ignition coil DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 710 of 2643

1F – 464IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0351
IGNITION CONTROL CIRCUIT A FAULT (CYLINDER 1 & 4)
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) provides a ground for
the electronic spark timing A circuit. When the ECM re-
moves the ground path of the ignition primary coil, the
magnetic field produced by the coil collapses. The collaps-
ing magnetic field produces a voltage in the secondary coil
which fires the spark plug.
The circuit between the ECM and the electronic ignition
system ignition coil is monitored for an open circuit, short
to voltage, and short to ground. When the ECM detects a
problem in the electronic spark timing A circuit, it will set
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0351.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Monitor fault feedback signal.
S Ignition ON.
S Fault flag increments fail count.
S Must receive more than 200 failures within 255 test
cycles.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S Low speed coolant fan turns on.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
S Poor connection – Inspect the ECM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks, im-
properly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal–towire connection.
Page 711 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 465
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, discon-
nect the ECM, turn the ignition on, and observe a
voltmeter connected to the 58X reference circuit at
the ECM harness connector while moving connec-
tors and wiring harnesses related to the ECM. A
change in voltage will indicate the location of thefault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
DTC P0351 – Ignition Control Circuit A Fault (Cylinder 1 and 4)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
2Check for a faulty connection or damaged terminal
C at the Electronic Ignition (EI) system ignition coil
and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 3
3Check for a faulty connection or damaged terminal
M51/M35 at the Engine Control Module (ECM) and
repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 4
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM connector.
3. Check the ignition control circuit for a short to
ground and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 5
5Check the ignition control circuit for a short to voltage
and repair as necessary.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 6
6Check an open ignition control circuit and repair as
needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 7
71. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8–
81. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the conditions for
setting this DTC as supported in the text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran
and passed?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 2
9Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to applica-
ble DTC tableSystem OK
Page 712 of 2643

1F – 466IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0352
IGNITION CONTROL CIRCUIT B FAULT (CYLINDER 2 & 3)
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) provides a ground for
the electronic spark timing A circuit. When the ECM re-
moves the ground path of the ignition primary coil, the
magnetic field produced by the coil collapses. The collaps-
ing magnetic field produces a voltage in the secondary coil
which fires the spark plug.
The circuit between the ECM and the electronic ignition
system ignition coil is monitored for an open circuit, short
to voltage, and short to ground. When the ECM detects a
problem in the electronic spark timing A circuit, it will set
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0351.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Monitor fault feedback signal.
S Ignition ON.
S Fault flag increments fail count.
S Must receive more than 200 failures within 255 test
cycles.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S Low speed coolant fan turns on.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
S Poor connection – Inspect the ECM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks, im-
properly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal–towire connection.
Page 713 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 467
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, discon-
nect the ECM, turn the ignition on, and observe a
voltmeter connected to the 58X reference circuit at
the ECM harness connector while moving connec-
tors and wiring harnesses related to the ECM. A
change in voltage will indicate the location of thefault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
DTC P0352 – Ignition Control Circuit B Fault (Cylinder 2 and 3)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
2Check for a faulty connection or damaged terminal
A at the Electronic Ignition (EI) system ignition coil
and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 3
3Check for a faulty connection or damaged terminal
M33/M1 at the Engine Control Module (ECM) and
repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 4
41. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM connector.
3. Check the ignition control circuit for a short to
ground and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 5
5Check the ignition control circuit for a short to voltage
and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 6
6Check for an open in the ignition control circuit and
repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 7
71. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8–
81. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the conditions for
setting this DTC as supported in the text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran
and passed?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 2
9Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to applica-
ble DTC tableSystem OK
Page 848 of 2643

1F – 602IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
9. Connect the PCV hose to the valve cover.
10. Connect the breather hose to the valve cover.
11. Connect the IAT sensor connector.
12. Connect the negative battery cable.
13. Perform a leak check of the fuel rail and fuel injec-
tors.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Relieve the coolant system pressure.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Disconnect the engine coolant temperature (ECT)
sensor connector.
Notice : Take care when handling the engine coolant tem-
perature sensor. Damage to the sensor will affect the prop-
er operation of the fuel injection system.
4. Remove the ECT sensor
Installation Procedure
1. Install the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sen-
sor.
Tighten
Tighten the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
to 17.5 NSm (13 lb–ft).
2. Connect the ECT sensor connector.
3. Connect the negative battery cable.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR (1.8L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Relieve the coolant system pressure.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Disconnect the engine coolant temperature (ECT)
sensor connector.
Notice : Take care when handling the engine coolant tem-
perature sensor. Damage to the sensor will affect the prop-
er operation of the fuel injection system.
4. Remove the ECT sensor from the electronic ignition
(EI) system ignition coil adapter.
Page 849 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 603
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
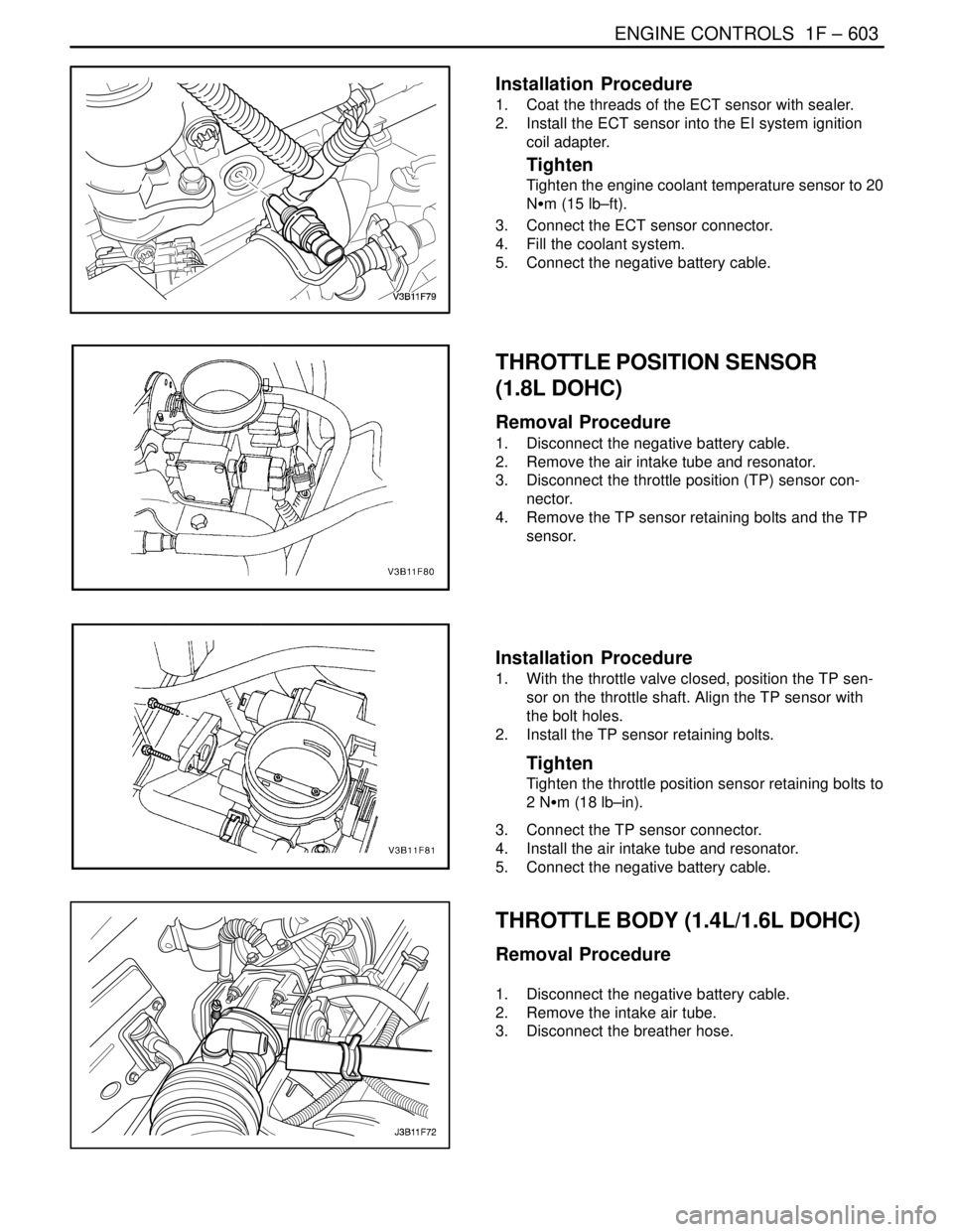
Installation Procedure
1. Coat the threads of the ECT sensor with sealer.
2. Install the ECT sensor into the EI system ignition
coil adapter.
Tighten
Tighten the engine coolant temperature sensor to 20
NSm (15 lb–ft).
3. Connect the ECT sensor connector.
4. Fill the coolant system.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
(1.8L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the air intake tube and resonator.
3. Disconnect the throttle position (TP) sensor con-
nector.
4. Remove the TP sensor retaining bolts and the TP
sensor.
Installation Procedure
1. With the throttle valve closed, position the TP sen-
sor on the throttle shaft. Align the TP sensor with
the bolt holes.
2. Install the TP sensor retaining bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the throttle position sensor retaining bolts to
2 NSm (18 lb–in).
3. Connect the TP sensor connector.
4. Install the air intake tube and resonator.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
THROTTLE BODY (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the intake air tube.
3. Disconnect the breather hose.
Page 858 of 2643
1F – 612IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
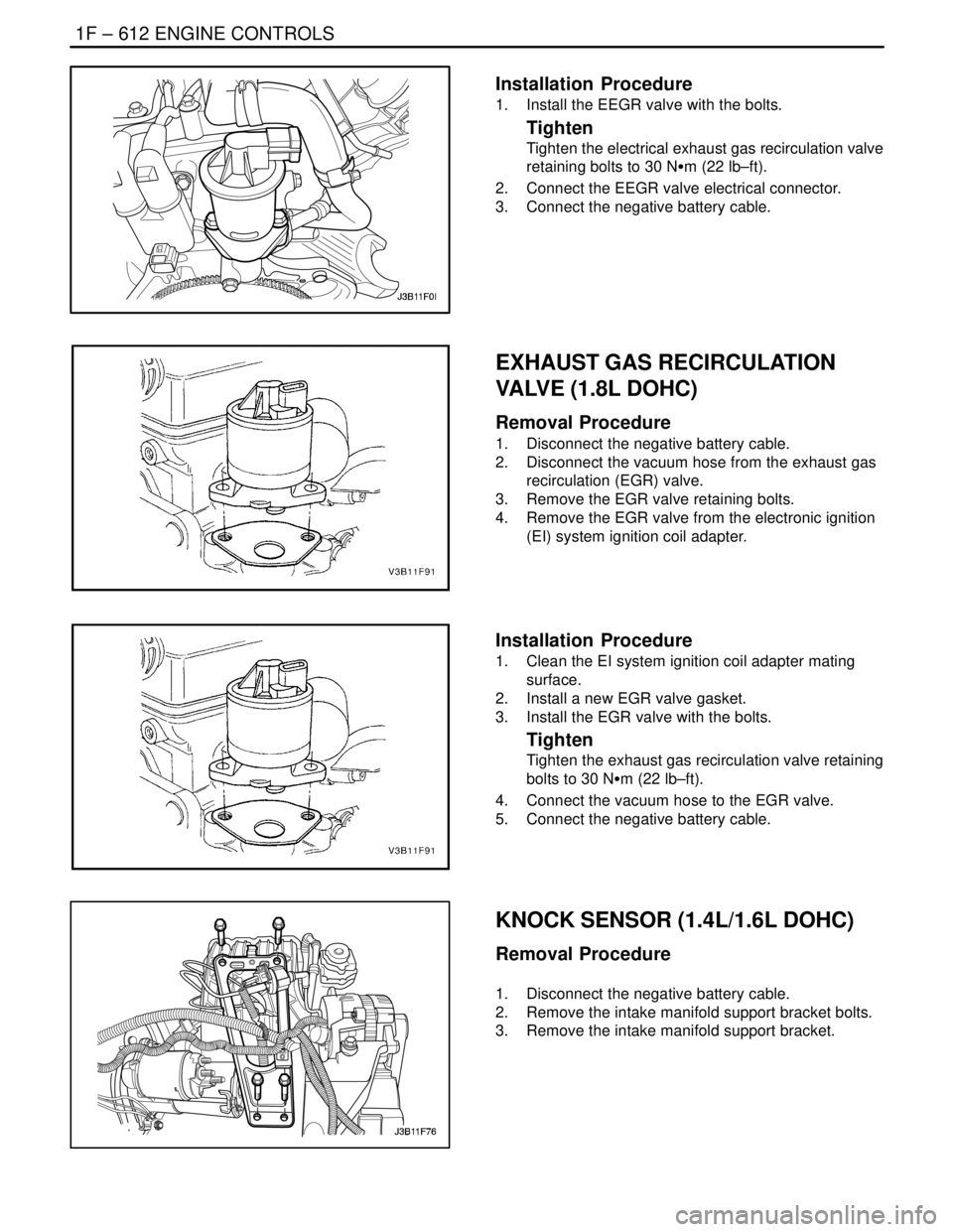
Installation Procedure
1. Install the EEGR valve with the bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the electrical exhaust gas recirculation valve
retaining bolts to 30 NSm (22 lb–ft).
2. Connect the EEGR valve electrical connector.
3. Connect the negative battery cable.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
VALVE (1.8L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the exhaust gas
recirculation (EGR) valve.
3. Remove the EGR valve retaining bolts.
4. Remove the EGR valve from the electronic ignition
(EI) system ignition coil adapter.
Installation Procedure
1. Clean the EI system ignition coil adapter mating
surface.
2. Install a new EGR valve gasket.
3. Install the EGR valve with the bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the exhaust gas recirculation valve retaining
bolts to 30 NSm (22 lb–ft).
4. Connect the vacuum hose to the EGR valve.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
KNOCK SENSOR (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the intake manifold support bracket bolts.
3. Remove the intake manifold support bracket.
Page 867 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 621
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
(1.8L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the air intake tube and resonator.
3. Disconnect the ECM connectors from the ECM.
4. Remove the engine Control module.
Installation Procedure
1. Connect the ECM connectors to the ECM.
2. Align the ECM into the mounting base.
3. Snap the ECM into its mounting base.
4. Install the ECM trim locks.
5. Install the passenger side kick panel. Refer to Sec-
tion 9G, Interior Trim.
6. Connect the negative battery cable.
7. Perform a crankshaft position system variation
learning procedure. Refer to ”DTC P1336” in this
section.
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
IGNITION COIL (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the electronic ignition (EI) system igni-
tion coil connector.
3. Note the ignition wire location and remove the igni-
tion wire.
4. Remvoe the EI system ignition coil retaining nuts.
5. Remove the EI system ignition coil.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the EI system ignition coil into the mounting
location and install the retaining nuts.
Tighten
Tighten the EI system ignition coil retaining nuts to 10
NSm (89 lb–in).
2. Connect the EI system ignition coil connector.
3. Connect the negative battery cable.
Page 868 of 2643
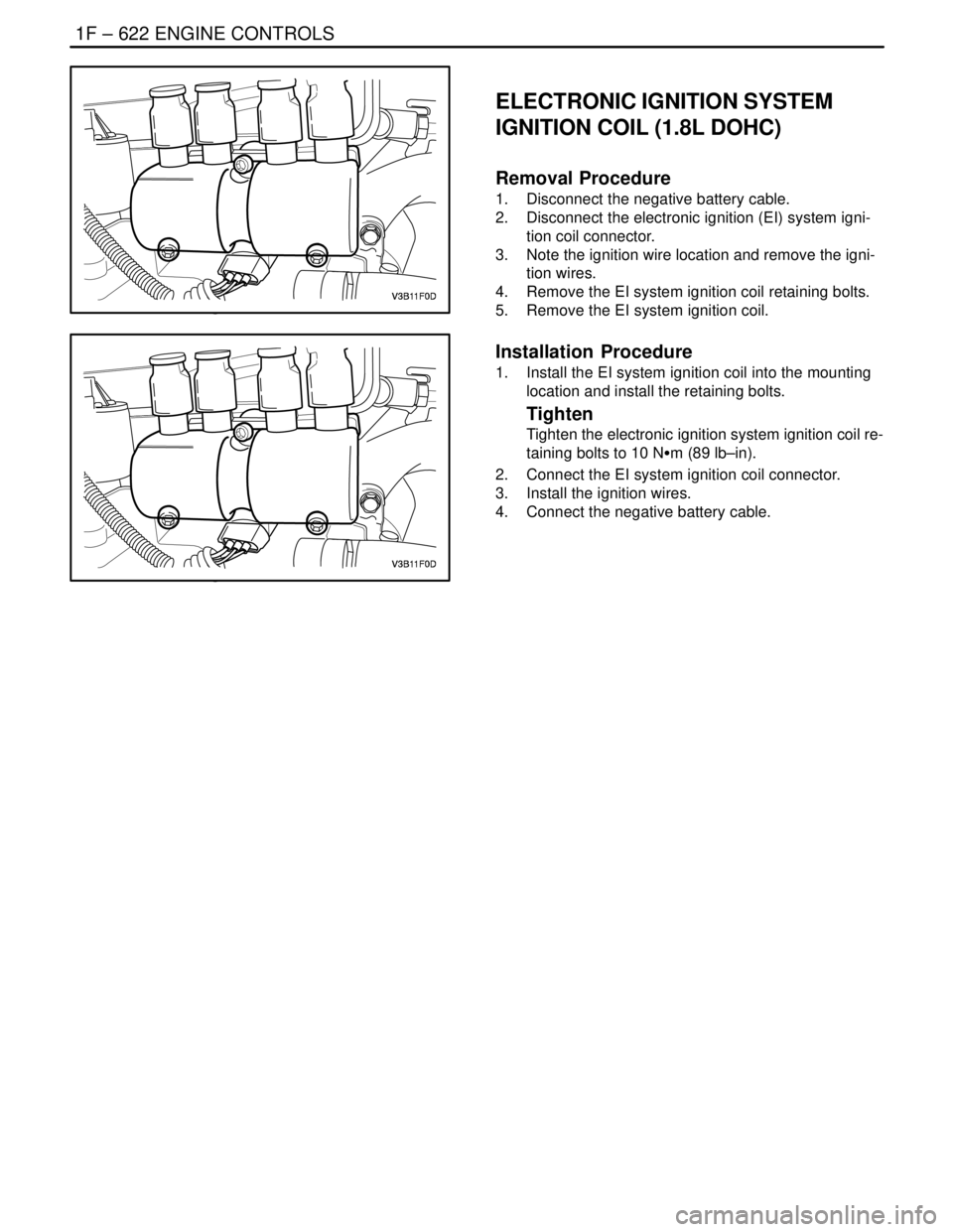
1F – 622IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
IGNITION COIL (1.8L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the electronic ignition (EI) system igni-
tion coil connector.
3. Note the ignition wire location and remove the igni-
tion wires.
4. Remove the EI system ignition coil retaining bolts.
5. Remove the EI system ignition coil.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the EI system ignition coil into the mounting
location and install the retaining bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the electronic ignition system ignition coil re-
taining bolts to 10 NSm (89 lb–in).
2. Connect the EI system ignition coil connector.
3. Install the ignition wires.
4. Connect the negative battery cable.
Page 869 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 623
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
IGNITION SYSTEM OPERATION
This ignition system does not use a conventional distribu-
tor and coil. It uses a crankshaft position sensor input to
the engine control module (ECM). The ECM then deter-
mines Electronic Spark Timing (EST) and triggers the di-
rect ignition system ignition coil.
This type of distributorless ignition system uses a ”waste
spark” method of spark distribution. Each cylinder is
paired with the cylinder that is opposite it (1–4 or 2–3). The
spark occurs simultaneously in the cylinder coming up on
the compression stroke and in the cylinder coming up on
the exhaust stroke. The cylinder on the exhaust stroke re-
quires very little of the available energy to fire the spark
plug. The remaining energy is available to the spark plug
in the cylinder on the compression stroke.
These systems use the EST signal from the ECM to con-
trol the electronic spark timing. The ECM uses the follow-
ing information:
S Engine load (manifold pressure or vacuum).
S Atmospheric (barometric) pressure.
S Engine temperature.
S Intake air temperature.
S Crankshaft position.
S Engine speed (rpm).
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
IGNITION COIL
The Electronic Ignition (EI) system ignition coil provides
the spark for two spark plugs simultaneously. The EI sys-
tem ignition coil is not serviceable and must be replaced
as an assembly.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
This direct ignition system uses a magnetic crankshaft
position sensor. This sensor protrudes through its mount
to within approximately 0.05 inch (1.3 mm) of the crank-
shaft reluctor. The reluctor is a special wheel attached to
the crankshaft or crankshaft pulley with 58 slots machined
into it, 57 of which are equally spaced in 6 degree intervals.
The last slot is wider and serves to generate a ”sync
pulse.” As the crankshaft rotates, the slots in the reluctor
change the magnetic field of the sensor, creating an in-
duced voltage pulse. The longer pulse of the 58th slot
identifies a specific orientation of the crankshaft and al-
lows the engine control module (ECM) to determine the
crankshaft orientation at all times. The ECM uses this in-
formation to generate timed ignition and injection pulses
that it sends to the ignition coils and to the fuel injectors.
CAMAHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor sends a CMP sen-
sor signal to the engine control module (ECM). The ECM
uses this signal as a ”sync pulse” to trigger the injectors in
the proper sequence. The ECM uses the CMP sensor sig-
nal to indicate the position of the #1 piston during its power
stroke. This allows the ECM to calculate true sequential
fuel injection mode of operation. If the ECM detects an in-
correct CMP sensor signal while the engine is running,
DTC P0341 will set. If the CMP sensor signal is lost while
the engine is running, the fuel injection system will shift to
a calculated sequential fuel injection mode based on the
last fuel injection pulse, and the engine will continue to run.
As long as the fault is present, the engine can be restarted.
It will run in the calculated sequential mode with a 1–in–6
chance of the injector sequence being correct.
IDLE AIR SYSTEM OPERATION
The idle air system operation is controlled by the base idle
setting of the throttle body and the Idle Air Control (IAC)
valve.
The engine control module (ECM) uses the IAC valve to
set the idle speed dependent on conditions. The ECM
uses information from various inputs, such as coolant tem-
perature, manifold vacuum, etc., for the effective control
of the idle speed.
FUEL CONTROL SYSTEM
OPERATION
The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the
correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating
conditions. The fuel is delivered to the engine by the indi-
vidual fuel injectors mounted into the intake manifold near
each cylinder.
The two main fuel control sensors are the Manifold Abso-
lute Pressure (MAP) sensor, the Front Heated Oxygen
Sensor (HO2S1) and the Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2).
The MAP sensor measures or senses the intake manifold
vacuum. Under high fuel demands the MAP sensor reads
a low vacuum condition, such as wide open throttle. The
engine control module (ECM) uses this information to ri-
chen the mixture, thus increasing the fuel injector on–time,
to provide the correct amount of fuel. When decelerating,
the vacuum increases. This vacuum change is sensed by
the MAP sensor and read by the ECM, which then de-
creases the fuel injector on–time due to the low fuel de-
mand conditions.
HO2S Sensors
The HO2S sensor is located in the exhaust manifold. The
HO2S sensor indicates to the ECM the amount of oxygen
in the exhaust gas and the ECM changes the air/fuel ratio
to the engine by controlling the fuel injectors. The best air/
fuel ratio to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7 to 1, which
allows the catalytic converter to operate most efficiently.