car key DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 106 of 2643

1.4L/1.6L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C1 – 63
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
4. Inspect the dimension for the valve seat width.
S Intake: 1.17 to 1.57 mm (0.046 to 0.062 inch).
S Exhaust: 1.4 to 1.8 mm (0.055 to 0.071 inch).
5. Inspect the assembly height of the intake valves
and the exhaust valves. If the dimension is exceed-
ed, install new valves. Inspect the assembly height
of the intake valves and the exhaust valves again. If
the valve assembly height is still too large despite
replacing the valves, replace the cylinder head.
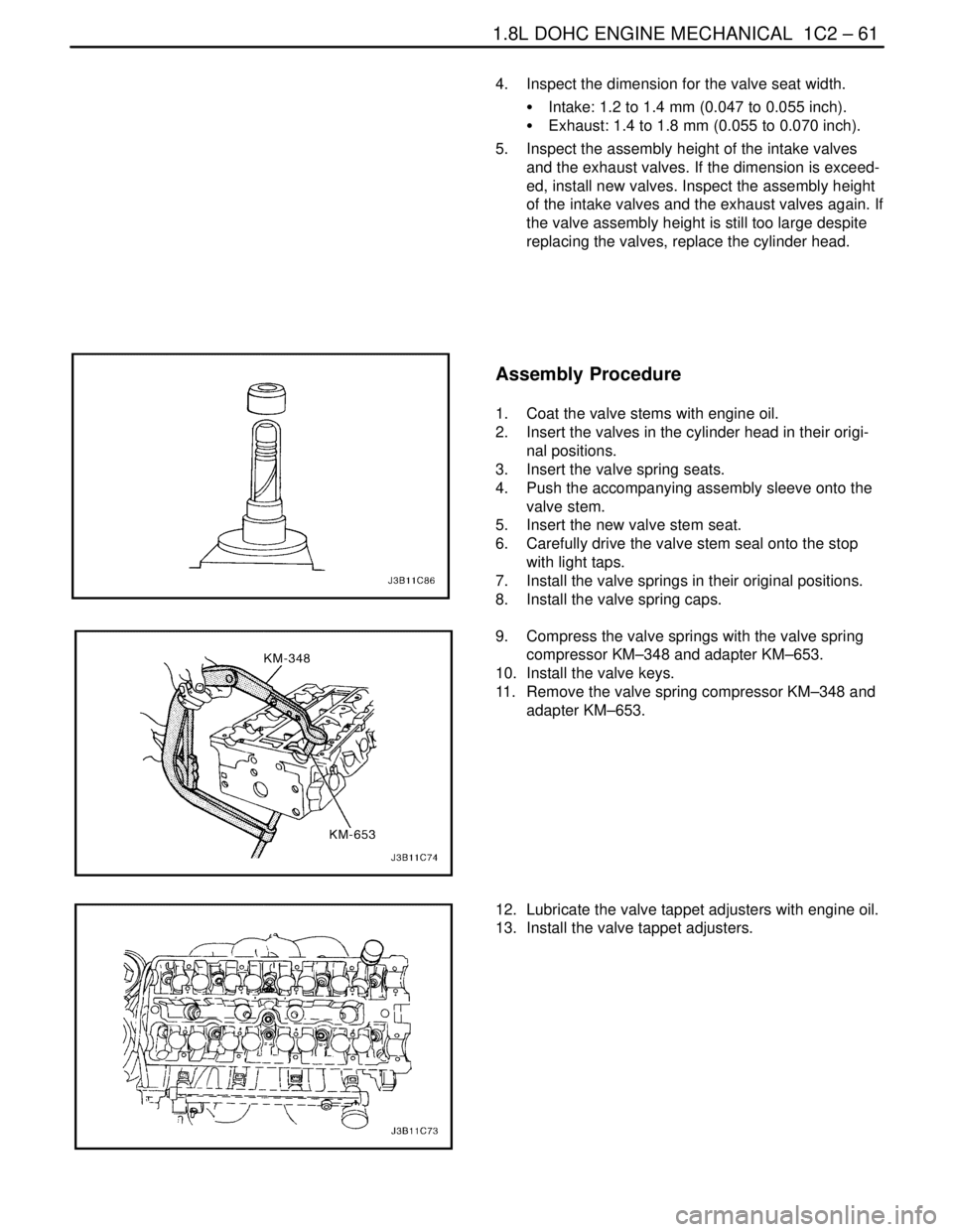
Assembly Procedure
1. Install the valve stem seals.
2. Lubricate the valve stems with engine oil.
3. Carefully install the valves in their original positions.
Do not damage the valve stem seals.
4. Install the valve springs in their original positions.
5. Install the valve spring caps.
6. Compress the valve springs with the valve spring
compressor KM–348 and adapter KM–653.
7. Install the valve keys.
8. Remove the valve spring compressor KM–348 and
adapter KM–653.
9. Lubricate the valve tappet adjusters with engine oil.
10. Install the valve tappet adjusters.
Page 181 of 2643
1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C2 – 61
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
4. Inspect the dimension for the valve seat width.
S Intake: 1.2 to 1.4 mm (0.047 to 0.055 inch).
S Exhaust: 1.4 to 1.8 mm (0.055 to 0.070 inch).
5. Inspect the assembly height of the intake valves
and the exhaust valves. If the dimension is exceed-
ed, install new valves. Inspect the assembly height
of the intake valves and the exhaust valves again. If
the valve assembly height is still too large despite
replacing the valves, replace the cylinder head.
Assembly Procedure
1. Coat the valve stems with engine oil.
2. Insert the valves in the cylinder head in their origi-
nal positions.
3. Insert the valve spring seats.
4. Push the accompanying assembly sleeve onto the
valve stem.
5. Insert the new valve stem seat.
6. Carefully drive the valve stem seal onto the stop
with light taps.
7. Install the valve springs in their original positions.
8. Install the valve spring caps.
9. Compress the valve springs with the valve spring
compressor KM–348 and adapter KM–653.
10. Install the valve keys.
11. Remove the valve spring compressor KM–348 and
adapter KM–653.
12. Lubricate the valve tappet adjusters with engine oil.
13. Install the valve tappet adjusters.
Page 184 of 2643
1C2 – 64I1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
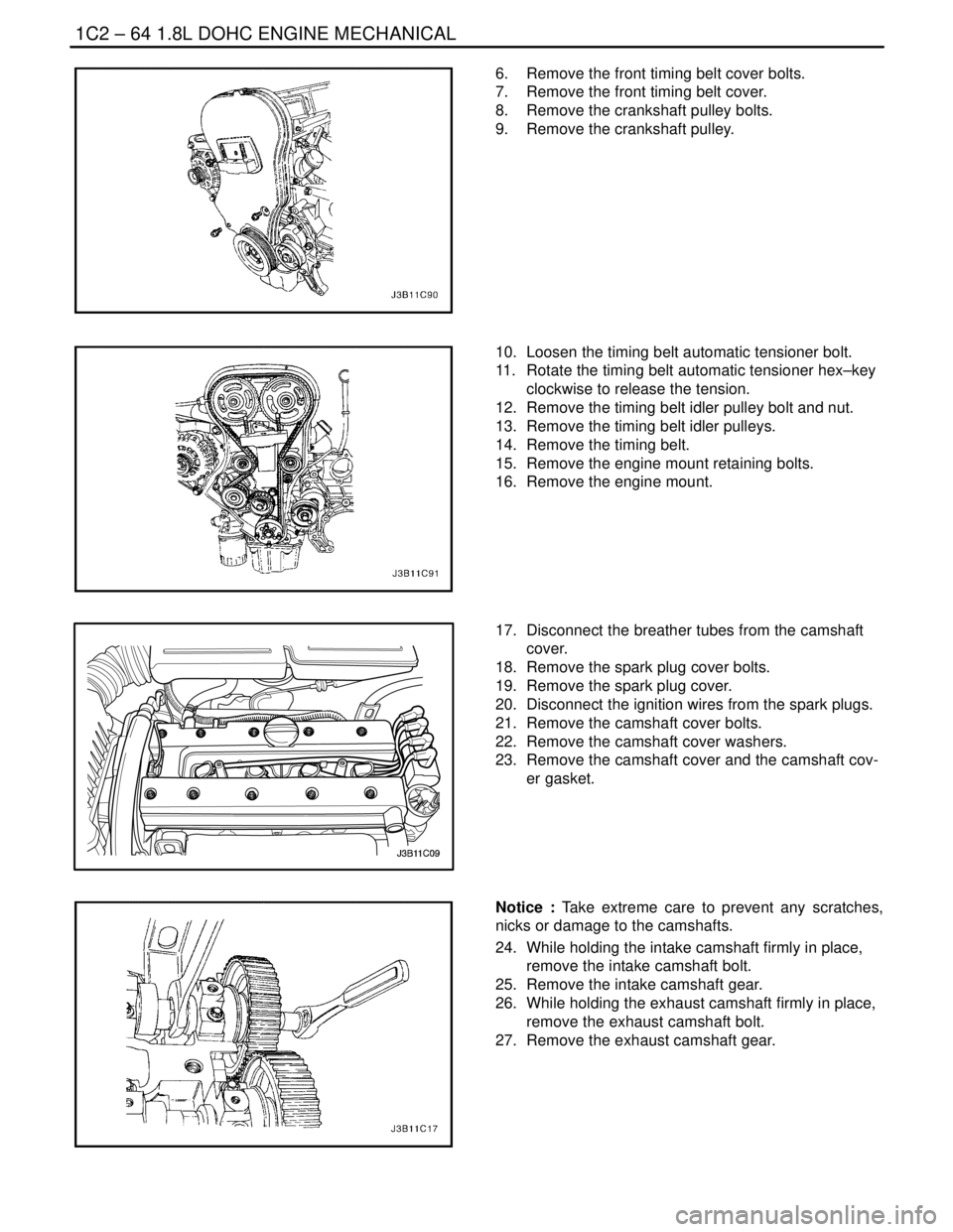
6. Remove the front timing belt cover bolts.
7. Remove the front timing belt cover.
8. Remove the crankshaft pulley bolts.
9. Remove the crankshaft pulley.
10. Loosen the timing belt automatic tensioner bolt.
11. Rotate the timing belt automatic tensioner hex–key
clockwise to release the tension.
12. Remove the timing belt idler pulley bolt and nut.
13. Remove the timing belt idler pulleys.
14. Remove the timing belt.
15. Remove the engine mount retaining bolts.
16. Remove the engine mount.
17. Disconnect the breather tubes from the camshaft
cover.
18. Remove the spark plug cover bolts.
19. Remove the spark plug cover.
20. Disconnect the ignition wires from the spark plugs.
21. Remove the camshaft cover bolts.
22. Remove the camshaft cover washers.
23. Remove the camshaft cover and the camshaft cov-
er gasket.
Notice : Take extreme care to prevent any scratches,
nicks or damage to the camshafts.
24. While holding the intake camshaft firmly in place,
remove the intake camshaft bolt.
25. Remove the intake camshaft gear.
26. While holding the exhaust camshaft firmly in place,
remove the exhaust camshaft bolt.
27. Remove the exhaust camshaft gear.
Page 223 of 2643

ENGINE ELECTRICAL 1E – 9
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
STARTER MOTOR NOISE
To correct starter motor noise during starting, use the following procedure:
Checks
Action
Check for a high–pitched whine during cranking, before
the engine fires. The engine cranks and fires properly.The distance is too great between the starter pinion and
the flywheel. Shimming the starter toward the flywheel is
required.
Check for a high–pitched whine after the engine fires, as
the key is being released. The engine cranks and fires
properly. This intermittent complaint is often diagnosed as
”starter hang–in” or ”solenoid weak.”The distance is too small between the starter pinion and
the flywheel. Shimming the starter away from the flywheel
is required.
Check for a loud ”whoop” after the engine fires but while
the starter is still held engaged. The sound is like a siren
if the engine is revved while the starter is engaged.The most probable cause is a defective clutch. A new
clutch will often correct this problem.
Check for a ”rumble,” a ”growl,” or, in severe cases, a
”knock” as the starter is coasting down to a stop after start-
ing the engine.The most probable cause is a bent or unbalanced starter
armature. A new armature will often correct this problem.
If the complaint is noise, correction can be achieved by
proper shimming as follows:
1. Check for a bent or a worn flywheel.
2. Start the engine and carefully touch the outside di-
ameter of the rotating flywheel ring gear with chalk
or a crayon to show the high point of the tooth run-
out. Turn the engine OFF and rotate the flywheel so
that the marked teeth are in the area of the starter
pinion gear.
3. Disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent
cranking the engine.
4. Check the pinion–to–flywheel clearance by using a
wire gauge of 0.5 mm (0.02 inch) minimum thick-
ness (or diameter). Center a pinion tooth between
two flywheel teeth and the gauge. Do not gauge in
the corners, where a misleading larger dimension
may be observed. If the clearance is under this
minimum, shimming the starter away from the fly-
wheel is required.
5. If the clearance approaches 1.5 mm (0.06 inch) or
more, shimming the starter toward the flywheel is
required. This condition is generally the cause of
broken flywheel teeth or the starter housing. Shim
the starter toward the flywheel by shimming only
the outboard starter mounting pad. A shim of 0.40
mm (0.016 inch) thickness at this location will de-
crease the clearance by approximately 0.30 mm
(0.012 inch). If normal starter shims are not avail-
able, plain washers or other suitable material may
be used as shims.BATTERY LOAD TEST
1. Check the battery for obvious damage, such as a
cracked or broken case or cover, which could per-
mit the loss of electrolyte. If obvious damage is
noted, replace the battery.
CAUTION : Do not charge the battery if the hydrome-
ter is clear or light yellow. Instead, replace the battery.
If the battery feels hot, or if violent gassing or spew-
ing of electrolyte through the vent hole occurs, dis-
continue charging or reduce the charging rate to
avoid personal injury.
2. Check the hydrometer. If the green dot is visible, go
to the load test procedure. If the indicator is dark
but green is not visible, charge the battery. For
charging a battery removed from the vehicle, refer
to ”Charging a Completely Discharged Battery” in
this section.
3. Connect a voltmeter and a battery load tester
across the battery terminals.
4. Apply a 300–ampere load for 15 seconds to remove
any surface charge from the battery.
5. Remove the load.
6. Wait 15 seconds to let the battery recover, and ap-
ply a 270–ampere load.
Important : The battery temperature must be estimated
by touch and by the temperature condition the battery has
been exposed for the preceding few hours.
7. If the voltage does not drop below the minimum
listed, the battery is good and should be reinstalled.
If the voltage is less than the minimum listed, re-
place the battery. Refer to ”Battery Specifications”
in this section.
Page 352 of 2643

1F – 106IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DATA LINK CONNECTOR DIAGNOSIS (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The provision for communicating with the Engine Control
Module (ECM) is the Data Link Connector (DLC). It is lo-
cated under the instrument panel. The DLC is used to con-
nect the scan tool. Battery power and ground is supplied
for the scan tool through the DLC. The Keyword 2000 seri-
al data circuit to the DLC allows the ECM to communicate
with the scan tool. A Universal Asynchronous Receiver
Transmitter (UART) serial data line is used to communi-
cate with the other modules such as the Electronic Brake
Control Module (EBCM), the Supplemental Inflatable Re-
straint (SIR) system. and the Instrument Panel Cluster.
Diagnostic Aids
Ensure that the correct application (model line, car year,
etc.) has been selected on the scan tool. If communication
still cannot be established, try the scan tool on another ve-
hicle to ensure that the scan tool or cables are not the
cause of the condition.
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed through wire insulation, or a broken wire inside the
insulation.
Any circuitry that is suspected of causing an intermittent
complaint should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions:
S Backed–out terminals.S Improper mating of terminals.
S Broken locks.
S Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
S Poor terminal–to–wiring connection.
S Physical damage to the wiring harness.
S Corrosion.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. Unlike the UART serial data circuit, the only time a
Class II serial data circuit has any voltage on it is
when a scan tool asks the ECM for information and
sends the information out.
5. Locate and repair any shorts that may have caused
the fuse to open before replacement, if the no volt-
age condition was due to an open fuse.
10. The scan tool or associated cables could be mal-
functioning. Refer to the scan tool’s manual for re-
pair information.
Page 354 of 2643

1F – 108IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DATA LINK CONNECTOR DIAGNOSIS (1.8L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The provision for communicating with the Engine Control
Module (ECM) is the Data Link Connector (DLC). It is lo-
cated under the instrument panel. The DLC is used to con-
nect the scan tool. Battery power and ground is supplied
for the scan tool through the DLC. The Keyword 2000 seri-
al data circuit to the DLC allows the ECM to communicate
with the scan tool. A Universal Asynchronous Receiver
Transmitter (UART) serial data line is used to communi-
cate with the other modules such as the Electronic Brake
Control Module (EBCM), the Supplemental Inflatable Re-
straint (SIR) system. and the Instrument Panel Cluster.
Diagnostic Aids
Ensure that the correct application (model line, car year,
etc.) has been selected on the scan tool. If communication
still cannot be established, try the scan tool on another ve-
hicle to ensure that the scan tool or cables are not the
cause of the condition.
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed through wire insulation, or a broken wire inside the
insulation.
Any circuitry that is suspected of causing an intermittent
complaint should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions:
S Backed–out terminals.S Improper mating of terminals.
S Broken locks.
S Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
S Poor terminal–to–wiring connection.
S Physical damage to the wiring harness.
S Corrosion.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. Unlike the UART serial data circuit, the only time a
Class II serial data circuit has any voltage on it is
when a scan tool asks the ECM for information and
sends the information out.
5. Locate and repair any shorts that may have caused
the fuse to open before replacement, if the no volt-
age condition was due to an open fuse.
10. The scan tool or associated cables could be mal-
functioning. Refer to the scan tool’s manual for re-
pair information.
Page 875 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 629
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
tentially interfere with the operation of the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve and thereby turn on the MIL.
Small leaks in the exhaust system near the post catalyst
oxygen sensor can also cause the MIL to turn on.
Aftermarket electronics, such as cellular phones, stereos,
and anti–theft devices, may radiate electromagnetic inter-
ference (EMI) into the control system if they are improperly
installed. This may cause a false sensor reading and turn
on the MIL.
Environment
Temporary environmental conditions, such as localized
flooding, will have an effect on the vehicle ignition system.
If the ignition system is rain–soaked, it can temporarily
cause engine misfire and turn on the MIL.
Refueling
A new EOBD diagnostic checks the integrity of the entire
Evaporative (EVAP) Emission system. If the vehicle is re-
started after refueling and the fuel cap is not secured cor-
rectly, the on–board diagnostic system will sense this as
a system fault, turn on the MIL, and set DTC P0440.
Vehicle Marshaling
The transportation of new vehicles from the assembly
plant to the dealership can involve as many as 60 key
cycles within 2 to 3 miles of driving. This type of operation
contributes to the fuel fouling of the spark plugs and will
turn on the MIL with a set DTC P0300.
Poor Vehicle Maintenance
The sensitivity of EOBD diagnostics will cause the MIL to
turn on if the vehicle is not maintained properly. Restricted
air filters, fuel filters, and crankcase deposits due to lack
of oil changes or improper oil viscosity can trigger actual
vehicle faults that were not previously monitored prior to
EOBD. Poor vehicle maintenance can not be classified as
a ”non–vehicle fault,” but with the sensitivity of EOBD
diagnostics, vehicle maintenance schedules must be
more closely followed.
Severe Vibration
The Misfire diagnostic measures small changes in the
rotational speed of the crankshaft. Severe driveline vibra-
tions in the vehicle, such as caused by an excessive
amount of mud on the wheels, can have the same effect
on crankshaft speed as misfire and, therefore, may set
DTC P0300.
Related System Faults
Many of the EOBD system diagnostics will not run if the
engine controlmodule (ECM) detects a fault on a related
system or component. One example would be that if the
ECM detected a Misfire fault, the diagnostics on the cata-
lytic converter would be suspended until the Misfire fault
was repaired. If the Misfire fault is severe enough, the cat-
alytic converter can be damaged due to overheating andwill never set a Catalyst DTC until the Misfire fault is re-
paired and the Catalyst diagnostic is allowed to run to
completion. If this happens, the customer may have to
make two trips to the dealership in order to repair the ve-
hicle.
SERIAL DATA COMMUNICATIONS
Class II Serial Data Communications
Government regulations require that all vehicle manufac-
turers establish a common communication system. This
vehicle utilizes the ”Class II” communication system. Each
bit of information can have one of two lengths: long or
short. This allows vehicle wiring to be reduced by transmit-
ting and receiving multiple signals over a single wire. The
messages carried on Class II data streams are also priori-
tized. If two messages attempt to establish communica-
tions on the data line at the same time, only the message
with higher priority will continue. The device with the lower
priority message must wait. Themost significant result of
this regulation is that it provides scan tool manufacturers
with the capability to access data from any make or model
vehicle that is sold.
The data displayed on the other scan tool will appear the
same, with some exceptions. Some scan tools will only be
able to display certain vehicle parameters as values that
are a coded representation of the true or actual value. On
this vehicle the scan tool displays the actual values for ve-
hicle parameters. It will not be necessary to perform any
conversions from coded values to actual values.
ON–BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (EOBD)
On–Board Diagnostic Tests
A diagnostic test is a series of steps, the result of which is
a pass or fail reported to the diagnostic executive. When
a diagnostic test reports a pass result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
S The diagnostic test has been completed since the
last ignition cycle.
S The diagnostic test has passed during the current
ignition cycle.
S The fault identified by the diagnostic test is not cur-
rently active.
When a diagnostic test reports a fail result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
S The diagnostic test has been completed since the
last ignition cycle.
S The fault identified by the diagnostic test is current-
ly active.
S The fault has been active during this ignition cycle.
S The operating conditions at the time of the failure.
Remember, a fuel trim Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
may be triggered by a list of vehicle faults. Make use of all
information available (other DTCs stored, rich or lean con-
dition, etc.) when diagnosing a fuel trim fault.
Page 878 of 2643

1F – 632IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
READING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODES
The procedure for reading diagnostic trouble code(s) is to
use a diagnostic scan tool. When reading Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs), follow the instructions supplied by
tool manufacturer.
DTC Modes
On On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) passenger cars there
are five options available in the scan tool DTC mode to dis-
play the enhanced information available. A description of
the new modes, DTC Info and Specific DTC, follows. After
selecting DTC, the following menu appears:
S DTC Info.
S Specific DTC.
S Freeze Frame.
S Fail Records (not all applications).
S Clear Info.
The following is a brief description of each of the sub me-
nus in DTC Info and Specific DTC. The order in which they
appear here is alphabetical and not necessarily the way
they will appear on the scan tool.
DTC Information Mode
Use the DTC info mode to search for a specific type of
stored DTC information. There are seven choices. The
service manual may instruct the technician to test for
DTCs in a certain manner. Always follow published service
procedures.
To get a complete description of any status, press the ”En-
ter” key before pressing the desired F–key. For example,
pressing ”Enter” then an F–key will display a definition of
the abbreviated scan tool status.
DTC Status
This selection will display any DTCs that have not run dur-
ing the current ignition cycle or have reported a test failure
during this ignition up to a maximum of 33 DTCs. DTC
tests which run and pass will cause that DTC number to
be removed from the scan tool screen.
Fail This Ign. (Fail This Ignition)
This selection will display all DTCs that have failed during
the present ignition cycle.
History
This selection will display only DTCs that are stored in the
ECM’s history memory. It will not display type CNL DTCs
that have not requested the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL). It will display all type A, B and E DTCs that have re-
quested the MIL and have failed within the last 40 warm–
up cycles. In addition, it will display all type C and type D
DTCs that have failed within the last 40 warm–up cycles.
Last Test Fail
This selection will display only DTCs that failed the last
time the test ran. The last test may have run during a pre-
vious ignition cycle if a type A or type B DTC is displayed.
For type C and type D DTCs, the last failure must have oc-
curred during the current ignition cycle to appear as Last
Test Fail.
MIL Request
This selection will display only DTCs that are requesting
the MIL. Type C and type D DTCs cannot be displayed us-
ing this option. This selection will report type B DTCs only
after the MIL has been requested.
Not Run SCC (Not Run Since Code Clear)
This option will display up to 33 DTCs that have not run
since the DTCs were last cleared. Since any displayed
DTCs have not run, their condition (passing or failing) is
unknown.
Test Fail SCC (Test Failed Since Code
Clear)
This selection will display all active and history DTCs that
have reported a test failure since the last time DTCs were
cleared. DTCs that last failed more than 40 warm–up
cycles before this option is selected will not be displayed.
Specific DTC Mode
This mode is used to check the status of individual diag-
nostic tests by DTC number. This selection can be ac-
cessed if a DTC has passed, failed or both. Many EOBD
DTC mode descriptions are possible because of the ex-
tensive amount of information that the diagnostic execu-
tive monitors regarding each test. Some of the many pos-
sible descriptions follow with a brief explanation.
The ”F2” key is used, in this mode, to display a description
of the DTC. The ”Yes” and ”No” keys may also be used to
display more DTC status information. This selection will
only allow entry of DTC numbers that are supported by the
vehicle being tested. If an attempt is made to enter DTC
numbers for tests which the diagnostic executive does not
recognize, the requested information will not be displayed
correctly and the scan tool may display an error message.
The same applies to using the DTC trigger option in the
Snapshot mode. If an invalid DTC is entered, the scan tool
will not trigger.
Failed Last Test
This message display indicates that the last diagnostic
test failed for the selected DTC. For type A and type B
DTCs, this message will be displayed during subsequent
ignition cycles until the test passes or DTCs are cleared.
For type C and type D DTCs, this message will clear when
the ignition is cycled.
Failed Since Clear
This message display indicates that the DTC has failed at
least once within the last 40 warm–up cycles since the last
time DTCs were cleared.
Page 1389 of 2643

5A1 – 40IZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
1. Inner Disc Carrier F
2. Clutch Plate F
3. Line Clutch Disc F
4. Clutch Outer Disc F
5. Spring Disc
6. Stop Ring
7. Cup Spring
8. O–ring
9. O–ring
10. Piston D
11. Slotted Nut
12. Roller Bearing
13. Adjust Ring
14. Bearing Plate
15. Roller Bearing
16. Spur Gear
17. Piston D
18. Spring Disc
19. Snap Ring
20. Clutch Plate D
21. Cup Spring
22. Line Clutch Disc D
23. Spring Disc
24. Disc Carrier C/D
25. Pitting Key
26. Line Clutch Disc C
27. Clutch Outer Disc C
28. Cup Spring
29. Line Clutch Disc C
30. Snap Ring
31. Piston C
32. Cylinder C
33. Snap Ring
34. Front Ring Gear
35. Oil Tray
36. Front Planetary Gear
37. Front Sun Gear
38. Snap Ring
39. Needle Bearing40. Rear Planetary Gear Set
41. Snap Ring
42. Rear Sun Gear
43. Needle Bearing
44. Snap Ring
45. Piston B
46. Clutch Plate B
47. Clutch Outer Disc B
48. Line Clutch Disc B
49. Spring Disc
50. Piston Ring
51. Inner Disc Carrier E
52. Needle Bearing
53. Snap Ring
54. Clutch Plate Disc E
55. Line Clutch Disc E
56. Clutch Outer Disc E
57. Spring Disc
58. Retainer Ring
59. O–ring
60. Oil Dam
61. Cup Spring
62. O–ring
63. Piston E
64. O–ring
65. Input Shaft
66. O–ring
67. O–ring
68. Piston
69. Oil Dam
70. O–ring
71. Cup Spring
72. Stop Ring
73. Shim
74. Needle Bearing
75. O–ring
76. Piston Ring
77. Rear Cover
Page 1398 of 2643

ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 49
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Functional Check Procedure
Inspect
1. Install a tachometer or scan tool.
2. Operate the vehicle unit proper operating tempera-
ture is reached.
3. Drive the vehicle at 80 to 88km/h (50 to 55 mph)
with light throttle(road load).
4. Maintaining throttle position, lightly touch the brake
pedal and check for release of the TCC and a slight
increase in engine speed(rpm).
5. Release the brake slowly accelerate and check for
a reapply of the Lock up clutch and a slight de-
crease in engine speed(rpm).
Torque Converter Evaluation
Torque Converter Stator
The torque converter stator roller clutch can have one of
two different type malfunctions :
A. Stator assembly freewheels in both directions.
B. Stator assembly remains Locked up at all times.
Condition A – Poor Acceleration Low
Speed
The car tends to have poor acceleration from a stand still.
At speeds above 50 to 55km/h(30 to 35mph), the car may
act normal. If poor acceleration is noted, it should first be
determined that the exhaust system is not blocked, and
the transaxle is in 1st(First) gear when starting out.
If the engine freely accelerates to high rpm in N(Neutral),
it can be assumed that the engine and exhaust system are
normal. Checking for poor performance in ”Drive” and ”Re-
verse” will help determine if the stator is freewheeling at all
times.
Condition B – Poor Acceleration High
Speed
Engine rpm and car speed limited or restricted at high
speeds. Performance when accelerating from a standstill
is normal. Engine may overheat. Visual examination of the
converter may reveal a blue color from overheating.
If the converter has been removed, the stator roller clutch
can be checked by inserting two fingers into the splined in-
ner race of the roller clutch and trying to turn freely clock-
wise, but not turn or be very difficult to turn counter clock-
wise.
Noise
Torque converter whine is usually noticed when the ve-
hicle is stopped and the transaxle is in ”Drive” or ”Re-
verse”. The noise will increase when engine rpm is in-
creased. The noise will stop when the vehicle is moving or
when the torque converter clutch is applied because both
halves of the converter are turning at the same speed.
Perform a stall test to make sure the noise is actually com-
ing from the converter :1. Place foot on brake.
2. Put gear selector in ”Drive”.
3. Depress accelerator to approximately 1200rpm for
no more than six seconds.
Notice : If the accelerator is depressed for more than six
seconds, damage to the transaxle may occur.
A torque converter noise will increase under this load.
Important : This noise should not be confused with pump
whine noise which is usually noticeable in P (Park), N
(Neutral) and all other gear ranges. Pump whine will vary
with pressure ranges.
The torque converter should be replaced under any of the
following conditions:
S External leaks in the hub weld area.
S Converter hub is scored or damaged.
S Converter pilot is broken, damaged or fits poorly
into crankshaft.
S Steel particles are found after flushing the cooler
and cooler lines.
S Pump is damaged or steel particles are found in the
converter.
S Vehicle has TCC shudder and/or no TCC apply.
Replace only after all hydraulic and electrical diag-
noses have been made.(Lock up clutch material
may be glazed.)
S Converter has an imbalance which cannot be cor–
rected. (Refer To Converter Vibration Test Proce-
dure.)
S Converter is contaminated with engine coolant con-
taining antifreeze.
S Internal failure of stator roller clutch.
S Excess end play.
S Heavy clutch debris due to overheating (blue con-
verter).
S Steel particles or clutch lining material found in fluid
filter or on magnet when no internal parts in unit are
worn or damaged(indicates that lining material
came from converter).
The torque converter should not be replace if :
S The oil has an odor, is discolored, and there is no
evidence of metal or clutch facing particles.
S The threads in one or more of the converter bolt
holes are damaged.
–correct with thread insert.
S Transaxle failure did not display evidence of dam-
age or worn internal parts, steel particles or clutch
plate lining material in unit and inside the fluid filter.
S Vehicle has been exposed to high mileage(only).
The exception may be where the Lock up clutch
damper plate lining has seen excess wear by ve-
hicles operated in heavy and/or constant traffic,
such as taxi, delivery or police use.
Lock–Up Clutch Shudder Diagnosis
The key to diagnosing lock–up clutch(TCC) shudder is to
note when it happens and under what conditions.