inflation pressure CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 124 of 2585

²Engine
²Transmission
²Exhaust
²Propeller shaft (vibration)
²Vehicle body (drumming)
Driveline module noises are normally divided into
two categories: gear noise or bearing noise. A thor-
ough and careful inspection should be completed to
determine the actual source of the noise before
replacing the driveline module.
The rubber mounting bushings help to dampen-out
driveline module noise when properly installed.
Inspect to confirm that no metal contact exists
between the driveline module case and the body. The
complete isolation of noise to one area requires
expertise and experience. Identifying certain types of
vehicle noise baffles even the most capable techni-
cians. Often such practices as:
²Increase tire inflation pressure to eliminate tire
noise.
²Listen for noise at varying speeds with different
driveline load conditions
²Swerving the vehicle from left to right to detect
wheel bearing noise.
All driveline module assemblies produce noise to a
certain extent. Slight carrier noise that is noticeable
only at certain speeds or isolated situations should be
considered normal. Carrier noise tends to peak at a
variety of vehicle speeds. Noise isNOT ALWAYSan
indication of a problem within the carrier.
TIRE NOISE
Tire noise is often mistaken for driveline module
noise. Tires that are unbalanced, worn unevenly or
are worn in a saw-tooth manner are usually noisy.
They often produce a noise that appears to originate
in the driveline module.
Tire noise changes with different road surfaces, but
driveline module noise does not. Inflate all four tires
with approximately 20 psi (138 kPa) more than the
recommended inflation pressure (for test purposes
only). This will alter noise caused by tires, but will
not affect noise caused by the differential. Rear axle
noise usually ceases when coasting at speeds less
than 30 mph (48 km/h); however, tire noise contin-
ues, but at a lower frequency, as the speed is
reduced.
After test has been completed lower tire pressure
back to recommended pressure.
GEAR NOISE (DRIVE PINION AND RING GEAR)
Abnormal gear noise is rare and is usually caused
by scoring on the ring gear and drive pinion. Scoring
is the result of insufficient or incorrect lubricant in
the carrier housing.Abnormal gear noise can be easily recognized. It
produces a cycling tone that will be very pronounced
within a given speed range. The noise can occur dur-
ing one or more of the following drive conditions:
²Drive
²Road load
²Float
²Coast
Abnormal gear noise usually tends to peak within
a narrow vehicle speed range or ranges. It is usually
more pronounced between 30 to 40 mph (48 to 64
km/h) and 50 to 60 mph (80 to 96 km/h). When objec-
tionable gear noise occurs, note the driving condi-
tions and the speed range.
BEARING NOISE (DRIVE PINION AND
DIFFERENTIAL)
Defective bearings produce a rough growl that is
constant in pitch and varies with the speed of vehi-
cle. Being aware of this will enable a technician to
separate bearing noise from gear noise.
Drive pinion bearing noise that results from defec-
tive or damaged bearings can usually be identified by
its constant, rough sound. Drive pinion front bearing
is usually more pronounced during a coast condition.
Drive pinion rear bearing noise is more pronounced
during a drive condition. The drive pinion bearings
are rotating at a higher rate of speed than either the
differential side bearings or the axle shaft bearing.
Differential side bearing noise will usually produce
a constant, rough sound. The sound is much lower in
frequency than the noise caused by drive pinion bear-
ings.
Bearing noise can best be detected by road testing
the vehicle on a smooth road (black top). However, it
is easy to mistake tire noise for bearing noise. If a
doubt exists, the tire treads should be examined for
irregularities that often causes a noise that resem-
bles bearing noise.
ENGINE AND TRANSMISSION NOISE
Sometimes noise that appears to be in the driv-
eline module assembly is actually caused by the
engine or the transmission. To identify the true
source of the noise, note the approximate vehicle
speed and/or RPM when the noise is most noticeable.
Stop the vehicle next to a flat brick or cement wall
(this will help reflect the sound). Place the transaxle
inNEUTRAL. Accelerate the engine slowly up
through the engine speed that matches the vehicle
speed noted when the noise occurred. If the same
noise is produced, it usually indicates that the noise
is being caused by the engine or transaxle.
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-25
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
Page 2080 of 2585

TIRES/WHEELS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TIRES/WHEELS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE AND
WHEEL VIBRATION.....................1
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE AND
WHEEL BALANCE......................5
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE AND
WHEEL MATCH MOUNTING..............7
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE AND
WHEEL ROTATION.....................7
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - TIRE AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY
(ALUMINUM WHEEL)....................7
REMOVAL - TIRE AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY
(STEEL WHEEL).......................8
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - TIRE AND WHEEL
ASSEMBLY (ALUMINUM WHEEL)..........8
INSTALLATION - TIRE AND WHEEL
ASSEMBLY (STEEL WHEEL)..............8
TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION............................9
SENSOR - TPM
DESCRIPTION.........................10
OPERATION...........................10
CAUTION.............................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE PRESSURE
SENSOR............................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE PRESSURE
SENSOR RETRAIN....................10
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................12
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - TIRE..................13
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL-PLY TIRES.......14DESCRIPTION - REPLACEMENT TIRES....14
DESCRIPTION - SPARE TIRE
(TEMPORARY).......................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE . . . 14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE/VEHICLE
LEAD...............................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE WEAR
PATTERNS..........................16
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TREAD WEAR
INDICATORS.........................16
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE INFLATION
PRESSURES.........................16
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE
PRESSURE FOR HIGH SPEED
OPERATION.........................17
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE LEAK
REPAIRING..........................17
CLEANING - TIRES.....................17
WHEELS
DESCRIPTION - WHEEL..................18
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WHEEL
INSPECTION.........................18
CLEANING - ALUMINUM WHEEL CARE......18
SPECIFICATIONS
WHEEL.............................19
WHEEL COVER
DESCRIPTION.........................19
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................19
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS - FRONT
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................21
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS - REAR
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................22
TIRES/WHEELS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE AND WHEEL
VIBRATION
Tire and wheel imbalance, runout and force varia-
tion can cause vehicles to exhibit steering wheel
vibration.
VISUAL INSPECTION
Visual inspection of the vehicle is recommended
prior to road testing or performing any other proce-
dure. Raise vehicle on a suitable hoist. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/HOISTING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Inspect for the following:
²Verify correct (OEM) wheel and tire, as well as
correct wheel weights. Aluminum wheels require
RSTIRES/WHEELS22-1
Page 2089 of 2585

If a road tire is replaced by the spare, the TPM
system will detect the swap and the message9SPARE
TIRE IN USE? Y/N9(along with a chime) will be dis-
played.
For further information, refer to the Owners Man-
ual or the Appropriate Diagnostic Information.
TPM THRESHOLD PRESSURES
High Pressure ON Threshold 48 PSI (331 kPa)
High Pressure OFF Threshold 43 PSI (296 kPa)
Placard Pressure (Cold) 36 PSI (248 kPa)
Low Pressure OFF Threshold 33 PSI (228 kPa)
Low Pressure ON Threshold 28 PSI (193 kPa)
SENSOR - TPM
DESCRIPTION
On vehicles equipped with Tire Pressure Monitor-
ing, one tire pressure sensor is mounted to each
wheel (Fig. 19). Each sensor has an internal battery
that lasts up to 10 years. The battery is not service-
able. At the time of battery failure, the sensor must
be replaced. The serviceable components of the tire
pressure sensor are:
²Sensor-To-Wheel Grommet
²Valve Stem Cap
²Valve Stem Core
Valve stem caps and cores are specifically designed
for the tire pressure monitoring sensors. Although
similar to standard valve stem caps and cores, they
are different.
CAUTION: Do not use a standard valve stem cap or
core in a tire pressure sensor. Always use the orig-
inal equipment style sensor cap and core.
CAUTION: Do not reuse the Sensor-To Wheel Grom-
met. Always use a new grommet when installing a
pressure sensor and properly torque the sensor
nut.
CAUTION: Do not try to install a tire pressure sen-
sor in a steel wheel or aftermarket wheel. Use only
in original style factory wheels.
OPERATION
Tire pressure sensors are battery operated. They
transmit tire pressure data once every minute at
speeds above 20 mph (32 km/h) or up to once every
hour when stationary (parked). For additional infor-
mation, refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Information.
CAUTION
CAUTION: The use of tire sealants is strictly prohib-
ited for vehicles equipped with the Tire Pressure
Monitoring system. Tire sealants can clog tire pres-
sure sensors.
CAUTION: Tire pressure sensor valve stem caps
and cores are specially designed for the sensors.
Due to risk of corrosion, do not use a standard
valve stem cap or core in a tire pressure sensor in
place of the original equipment style sensor cap
and core.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to install a tire pressure
sensor in a steel wheel or aftermarket wheel. Use
tire pressure sensors in original style factory
wheels only.
NOTE: TPM thresholds have been established for
the original tire size equipped on the vehicle. Use
original size tires only to maintain system accuracy.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE PRESSURE
SENSOR
NOTE: Tire pressure may increase from 2 to 6 psi
(14 to 41 kPa) during normal driving conditions. Do
NOT reduce this normal pressure build up.
If a fault in the system is detected, always check
air pressure in the tires first with a known accurate
air gauge and correct the inflation pressure. If any
tire is low, inspectalltires.
If gauge-read pressure in the tires does not reflect
the reading on the EVIC, retrain the sensors, then
reevaluate (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/TIRE
PRESSURE MONITORING/SENSOR - STANDARD
PROCEDURE). Refer to the appropriate diagnostic
information for complete diagnosis of the Tire Pres-
sure Monitoring System.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE PRESSURE
SENSOR RETRAIN
WARNING: DEATH OR SERIOUS INJURY CAN
OCCUR IF MAGNETICALLY SENSITIVE DEVICES
ARE EXPOSED TO THE RELEARN MAGNET. MAG-
NETS CAN AFFECT PACEMAKERS.
22 - 10 TIRES/WHEELSRS
TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING (Continued)
Page 2093 of 2585
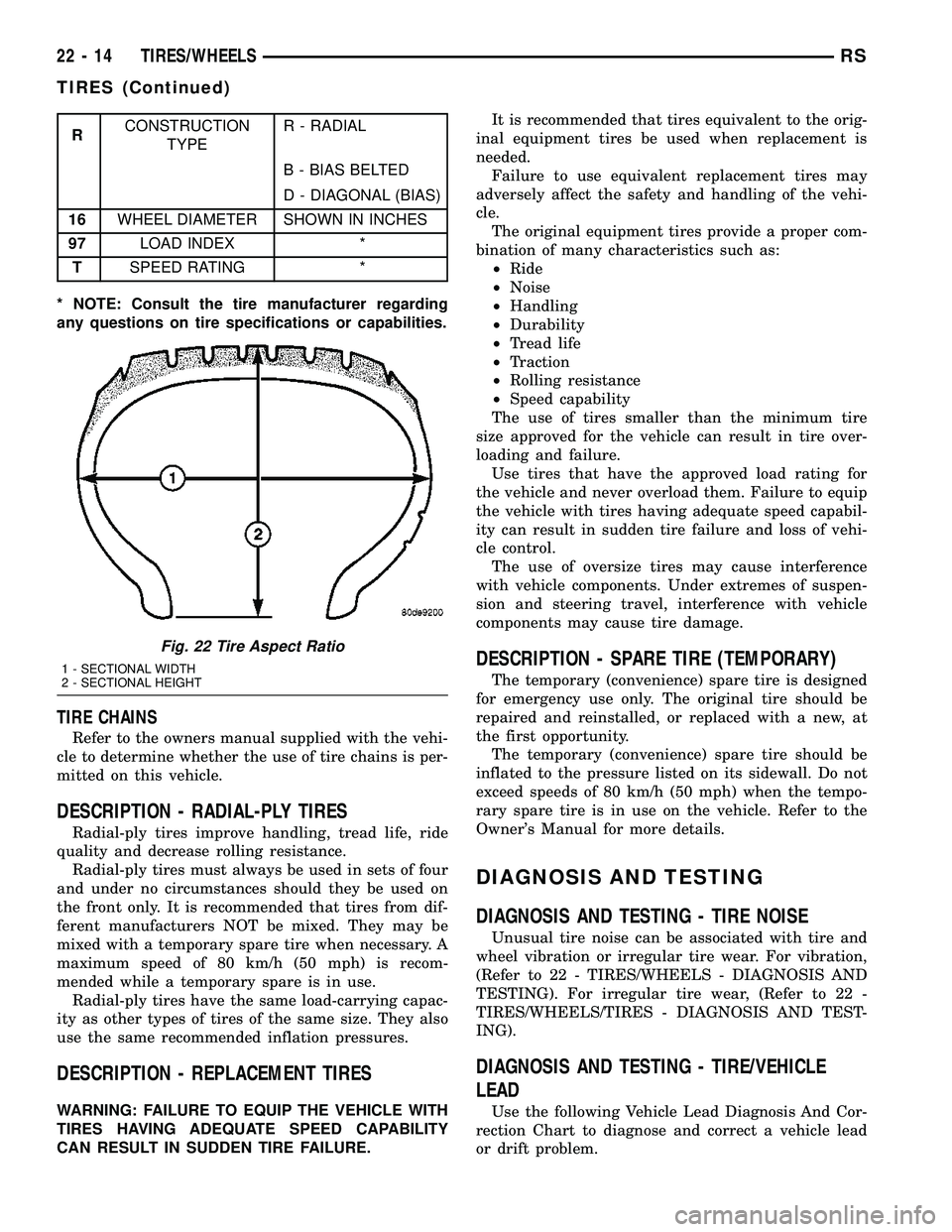
RCONSTRUCTION
TYPER - RADIAL
B - BIAS BELTED
D - DIAGONAL (BIAS)
16WHEEL DIAMETER SHOWN IN INCHES
97LOAD INDEX *
TSPEED RATING *
* NOTE: Consult the tire manufacturer regarding
any questions on tire specifications or capabilities.
TIRE CHAINS
Refer to the owners manual supplied with the vehi-
cle to determine whether the use of tire chains is per-
mitted on this vehicle.
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL-PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life, ride
quality and decrease rolling resistance.
Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of four
and under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. It is recommended that tires from dif-
ferent manufacturers NOT be mixed. They may be
mixed with a temporary spare tire when necessary. A
maximum speed of 80 km/h (50 mph) is recom-
mended while a temporary spare is in use.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
DESCRIPTION - REPLACEMENT TIRES
WARNING: FAILURE TO EQUIP THE VEHICLE WITH
TIRES HAVING ADEQUATE SPEED CAPABILITY
CAN RESULT IN SUDDEN TIRE FAILURE.It is recommended that tires equivalent to the orig-
inal equipment tires be used when replacement is
needed.
Failure to use equivalent replacement tires may
adversely affect the safety and handling of the vehi-
cle.
The original equipment tires provide a proper com-
bination of many characteristics such as:
²Ride
²Noise
²Handling
²Durability
²Tread life
²Traction
²Rolling resistance
²Speed capability
The use of tires smaller than the minimum tire
size approved for the vehicle can result in tire over-
loading and failure.
Use tires that have the approved load rating for
the vehicle and never overload them. Failure to equip
the vehicle with tires having adequate speed capabil-
ity can result in sudden tire failure and loss of vehi-
cle control.
The use of oversize tires may cause interference
with vehicle components. Under extremes of suspen-
sion and steering travel, interference with vehicle
components may cause tire damage.
DESCRIPTION - SPARE TIRE (TEMPORARY)
The temporary (convenience) spare tire is designed
for emergency use only. The original tire should be
repaired and reinstalled, or replaced with a new, at
the first opportunity.
The temporary (convenience) spare tire should be
inflated to the pressure listed on its sidewall. Do not
exceed speeds of 80 km/h (50 mph) when the tempo-
rary spare tire is in use on the vehicle. Refer to the
Owner's Manual for more details.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE
Unusual tire noise can be associated with tire and
wheel vibration or irregular tire wear. For vibration,
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). For irregular tire wear, (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS/TIRES - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE/VEHICLE
LEAD
Use the following Vehicle Lead Diagnosis And Cor-
rection Chart to diagnose and correct a vehicle lead
or drift problem.
Fig. 22 Tire Aspect Ratio
1 - SECTIONAL WIDTH
2 - SECTIONAL HEIGHT
22 - 14 TIRES/WHEELSRS
TIRES (Continued)
Page 2095 of 2585

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE WEAR
PATTERNS
Under inflation will cause wear on the shoulders of
tire. Over inflation will cause wear at the center of
tire.
Excessive camber causes the tire to run at an
angle to the road. One side of tread is then worn
more than the other (Fig. 23).
Excessive toe-in or toe-out causes wear on the
tread edges and a feathered effect across the tread
(Fig. 23).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TREAD WEAR
INDICATORS
Tread wear indicators are molded into the bottom
of the tread grooves. When tread depth is 1.6 mm
(1/16 in.), the tread wear indicators will appear as a
13 mm (1/2 in.) band (Fig. 24).
Tire replacement is necessary when indicators
appear in two or more grooves or if localized balding
occurs.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE INFLATION
PRESSURES
The specified tire pressures have been chosen to
provide safe operation, vehicle stability, and a smooth
ride. The proper tire pressure specification can be
found on the Tire Inflation Pressure Label provided
with the vehicle (usually on the rear face of the driv-
er's door).
A quality air pressure gauge is recommended to
check tire air pressure. Tire pressure should bechecked cold once per month. Check tire pressure
more frequently when the weather temperature var-
ies widely. Tire pressure will decrease when the out-
door temperature drops. After checking the air
pressure, replace valve cap finger tight.
Inflation pressures specified on the Tire Inflation
Pressure Label are always the cold inflation pressure
of the tire. Cold inflation pressure is obtained after
the vehicle has not been operated for at least 3
hours, or the vehicle is driven less than one mile
after being inoperative for 3 hours. Tire inflation
Fig. 23 Tire Wear Patterns
Fig. 24 Tread Wear Indicators
1 - TREAD ACCEPTABLE
2 - TREAD UNACCEPTABLE
3 - WEAR INDICATOR
22 - 16 TIRES/WHEELSRS
TIRES (Continued)
Page 2096 of 2585
pressures may increase from 2 to 6 pounds per
square inch (psi) (14 to 41 kPa) during operation. Do
not reduce this normal pressure buildup.
Improper inflation can cause:
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
²Unsatisfactory ride
²The vehicle to drift.
WARNING: OVER OR UNDER INFLATED TIRES CAN
AFFECT VEHICLE HANDLING. THE TIRE CAN FAIL
SUDDENLY, RESULTING IN LOSS OF VEHICLE
CONTROL.
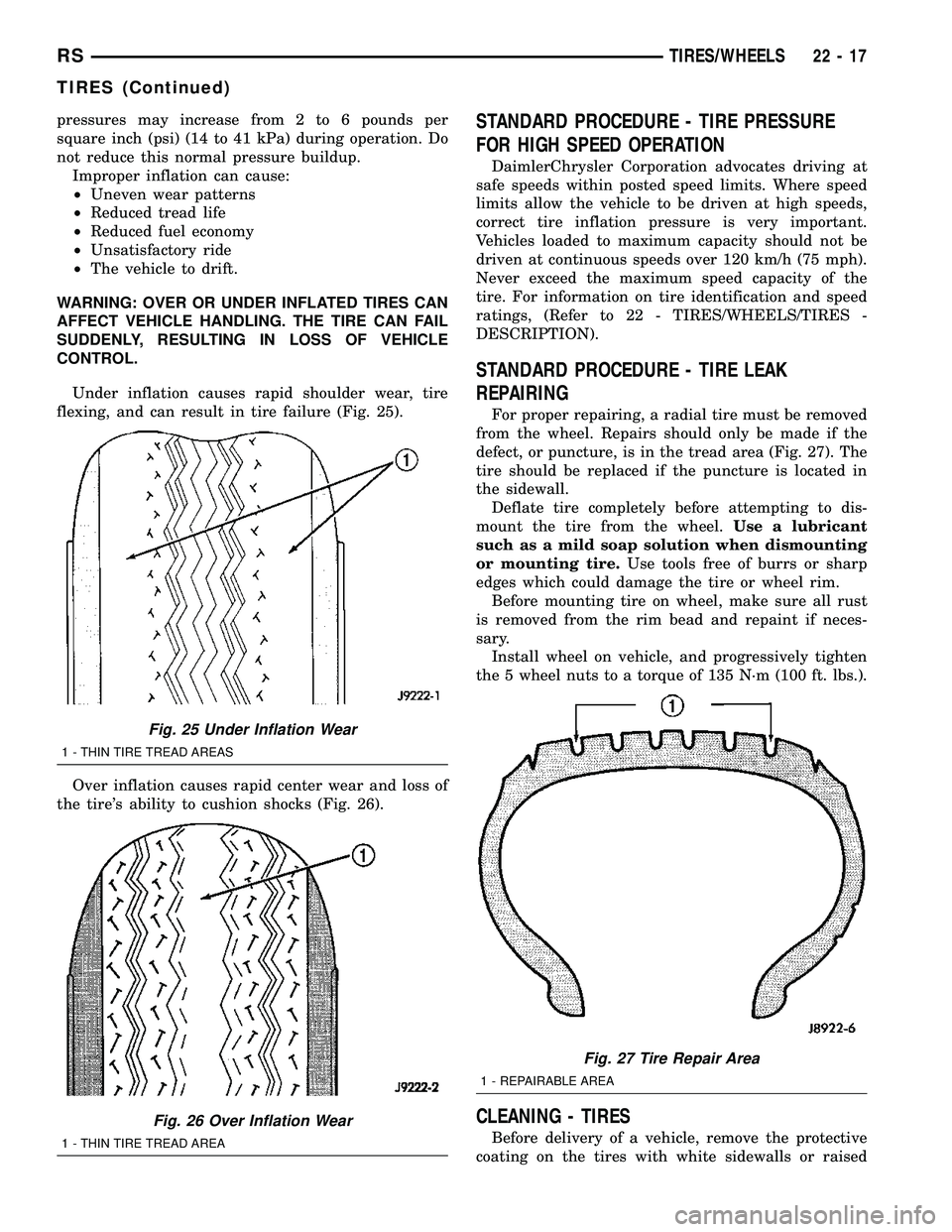
Under inflation causes rapid shoulder wear, tire
flexing, and can result in tire failure (Fig. 25).
Over inflation causes rapid center wear and loss of
the tire's ability to cushion shocks (Fig. 26).STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE PRESSURE
FOR HIGH SPEED OPERATION
DaimlerChrysler Corporation advocates driving at
safe speeds within posted speed limits. Where speed
limits allow the vehicle to be driven at high speeds,
correct tire inflation pressure is very important.
Vehicles loaded to maximum capacity should not be
driven at continuous speeds over 120 km/h (75 mph).
Never exceed the maximum speed capacity of the
tire. For information on tire identification and speed
ratings, (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/TIRES -
DESCRIPTION).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE LEAK
REPAIRING
For proper repairing, a radial tire must be removed
from the wheel. Repairs should only be made if the
defect, or puncture, is in the tread area (Fig. 27). The
tire should be replaced if the puncture is located in
the sidewall.
Deflate tire completely before attempting to dis-
mount the tire from the wheel.Use a lubricant
such as a mild soap solution when dismounting
or mounting tire.Use tools free of burrs or sharp
edges which could damage the tire or wheel rim.
Before mounting tire on wheel, make sure all rust
is removed from the rim bead and repaint if neces-
sary.
Install wheel on vehicle, and progressively tighten
the 5 wheel nuts to a torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
CLEANING - TIRES
Before delivery of a vehicle, remove the protective
coating on the tires with white sidewalls or raised
Fig. 25 Under Inflation Wear
1 - THIN TIRE TREAD AREAS
Fig. 26 Over Inflation Wear
1 - THIN TIRE TREAD AREA
Fig. 27 Tire Repair Area
1 - REPAIRABLE AREA
RSTIRES/WHEELS22-17
TIRES (Continued)
Page 2103 of 2585

CAUTION: Do not try to install a tire pressure sen-
sor in a steel wheel or aftermarket wheel. Use only
in original style factory wheels.
OPERATION
The tire pressure sensors are battery operated.
Each sensor transmits tire pressure data approxi-
mately once every minute at speeds above 13 mph
(20 km/h). Each sensor's (transmitter) broadcast is
uniquely coded so that the SKREEM can monitor the
states of each individual sensor on the vehicle.
Unlike prior model year TPM systems, a magnet is
not required to retrain the system. The SKREEM
automatically learns while driving after a sensor has
been replaced. (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/TIRE
PRESSURE MONITORING/SENSOR - STANDARD
PROCEDURE) For additional information, refer to Appropriate
Diagnostic Information.
CAUTION
CAUTION: The use of tire sealants is strictly prohib-
ited for vehicles equipped with the Tire Pressure
Monitoring system. Tire sealants can clog tire pres-
sure sensors.
CAUTION: Tire pressure sensor valve stem caps
and cores are specially designed for the sensors.
Due to risk of corrosion, do not use a standard
valve stem cap or core in a tire pressure sensor in
place of the original equipment style sensor cap
and core.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to install a tire pressure
sensor in a steel wheel or aftermarket wheel. Use
tire pressure sensors in original style factory
wheels only.
NOTE: TPM thresholds have been established for
the original tire size equipped on the vehicle. Use
original size tires only to maintain system accuracy.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE PRESSURE
SENSOR
NOTE: Tire pressure may increase from 2 to 6 psi
(14 to 41 kPa) during normal driving conditions. Do
NOT reduce this normal pressure build up.
If a fault in the system is detected, always check
air pressure in the tires first with a known accurate
air gauge and correct the inflation pressure. If any
tire is low, inspect allthe tires. If the gauge-read pressure in the tires does not
indicate a tire pressure issue, refer to the appropri-
ate diagnostic information.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE PRESSURE
SENSOR RETRAIN
CAUTION: If a sensor is replaced, the vehicle must
be parked for a minimum of 15 minutes for the sys-
tem to be ready to learn the new sensor ID code.
(1) Park the car for a minimum of 15 minutes.
(2) Drive the vehicle for a minimum of five min-
utes while maintaining a continuous speed above 13
mph (20 km/h). During this time the system will
learn the new sensor ID code and will clear any
DTC's automatically.
NOTE: If a sensor cannot be trained, refer to appro-
priate diagnostic information.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove tire and wheel assembly from vehicle.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - REMOVAL)
CAUTION: The cap used on this valve stem con-
tains an O-ring seal to prevent contamination and
moisture from entering the valve stem. Retain this
valve stem cap for reuse. Do not substitute a regu-
lar valve stem cap in its place.
CAUTION: The valve stem used on this vehicle is
made of aluminum and the core is nickel plated
brass. The original valve stem core must be rein-
stalled and not substituted with a valve stem core
made of a different material. This is required to pre-
vent corrosion in the valve stem caused by the dif-
ferent metals.
(2) Dismount tire from wheel following tire
changer manufacturers instructions while paying
special attention to the following to avoid damaging
the pressure sensor: (a) When breaking the tire bead loose from the
wheel rim, avoid using the Bead Breaker in the
area of the sensor. That includes both front and
rear beads of the tire. (b) When preparing to dismount the tire from
the wheel, carefully insert the mounting/dimount-
ing tool at the valve stem 10É (Fig. 1), then pro-
ceed to dismount the tire from the wheel. Use this
process on both the upper and lower tire beads.
(3) Using a thin wall socket, remove special nut
retaining sensor to wheel (Fig. 2). (4) Remove sensor from wheel (Fig. 2).
22s - 2 TIRE PRESSURE MONITORINGRS
SENSOR - TPM (Continued)
Page 2106 of 2585
TIRES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TIRES DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION - TIRE ...................5
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL-PLY TIRES ........6
DESCRIPTION - REPLACEMENT TIRES .....6
DESCRIPTION - SPARE TIRE (TEMPORARY) ........................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE ....6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE/VEHICLE LEAD ................................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE WEAR PATTERNS ...........................8 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TREAD WEAR
INDICATORS ..........................8
STANDARD PROCEDURE STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE INFLATIONPRESSURES ..........................8
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH SPEED
OPERATION ..........................9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE LEAK REPAIRING ...........................9
CLEANING - TIRES .....................10
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - TIRE
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle. They provide the best overall performance
for normal operation. The ride and handling charac-
teristics match the vehicle's requirements. With
proper care they will give excellent reliability, trac-
tion, skid resistance, and tread life. Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain, in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are: ² Rapid acceleration
² Severe application of brakes
² High-speed driving
² Taking turns at excessive speeds
² Striking curbs and other obstacles
² Operating vehicle with over or under inflated
tire pressures Radial ply tires are more prone to irregular tread
wear. It is important to follow the tire rotation inter-
val shown in the section on Tire Rotation. This will
help to achieve a greater tread-life potential.
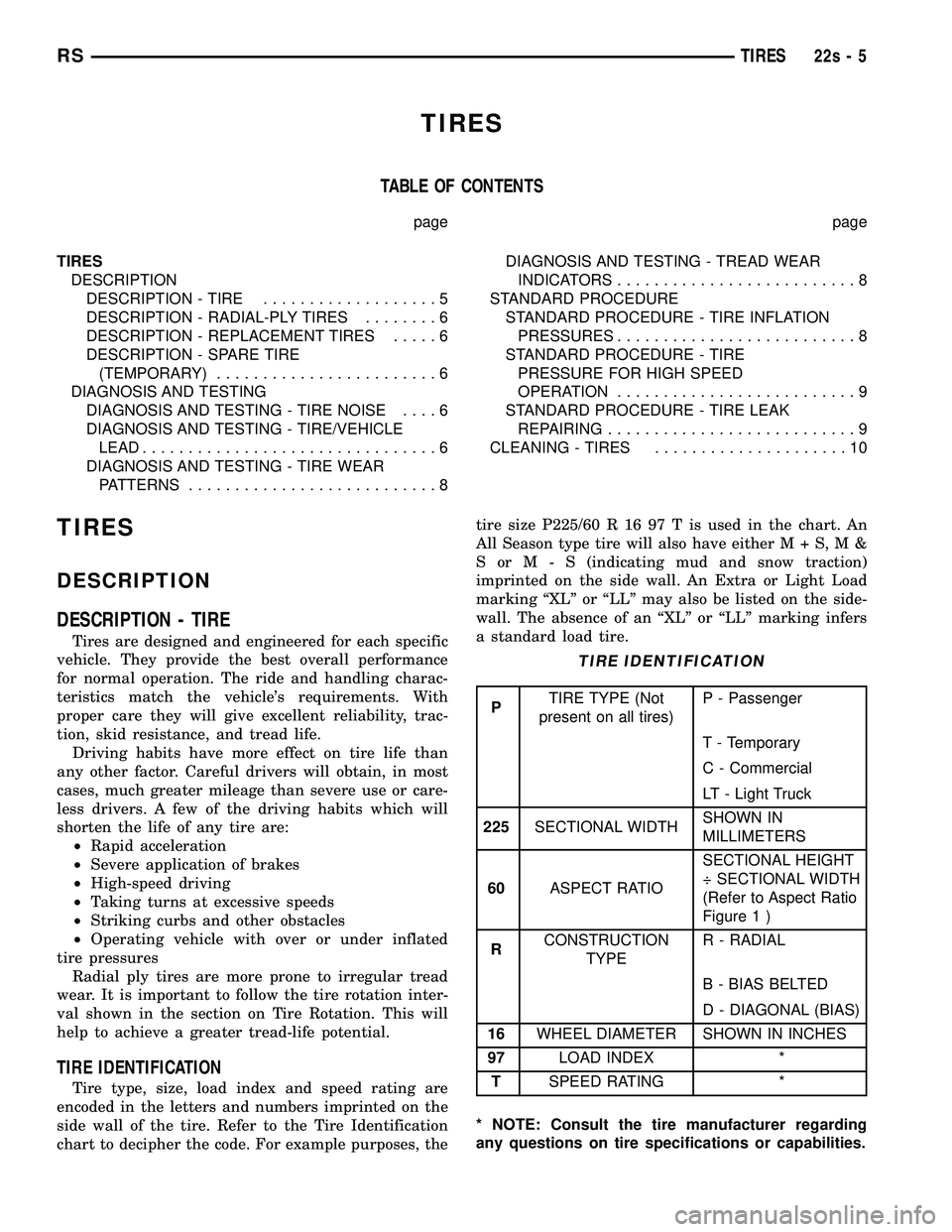
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, load index and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the Tire Identification
chart to decipher the code. For example purposes, the tire size P225/60 R 16 97 T is used in the chart. An
All Season type tire will also have eithe
rM+S,M&
SorM-S (indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall. An Extra or Light Load
marking ªXLº or ªLLº may also be listed on the side-
wall. The absence of an ªXLº or ªLLº marking infers
a standard load tire.
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
P TIRE TYPE (Not
present on all tires) P - Passenger
T - Temporary
C - Commercial
LT - Light Truck
225 SECTIONAL WIDTH SHOWN IN
MILLIMETERS
60 ASPECT RATIO SECTIONAL HEIGHT
÷ SECTIONAL WIDTH
(Refer to Aspect Ratio
Figure 1 )
R CONSTRUCTION
TYPE R - RADIAL
B - BIAS BELTED
D - DIAGONAL (BIAS)
16 WHEEL DIAMETER SHOWN IN INCHES
97 LOAD INDEX *
T SPEED RATING *
* NOTE: Consult the tire manufacturer regarding
any questions on tire specifications or capabilities.
RS TIRES22s-5
Page 2107 of 2585

TIRE CHAINS
Refer to the owners manual supplied with the vehi-
cle to determine whether the use of tire chains is per-
mitted on this vehicle.
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL-PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life, ride
quality and decrease rolling resistance. Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of four
and under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. It is recommended that tires from dif-
ferent manufacturers NOT be mixed. They may be
mixed with a temporary spare tire when necessary. A
maximum speed of 80 km/h (50 mph) is recom-
mended while a temporary spare is in use. Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
DESCRIPTION - REPLACEMENT TIRES
WARNING: FAILURE TO EQUIP THE VEHICLE WITH
TIRES HAVING ADEQUATE SPEED CAPABILITY
CAN RESULT IN SUDDEN TIRE FAILURE.
WARNING: IN ORDER TO MAINTAIN THE SPEED
CAPABILITY OF THE VEHICLE, REPLACEMENT
TIRES MUST HAVE SPEED RATINGS EQUAL TO OR
HIGHER THAN THOSE FITTED TO THE VEHICLE AS
ORIGINAL EQUIPMENT. IF TIRES WITH LOWER
SPEED RATINGS ARE FITTED, THE VEHICLE'S
HANDLING MAY BE AFFECTED AND THE SPEED
CAPABILITY OF THE VEHICLE MAY BE LOWERED
TO THE MAXIMUM SPEED CAPABILITY OF THE
REPLACEMENT TIRES. TO AVOID AN ACCIDENT
RESULTING IN SEVERE OR FATAL INJURY, CON-
SULT THE TIRE MANUFACTURER IN REGARDS TO
MAXIMUM SPEED RATINGS. It is recommended that tires equivalent to the orig-
inal equipment tires be used when replacement is
needed. Failure to use equivalent replacement tires may
adversely affect the safety and handling of the vehi-
cle. The original equipment tires provide a proper com-
bination of many characteristics such as: ² Ride
² Noise
² Handling
² Durability
² Tread life
² Traction
² Rolling resistance
² Speed capability
The use of tires smaller than the minimum tire
size approved for the vehicle can result in tire over-
loading and failure. Use tires that have the approved load rating for
the vehicle and never overload them. Failure to equip
the vehicle with tires having adequate speed capabil-
ity can result in sudden tire failure and loss of vehi-
cle control. The use of oversize tires may cause interference
with vehicle components. Under extremes of suspen-
sion and steering travel, interference with vehicle
components may cause tire damage.
DESCRIPTION - SPARE TIRE (TEMPORARY)
The temporary (convenience) spare tire is designed
for emergency use only. The original tire should be
repaired and reinstalled, or replaced with a new, at
the first opportunity. The temporary (convenience) spare tire should be
inflated to the pressure listed on its sidewall. Do not
exceed speeds of 80 km/h (50 mph) when the tempo-
rary spare tire is in use on the vehicle. Refer to the
Owner's Manual for more details.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE
Unusual tire noise can be associated with tire and
wheel vibration or irregular tire wear. For vibration,
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). For irregular tire wear, (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS/TIRES - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE/VEHICLE
LEAD
Use the following Vehicle Lead Diagnosis And Cor-
rection Chart to diagnose and correct a vehicle lead
or drift problem.
Fig. 1 Tire Aspect Ratio
1 - SECTIONAL WIDTH
2 - SECTIONAL HEIGHT
22s - 6 TIRESRS
TIRES (Continued)
Page 2109 of 2585

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE WEAR
PATTERNS
Under inflation will cause wear on the shoulders of
tire. Over inflation will cause wear at the center of
tire. Excessive camber causes the tire to run at an
angle to the road. One side of tread is then worn
more than the other (Fig. 2). Excessive toe-in or toe-out causes wear on the
tread edges and a feathered effect across the tread
(Fig. 2).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TREAD WEAR
INDICATORS
Tread wear indicators are molded into the bottom
of the tread grooves. When tread depth is 1.6 mm
(1/16 in.), the tread wear indicators will appear as a
13 mm (1/2 in.) band (Fig. 3). Tire replacement is necessary when indicators
appear in two or more grooves or if localized balding
occurs.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE INFLATION
PRESSURES
The specified tire pressures have been chosen to
provide safe operation, vehicle stability, and a smooth
ride. The proper tire pressure specification can be
found on the Tire Inflation Pressure Label provided
with the vehicle (usually on the driver's side B-pil-
lar). A quality air pressure gauge is recommended to
check tire air pressure. Tire pressure should be checked cold once per month. Check tire pressure
more frequently when the weather temperature var-
ies widely. Tire pressure will decrease when the out-
door temperature drops. After checking the air
pressure, replace valve cap finger tight.
Inflation pressures specified on the Tire Inflation
Pressure Label are always the cold inflation pressure
of the tire. Cold inflation pressure is obtained after
the vehicle has not been operated for at least 3
hours, or the vehicle is driven less than one mile
after being inoperative for 3 hours. Tire inflation
Fig. 2 Tire Wear Patterns
Fig. 3 Tread Wear Indicators
1 - TREAD ACCEPTABLE
2 - TREAD UNACCEPTABLE
3 - WEAR INDICATOR
22s - 8 TIRESRS
TIRES (Continued)