change key battery DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 360 of 2643

1F – 114IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0107
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR LOW
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) uses the Manifold Ab-
solute Pressure (MAP) sensor to control the fuel delivery
and the ignition timing. The MAP sensor measures the
changes in the intake manifold pressure, which results
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and the rpm
changes; and converts these into voltage outputs. The
ECM sends a 5 volt–reference voltage to the MAP sensor.
As the manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of
the MAP sensor also changes. By monitoring the MAP
sensor output voltage, the ECM knows the manifold pres-
sure. A low–pressure (low voltage) output voltage will be
about 1.0 to 1.5 volts at idle, while higher pressure (high
voltage) output voltage will be about 4.5 to 4.8 at wide
open throttle (WOT). The MAP sensor is metric pressure,
allowing the ECM to make adjustments for different alti-
tudes.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S This DTC can be stored in ”key–on” status.
(Case A)
S When the engine idling.
S No throttle position(TP) sensor MTIA fail conditions
present.
S Engine speed(rpm) is less than 2,500rpm.
S The MAP is less than 12.0 kPa.
(Case A)
S When the engine part load.
S The engine revolution speed is less than 4,000rpm.S No Throttle Position (TP) Sensor fails conditions
present.
S The Throttle Position (TP) angle greather than
30.0°.
S The MAP is less than 11.5 kPa.
S An open or low voltage condition exists.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The coolant fan turns ON.
S The ECM will substitutes a fixed MAP value and
use TP to control the fuel delivery (the scan tool will
not show defaulted)
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
With the ignition ON and the engine stopped, the manifold
pressure is equal to atmosphere pressure and the signal
voltage will be high.
Page 363 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 117
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0108
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR HIGH
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) uses the Manifold Ab-
solute Pressure (MAP) sensor to control the fuel delivery
and the ignition timing. The MAP sensor measures the
changes in the intake manifold pressure, which results
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and the rpm
changes; and converts these into voltage outputs. The
ECM sends a 5 volt–reference voltage to the MAP sensor.
As the manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of
the MAP sensor also changes. By monitoring the MAP
sensor output voltage, the ECM knows the manifold pres-
sure. A low–pressure (low voltage) output voltage will be
about 1.0 to 1.5 volts at idle, while higher pressure (high
voltage) output voltage will be about 4.5 to 4.8 at wide
open throttle (WOT). The MAP sensor is metric pressure,
allowing the ECM to make adjustments for different alti-
tudes.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S This DTC can be stored in ”key–on” status.
S When the engine idling.
S Engine speed is greater than 700rpm.
S No throttle position sensor (TPS) fail conditions
present.
S The MAP is greater than 95kPA.
S A high voltage condition exists.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
S The ECM will substitutes a fixed MAP value and
use TP to control the fuel delivery (the scan tool will
not show defaulted)
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
With the ignition ON and the engine stopped, the manifold
pressure is equal to atmosphere pressure and the signal
voltage will be high.
The ECM as an indication of vehicle altitude uses this in-
formation. Comparison of this reading with a known good
vehicle with the same sensor is a good way to check the
accuracy of a suspect sensor. Readings should be the
same ±0.4volt.
If a DTC P0108 is intermittent, refer to ”Manifold Absolute
Pressure Check” in this section for further diagnosis.
If the connections are OK monitor the manifold absolute
pressure(MAP) sensor signal voltage while moving re-
lated connectors and the wiring harness. If the failure is in-
duced, the display on the scan tool will change. This may
help to isolate the location of an intermittent malfunction.
Page 450 of 2643

1F – 204IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0336
58X CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR NO PLAUSIBLE
SIGNAL
Circuit Description
The 58X reference signal is produced by the crankshaft
position (CKP) sensor. During one crankshaft revolution,
58 crankshaft pulses will be produced. The transaxle con-
trol module(TCM)/engine control module(ECM) uses the
58X reference signal to calculate engine rpm and CKP.
The ECM constantly monitors the number of pulses on the
58X reference circuit and compares them to the number
of camshaft position (CKP) signal pulses being received.
If the ECM receive and incorrect number of pulses on the
58X reference circuit, DTC P0336 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S This DTC can be stored in ”key–on” status.
S Detected number of teeth is differs by 3 or higher.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTCS The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for :
Poor connection – inspect the ECM harness and connec-
tors for improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed
or damaged terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire connec-
tion.
Damaged harness – inspect the wiring harness for dam-
age. If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect the
ECM, turn the ignition ON and observe a voltmeter con-
nected to the 58X reference circuit at the ECM harness
connector while moving the connectors and the wiring har-
ness related to the ECM. A change in voltage will indicate
the location of the fault.
Review the failure records vehicle mileage since the diag-
nostic test failed may help determine how often the condi-
tion that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This may assist
in diagnosing the condition.
Page 453 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 207
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0337
58X CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR NO SIGNAL
Circuit Description
The 58X reference signal is produced by the crankshaft
position (CKP) sensor. During one crankshaft revolution,
58 crankshaft pulses will be produced. The transaxle con-
trol module(TCM)/engine control module(ECM) uses the
58X reference signal to calculate engine rpm and CKP.
The ECM constantly monitors the number of pulses on the
58X reference circuit and compares them to the number
of camshaft position (CKP) signal pulses being received.
If the ECM receive and incorrect number of pulses on the
58X reference circuit, DTC P0336 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S This DTC can be stored in ”key–on” status.
S No crankshaft teeth detected.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTCS The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for :
Poor connection – inspect the ECM harness and connec-
tors for improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed
or damaged terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire connec-
tion.
Damaged harness – inspect the wiring harness for dam-
age. If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect the
ECM, turn the ignition ON and observe a voltmeter con-
nected to the 58X reference circuit at the ECM harness
connector while moving the connectors and the wiring har-
ness related to the ECM. A change in voltage will indicate
the location of the fault.
Review the failure records vehicle mileage since the diag-
nostic test failed may help determine how often the condi-
tion that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This may assist
in diagnosing the condition.
Page 638 of 2643
1F – 392IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
S Rich exhaust – An overly rich exhaust may load the
catalyst, causing high HO2S2 signal voltages.
S Silicone contamination – A false rich condition may
be caused by silicone contamination of the HO2S2.
This will be indicated by a powdery white deposit on
the sensor.
S Faulty HO2S2 – If HO2S2 is internally shorted, the
HO2S2 voltage displayed on a scan tool will be
over 1 volt. Disconnect the HO2S2 and jumper the
sensor low circuit to engine ground; if the displayed
voltage goes from over 1000 millivolt to around 450
millivolt, replace the HO2S2.S Intermittent test – Observe HO2S2 on the scan tool
while moving related connectors and the wiring har-
ness with the key in the ON position. If the failure is
induced, the HO2S2 display will change. This may
help isolate the location of the malfunction.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. This step determines if DTC P0138 is the result of
a hard failure or an intermittent condition.
5. Disconnecting the HO2S2 and jumpering the sen-
sor signal circuit and the sensor low circuit to
ground should cause the scan tool to display
HO2S2 voltage below 100 mv (0.1 v). If the signal
voltage is still high, the ECM is malfunctioning.
6. The replacement ECM must be reprogrammed.
Refer to the latest Techline procedure for ECM re-
programming.
DTC P0138 – Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S2) High Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Turn the ignition ON.
Is the Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S2) volt-
age above the value specified?0.9 VGo to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Review the Freeze Frame data and note the
parameters.
2. Operate the vehicle within the Freeze frame
conditions and Conditions For Setting the DTC
as noted.
Is the HO2S2 voltage above the specified value?0.9 VGo to Step 4Go to Step 9
41. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect HO2S2 connector.
3. Disconnect the Engine Control Module (ECM)
connector.
4. With voltmeter connected to ground, probe the
HO2S2 high signal circuit, terminal K36.
Is the voltage within the specified value?±0 VGo to Step 5Go to Step 6
Page 768 of 2643

1F – 522IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1106
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE INTERMITTENT HIGH
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
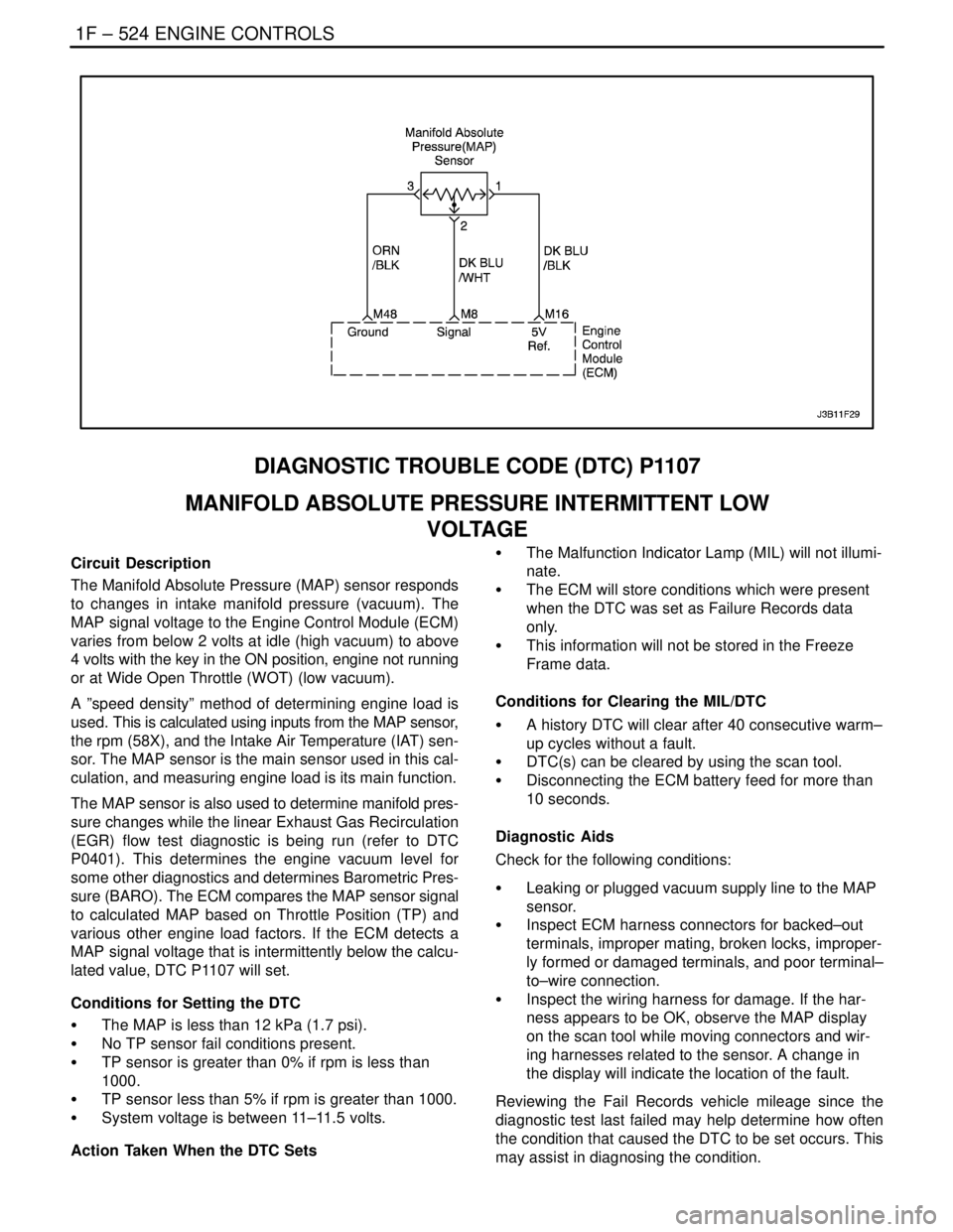
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP signal voltage to the Engine Control Module (ECM)
varies from below 2 volts at idle (high vacuum) to above
4 volts with the key in the ON position, engine not running
or at Wide Open Throttle (WOT) (low vacuum).
A ”speed density” method of determining engine load is
used. This is calculated using inputs from the MAP sensor,
the rpm (58X), and the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sen-
sor. The MAP sensor is the main sensor used in this cal-
culation, and measuring engine load is its main function.
The MAP sensor is also used to determine manifold pres-
sure changes while the linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) flow test diagnostic is being run (refer to DTC
P0401). This determines the engine vacuum level for
some other diagnostics and determines Barometric Pres-
sure (BARO). The ECM compares the MAP sensor signal
to calculated MAP based on Throttle Position (TP) and
various other engine load factors. If the ECM detects a
MAP signal voltage that is intermittently above the calcu-
lated value, DTC P1106 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The MAP is greater than 103 kPa (15 psi).
S No TP sensor fail conditions present.
S Engine running more than 10 seconds
S TP sensor is less than 15 % if rpm is less than
2500.
S TP sensor less than 35% if rpm is greater than
2500.
Action Taken When the DTC SetsS The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records data
only.
S This information will not be stored in the Freeze
Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
S Leaking or plugged vacuum supply line to the MAP
sensor.
S Inspect ECM harness connectors for backed–out
terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improper-
ly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal–
towire connection.
S Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the har-
ness appears to be OK, observe the MAP display
on the scan tool while moving connectors and wir-
ing harnesses related to the sensor. A change in
the display will indicate the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Page 770 of 2643
1F – 524IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1107
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE INTERMITTENT LOW
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP signal voltage to the Engine Control Module (ECM)
varies from below 2 volts at idle (high vacuum) to above
4 volts with the key in the ON position, engine not running
or at Wide Open Throttle (WOT) (low vacuum).
A ”speed density” method of determining engine load is
used. This is calculated using inputs from the MAP sensor,
the rpm (58X), and the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sen-
sor. The MAP sensor is the main sensor used in this cal-
culation, and measuring engine load is its main function.
The MAP sensor is also used to determine manifold pres-
sure changes while the linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) flow test diagnostic is being run (refer to DTC
P0401). This determines the engine vacuum level for
some other diagnostics and determines Barometric Pres-
sure (BARO). The ECM compares the MAP sensor signal
to calculated MAP based on Throttle Position (TP) and
various other engine load factors. If the ECM detects a
MAP signal voltage that is intermittently below the calcu-
lated value, DTC P1107 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The MAP is less than 12 kPa (1.7 psi).
S No TP sensor fail conditions present.
S TP sensor is greater than 0% if rpm is less than
1000.
S TP sensor less than 5% if rpm is greater than 1000.
S System voltage is between 11–11.5 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC SetsS The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records data
only.
S This information will not be stored in the Freeze
Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
S Leaking or plugged vacuum supply line to the MAP
sensor.
S Inspect ECM harness connectors for backed–out
terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improper-
ly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal–
to–wire connection.
S Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the har-
ness appears to be OK, observe the MAP display
on the scan tool while moving connectors and wir-
ing harnesses related to the sensor. A change in
the display will indicate the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.