service CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 541 of 2339

(PCM) based upon the results. The ªVALID/INVALID
KEYº message communication is performed using a
rolling code algorithm via the Programmable Com-
munication Interface (PCI) data bus. A ªVALID KEYº
message must be sent to the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) within two seconds of ignition ON to
free the engine from immobilization.
The SKREEM contains a Radio Frequency (RF)
transceiver and a microprocessor. The SKREEM
retains in memory the ID numbers of any Sentry Key
that is programmed to it. The maximum number of
keys that may be programmed to each module is
eight (8). The SKREEM also communicates over the
Programmable Communication Interface (PCI) data
bus with the Powertrain Control Module (PCM), the
Body Control Module (BCM), the Mechanical Instru-
ment Cluster (MIC), and the DRB IIItscan tool. The
SKREEM transmits and receives RF signals through
a tuned antenna enclosed within a molded plastic
ring formation that is integral to the SKREEM hous-
ing. When the SKREEM is properly installed on the
steering column, the antenna ring fits snugly around
the circumference of the ignition lock cylinder hous-
ing. If this ring is not mounted properly, communica-
tion problems may arise in the form of transponder-
related faults.
For added system security, each SKREEM is pro-
grammed with a unique9Secret Key9code. This code
is stored in memory and is sent over the PCI bus to
the PCM and to each key that is programmed to
work with the vehicle. The9Secret Key9code is there-
fore a common element found in all components of
the Sentry Key Immobilizer System (SKIS). In the
event that a SKREEM replacement is required, the
9Secret Key9code can be restored from the PCM by
following the SKIM replacement procedure found in
the DRB IIItscan tool. Proper completion of this
task will allow the existing ignition keys to be repro-
grammed. Therefore, new keys will NOT be needed.
In the event that the original9Secret Key9code can
not be recovered, new ignition keys will be required.
The DRB IIItscan tool will alert the technician if
key replacement is necessary. Another security code,
called a PIN, is used to gain secured access to the
SKREEM for service. The SKREEM also stores in its
memory the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN),
which it learns through a bus message from the
assembly plant tester. The SKIS scrambles the infor-
mation that is communicated between its components
in order to reduce the possibility of unauthorized
SKREEM access and/or disabling.
REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY (RKE)
The RKE transmitter uses radio frequency signals
to communicate with the SKREEM. The SKREEM is
on the PCI bus. When the operator presses a buttonon the transmitter, it sends a specific request to the
SKREEM. In turn the SKREEM sends the appropri-
ate request over the PCI Bus to the:
²Body Control Module (BCM) to control the door
lock and unlock functions, the liftgate lock and
unlock functions, the arming and disarming of the
Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS) (if equipped),
and the activation of illuminated entry.
²Integrated Power Module (IPM) to activate the
park lamps, the headlamps, and the horn for horn
chirp. If requested, the BCM sends a request over
the PCI Bus to the:
TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING (TPM)
If equipped with the Tire Pressure Monitoring
(TPM) System, each of the vehicles four wheels will
have a valve stem with a pressure sensor and radio
transmitter built in. Signals from the tire pressure
sensor/transmitter are received and interpreted by
the SKREEM.
A sensor/transmitter in a mounted wheel will
broadcast its detected pressure once per minute
when the vehicle is moving faster than 15 mph (24
km/h). Each sensor/transmitter's broadcast is
uniquely coded so that the SKREEM can determine
the location.
OPERATION
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER
The Sentry Key Remote Entry Module (SKREEM)
receives an encrypted Radio Frequency (RF) signal
from the transponder key. The SKREEM then
decrypts the signal and broadcasts the requested
remote commands to the appropriate modules in the
vehicle over the Programmable Communication
Interface (PCI) data bus. A valid transponder key ID
must be incorporated into the RF signal in order for
the SKREEM to pass the message on to the appro-
priate modules.
Automatic transponder key synchronization is done
by the SKREEM if a valid transponder key is
inserted into the ignition cylinder, and the ignition is
turned ON. This provides a maximum operation win-
dow for RKE functions.
Each Sentry Key Remote Entry System (SKREES)
consists of a SKREEM and a transponder key. Each
system has a secret key code unique to that system.
The secret key is electronically coded in the
SKREEM and in all programmed transponder keys.
It is used for immobilization and RKE functions for
data security. In addition, each transponder key will
have a unique identification. For North America, the
options are a 3-button or 6 button integrated keys.
For Export, the options are 2-button or 5 button key
fobs. (Export does not get the integrated key).
8Q - 4 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITYRS
SENTRY KEY REMOTE ENTRY MODULE (Continued)
Page 542 of 2339

When the ignition switch is moved to the RUN
position, the SKREEM transmits an Radio Frequency
(RF) signal to the transponder in the ignition key.
The SKREEM then waits for a response RF signal
from the transponder in the key. If the response
received identifies the key as valid, the SKREEM
sends a9valid key9message to the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM) over the Programmable Commu-
nication Interface (PCI) data bus. If the response
received identifies the key as invalid or no response
is received from the transponder in the ignition key,
the SKREEM sends an9invalid key9message to the
PCM. The PCM will enable or disable engine opera-
tion based upon the status of the SKREEM mes-
sages. It is important to note that the default
condition in the PCM is9invalid key.9Therefore, if no
response is received by the PCM, the engine will be
immobilized after two (2) seconds of running.
The SKREEM also sends indicator light status
messages to the Mechanical Instrument Cluster
(MIC) to operate the light. This is the method used to
turn the light ON solid or to flash it after the indi-
cator light test is complete to signify a fault in the
SKREES. If the light comes ON and stays ON solid
after the indicator light test, this signifies that the
SKREEM has detected a system malfunction and/or
that the SKREES has become inoperative. If the
SKREEM detects an invalid keyORa key-related
fault exists, the indicator light will flash following
the indicator light test. The SKREEM may also
request an audible chime if the customer key pro-
gramming feature is available and the procedure is
being utilized (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/VEHICLE
THEFT SECURITY/TRANSPONDER KEY - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY (RKE)
After pressing the lock button on the RKE trans-
mitter, all of the door locks will lock, the illuminated
entry will turn off (providing all doors are closed),
and the VTSS (if equipped) will arm. After pressing
the unlock button, on the RKE transmitter, one time,
the driver door lock will unlock, the illuminated
entry will turn on the courtesy lamps, and the VTSS
(if equipped) will disarm. After pressing the unlock
button a second time, the remaining door locks will
unlock. The Electronic Vehicle Information Center
(EVIC) or the DRBIIItscan tool can reprogram this
feature to unlock all of the door locks with one press
of the unlock button. If the vehicle is equipped with
the memory system, the memory message will iden-
tify which transmitter (1 or 2) sent the signal.The SKREEM is capable of retaining up to 8 indi-
vidual access codes (8 transmitters). If the PRNDL is
in any position except park, the SKREEM will dis-
able the RKE. The 4 button transmitter uses
1-CR2032 battery. The minimum battery life is
approximately 4.7 years based on 20 transmissions a
day at 84ÉF (25ÉC). Use the DRBIIItscan tool or the
Miller Tool 9001 RF Detector to test the RKE trans-
mitter. Use the DRBIIItor the customer program-
ming method to program the RKE system. However,
the SKREEM will only allow RKE programming
when the ignition is in the ON position, the PRNDL
is in park position, and the VTSS (if equipped) is dis-
armed.
TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING (TPM)
The SKREEM monitors the signals from the tire
pressure sensor/transmitters and determines if any
tire has gone below the low pressure threshold LOW
TIRE PRESSURE THRESHOLDS table.
LOW TIRE PRESSURE THRESHOLDS
SYSTEM STATUS
INDICATORTIRE PRESSURE
ON 193 kPa (28 PSI)
OFF 227 kPa (33 PSI)
CRITICAL AND NON-CRITICAL SYSTEM ALERTS
CRITICAL:A critical alert will be triggered when
a tire pressure has gone below a set threshold pres-
sure. The EVIC display will display ªX TIRE(S) LOW
PRESSUREº. ªXº will be the number of tires report-
ing low pressure. The message will display for the
duration of the current ignition cycle or until an
EVIC button is pressed. If the display is removed
without correcting the condition, it will reappear 300
seconds to warn the driver of the low pressure condi-
tion.
NON-CRITICAL:A non-critical alert will be trig-
gered when no signal is received from a sensor/trans-
mitter. The EVIC display in the cluster will display
ªSERVICE TIRE SYSTEM SOON.º
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SENTRY KEY
REMOTE ENTRY MODULE
For proper diagnosis and testing of the Sentry Key
Remote Entry Module (SKREEM), use a DRBllltand
refer to the proper Body Diagnostic Procedures infor-
mation.
RSVEHICLE THEFT SECURITY8Q-5
SENTRY KEY REMOTE ENTRY MODULE (Continued)
Page 545 of 2339

VTSS/SKIS INDICATOR LAMP
DESCRIPTION
The Sentry Key Remote Entry System (SKREES)
uses an indicator light to convey information on the
status of the system to the customer. This light is
shared with the Vehicle Theft Security System
(VTSS). The light is located in the Mechanical
Instrument Cluster (MIC). The VTSS status is con-
trolled by the Body Control Module (BCM), via Pro-
grammable Communication Interface (PCI) data bus
communication with the MIC, based upon messages
it receives from the Sentry Key Remote Entry Mod-
ule (SKREEM) on the PCI data bus.
OPERATION
The Mechanical Instrument Cluster (MIC) per-
forms a four second bulb check via PCI communica-
tion with the Sentry Key Remote Entry Module
(SKREEM). After the bulb check, the lamp is con-
trolled according to SKREEM messages. Then, the
SKREEM sends messages to the BCM to operate thelight based upon the results of the Sentry Key
Remote Entry System (SKREES) self tests. The light
may be actuated in two possible ways, flashing or on
solid. If the light comes on and stays on solid after a
power-up test, this indicates that the SKREEM has
detected a system malfunction. If the SKREEM
detects an invalid key when the ignition switch is
moved to the ON position, it sends a message on the
PCI bus to the MIC, to flash the light. The SKREEM
can also send a message to flash the light and gen-
erate a single audible chime at the same time. These
two events occurring simultaneously indicate that
the SKIS has been placed into the9Customer Learn9
mode (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/VEHICLE THEFT
SECURITY/TRANSPONDER KEY - STANDARD
PROCEDURE). If the light comes on and stays on
after the power-up test, diagnosis of the SKREES
should be performed using a DRBIIItscan tool and
the appropriate Body Diagnostic Procedures informa-
tion. The light is a Light Emitting Diode (LED) and
is not a serviceable component.
8Q - 8 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITYRS
Page 555 of 2339

(5) Remove wiper linkage from motor crank. DO
NOT remove crank from motor.
(6) Remove bolts holding wiper motor and remove
motor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place wiper module on a suitable work surface.
(2) Install wiper linkage into wiper unit.
(3) Connect wire connectors to wiper motor.
(4) Place the wiper module into engine compart-
ment and connect wiper module wire connector to
engine wire harness (Fig. 7).
(5) Install the four backwall bolts and four brace
nuts to wiper module.
(6) Operate wiper motor and verify that the wiper
motor parks when wiper switch is turned OFF.
REAR WIPER ARM
REMOVAL
(1) Remove arm nut cap.
(2) Remove wiper arm nut.
(3) Pull wiper from pivot by rocking back and
forth.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify that wipers are in parked position.
(2) Position arm on pivot.
(3) Install wiper arm nut and torque to 20 N´m
(175 in. lbs.).
REAR WIPER MOTOR
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove rear wiper arm. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/REAR WIPER ARM -
REMOVAL) in this section.
(3) Open liftgate.
(4) Remove liftgate trim panel. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE/
TRIM PANEL - REMOVAL).
(5) Disconnect wire connector from rear wiper
motor.
(6) Remove screws holding rear wiper motor to lift-
gate.
(7) Remove wiper motor from liftgate.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the wiper motor in the liftgate.
(2) Install the retaining screws.
(3) Connect the wire harness connector.(4) Install the liftgate trim panel. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE/
TRIM PANEL - INSTALLATION).
(5) Connect wire connector to rear wiper motor.
(6) Install the screws holding rear wiper motor to
liftgate.
(7) Install the wiper motor to the liftgate.
(8) Close the liftgate.
(9) Install the wiper arm. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/REAR WIPER ARM -
INSTALLATION) in this section.
(10) Connect the battery negative cable.
REAR WIPER/WASHER
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
On Automatic Temperature Control (ATC) vehicles
only, the rear window wiper/washer switches are
located on the center bezel with the hazard and
heated seat switches (Fig. 3). They are not service-
able separately from the hazard and heated seat
switches. If defective, the entire switch assembly
must be replaced.
On Manual Temperature Control (MTC) vehicles
only, the rear window wiper/washer switch is located
on the HVAC control head (Fig. 4) attached to the
center bezel. They are not serviceable separately
from the control head. If found faulty, the entire
MTC head must be replaced.
Fig. 3 INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER BEZEL
1 - TRIM BEZEL
2 - IN CAR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
3 - A/C REQUEST SWITCH
4 - REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER/HEATED MIRRORS SWITCH
COMBO
5 - FRONT WINDOW DEFROSTER MODE SELECTOR
8R - 10 WIPERS/WASHERSRS
FRONT WIPER MOTOR (Continued)
Page 560 of 2339

NAVIGATION/TELECOMMUNICATION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
NAVIGATION/TELECOMMUNICATION
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TELECOMMUNICATION.................1HANDS FREE MODULE
REMOVAL.............................3
INSTALLATION..........................3
NAVIGATION/
TELECOMMUNICATION
DESCRIPTION
TELECOMMUNICATIONS
A hands-free cellular system is an available option
on this vehicle. It uses BluetoothŸ technology to pro-
vide wireless communication between the operator's
compatible cellular telephone and the vehicle's
on-board receiver.
The system uses voice recognition technology to
control operation. The incoming voice is broadcast
through the vehicle's radio speakers, automatically
overriding any other audio signals on the speakers
when the hands-free system is in use. A microphone
in the rearview mirror picks up vehicle occupant's
voices. If a call is in progress when the ignition is
switched off, the hands-free system will continue to
operate for up to 45 seconds as part of the Accessory
Relay Delay function. Thereafter, the call can con-
tinue on the hand-held telephone.
The center console front storage compartment
includes a cellular telephone holder, but the system
will communicate with a telephone that is anywhere
within the vehicle. However, covering the hand held
phone or the hands-free phone module with a metal
object may block the signal. The system will recog-
nize up to seven telephones, each of which is given a
spoken identification by the user during the setup
process. The system includes Spanish voice recogni-
tion in addition to English.
Two buttons on the rearview mirror, identified with
ISO icons, control the system: A9phone9button turns
the system on and off; a9voice recognition9(or voice
command) button prompts the hands-free system to
listen for a voice command.
OPERATION
TELECOMMUNICATION
Two buttons on the rearview mirror, identified with
ISO icons, control the system: A9phone9button turns
the system on and off; a9voice recognition9(or voice
command) button prompts the hands-free system to
listen for a voice command. The system includes the
following features:
²Phonebook - Stores telephone numbers for later
recall by name or other verbal identification, called a
voice tag, and memory location.
²Four memory locations - Home, Work, Mobile
and Pager. A maximum of 32 unique names or voice
tags may be stored at the same time, with a different
number in each of the four memory locations.
²Voice tag dialing - Dials the number associated
with a voice tag and memory location.
²Digit dialing - Dials the telephone number by
recognizing the names of the digits as they are spo-
ken.
²Receiving calls - A voice prompt notifies the user
of an incoming call. Pressing the ªphoneº button
answers the call.
²Privacy Mode - Switches the call to the hand-
held telephone and the hands-free system and back
again using the ªvoice recognitionº (or ªvoice com-
mandº) button and a voice command, if desired.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TELECOMMUNICATION
Any diagnosis of the Telecommunication sys-
tem should begin with the use of the DRB IIIt
diagnostic tool. For information on the use of
the DRB IIIt, refer to the appropriate Diagnos-
tic Service Information.
For complete circuit diagrams, refer to the appro-
priate wiring information.
RSNAVIGATION/TELECOMMUNICATION8T-1
Page 561 of 2339
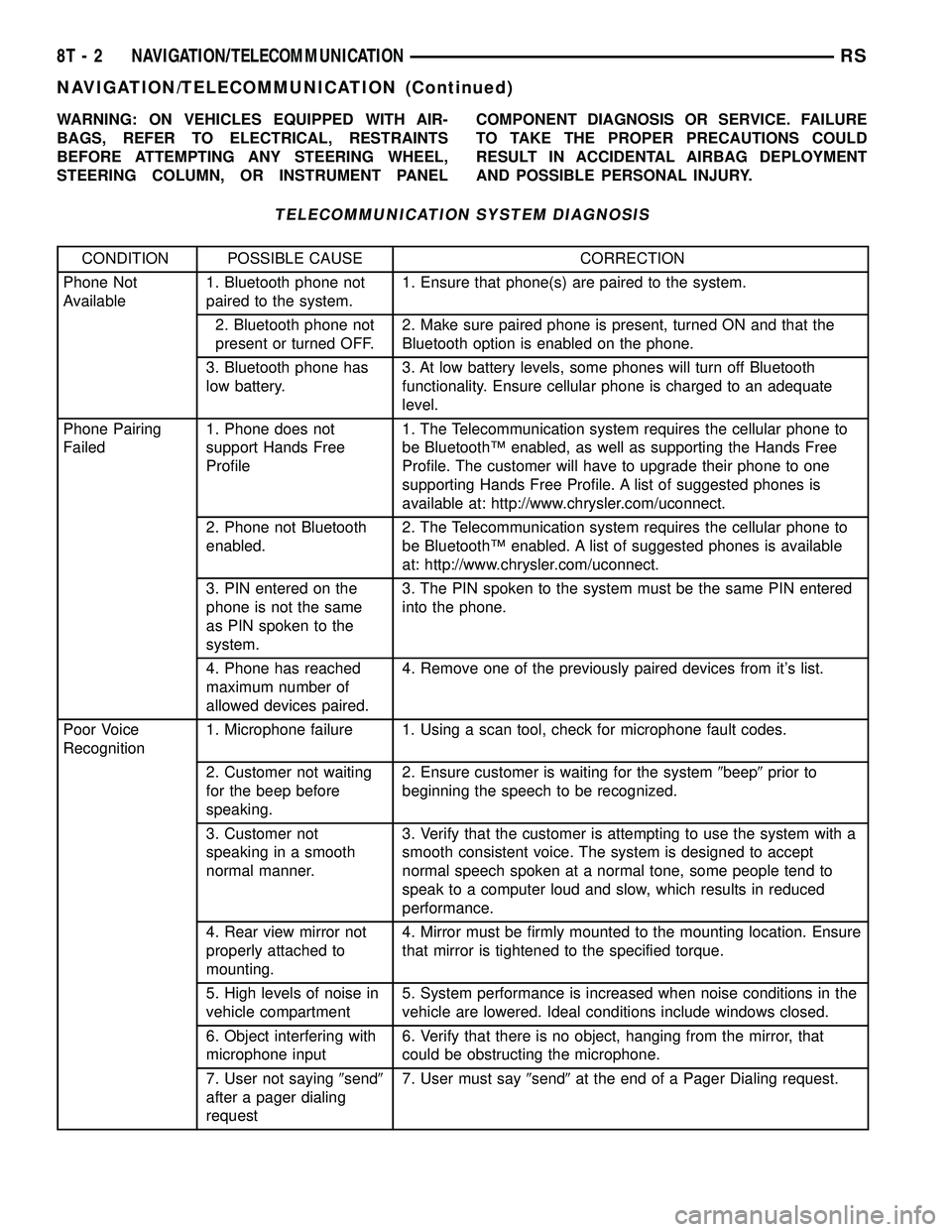
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO ELECTRICAL, RESTRAINTS
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANELCOMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE
TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT
AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Phone Not
Available1. Bluetooth phone not
paired to the system.1. Ensure that phone(s) are paired to the system.
2. Bluetooth phone not
present or turned OFF.2. Make sure paired phone is present, turned ON and that the
Bluetooth option is enabled on the phone.
3. Bluetooth phone has
low battery.3. At low battery levels, some phones will turn off Bluetooth
functionality. Ensure cellular phone is charged to an adequate
level.
Phone Pairing
Failed1. Phone does not
support Hands Free
Profile1. The Telecommunication system requires the cellular phone to
be BluetoothŸ enabled, as well as supporting the Hands Free
Profile. The customer will have to upgrade their phone to one
supporting Hands Free Profile. A list of suggested phones is
available at: http://www.chrysler.com/uconnect.
2. Phone not Bluetooth
enabled.2. The Telecommunication system requires the cellular phone to
be BluetoothŸ enabled. A list of suggested phones is available
at: http://www.chrysler.com/uconnect.
3. PIN entered on the
phone is not the same
as PIN spoken to the
system.3. The PIN spoken to the system must be the same PIN entered
into the phone.
4. Phone has reached
maximum number of
allowed devices paired.4. Remove one of the previously paired devices from it's list.
Poor Voice
Recognition1. Microphone failure 1. Using a scan tool, check for microphone fault codes.
2. Customer not waiting
for the beep before
speaking.2. Ensure customer is waiting for the system9beep9prior to
beginning the speech to be recognized.
3. Customer not
speaking in a smooth
normal manner.3. Verify that the customer is attempting to use the system with a
smooth consistent voice. The system is designed to accept
normal speech spoken at a normal tone, some people tend to
speak to a computer loud and slow, which results in reduced
performance.
4. Rear view mirror not
properly attached to
mounting.4. Mirror must be firmly mounted to the mounting location. Ensure
that mirror is tightened to the specified torque.
5. High levels of noise in
vehicle compartment5. System performance is increased when noise conditions in the
vehicle are lowered. Ideal conditions include windows closed.
6. Object interfering with
microphone input6. Verify that there is no object, hanging from the mirror, that
could be obstructing the microphone.
7. User not saying9send9
after a pager dialing
request7. User must say9send9at the end of a Pager Dialing request.
8T - 2 NAVIGATION/TELECOMMUNICATIONRS
NAVIGATION/TELECOMMUNICATION (Continued)
Page 572 of 2339

DESCRIPTION - CONNECTOR, GROUND AND
SPLICE INFORMATION
CAUTION: Not all connectors are serviced. Some
connectors are serviced only with a harness. A typ-
ical example might be the Supplemental Restraint
System connectors. Always check parts availability
before attempting a repair.
IDENTIFICATION
In-line connectors are identified by a number, as
follows:
²In-line connectors located in the engine compart-
ment are C100 series numbers
²In-line connectors located in the Instrument
Panel area are C200 series numbers.
²In-line connectors located in the body are C300
series numbers.
²Jumper harness connectors are C400 series
numbers.
²Grounds and ground connectors are identified
with a ªGº and follow the same series numbering as
the in-line connectors.
²Splices are identified with an ªSº and follow the
same series numbering as the in-line connectors.
²Component connectors are identified by the com-
ponent name instead of a number. Multiple connec-
tors on a component use a C1, C2, etc. identifier.
LOCATIONS
Section 8W-91 contains connector/ground/splice
location illustrations. The illustrations contain the
connector name (or number)/ground number/splice
number and component identification. Connector/
ground/splice location charts in section 8W-91 refer-
ence the figure numbers of the illustrations.
The abbreviation T/O is used in the component
location section to indicate a point in which the wir-
ing harness branches out to a component. The abbre-
viation N/S means Not Shown in the illustrations
WARNING
WARNINGS - GENERAL
WARNINGSprovide information to prevent per-
sonal injury and vehicle damage. Below is a list of
general warnings that should be followed any time a
vehicle is being serviced.
WARNING: ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES FOR
EYE PROTECTION.
WARNING: USE SAFETY STANDS ANYTIME A PRO-
CEDURE REQUIRES BEING UNDER A VEHICLE.WARNING: BE SURE THAT THE IGNITION SWITCH
ALWAYS IS IN THE OFF POSITION, UNLESS THE
PROCEDURE REQUIRES IT TO BE ON.
WARNING: SET THE PARKING BRAKE WHEN
WORKING ON ANY VEHICLE. AN AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION SHOULD BE IN PARK. A MANUAL
TRANSMISSION SHOULD BE IN NEUTRAL.
WARNING: OPERATE THE ENGINE ONLY IN A
WELL-VENTILATED AREA.
WARNING: KEEP AWAY FROM MOVING PARTS
WHEN THE ENGINE IS RUNNING, ESPECIALLY THE
FAN AND BELTS.
WARNING: TO PREVENT SERIOUS BURNS, AVOID
CONTACT WITH HOT PARTS SUCH AS THE RADIA-
TOR, EXHAUST MANIFOLD(S), TAIL PIPE, CATA-
LYTIC CONVERTER AND MUFFLER.
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW FLAME OR SPARKS
NEAR THE BATTERY. GASES ARE ALWAYS
PRESENT IN AND AROUND THE BATTERY.
WARNING: ALWAYS REMOVE RINGS, WATCHES,
LOOSE HANGING JEWELRY AND AVOID LOOSE
CLOTHING.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WIRING HARNESS
TROUBLESHOOTING TOOLS
When diagnosing a problem in an electrical circuit
there are several common tools necessary. These tools
are listed and explained below.
²Jumper Wire - This is a test wire used to con-
nect two points of a circuit. It can be used to bypass
an open in a circuit.
WARNING: NEVER USE A JUMPER WIRE ACROSS
A LOAD, SUCH AS A MOTOR, CONNECTED
BETWEEN A BATTERY FEED AND GROUND.
²Voltmeter - Used to check for voltage on a cir-
cuit. Always connect the black lead to a known good
ground and the red lead to the positive side of the
circuit.
CAUTION: Most of the electrical components used
in today's vehicles are Solid State. When checking
voltages in these circuits, use a meter with a 10 -
megohm or greater impedance rating.
RS8W-01 WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION8W-01-7
WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1176 of 2339

(5) Connect the negative and positive battery
cables.
(6) Using a scan tool, check for any stored diagnos-
tic trouble codes. Ensure that all vehicle options are
operational.
IOD FUSE
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles are equipped with an Ignition-Off
Draw (IOD) fuse that is removed from its normal
cavity in the Integrated Power Module (IPM) when
the vehicle is shipped from the factory. Dealer per-
sonnel are to remove the IOD fuse from the storage
location and install it into the IPM fuse cavity
marked IOD as part of the preparation procedures
performed just prior to new vehicle delivery.
The IOD fuse is a 20 ampere blade-type mini fuse
and, when removed, it is stored in a fuse cavity adja-
cent to the washer fuse within the IPM.
OPERATION
The term ignition-off draw (IOD) identifies a nor-
mal condition where power is being drained from the
battery with the ignition switch in the Off position.
The IOD fuse feeds the memory and sleep mode func-
tions for some of the electronic modules in the vehicle
as well as various other accessories that require bat-
tery current when the ignition switch is in the Off
position, including the clock. The only reason the
IOD fuse is removed is to reduce the normal IOD of
the vehicle electrical system during new vehicle
transportation and pre-delivery storage to reduce
battery depletion, while still allowing vehicle opera-
tion so that the vehicle can be loaded, unloaded and
moved as needed by both vehicle transportation com-
pany and dealer personnel.
The IOD fuse is removed from the Integrated
Power Module (IPM) fuse cavity when the vehicle is
shipped from the assembly plant. Dealer personnel
must install the IOD fuse when the vehicle is being
prepared for delivery in order to restore full electrical
system operation. Once the vehicle is prepared for
delivery, the IOD function of this fuse becomes trans-
parent and the fuse that has been assigned the IOD
designation becomes only another Fused B(+) circuit
fuse. The IOD fuse serves no useful purpose to the
dealer technician in the service or diagnosis of any
vehicle system or condition, other than the same pur-
pose as that of any other standard circuit protection
device.
The IOD fuse can be used by the vehicle owner as
a convenient means of reducing battery depletion
when a vehicle is to be stored for periods not to
exceed approximately thirty days. However, it mustbe remembered that removing the IOD fuse will not
eliminate IOD, but only reduce this normal condition.
If a vehicle will be stored for more than thirty days,
the battery negative cable should be disconnected to
eliminate normal IOD; and, the battery should be
tested and recharged at regular intervals during the
vehicle storage period to prevent the battery from
becoming discharged or damaged.
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION
Two power outlets are installed in the instrument
panel center lower bezel. Two additional power out-
lets are incorporated into the left rear C-pillar and
the center console (if equipped). The power outlets
bases are secured by a snap fit. A hinged plug flips
closed to conceal and protect the power outlet base
when not in use.
OPERATION
The power outlet base or receptacle shell is con-
nected to ground, and an insulated contact in the
bottom of the shell is connected to battery current.
The power outlet on the instrument panel marked
with a battery receives battery voltage from a fuse in
the Integrated Power Module (IPM) at all times. The
other power outlet on the instrument panel marked
with a key receives battery voltage only when the
key is in the on position.
The power outlet located in the center console
receives battery voltage all the time when positioned
between thefront seatsand key-on voltage when
positioned between therear seats. The power outlet
located on the C-pillar receives battery voltage only
when the key is in the ON position.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - POWER OUTLET
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO RESTRAINTS BEFORE ATTEMPT-
ING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN,
SEAT OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAG-
NOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse in the Integrated
Power Module (IPM). If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK,
repair the shorted circuit or component as required
and replace the faulty fuse.
RS8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM8W-97-3
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (Continued)
Page 1180 of 2339

REMOVAL - CAMSHAFT SPROCKETS.....66
REMOVAL - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET....66
CLEANING............................67
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET . 67
INSTALLATION - CAMSHAFT SPROCKETS . . 67
INSTALLATION - TIMING BELT...........67
TIMING BELT TENSIONER & PULLEY
REMOVAL.............................69INSTALLATION.........................70
BALANCE SHAFTS AND CARRIER ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION.........................71
OPERATION...........................71
REMOVAL.............................71
INSTALLATION.........................73
ENGINE 2.4L
DESCRIPTION
The 2.4 Liter (148 cu. in.) in-line four cylinder
engine is a double over head camshaft with hydraulic
lash adjusters and four valve per cylinder design.
The engine is free-wheeling; meaning it has provi-
sions for piston-to-valve clearance. However valve-to-
valve interference can occur, if camshafts are rotated
independently.
The cylinders are numbered from front of the
engine to the rear. The firing order is 1±3±4±2.
The engine identification number is located on the
rear of the cylinder block (Fig. 1).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
Refer to the Engine Mechanical and the Engine
Performance diagnostic charts, for possible causes
and corrections of malfunctions (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MECHANICAL)
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
- PERFORMANCE).
For fuel system diagnosis, (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
²Hydraulic Lash Adjuster Noise Diagnosis
²Engine Oil Leak Inspection
Fig. 1 Engine Identification
1 - ENGINE IDENTIFICATION LOCATION
RSENGINE 2.4L9-3
Page 1185 of 2339

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL CONSUMPTION OR SPARK
PLUGS FOULED1. PCV system malfunction. 1. Check system and repair as
necessary. (Refer to 25 -
EMISSIONS CONTROL/
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS/PCV
VALVE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
2. Worn, scuffed or broken rings. 2. Hone cylinder bores. Install new
rings.
3. Carbon in oil ring slots. 3. Install new rings.
4. Rings fitted too tightly in grooves. 4. Remove rings and check
grooves. If groove is not proper
width, replace piston.
5. Worn valve guide(s). 5. Replace cylinder head assembly.
6. Valve stem seal(s) worn or
damaged.6. Replace seal(s).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL LEAK
INSPECTION
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair as necessary.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24 km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.
(5)If the oil leak source is not positively
identified at this time, proceed with the air leak
detection test method as follows:
²Disconnect the fresh air hose (make-up air) at
the cylinder head cover and plug or cap the outlet on
the cover.
²Remove the PCV valve hose from the cylinder
head cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve outlet on the
cover.
²Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and reg-
ulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.²Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provides the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
²If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil
seal area, refer to the section, Inspection for Rear
Seal Area Leak.
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply.
Remove the air hose, all plugs, and caps. Install the
PCV valve and fresh air hose (make-up air). Proceed
to next step.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
NOTE: If oil leakage is observed at the dipstick tube
to block location; remove the tube, clean and reseal
using MoparTStud & Bearing Mount (press fit tube
applications only), and for O-ring style tubes,
remove tube and replace the O-ring seal.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
9 - 8 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)