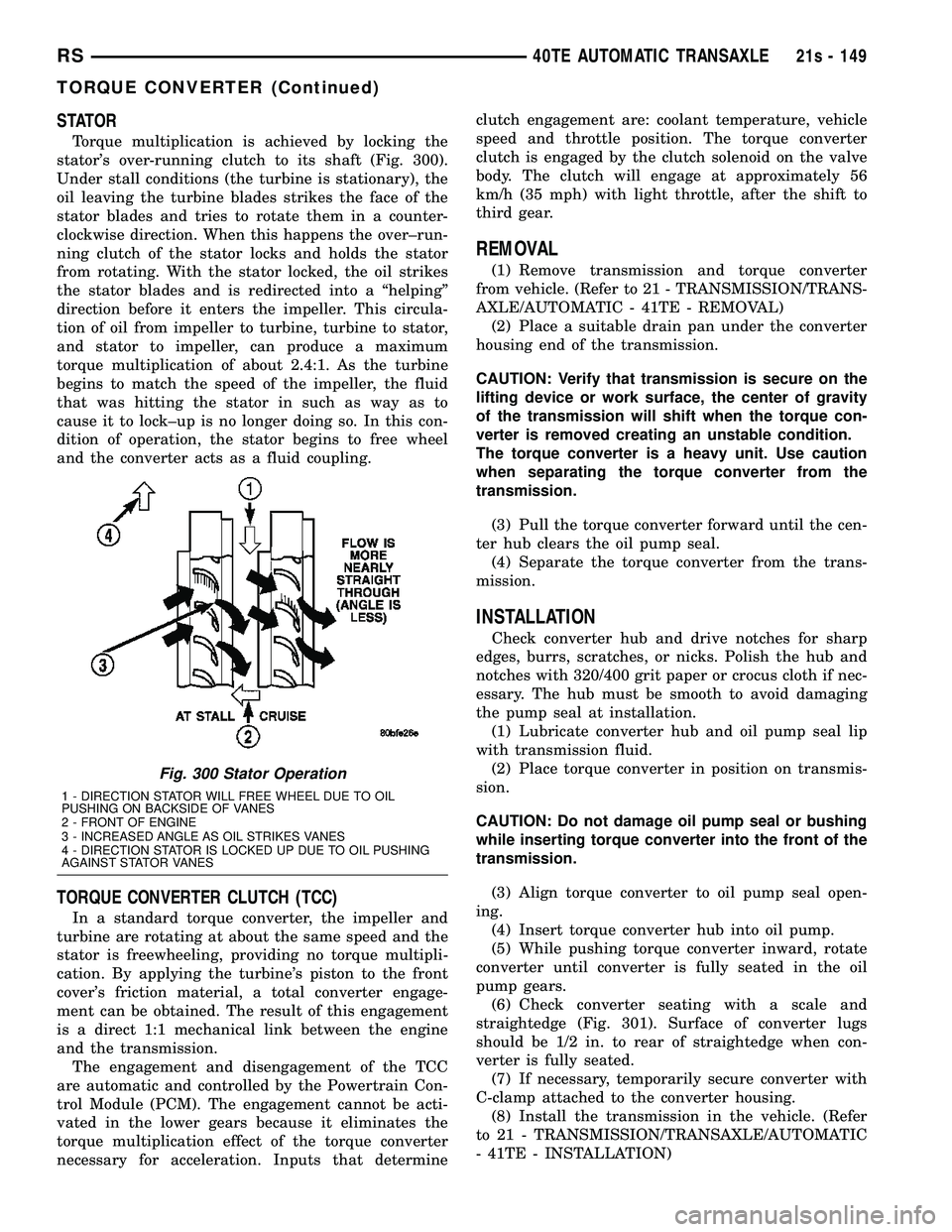
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 300).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the over±run-
ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock±up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and
turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the
stator is freewheeling, providing no torque multipli-
cation. By applying the turbine's piston to the front
cover's friction material, a total converter engage-
ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission. The engagement and disengagement of the TCC
are automatic and controlled by the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). The engagement cannot be acti-
vated in the lower gears because it eliminates the
torque multiplication effect of the torque converter
necessary for acceleration. Inputs that determine clutch engagement are: coolant temperature, vehicle
speed and throttle position. The torque converter
clutch is engaged by the clutch solenoid on the valve
body. The clutch will engage at approximately 56
km/h (35 mph) with light throttle, after the shift to
third gear.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE - REMOVAL) (2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal. (4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation. (1) Lubricate converter hub and oil pump seal lip
with transmission fluid. (2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing. (4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears. (6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 301). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated. (7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing. (8) Install the transmission in the vehicle. (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE - INSTALLATION)
Fig. 300 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 149
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2014 of 2585
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
The solenoid switch valve controls line pressure
from the LR/CC solenoid. In one position, it allows
the low/reverse clutch to be pressurized. In the other,
it directs line pressure to the converter control and
converter clutch valves.
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve is operated by the mechanical
shift linkage. Its primary responsibility is to send
line pressure to the appropriate hydraulic circuits
and solenoids. The valve has three operating ranges
or positions.
CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
The main responsibility of the converter clutch
switch valve is to control hydraulic pressure applied
to the front (off) side of the converter clutch piston.
Line pressure from the regulator valve is fed to the
torque converter regulator valve, where it passes
through the valve, and is slightly regulated. The
pressure is then directed to the converter clutch
switch valve and to the front side of the converter
clutch piston. This pressure pushes the piston back
and disengages the converter clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH CONTROL VALVE
The converter clutch control valve controls the
back (on) side of the torque converter clutch. When
the PCM/TCM energizes or modulates the LR/CC
solenoid to apply the converter clutch piston, both
the converter clutch control valve and the converter
control valve move, allowing pressure to be applied to
the back side of the clutch.
T/C REGULATOR VALVE
The torque converter regulator valve slightly regu-
lates the flow of fluid to the torque converter.
LOW/REVERSE SWITCH VALVE
The low/reverse clutch is applied from different
sources, depending on whether low (1st) gear or
reverse is selected. The low/reverse switch valve
alternates positions depending on from which direc-
tion fluid pressure is applied. By design, when the
valve is shifted by fluid pressure from one channel,
the opposing channel is blocked. The switch valve
alienates the possibility of a sticking ball check, thus
providing consistent application of the low/reverse
clutch under all operating conditions.
REMOVAL
NOTE: If valve body is replaced or reconditioned,
the TCM Quick Learn Procedure must be per-
formed. (Refer t o 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect gearshift cable from manual valve
lever. (3) Remove manual valve lever from manual shaft.
(4) Raise vehicle on hoist.
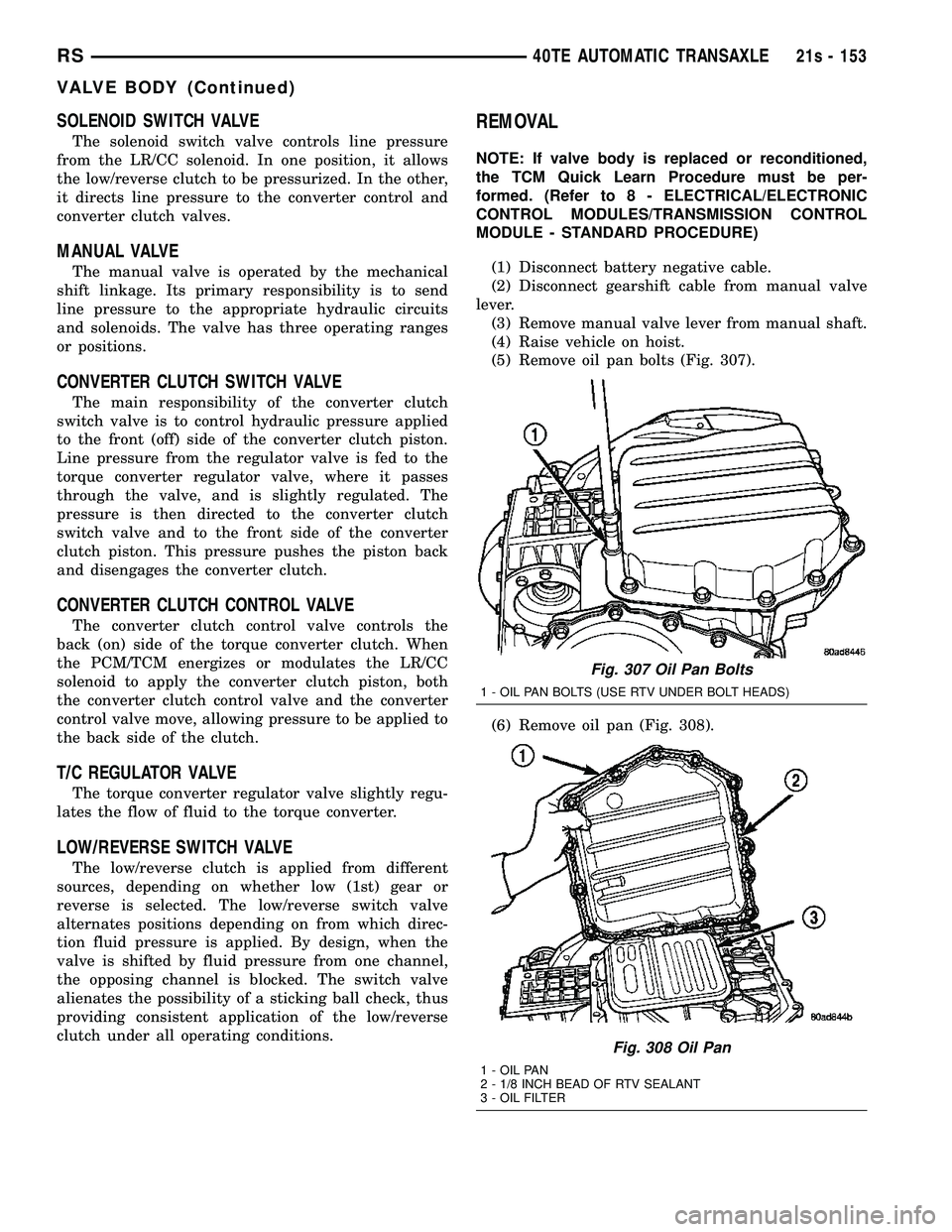
(5) Remove oil pan bolts (Fig. 307).
(6) Remove oil pan (Fig. 308).
Fig. 307 Oil Pan Bolts
1 - OIL PAN BOLTS (USE RTV UNDER BOLT HEADS)
Fig. 308 Oil Pan
1 - OIL PAN
2 - 1/8 INCH BEAD OF RTV SEALANT
3 - OIL FILTER
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 153
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 2081 of 2585

unique wheel weights. They are designed to fit the
contour of the wheel (Fig. 1).
²Inspect tires and wheels for damage, mud pack-
ing and unusual wear; correct as necessary.
²Check and adjust tire air pressure to the pres-
sure listed on the label attached to the rear face of
the driver's door.
ROAD TEST
Road test vehicle on a smooth road for a least five
miles to warm tires (remove any flat spots). Lightly
place hands on steering wheel at the 10:00 and 2:00
positions while slowly sweeping up and down from 90
to 110 km/h (55 to 70 mph) where legal speed limits
allow.
Observe the steering wheel for:
²Visual Nibble (oscillation: clockwise/counter-
clockwise, usually due to tire imbalance)
²Visual Buzziness (high frequency, rapid vibra-
tion up and down)
To rule out vibrations due to brakes or powertrain:
²Lightly apply brakes at speed; if vibration occurs
or is enhanced, vibration is likely due to causes other
than tire and wheel assemblies.
²Shift transmission into neutral while vibration
is occurring; if vibration is eliminated, vibration is
likely due to causes other than tire and wheel assem-
blies.
For brake vibrations, (Refer to 5 - BRAKES -
BASE/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
For powertrain vibrations, (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
For tire and wheel assembly vibrations, continue
with this diagnosis and testing procedure.
TIRE AND WHEEL BALANCE
(1) Balance the tire and wheel assemblies as nec-
essary following the wheel balancer manufacturer's
instructions and using the information listed in Stan-
dard Procedure - Tire And Wheel Balance. (Refer to
22 - TIRES/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(2) Road test the vehicle for at least 5 miles, fol-
lowing the format described in Road Test.
(3) If the vibration persists, continue with this
diagnosis and testing procedure.
TIRE AND WHEEL RUNOUT/MATCH MOUNTING
(1)System Radial Runout.This on-the-vehicle
system check will measure the radial runout includ-
ing the hub, wheel and tire.
(a) Raise vehicle so tires clear floor. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/HOISTING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(b) Apply masking tape around the circumfer-
ence of the tire in the locations to be measured
(Fig. 2). Do not overlap the tape.
(c) Check system runout using Dial Indicator
Set, Special Tool C-3339A with 25-W wheel, or
equivalent. Place the end of the indicator against
each taped area (one at a time) (Fig. 2) and rotate
the tire and wheel. System radial runout should
not exceed 0.76 mm (0.030 inch) with no tread
ªdipsº or ªsteps.º Tread ªdipsº and ªstepsº can be
identified by spikes of the dial indicator gauge.
²Tread9dips9; Rapid decrease then increase in
dial indicator reading over 101.6 mm (4.0 inch) of
tread circumference.
²Tread9steps9; Rapid decrease or increase in dial
indicator reading over 101.6 mm (4.0 inch) of tread
circumference.
(d) If system runout is excessive, re-index the
tire and wheel assembly on the hub. Remove
assembly from vehicle and install it back on the
hub two studs over from original mounting posi-
tion. If re-indexing the tire and wheel assembly
corrects or reduces system runout, check hub
runout and repair as necessary (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - BASE/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
ROTORS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(e) If system runout is still excessive, continue
with this diagnosis and testing procedure.
(2)Tire and Wheel Assembly Radial Runout.
This radial runout check is performed with the tire
and wheel assembly off the vehicle.
(a) Remove tire and wheel assembly from vehicle
and install it on a suitable wheel balancer.
(b) Check system runout using Dial Indicator
Set, Special Tool C-3339A with 25-W wheel, or
equivalent. Place the end of the indicator against
each taped area (one at a time) (Fig. 2) and rotate
the tire and wheel. Radial runout should not
Fig. 1 Aluminum Wheel Weight
1 - TIRE
2 - WHEEL
3 - WHEEL WEIGHT
22 - 2 TIRES/WHEELSRS
TIRES/WHEELS (Continued)
Page 2087 of 2585
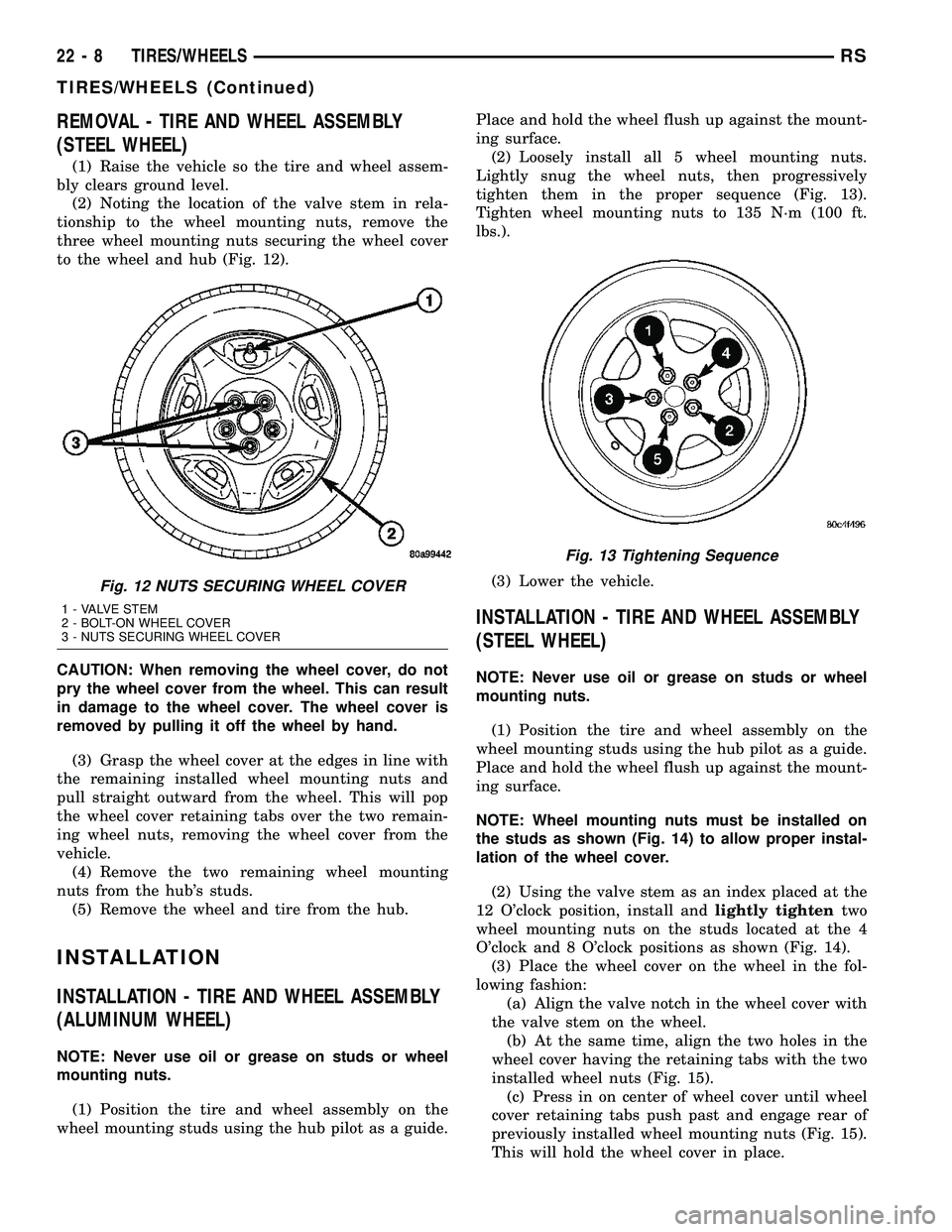
REMOVAL - TIRE AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY
(STEEL WHEEL)
(1) Raise the vehicle so the tire and wheel assem-
bly clears ground level.
(2) Noting the location of the valve stem in rela-
tionship to the wheel mounting nuts, remove the
three wheel mounting nuts securing the wheel cover
to the wheel and hub (Fig. 12).
CAUTION: When removing the wheel cover, do not
pry the wheel cover from the wheel. This can result
in damage to the wheel cover. The wheel cover is
removed by pulling it off the wheel by hand.
(3) Grasp the wheel cover at the edges in line with
the remaining installed wheel mounting nuts and
pull straight outward from the wheel. This will pop
the wheel cover retaining tabs over the two remain-
ing wheel nuts, removing the wheel cover from the
vehicle.
(4) Remove the two remaining wheel mounting
nuts from the hub's studs.
(5) Remove the wheel and tire from the hub.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - TIRE AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY
(ALUMINUM WHEEL)
NOTE: Never use oil or grease on studs or wheel
mounting nuts.
(1) Position the tire and wheel assembly on the
wheel mounting studs using the hub pilot as a guide.Place and hold the wheel flush up against the mount-
ing surface.
(2) Loosely install all 5 wheel mounting nuts.
Lightly snug the wheel nuts, then progressively
tighten them in the proper sequence (Fig. 13).
Tighten wheel mounting nuts to 135 N´m (100 ft.
lbs.).
(3) Lower the vehicle.
INSTALLATION - TIRE AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY
(STEEL WHEEL)
NOTE: Never use oil or grease on studs or wheel
mounting nuts.
(1) Position the tire and wheel assembly on the
wheel mounting studs using the hub pilot as a guide.
Place and hold the wheel flush up against the mount-
ing surface.
NOTE: Wheel mounting nuts must be installed on
the studs as shown (Fig. 14) to allow proper instal-
lation of the wheel cover.
(2) Using the valve stem as an index placed at the
12 O'clock position, install andlightly tightentwo
wheel mounting nuts on the studs located at the 4
O'clock and 8 O'clock positions as shown (Fig. 14).
(3) Place the wheel cover on the wheel in the fol-
lowing fashion:
(a) Align the valve notch in the wheel cover with
the valve stem on the wheel.
(b) At the same time, align the two holes in the
wheel cover having the retaining tabs with the two
installed wheel nuts (Fig. 15).
(c) Press in on center of wheel cover until wheel
cover retaining tabs push past and engage rear of
previously installed wheel mounting nuts (Fig. 15).
This will hold the wheel cover in place.
Fig. 12 NUTS SECURING WHEEL COVER
1 - VALVE STEM
2 - BOLT-ON WHEEL COVER
3 - NUTS SECURING WHEEL COVER
Fig. 13 Tightening Sequence
22 - 8 TIRES/WHEELSRS
TIRES/WHEELS (Continued)
Page 2088 of 2585

(4) Install andlightly tightenthe three remain-
ing wheel mounting nuts, securing the wheel cover in
place (Fig. 12).
(5) Progressively tighten all five wheel mounting
nuts in the proper sequence (Fig. 16). Tighten wheel
nuts to a torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(6) Lower the vehicle.
TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING
DESCRIPTION
Some versions of this vehicle are equipped with a
Tire Pressure Monitoring (TPM) system. It monitors
air pressure in the four road tires (excludes spare).
Pressure in the spare tire is not monitored.
There is a sensor (transmitter) in each of the vehi-
cle's four road wheels. The system alerts the driver
when tire pressure falls outside predetermined
thresholds (pressure too low or too high). A message
is then displayed on the Electronic Vehicle Informa-
tion Center (EVIC) located in the overhead console.
For further information, refer to the Owners Man-
ual or the appropriate diagnostic information.
OPERATION
The Tire Pressure Monitoring (TPM) system uses
radio and sensor technology to monitor tire air pres-
sure levels. Sensors, mounted to each road wheel as
part of the valve stem, transmit tire pressure read-
ings to a receiver located in the overhead console.
These transmissions occur once every minute at
speeds over 20 mph (32 km/h). The Tire Pressure
Monitoring system remains active even if no tire
pressure related message is displayed in the EVIC.
If any road tire pressure has exceeded the low or
high pressure threshold (refer to chart below), the
TPM system will display a message in the EVIC and
sound a chime. This message will be displayed for
the rest of the ignition cycle, or until either the Low/
High Tire pressure condition has been corrected. If
the C/T, MENU, STEP or RESET button is pressed,
the message is replaced by the new message
requested; however, if the Low/High Tire condition
has not been corrected, the Low/High Tire pressure
message will again be displayed.
Fig. 14 TWO WHEEL MOUNTING NUTS INSTALLED
1 - WHEEL
2 - VALVE STEM
3 - HUB PILOT
4 - NUTS
Fig. 15 WHEEL COVER INSTALLATION OVER TWO
NUTS
1 - RETAINING TABS
2 - VALVE STEM
3 - BOLT-ON WHEEL COVER
Fig. 16 NUT TIGHTENING SEQUENCE
RSTIRES/WHEELS22-9
TIRES/WHEELS (Continued)
Page 2092 of 2585
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - TIRE
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle. They provide the best overall performance
for normal operation. The ride and handling charac-
teristics match the vehicle's requirements. With
proper care they will give excellent reliability, trac-
tion, skid resistance, and tread life.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain, in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are:
²Rapid acceleration
²Severe application of brakes
²High-speed driving
²Taking turns at excessive speeds
²Striking curbs and other obstacles
²Operating vehicle with over or under inflated
tire pressures
Radial ply tires are more prone to irregular tread
wear. It is important to follow the tire rotation inter-
val shown in the section on Tire Rotation. This will
help to achieve a greater tread-life potential.
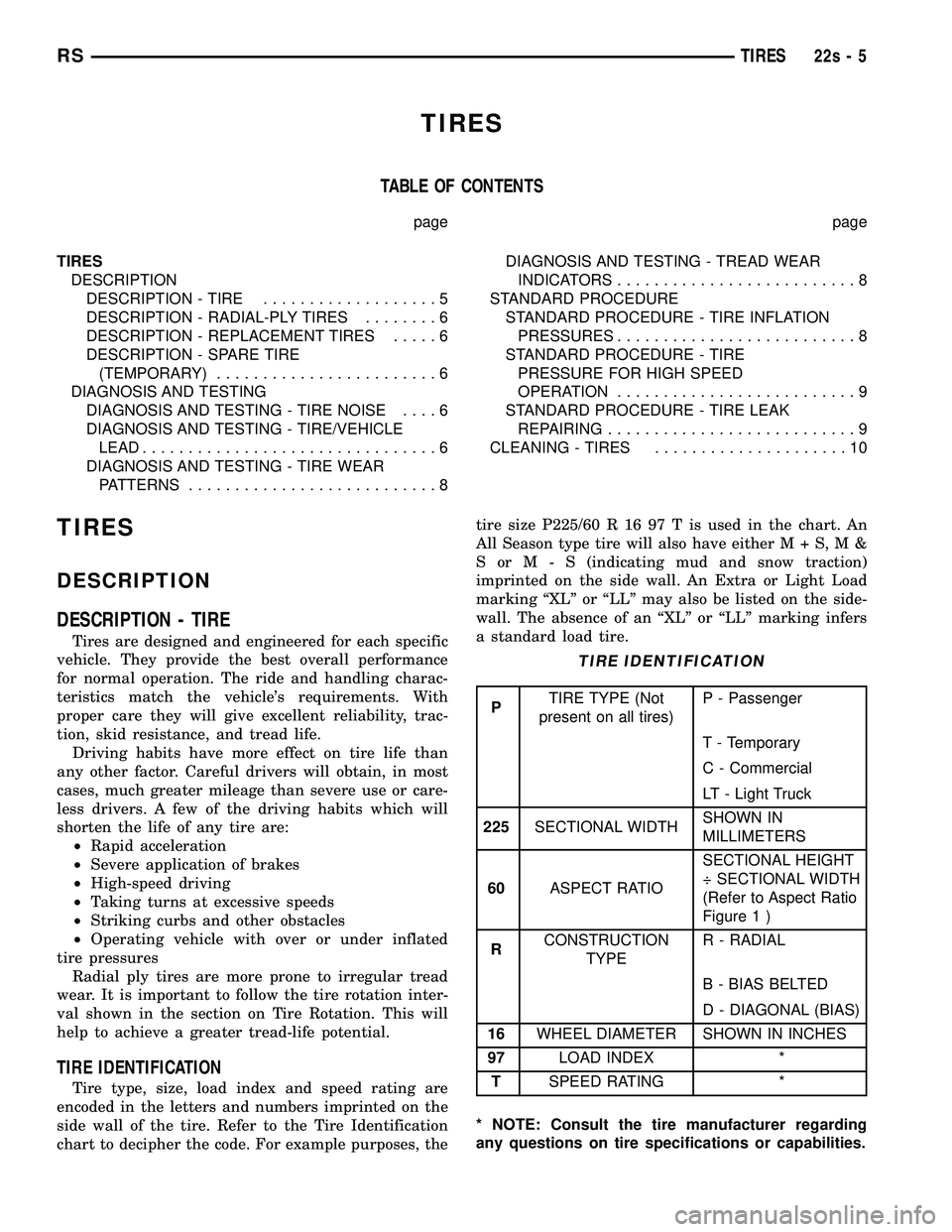
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, load index and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the Tire Identification
chart to decipher the code. For example purposes, the
tire size P225/60 R 16 97 T is used in the chart. An
All Season type tire will also have eitherM+S,M&
SorM-S(indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall. An Extra or Light Load
marking ªXLº or ªLLº may also be listed on the side-
wall. The absence of an ªXLº or ªLLº marking infers
a standard load tire.
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
PTIRE TYPE (Not
present on all tires)P - Passenger
T - Temporary
C - Commercial
LT - Light Truck
225SECTIONAL WIDTHSHOWN IN
MILLIMETERS
60ASPECT RATIOSECTIONAL HEIGHT
÷ SECTIONAL WIDTH
(Refer to Aspect Ratio
Figure 22 )
Fig. 20 Mounting Tire Using Rotating Wheel
Machine
1 - HEAD OF CHANGER LOCATED HERE
2 - VALVE STEM
Fig. 21 Mounting Tire Using Rotating Tool Machine
1 - VALVE STEM
2 - MOUNTING END OF TOOL
3 - BEAD BREAKER (KEEP CLEAR OF SENSOR)
RSTIRES/WHEELS22-13
SENSOR - TPM (Continued)
Page 2099 of 2585
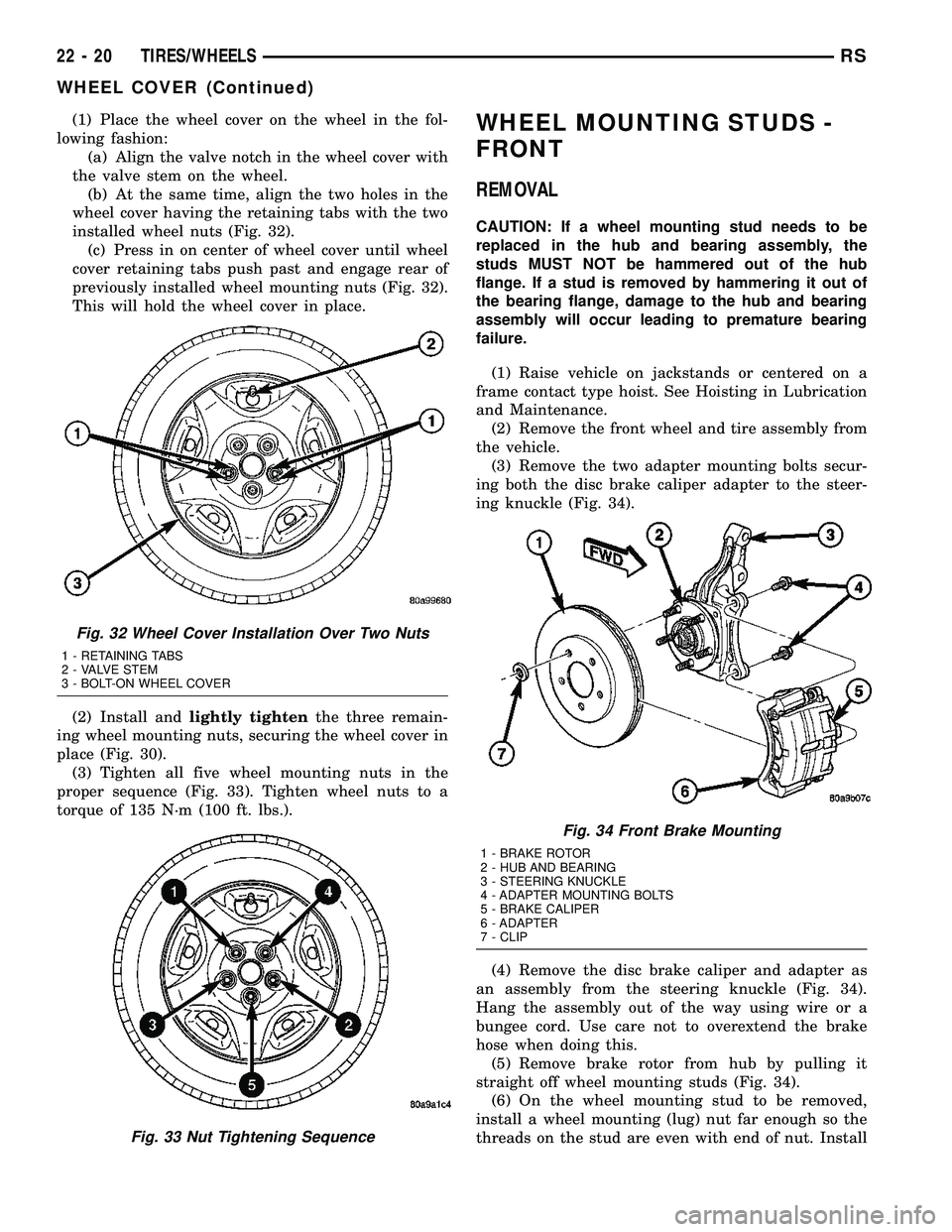
(1) Place the wheel cover on the wheel in the fol-
lowing fashion:
(a) Align the valve notch in the wheel cover with
the valve stem on the wheel.
(b) At the same time, align the two holes in the
wheel cover having the retaining tabs with the two
installed wheel nuts (Fig. 32).
(c) Press in on center of wheel cover until wheel
cover retaining tabs push past and engage rear of
previously installed wheel mounting nuts (Fig. 32).
This will hold the wheel cover in place.
(2) Install andlightly tightenthe three remain-
ing wheel mounting nuts, securing the wheel cover in
place (Fig. 30).
(3) Tighten all five wheel mounting nuts in the
proper sequence (Fig. 33). Tighten wheel nuts to a
torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS -
FRONT
REMOVAL
CAUTION: If a wheel mounting stud needs to be
replaced in the hub and bearing assembly, the
studs MUST NOT be hammered out of the hub
flange. If a stud is removed by hammering it out of
the bearing flange, damage to the hub and bearing
assembly will occur leading to premature bearing
failure.
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in Lubrication
and Maintenance.
(2) Remove the front wheel and tire assembly from
the vehicle.
(3) Remove the two adapter mounting bolts secur-
ing both the disc brake caliper adapter to the steer-
ing knuckle (Fig. 34).
(4) Remove the disc brake caliper and adapter as
an assembly from the steering knuckle (Fig. 34).
Hang the assembly out of the way using wire or a
bungee cord. Use care not to overextend the brake
hose when doing this.
(5) Remove brake rotor from hub by pulling it
straight off wheel mounting studs (Fig. 34).
(6) On the wheel mounting stud to be removed,
install a wheel mounting (lug) nut far enough so the
threads on the stud are even with end of nut. Install
Fig. 32 Wheel Cover Installation Over Two Nuts
1 - RETAINING TABS
2 - VALVE STEM
3 - BOLT-ON WHEEL COVER
Fig. 33 Nut Tightening Sequence
Fig. 34 Front Brake Mounting
1 - BRAKE ROTOR
2 - HUB AND BEARING
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
4 - ADAPTER MOUNTING BOLTS
5 - BRAKE CALIPER
6 - ADAPTER
7 - CLIP
22 - 20 TIRES/WHEELSRS
WHEEL COVER (Continued)
Page 2106 of 2585
TIRES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TIRES DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION - TIRE ...................5
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL-PLY TIRES ........6
DESCRIPTION - REPLACEMENT TIRES .....6
DESCRIPTION - SPARE TIRE (TEMPORARY) ........................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE ....6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE/VEHICLE LEAD ................................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE WEAR PATTERNS ...........................8 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TREAD WEAR
INDICATORS ..........................8
STANDARD PROCEDURE STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE INFLATIONPRESSURES ..........................8
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH SPEED
OPERATION ..........................9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE LEAK REPAIRING ...........................9
CLEANING - TIRES .....................10
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - TIRE
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle. They provide the best overall performance
for normal operation. The ride and handling charac-
teristics match the vehicle's requirements. With
proper care they will give excellent reliability, trac-
tion, skid resistance, and tread life. Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain, in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are: ² Rapid acceleration
² Severe application of brakes
² High-speed driving
² Taking turns at excessive speeds
² Striking curbs and other obstacles
² Operating vehicle with over or under inflated
tire pressures Radial ply tires are more prone to irregular tread
wear. It is important to follow the tire rotation inter-
val shown in the section on Tire Rotation. This will
help to achieve a greater tread-life potential.
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, load index and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the Tire Identification
chart to decipher the code. For example purposes, the tire size P225/60 R 16 97 T is used in the chart. An
All Season type tire will also have eithe
rM+S,M&
SorM-S (indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall. An Extra or Light Load
marking ªXLº or ªLLº may also be listed on the side-
wall. The absence of an ªXLº or ªLLº marking infers
a standard load tire.
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
P TIRE TYPE (Not
present on all tires) P - Passenger
T - Temporary
C - Commercial
LT - Light Truck
225 SECTIONAL WIDTH SHOWN IN
MILLIMETERS
60 ASPECT RATIO SECTIONAL HEIGHT
÷ SECTIONAL WIDTH
(Refer to Aspect Ratio
Figure 1 )
R CONSTRUCTION
TYPE R - RADIAL
B - BIAS BELTED
D - DIAGONAL (BIAS)
16 WHEEL DIAMETER SHOWN IN INCHES
97 LOAD INDEX *
T SPEED RATING *
* NOTE: Consult the tire manufacturer regarding
any questions on tire specifications or capabilities.
RS TIRES22s-5