spark CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 1480 of 2585
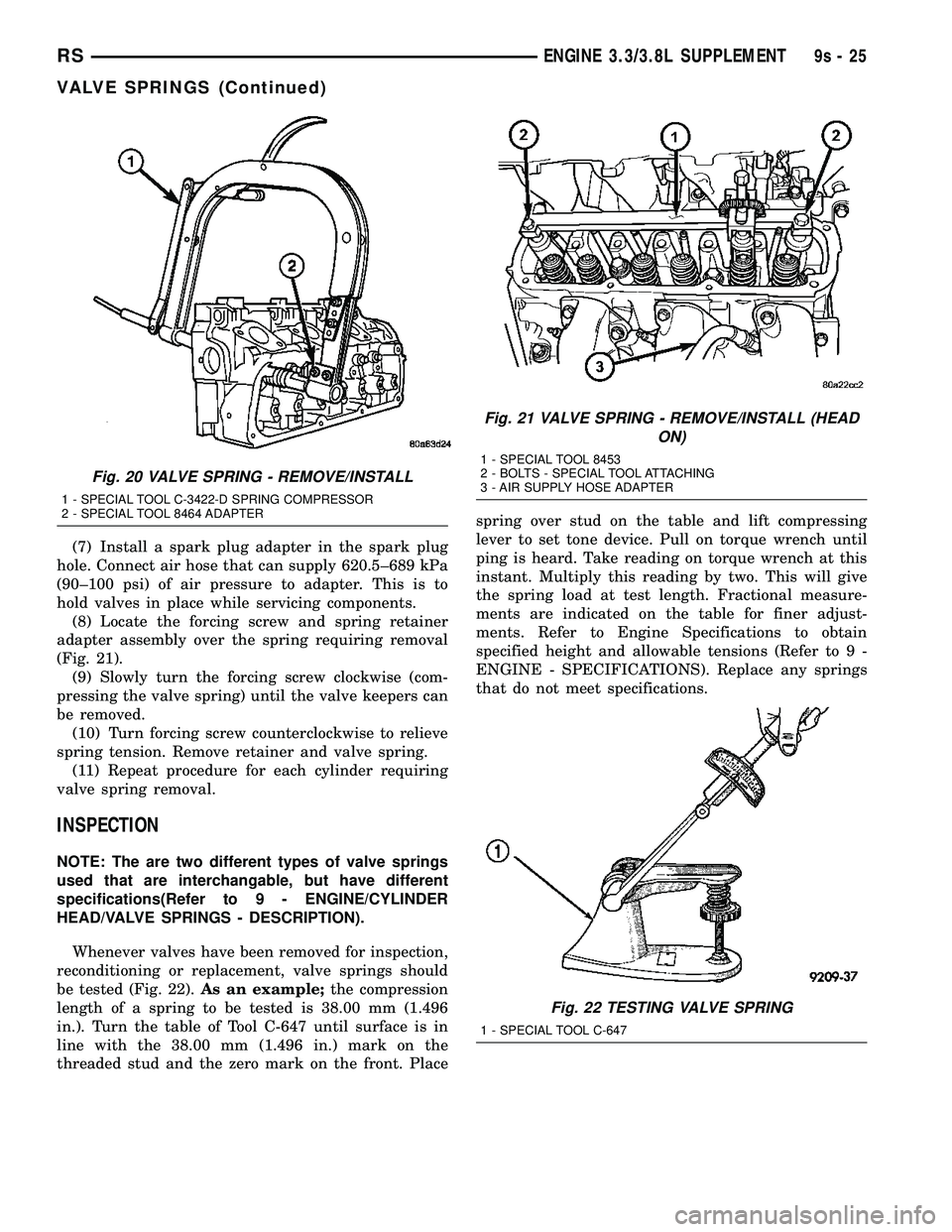
(7) Install a spark plug adapter in the spark plug
hole. Connect air hose that can supply 620.5±689 kPa
(90±100 psi) of air pressure to adapter. This is to
hold valves in place while servicing components.
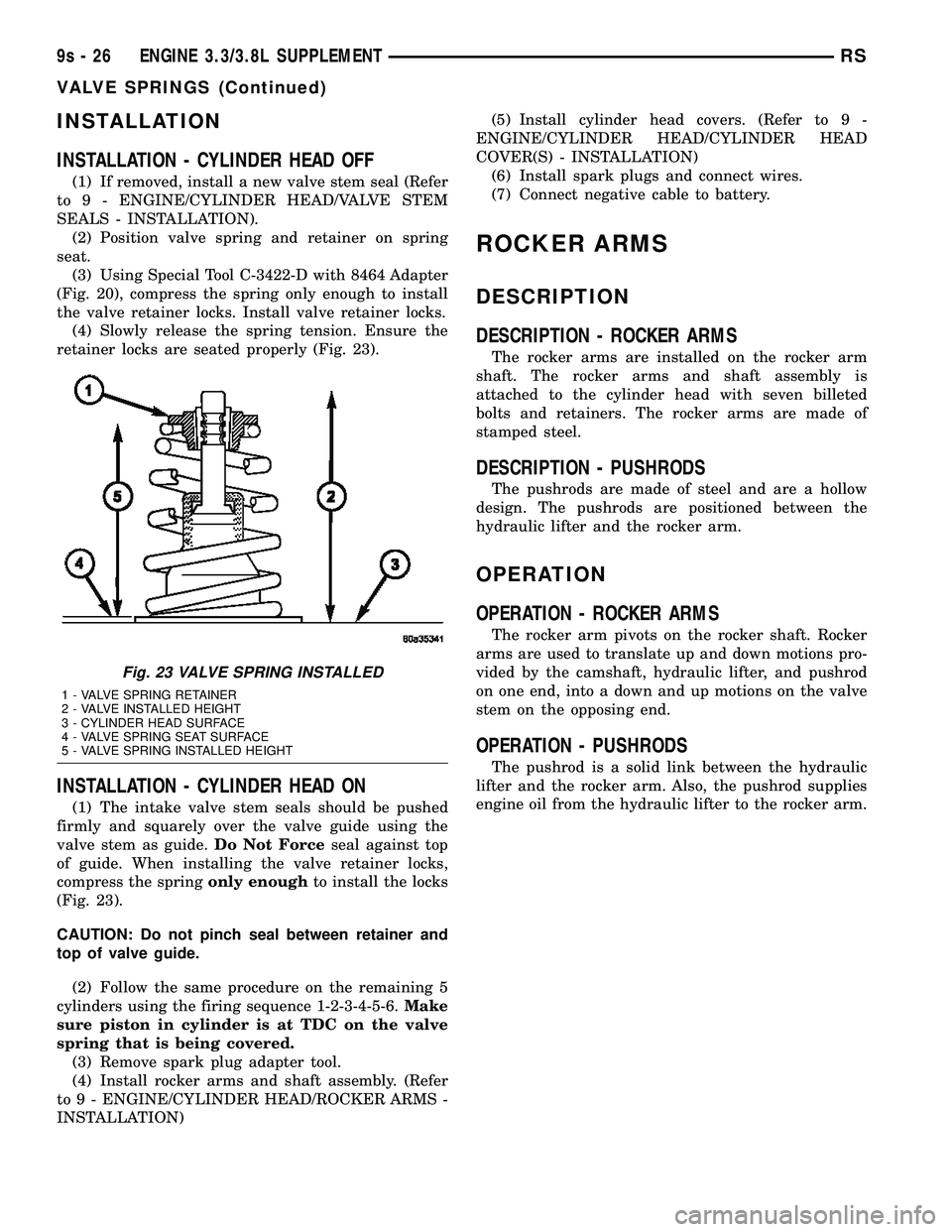
(8) Locate the forcing screw and spring retainer
adapter assembly over the spring requiring removal
(Fig. 21).
(9) Slowly turn the forcing screw clockwise (com-
pressing the valve spring) until the valve keepers can
be removed.
(10) Turn forcing screw counterclockwise to relieve
spring tension. Remove retainer and valve spring.
(11) Repeat procedure for each cylinder requiring
valve spring removal.
INSPECTION
NOTE: The are two different types of valve springs
used that are interchangable, but have different
specifications(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/VALVE SPRINGS - DESCRIPTION).
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested (Fig. 22).As an example;the compression
length of a spring to be tested is 38.00 mm (1.496
in.). Turn the table of Tool C-647 until surface is in
line with the 38.00 mm (1.496 in.) mark on the
threaded stud and the zero mark on the front. Placespring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by two. This will give
the spring load at test length. Fractional measure-
ments are indicated on the table for finer adjust-
ments. Refer to Engine Specifications to obtain
specified height and allowable tensions (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). Replace any springs
that do not meet specifications.
Fig. 20 VALVE SPRING - REMOVE/INSTALL
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3422-D SPRING COMPRESSOR
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8464 ADAPTER
Fig. 21 VALVE SPRING - REMOVE/INSTALL (HEAD
ON)
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8453
2 - BOLTS - SPECIAL TOOL ATTACHING
3 - AIR SUPPLY HOSE ADAPTER
Fig. 22 TESTING VALVE SPRING
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-647
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L SUPPLEMENT9s-25
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)
Page 1481 of 2585
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD OFF
(1) If removed, install a new valve stem seal (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE STEM
SEALS - INSTALLATION).
(2) Position valve spring and retainer on spring
seat.
(3) Using Special Tool C-3422-D with 8464 Adapter
(Fig. 20), compress the spring only enough to install
the valve retainer locks. Install valve retainer locks.
(4) Slowly release the spring tension. Ensure the
retainer locks are seated properly (Fig. 23).
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD ON
(1) The intake valve stem seals should be pushed
firmly and squarely over the valve guide using the
valve stem as guide.Do Not Forceseal against top
of guide. When installing the valve retainer locks,
compress the springonly enoughto install the locks
(Fig. 23).
CAUTION: Do not pinch seal between retainer and
top of valve guide.
(2) Follow the same procedure on the remaining 5
cylinders using the firing sequence 1-2-3-4-5-6.Make
sure piston in cylinder is at TDC on the valve
spring that is being covered.
(3) Remove spark plug adapter tool.
(4) Install rocker arms and shaft assembly. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS -
INSTALLATION)(5) Install cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(6) Install spark plugs and connect wires.
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
ROCKER ARMS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ROCKER ARMS
The rocker arms are installed on the rocker arm
shaft. The rocker arms and shaft assembly is
attached to the cylinder head with seven billeted
bolts and retainers. The rocker arms are made of
stamped steel.
DESCRIPTION - PUSHRODS
The pushrods are made of steel and are a hollow
design. The pushrods are positioned between the
hydraulic lifter and the rocker arm.
OPERATION
OPERATION - ROCKER ARMS
The rocker arm pivots on the rocker shaft. Rocker
arms are used to translate up and down motions pro-
vided by the camshaft, hydraulic lifter, and pushrod
on one end, into a down and up motions on the valve
stem on the opposing end.
OPERATION - PUSHRODS
The pushrod is a solid link between the hydraulic
lifter and the rocker arm. Also, the pushrod supplies
engine oil from the hydraulic lifter to the rocker arm.
Fig. 23 VALVE SPRING INSTALLED
1 - VALVE SPRING RETAINER
2 - VALVE INSTALLED HEIGHT
3 - CYLINDER HEAD SURFACE
4 - VALVE SPRING SEAT SURFACE
5 - VALVE SPRING INSTALLED HEIGHT
9s - 26 ENGINE 3.3/3.8L SUPPLEMENTRS
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)
Page 1490 of 2585
The combustion reaction caused by the catalyst
releases additional heat in the exhaust system, caus-
ing temperature increases in the area of the reactor
under severe operating conditions. Such conditions
can exist when the engine misfires or otherwise does
not operate at peak efficiency.Do notremove spark
plug wires from plugs or by any other means short
out cylinders, if exhaust system is equipped with a
catalytic converter. Failure of the catalytic converter
can occur due to temperature increases caused by
unburned fuel passing through the converter. This
deterioration of the catalyst core can result in exces-
sively high emission levels, noise complaints, and
exhaust restrictions.
Unleaded gasoline must be used to avoid ruining
the catalyst core. Do not allow engine to operate
above 1200 RPM in neutral for extended periods over
5 minutes. This condition may result in excessive
exhaust system/floor pan temperatures because of no
air movement under the vehicle.
The flex joint allows flexing as the engine moves,
preventing breakage that could occur from the back-
and-forth motion of a transverse mounted engine.
CAUTION: Due to exterior physical similarities of
some catalytic converters with pipe assemblies,
extreme care should be taken with replacement
parts. There are internal converter differences
required in some parts of the country (particularly
vehicles built for States with strict emission
requirements) and between model years.
REMOVAL
(1) Loosen clamp and disconnect the muffler/reso-
nator assembly from catalytic converter pipe.
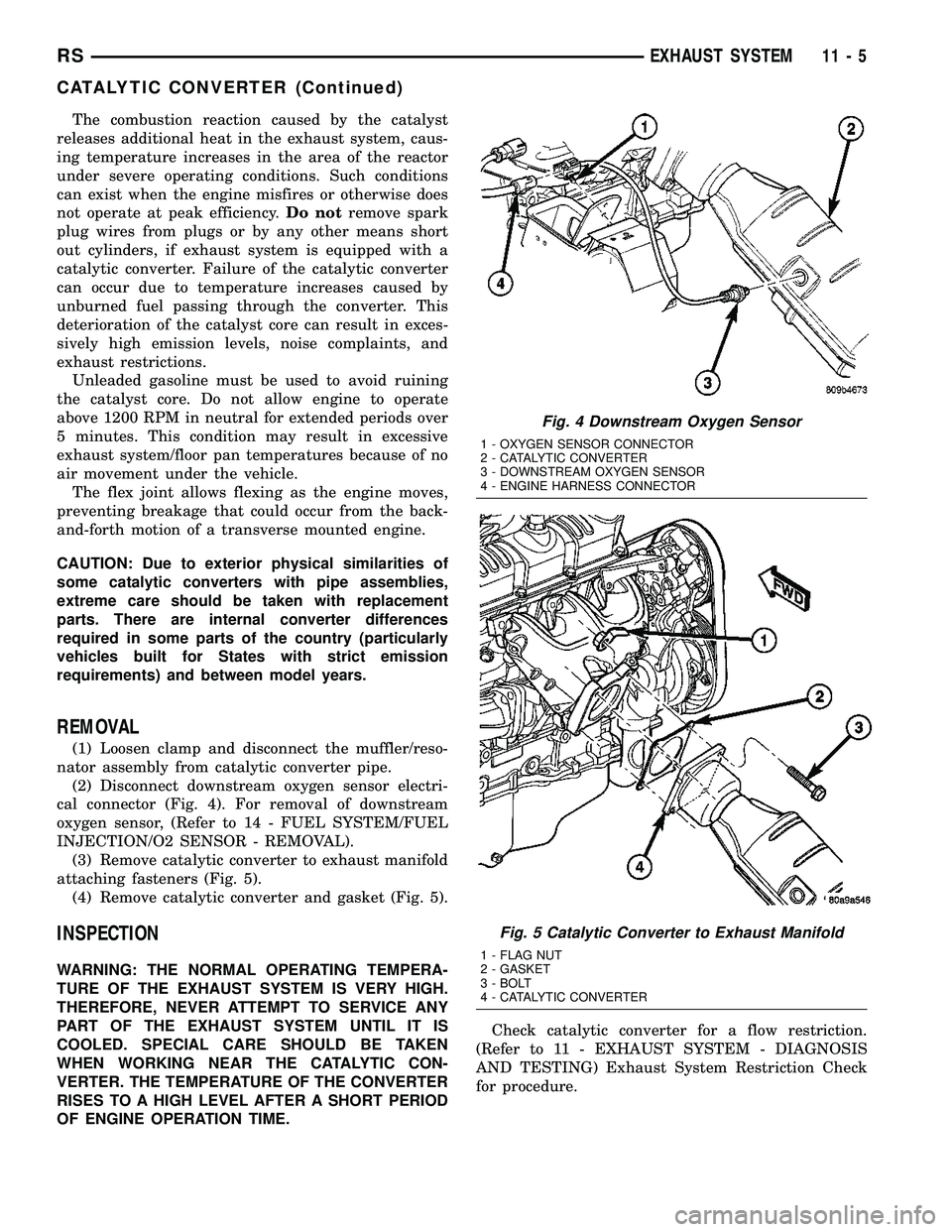
(2) Disconnect downstream oxygen sensor electri-
cal connector (Fig. 4). For removal of downstream
oxygen sensor, (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/O2 SENSOR - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove catalytic converter to exhaust manifold
attaching fasteners (Fig. 5).
(4) Remove catalytic converter and gasket (Fig. 5).
INSPECTION
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER ATTEMPT TO SERVICE ANY
PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM UNTIL IT IS
COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE TAKEN
WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC CON-
VERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CONVERTER
RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT PERIOD
OF ENGINE OPERATION TIME.Check catalytic converter for a flow restriction.
(Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) Exhaust System Restriction Check
for procedure.
Fig. 4 Downstream Oxygen Sensor
1 - OXYGEN SENSOR CONNECTOR
2 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
3 - DOWNSTREAM OXYGEN SENSOR
4 - ENGINE HARNESS CONNECTOR
Fig. 5 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
1 - FLAG NUT
2 - GASKET
3 - BOLT
4 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
RSEXHAUST SYSTEM11-5
CATALYTIC CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1537 of 2585
the O-RINGS ONLY (Fig. 18)to aid assembly. Use
care when removing hoses to prevent damage to hose
or hose nipple.
(1) Carefully place idle air control motor into
throttle body.
(2) Install mounting screw. Tighten screw to 7 N´m
(62 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect electrical connector to idle air control
motor.
(4) Connect negative cable to battery.
INLET AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The IAT Sensor is a Negative Temperature Coeffi-
cient (NTC) Sensor that provides information to the
PCM regarding the temperature of the air entering
the intake manifold (Fig. 19).
MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The MAP sensor (Fig. 20) or (Fig. 21) mounts to
the intake manifold. The sensor is connects electri-
cally to the PCM.
OPERATION
The MAP serves as a PCM input, using a silicon
based sensing unit, to provide data on the manifold
vacuum that draws the air/fuel mixture into the com-
bustion chamber. The PCM requires this information
to determine injector pulse width and spark advance.
When MAP equals Barometric pressure, the pulse
width will be at maximum.
Also like the cam and crank sensors, a 5 volt ref-
erence is supplied from the PCM and returns a volt-age signal to the PCM that reflects manifold
pressure. The zero pressure reading is 0.5V and full
scale is 4.5V. For a pressure swing of0Ð15psithe
voltage changes 4.0V. The sensor is supplied a regu-
lated 4.8 to 5.1 volts to operate the sensor. Like the
cam and crank sensors ground is provided through
the sensor return circuit.
The MAP sensor input is the number one contrib-
utor to pulse width. The most important function of
the MAP sensor is to determine barometric pressure.
The PCM needs to know if the vehicle is at sea level
or is it in Denver at 5000 feet above sea level,
because the air density changes with altitude. It will
also help to correct for varying weather conditions. If
a hurricane was coming through the pressure would
be very, very low or there could be a real fair
Fig. 18 O-RINGS
1 - O-rings
Fig. 19 3.3/3.8L IAT SENSOR
Fig. 20 MAP SENSOR - 2.4L
14 - 30 FUEL INJECTIONRS
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (Continued)
Page 1538 of 2585

weather, high pressure area. This is important
because as air pressure changes the barometric pres-
sure changes. Barometric pressure and altitude have
a direct inverse correlation, as altitude goes up baro-
metric goes down. The first thing that happens as
the key is rolled on, before reaching the crank posi-
tion, the PCM powers up, comes around and looks at
the MAP voltage, and based upon the voltage it sees,
it knows the current barometric pressure relative to
altitude. Once the engine starts, the PCM looks at
the voltage again, continuously every 12 milliseconds,
and compares the current voltage to what it was at
key on. The difference between current and what it
was at key on is manifold vacuum.
During key On (engine not running) the sensor
reads (updates) barometric pressure. A normal range
can be obtained by monitoring known good sensor in
you work area.
As the altitude increases the air becomes thinner
(less oxygen). If a vehicle is started and driven to a
very different altitude than where it was at key On
the barometric pressure needs to be updated. Any
time the PCM sees Wide Open throttle, based upon
TPS angle and RPM it will update barometric pres-
sure in the MAP memory cell. With periodic updates,
the PCM can make its calculations more effectively.
The PCM uses the MAP sensor to aid in calculat-
ing the following:
²Barometric pressure
²Engine load
²Manifold pressure
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance programs
²Shift-point strategies (F4AC1 transmissions
only, via the PCI bus)
²Idle speed²Decel fuel shutoff
The PCM recognizes a decrease in manifold pres-
sure by monitoring a decrease in voltage from the
reading stored in the barometric pressure memory
cell. The MAP sensor is a linear sensor; as pressure
changes, voltage changes proportionately. The range
of voltage output from the sensor is usually between
4.6 volts at sea level to as low as 0.3 volts at 26 in. of
Hg. Barometric pressure is the pressure exerted by
the atmosphere upon an object. At sea level on a
standard day, no storm, barometric pressure is 29.92
in Hg. For every 100 feet of altitude barometric pres-
sure drops .10 in. Hg. If a storm goes through it can
either add, high pressure, or decrease, low pressure,
from what should be present for that altitude. You
should make a habit of knowing what the average
pressure and corresponding barometric pressure is
for your area.REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector and vacuum
hose from MAP sensor (Fig. 20).
(3) Remove two screws holding sensor to the
intake manifold.
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Remove vacuum hose and mounting screws
from manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor (Fig.
21).
(3) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor.
Remove sensor.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Install sensor.
(2) Install two screws and tighten.
(3) Connect the electrical connector and vacuum
hose to the MAP sensor (Fig. 20).
(4) Connect the negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Install sensor (Fig. 21).
(2) Install screws and tighten toPLASTIC MAN-
IFOLD 1.7 N´m (15 in. lbs.) ALUMINUM MANI-
FOLD 3.3 N´m (30 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the electrical connector to the sensor.
Install vacuum hose.
(4) Connect the negative battery cable.
Fig. 21 MAP SENSOR - 3.3/3.8L
RSFUEL INJECTION14-31
MAP SENSOR (Continued)
Page 2520 of 2585

period the switch ratio reaches a predetermined
value, a counter is incremented by one. The monitor
is enabled to run another test during that trip. When
the test fails 6 times, the counter increments to 3, a
malfunction is entered, and a Freeze Frame is stored,
the code is matured and the MIL is illuminated. If
the first test passes, no further testing is conducted
during that trip.
The MIL is extinguished after three consecutive
good trips. The good trip criteria for the catalyst
monitor is more stringent than the failure criteria. In
order to pass the test and increment one good trip,
the downstream sensor switch rate must be less than
45% of the upstream rate. The failure percentages
are 59% respectively.
Enabling ConditionsÐThe following conditions
must typically be met before the PCM runs the cat-
alyst monitor. Specific times for each parameter may
be different from engine to engine.
²Accumulated drive time
²Enable time
²Ambient air temperature
²Barometric pressure
²Catalyst warm-up counter
²Engine coolant temperature
²Vehicle speed
²MAP
²RPM
²Engine in closed loop
²Fuel level
Pending ConditionsÐ
²Misfire DTC
²Front Oxygen Sensor Response
²Front Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Front Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Rationality (middle check)
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Fuel System Monitor
²All TPS faults
²All MAP faults
²All ECT sensor faults
²Purge flow solenoid functionality
²Purge flow solenoid electrical
²All PCM self test faults
²All CMP and CKP sensor faults
²All injector and ignition electrical faults
²Idle Air Control (IAC) motor functionality
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Brake switch (auto trans only)
²Intake air temperature
ConflictÐThe catalyst monitor does not run if any
of the following are conditions are present:
²EGR Monitor in progress (if equipped)
²Fuel system rich intrusive test in progress
²EVAP Monitor in progress²Time since start is less than 60 seconds
²Low fuel level-less than 15 %
²Low ambient air temperature
²Ethanol content learn is taking place and the
ethanol used once flag is set
SuspendÐThe Task Manager does not mature a
catalyst fault if any of the following are present:
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Priority 1
²Oxygen Sensor Heater, Priority 1
²EGR Monitor, Priority 1 (if equipped)
²EVAP Monitor, Priority 1
²Fuel System Monitor, Priority 2
²Misfire Monitor, Priority 2
OPERATION - NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor all circuits, systems
and conditions that could have malfunctions causing
driveability problems. However, problems with these
systems may cause the PCM to store diagnostic trou-
ble codes for other systems or components. For exam-
ple, a fuel pressure problem will not register a fault
directly, but could cause a rich/lean condition or mis-
fire. This could cause the PCM to store an oxygen
sensor or misfire diagnostic trouble code.
The major non-monitored circuits are listed below
along with examples of failures modes that do not
directly cause the PCM to set a DTC, but for a sys-
tem that is monitored.
FUEL PRESSURE
The fuel pressure regulator controls fuel system
pressure. The PCM cannot detect a clogged fuel
pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel filter, or a
pinched fuel supply or return line. However, these
could result in a rich or lean condition causing the
PCM to store an oxygen sensor, fuel system, or mis-
fire diagnostic trouble code.
SECONDARY IGNITION CIRCUIT
The PCM cannot detect an inoperative ignition coil,
fouled or worn spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or
open spark plug cables. The misfire will however,
increase the oxygen content in the exhaust, deceiving
the PCM in to thinking the fuel system is too lean.
Also see misfire detection.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
The PCM cannot detect uneven, low, or high engine
cylinder compression. Low compression lowers O2
content in the exhaust. Leading to fuel system, oxy-
gen sensor, or misfire detection fault.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The PCM cannot detect a plugged, restricted or
leaking exhaust system. It may set a EGR (if
equipped) or Fuel system or O2S fault.
RSEMISSIONS CONTROL25-5
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2524 of 2585
OPERATION
OPERATION - SYSTEM
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
many different circuits in the fuel injection, ignition,
emission and engine systems. If the PCM senses a
problem with a monitored circuit often enough to
indicate an actual problem, it stores a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) in the PCM's memory. If the
code applies to a non-emissions related component or
system, and the problem is repaired or ceases to
exist, the PCM cancels the code after 40 warmup
cycles. Diagnostic trouble codes that affect vehicle
emissions illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL). Refer to Malfunction Indicator Lamp in this
section.
Certain criteria must be met before the PCM
stores a DTC in memory. The criteria may be a spe-
cific range of engine RPM, engine temperature,
and/or input voltage to the PCM.
The PCM might not store a DTC for a monitored
circuit even though a malfunction has occurred. This
may happen because one of the DTC criteria for the
circuit has not been met.For example, assume the
diagnostic trouble code criteria requires the PCM to
monitor the circuit only when the engine operates
between 750 and 2000 RPM. Suppose the sensor's
output circuit shorts to ground when engine operates
above 2400 RPM (resulting in 0 volt input to the
PCM). Because the condition happens at an engine
speed above the maximum threshold (2000 rpm), the
PCM will not store a DTC.
There are several operating conditions for which
the PCM monitors and sets DTC's. Refer to Moni-
tored Systems, Components, and Non-Monitored Cir-
cuits in this section.
NOTE: Various diagnostic procedures may actually
cause a diagnostic monitor to set a DTC. For
instance, pulling a spark plug wire to perform a
spark test may set the misfire code. When a repair
is completed and verified, use the DRBIIITscan tool
to erase all DTC's and extinguish the MIL.Technicians can display stored DTC's. Refer to
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/POWER-
TRAIN CONTROL MODULE - DESCRIPTION). For
obtaining the DTC information, use the Data Link
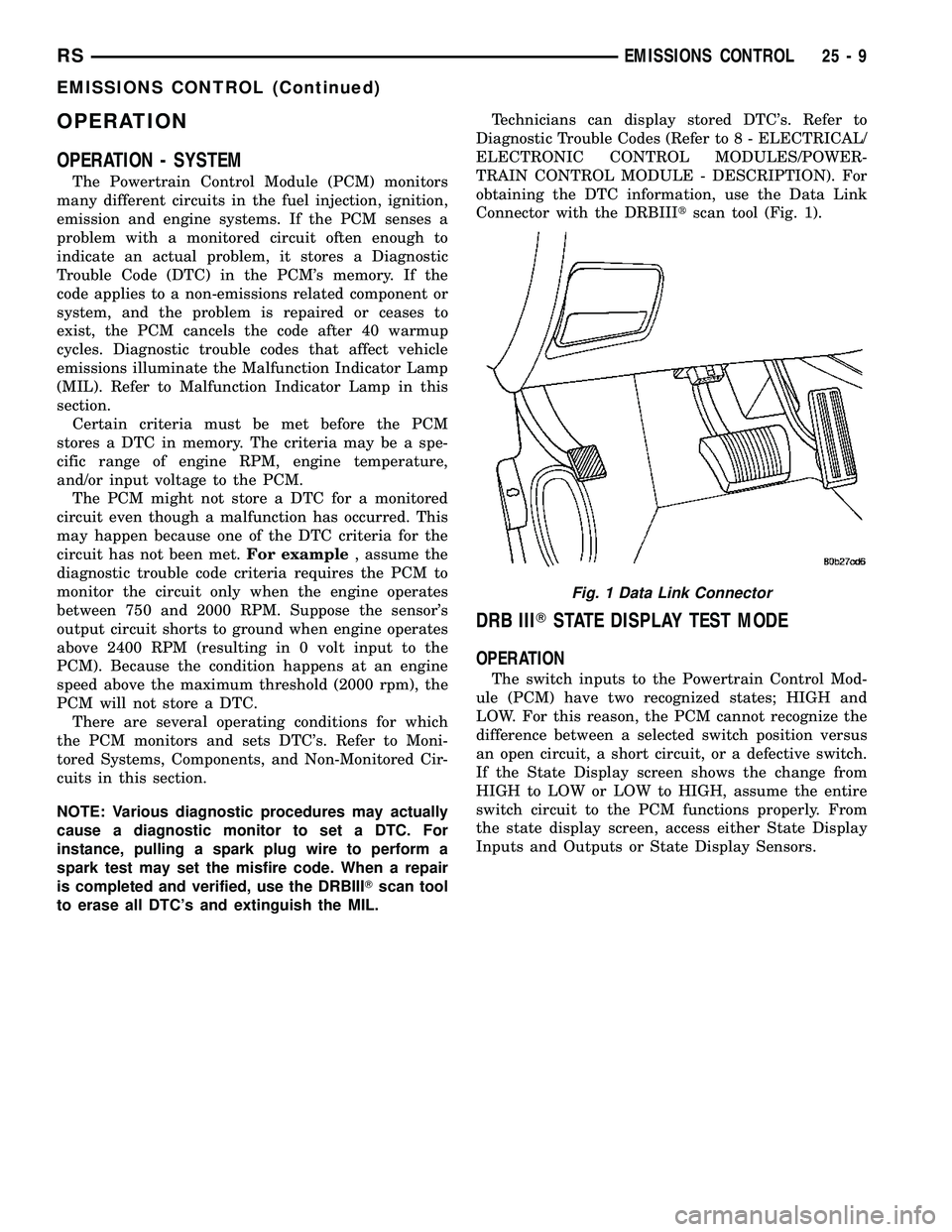
Connector with the DRBIIItscan tool (Fig. 1).
DRB IIITSTATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
OPERATION
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. From
the state display screen, access either State Display
Inputs and Outputs or State Display Sensors.
Fig. 1 Data Link Connector
RSEMISSIONS CONTROL25-9
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2538 of 2585

De-energizing the solenoid, but not fully closing the
transducer bleed hole (because of low back-pressure),
varies the strength of vacuum applied to the EGR
valve. Varying the strength of the vacuum changes
the amount of EGR supplied to the engine. This pro-
vides the correct amount of exhaust gas recirculation
for different operating conditions.
This system does not allow EGR at idle.
A failed or malfunctioning EGR system can cause
engine spark knock, sags or hesitation, rough idle,
engine stalling and increased emissions.
REMOVAL - 2.4L
The EGR valve and Electrical EGR Transducer are
serviced as an assembly (Fig. 1).
(1) Disconnect vacuum tube from electric EGR
transducer. Inspect vacuum tube for damage.
(2) Remove electrical connector from solenoid.
(3) Remove EGR tube bolts from EGR valve.
(4) Remove EGR valve from cylinder head adaptor.
(5) Clean gasket surface and discard old gasket.
Check for any signs of leakage or cracked surfaces.
Repair or replace as necessary.
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
The EGR valve and Electrical EGR Transducer are
serviced as an assembly (Fig. 1).
(1) Assemble EGR valve with new gasket onto the
cylinder head adaptor.
(2) Loose assemble the bolts from EGR valve to
EGR tube.
(3) Loose assemble the bolts from EGR valve to
cylinder head.
(4) Tighten bolts from EGR valve to cylinder head
to 22.8 N´m (200 25 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Tighten bolts from EGR valve to EGR tube to
11.9 N´m (105 20 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Reconnect vacuum hose and electrical connec-
tor to electrical EGR transducer.
RSEXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION25-23
VALVE (Continued)
Page 2548 of 2585
BRAKE CABLE (LEFT REAR) - REMOVAL,
PARKING.......................5-62,5s-64
BRAKE CABLE (RIGHT REAR) -
INSTALLATION, PARKING..........5-63,5s-66
BRAKE CABLE (RIGHT REAR) -
REMOVAL, PARKING..............5-60,5s-63
BRAKE CABLES - ADJUSTMENT,
PARKING.......................5-64,5s-66
BRAKE CALIPER - INSTALLATION, REAR
DISC..........................5-30,5s-29
BRAKE CALIPER - REMOVAL, REAR
DISC..........................5-27,5s-26
BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER -
INSTALLATION, FRONT DISC........5-31,5s-30
BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER - REMOVAL,
FRONT DISC....................5-31,5s-30
BRAKE CALIPER (CONTINENTAL TEVES
BRAKES) - INSTALLATION, FRONT
DISC..............................5s-26
BRAKE CALIPER (CONTINENTAL TEVES
BRAKES) - REMOVAL, FRONT DISC......5s-23
BRAKE CALIPER (DISC/DISC BRAKES) -
INSTALLATION, FRONT DISC.............5-27
BRAKE CALIPER (DISC/DISC BRAKES) -
REMOVAL, FRONT DISC................5-24
BRAKE CALIPER (DISC/DRUM BRAKES) -
INSTALLATION, FRONT DISC.............5-27
BRAKE CALIPER (DISC/DRUM BRAKES) -
REMOVAL, FRONT DISC................5-24
BRAKE CALIPER GUIDE PINS (DISC/
DRUM BRAKES) - INSTALLATION, DISC....5-31
BRAKE CALIPER GUIDE PINS (DISC/
DRUM BRAKES) - REMOVAL, DISC.......5-31
BRAKE CALIPER GUIDE PINS (TRW
BRAKES) - INSTALLATION, DISC.........5s-30
BRAKE CALIPER GUIDE PINS (TRW
BRAKES) - REMOVAL, DISC............5s-30
BRAKE CALIPER (TRW BRAKES) -
INSTALLATION, FRONT DISC............5s-26
BRAKE CALIPER (TRW BRAKES) -
REMOVAL, FRONT DISC...............5s-23
BRAKE FASTENER TORQUE,
SPECIFICATIONS...................5-9,5s-8
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.........5-32,5s-31
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL CHECKING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE...........5-32,5s-31
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION....................5-10,5s-9
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH -
INSTALLATION...................5-11,5s-10
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH -
OPERATION......................5-10,5s-9
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH -
REMOVAL......................5-11,5s-10
BRAKE FLUID, SPECIFICATIONS.....5-33,5s-32
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - DESCRIPTION....8L-4
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING........................8L-4
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - INSTALLATION....8L-5
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - OPERATION......8L-4
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - REMOVAL.......8L-5
BRAKE LEVER AND FRONT CABLE -
INSTALLATION, PARKING..........5-66,5s-69
BRAKE LEVER AND FRONT CABLE -
REMOVAL, PARKING
..............5-65,5s-68
BRAKE PROPORTIONING -
DESCRIPTION, ELECTRONIC VARIABLE
....5-75
BRAKE PROPORTIONING - OPERATION,
ELECTRONIC VARIABLE
................5-77
BRAKE ROTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING
.......................5-51,5s-54
BRAKE ROTOR - INSTALLATION, FRONT
. . . 5-54,
5s-57
BRAKE ROTOR - REMOVAL, FRONT
. . 5-54,5s-57
BRAKE ROTOR, EXPORT
...........5-55,5s-58
BRAKE ROTOR MACHINING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE
....................5-53,5s-56
BRAKE ROTOR, SPECIFICATIONS
....5-55,5s-57
BRAKE SHOE LINING - INSPECTION,
REAR DRUM
....................5-22,5s-21
BRAKE SHOES - ADJUSTMENT, PARKING
. . 5-73,
5s-76
BRAKE SHOES - ADJUSTMENT, REAR
DRUM
.........................5-23,5s-22
BRAKE SHOES - CLEANING, DISC
....5-16,5-18,
5s-15,5s-17BRAKE SHOES - INSPECTION, DISC . . 5-16,5-18,
5s-15,5s-17
BRAKE SHOES - INSTALLATION, REAR
DISC..........................5-19,5s-18
BRAKE SHOES - INSTALLATION, REAR
DRUM.........................5-22,5s-21
BRAKE SHOES - REMOVAL, REAR DISC . . . 5-17,
5s-16
BRAKE SHOES - REMOVAL, REAR DRUM . . 5-19,
5s-18
BRAKE SHOES (CONTINENTAL TEVES
BRAKES) - INSTALLATION, FRONT
DISC..............................5s-15
BRAKE SHOES (CONTINENTAL TEVES
BRAKES) - REMOVAL, FRONT DISC......5s-14
BRAKE SHOES (DISC/DISC BRAKES) -
INSTALLATION, FRONT DISC.............5-16
BRAKE SHOES (DISC/DISC BRAKES) -
REMOVAL, FRONT DISC................5-14
BRAKE SHOES (DISC/DRUM BRAKES) -
INSTALLATION, FRONT DISC.............5-17
BRAKE SHOES (DISC/DRUM BRAKES) -
REMOVAL, FRONT DISC................5-15
BRAKE SHOES (TRW BRAKES) -
INSTALLATION, FRONT DISC............5s-16
BRAKE SHOES (TRW BRAKES) -
REMOVAL, FRONT DISC...............5s-14
BRAKE SYSTEM - DESCRIPTION,
ANTILOCK...........................5-75
BRAKE SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, BASE....................5-4,5s-4
BRAKE SYSTEM - OPERATION,
ANTILOCK...........................5-76
BRAKE SYSTEM BLEEDING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, ANTILOCK................5-78
BRAKE SYSTEM (EXPORT) -
DESCRIPTION, ANTILOCK...............5-75
BRAKE SYSTEM, SPECIAL TOOLS - BASE . . 5-10,
5s-9
BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES -
DESCRIPTION...................5-14,5s-13
BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES -
INSPECTION....................5-14,5s-13
BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES - OPERATION . . 5-14,
5s-13
BRAKES - DESCRIPTION, BASE.......5-3,5s-3
BRAKES - OPERATION, BASE.........5-3,5s-3
BRAKES (EXPORT) - DESCRIPTION,
BASE............................5-3,5s-3
BRAKES (EXPORT) - DESCRIPTION, DISC . . 5-13,
5s-12
BRAKES (FRONT) - DESCRIPTION, DISC . . . 5-11,
5s-10
BRAKES (FRONT) - OPERATION, DISC.....5-13,
5s-12
BRAKES (REAR) - DESCRIPTION, DISC....5-12,
5s-12
BRAKES (REAR) - DESCRIPTION, DRUM . . . 5-13,
5s-12
BRAKES (REAR) - OPERATION, DISC . 5-13,5s-13
BRAKE/TRANSMISSION SHIFT
INTERLOCK SOLENOID - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING...............21-235,21s-135
BUCKET - INSTALLATION, BUCKET SEAT
BACK - QUAD.......................23-99
BUCKET - INSTALLATION, SEAT BELT
BUCKLE - FIRST ROW INBOARD -
QUAD.............................8O-12
BUCKET - REMOVAL, BUCKET SEAT
BACK - QUAD.......................23-98
BUCKET - REMOVAL, SEAT BELT BUCKLE
- FIRST ROW INBOARD - QUAD.........8O-12
BUCKET, 50/50 SPLIT, BENCH -
INSTALLATION, SEAT BACK HINGE
COVERS - QUAD....................23-101
BUCKET, 50/50 SPLIT, BENCH -
INSTALLATION, SEAT CUSHION COVER
- QUAD
...........................23-100
BUCKET, 50/50 SPLIT, BENCH -
REMOVAL, SEAT BACK HINGE COVERS
- QUAD
...........................23-101
BUCKET, 50/50 SPLIT, BENCH -
REMOVAL, SEAT CUSHION COVER -
QUAD
.............................23-100
BUCKET SEAT BACK - QUAD BUCKET -
INSTALLATION
.......................23-99
BUCKET SEAT BACK - QUAD BUCKET -
REMOVAL
..........................23-98BUCKET SEAT RISER - INSTALLATION,
QUAD..............................23-98
BUCKET SEAT RISER - REMOVAL, QUAD . . 23-98
BUCKET SEAT SIDE SHIELD - NO
CUPHOLDER - INSTALLATION, QUAD.....23-97
BUCKET SEAT SIDE SHIELD - NO
CUPHOLDER - REMOVAL, QUAD........23-97
BUCKET SEAT SIDE SHIELD/CUPHOLDER
- FLAP AND SPRING ASSEMBLY -
INSTALLATION, QUAD................23-107
BUCKET SEAT SIDE SHIELD/CUPHOLDER
- FLAP AND SPRING ASSEMBLY -
REMOVAL, QUAD....................23-107
BUCKET SEAT SIDE SHIELD/CUPHOLDER
- INSTALLATION, QUAD................23-96
BUCKET SEAT SIDE SHIELD/CUPHOLDER
- REMOVAL, QUAD...................23-96
BUCKLE - FIRST ROW - BENCH -
INSTALLATION, SEAT BELT.............8O-13
BUCKLE - FIRST ROW - BENCH -
REMOVAL, SEAT BELT................8O-13
BUCKLE - FIRST ROW INBOARD - QUAD
BUCKET - INSTALLATION, SEAT BELT....8O-12
BUCKLE - FIRST ROW INBOARD - QUAD
BUCKET - REMOVAL, SEAT BELT........8O-12
BUCKLE - FRONT INBOARD -
INSTALLATION, SEAT BELT.............8O-12
BUCKLE - FRONT INBOARD - REMOVAL,
SEAT BELT .........................8O-12
BUCKLE - SECOND ROW - THREE
PASSENGER BENCH - INSTALLATION,
SEAT BELT .........................8O-15
BUCKLE - SECOND ROW - THREE
PASSENGER BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT
BELT................................8O-15
BUCKLE - SECOND ROW INBOARD -
50/50 BENCH - INSTALLATION, SEAT
BELT ..............................8O-13
BUCKLE - SECOND ROW INBOARD -
50/50 BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT BELT....8O-13
BUMPER - DESCRIPTION, JOUNCE........2-36
BUMPER - INSTALLATION, STOP........23-25
BUMPER - OPERATION, JOUNCE.........2-36
BUMPER - REMOVAL, STOP............23-25
BUMPER BEZEL - INSTALLATION,
SLIDING DOOR STOP.................23-25
BUMPER BEZEL - REMOVAL, SLIDING
DOOR STOP........................23-25
BUMPER REINFORCEMENT -
INSTALLATION, FRONT.................13-2
BUMPER REINFORCEMENT -
INSTALLATION, REAR..................13-3
BUMPER REINFORCEMENT - REMOVAL,
FRONT..............................13-2
BUMPER REINFORCEMENT - REMOVAL,
REAR...............................13-3
BUS COMMUNICATION RECEIVE - PCM
INPUT - OPERATION, DATA.............8E-15
BUS, OPERATION - PROGRAMMABLE
COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE (PCI).....14-21
BUSHING - INSTALLATION, LEAF SPRING
FRONT..............................2-30
BUSHING - REMOVAL, LEAF SPRING
FRONT..............................2-29
BUSHINGS - INSTALLATION, FRONT
CROSSMEMBER MOUNT...............13-12
BUSHINGS - REMOVAL, FRONT
CROSSMEMBER MOUNT...............13-12
BUSHINGS (CONTINENTAL TEVES
BRAKES) - ASSEMBLY, CALIPER GUIDE
PIN................................5s-24
BUSHINGS (CONTINENTAL TEVES
BRAKES) - DISASSEMBLY, CALIPER
GUIDE PIN..........................5s-23
BUSHINGS (DISC/DISC BRAKES) -
ASSEMBLY, CALIPER GUIDE PIN.........5-25
BUSHINGS (DISC/DISC BRAKES) -
DISASSEMBLY, CALIPER GUIDE PIN.......5-24
CABIN HEATER - DESCRIPTION........24-112
CABIN HEATER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, DIESEL SUPPLEMENTAL......24-113
CABLE - CROSSOVER - INSTALLATION,
GEARSHIFT
.........................21-76
CABLE - CROSSOVER - REMOVAL,
GEARSHIFT
.........................21-73
CABLE - DESCRIPTION
.................8P-4
CABLE - DESCRIPTION, ANTENNA BODY
. . . 8A-4
CABLE - DESCRIPTION, SPARK PLUG
.....8I-10
RSINDEX5
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page
Page 2549 of 2585
CABLE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
ANTENNA BODY......................8A-4
CABLE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
BATTERY...........................8F-16
CABLE - INSTALLATION................8P-4
CABLE - INSTALLATION, ANTENNA BODY . . 8A-6
CABLE - INSTALLATION, FRONT.....5-64,5s-67
CABLE - INSTALLATION, GEAR SHIFT....21-205
CABLE - INSTALLATION, HOLD OPEN
LATCH .............................23-38
CABLE - INSTALLATION, INSIDE HANDLE . . 23-38
CABLE - INSTALLATION, INSTRUMENT
PANEL ANTENNA......................8A-9
CABLE - INSTALLATION, LATCH RELEASE . 23-62
CABLE - INSTALLATION, OUTSIDE
HANDLE............................23-37
CABLE - INSTALLATION, PARKING
BRAKE LEVER AND FRONT.........5-66,5s-69
CABLE - INSTALLATION, THROTTLE
CONTROL..........................14-36
CABLE - OPERATION...................8P-4
CABLE - OPERATION, ANTENNA BODY.....8A-4
CABLE - REMOVAL....................8P-4
CABLE - REMOVAL, ANTENNA BODY......8A-5
CABLE - REMOVAL, FRONT.........5-64,5s-67
CABLE - REMOVAL, GEAR SHIFT.......21-204,
21s-105
CABLE - REMOVAL, HOLD OPEN LATCH . . . 23-38
CABLE - REMOVAL, INSIDE HANDLE.....23-37
CABLE - REMOVAL, INSTRUMENT PANEL
ANTENNA...........................8A-8
CABLE - REMOVAL, LATCH RELEASE.....23-61
CABLE - REMOVAL, OUTSIDE HANDLE....23-37
CABLE - REMOVAL, PARKING BRAKE
LEVER AND FRONT...............5-65,5s-68
CABLE - REMOVAL, THROTTLE
CONTROL..........................14-35
CABLE - SELECTOR - INSTALLATION,
GEARSHIFT.........................21-84
CABLE - SELECTOR - REMOVAL,
GEARSHIFT.........................21-81
CABLE ADJUSTMENT, ADJUSTMENTS -
GEARSHIFT........................21-206
CABLE ADJUSTMENT, INSTALLATION -
SYNCHRONIZING...............23-102,23-88
CABLE (FRONT) - INSTALLATION,
PARKING BRAKE.................5-63,5s-65
CABLE (FRONT) - REMOVAL, PARKING
BRAKE.........................5-59,5s-62
CABLE (INTERMEDIATE) -
INSTALLATION, PARKING BRAKE
....5-63,5s-66
CABLE (INTERMEDIATE) - REMOVAL,
PARKING BRAKE
.................5-60,5s-62
CABLE (LEFT REAR) - INSTALLATION,
PARKING BRAKE
.................5-64,5s-66
CABLE (LEFT REAR) - REMOVAL,
PARKING BRAKE
.................5-62,5s-64
CABLE RESISTANCE, SPECIFICATIONS -
SPARK PLUG
.........................8I-2
CABLE (RIGHT REAR) - INSTALLATION,
PARKING BRAKE
.................5-63,5s-66
CABLE (RIGHT REAR) - REMOVAL,
PARKING BRAKE
.................5-60,5s-63
CABLES - ADJUSTMENT, PARKING
BRAKE
.........................5-64,5s-66
CABLES - DESCRIPTION, BATTERY
.......8F-16
CABLES - INSTALLATION, BATTERY
......8F-18
CABLES - OPERATION, BATTERY
........8F-16
CABLES - REMOVAL, BATTERY
..........8F-18
CALIBRATION - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
A/C-HEATER CONTROL
................24-20
CALIBRATION - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
COMPASS
...........................8M-3
CALIPER - CLEANING
....5-25,5-29,5s-24,5s-28
CALIPER - INSPECTION
. . . 5-25,5-29,5s-24,5s-28
CALIPER - INSTALLATION, REAR DISC
BRAKE
.........................5-30,5s-29
CALIPER - REMOVAL, REAR DISC
BRAKE
.........................5-27,5s-26
CALIPER ADAPTER - INSTALLATION,
FRONT DISC BRAKE
..............5-31,5s-30
CALIPER ADAPTER - REMOVAL, FRONT
DISC BRAKE
....................5-31,5s-30
CALIPER (CONTINENTAL TEVES
BRAKES) - INSTALLATION, FRONT
DISC BRAKE
........................5s-26CALIPER (CONTINENTAL TEVES
BRAKES) - REMOVAL, FRONT DISC
BRAKE.............................5s-23
CALIPER (DISC/DISC BRAKES) -
INSTALLATION, FRONT DISC BRAKE......5-27
CALIPER (DISC/DISC BRAKES) -
REMOVAL, FRONT DISC BRAKE..........5-24
CALIPER (DISC/DRUM BRAKES) -
INSTALLATION, FRONT DISC BRAKE......5-27
CALIPER (DISC/DRUM BRAKES) -
REMOVAL, FRONT DISC BRAKE..........5-24
CALIPER GUIDE PIN BUSHINGS
(CONTINENTAL TEVES BRAKES) -
ASSEMBLY..........................5s-24
CALIPER GUIDE PIN BUSHINGS
(CONTINENTAL TEVES BRAKES) -
DISASSEMBLY.......................5s-23
CALIPER GUIDE PIN BUSHINGS
(DISC/DISC BRAKES) - ASSEMBLY........5-25
CALIPER GUIDE PIN BUSHINGS
(DISC/DISC BRAKES) - DISASSEMBLY.....5-24
CALIPER GUIDE PINS (DISC/DRUM
BRAKES) - INSTALLATION, DISC
BRAKE..............................5-31
CALIPER GUIDE PINS (DISC/DRUM
BRAKES) - REMOVAL, DISC BRAKE.......5-31
CALIPER GUIDE PINS (TRW BRAKES) -
INSTALLATION, DISC BRAKE............5s-30
CALIPER GUIDE PINS (TRW BRAKES) -
REMOVAL, DISC BRAKE...............5s-30
CALIPER PISTON AND SEAL -
ASSEMBLY.............5-26,5-29,5s-25,5s-28
CALIPER PISTON AND SEAL -
DISASSEMBLY..........5-24,5-28,5s-23,5s-27
CALIPER (TRW BRAKES) -
INSTALLATION, FRONT DISC BRAKE......5s-26
CALIPER (TRW BRAKES) - REMOVAL,
FRONT DISC BRAKE..................5s-23
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) -
DESCRIPTION.......................9-115
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) -
INSPECTION........................9-115
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) -
INSTALLATION.......................9-115
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) -
OPERATION.........................9-115
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) -
REMOVAL..........................9-115
CAMSHAFT END PLAY - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, MEASURING..............9-29
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL(S) - INSTALLATION . . 9-28
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL(S) - REMOVAL......9-27
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
DESCRIPTION.........................8I-4
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
OPERATION..........................8I-4
CAMSHAFT SPROCKET - INSTALLATION,
TIMING CHAIN.......................9-157
CAMSHAFT SPROCKET - REMOVAL,
TIMING CHAIN.......................9-156
CAMSHAFT SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION . . 9-65
CAMSHAFT SPROCKETS - REMOVAL......9-64
CAMSHAFT(S) - CLEANING..............9-29
CAMSHAFT(S) - DESCRIPTION...........9-28
CAMSHAFT(S) - INSPECTION............9-30
CAMSHAFT(S) - INSTALLATION..........9-30
CAMSHAFT(S) - OPERATION.............9-28
CAMSHAFT(S) - REMOVAL..............9-29
CANISTER - DESCRIPTION, VAPOR......25-18
CANISTER - INSTALLATION, REAR EVAP . . 25-20
CANISTER - OPERATION, VAPOR........25-18
CANISTER - REMOVAL, REAR EVAP......25-19
CAP - DESCRIPTION, FUEL FILLER.......25-12
CAP - DESCRIPTION, RADIATOR
PRESSURE..........................7-26
CAP - INSTALLATION, INSTRUMENT
PANEL END.........................23-68
CAP - OPERATION, FUEL FILLER........25-12
CAP - OPERATION, RADIATOR
PRESSURE
..........................7-27
CAP - REMOVAL, INSTRUMENT PANEL
END
...............................23-68
CAP TESTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, COOLING SYSTEM
PRESSURE
..........................7-27
CAP TO FILLER NECK SEAL -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, RADIATOR
.....7-27
CAPACITIES - SPECIFICATIONS, FLUID
......0-6CARE - CLEANING, ALUMINUM WHEEL . . . 22-18
CARGO - INSTALLATION, AWD, HEAVY
DUTY...............................2-36
CARGO - INSTALLATION, SPRING........2-40
CARGO - REMOVAL, AWD, HEAVY DUTY . . . 2-36
CARGO - REMOVAL, SPRING............2-40
CARPETS AND FLOOR MATS -
INSTALLATION.......................23-76
CARPETS AND FLOOR MATS - REMOVAL . 23-75
CARRIER ASSEMBLY - DESCRIPTION,
BALANCE SHAFTS.....................9-69
CARRIER ASSEMBLY - INSTALLATION,
BALANCE SHAFTS.....................9-72
CARRIER ASSEMBLY - OPERATION,
BALANCE SHAFTS.....................9-69
CARRIER ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL,
BALANCE SHAFTS.....................9-69
CARRIER SEAL - INSTALLATION,
DIFFERENTIAL........................21-9
CARRIER SEAL - REMOVAL,
DIFFERENTIAL........................21-9
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - DESCRIPTION . . . 11-4
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - INSPECTION....11-5
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - INSTALLATION . . . 11-6
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - OPERATION.....11-4
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - REMOVAL......11-5
CAUSES - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
COMMON PROBLEM..................21-30
CAUTION - A/C SYSTEM...............24-66
CAUTION - CAUTIONS...................5-78
CAUTION, DESCRIPTION.............5-4,5s-4
CAUTION, DESCRIPTION...............19-37
CAUTION, SENSOR - TPM.........22-10,22s-2
CAUTIONS, CAUTION..................5-78
CAUTIONS, WARNING - WARNINGS . 19-10,19-27
CD CHANGER - DESCRIPTION...........8A-7
CD CHANGER - INSTALLATION...........8A-8
CD CHANGER - OPERATION.............8A-7
CD CHANGER - REMOVAL..............8A-8
CENTER - DESCRIPTION, ELECTRONIC
VEHICLE INFO.......................8M-6
CENTER - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFORMATION.....8M-7
CENTER - INSTALLATION, ELECTRONIC
VEHICLE INFO.......................8M-9
CENTER - OPERATION, ELECTRONIC
VEHICLE INFO.......................8M-7
CENTER - REMOVAL, ELECTRONIC
VEHICLE INFO.......................8M-9
CENTER BEZEL - INSTALLATION,
INSTRUMENT PANEL..................23-68
CENTER BEZEL - REMOVAL,
INSTRUMENT PANEL..................23-68
CENTER BEZEL OUTLETS -
INSTALLATION.......................24-45
CENTER BEZEL OUTLETS - REMOVAL....24-44
CENTER CONSOLE LAMP -
INSTALLATION.......................8L-21
CENTER CONSOLE LAMP - REMOVAL....8L-21
CENTER CONSOLE LAMP SWITCH -
INSTALLATION.......................8L-21
CENTER CONSOLE LAMP SWITCH -
REMOVAL..........................8L-21
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP -
INSTALLATION........................8L-6
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP -
REMOVAL...........................8L-6
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
UNIT - INSTALLATION..................8L-6
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
UNIT - REMOVAL.....................8L-6
CENTER HINGE - INSTALLATION.........23-24
CENTER HINGE - REMOVAL............23-24
CENTER PROGRAMMING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, ELECTRONIC VEHICLE
INFORMATION.......................8M-7
CENTER STRIKER - INSTALLATION.......23-28
CENTER STRIKER - REMOVAL..........23-28
CENTERING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
CLOCK SPRING.......................8O-5
CERTIFICATION LABEL - DESCRIPTION,
VEHICLE
.........................Intro.-11
CHAIN AND CAMSHAFT SPROCKET -
INSTALLATION, TIMING
................9-157
CHAIN AND CAMSHAFT SPROCKET -
REMOVAL, TIMING
...................9-156
CHAIN COVER - INSTALLATION, TIMING
. . 9-155
CHAIN COVER - REMOVAL, TIMING
......9-153
6 INDEXRS
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page