Section 5 DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 663 of 2643
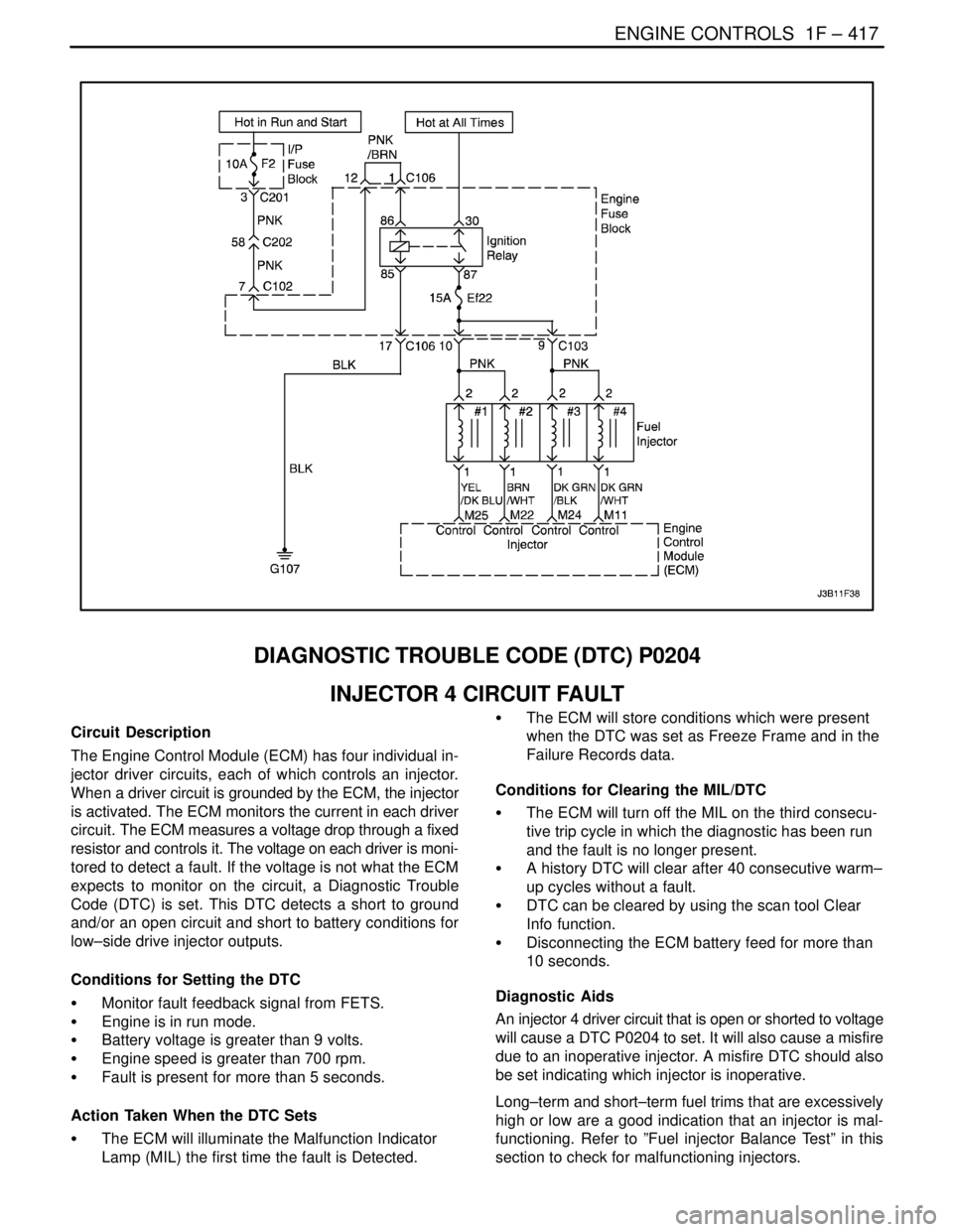
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 417
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0204
INJECTOR 4 CIRCUIT FAULT
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) has four individual in-
jector driver circuits, each of which controls an injector.
When a driver circuit is grounded by the ECM, the injector
is activated. The ECM monitors the current in each driver
circuit. The ECM measures a voltage drop through a fixed
resistor and controls it. The voltage on each driver is moni-
tored to detect a fault. If the voltage is not what the ECM
expects to monitor on the circuit, a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) is set. This DTC detects a short to ground
and/or an open circuit and short to battery conditions for
low–side drive injector outputs.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Monitor fault feedback signal from FETS.
S Engine is in run mode.
S Battery voltage is greater than 9 volts.
S Engine speed is greater than 700 rpm.
S Fault is present for more than 5 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The ECM will illuminate the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) the first time the fault is Detected.S The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The ECM will turn off the MIL on the third consecu-
tive trip cycle in which the diagnostic has been run
and the fault is no longer present.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool Clear
Info function.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An injector 4 driver circuit that is open or shorted to voltage
will cause a DTC P0204 to set. It will also cause a misfire
due to an inoperative injector. A misfire DTC should also
be set indicating which injector is inoperative.
Long–term and short–term fuel trims that are excessively
high or low are a good indication that an injector is mal-
functioning. Refer to ”Fuel injector Balance Test” in this
section to check for malfunctioning injectors.
Page 667 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 421
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0300
MULTIPLE CYLINDER MISFIRE DETECTED
System Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors the crank-
shaft and camshaft positions to detect if the engine is mis-
firing. The ECM looks for a quick drop in crankshaft speed.
This test is executed in blocks of 100 engine revolution
tests. It may take between one to several tests to store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator Lamp (MIL). Under light misfire condi-
tions, it may also take more than one trip to set a DTC. Se-
vere misfire will flash the MIL, indicating that catalyst
damage is possible.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Emission threshold is 3%.
S 20 engine cycles have occurred since cranking has
started.
S A/C compressor clutch has not just engaged or dis-
engaged.
S Engine load and engine speed is in a detectable
region and is at or above zero torque.
S Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor is in synchroniza-
tion.
S Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) flow diagnostic is
not in progress.
S Fuel level is greater than 12% of rated tank capac-
ity.
S Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) not active.
S Throttle position change is less than 3% per 125
ms.
S Vehicle has not encountered an abusive engine
speed of 7000 rpm.
S Crankshaft speed patters are normal.
S Throttle position is less than 3% when vehicle
speed is greater than 10 km/h (6 mph).
S Vehicle voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is between
–7°C (19°F) and 120°C (248°F).
S There is the correct ratio between Crankshaft Posi-
tion (CKP) sensor pulses and CMP sensor pulses.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0336, P0337, P0341, P0342 and
P0502 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The MIL will illuminate after two consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault
active.
Or
S The MIL will illuminate immediately and flash if mis-
fire is present.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault
within the freeze frame conditions that the DTC
failed.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent can also be the result of a defective reluctor
wheel. Remove the CKP sensor and inspect the reluctor
wheel through the sensor mount hole. Check for porosity
and the condition of wheel. If the DTC is intermittent refer
to ”Symptoms Diagnosis” in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
3. A visual/physical inspection should include check-
ing the following components:
S The wiring for proper connections, pinches or
cuts.
S The ECM grounds for being clean and tight.
S The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections as shown on the Vehicle Emission
Information label. Check thoroughly for any type
of leak or restriction.
S For air leaks at the throttle body mounting area
and intake manifold sealing surfaces.
5. When all the accumulators are relatively equal, then
the misfire is being caused by something that af-
fects the entire engine. When they are not then the
misfire is being caused by something that is specif-
ic to two or more cylinders.
6. Whenever the misfire is not present operating the
vehicle may be necessary to duplicate the condi-
tions in the Freeze Frame Data in order to detect
misfire. Depending on the engine load, the condi-
tions may have to be maintained for up to 20 sec-
onds. Whenever the misfire accumulators start to
increment, then misfire is present. A history misfire
counter will store the number of misfires that have
occurred until the DTC is cleared.
Page 672 of 2643

1F – 426IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0301
CYLINDER 1 MISFURE
System Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors the crank-
shaft and camshaft positions to detect if the engine is mis-
firing. The ECM looks for a quick drop in crankshaft speed.
This test is executed in blocks of 100 engine revolution
tests. It may take between one to several tests to store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator Lamp (MIL). Under light misfire condi-
tions, it may also take more than one trip to set a DTC. Se-
vere misfire will flash the MIL, indicating that catalyst
damage is possible.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Emission threshold is 3%.
S 20 engine cycles have occurred since cranking has
started.
S A/C compressor clutch has not just engaged or dis-
engaged.
S Engine load and engine speed is in a detectable
region and is at or above zero torque.
S Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor is in synchroniza-
tion.
S Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) flow diagnostic is
not in progress.
S Fuel level is greater than 12% of rated tank capac-
ity.
S Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) not active.
S Throttle position change is less than 3% per 125
ms.
S Vehicle has not encountered an abusive engine
speed of 7000 rpm.
S Crankshaft speed patters are normal.
S Throttle position is less than 3% when vehicle
speed is greater than 10 km/h (6 mph).
S Vehicle voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is between
–7°C (19°F) and 120°C (248°F).
S There is the correct ratio between Crankshaft Posi-
tion (CKP) sensor pulses and CMP sensor pulses.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0336, P0337, P0341, P0342 and
P0502 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The MIL will illuminate after two consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault
active.
Or
S The MIL will illuminate immediately and flash if mis-
fire is present.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault
within the freeze frame conditions that the DTC
failed.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent can also be the result of a defective reluctor
wheel. Remove the CKP sensor and inspect the reluctor
wheel through the sensor mount hole. Check for porosity
and the condition of wheel. If the DTC is intermittent refer
to ”Symptoms Diagnosis” in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
3. A visual/physical inspection should include check-
ing the following components:
S The wiring for proper connections, pinches or
cuts.
S The ECM grounds for being clean and tight.
S The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections as shown on the Vehicle Emission
Information label.
S Check thoroughly for any type of leak or restric-
tion.
S For air leaks at the throttle body mounting area
and intake manifold sealing surfaces.
5. When all the accumulators are relatively equal, then
the misfire is being caused by something that af-
fects the entire engine. When they are not then the
misfire is being caused by something that is specif-
ic to two or more cylinders.
6. Whenever the misfire is not present operating the
vehicle may be necessary to duplicate the condi-
tions in the Freeze Frame Data in order to detect
Page 677 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 431
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0302
CYLINDER 2 MISFIRE
System Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors the crank-
shaft and camshaft positions to detect if the engine is mis-
firing. The ECM looks for a quick drop in crankshaft speed.
This test is executed in blocks of 100 engine revolution
tests. It may take between one to several tests to store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator Lamp (MIL). Under light misfire condi-
tions, it may also take more than one trip to set a DTC. Se-
vere misfire will flash the MIL, indicating that catalyst
damage is possible.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Emission threshold is 3%.
S 20 engine cycles have occurred since cranking has
started.
S A/C compressor clutch has not just engaged or dis-
engaged.
S Engine load and engine speed is in a detectable
region and is at or above zero torque.
S Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor is in synchroniza-
tion.
S Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) flow diagnostic is
not in progress.
S Fuel level is greater than 12% of rated tank capac-
ity.
S Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) not active.
S Throttle position change is less than 3% per 125
ms.
S Vehicle has not encountered an abusive engine
speed of 7000 rpm.
S Crankshaft speed patters are normal.
S Throttle position is less than 3% when vehicle
speed is greater than 10 km/h (6 mph).
S Vehicle voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is between
–7°C (19°F) and 120°C (248°F).
S There is the correct ratio between Crankshaft Posi-
tion (CKP) sensor pulses and CMP sensor pulses.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0336, P0337, P0341, P0342 and
P0502 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The MIL will illuminate after two consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault
active.
Or
S The MIL will illuminate immediately and flash if mis-
fire is present.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault
within the freeze frame conditions that the DTC
failed.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent can also be the result of a defective reluctor
wheel. Remove the CKP sensor and inspect the reluctor
wheel through the sensor mount hole. Check for porosity
and the condition of wheel. If the DTC is intermittent refer
to”Symptoms Diagnosis” in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
3. A visual/physical inspection should include check-
ing the following components:
S The wiring for proper connections, pinches or
cuts.
S The ECM grounds for being clean and tight.
S The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections as shown on the Vehicle Emission
Information label. Check thoroughly for any type
of leak or restriction.
S For air leaks at the throttle body mounting area
and intake manifold sealing surfaces.
5. When all the accumulators are relatively equal, then
the misfire is being caused by something that af-
fects the entire engine. When they are not then the
misfire is being caused by something that is specif-
ic to two or more cylinders.
6. Whenever the misfire is not present operating the
vehicle may be necessary to duplicate the condi-
tions in the Freeze Frame Data in order to detect
misfire. Depending on the engine load, the condi-
tions may have to be maintained for up to 20 sec-
onds. Whenever the misfire accumulators start to
increment, then misfire is present. A history misfire
counter will store the number of misfires that have
occurred until the DTC is cleared.
Page 682 of 2643

1F – 436IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0303
CYLINDER 3 MISFIRE
System Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors the crank-
shaft and camshaft positions to detect if the engine is mis-
firing. The ECM looks for a quick drop in crankshaft speed.
This test is executed in blocks of 100 engine revolution
tests. It may take between one to several tests to store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator Lamp (MIL). Under light misfire condi-
tions, it may also take more than one trip to set a DTC. Se-
vere misfire will flash the MIL, indicating that catalyst
damage is possible.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Emission threshold is 3%.
S 20 engine cycles have occurred since cranking has
started.
S A/C compressor clutch has not just engaged or dis-
engaged.
S Engine load and engine speed is in a detectable
region and is at or above zero torque.
S Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor is in synchroniza-
tion.
S Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) flow diagnostic is
not in progress.
S Fuel level is greater than 12% of rated tank capac-
ity.
S Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) not active.
S Throttle position change is less than 3% per 125
ms.
S Vehicle has not encountered an abusive engine
speed of 7000 rpm.
S Crankshaft speed patters are normal.
S Throttle position is less than 3% when vehicle
speed is greater than 10 km/h (6 mph).
S Vehicle voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is between
–7°C (19°F) and 120°C (248°F).
S There is the correct ratio between Crankshaft Posi-
tion (CKP) sensor pulses and CMP sensor pulses.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0336, P0337, P0341, P0342 and
P0502 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The MIL will illuminate after two consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault
active.
Or
S The MIL will illuminate immediately and flash if mis-
fire is present.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault
within the freeze frame conditions that the DTC
failed.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent can also be the result of a defective reluctor
wheel. Remove the CKP sensor and inspect the reluctor
wheel through the sensor mount hole. Check for porosity
and the condition of wheel. If the DTC is intermittent refer
to”Symptoms Diagnosis” in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
3. A visual/physical inspection should include check-
ing the following components:
S The wiring for proper connections, pinches or
cuts.
S The ECM grounds for being clean and tight.
S The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections as shown on the Vehicle Emission
Information label. Check thoroughly for any type
of leak or restriction.
S For air leaks at the throttle body mounting area
and intake manifold sealing surfaces.
5. When all the accumulators are relatively equal, then
the misfire is being caused by something that af-
fects the entire engine. When they are not then the
misfire is being caused by something that is specif-
ic to two or more cylinders.
6. Whenever the misfire is not present operating the
vehicle may be necessary to duplicate the condi-
tions in the Freeze Frame Data in order to detect
misfire. Depending on the engine load, the condi-
tions may have to be maintained for up to 20 sec-
onds. Whenever the misfire accumulators start to
increment, then misfire is present. A history misfire
counter will store the number of misfires that have
occurred until the DTC is cleared.
Page 687 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 441
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0304
CYLINDER 4 MISFIRE
System Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors the crank-
shaft and camshaft positions to detect if the engine is mis-
firing. The ECM looks for a quick drop in crankshaft speed.
This test is executed in blocks of 100 engine revolution
tests. It may take between one to several tests to store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator Lamp (MIL). Under light misfire condi-
tions, it may also take more than one trip to set a DTC. Se-
vere misfire will flash the MIL, indicating that catalyst
damage is possible.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Emission threshold is 3%.
S 20 engine cycles have occurred since cranking has
started.
S A/C compressor clutch has not just engaged or dis-
engaged.
S Engine load and engine speed is in a detectable
region and is at or above zero torque.
S Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor is in synchroniza-
tion.
S Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) flow diagnostic is
not in progress.
S Fuel level is greater than 12% of rated tank capac-
ity.
S Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) not active.
S Throttle position change is less than 3% per 125
ms.
S Vehicle has not encountered an abusive engine
speed of 7000 rpm.
S Crankshaft speed patters are normal.
S Throttle position is less than 3% when vehicle
speed is greater than 10 km/h (6 mph).
S Vehicle voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is between
–7°C (19°F) and 120°C (248°F).
S There is the correct ratio between Crankshaft Posi-
tion (CKP) sensor pulses and CMP sensor pulses.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0336, P0337, P0341, P0342 and
P0502 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The MIL will illuminate after two consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault
active.
Or
S The MIL will illuminate immediately and flash if mis-
fire is present.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault
within the freeze frame conditions that the DTC
failed.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent can also be the result of a defective reluctor
wheel. Remove the CKP sensor and inspect the reluctor
wheel through the sensor mount hole. Check for porosity
and the condition of wheel. If the DTC is intermittent refer
to”Symptoms Diagnosis” in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
3. A visual/physical inspection should include check-
ing the following components:
S The wiring for proper connections, pinches or
cuts.
S The ECM grounds for being clean and tight.
S The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections as shown on the Vehicle Emission
Information label. Check thoroughly for any type
of leak or restriction.
S For air leaks at the throttle body mounting area
and intake manifold sealing surfaces.
5. When all the accumulators are relatively equal, then
the misfire is being caused by something that af-
fects the entire engine. When they are not then the
misfire is being caused by something that is specif-
ic to two or more cylinders.
6. Whenever the misfire is not present operating the
vehicle may be necessary to duplicate the condi-
tions in the Freeze Frame Data in order to detect
misfire. Depending on the engine load, the condi-
tions may have to be maintained for up to 20 sec-
onds. Whenever the misfire accumulators start to
increment, then misfire is present. A history misfire
counter will store the number of misfires that have
occurred until the DTC is cleared.
Page 717 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 471
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
The EGR Decel Filter value should always be at –3 or low-
er. If the EGR Decel Filter number becomes more positive
(towards 0 or more), then the EGR system is becoming re-
stricted. Look for possible damage to the EGR pipe or for
a restriction caused by carbon deposits in the EGR pas-
sages or on the EGR valve.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. Commanding the EGR valve open determines
whether the EGR system can control the EGR
valve accurately and if the fault is present. The dif-
ference between the current and commanded posi-
tion is greater than 15%.
3. When the EGR valve electrical connector is discon-
nected, the scan tool should display the Actual
EGR Position as 0%. If it does not, the fault lies
either in the EGR signal circuit or the ECM.
4. There may be a slight delay for the voltage dis-
played on the DVM to change after the scan tool
commands the EGR valve to operate.
5. An open or poor connection condition may have
caused this DTC to set. Be sure to check the termi-
nals for being backed out, improperly formed or
damaged, and for poor tension.
7. The test light will have glowed brightly in the pre-
vious step if the EGR control circuit was shorted to
B+ and the Actual EGR Position on the scan toolwill display 100%. A test light that did not illuminate,
indicates that the circuit may be open or shorted to
ground.
9. If the EGR valve 5 volt reference is shorted to volt-
age, the digital voltmeter (DVM) will read battery
voltage and additional DTCs may be set and the
engine performance will be poor.
12. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.
13. Although the circuitry acted correctly when
checked, a problem may still lie within the terminals
which would not show up in probe type testing. Be
sure to check the terminals for being backed out,
improperly formed or damaged, and for poor ten-
sion.
17. All circuits to the EGR valve are OK at this point.
The fault lies internally in the EGR valve and, there-
fore, must be replaced. Be sure all gasket material
is removed from the EGR mounting surface. Even
a small amount of material may cause a DTC
P0401 to set.
18. Check the terminals for being backed out, improp-
erly formed or damaged, and for poor tension.
19. Clearing DTCs is a very important step for this
diagnostic. The clearing function allows the EGR
valve to relearn a new pintle position as the old
pintle position was inaccurate due to the failure that
caused the DTC. The DTC must be cleared with
the ignition ON, engine OFF or when the engine is
idling. If the ECM sees a EGR command, the new
pintle will not be learned.
20. If no malfunctions have been found at this point and
no additional DTCs were set, refer to ”Diagnostic
Aids” in this section for additional checks and infor-
mation.
DTC P0402 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Excessive Flow
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data link Connector
(DLC).
2. Turn the ignition ON.
3. Command the Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve to the specific values.
Does the Actual EGR Position follow the Desired
EGR Position?25%, 50%,
75%, 100%Go to Step 19Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the EGR valve.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. With a test light connected to B+, probe the
EGR valve wiring harness connector terminal
2.
Does the test light illuminate?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
Page 721 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 475
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
the Actual EGR and Desired EGR Positions on a cold ve-
hicle with a scan tool, the fault can be easily verified.
Check the freeze frame data to determine if the DTC set
when the vehicle was cold by viewing the Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT).
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. Commanding the EGR valve open determines
whether the EGR system can control the EGR
valve accurately and if the fault is present. The dif-
ference between the current and commanded posi-
tion is greater than 15%.
3. When the EGR valve electrical connector is discon-
nected, the scan tool should display the Actual
EGR Position as 0%. If it does not, the fault lies
either in the EGR signal circuit or the ECM.
4. There may be a slight delay for the voltage dis-
played on the DVM to change after the scan tool
commands the EGR valve to operate.
5. An open or poor connection condition may have
caused this DTC to set. Be sure to check the termi-
nals for being backed out, improperly formed or
damaged, and for poor tension.
7. The test light will have glowed brightly in the pre-
vious step if the EGR control circuit was shorted to
B+ and the Actual EGR Position on the scan toolwill display 100%. A test light that did not illuminate,
indicates that the circuit may be open or shorted to
ground.
9. If the EGR valve 5 volt reference is shorted to volt-
age, the digital voltmeter (DVM) will read battery
voltage and additional DTCs may be set and the
engine performance will be poor.
12. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.
13. Although the circuitry acted correctly when
checked, a problem may still lie within the terminals
which would not show up in probe type testing. Be
sure to check the terminals for being backed out,
improperly formed or damaged, and for poor ten-
sion.
17. All circuits to the EGR valve are OK at this point.
The fault lies internally in the EGR valve and, there-
fore, must be replaced. Be sure all gasket material
is removed from the EGR mounting surface. Even
a small amount of material may cause a DTC
P0401 to set.
18. Check the terminals for being backed out, improp-
erly formed or damaged, and for poor tension.
19. Clearing DTCs is a very important step for this
diagnostic. The clearing function allows the EGR
valve to relearn a new pintle position as the old
pintle position was inaccurate due to the failure that
caused the DTC. The DTC must be cleared with
the ignition ON, engine OFF or when the engine is
idling. If the ECM sees a EGR command, the new
pintle will not be learned.
20. If no malfunctions have been found at this point and
no additional DTCs were set, refer to ”Diagnostic
Aids” in this section for additional checks and infor-
mation.
DTC P0404 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Open Valve Position Error
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Turn the ignition ON.
3. Command the Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve to the specific values.
Does the Actual EGR Position follow the Desired
EGR Position?25%, 50%,
75%, 100%Go to Step 19Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the EGR valve.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. With a test light connected to B+, probe the
EGR valve wiring harness connector terminal
2.
Does the test light illuminate?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
Page 725 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 479
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. Commanding the EGR valve open determines
whether the EGR system can control the EGR
valve accurately and if the fault is present.
3. If the EGR valve 5 volt reference is shorted to
ground, the digital voltmeter (DVM) will read no
voltage and additional DTCs may be set and the
engine performance will be poor. When this circuit
is open, only a DTC P0405 will be set.
4. Jumpering the 5 volt reference circuit to the signal
circuit checks the signal circuit and the ECM. The
scan tool should display the Actual EGR Position
as 100% if the signal circuit and ECM are OK.
6. Although the ECM and circuitry acted correctly in
the previous step, a problem may still lie within the
terminals which would not show up in probe typetesting. Be sure to check the terminals for being
backed out, improperly formed or damaged, and for
poor tension.
10. All circuits to the EGR valve are OK at this point.
The fault lies internally in the EGR valve and there-
fore must be replaced. Be sure all gasket material
is removed from the EGR mounting surface. Even
a small amount of material may cause a DTC
P0401 to set.
13. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.
14. Check the terminals for being backed out, improp-
erly formed or damaged, and for poor tension.
15. Clearing DTCs is a very important step for this
diagnostic. The clearing function allows the EGR
valve to relearn a new pintle position as the old
pintle position was inaccurate due to the failure that
caused the DTC. The DTC must be cleared with
the ignition ON, engine OFF or when the engine is
idling. If the ECM sees an EGR command, the new
pintle will not be learned.
16. If no malfunctions have been found at this point and
no additional DTCs were set, refer to ”Diagnostic
Aids” in this section for additional checks and infor-
mation.
DTC P0405 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Pintle Position Low
Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Turn the ignition ON.
3. Command the Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve to the specific values.
Does the Actual EGR Position follow the Desired
EGR Position?25%, 50%,
75%, 100%Go to Step 15Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the EGR valve.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. With a voltmeter connected to the ground,
probe the 5 volt reference circuit at terminal 4
of the EGR valve wiring harness connector.
Is the voltage near the specified value?5 VGo to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Jumper the 5 volt reference circuit to the signal cir-
cuit at terminal 4 and C at the EGR valve wiring har-
ness connector.
Does the Actual EGR Position display the specific
value?100%Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
Page 728 of 2643
1F – 482IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. Commanding the EGR valve open determines
whether the EGR system can control the EGR
valve accurately and if the fault is present.
3. If the EGR valve 5 volt reference is shorted to
ground, the digital voltmeter (DVM) will read no
voltage and additional DTCs may be set and the
engine performance will be poor. When this circuit
is open, only a DTC P0405 will be set.
4. Jumpering the 5 volt reference circuit to the signal
circuit checks the signal circuit and the ECM. The
scan tool should display the Actual EGR Position
as 100% if the signal circuit and ECM are OK.
6. Although the ECM and circuitry acted correctly in
the previous step, a problem may still lie within the
terminals which would not show up in probe typetesting. Be sure to check the terminals for being
backed out, improperly formed or damaged, and for
poor tension.
10. All circuits to the EGR valve are OK at this point.
The fault lies internally in the EGR valve and, there-
fore, must be replaced. Be sure all gasket material
is removed from the EGR mounting surface. Even
a small amount of material may cause a DTC
P0401 to set.
12. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.
13. Check the terminals for being backed out, improp-
erly formed or damaged, and for poor tension.
14. Clearing DTCs is a very important step for this
diagnostic. The clearing function allows the EGR
valve to relearn a new pintle position as the old
pintle position was inaccurate due to the failure that
caused the DTC. The DTC must be cleared with
the ignition ON, engine OFF or when the engine is
idling. If the ECM sees an EGR command, the new
pintle will not be learned.
15. no malfunctions have been found at this point and
no additional DTCs were set, refer to ”Diagnostic
Aids” in this section for additional checks and infor-
mation.
DTC P0406 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Pintle Position High
Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
3. Command the Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve to the specific values.
Does the Actual EGR Position follow the Desired
EGR Position?25%, 50%,
75%, 100%Go to Step 14Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the EGR valve.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. With a voltmeter connected to the ground,
probe the 5 volt reference circuit at terminal 4
of the EGR valve wiring harness connector.
Is the voltage near the specified value?5 VGo to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Jumper the 5 volt reference circuit to the signal cir-
cuit at terminal 4 and C at the EGR valve wiring har-
ness connector.
Does the Actual EGR Position display the specific
value?100%Go to Step 6Go to Step 7