braking CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 93 of 2339
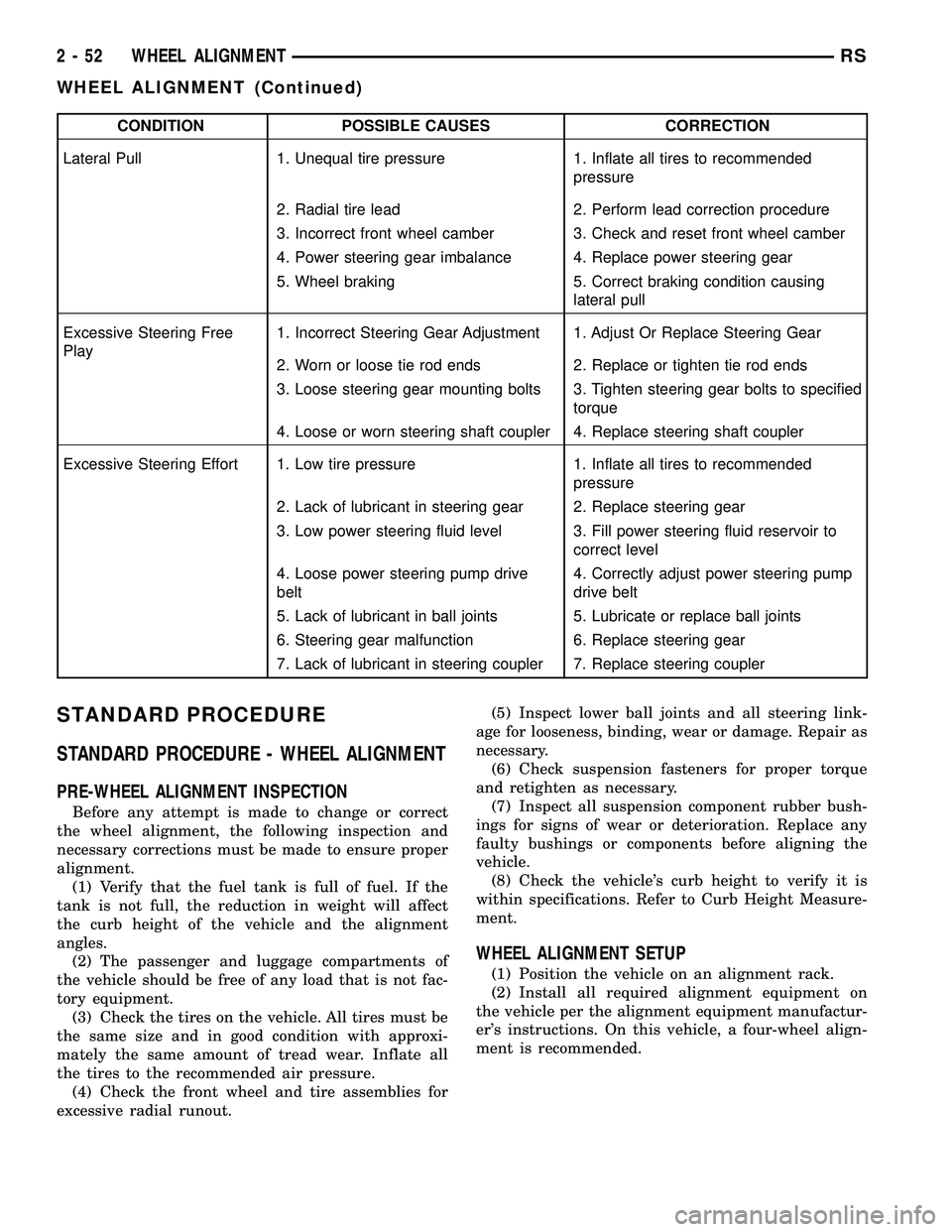
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Lateral Pull 1. Unequal tire pressure 1. Inflate all tires to recommended
pressure
2. Radial tire lead 2. Perform lead correction procedure
3. Incorrect front wheel camber 3. Check and reset front wheel camber
4. Power steering gear imbalance 4. Replace power steering gear
5. Wheel braking 5. Correct braking condition causing
lateral pull
Excessive Steering Free
Play1. Incorrect Steering Gear Adjustment 1. Adjust Or Replace Steering Gear
2. Worn or loose tie rod ends 2. Replace or tighten tie rod ends
3. Loose steering gear mounting bolts 3. Tighten steering gear bolts to specified
torque
4. Loose or worn steering shaft coupler 4. Replace steering shaft coupler
Excessive Steering Effort 1. Low tire pressure 1. Inflate all tires to recommended
pressure
2. Lack of lubricant in steering gear 2. Replace steering gear
3. Low power steering fluid level 3. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
correct level
4. Loose power steering pump drive
belt4. Correctly adjust power steering pump
drive belt
5. Lack of lubricant in ball joints 5. Lubricate or replace ball joints
6. Steering gear malfunction 6. Replace steering gear
7. Lack of lubricant in steering coupler 7. Replace steering coupler
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL ALIGNMENT
PRE-WHEEL ALIGNMENT INSPECTION
Before any attempt is made to change or correct
the wheel alignment, the following inspection and
necessary corrections must be made to ensure proper
alignment.
(1) Verify that the fuel tank is full of fuel. If the
tank is not full, the reduction in weight will affect
the curb height of the vehicle and the alignment
angles.
(2) The passenger and luggage compartments of
the vehicle should be free of any load that is not fac-
tory equipment.
(3) Check the tires on the vehicle. All tires must be
the same size and in good condition with approxi-
mately the same amount of tread wear. Inflate all
the tires to the recommended air pressure.
(4) Check the front wheel and tire assemblies for
excessive radial runout.(5) Inspect lower ball joints and all steering link-
age for looseness, binding, wear or damage. Repair as
necessary.
(6) Check suspension fasteners for proper torque
and retighten as necessary.
(7) Inspect all suspension component rubber bush-
ings for signs of wear or deterioration. Replace any
faulty bushings or components before aligning the
vehicle.
(8) Check the vehicle's curb height to verify it is
within specifications. Refer to Curb Height Measure-
ment.
WHEEL ALIGNMENT SETUP
(1) Position the vehicle on an alignment rack.
(2) Install all required alignment equipment on
the vehicle per the alignment equipment manufactur-
er's instructions. On this vehicle, a four-wheel align-
ment is recommended.
2 - 52 WHEEL ALIGNMENTRS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 102 of 2339
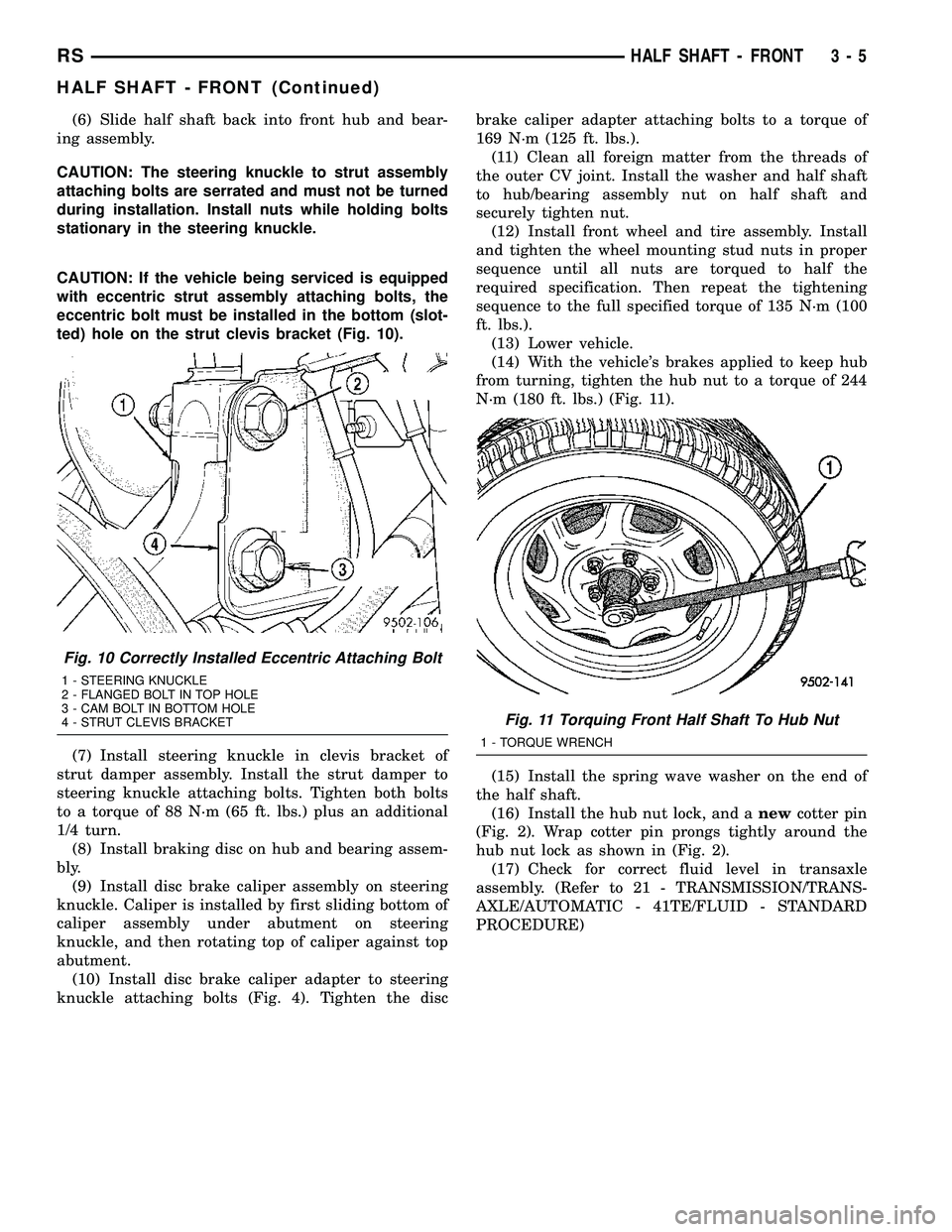
(6) Slide half shaft back into front hub and bear-
ing assembly.
CAUTION: The steering knuckle to strut assembly
attaching bolts are serrated and must not be turned
during installation. Install nuts while holding bolts
stationary in the steering knuckle.
CAUTION: If the vehicle being serviced is equipped
with eccentric strut assembly attaching bolts, the
eccentric bolt must be installed in the bottom (slot-
ted) hole on the strut clevis bracket (Fig. 10).
(7) Install steering knuckle in clevis bracket of
strut damper assembly. Install the strut damper to
steering knuckle attaching bolts. Tighten both bolts
to a torque of 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.) plus an additional
1/4 turn.
(8) Install braking disc on hub and bearing assem-
bly.
(9) Install disc brake caliper assembly on steering
knuckle. Caliper is installed by first sliding bottom of
caliper assembly under abutment on steering
knuckle, and then rotating top of caliper against top
abutment.
(10) Install disc brake caliper adapter to steering
knuckle attaching bolts (Fig. 4). Tighten the discbrake caliper adapter attaching bolts to a torque of
169 N´m (125 ft. lbs.).
(11) Clean all foreign matter from the threads of
the outer CV joint. Install the washer and half shaft
to hub/bearing assembly nut on half shaft and
securely tighten nut.
(12) Install front wheel and tire assembly. Install
and tighten the wheel mounting stud nuts in proper
sequence until all nuts are torqued to half the
required specification. Then repeat the tightening
sequence to the full specified torque of 135 N´m (100
ft. lbs.).
(13) Lower vehicle.
(14) With the vehicle's brakes applied to keep hub
from turning, tighten the hub nut to a torque of 244
N´m (180 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 11).
(15) Install the spring wave washer on the end of
the half shaft.
(16) Install the hub nut lock, and anewcotter pin
(Fig. 2). Wrap cotter pin prongs tightly around the
hub nut lock as shown in (Fig. 2).
(17) Check for correct fluid level in transaxle
assembly. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
Fig. 10 Correctly Installed Eccentric Attaching Bolt
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - FLANGED BOLT IN TOP HOLE
3 - CAM BOLT IN BOTTOM HOLE
4 - STRUT CLEVIS BRACKET
Fig. 11 Torquing Front Half Shaft To Hub Nut
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
RSHALF SHAFT - FRONT3-5
HALF SHAFT - FRONT (Continued)
Page 114 of 2339

STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PARKING
BRAKE AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER TENSION
RELEASE...........................63
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PARKING
BRAKE AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER TENSION
RESET.............................64
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CABLE END
CLEANING AND LUBRICATION...........65
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - PARKING BRAKE
CABLES............................65
CABLE - PARKING BRAKE FRONT
REMOVAL
REMOVAL...........................66
REMOVAL - FOLD-IN-FLOOR SEATING.....66
REMOVAL - EXPORT..................67
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION.......................67
INSTALLATION - FOLD-IN-FLOOR SEATING . 68
INSTALLATION - EXPORT...............68
CABLE - PARKING BRAKE INTERMEDIATE
REMOVAL.............................69
INSTALLATION.........................69CABLE - PARKING BRAKE REAR
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - RIGHT REAR...............70
REMOVAL - LEFT REAR................71
REMOVAL - FOLD-IN-FLOOR SEATING.....72
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - RIGHT REAR...........74
INSTALLATION - LEFT REAR............75
INSTALLATION - FOLD-IN-FLOOR
SEATING............................75
LEVER - PARKING BRAKE
REMOVAL.............................75
INSTALLATION.........................76
LEVER - PARKING BRAKE (EXPORT)
REMOVAL - PARKING BRAKE LEVER AND
FRONT CABLE.......................77
INSTALLATION - PARKING BRAKE LEVER
AND FRONT CABLE...................77
SHOES - PARKING BRAKE
REMOVAL.............................78
INSTALLATION.........................84
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - PARKING BRAKE SHOES . . 85
BRAKES - BASE
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - BASE BRAKES
The base brake system consists of the following
components:
²Brake pedal
²Power brake booster
²Master cylinder
²Brake tubes and hoses
²Proportioning valve (non-ABS vehicles only)
²Disc brakes
²Drum brakes
²Brake lamp switch
²Brake fluid level switch
²Parking brakes
Front disc brakes control the braking of the front
wheels; rear braking is controlled by rear drum
brakes or rear disc brakes depending on options.
The hydraulic brake system is diagonally split on
both the non-antilock braking systems and antilock
braking systems. That means the left front and right
rear brakes are on one hydraulic circuit and the right
front and left rear are on the other.
For information on the brake lamp switch, (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERI-
OR/BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - DESCRIPTION)Vehicles equipped with the optional antilock brake
system (ABS) use a system designated Mark 20e. It
is available with or without traction control. This
system shares most base brake hardware used on
vehicles without ABS. ABS components are described
in detail in ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM.DESCRIPTION - BASE BRAKES (EXPORT)
Four-Wheel Disc Antilock Brakes are standard on
all models.
OPERATION - BASE BRAKES
When a vehicle needs to be stopped, the driver
applies the brake pedal. The brake pedal pushes the
input rod of the power brake booster into the booster.
The booster uses vacuum to ease pedal effort as force
is transferred through the booster to the master cyl-
inder. The booster's output rod pushes in the master
cylinder's primary and secondary pistons applying
hydraulic pressure through the chassis brake tubes
to the brakes at each tire and wheel assembly.
The parking brakes are foot-operated. When
applied, the parking brake lever pulls on cables that
actuate brake shoes at each rear wheel. These shoes
come in contact with a hub mounted drum (drum for
disc/drum brakes or drum-in-hat for disc/disc brakes)
and hold it in place.
RSBRAKES - BASE5-3
Page 115 of 2339

WARNING
WARNING: DUST AND DIRT ACCUMULATING ON
BRAKE PARTS DURING NORMAL USE MAY CON-
TAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS FROM PRODUCTION OR
AFTERMARKET BRAKE LININGS. BREATHING
EXCESSIVE CONCENTRATIONS OF ASBESTOS
FIBERS CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM.
EXERCISE CARE WHEN SERVICING BRAKE
PARTS. DO NOT SAND OR GRIND BRAKE LINING
UNLESS EQUIPMENT USED IS DESIGNED TO CON-
TAIN THE DUST RESIDUE. DO NOT CLEAN BRAKE
PARTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR OR BY DRY
BRUSHING. CLEANING SHOULD BE DONE BY
DAMPENING THE BRAKE COMPONENTS WITH A
FINE MIST OF WATER, THEN WIPING THE BRAKE
COMPONENTS CLEAN WITH A DAMPENED CLOTH.
DISPOSE OF CLOTH AND ALL RESIDUE CONTAIN-
ING ASBESTOS FIBERS IN AN IMPERMEABLE
CONTAINER WITH THE APPROPRIATE LABEL. FOL-
LOW PRACTICES PRESCRIBED BY THE OCCUPA-
TIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMINISTRATION
(OSHA) AND THE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
AGENCY (EPA) FOR THE HANDLING, PROCESSING,
AND DISPOSING OF DUST OR DEBRIS THAT MAY
CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS.
CAUTION
CAUTION: During service procedures, grease or
any other foreign material must be kept off brake
shoes and braking surfaces of brake rotor or drum,
and external surfaces of hub and bearing assembly.
CAUTION: Brake rotor and caliper handling must be
done in such a way as to avoid damage to the rotor,
especially the machined surfaces, and scratching or
nicking of the brake linings.
CAUTION: Only the recommended jacking or hoist-
ing procedures for this vehicle are to be used
whenever it is necessary to lift a vehicle. Failure to
raise a vehicle utilizing the recommended lift points
can result in damage to the vehicle. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BASE BRAKE
SYSTEM
NOTE: There are three diagnosis charts following
that cover the RED BRAKE WARNING INDICATOR
LAMP, BRAKE NOISE and OTHER BRAKE CONDI-
TIONS.
RED BRAKE WARNING INDICATOR LAMP
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
RED BRAKE WARNING
LAMP ON1. Parking brake lever not fully
released.1. Release parking brake lever.
2. Parking brake warning lamp
switch on parking brake lever.2. Inspect and replace switch as necessary.
3. Brake fluid level low in reservoir. 3. Fill reservoir. Check entire system for
leaks. Repair or replace as required.
4. Brake fluid level switch. 4. Disconnect switch wiring connector. If
lamp goes out, replace switch.
5. Mechanical instrument cluster
(MIC) problem.5. Refer to appropriate Diagnostic
information.
6. Amber ABS Warning Indicator
Lamp also illuminated.6. Refer to appropriate Diagnostic
information.
5 - 4 BRAKES - BASERS
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 116 of 2339
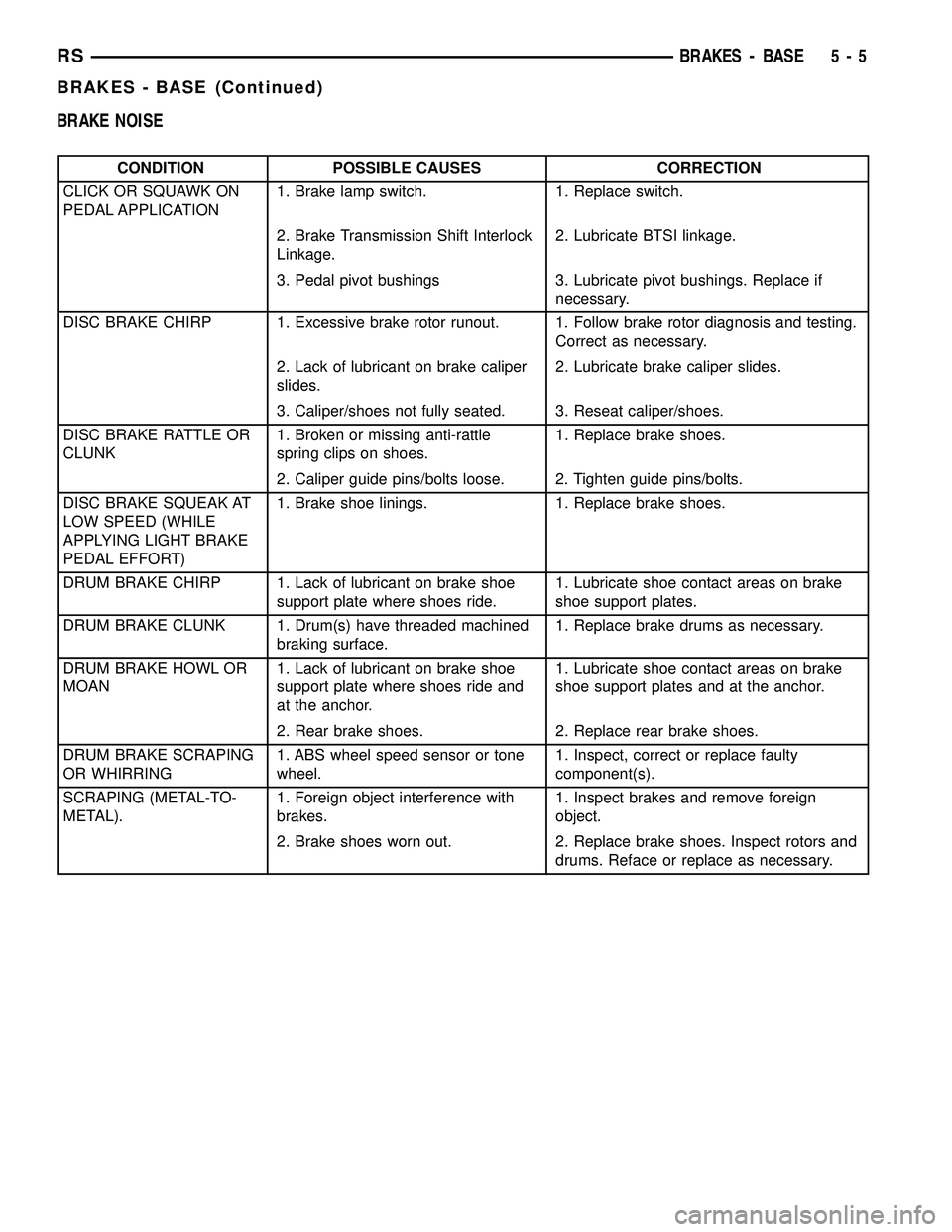
BRAKE NOISE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CLICK OR SQUAWK ON
PEDAL APPLICATION1. Brake lamp switch. 1. Replace switch.
2. Brake Transmission Shift Interlock
Linkage.2. Lubricate BTSI linkage.
3. Pedal pivot bushings 3. Lubricate pivot bushings. Replace if
necessary.
DISC BRAKE CHIRP 1. Excessive brake rotor runout. 1. Follow brake rotor diagnosis and testing.
Correct as necessary.
2. Lack of lubricant on brake caliper
slides.2. Lubricate brake caliper slides.
3. Caliper/shoes not fully seated. 3. Reseat caliper/shoes.
DISC BRAKE RATTLE OR
CLUNK1. Broken or missing anti-rattle
spring clips on shoes.1. Replace brake shoes.
2. Caliper guide pins/bolts loose. 2. Tighten guide pins/bolts.
DISC BRAKE SQUEAK AT
LOW SPEED (WHILE
APPLYING LIGHT BRAKE
PEDAL EFFORT)1. Brake shoe linings. 1. Replace brake shoes.
DRUM BRAKE CHIRP 1. Lack of lubricant on brake shoe
support plate where shoes ride.1. Lubricate shoe contact areas on brake
shoe support plates.
DRUM BRAKE CLUNK 1. Drum(s) have threaded machined
braking surface.1. Replace brake drums as necessary.
DRUM BRAKE HOWL OR
MOAN1. Lack of lubricant on brake shoe
support plate where shoes ride and
at the anchor.1. Lubricate shoe contact areas on brake
shoe support plates and at the anchor.
2. Rear brake shoes. 2. Replace rear brake shoes.
DRUM BRAKE SCRAPING
OR WHIRRING1. ABS wheel speed sensor or tone
wheel.1. Inspect, correct or replace faulty
component(s).
SCRAPING (METAL-TO-
METAL).1. Foreign object interference with
brakes.1. Inspect brakes and remove foreign
object.
2. Brake shoes worn out. 2. Replace brake shoes. Inspect rotors and
drums. Reface or replace as necessary.
RSBRAKES - BASE5-5
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 117 of 2339
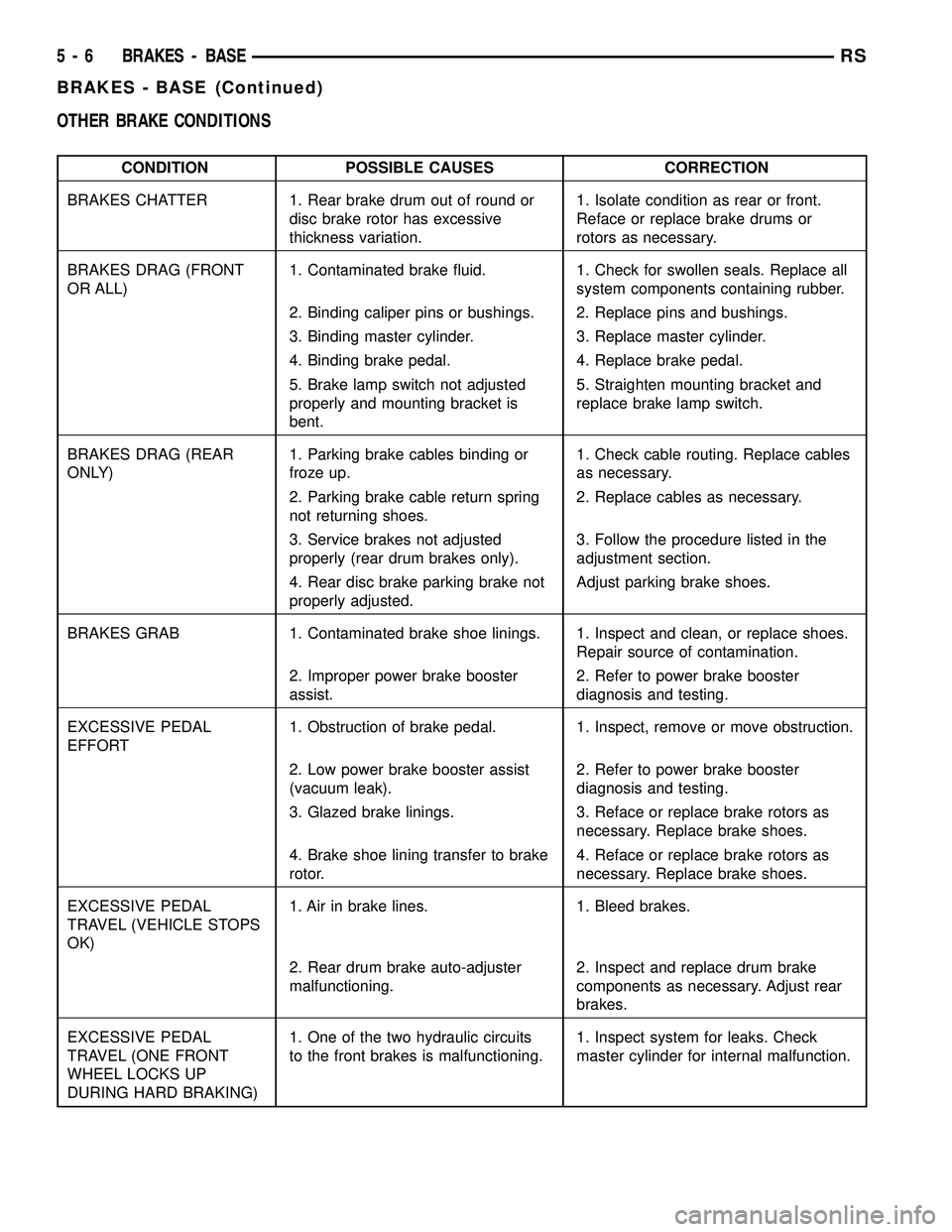
OTHER BRAKE CONDITIONS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BRAKES CHATTER 1. Rear brake drum out of round or
disc brake rotor has excessive
thickness variation.1. Isolate condition as rear or front.
Reface or replace brake drums or
rotors as necessary.
BRAKES DRAG (FRONT
OR ALL)1. Contaminated brake fluid. 1. Check for swollen seals. Replace all
system components containing rubber.
2. Binding caliper pins or bushings. 2. Replace pins and bushings.
3. Binding master cylinder. 3. Replace master cylinder.
4. Binding brake pedal. 4. Replace brake pedal.
5. Brake lamp switch not adjusted
properly and mounting bracket is
bent.5. Straighten mounting bracket and
replace brake lamp switch.
BRAKES DRAG (REAR
ONLY)1. Parking brake cables binding or
froze up.1. Check cable routing. Replace cables
as necessary.
2. Parking brake cable return spring
not returning shoes.2. Replace cables as necessary.
3. Service brakes not adjusted
properly (rear drum brakes only).3. Follow the procedure listed in the
adjustment section.
4. Rear disc brake parking brake not
properly adjusted.Adjust parking brake shoes.
BRAKES GRAB 1. Contaminated brake shoe linings. 1. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
2. Improper power brake booster
assist.2. Refer to power brake booster
diagnosis and testing.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
EFFORT1. Obstruction of brake pedal. 1. Inspect, remove or move obstruction.
2. Low power brake booster assist
(vacuum leak).2. Refer to power brake booster
diagnosis and testing.
3. Glazed brake linings. 3. Reface or replace brake rotors as
necessary. Replace brake shoes.
4. Brake shoe lining transfer to brake
rotor.4. Reface or replace brake rotors as
necessary. Replace brake shoes.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (VEHICLE STOPS
OK)1. Air in brake lines. 1. Bleed brakes.
2. Rear drum brake auto-adjuster
malfunctioning.2. Inspect and replace drum brake
components as necessary. Adjust rear
brakes.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (ONE FRONT
WHEEL LOCKS UP
DURING HARD BRAKING)1. One of the two hydraulic circuits
to the front brakes is malfunctioning.1. Inspect system for leaks. Check
master cylinder for internal malfunction.
5 - 6 BRAKES - BASERS
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 118 of 2339
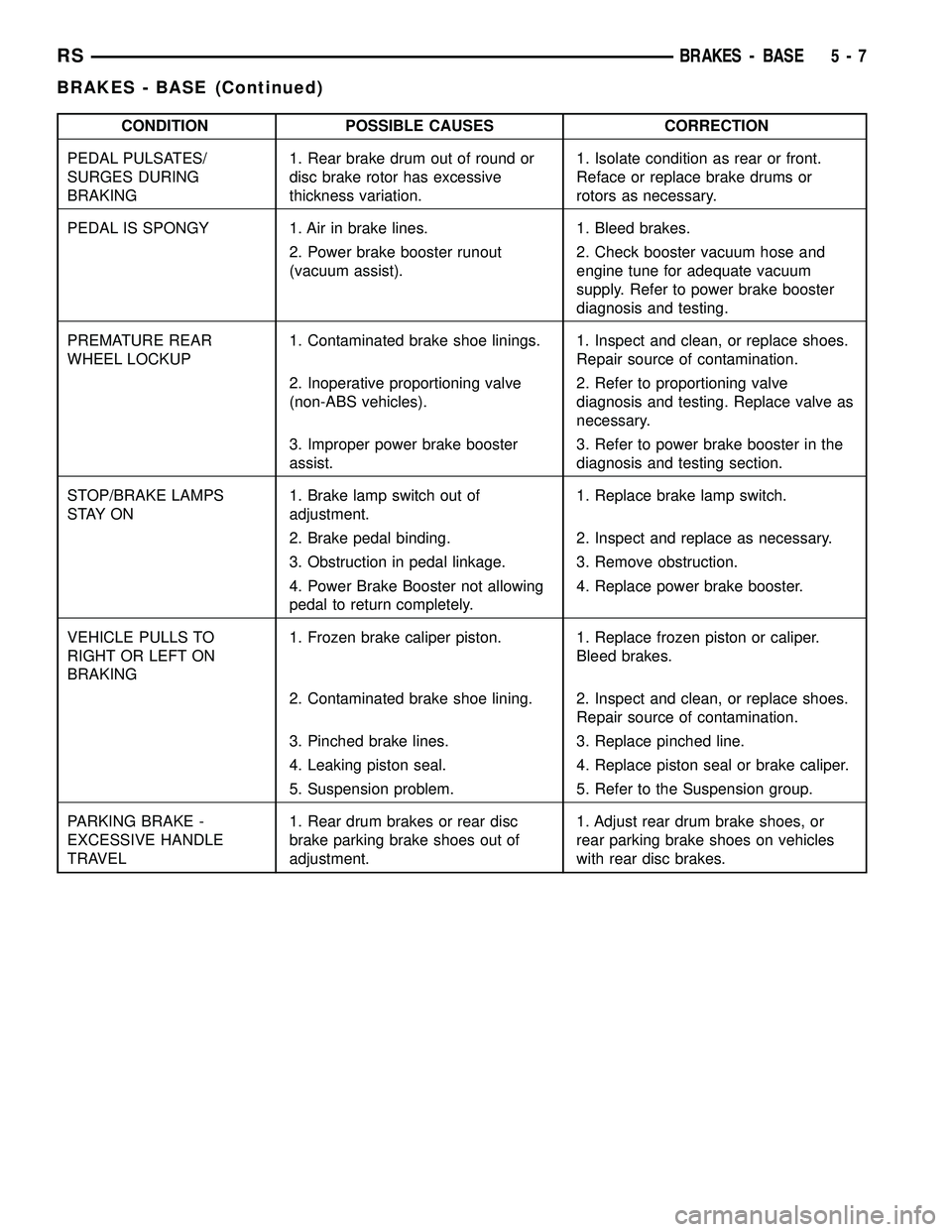
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
PEDAL PULSATES/
SURGES DURING
BRAKING1. Rear brake drum out of round or
disc brake rotor has excessive
thickness variation.1. Isolate condition as rear or front.
Reface or replace brake drums or
rotors as necessary.
PEDAL IS SPONGY 1. Air in brake lines. 1. Bleed brakes.
2. Power brake booster runout
(vacuum assist).2. Check booster vacuum hose and
engine tune for adequate vacuum
supply. Refer to power brake booster
diagnosis and testing.
PREMATURE REAR
WHEEL LOCKUP1. Contaminated brake shoe linings. 1. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
2. Inoperative proportioning valve
(non-ABS vehicles).2. Refer to proportioning valve
diagnosis and testing. Replace valve as
necessary.
3. Improper power brake booster
assist.3. Refer to power brake booster in the
diagnosis and testing section.
STOP/BRAKE LAMPS
S TAY O N1. Brake lamp switch out of
adjustment.1. Replace brake lamp switch.
2. Brake pedal binding. 2. Inspect and replace as necessary.
3. Obstruction in pedal linkage. 3. Remove obstruction.
4. Power Brake Booster not allowing
pedal to return completely.4. Replace power brake booster.
VEHICLE PULLS TO
RIGHT OR LEFT ON
BRAKING1. Frozen brake caliper piston. 1. Replace frozen piston or caliper.
Bleed brakes.
2. Contaminated brake shoe lining. 2. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
3. Pinched brake lines. 3. Replace pinched line.
4. Leaking piston seal. 4. Replace piston seal or brake caliper.
5. Suspension problem. 5. Refer to the Suspension group.
PARKING BRAKE -
EXCESSIVE HANDLE
TRAVEL1. Rear drum brakes or rear disc
brake parking brake shoes out of
adjustment.1. Adjust rear drum brake shoes, or
rear parking brake shoes on vehicles
with rear disc brakes.
RSBRAKES - BASE5-7
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 123 of 2339
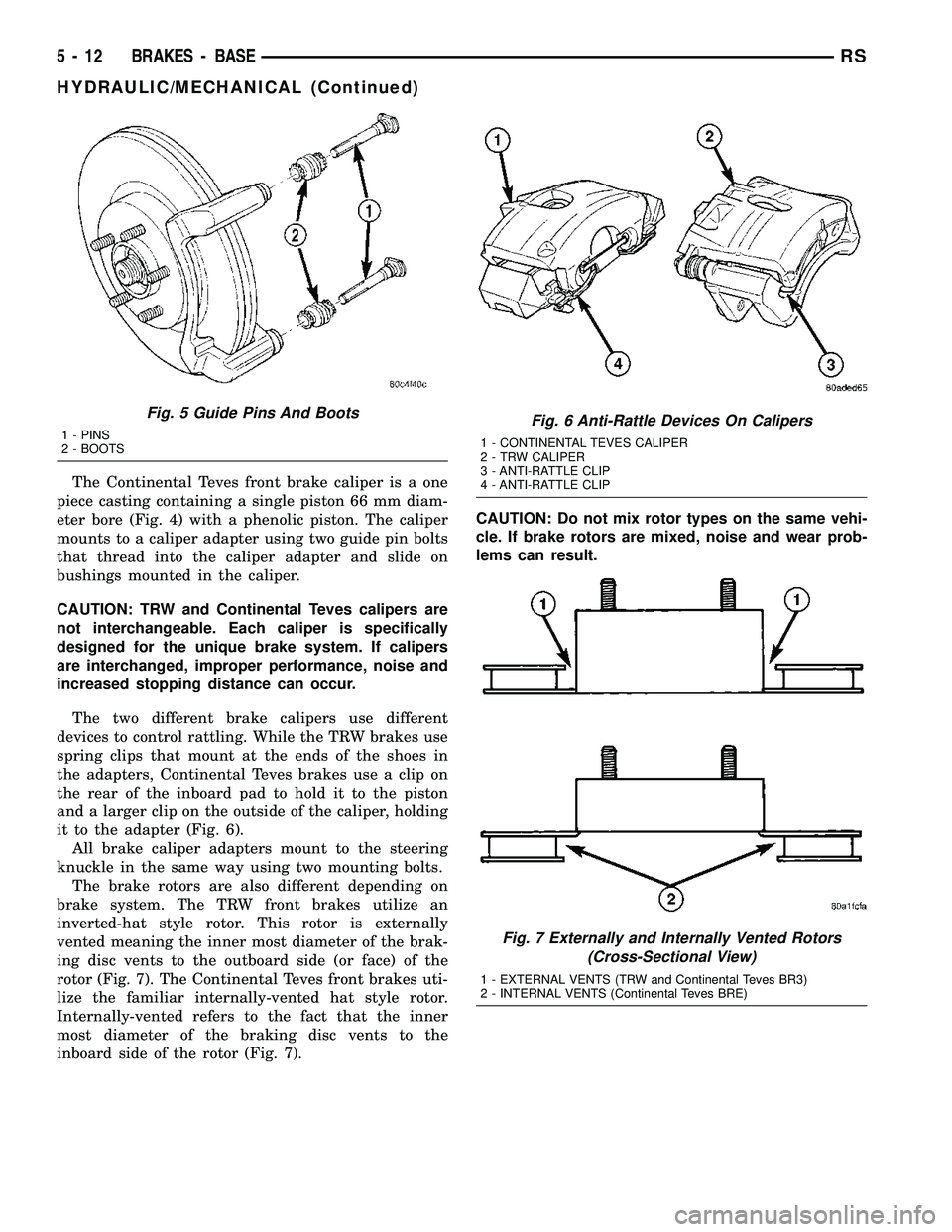
The Continental Teves front brake caliper is a one
piece casting containing a single piston 66 mm diam-
eter bore (Fig. 4) with a phenolic piston. The caliper
mounts to a caliper adapter using two guide pin bolts
that thread into the caliper adapter and slide on
bushings mounted in the caliper.
CAUTION: TRW and Continental Teves calipers are
not interchangeable. Each caliper is specifically
designed for the unique brake system. If calipers
are interchanged, improper performance, noise and
increased stopping distance can occur.
The two different brake calipers use different
devices to control rattling. While the TRW brakes use
spring clips that mount at the ends of the shoes in
the adapters, Continental Teves brakes use a clip on
the rear of the inboard pad to hold it to the piston
and a larger clip on the outside of the caliper, holding
it to the adapter (Fig. 6).
All brake caliper adapters mount to the steering
knuckle in the same way using two mounting bolts.
The brake rotors are also different depending on
brake system. The TRW front brakes utilize an
inverted-hat style rotor. This rotor is externally
vented meaning the inner most diameter of the brak-
ing disc vents to the outboard side (or face) of the
rotor (Fig. 7). The Continental Teves front brakes uti-
lize the familiar internally-vented hat style rotor.
Internally-vented refers to the fact that the inner
most diameter of the braking disc vents to the
inboard side of the rotor (Fig. 7).CAUTION: Do not mix rotor types on the same vehi-
cle. If brake rotors are mixed, noise and wear prob-
lems can result.
Fig. 5 Guide Pins And Boots
1 - PINS
2 - BOOTSFig. 6 Anti-Rattle Devices On Calipers
1 - CONTINENTAL TEVES CALIPER
2 - TRW CALIPER
3 - ANTI-RATTLE CLIP
4 - ANTI-RATTLE CLIP
Fig. 7 Externally and Internally Vented Rotors
(Cross-Sectional View)
1 - EXTERNAL VENTS (TRW and Continental Teves BR3)
2 - INTERNAL VENTS (Continental Teves BRE)
5 - 12 BRAKES - BASERS
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
Page 144 of 2339

FLUID
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts.
Swollen rubber parts indicate the presence of
petroleum in the brake fluid.
To test for contamination, put a small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If fluid sepa-
rates into layers, there is mineral oil or other fluid
contamination of the brake fluid.
If brake fluid is contaminated, drain and thor-
oughly flush system. Replace master cylinder, propor-
tioning valve, caliper seals, wheel cylinder seals,
Antilock Brake hydraulic unit and all hydraulic fluid
hoses.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BRAKE FLUID
LEVEL CHECKING
Check master cylinder reservoir fluid level a mini-
mum of twice annually.
Fluid reservoirs are marked with the words FULL
and ADD to indicate proper brake fluid fill level of
the master cylinder.
If necessary, add brake fluid to bring the level to
the bottom of the FULL mark on the side of the mas-
ter cylinder fluid reservoir.
Use only Mopartbrake fluid or equivalent from a
sealed container. Brake fluid must conform to DOT 3
specifications (DOT 4 or DOT 4+ are acceptable).
DO NOTuse brake fluid with a lower boiling
point, as brake failure could result during prolonged
hard braking.
Use only brake fluid that was stored in a tightly-
sealed container.
DO NOTuse petroleum-based fluid because seal
damage will result. Petroleum based fluids would be
items such as engine oil, transmission fluid, power
steering fluid etc.
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID
The brake fluid used in this vehicle must conform
to DOT 3 specifications (DOT 4 and DOT 4+ are
acceptable) and SAE J1703 standards. No other type
of brake fluid is recommended or approved for usage
in the vehicle brake system. Use only MopartBrake
Fluid or equivalent from a tightly sealed container.CAUTION: Never use reclaimed brake fluid or fluid
from an container which has been left open. An
open container of brake fluid will absorb moisture
from the air and contaminate the fluid.
CAUTION: Never use any type of a petroleum-based
fluid in the brake hydraulic system. Use of such
type fluids will result in seal damage of the vehicle
brake hydraulic system causing a failure of the
vehicle brake system. Petroleum based fluids would
be items such as engine oil, transmission fluid,
power steering fluid, etc.
JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
A junction block is used on vehicles that are not
equipped with antilock brakes (ABS). The junction
block mounts in the same location as the integrated
control unit (ICU) does on vehicles equipped with
ABS. This allows for use of the same brake tube con-
figuration on all vehicles. The junction block is
located on the driver's side of the front suspension
cradle/crossmember below the master cylinder (Fig.
44).
It has six threaded ports to which the brake tubes
connect. Two are for the primary and secondary
brake tubes coming from the master cylinder. The
remaining four are for the chassis brake tubes going
to each brake assembly.
OPERATION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
The junction block distributes the brake fluid com-
ing from the master cylinder primary and secondary
ports to the four chassis brake tubes leading to the
brakes at each wheel. Since the junction block
mounts in the same location as the ABS integrated
control unit (ICU), it allows for the common use of
brake tubes going to the brakes whether the vehicle
is equipped with or without ABS.
NOTE: Although the brake tubes coming from the
master cylinder to the junction block or ABS ICU
may appear to be the same, they are not. They are
unique to each brake system application.
RSBRAKES - BASE5-33
Page 164 of 2339

PROPORTIONING VALVE
DESCRIPTION - PROPORTIONING VALVE
(HEIGHT SENSING)
NOTE: Only vehicles without antilock brakes (ABS)
have a proportioning valve. Vehicles with ABS uti-
lize electronic brake distribution which is controlled
through the ABS integrated control unit.
Vehicles not equipped with ABS use a height sens-
ing proportioning valve. It is mounted to the body of
the vehicle above the rear axle (Fig. 80). It has an
actuator lever that attaches to the rear axle and
moves with the axle to help the valve sense the vehi-
cle height.
CAUTION: The height sensing proportioning valve
is not adjustable. No attempt should be made to
adjust it. It is replaced as a complete assembly.
CAUTION: The use of after-market load leveling or
load capacity increasing devices on this vehicle are
prohibited. Using air shock absorbers or helper
springs on this vehicle will cause the height sens-
ing proportioning valve to inappropriately reduce
the hydraulic pressure to the rear brakes. This inap-
propriate reduction in hydraulic pressure potentially
could result in increased stopping distance of the
vehicle.
OPERATION - PROPORTIONING VALVE
(HEIGHT SENSING)
Vehicles not equipped with ABS use a height sens-
ing proportioning valve.
The height sensing proportioning valve operates
similarly to a standard proportioning valve in the fol-
lowing way. As hydraulic pressure is applied to the
valve, full input hydraulic pressure is supplied to the
rear brakes up to a certain pressure point, called the
split point. Beyond the split point, the proportioning
valve reduces the amount of hydraulic pressure to
the rear brakes according to a given ratio. Thus, on
light brake applications, approximately equal
hydraulic pressure will be transmitted to both the
front and rear brakes. Upon heavier brake applica-
tions, the hydraulic pressure transmitted to the rear
brakes will be lower than the front brakes. This will
prevent premature rear wheel lockup and skid.
Here is how the height sensing proportioning valve
differs from a standard proportioning valve. As the
height of the rear suspension changes, the height
sensing portion of the proportioning valve changes
the split point of the proportioning valve. When the
height of the rear suspension is low, the proportion-
ing valve interprets this as extra load and the split
point of the proportioning valve is raised to a higher
pressure to allow for more rear braking. When the
height of the rear suspension is high, the proportion-
ing valve interprets this as a light load and the split
point of the proportioning valve is lowered to a lower
pressure and rear braking is reduced.
The height sensing proportioning valve regulates
the pressure by sensing the load condition of the
vehicle through the movement of the proportioning
valve actuator lever (Fig. 80). As the position of the
rear axle changes, depending on the load the vehicle
is carrying, the movement is transferred to the pro-
portioning valve. The proportioning valve adjusts the
hydraulic pressure accordingly.
The height sensing proportioning valve allows the
brake system to maintain the optimal front to rear
brake balance regardless of the vehicle load condi-
tion. Under a light load condition, hydraulic pressure
to the rear brakes is minimized. As the rear load con-
dition increases, so does the hydraulic pressure to
the rear brakes.
Fig. 80 HEIGHT SENSING PROPORTIONING VALVE
1 - PROPORTIONING VALVE
2 - ACTUATOR LEVER
3 - AXLE BRACKET
4 - REAR AXLE
RSBRAKES - BASE5-53