Power booster DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 5 of 2643
v
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section 0B General Information
Section 1 Engine
Section 1A General Engine Information
Section 1C1 1.4L/1.6L DOHC Engine Mechanical
Section 1C2 1.8L DOHC Engine Mechanical
Section 1D Engine Cooling
Section 1E Engine Electrical
Section 1F Engine Controls
Section 1G Engine Exhaust
Section 2 Suspension
Section 2A Suspension Diagnosis
Section 2B Wheel Alignment
Section 2C Front Suspension
Section 2D Rear Suspension
Section 2E Tires and Wheels
Section 3 Driveline/Axle
Section 3A Automatic Transaxle Drive Axle
Section 3B Manual Transaxle Drive Axle
Section 4 Brakes
Section 4A Hydraulic Brakes
Section 4B Master Cylinder
Section 4C Power Booster
Section 4D Front Disc Brakes
Section 4E1 Rear Disc Brakes
Section 4E2 Rear Drum Brakes
Section 4F Antilock Brake System
Section 4G Parking Brake
Section 5 Transmission/Transaxle
Section 5A1 ZF 4HP16 Automatic Transaxle
Section 5A2 AISIN Automatic Transaxle
Section 5B Five-Speed Manual Transaxle
Section 5C Clutch
Section 6 Steering
Section 6A Power Steering System
Section 6B Power Steering PumpSection 6C Power Steering Gear
Section 6E Steering Wheel and Column
Section 7 Heating, Ventilation, and Air
Conditioning (HVAC)
Section 7A Heating and Ventilation System
Section 7B Manual Control Heating, Ventilation,
and Air Conditioning System
Section 7D Automatic Temperature Control HVAC
Section 8 Restraints
Section 8A Seat Belts
Section 8B Supplemental Inflatable Restraints
(SIR)
Section 9 Body and Accessories
Section 9A Body Wiring System
Section 9B Lighting Systems
Section 9C Horns
Section 9D Wipers/Washer Systems
Section 9E Instrumentation/Driver Information
Section 9F Audio Systems
Section 9G Interior Trim
Section 9H Seats
Section 9I Waterleaks
Section 9J Windnoise
Section 9K Squeaks and Rattles
Section 9L Glass and Mirrors
Section 9M Exterior Trim
Section 9N Frame and Underbody
Section 9O Bumpers and Fascias
Section 9P Doors
Section 9Q Roof
Section 9R Body Front End
Section 9S Body Rear End
Section 9T1 Remote Keyless Entry and Anti–Theft
System
Section 9T2 Immobilizer Anti–Theft System
Page 18 of 2643
GENERAL INFORMATION 0B – 11
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
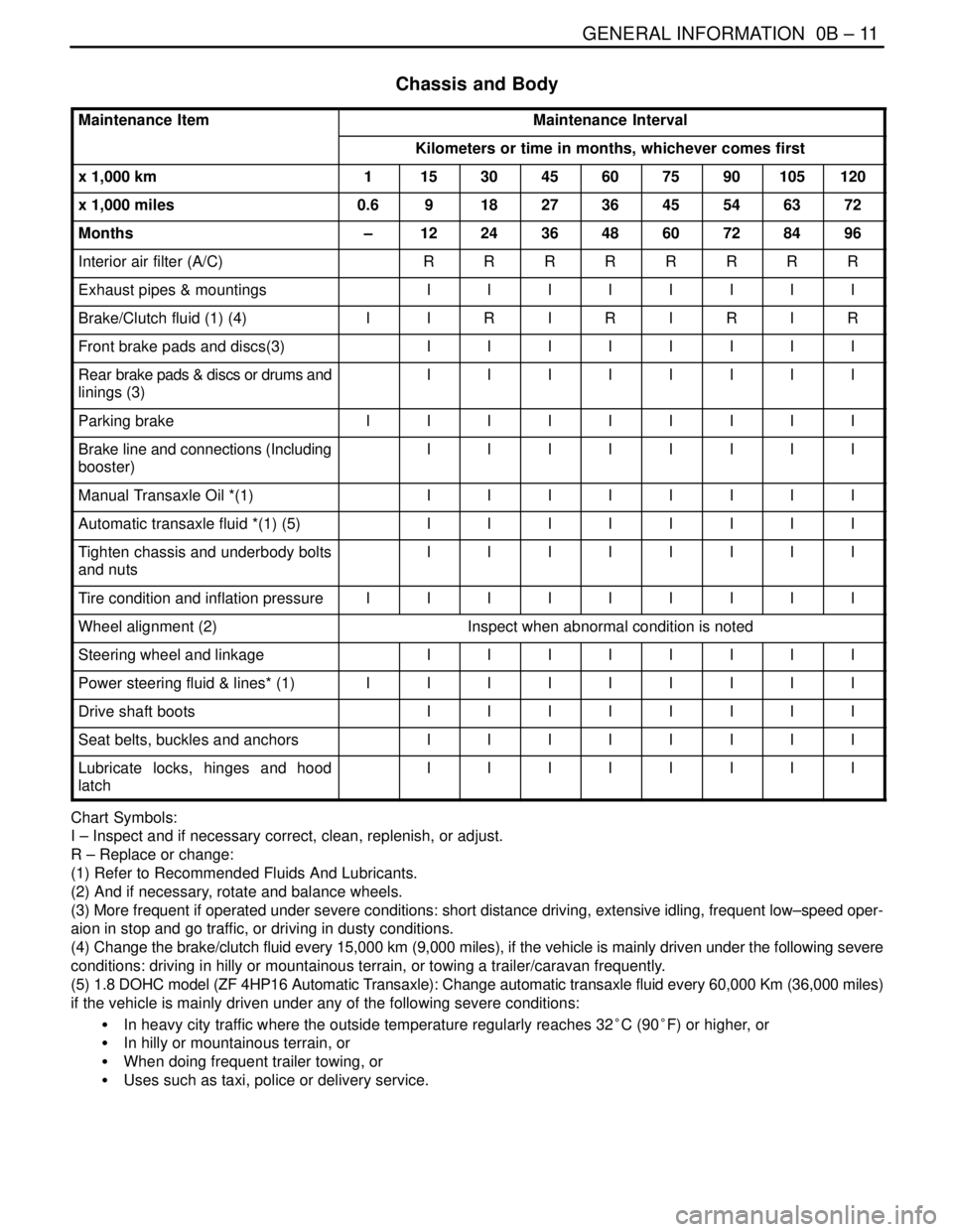
Chassis and Body
Maintenance ItemMaintenance Interval
Kilometers or time in months, whichever comes first
x 1,000 km1153045607590105120
x 1,000 miles0.6918273645546372
Months–1224364860728496
Interior air filter (A/C)RRRRRRRR
Exhaust pipes & mountingsIIIIIIII
Brake/Clutch fluid (1) (4)IIRIRIRIR
Front brake pads and discs(3)IIIIIIII
Rear brake pads & discs or drums and
linings (3)IIIIIIII
Parking brakeIIIIIIIII
Brake line and connections (Including
booster)IIIIIIII
Manual Transaxle Oil *(1)IIIIIIII
Automatic transaxle fluid *(1) (5)IIIIIIII
Tighten chassis and underbody bolts
and nutsIIIIIIII
Tire condition and inflation pressureIIIIIIIII
Wheel alignment (2)Inspect when abnormal condition is noted
Steering wheel and linkageIIIIIIII
Power steering fluid & lines* (1)IIIIIIIII
Drive shaft bootsIIIIIIII
Seat belts, buckles and anchorsIIIIIIII
Lubricate locks, hinges and hood
latchIIIIIIII
Chart Symbols:
I – Inspect and if necessary correct, clean, replenish, or adjust.
R – Replace or change:
(1) Refer to Recommended Fluids And Lubricants.
(2) And if necessary, rotate and balance wheels.
(3) More frequent if operated under severe conditions: short distance driving, extensive idling, frequent low–speed oper-
aion in stop and go traffic, or driving in dusty conditions.
(4) Change the brake/clutch fluid every 15,000 km (9,000 miles), if the vehicle is mainly driven under the following severe
conditions: driving in hilly or mountainous terrain, or towing a trailer/caravan frequently.
(5) 1.8 DOHC model (ZF 4HP16 Automatic Transaxle): Change automatic transaxle fluid every 60,000 Km (36,000 miles)
if the vehicle is mainly driven under any of the following severe conditions:
S In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly reaches 32°C (90°F) or higher, or
S In hilly or mountainous terrain, or
S When doing frequent trailer towing, or
S Uses such as taxi, police or delivery service.
Page 66 of 2643

1.4L/1.6L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C1 – 23
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
12. Remove the all the vaccum hoses from the intake
manifold including brake booster vaccum hose.
13. Remove the ignition cables from the spark plugs.
14. Remove the direct ignition coil(DIS) and the bracket
from the cylinder head.
15. Remove the serpentine accessory drive belt by ro-
tating the tensioner pulley bolt to clockwise using
DW110–080. Refer to Section 6B, Power Steering
Pump.
16. Remove the front passenger side tire. Refer to Sec-
tion 2E, Tires and Wheels.
17. Remove front wheel housing shield.
18. Remove the upper front timing belt cover bolts.
19. Remove the upper front timing belt cover.
20. Align the camshaft gear timing marks.
21. Remove the crank shaft pulley.
22. Remove the lower front timing belt cover bolts and
cover.
Page 92 of 2643

1.4L/1.6L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C1 – 49
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
17. Disconnect the oxygen (O2) sensor connector, if
equipped.
18. Disconnect the fuel injector harness connectors.
19. Disconnect the MAT, MAP sensor connectors.
20. Disconnect the throttle position sensor (TPS) con-
nector.
21. Disconnect the generator voltage regulator connec-
tor and power lead.
22. Remove the electrical harness clamp bolt.
23. Disconnect all of the necessary vacuum lines, in-
cluding the brake booster vacuum hose.
24. Disconnect the fuel feed line at the fuel rail.
25. Disconnect the throttle cable from the throttle body
and the intake manifold bracket.
26. Disconnect the surge tank coolant hose at the
throttle body.
27. Disconnect the heater outlet hose at the coolant
pipe.
28. Disconnect the heater inlet hose from the cylinder
head.
29. Disconnect the surge tank coolant hose from the
coolant pipe.
30. Disconnect the lower radiator hose from the coolant
pipe. Disconnect the starter solenoid ”S” terminal
wire. Remove the A/C compressor, if equipped. Re-
fer to Section 7B, Manual Control Heating, Ventila-
tion, and Air Conditioning Systems.
31. Remove the catalytic converter retaining nuts from
the exhaust pipe.
32. Remove the exhaust pipe.
Page 95 of 2643
1C1 – 52I1.4L/1.6L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
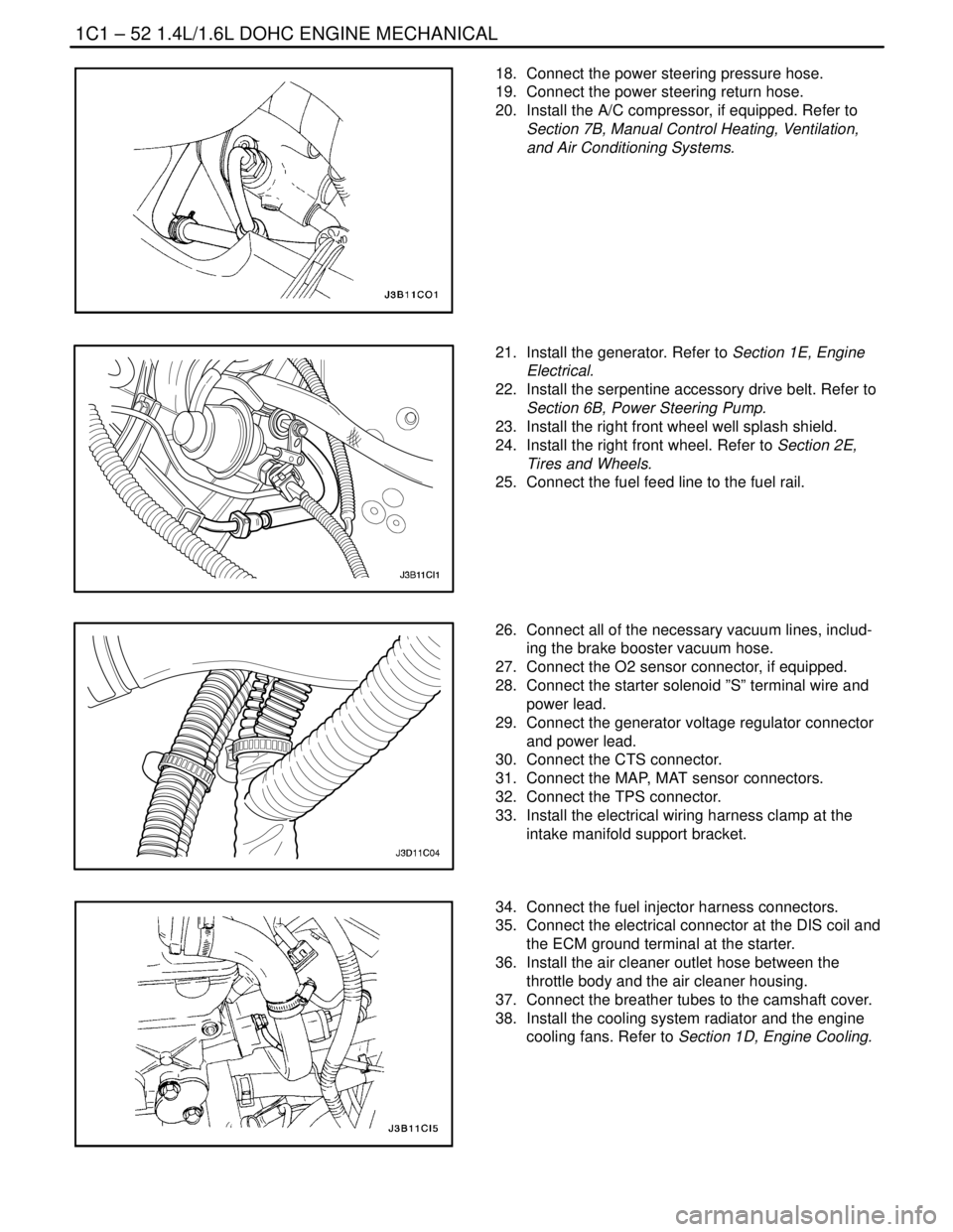
18. Connect the power steering pressure hose.
19. Connect the power steering return hose.
20. Install the A/C compressor, if equipped. Refer to
Section 7B, Manual Control Heating, Ventilation,
and Air Conditioning Systems.
21. Install the generator. Refer to Section 1E, Engine
Electrical.
22. Install the serpentine accessory drive belt. Refer to
Section 6B, Power Steering Pump.
23. Install the right front wheel well splash shield.
24. Install the right front wheel. Refer to Section 2E,
Tires and Wheels.
25. Connect the fuel feed line to the fuel rail.
26. Connect all of the necessary vacuum lines, includ-
ing the brake booster vacuum hose.
27. Connect the O2 sensor connector, if equipped.
28. Connect the starter solenoid ”S” terminal wire and
power lead.
29. Connect the generator voltage regulator connector
and power lead.
30. Connect the CTS connector.
31. Connect the MAP, MAT sensor connectors.
32. Connect the TPS connector.
33. Install the electrical wiring harness clamp at the
intake manifold support bracket.
34. Connect the fuel injector harness connectors.
35. Connect the electrical connector at the DIS coil and
the ECM ground terminal at the starter.
36. Install the air cleaner outlet hose between the
throttle body and the air cleaner housing.
37. Connect the breather tubes to the camshaft cover.
38. Install the cooling system radiator and the engine
cooling fans. Refer to Section 1D, Engine Cooling.
Page 167 of 2643

1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C2 – 47
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
19. Disconnect the oxygen (O2) sensor connector, if
equipped.
20. Disconnect the idle air control (IAC) valve connec-
tor.
21. Disconnect the throttle position sensor (TPS) con-
nector.
22. Disconnect the engine coolant temperature sensor
(CTS) connector.
23. Disconnect the CTS connector.
24. Disconnect the generator voltage regulator connec-
tor and power lead.
25. Disconnect all of the necessary vacuum lines, in-
cluding the brake booster vacuum hose.
26. Disconnect the fuel return line at the fuel rail.
27. Disconnect the fuel feed line at the fuel rail.
28. Remove the fuel rail and injector channel cover as
an assembly. Refer to Section 1F, Engine Controls.
29. Disconnect the throttle cable from the throttle body
and the intake manifold bracket.
30. Disconnect the coolant hose at the throttle body.
31. Disconnect the heater outlet hose at the coolant
pipe.
32. Disconnect the coolant bypass hose from the cylin-
der head.
33. Disconnect the surge tank coolant hose from the
coolant pipe.
34. Disconnect the lower radiator hose from the coolant
pipe.
35. Disconnect the starter solenoid ”S” terminal wire
and power lead.
36. Remove the A/C compressor. Refer to Section 7B,
Manual Control Heating, Ventilation, and Air Condi-
tioning Systems.
37. Remove the exhaust flex pipe retaining nuts from
the exhaust manifold studs.
38. Remove the exhaust flex pipe retaining nuts from
the catalytic converter or the connecting pipe.
39. Remove the exhaust flex pipe.
Page 170 of 2643

1C2 – 50I1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
18. Install the exhaust flex pipe retaining nuts to the
catalytic converter or the connecting pipe.
Tighten
Tighten the exhaust flex pipe–to–catalytic converter
or connecting pipe retaining nuts to 35 NSm (26 lb–ft).
19. Connect the power steering pressure hose.
20. Connect the power steering return hose.
21. Install the A/C compressor, if equipped. Refer to
Section 7B, Manual Control Heating, Ventilation,
and Air Conditioning System.
22. Install the serpentine accessory drive belt. Refer to
Section 6B, Power Steering Pump.
23. Install the right front wheel well splash shield.
24. Install the right front wheel. Refer to Section 2E,
Tires and Wheels.
25. Connect the fuel feed line to the fuel rail.
26. Connect the fuel return line to fuel rail.
27. Install the fuel rail and injector channel cover as an
assembly. Refer to Section 1F, Engine Controls.
28. Connect all of the necessary vacuum lines including
the brake booster vacuum hose.
29. Connect the O2 sensor connector, if equipped.
30. Connect the starter solenoid ”S” terminal wire and
power lead.
31. Connect the generator voltage regulator connector.
32. Connect the CTS connector.
33. Connect the engine CTS connector.
34. Connect the TPS connector.
35. Connect the IAC valve connector.
36. Connect the MAP sensor connector.
37. Connect the knock sensor, if necessary
38. Connect the electrical connector at the DIS ignition
coil and the ECM ground terminal and at the starter
motor.
39. Install the air cleaner outlet hose between the
throttle body and the air cleaner housing.
40. Connect the breather tubes to the camshaft cover.
41. Connect the MAT sensor connector.
42. Install the cooling system radiator and the engine
cooling fans. Refer to Section 1D, Engine Cooling.
Page 404 of 2643

1F – 158IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0171
FUEL TRIM SYSTEM TOO LEAN
System Description
If the adaptation value threshold is permanently exceed-
ed, the deviation of the adaptive terms enables to detect
a slow default coming out. Two time counters (one for the
rich side and another one for the lean side) are increased
while the lambda controller exceeds the adaptation
thresholds. As soon as one of the time counters reaches
its maximum value, the error is detected.
The aim of this test is to simulate a failure that would result
in exceeding the adaptive terms. Two kinds of failure must
be created.
S A lean side deviation: P0171
S A rich side deviation : P0172
It is thus necessary to determine, for each kind of failure,
the limit good and the limit bad. For a given failure, mea-
sure the emission threshold until the legal emission
thresholds are exceeded.
Note that the problem is due to the emission thresholds re-
quired, it is not simple to disturb the system so that the
emission thresholds will be exceeded. The tuning has
been made thanks to a dedicated calibration but, as such
a procedure is not permitted by the regulation, it is neces-
sary to create some material malfunction (fuel pressure
regulator, fuel injector, air leakage...).
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S DTCs P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117,
P0118, P0122, P0123, P0131, P0132, P0337,
P0338, P0341, P0342, P0400, P1319, P1402,
P1404, P1405, P1671 and P1672 are not set.
S Coolant temperature is greater than 20°C (68°F).
(1.4L DOHC)
S Coolant temperature is greater than 80°C (176°F).
(1.6L DOHC)
S Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) is greater than
70 kPa (10.2 psi).
S System is in closed loop.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
Important : After repairs, use the scan tool Fuel Trim Re-
set function to reset the long–term fuel trim to 128 (0%).
S Fuel pressure – The system will be lean if the pres-
sure is too low. It may be necessary to monitor fuel
pressure while driving the vehicle at various road
speeds and/or loads to confirm.
S Map sensor – An output that causes the ECM to
sense a lower than normal manifold pressure (high
vacuum) can cause the system to go lean. Discon-
necting the MAP sensor will allow the ECM to sub-
stitute a fixed (default) value for the MAP sensor. If
the lean condition is gone when the sensor is dis-
connected, substitute a known good sensor and
recheck.
S Fuel contamination – Water, in even small amounts,
near the in–tank fuel pump inlet can be delivered to
the injector. The water causes a lean exhaust and
can set DTC P0171.
Check for poor O2S or MAP sensor connection at the
ECM. Inspect the harness connectors for the following
conditions:
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness ap-
pears to be OK, observe the O2S display on the scan tool
while moving the connectors and the wiring harness re-
lated to the engine harness. A change in the display will
indicate the location of the fault.
Check the brake power booster check valve for possible
leaks.
Page 646 of 2643

1F – 400IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0171
FUEL TRIM SYSTEM TOO LEAN
System Description
To provide the best possible combination of driveability,
fuel economy, and emission control, a Closed Loop air/fuel
metering system is used. While in Closed Loop, the En-
gine Control Module (ECM) monitors the Front Heated
Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) signal voltage and adjusts fuel
delivery based on signal voltage. A change made to fuel
delivery will be indicated by the long and short term fuel
trim values which can be monitored with the scan tool.
Ideal fuel trim values are around 128 (0%). If the HO2S1
signal is indicating a lean condition, the ECM will add fuel
resulting in fuel trim values above 128 (0% to 100%). If a
rich condition is detected, the fuel trim values will be below
128 (0% to –100%), indicating that the ECM is reducing
the amount of fuel delivered. If exhaust emissions reach
an excessive level due to a lean or rich condition, a fuel
trim Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The average of adaptive index multiplier value is
greater than 1.28.
S No intrusive tests active.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113,
P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0131, P0132,
P0133, P0134, P0135, P1167, P1171, P0300,
P0336, P0337, P0341, P0342, P0402, P0404,
P1404, P0405, P0406, P0443, P0506, and P0507
are not set.
S Throttle Position (TP) is less than 95%.
S Engine speed is between 700 and 6000 rpm.
S Barometric Pressure (BARO) is greater than 72.0
kPa (10.4 psi).
S Coolant temperature is between 70°C (158°F) and
11 5°C (239°F).
S Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) is between 25
kPa (3.6 psi) and 99.7 kPa (14.5 psi).
S Intake Air Temperature (IAT) is between –40°C
(–40°F) and 120°C (248°F).
S Airflow is between 1.5 and 45 g/sec.
S Vehicle speed is less than 140 km/h (87 mph).
S System is in closed loop.
S Adaptive index is ready.
S System voltage is greater than 11 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after two consecutive ignitions cycle in which the
diagnostic runs with the fault active.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after two consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault
within the freeze frame conditions that the DTC
failed.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Important : After repairs, use the scan tool Fuel Trim Re-
set function to reset the long–term fuel trim to 128 (0%).
S Fuel pressure – The system will be lean if the pres-
sure is too low. It may be necessary to monitor fuel
pressure while driving the vehicle at various road
speeds and/or loads to confirm.
S Map sensor – An output that causes the ECM to
sense a lower than normal manifold pressure (high
vacuum) can cause the system to go lean. Discon-
necting the MAP sensor will allow the ECM to sub-
stitute a fixed (default) value for the MAP sensor. If
the lean condition is gone when the sensor is dis-
connected, substitute a known good sensor and
recheck.
S Fuel contamination – Water, in even small amounts,
near the in–tank fuel pump inlet can be delivered to
the injector. The water causes a lean exhaust and
can set DTC P0171.
Check for poor HO2S1 or MAP sensor connection at the
ECM. Inspect the harness connectors for the following
conditions:
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness ap-
pears to be OK, observe the HO2S1 display on the scan
tool while moving the connectors and the wiring harness
related to the engine harness. A change in the display will
indicate the location of the fault.
Check the brake power booster check valve for possible
leaks.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
Page 1021 of 2643

HYDRAULIC BRAKES 4A – 5
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSIS
BRAKE SYSTEM TESTING
Brakes should be tested on a dry, clean, reasonably
smooth and level roadway. A true test of brake perfor-
mance cannot be made if the roadway is wet, greasy, or
covered with loose dirt whereby all tires do not grip the
road equally. Testing will also be adversely affected if the
roadway is crowned so as to throw the weight so roughly
that the wheels tend to bounce.
Test the brakes at different vehicle speeds with both light
and heavy pedal pressure; however, avoid locking the
brakes and sliding the tires. Locked brakes and sliding
tires do not indicate brake efficiency since heavily braked,
but turning, wheels will stop the vehicle in less distance
than locked brakes. More tire–to–road friction is present
with a heavily–braked, turning tire than with a sliding tire.
Because of the high deceleration capability, a firmer pedal
may be felt at higher deceleration levels.
There are three major external conditions that affect brake
performance:
S Tires having unequal contact and grip of the road
will cause unequal braking. Tires must be equally
inflated, and the tread pattern of the right and the
left tires must be approximately equal.
S Unequal loading of the vehicle can affect the brake
performance since the most heavily loaded wheels
require more braking power, and thus more braking
effort, than the others.
S Misalignment of the wheels, particularly conditions
of excessive camber and caster, will cause the
brakes to pull to one side.
To check for brake fluid leaks, hold constant foot pressure
on the pedal with the engine running at idle and the shift
lever in NEUTRAL. If the pedal gradually falls away with
the constant pressure, the hydraulic system may be leak-
ing. Perform a visual check to confirm any suspected
leaks.
Check the master cylinder fluid level. While a slight drop
in the reservoir level results from normal lining wear, an ab-
normally low level indicates a leak in the system. The hy-
draulic system may be leaking either internally or external-
ly. Refer to the procedure below to check the master
cylinder. Also, the system may appear to pass this test
while still having a slight leak. If the fluid level is normal,
check the vacuum booster pushrod length. If an incorrect
pushrod length is found, adjust or replace the rod.
Check the master cylinder using the following procedure:
S Check for a cracked master cylinder casting or
brake fluid leaking around the master cylinder.
Leaks are indicated only if there is at least one drop
of fluid. A damp condition is not abnormal.S Check for a binding pedal linkage and for an incor-
rect pushrod length. If both of these parts are in
satisfactory condition, disassemble the master cyl-
inder and check for an elongated or swollen primary
cylinder or piston seals. If swollen seals are found,
substandard or contaminated brake fluid should be
suspected. If contaminated brake fluid is found, all
the components should be disassembled and
cleaned, and all the rubber components should be
replaced. All of the pipes must also be flushed.
Improper brake fluid, or mineral oil or water in the fluid,
may cause the brake fluid to boil or cause deterioration of
the rubber components. If the primary piston cups in the
master cylinder are swollen, then the rubber parts have
deteriorated. This deterioration may also be evidenced by
swollen wheel cylinder piston seals on the drum brake
wheels.
If deterioration of rubber is evident, disassemble all the hy-
draulic parts and wash the parts with alcohol. Dry these
parts with compressed air before reassembly to keep alco-
hol out of the system. Replace all the rubber parts in the
system, including the hoses. Also, when working on the
brake mechanisms, check for fluid on the linings. If exces-
sive fluid is found, replace the linings.
If the master cylinder piston seals are in satisfactory condi-
tion, check for leaks or excessive heat conditions. If these
conditions are not found, drain the fluid, flush the master
cylinder with brake fluid, refill the master cylinder, and
bleed the system. Refer to ”Manual Bleeding the Brakes”
or”Pressure Bleeding the Brakes” in this section.
BRAKE HOSE INSPECTION
The hydraulic brake hoses should be inspected at least
twice a year. The brake hose assembly should be checked
for road hazard damage, cracks, chafing of the outer cov-
er, and for leaks or blisters. Inspect the hoses for proper
routing and mounting. A brake hose that rubs on a suspen-
sion component will wear and eventually fail. A light and
a mirror may be needed for an adequate inspection. If any
of the above conditions are observed on the brake hose,
adjust or replace the hose as necessary.
WARNING LAMP OPERATION
This brake system uses a BRAKE warning lamp located
in the instrument panel cluster. When the ignition switch
is in the START position, the BRAKE warning lamp should
glow and go OFF when the ignition switch returns to the
RUN position.
The following conditions will activate the BRAKE lamp:
S Parking brake applied. The light should be ON
whenever the parking brake is applied and the igni-
tion switch is ON.
S Low fluid level. A low fluid level in the master cylin-
der will turn the BRAKE lamp ON.
S EBD system is disabled. The light should be ON
when the EBD system is malfunctioning.