ESP Citroen BX HATCHBACK 1992 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CITROEN, Model Year: 1992, Model line: BX HATCHBACK, Model: Citroen BX HATCHBACK 1992 2.GPages: 16, PDF Size: 0.47 MB
Page 2 of 16

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine LIVING WITH YOUR CITROEN BX
IntroductionPage0•4
Safety First!Page0•5
Roadside Repairs
Introduction Page0•6
If your car won’t startPage0•6
Jump startingPage0•7
Wheel changingPage0•8
Identifying leaksPage0•9
TowingPage0•9
Weekly Checks
IntroductionPage0•10
Underbonnet check points Page0•10
Engine oil levelPage0•11
Coolant levelPage0•11
Hydraulic fluid levelPage0•12
Screen washer fluid level Page0•12
Tyre condition and pressure Page0•13
Electrical systemsPage0•14
BatteryPage0•14
Wiper bladesPage0•15
Tyre pressuresPage0•15
Lubricants, fluids and capacitiesPage0•16
MAINTENANCE
Routine Maintenance and Servicing
Servicing Specifications Page1•2
Maintenance schedule Page1•4
Maintenance procedures Page1•8
Contents
Page 4 of 16

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine The Citroën BX was introduced in France in October of 1982 and
became available in the UK in September 1983. The original models
available in the range were the BX, BX 14 E, BX 14 RE, BX 16 RS and BX
16 TRS. The types of engine, transmission and equipment fitted being
dependent on the model and the body design being that of a Hatchback.
For the 1985 model year, the BX 19 GT was made available for the
driver requiring a higher performance model. Also in 1985, the BX
Leader replaced the BX and BX 14 models, the Leader being fitted with
the same engine and transmission as the BX 14. In the second half of
1985 the Estate was introduced, two versions being available, the BX
16 RS Estate and the BX 16 TRS Estate.
Changes for the 1987 model year included the introduction of the BX
16 RE Hatchback, the BX 19 GTi (fuel injection and ABS braking), the
BX 19 GTi 16v (16 valve engine) and the replacement for the BX 19 GT,
the BX 19 TRS. Also, a BX 19 TRS Estate fitted with automatic
transmission became available. The facia and instruments were
modified on all models, with round instruments being used. Other
aesthetic improvements were made to improve the external
appearance of certain models.For the 1988 model year, all BX 14 models were equipped with the
K1G engine with 2CA type 4 or 5-speed manual gearbox.
For the 1989 model year, BX 16 and BX 19 models were equipped
with the BE3 5-speed manual gearbox to replace the earlier BE1 5-
speed type.
In early 1990, BX 19 TZi Hatchback and Estate models became
available, these being equipped with catalytic converters.
In late 1992, BX 16 TXi catalytic converter equipped Hatchback and
Estate models were added to the range.
On all models, the engine and transmission is mounted transversely
and drives the front wheels through two driveshafts. The transmission
available (depending on model type) is a 4 or 5-speed manual gearbox
or a 4-speed automatic unit.
All models are extremely comfortable to ride in, thanks to the
hydropneumatic suspension and luxurious interior trim. The unique
design suspension is self-levelling and the ride height is maintained
automatically over all road conditions. A ground clearance lever inside
the car may be used to adjust the ride height when travelling over
rough ground, this also makes changing a roadwheel much simpler.
Your Citroën BX Manual
The aim of this Manual is to help you get the best value from your
vehicle. It can do so in several ways. It can help you decide what work
must be done (even should you choose to get it done by a garage),
provide information on routine maintenance and servicing, and give a
logical course of action and diagnosis when random faults occur.
However, it is hoped that you will use the Manual by tackling the work
yourself. On simpler jobs it may even be quicker than booking the car
into a garage and going there twice, to leave and collect it. Perhaps
most important, a lot of money can be saved by avoiding the costs a
garage must charge to cover its labour and overheads.
The Manual has drawings and descriptions to show the function of
the various components so that their layout can be understood. Then
the tasks are described and photographed in a clear step-by-step
sequence.
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to Champion Spark Plug who supplied the illustrations
showing spark plug conditions, and to Duckhams Oils, who provided
lubrication data. Certain other illustrations are the copyright of Citroën
(UK) Limited and are used with their permission. Thanks are also due to
Sykes-Pickavant Limited, who supplied some of the workshop tools,
and to all those people at Sparkford who helped in the production of
this Manual.
We take great pride in the accuracy of information given in this
manual, but vehicle manufacturers make alterations and design
changes during the production run of a particular vehicle of which
they do not inform us. No liability can be accepted by the authors
or publishers for loss, damage or injury caused by any errors in, or
omissions from the information given.
0•4Introduction
The Citroën BX Team
Haynes manuals are produced by dedicated and
enthusiastic people working in close co-operation. The
team responsible for the creation of this book included:
Authors Ian Coomber
Christopher Rogers
Sub-editors Sophie Yar
Carole Turk
Editor & Page Make-up Steve Churchill
Bob Jex
Workshop manager Paul Buckland
Photo Scans John Martin
Paul Tanswell
Steve Tanswell
Cover illustration & Line Art Roger Healing
We hope the book will help you to get the maximum
enjoyment from your car. By carrying out routine
maintenance as described you will ensure your car’s
reliability and preserve its resale value.
Citroën BX 19 GTiCitroën BX 16 TRS
Page 5 of 16

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Safety first!0•5
Working on your car can be dangerous.
This page shows just some of the potential
risks and hazards, with the aim of creating a
safety-conscious attitude.
General hazards
Scalding
• Don’t remove the radiator or expansion
tank cap while the engine is hot.
• Engine oil, automatic transmission fluid or
power steering fluid may also be dangerously
hot if the engine has recently been running.
Burning
• Beware of burns from the exhaust system
and from any part of the engine. Brake discs
and drums can also be extremely hot
immediately after use.
Crushing
• When working under or near
a raised vehicle,
always
supplement the
jack with axle
stands, or use
drive-on
ramps.
Never
venture
under a car which
is only supported by a jack.
• Take care if loosening or tightening high-
torque nuts when the vehicle is on stands.
Initial loosening and final tightening should
be done with the wheels on the ground.
Fire
• Fuel is highly flammable; fuel vapour is
explosive.
• Don’t let fuel spill onto a hot engine.
• Do not smoke or allow naked lights
(including pilot lights) anywhere near a
vehicle being worked on. Also beware of
creating sparks
(electrically or by use of tools).
• Fuel vapour is heavier than air, so don’t
work on the fuel system with the vehicle over
an inspection pit.
• Another cause of fire is an electrical
overload or short-circuit. Take care when
repairing or modifying the vehicle wiring.
• Keep a fire extinguisher handy, of a type
suitable for use on fuel and electrical fires.
Electric shock
• Ignition HT
voltage can be
dangerous,
especially to
people with heart
problems or a
pacemaker. Don’t
work on or near the
ignition system with
the engine running or
the ignition switched on.• Mains voltage is also dangerous. Make
sure that any mains-operated equipment is
correctly earthed. Mains power points should
be protected by a residual current device
(RCD) circuit breaker.
Fume or gas intoxication
• Exhaust fumes are
poisonous; they often
contain carbon
monoxide, which is
rapidly fatal if inhaled.
Never run the
engine in a
confined space
such as a garage
with the doors shut.
• Fuel vapour is also
poisonous, as are the vapours from some
cleaning solvents and paint thinners.
Poisonous or irritant substances
• Avoid skin contact with battery acid and
with any fuel, fluid or lubricant, especially
antifreeze, brake hydraulic fluid and Diesel
fuel. Don’t syphon them by mouth. If such a
substance is swallowed or gets into the eyes,
seek medical advice.
• Prolonged contact with used engine oil can
cause skin cancer. Wear gloves or use a
barrier cream if necessary. Change out of oil-
soaked clothes and do not keep oily rags in
your pocket.
• Air conditioning refrigerant forms a
poisonous gas if exposed to a naked flame
(including a cigarette). It can also cause skin
burns on contact.
Asbestos
• Asbestos dust can cause cancer if inhaled
or swallowed. Asbestos may be found in
gaskets and in brake and clutch linings.
When dealing with such components it is
safest to assume that they contain asbestos.
Special hazards
Hydrofluoric acid
• This extremely corrosive acid is formed
when certain types of synthetic rubber, found
in some O-rings, oil seals, fuel hoses etc, are
exposed to temperatures above 400
0C. The
rubber changes into a charred or sticky
substance containing the acid. Once formed,
the acid remains dangerous for years. If it
gets onto the skin, it may be necessary to
amputate the limb concerned.
• When dealing with a vehicle which has
suffered a fire, or with components salvaged
from such a vehicle, wear protective gloves
and discard them after use.
The battery
• Batteries contain sulphuric acid, which
attacks clothing, eyes and skin. Take care
when topping-up or carrying the battery.
• The hydrogen gas given off by the battery
is highly explosive. Never cause a spark or
allow a naked light nearby. Be careful when
connecting and disconnecting battery
chargers or jump leads.
Air bags
• Air bags can cause injury if they go off
accidentally. Take care when removing the
steering wheel and/or facia. Special storage
instructions may apply.
Diesel injection equipment
• Diesel injection pumps supply fuel at very
high pressure. Take care when working on
the fuel injectors and fuel pipes.
Warning: Never expose the hands,
face or any other part of the body
to injector spray; the fuel can
penetrate the skin with potentially fatal
results.
Remember...
DO
• Do use eye protection when using power
tools, and when working under the vehicle.
• Do wear gloves or use barrier cream to
protect your hands when necessary.
• Do get someone to check periodically
that all is well when working alone on the
vehicle.
• Do keep loose clothing and long hair well
out of the way of moving mechanical parts.
• Do remove rings, wristwatch etc, before
working on the vehicle – especially the
electrical system.
• Do ensure that any lifting or jacking
equipment has a safe working load rating
adequate for the job.
A few tips
DON’T
• Don’t attempt to lift a heavy component
which may be beyond your capability – get
assistance.
• Don’t rush to finish a job, or take
unverified short cuts.
• Don’t use ill-fitting tools which may slip
and cause injury.
• Don’t leave tools or parts lying around
where someone can trip over them. Mop
up oil and fuel spills at once.
• Don’t allow children or pets to play in or
near a vehicle being worked on.
Page 9 of 16

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Roadside repairs0•9
When all else fails, you may find yourself
having to get a tow home – or of course you
may be helping somebody else. Long-distance
recovery should only be done by a garage or
breakdown service. For shorter distances, DIY
towing using another car is easy enough, but
observe the following points:
MUse a proper tow-rope – they are not
expensive. The vehicle being towed must
display an ‘ON TOW’ sign in its rear window.
MAlways turn the ignition key to the ‘on’
position when the vehicle is being towed, so
that the steering lock is released, and that the
direction indicator and brake lights will work.
MOnly attach the tow-rope to the towing
eyes provided.MBefore being towed, release the handbrake
and select neutral on the transmission (Refer
to the Warningon the right).
MThe driver of the car being towed must
keep the tow-rope taut at all times to avoid
snatching.
MMake sure that both drivers know the route
before setting off.
MOnly drive at moderate speeds and keep
the distance towed to a minimum. Drive
smoothly and allow plenty of time for slowing
down at junctions.
MRemember that if the engine is not running,
there will be no hydraulic pressure (Refer to
the Warningon the right).Warning: BX, BX14 and Leader
with manual gearbox and all
automatic transmission models
should be towed with the front
wheels clear of the ground. If this is
impossible, restrict towing speed to 30
MPH and distance to 30 miles maximum.
Disregard of these instructions may cause
transmission damage due to lack of
lubrication. If in doubt, do not tow, or
transmission damage may result.
Once the reserve of hydraulic pressure has
been exhausted, the footbrake will not
work and the handbrake will have to be
used instead. Power steering assistance
(when applicable) will also be lost.
Towing
Puddles on the garage floor or drive, or
obvious wetness under the bonnet or
underneath the car, suggest a leak that needs
investigating. It can sometimes be difficult to
decide where the leak is coming from,
especially if the engine bay is very dirty
already. Leaking oil or fluid can also be blown
rearwards by the passage of air under the car,
giving a false impression of where the
problem lies.Warning: Most automotive oils
and fluids are poisonous. Wash
them off skin, and change out of
contaminated clothing, without
delay.
Identifying leaks
The smell of a fluid leaking
from the car may provide a
clue to what’s leaking. Some
fluids are distinctively
coloured. It may help to clean the car
carefully and to park it over some clean
paper overnight as an aid to locating the
source of the leak.
Remember that some leaks may only
occur while the engine is running.
Sump oil Gearbox oil
Brake fluid Power steering fluidOil from filter
Antifreeze
Engine oil may leak from the drain plug......or from the base of the oil filter.
Leaking antifreeze often leaves a crystalline
deposit like this.Gearbox oil can leak from the seals at the
inboard ends of the driveshafts.
A leak occurring at a wheel is almost
certainly brake fluid.Power steering fluid may leak from the pipe
connectors on the steering rack.
Page 13 of 16
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Weekly checks0•13
Tyre condition and pressure
It is very important that tyres are in good
condition, and at the correct pressure - having
a tyre failure at any speed is highly dangerous.
Tyre wear is influenced by driving style - harsh
braking and acceleration, or fast cornering,
will all produce more rapid tyre wear. As a
general rule, the front tyres wear out faster
than the rears. Interchanging the tyres from
front to rear ("rotating" the tyres) may result in
more even wear. However, if this is
completely effective, you may have the
expense of replacing all four tyres at once!
Remove any nails or stones embedded in the
tread before they penetrate the tyre to cause
deflation. If removal of a nail does reveal thatthe tyre has been punctured, refit the nail so
that its point of penetration is marked. Then
immediately change the wheel, and have the
tyre repaired by a tyre dealer.
Regularly check the tyres for damage in the
form of cuts or bulges, especially in the
sidewalls. Periodically remove the wheels,
and clean any dirt or mud from the inside and
outside surfaces. Examine the wheel rims for
signs of rusting, corrosion or other damage.
Light alloy wheels are easily damaged by
"kerbing" whilst parking; steel wheels may
also become dented or buckled. A new wheel
is very often the only way to overcome severe
damage.New tyres should be balanced when they are
fitted, but it may become necessary to re-
balance them as they wear, or if the balance
weights fitted to the wheel rim should fall off.
Unbalanced tyres will wear more quickly, as
will the steering and suspension components.
Wheel imbalance is normally signified by
vibration, particularly at a certain speed
(typically around 50 mph). If this vibration is
felt only through the steering, then it is likely
that just the front wheels need balancing. If,
however, the vibration is felt through the
whole car, the rear wheels could be out of
balance. Wheel balancing should be carried
out by a tyre dealer or garage.
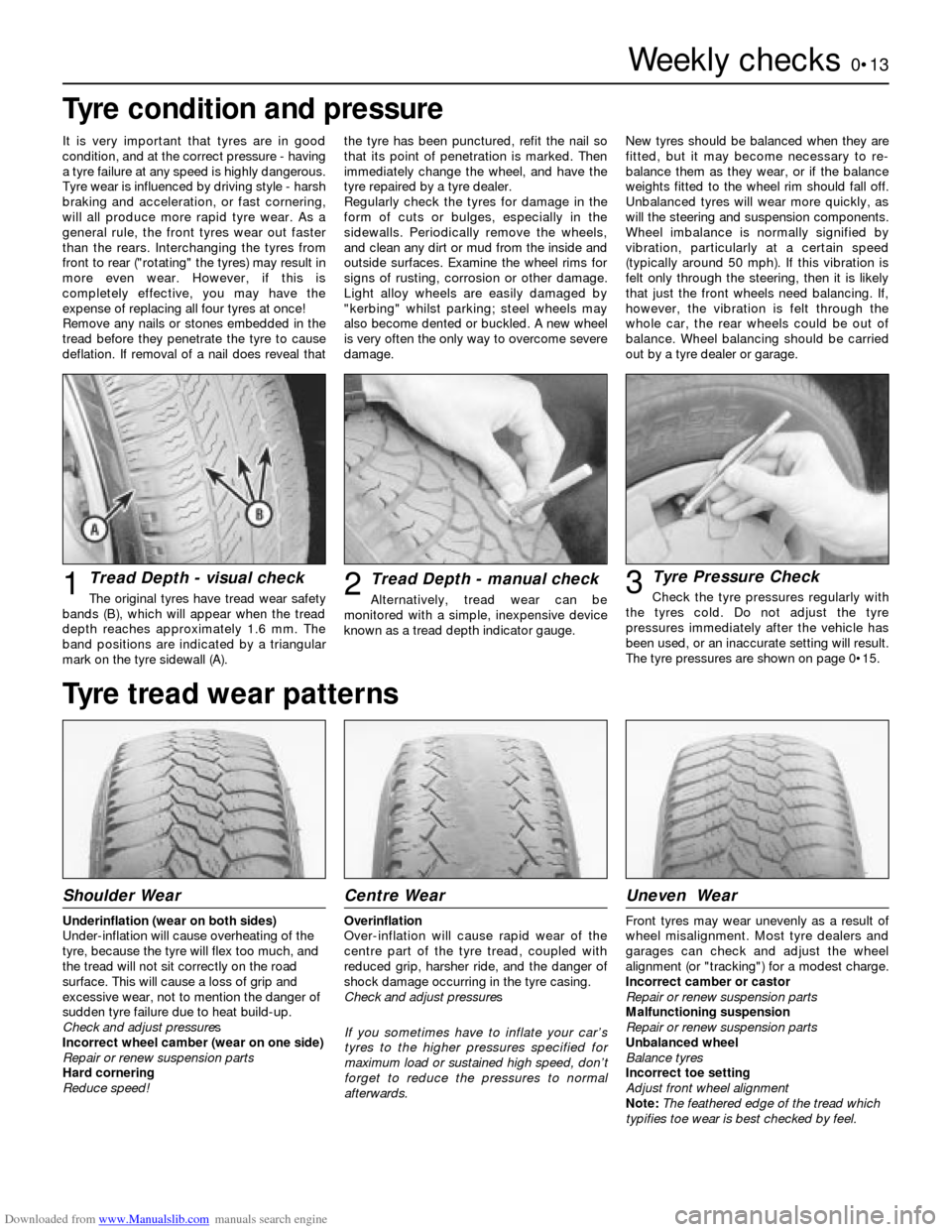
Tread Depth - visual check
The original tyres have tread wear safety
bands (B), which will appear when the tread
depth reaches approximately 1.6 mm. The
band positions are indicated by a triangular
mark on the tyre sidewall (A).1Tread Depth - manual check
Alternatively, tread wear can be
monitored with a simple, inexpensive device
known as a tread depth indicator gauge.2Tyre Pressure Check
Check the tyre pressures regularly with
the tyres cold. Do not adjust the tyre
pressures immediately after the vehicle has
been used, or an inaccurate setting will result.
The tyre pressures are shown on page 0•15.3
Tyre tread wear patterns
Shoulder Wear
Underinflation (wear on both sides)
Under-inflation will cause overheating of the
tyre, because the tyre will flex too much, and
the tread will not sit correctly on the road
surface. This will cause a loss of grip and
excessive wear, not to mention the danger of
sudden tyre failure due to heat build-up.
Check and adjust pressures
Incorrect wheel camber (wear on one side)
Repair or renew suspension parts
Hard cornering
Reduce speed!
Centre Wear
Overinflation
Over-inflation will cause rapid wear of the
centre part of the tyre tread, coupled with
reduced grip, harsher ride, and the danger of
shock damage occurring in the tyre casing.
Check and adjust pressures
If you sometimes have to inflate your car’s
tyres to the higher pressures specified for
maximum load or sustained high speed, don’t
forget to reduce the pressures to normal
afterwards.
Uneven Wear
Front tyres may wear unevenly as a result of
wheel misalignment. Most tyre dealers and
garages can check and adjust the wheel
alignment (or "tracking") for a modest charge.
Incorrect camber or castor
Repair or renew suspension parts
Malfunctioning suspension
Repair or renew suspension parts
Unbalanced wheel
Balance tyres
Incorrect toe setting
Adjust front wheel alignment
Note: The feathered edge of the tread which
typifies toe wear is best checked by feel.