agr DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 262 of 2643
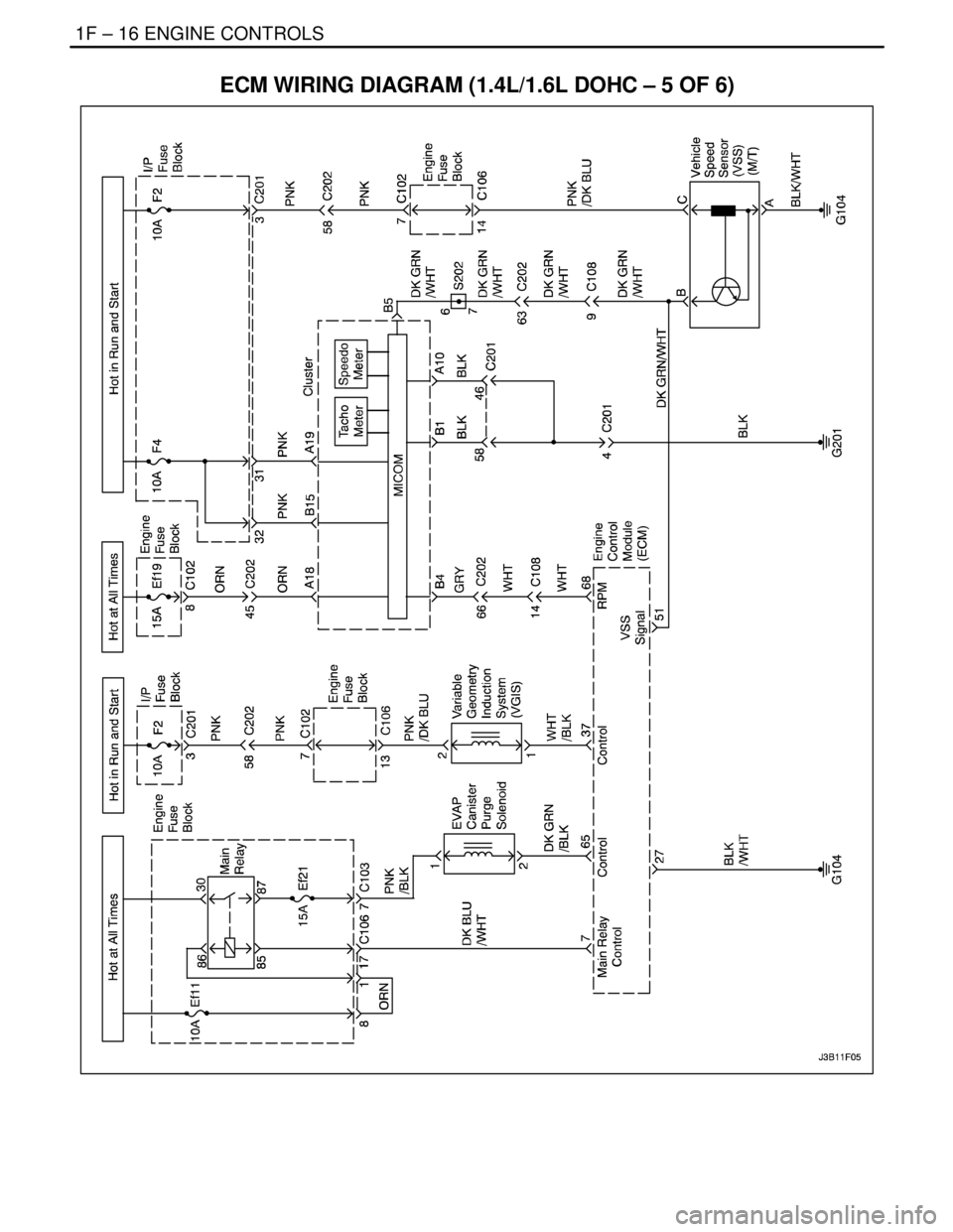
1F – 16IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1.4L/1.6L DOHC – 5 OF 6)
Page 263 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 17
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1.4L/1.6L DOHC – 6 OF 6)
Page 264 of 2643

1F – 18IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1.8L DOHC – 1 OF 6)
Page 265 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 19
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1.8L DOHC – 2 OF 6)
Page 266 of 2643

1F – 20IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1.8L DOHC – 3 OF 6)
Page 267 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 21
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1.8L DOHC – 4 OF 6)
Page 268 of 2643
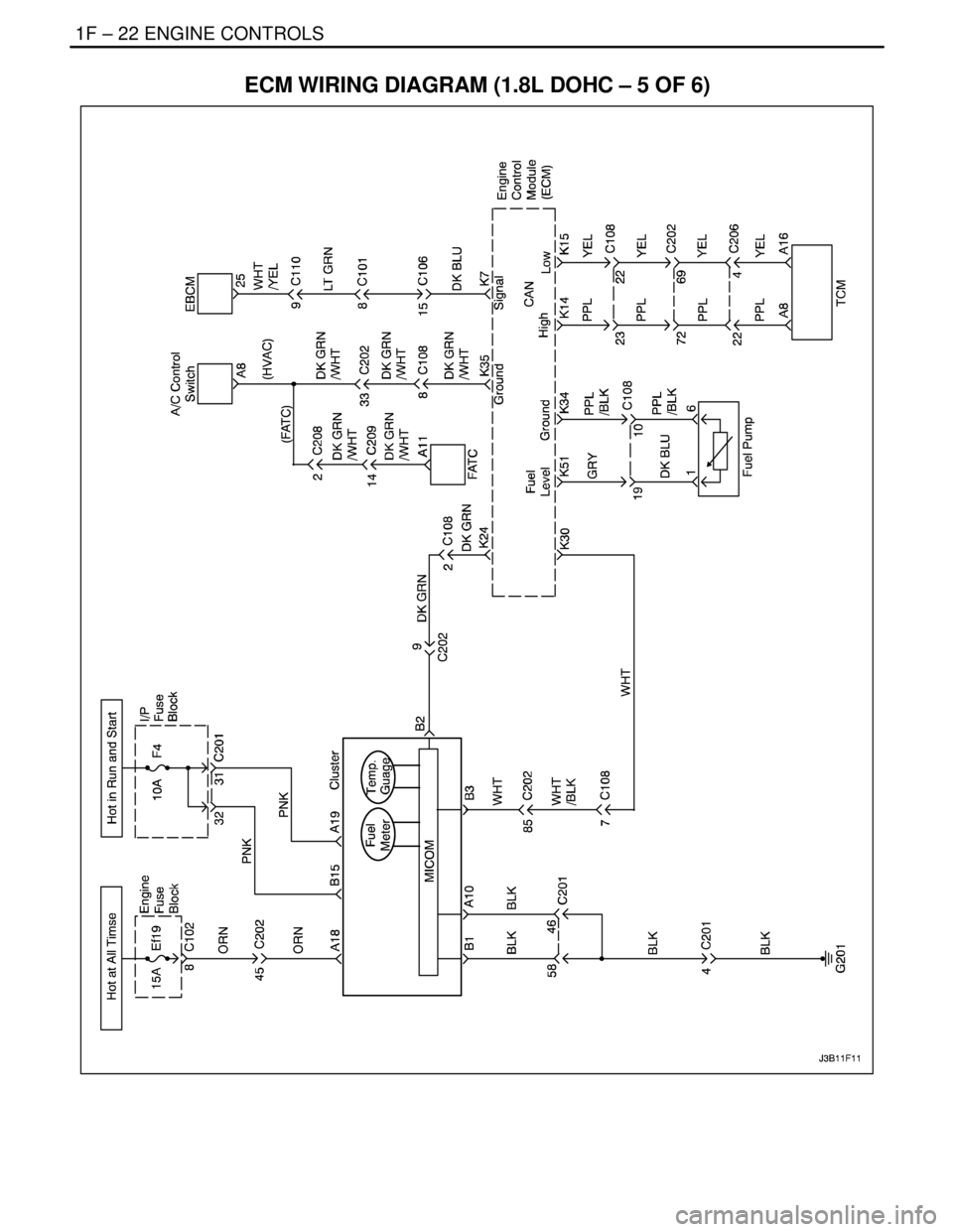
1F – 22IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1.8L DOHC – 5 OF 6)
Page 269 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 23
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1.8L DOHC – 6 OF 6)
Page 877 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 631
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S Barometric Pressure (BARO)
S Intake Air Temperature (IAT)
S Throttle Position (TP)
S High canister purge
S Fuel trim
S A/C on
Trip
Technically, a trip is a key–on run key–off cycle in which all
the enable criteria for a given diagnostic are met, allowing
the diagnostic to run. Unfortunately, this concept is not
quite that simple. A trip is official when all the enable crite-
ria for a given diagnostic are met. But because the enable
criteria vary from one diagnostic to another, the definition
of trip varies as well. Some diagnostics are run when the
vehicle is at operating temperature, some when the ve-
hicle first starts up; some require that the vehicle be cruis-
ing at a steady highway speed, some run only when the
vehicle is at idle; some diagnostics function with the
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) disabled. Some run only
immediately following a cold engine startup.
A trip then, is defined as a key–on run key–off cycle in
which the vehicle was operated in such a way as to satisfy
the enables criteria for a given diagnostic, and this diag-
nostic will consider this cycle to be one trip. However,
another diagnostic with a different set of enable criteria
(which were not met) during this driving event, would not
consider it a trip. No trip will occur for that particular diag-
nostic until the vehicle is driven in such a way as to meet
all the enable criteria
Diagnostic Information
The diagnostic charts and functional checks are designed
to locate a faulty circuit or component through a process
of logical decisions. The charts are prepared with the re-
quirement that the vehicle functioned correctly at the time
of assembly and that there are not multiple faults present.
There is a continuous self–diagnosis on certain control
functions. This diagnostic capability is complimented by
the diagnostic procedures contained in this manual. The
language of communicating the source of the malfunction
is a system of diagnostic trouble codes. When a malfunc-
tion is detected by the control module, a diagnostic trouble
code is set and the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) is illu-
minated.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) is required by On–
Board Diagnostics (EOBD) that it illuminates under a strict
set of guide lines.
Basically, the MIL is turned on when the engine control
module (ECM) detects a DTC that will impact the vehicle
emissions.The MIL is under the control of the Diagnostic Executive.
The MIL will be turned on if an emissions–related diagnos-
tic test indicates a malfunction has occurred. It will stay on
until the system or component passes the same test, for
three consecutive trips, with no emissions related faults.
Extinguishing the MIL
When the MIL is on, the Diagnostic Executive will turn off
the MIL after three consecutive trips that a ”test passed”
has been reported for the diagnostic test that originally
caused the MIL to illuminate. Although the MIL has been
turned off, the DTC will remain in the ECM memory (both
Freeze Frame and Failure Records) until forty (40) warm–
up cycles after no faults have been completed.
If the MIL was set by either a fuel trim or misfire–related
DTC, additional requirements must be met. In addition to
the requirements stated in the previous paragraph, these
requirements are as follows:
S The diagnostic tests that are passed must occur
with 375 rpm of the rpm data stored at the time the
last test failed.
S Plus or minus ten percent of the engine load that
was stored at the time the last test failed. Similar
engine temperature conditions (warmed up or
warming up) as those stored at the time the last
test failed.
Meeting these requirements ensures that the fault which
turned on the MIL has been corrected.
The MIL is on the instrument panel and has the following
functions:
S It informs the driver that a fault that affects vehicle
emission levels has occurred and that the vehicle
should be taken for service as soon as possible.
S As a system check, the MIL will come on with the
key ON and the engine not running. When the en-
gine is started, the MIL will turn OFF.
S When the MIL remains ON while the engine is run-
ning, or when a malfunction is suspected due to a
driveability or emissions problem, an EOBD System
Check must be performed. The procedures for
these checks are given in EOBD System Check.
These checks will expose faults which may not be
detected if other diagnostics are performed first.
Data Link Connector (DLC)
The provision for communicating with the control module
is the Data Link Connector (DLC). The DLC is used to con-
nect to a scan tool. Some common uses of the scan tool
are listed below:
S Identifying stored DTCs.
S Clearing DTCs.
S Performing output control tests.
S Reading serial data.
Page 972 of 2643

2E – 10ITIRES AND WHEELS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
turers of tire chains have a specific chain size for each tire
size to ensure a proper fit when the chain is installed. Be
sure to purchase the correct chains for the tires on which
they are to be used. Use rubber adjusters to take up any
slack or clearance in loose chains.
Use of chains may adversely affect vehicle handling.
When tire chains are installed, follow these precautions:
S Adjust speed to road conditions.
S Avoid sharp turns.
S Avoid locked–wheel braking.
To prevent chain damage to the vehicle, install the chains
on the front tires as tightly as possible. Tighten them again
after driving 0.4 to 0.8 kilometer (0.3 to 0.5 mile). The use
of chains on the rear tires is not recommended because
they may contact the vehicle and possibly damage it. If
chains must be used on the rear tires, be sure there is suffi-
cient clearance between the chains and the body. Do not
exceed 70 km/h (45 mph) or the chain manufacturer’s
speed limit, if lower. Avoid large bumps, potholes, severe
turns and any other maneuvers which could cause the
tires to bounce. Follow any other instructions of the chain
manufacturer which do not disagree with the above in-
structions.
REPLACEMENT TIRES
A tire performance criteria (TPC) specification number is
molded in the sidewall near the tire size of all original
equipment tires. This specification number assures that
the tire meets performance standards for traction, endur-
ance, dimensions, noise, handling and rolling resis–tance.
Usually a specific TPC number is assigned to each tire
size.
CAUTION : Do not mix different types of tires on the
same vehicle such as radial, bias and bias–belted
tires except in emergencies, because vehicle han-
dling may be seriously affected and may result in loss
of control.
Use only replacement tires with the same size, load range,
and construction as the original. The use of any other tire
size or construction type may seriously affect ride, han-
dling, speedometer/odometer calibration, vehicle ground
clearance, and tire clearance to the body and the chassis.
This does not apply to the spare tire furnished with the ve-
hicle.
It is recommended that new tires be installed in pairs on
the same axle.
If it is necessary to replace only one tire, pair it with the tire
having the most tread to equalize the braking action.
Although they may appear different in tread design, tires
built by different manufacturers with identical TPC specifi-
cations may be used on the same vehicle.
ALL SEASON TIRES
Most vehicles are now equipped with steel–belted all sea-
son radial tires as standard equipment. These tires qualify
as snow tires, with a 37 percent higher average rating for
snow traction than the non–all season radial tires pre-
viously used. Other performance areas, such as wet trac-
tion, rolling resistance, tread life, and air retention, have
also been improved. This was done by improvements in
both tread design and tread compounds. These tires are
identified by an ”M + S” molded in the tire sidewall following
the size number. The suffix ”MS” is also molded in the side-
wall after the TPC specification number.
The optional handling tires used on some vehicles are not
all season tires. These will not have the ”MS” marking after
the tire size or the TPC specification number.
PASSENGER METRIC SIZED TIRES
All Daewoo vehicles now use Passenger (P) metric sized
tires. P–metric tires are available in two load ranges: stan-
dard load (35 psi maximum) and extra load (41 psi maxi-
mum). Most passenger vehicle tires are standard load.
Most P–metric tire sizes do not have exact corresponding
alphanumeric tire sizes. For example, a P175/70R13 is
not exactly equal in size and load–carrying capacity to an
FR70–13. For this reason, replacement tires should be of
the same TPC specification number as the originals. If P–
metric tires must be replaced with other sizes, consult a
tire dealer. Tire companies can best recommend the clos-
est match of alphanumeric to P–metric sizes within their
own tire lines.
The metric term for measuring tire inflation pressure is the
kilopascal (kPa). Tire pressure may be printed in both kPa
and psi. One psi equals 6.895 kPa.
See the tire label or refer to ”Tire Size and Pressure Speci-
fications” in this section for tire inflation pressures.
TIRE LABEL
The tire label is permanently located on the rear face of the
driver’s door and should be referred to for tire information.
It lists the maximum vehicle load, the tire size (including
the spare tire), and the cold inflation pressure (including
the spare tire).
SPARE TIRE
The notchback and the wagon come equipped with a full–
sized tire on a steel wheel. The hatchback comes
equipped with a reduced–sized temporary tire on a steel
wheel.
WHEELS
Wheels must be replaced if they are bent, dented, have
excessive lateral or radial runout, leak air through welds,
have elongated bolt holes, or if the wheel bolts won’t stay
tight or are heavily rusted. Wheels with excessive runout
may cause vehicle vibration. Replacement wheels must
be equivalent to the original equipment wheels in load ca-