engine DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: NUBIRA, Model: DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 942 of 2643

FRONT SUSPENSION 2C – 25
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
FRONT SUSPENSION
The front suspension for this vehicle is a combination of
a strut assembly and a knuckle assembly. The strut as-
sembly combines a strut dampener and spring mounted
to the body of the vehicle. The upper end of the strut is iso-
lated by a rubber mount and contains a bearing to allow the
strut to turn. The knuckle is attached to the strut assembly
and pivots on a ball joint bolted to the control arm. The con-
trol arms pivot from the body using rubber bushings.
The ball joint is fastened to the steering knuckle with a
pinch bolt and nut, and to the lower control arm with rivets.
The stabilizer bar interconnects both strut assemblies ofthe vehicle through the stabilizer link and is attached to the
front suspension crossmember. Jounce and rebound
movements affecting one wheel are partially transmitted
to the opposite wheel of the vehicle to stabilize body roll.
When servicing the control arm–to–body attachment and
the stabilizer shaft–to–body insulators, make sure the at-
taching bolts are loose until the control arms are moved to
the trim height, which is curb height. Trim height is the nor-
mal position to which the control arms move when the ve-
hicle is sitting on the ground. Refer to ”General Specifica-
tions” in this section.
The springs in the front suspension of engine family II are
stronger and the strut dampeners heavier than are the
springs and strut dampeners found in the front suspension
of engine family I.
Page 966 of 2643
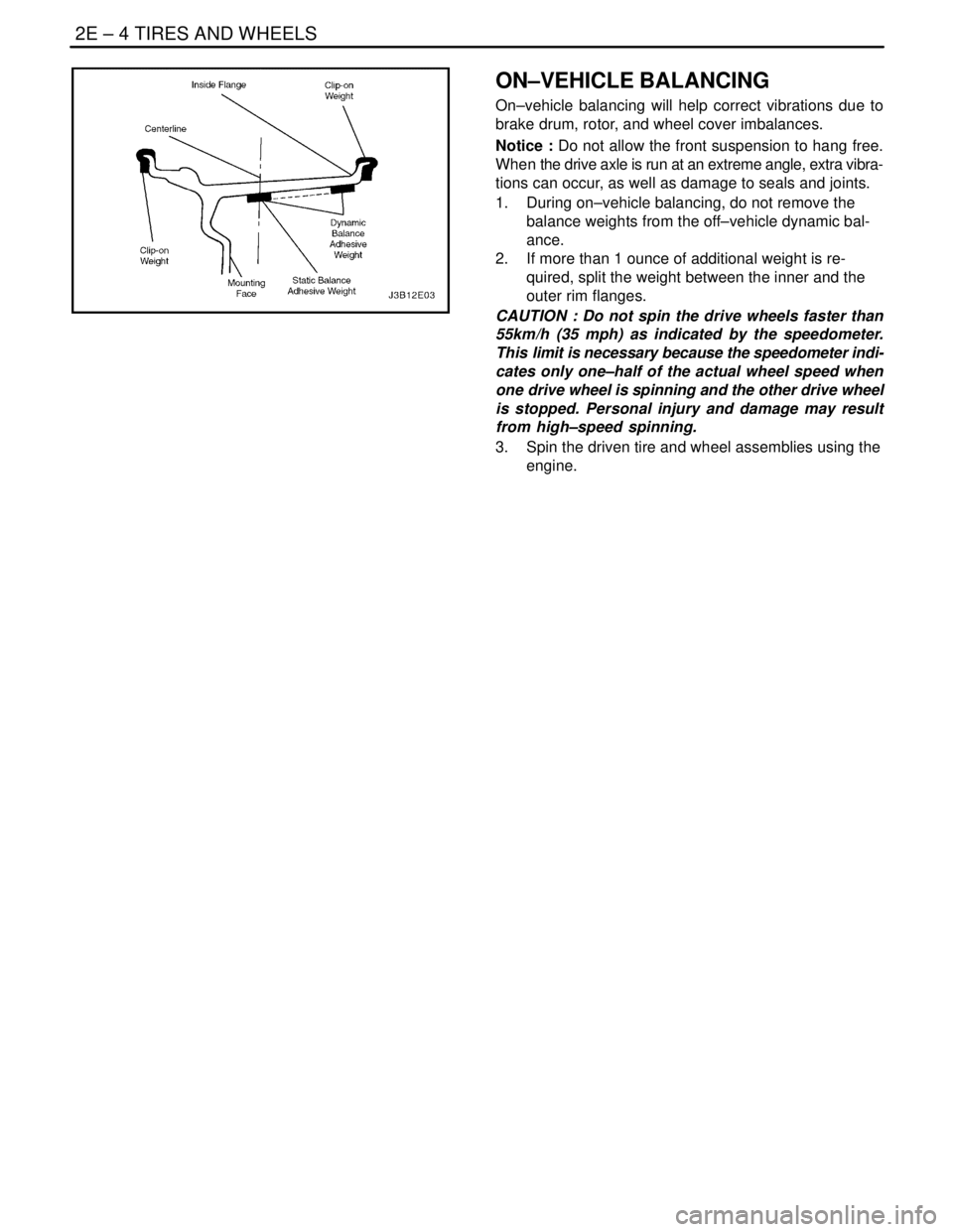
2E – 4ITIRES AND WHEELS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ON–VEHICLE BALANCING
On–vehicle balancing will help correct vibrations due to
brake drum, rotor, and wheel cover imbalances.
Notice : Do not allow the front suspension to hang free.
When the drive axle is run at an extreme angle, extra vibra-
tions can occur, as well as damage to seals and joints.
1. During on–vehicle balancing, do not remove the
balance weights from the off–vehicle dynamic bal-
ance.
2. If more than 1 ounce of additional weight is re-
quired, split the weight between the inner and the
outer rim flanges.
CAUTION : Do not spin the drive wheels faster than
55km/h (35 mph) as indicated by the speedometer.
This limit is necessary because the speedometer indi-
cates only one–half of the actual wheel speed when
one drive wheel is spinning and the other drive wheel
is stopped. Personal injury and damage may result
from high–speed spinning.
3. Spin the driven tire and wheel assemblies using the
engine.
Page 968 of 2643
2E – 6ITIRES AND WHEELS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S Amchem Alodine No. 1001. Stock No. DX50T or
equivalent coating chemical for alloys.
S Ditzler Delclear Acrylic Urethane Clear, Stock No.
DAU–75 or equivalent.
S Ditzler Delthane Ultra–Urethane Additive, Stock No.
DXR–80 or equivalent.
Before repairing the alloy damage or the clear coat dam-
age, prepare the wheels and the tires.
1. Remove the wheel from the vehicle.
2. Mark the location of the outboard weights and re-
move them.
3. Wash the wheel inside and out with a water–based,
all–purpose cleaner. Remove the grease and oil
with a solvent cleaner.
4. Mask the tire prior to painting.
5. Using a 400–grit wet or dry sandpaper, sand over
the painted areas that will not require recoloring.
Sanding will promote the adhesion of the clear coat.
Alloy Damage on Wheel Surface
1. Mount the wheel on a brake lathe and spin the as-
sembly slowly.
2. Sand the wheel with a backing block or pad. Hold
the backing block or pad flat to the surface of the
wheel and sand slowly back and forth from the cen-
ter to the outer edge of the tire to remove the dam-
age. Use the following sandpaper grits in the order
listed:
1) 80 grit.
2) 150 grit.
3) 240 grit.
Clear Coat Damage on Unpainted Wheels
1. Apply the chemical stripper Amchem Alumi Prep
No. 33. Use a small 1/4–inch detail brush to apply
the stripper around the perimeter and spoke–like
areas.
2. Remove the stripper according to the manufactur-
er’s recommendations.
CAUTION : To avoid serious personal injury, do not
use engine power to rotate the wheel while sanding.
3. Sand the wheel with 240–grit sandpaper by rotating
the wheel on a slow–spinning brake lathe or by
mounting the wheel on the car and spinning it by
hand. Sanding restores the machined appearance
and promotes adhesion.
After repairing the alloy or clear coat damage, the wheels
must be recoated.
Page 974 of 2643

SECTION 3
WIRING DIAGRAM FOR POWER SUPPLIES
CONTENTS
1. IGNITION SWITCH CIRCUIT3–2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2. 30 TER ”BAT+” POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT(I.P FUSE BLOCK) 3–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3. 15 TER ”IGN 1” POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT(I.P FUSE BLOCK) 3–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4. 15A TER ”IGN2”, 15C TER ”ACC” POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT(I.P FUSE BLOCK) 3–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5. ENGINE FUSE BLOCK & RELAY CIRCUIT 3–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 978 of 2643
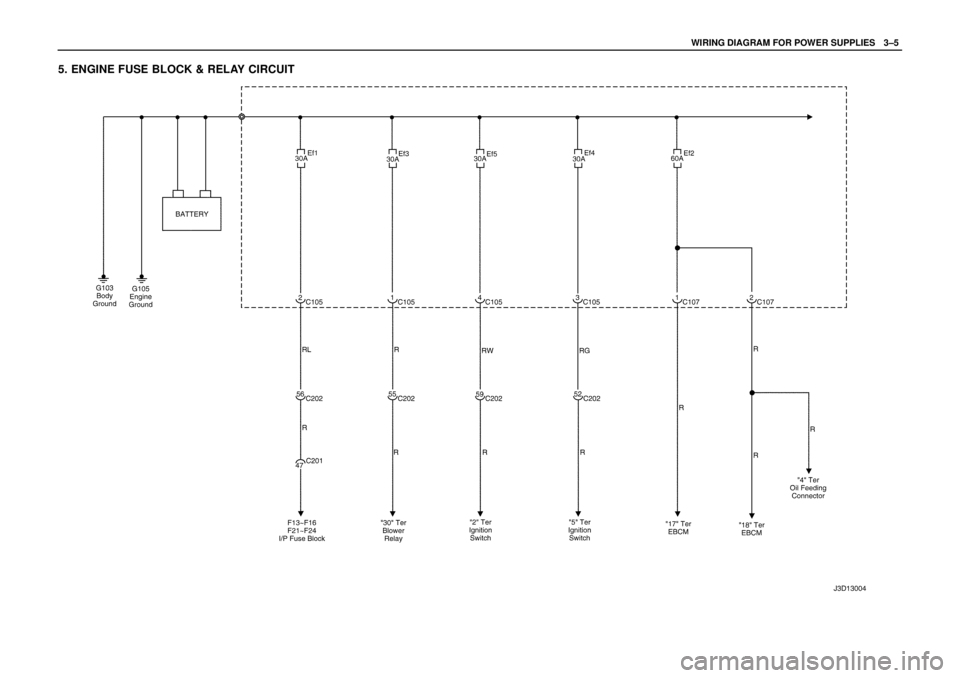
WIRING DIAGRAM FOR POWER SUPPLIESW3–5
5. ENGINE FUSE BLOCK & RELAY CIRCUIT
Page 1013 of 2643

SECTION 4
USAGE AND CAPACITY OF FUSES IN FUSE BLOCK
CONTENTS
1. ENGINE ROOM RELAY AND FUSE BLOCK 4–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2. I.P FUSE BLOCK4–3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3. POSITION OF CONTROL UNIT, RELAY AND PART NUMBER 4–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 1014 of 2643
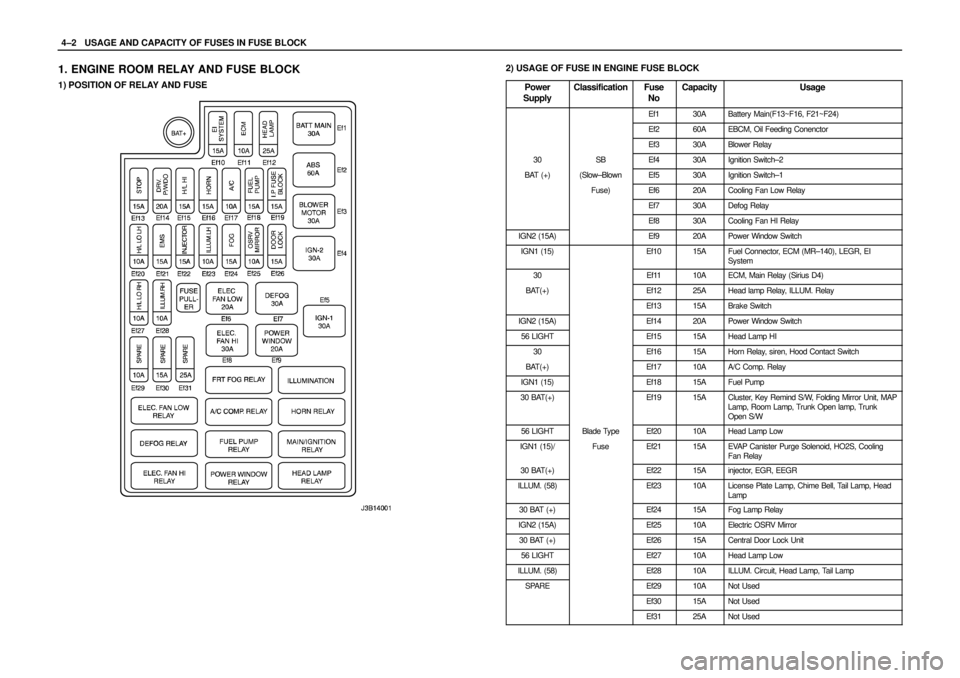

4–2WUSAGE AND CAPACITY OF FUSES IN FUSE BLOCK
1. ENGINE ROOM RELAY AND FUSE BLOCK
1) POSITION OF RELAY AND FUSE
2) USAGE OF FUSE IN ENGINE FUSE BLOCK
Power
Supply
ClassificationFuse
NoCapacityUsage
Ef130ABattery Main(F13~F16, F21~F24)
Ef260AEBCM, Oil Feeding Conenctor
Ef330ABlower Relay
30SBEf430AIgnition Switch–2
BAT (+)(Slow–BlownEf530AIgnition Switch–1
Fuse)Ef620ACooling Fan Low Relay
Ef730ADefog Relay
Ef830ACooling Fan HI Relay
IGN2 (15A)Ef920APower Window Switch
IGN1 (15)Ef1015AFuel Connector, ECM (MR–140), LEGR, EI
System
30Ef1110AECM, Main Relay (Sirius D4)
BAT(+)Ef1225AHead lamp Relay, ILLUM. Relay
Ef1315ABrake Switch
IGN2 (15A)Ef1420APower Window Switch
56 LIGHTEf1515AHead Lamp HI
30Ef1615AHorn Relay, siren, Hood Contact Switch
BAT(+)Ef1710AA/C Comp. Relay
IGN1 (15)Ef1815AFuel Pump
30 BAT(+)Ef1915ACluster, Key Remind S/W, Folding Mirror Unit, MAP
Lamp, Room Lamp, Trunk Open lamp, Trunk
Open S/W
56 LIGHTBlade TypeEf2010AHead Lamp Low
IGN1 (15)/FuseEf2115AEVAP Canister Purge Solenoid, HO2S, Cooling
Fan Relay
30 BAT(+)Ef2215Ainjector, EGR, EEGR
ILLUM. (58)Ef2310ALicense Plate Lamp, Chime Bell, Tail Lamp, Head
Lamp
30 BAT (+)Ef2415AFog Lamp Relay
IGN2 (15A)Ef2510AElectric OSRV Mirror
30 BAT (+)Ef2615ACentral Door Lock Unit
56 LIGHTEf2710AHead Lamp Low
ILLUM. (58)Ef2810AILLUM. Circuit, Head Lamp, Tail Lamp
SPAREEf2910ANot Used
Ef3015ANot Used
Ef3125ANot Used
Page 1016 of 2643
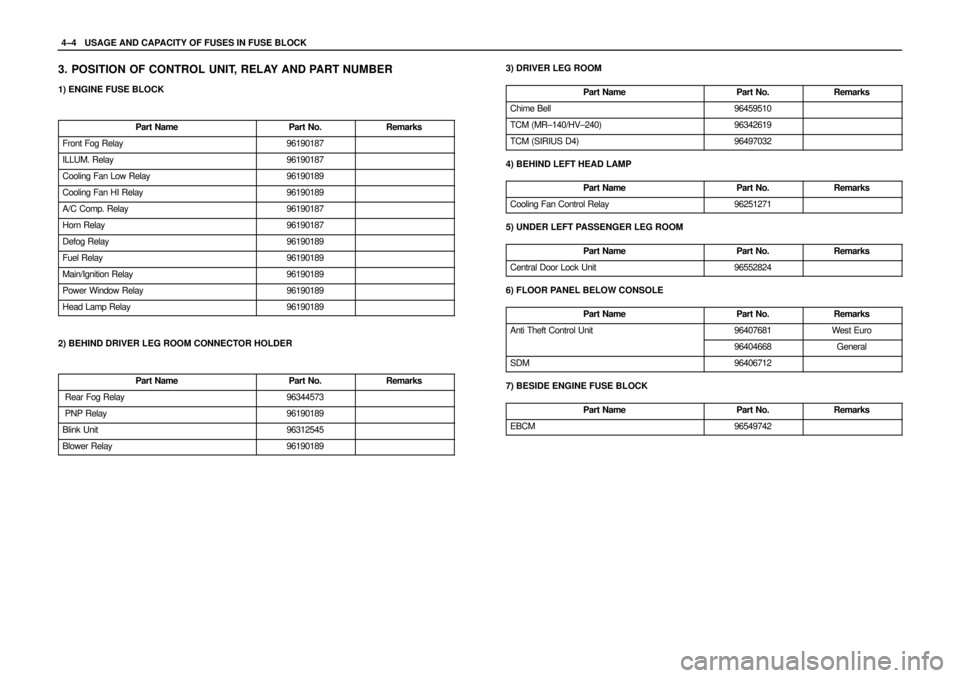

4–4WUSAGE AND CAPACITY OF FUSES IN FUSE BLOCK
3. POSITION OF CONTROL UNIT, RELAY AND PART NUMBER
1) ENGINE FUSE BLOCK
Part Name
Part No.Remarks
Front Fog Relay96190187
ILLUM. Relay96190187
Cooling Fan Low Relay96190189
Cooling Fan HI Relay96190189
A/C Comp. Relay96190187
Horn Relay96190187
Defog Relay96190189
Fuel Relay96190189
Main/Ignition Relay96190189
Power Window Relay96190189
Head Lamp Relay96190189
2) BEHIND DRIVER LEG ROOM CONNECTOR HOLDER
Part Name
Part No.Remarks
Rear Fog Relay96344573
PNP Relay96190189
Blink Unit96312545
Blower Relay96190189
3) DRIVER LEG ROOM
Part Name
Part No.Remarks
Chime Bell96459510
TCM (MR–140/HV–240)96342619
TCM (SIRIUS D4)96497032
4) BEHIND LEFT HEAD LAMP
Part Name
Part No.Remarks
Cooling Fan Control Relay96251271
5) UNDER LEFT PASSENGER LEG ROOM
Part Name
Part No.Remarks
Central Door Lock Unit96552824
6) FLOOR PANEL BELOW CONSOLE
Part Name
Part No.Remarks
Anti Theft Control Unit96407681Wes t Euro
96404668General
SDM96406712
7) BESIDE ENGINE FUSE BLOCK
Part Name
Part No.Remarks
EBCM96549742
Page 1018 of 2643
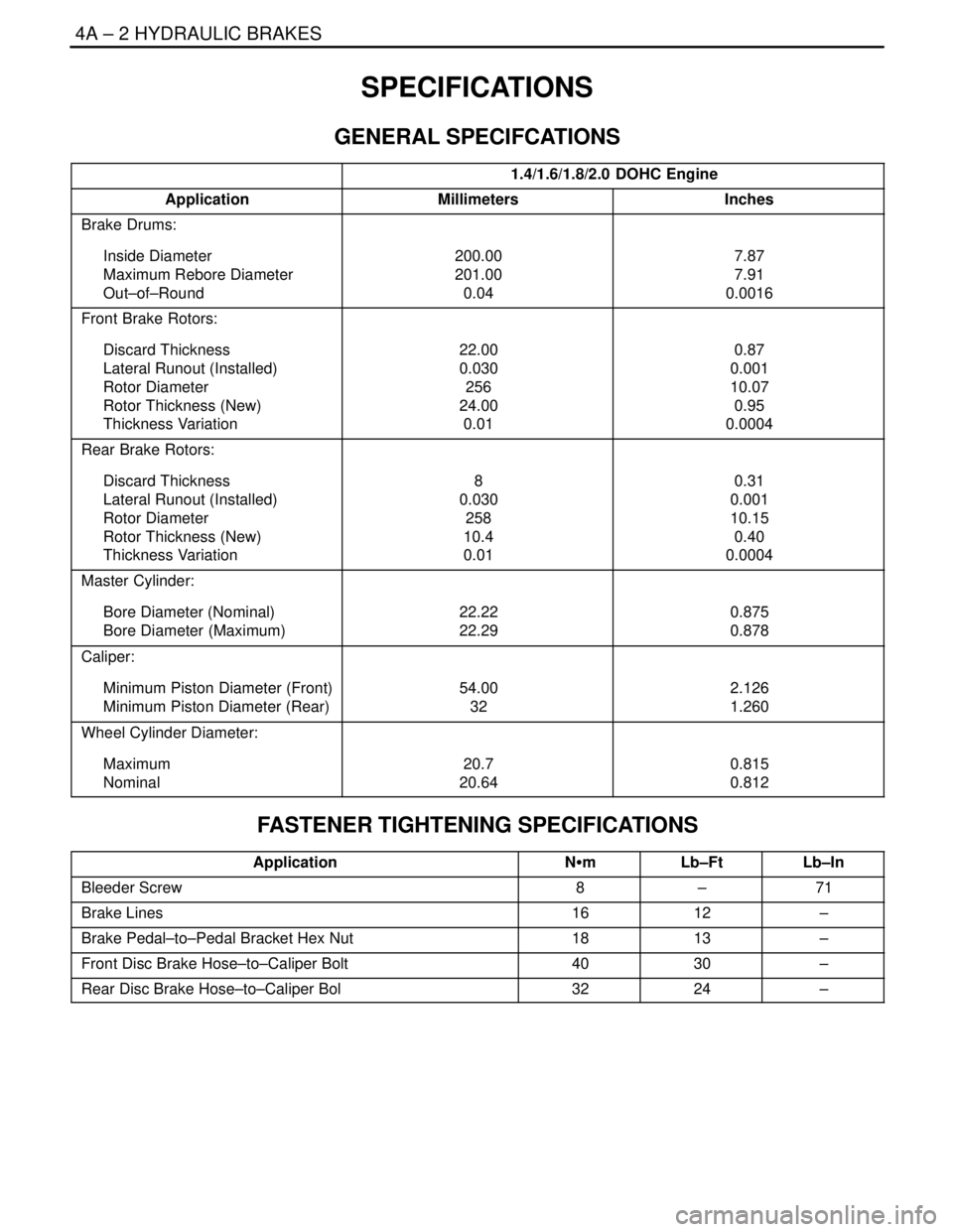
4A – 2IHYDRAULIC BRAKES
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL SPECIFCATIONS
1.4/1.6/1.8/2.0 DOHC Engine
ApplicationMillimetersInches
Brake Drums:
Inside Diameter
Maximum Rebore Diameter
Out–of–Round200.00
201.00
0.047.87
7.91
0.0016
Front Brake Rotors:
Discard Thickness
Lateral Runout (Installed)
Rotor Diameter
Rotor Thickness (New)
Thickness Variation22.00
0.030
256
24.00
0.010.87
0.001
10.07
0.95
0.0004
Rear Brake Rotors:
Discard Thickness
Lateral Runout (Installed)
Rotor Diameter
Rotor Thickness (New)
Thickness Variation8
0.030
258
10.4
0.010.31
0.001
10.15
0.40
0.0004
Master Cylinder:
Bore Diameter (Nominal)
Bore Diameter (Maximum)22.22
22.290.875
0.878
Caliper:
Minimum Piston Diameter (Front)
Minimum Piston Diameter (Rear)54.00
322.126
1.260
Wheel Cylinder Diameter:
Maximum
Nominal20.7
20.640.815
0.812
FASTENER TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationNSmLb–FtLb–In
Bleeder Screw8–71
Brake Lines1612–
Brake Pedal–to–Pedal Bracket Hex Nut1813–
Front Disc Brake Hose–to–Caliper Bolt4030–
Rear Disc Brake Hose–to–Caliper Bol3224–
Page 1021 of 2643

HYDRAULIC BRAKES 4A – 5
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSIS
BRAKE SYSTEM TESTING
Brakes should be tested on a dry, clean, reasonably
smooth and level roadway. A true test of brake perfor-
mance cannot be made if the roadway is wet, greasy, or
covered with loose dirt whereby all tires do not grip the
road equally. Testing will also be adversely affected if the
roadway is crowned so as to throw the weight so roughly
that the wheels tend to bounce.
Test the brakes at different vehicle speeds with both light
and heavy pedal pressure; however, avoid locking the
brakes and sliding the tires. Locked brakes and sliding
tires do not indicate brake efficiency since heavily braked,
but turning, wheels will stop the vehicle in less distance
than locked brakes. More tire–to–road friction is present
with a heavily–braked, turning tire than with a sliding tire.
Because of the high deceleration capability, a firmer pedal
may be felt at higher deceleration levels.
There are three major external conditions that affect brake
performance:
S Tires having unequal contact and grip of the road
will cause unequal braking. Tires must be equally
inflated, and the tread pattern of the right and the
left tires must be approximately equal.
S Unequal loading of the vehicle can affect the brake
performance since the most heavily loaded wheels
require more braking power, and thus more braking
effort, than the others.
S Misalignment of the wheels, particularly conditions
of excessive camber and caster, will cause the
brakes to pull to one side.
To check for brake fluid leaks, hold constant foot pressure
on the pedal with the engine running at idle and the shift
lever in NEUTRAL. If the pedal gradually falls away with
the constant pressure, the hydraulic system may be leak-
ing. Perform a visual check to confirm any suspected
leaks.
Check the master cylinder fluid level. While a slight drop
in the reservoir level results from normal lining wear, an ab-
normally low level indicates a leak in the system. The hy-
draulic system may be leaking either internally or external-
ly. Refer to the procedure below to check the master
cylinder. Also, the system may appear to pass this test
while still having a slight leak. If the fluid level is normal,
check the vacuum booster pushrod length. If an incorrect
pushrod length is found, adjust or replace the rod.
Check the master cylinder using the following procedure:
S Check for a cracked master cylinder casting or
brake fluid leaking around the master cylinder.
Leaks are indicated only if there is at least one drop
of fluid. A damp condition is not abnormal.S Check for a binding pedal linkage and for an incor-
rect pushrod length. If both of these parts are in
satisfactory condition, disassemble the master cyl-
inder and check for an elongated or swollen primary
cylinder or piston seals. If swollen seals are found,
substandard or contaminated brake fluid should be
suspected. If contaminated brake fluid is found, all
the components should be disassembled and
cleaned, and all the rubber components should be
replaced. All of the pipes must also be flushed.
Improper brake fluid, or mineral oil or water in the fluid,
may cause the brake fluid to boil or cause deterioration of
the rubber components. If the primary piston cups in the
master cylinder are swollen, then the rubber parts have
deteriorated. This deterioration may also be evidenced by
swollen wheel cylinder piston seals on the drum brake
wheels.
If deterioration of rubber is evident, disassemble all the hy-
draulic parts and wash the parts with alcohol. Dry these
parts with compressed air before reassembly to keep alco-
hol out of the system. Replace all the rubber parts in the
system, including the hoses. Also, when working on the
brake mechanisms, check for fluid on the linings. If exces-
sive fluid is found, replace the linings.
If the master cylinder piston seals are in satisfactory condi-
tion, check for leaks or excessive heat conditions. If these
conditions are not found, drain the fluid, flush the master
cylinder with brake fluid, refill the master cylinder, and
bleed the system. Refer to ”Manual Bleeding the Brakes”
or”Pressure Bleeding the Brakes” in this section.
BRAKE HOSE INSPECTION
The hydraulic brake hoses should be inspected at least
twice a year. The brake hose assembly should be checked
for road hazard damage, cracks, chafing of the outer cov-
er, and for leaks or blisters. Inspect the hoses for proper
routing and mounting. A brake hose that rubs on a suspen-
sion component will wear and eventually fail. A light and
a mirror may be needed for an adequate inspection. If any
of the above conditions are observed on the brake hose,
adjust or replace the hose as necessary.
WARNING LAMP OPERATION
This brake system uses a BRAKE warning lamp located
in the instrument panel cluster. When the ignition switch
is in the START position, the BRAKE warning lamp should
glow and go OFF when the ignition switch returns to the
RUN position.
The following conditions will activate the BRAKE lamp:
S Parking brake applied. The light should be ON
whenever the parking brake is applied and the igni-
tion switch is ON.
S Low fluid level. A low fluid level in the master cylin-
der will turn the BRAKE lamp ON.
S EBD system is disabled. The light should be ON
when the EBD system is malfunctioning.