coolant level DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: NUBIRA, Model: DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 17 of 2643
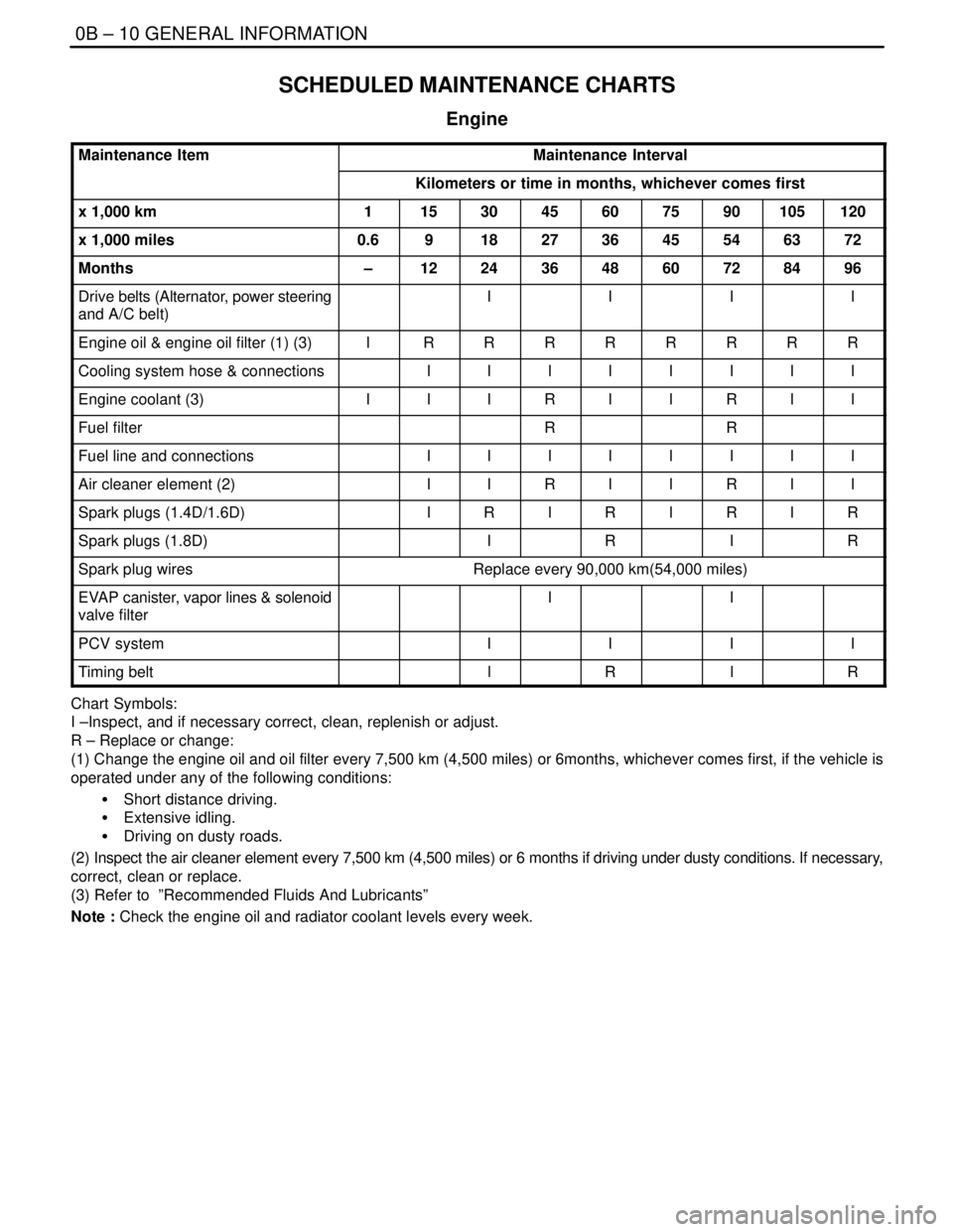
0B – 10IGENERAL INFORMATION
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE CHARTS
Engine
Maintenance ItemMaintenance Interval
Kilometers or time in months, whichever comes first
x 1,000 km1153045607590105120
x 1,000 miles0.6918273645546372
Months–1224364860728496
Drive belts (Alternator, power steering
and A/C belt)IIII
Engine oil & engine oil filter (1) (3)IRRRRRRRR
Cooling system hose & connectionsIIIIIIII
Engine coolant (3)IIIRIIRII
Fuel filterRR
Fuel line and connectionsIIIIIIII
Air cleaner element (2)IIRIIRII
Spark plugs (1.4D/1.6D)IRIRIRIR
Spark plugs (1.8D)IRIR
Spark plug wiresReplace every 90,000 km(54,000 miles)
EVAP canister, vapor lines & solenoid
valve filterII
PCV systemIIII
Timing beltlRlR
Chart Symbols:
I –Inspect, and if necessary correct, clean, replenish or adjust.
R – Replace or change:
(1) Change the engine oil and oil filter every 7,500 km (4,500 miles) or 6months, whichever comes first, if the vehicle is
operated under any of the following conditions:
S Short distance driving.
S Extensive idling.
S Driving on dusty roads.
(2) Inspect the air cleaner element every 7,500 km (4,500 miles) or 6 months if driving under dusty conditions. If necessary,
correct, clean or replace.
(3) Refer to ”Recommended Fluids And Lubricants”
Note : Check the engine oil and radiator coolant levels every week.
Page 19 of 2643

0B – 12IGENERAL INFORMATION
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
OWNER INSPECTIONS AND SERVICES
WHLE OPERATING THE VEHICLE
Horn Operation
Blow the horn occasionally tomake sure it works. Check
all the button locations.
Brake System Operation
Be alert for abnormal sounds, increased brake pedal trav-
el or repeated pulling to one side when braking. Also, if the
brake warning light goes on, or flashes, something may be
wrong with part of the brake system.
Exhaust System Operation
Be alert to any changes in the sound of the system or the
smell of the fumes. These are signs that the system may
be leaking or overheating. Have the system inspected and
repaired immediately.
Tires,Wheels and Alignment Operation
Be alert to any vibration of the steering wheel or the seats
at normal highway speeds. This may mean a wheel needs
to be balanced. Also, a pull right or left on a straight, level
road may show the need for a tire pressure adjustment or
a wheel alignment.
Steering System Operation
Be alert to changes in the steering action. An inspection
is needed when the steering wheel is hard to turn or has
too much free play, or if unusual sounds are noticed when
turning or parking.
Headlight Aim
Take note of the light pattern occasionally. Adjust the
headlights if the beams seem improperly aimed.
AT EACH FUEL FILL
A fluid loss in any (except windshield washer) system may
indicate a problem. Have the system inspected and re-
paired immediately.
Engine Oil Level
Check the oil level and add oil if necessary. The best time
to check the engine oil level is when the oil is warm.
1. After stopping the engine, wait a few minutes for
the oil to drain back to the oil pan.
2. Pull out the oil level indicator (dip stick).
3. Wipe it clean, and push the oil level indicator back
down all the way.
4. Pull out the oil level indicator and look at the oil lev-
el on it.
5. Add oil, if needed, to keep the oil level above the
MIN line and within the area labeled ”Operating
Range.” Avoid overfilling the engine, since this may
cause engine damage.
6. Push the indicator all the way back down into the
engine after taking the reading.If you check the oil level when the oil is cold, do not run the
engine first. The cold oil will not drain back to the pan fast
enough to give a true oil level reading.
Engine Coolant Level and Condition
Check the coolant level in the coolant reservoir tank and
add coolant if necessary. Inspect the coolant. Replace
dirty or rusty coolant.
Windshield Washer Fluid Level
Check the washer fluid level in the reservoir. Add fluid if
necessary.
AT LEAST MONTHLY
Tire And Wheel Inspection and Pressure
Check
Check the tires for abnormal wear or damage. Also check
for damaged wheels. Check the tire pressure when the
tires are cold (check the spare also, unless it is a stow-
away). Maintain the recommended pressures that are on
the tire placard that is in the glove box.
Light Operation
Check the operation of the license plate light, the head-
lights (including the high beams), the parking lights, the
fog lights, the taillight, the brake lights, the turn signals, the
backup lights and the hazard warning flasher.
Fluid Leak Check
Periodically inspect the surface beneath the vehicle for
water, oil, fuel or other fluids, after the vehicle has been
parked for a while. Water dripping from the air conditioning
system after use is normal. If you notice fuel leaks or
fumes, find the cause and correct it at once.
AT LEAST TWICE A YEAR
Power Steering System Reservoir Level
Check the power steering fluid level. Keep the power
steering fluid at the proper level. Refer to Section 6A, Pow-
er Steering System.
Brake Master Cylinder Reservoir Level
Check the fluid and keep it at the proper level. A low fluid
level can indicate worn disc brake pads which may need
to be serviced. Check the breather hole in the reservoir
cover to be free from dirt and check for an open passage.
Clutch Pedal Free Travel
Check clutch pedal free travel and adjust as necessary.
Measure the distance from the center of the clutch pedal
to the outer edge of the steering wheel with the clutch ped-
al not depressed. Then measure the distance from the
center of the clutch pedal to the outer edge of the steering
wheel with the clutch pedal fully depressed. The difference
between the two values must be greater than 130 mm
(5.19 inches).
Weather–Strip Lubrication
Apply a thin film silicone grease using a clean cloth.
Page 199 of 2643
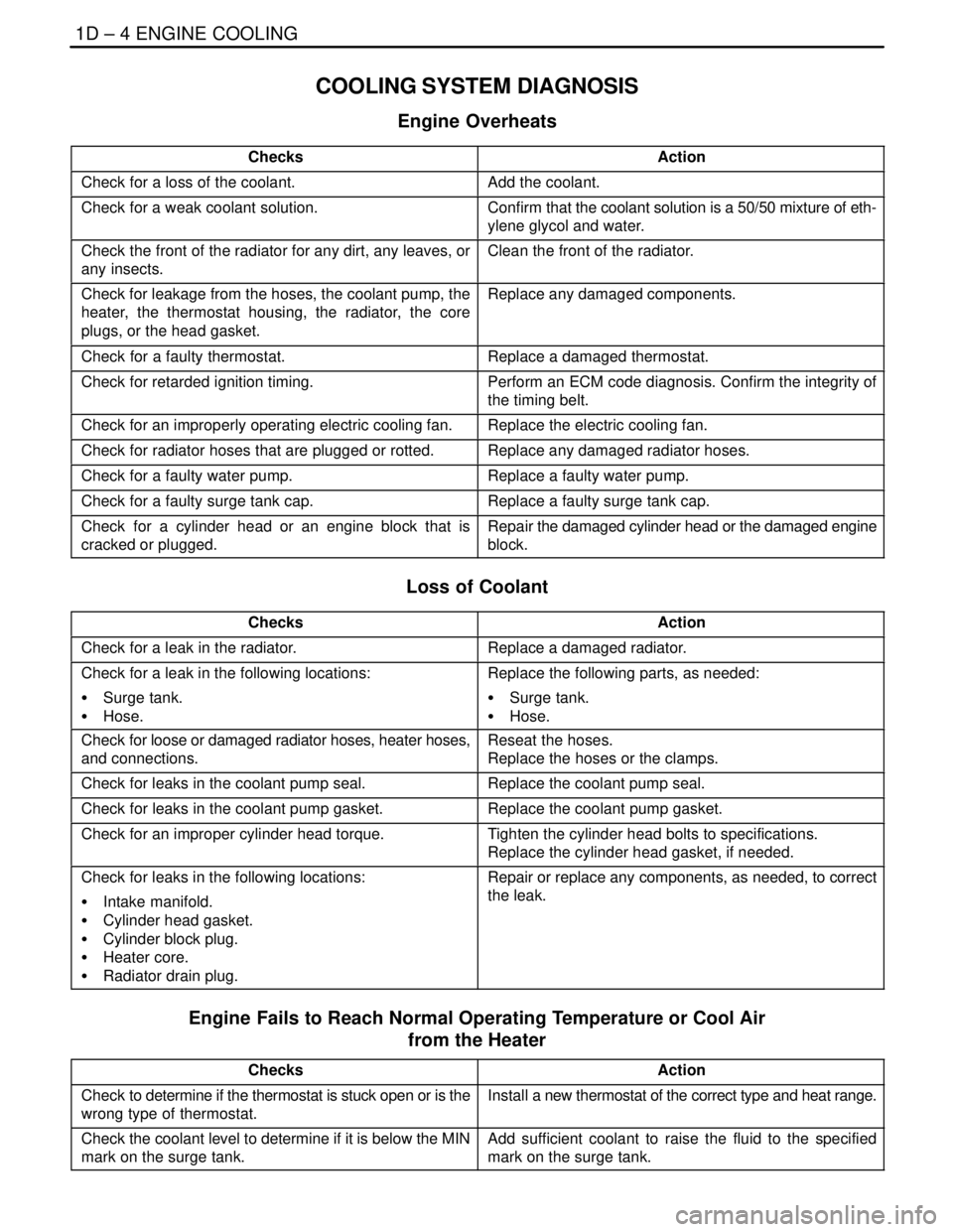
1D – 4IENGINE COOLING
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
Engine Overheats
ChecksAction
Check for a loss of the coolant.Add the coolant.
Check for a weak coolant solution.Confirm that the coolant solution is a 50/50 mixture of eth-
ylene glycol and water.
Check the front of the radiator for any dirt, any leaves, or
any insects.Clean the front of the radiator.
Check for leakage from the hoses, the coolant pump, the
heater, the thermostat housing, the radiator, the core
plugs, or the head gasket.Replace any damaged components.
Check for a faulty thermostat.Replace a damaged thermostat.
Check for retarded ignition timing.Perform an ECM code diagnosis. Confirm the integrity of
the timing belt.
Check for an improperly operating electric cooling fan.Replace the electric cooling fan.
Check for radiator hoses that are plugged or rotted.Replace any damaged radiator hoses.
Check for a faulty water pump.Replace a faulty water pump.
Check for a faulty surge tank cap.Replace a faulty surge tank cap.
Check for a cylinder head or an engine block that is
cracked or plugged.Repair the damaged cylinder head or the damaged engine
block.
Loss of Coolant
ChecksAction
Check for a leak in the radiator.Replace a damaged radiator.
Check for a leak in the following locations:
S Surge tank.
S Hose.Replace the following parts, as needed:
S Surge tank.
S Hose.
Check for loose or damaged radiator hoses, heater hoses,
and connections.Reseat the hoses.
Replace the hoses or the clamps.
Check for leaks in the coolant pump seal.Replace the coolant pump seal.
Check for leaks in the coolant pump gasket.Replace the coolant pump gasket.
Check for an improper cylinder head torque.Tighten the cylinder head bolts to specifications.
Replace the cylinder head gasket, if needed.
Check for leaks in the following locations:
S Intake manifold.
S Cylinder head gasket.
S Cylinder block plug.
S Heater core.
S Radiator drain plug.Repair or replace any components, as needed, to correct
the leak.
Engine Fails to Reach Normal Operating Temperature or Cool Air
from the Heater
ChecksAction
Check to determine if the thermostat is stuck open or is the
wrong type of thermostat.Install a new thermostat of the correct type and heat range.
Check the coolant level to determine if it is below the MIN
mark on the surge tank.Add sufficient coolant to raise the fluid to the specified
mark on the surge tank.
Page 209 of 2643

1D – 14IENGINE COOLING
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Tighten
Tighten the fan motor retaining screws to 4 NSm (35
lb–in).
3. Turn over the fan shroud assembly.
4. Install the fan to the fan shroud assembly with the
single nut in the center of the fan hub.
Tighten
Tighten the fan motor nut to 3.2 NSm (28 lb–in).
5. Install the fan shroud assembly to the radiator.
Important : Be careful to seat the mounting post on the
fan shroud into the socket at the radiator left tank. Be sure
to slip the tab at the bottom edge of the shroud into the re-
taining clip near the center of the radiator.
6. Secure the shroud to the top of the radiator with the
mounting bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the fan assembly mounting bolts to 4 NSm (35
lb–in).
7. Connect the cooling fan electrical connector.
8. Connect the negative battery cable.
SURGE TANK
Removal Procedure
CAUTION : To prevent personal injury, do not remove
the surge tank cap while the engine and the radiator
are hot, because the heat causes the system to re-
main under pressure. Scalding fluid and steam may
be blown out under pressure.
1. Drain the engine coolant to below the level of the
surge tank.
2. Loosen the return hose clamp and disconnect the
return hose from the top of the surge tank.
Page 213 of 2643

1D – 18IENGINE COOLING
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The cooling system maintains the engine temperature at
an efficient level during all engine operating conditions.
When the engine is cold, the cooling system cools the en-
gine slowly or not at all. This slow cooling of the engine al-
lows the engine to warm up quickly.
The cooling system includes a radiator and recovery sub-
system, cooling fans, a thermostat and housing, a coolant
pump, and a coolant pump drive belt. The timing belt
drives the coolant pump.
All components must function properly in order for the
cooling system to operate. The coolant pump draws the
coolant from the radiator. The coolant then circulates
through water jackets in the engine block, the intake man-
ifold, and the cylinder head. When the coolant reaches the
operating temperature of the thermostat, the thermostat
opens. The coolant then goes back to the radiator where
it cools.
This system directs some coolant through the hoses to the
heater core. This provides for heating and defrosting. The
surge tank is connected to the radiator to recover the cool-
ant displaced by expansion from the high temperatures.
The surge tank maintains the correct coolant level.
The cooling system for this vehicle has no radiator cap or
filler neck. The coolant is added to the cooling system
through the surge tank.
RADIATOR
This vehicle has a lightweight tube–and–fin aluminum ra-
diator. Plastic tanks are mounted on the right and the left
sides of the radiator core.
On vehicles equipped with automatic transaxles, the
transaxle fluid cooler lines run through the left radiator
tank. A radiator drain cock is on this radiator.
To drain the cooling system, open the drain cock.
SURGE TANK
The surge tank is a transparent plastic reservoir, similar to
the windshield washer reservoir.
The surge tank is connected to the radiator by a hose and
to the engine cooling system by another hose. As the ve-
hicle is driven, the engine coolant heats and expands. The
portion of the engine coolant displaced by this expansion
flows from the radiator and the engine into the surge tank.
The air trapped in the radiator and the engine is degassed
into the surge tank.When the engine stops, the engine coolant cools and con-
tracts. The displaced engine coolant is then drawn back
into the radiator and the engine. This keeps the radiator
filled with the coolant to the desired level at all times and
increases the cooling efficiency.
Maintain the coolant level between the MIN and the MAX
marks on the surge tank when the system is cold.
WATER PUMP
The belt–driven centrifugal water pump consists of an im-
peller, a drive shaft, and a belt pulley. The water pump is
mounted on the front of the transverse–mounted engine,
and is driven by the timing belt.
The impeller is supported by a completely sealed bearing.
The water pump is serviced as an assembly and, there-
fore, cannot be disassembled.
THERMOSTAT
A wax pellet–type thermostat controls the flow of the en-
gine coolant through the engine cooling system. The ther-
mostat is mounted in the thermostat housing to the front
of the cylinder head.
The thermostat stops the flow of the engine coolant from
the engine to the radiator in order to provide faster warm–
up, and to regulate the coolant temperature. The thermo-
stat remains closed while the engine coolant is cold, pre-
venting circulation of the engine coolant through the
radiator. At this point, the engine coolant is allowed to cir-
culate only throughout the heater core to warm it quickly
and evenly.
As the engine warms, the thermostat opens. This allows
the engine coolant to flow through the radiator, where the
heat is dissipated through the radiator. This opening and
closing of the thermostat permits enough engine coolant
to enter the radiator to keep the engine within proper en-
gine temperature operating limits.
The wax pellet in the thermostat is hermetically sealed in
a metal case. The wax element of the thermostat expands
when it is heated and contracts when it is cooled.
As the vehicle is driven and the engine warms, the engine
coolant temperature increases. When the engine coolant
reaches a specified temperature, the wax pellet element
in the thermostat expands and exerts pressure against the
metal case, forcing the valve open. This allows the engine
coolant to flow through the engine cooling system and cool
the engine.
As the wax pellet cools, the contraction allows a spring to
close the valve.
The thermostat begins to open at 87°C (189°F) and is fully
open at 102°C (216°F). The thermostat closes at 86°C
(187°F).
Page 248 of 2643

1F – 2IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–111. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clearing Trouble Codes 1F–111. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (1.4L/1.6L DOHC) 1F–111.
DTC P0107 Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Low Voltage 1F–114. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0108 Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
High Voltage 1F–117. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0112 Intake Air Temperature Sensor Low
Voltage 1F–120. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0113 Intake Air Temperature Sensor High
Voltage 1F–122. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0117 Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor Low Voltage 1F–125. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0118 Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor High Voltage 1F–128. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0122 Throttle Position Sensor Low
Voltage 1F–131. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0123 Throttle Position Sensor High
Voltage 1F–134. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0131 Front Heated Oxygen Sensor Low
Voltage 1F–137. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0132 Front Heated Oxygen Sensor High
Voltage 1F–140. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0133 Front Heated Oxygen Sensor No
Activity 1F–142. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0135 Front Heated Oxygen Sensor Heater
Circuit Not Functioning 1F–145. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0137 Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor Low
Voltage 1F–148. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0138 Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor High
Voltage 1F–151. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0140 Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor No
Activity 1F–153. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0141 Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor Heater
Malfunction 1F–156. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0171 Fuel Trim System Too Lean 1F–158. . . .
DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Too Rich 1F–162. . . . .
DTC P0222 Main Throttle Idle Actuator (MTIA)
Low Voltage 1F–165. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0223 Main Throttle Idle Actuator (MTIA)
High Voltage 1F–168. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0261 Injector 1 Low Voltage 1F–171. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0262 Injector 1 High Voltage 1F–173. . . . . . . .
DTC P0264 Injector 2 Low Voltage 1F–175. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0265 Injector 2 High Voltage 1F–177. . . . . . . .
DTC P0267 Injector 3 Low Voltage 1F–179. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0268 Injector 3 High Voltage 1F–181. . . . . . . .
DTC P0270 Injector 4 Low Voltage 1F–183. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0271 Injector 4 High Voltage 1F–185. . . . . . . . DTC P0300 Multiple Cylinder Misfire(Catalyst
Damage) 1F–188. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0300 Multiple Cylinder Misfire(Increase
Emission) 1F–192. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0327 Knock Sensor Circuit Fault
(1.4L DOHC) 1F–195. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0327 Knock Sensor Circuit Fault
(1.6L DOHC) 1F–198. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0335 Magnetic Crankshaft Position
Sensor Electrical Error 1F–201. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0336 58X Crankshaft Position Sensor
No Plausible Signal 1F–204. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0337 58X Crankshaft Position Sensor
No Signal 1F–207. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0341 Camshaft Position Sensor
Rationality 1F–210. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0342 Camshaft Position Sensor Signal 1F–212
DTC P0351 Ignition Signal Coil A Fault 1F–214. . . . .
DTC P0352 Ignition Signal Coil B Fault 1F–216. . . . .
DTC P0400 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Out
Of Limit 1F–218. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0404 Exhaust Gas Recirculation
Opened 1F–221. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0405 EGR Pintle Position Sensor Low
Voltage 1F–224. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0406 EGR Pintle Position Sensor High
Voltage 1F–227. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0420 Catalyst Low Efficiency 1F–230. . . . . . . .
DTC P0444 EVAP Purge Control Circuit No
Signal 1F–232. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0445 EVAP Purge Control Circuit Fault 1F–235
DTC P0462 Fuel Level Sensor Low Voltage
(1.6L DOHC Only) 1F–238. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0463 Fuel Level Sensor High Voltage
(1.6L DOHC Only) 1F–241. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0480 Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay
Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC) 1F–245. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0480 Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay
Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC) 1F–248. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0481 High Speed Cooling Fan Relay
Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC) 1F–251. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0481 High Speed Cooling Fan Relay
Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC) 1F–254. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0501 Vehicle Speed No Signal
(M/T Only) 1F–257. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0510 Throttle Position Switch Circuit Fault
(1.4L DOHC) 1F–260. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0510 Throttle Position Switch Circuit
Fault (1.6L DOHC) 1F–262. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0532 A/C Pressure Sensor Low Voltage 1F–264
DTC P0533 A/C Pressure Sensor High
Voltage 1F–267. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 249 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 3
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P0562 System Voltage(Engine Side) Too
Low 1F–270. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0563 System Voltage(Engine Side) Too
High 1F–272. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0601 Engine Control Module Checksum
Error 1F–274. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0604 Engine Control Module Internal/External
RAM Error 1F–275. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0605 Engine Control Module INMVY Write
Error 1F–276. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0656 Fuel Level Gauge Circuit Fault 1F–277. .
DTC P1181 Variable Intake Manifold Solenoid
Low Voltage 1F–279. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1182 Variable Intake Manifold Solenoid
High Voltage 1F–281. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1230 Fuel Pump Relay Low Voltage
(1.4L DOHC) 1F–283. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1230 Fuel Pump Relay Low Voltage
(1.6L DOHC) 1F–286. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1231 Fuel Pump Relay High Voltage
(1.4L DOHC) 1F–289. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1231 Fuel Pump Relay High Voltage
(1.6L DOHC) 1F–292. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1320 Crankshaft Segment Period
Segment Adaptation At Limit 1F–295. . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1321 Crankshaft Segment Period Tooth
Error 1F–297. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1382 Rough Road Data Invalid
(NON ABS) 1F–299. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1382 Rough Road Data Invalid (ABS) 1F–302
DTC P1385 Rough Road Sensor Circuit Fault
(NON ABS) 1F–305. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1402 Exhaust Gas Recirculation
Blocked 1F–308. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1403 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve
Failure 1F–310. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1404 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Closed1F–313
DTC P1511 Idle Charge Actuator Circuit Fault 1F–316
DTC P1512 Idle Charge Actuator Mechanical
Error 1F–319. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1513 Idle Charge Actuator Functional
Error 1F–321. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1537 A/C Compressor Relay High
Voltage 1F–324. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1538 A/C Compressor Relay Low
Voltage 1F–326. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1610 Main Relay High Voltage
(1.4L DOCH) 1F–328. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1610 Main Relay High Voltage
(1.6L DOHC) 1F–330. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1611 Main Relay Low Voltage
(1.4L DOHC) 1F–332. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . DTC P1611 Main Relay Low Voltage
(1.6L DOHC) 1F–334. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1628 Immobilizer No Successful
Communication 1F–336. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1629 Immobilizer Wrong Computation 1F–338
DTC P1660 Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
High Voltage 1F–340. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1661 Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
Low Voltage 1F–342. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS (1.8L DOHC) 1F–344.
Clearing Trouble Codes 1F–344. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (1.8L DOHC) 1F–344. . . .
DTC P0106 Manifold Absolute Pressure
Rationality 1F–347. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0107 Manifold Absolut Pressure Low
Voltage 1F–349. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0108 Manifold Absolut Pressure High
Voltage 1F–352. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0112 Intake Air Temperature Low
Voltage 1F–355. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0113 Intake Air Temperature High
Voltage 1F–358. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0117 Engine Coolant Temperature Low
Voltage 1F–361. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0118 Engine Coolant Temperature High
Voltage 1F–363. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0122 Throttle Position Sensor Low
Voltage 1F–366. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0123 Throttle Position Sensor High
Voltage 1F–369. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0131 Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1) Low Voltage 1F–372. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0132 Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1) High Voltage 1F–375. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0133 Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1) Slow Response 1F–378. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0134 Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1) No Activity or Open 1F–382. . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0135 Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1) Heater Circuit Not Functioning 1F–385. . .
DTC P0137 Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2) Low Voltage 1F–388. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0138 Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2) High Voltage 1F–391. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0140 Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2) No Activity or Open 1F–394. . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0141 Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2) Heater Circuit Not Functioning 1F–397. . .
DTC P0171 Fuel Trim System Too Lean 1F–400. . . .
DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Too Rich 1F–404. . . . .
DTC P0201 Injector 1 Circuit Fault 1F–408. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0202 Injector 2 Circuit Fault 1F–411. . . . . . . . .
Page 250 of 2643

1F – 4IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P0203 Injector 3 Circuit Fault 1F–414. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0204 Injector 4 Circuit Fault 1F–417. . . . . . . . .
DTC P0300 Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected 1F–421
DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire 1F–426. . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire 1F–431. . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire 1F–436. . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0304 Cylinder 4 Misfire 1F–441. . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0317 Rough Road Sensor Source Not
Detected 1F–445. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0325 Knock Sensor Internal
Malfunction 1F–447. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0327 Knock Sensor Circuit Fault 1F–449. . . . .
DTC P0336 58X Crank Position Extra/Missing
Pulses 1F–452. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0337 58X Crank Position Sensor No
Signal 1F–455. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0341 Camshaft Position Sensor
Rationality 1F–458. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0342 Camshaft Position Sensor No
Signal 1F–461. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0351 Ignition Control Circuit A Fault
(Cylinder 1 and 4) 1F–464. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0352 Ignition Control Circuit B Fault
(Cylinder 2 and 3) 1F–466. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0401 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Insufficient
Flow 1F–468. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0402 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Excessive
Flow 1F–470. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0404 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Open
Valve Position Error 1F–474. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0405 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Pintle
Position Low Voltage 1F–478. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0406 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Pintle
Position High Voltage 1F–481. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0420 Catalyst Oxygen Sensor Low
Efficiency 1F–484. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0443 Evaporative Emission System Purge
Solenoid Control Circuit 1F–486. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0461 Fuel Level Struck 1F–489. . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0462 Fuel Level Low Voltage 1F–492. . . . . . . .
DTC P0463 Fuel Level High Voltage 1F–495. . . . . . .
DTC P0502 Vehicle Speed Sensor No Signal
(Engine Side) 1F–498. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0506 Idle Speed RPM Lower Than Desired
Idle Speed 1F–501. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0507 Idle Speed RPM Higher Than Desired
Idle Speed 1F–504. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0532 A/C Pressure Sensor Low Voltage 1F–507
DTC P0533 A/C Pressure Sensor High
Voltage 1F–510. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . DTC P0562 System Voltage Too Low
(Engine Side) 1F–513. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0563 System Voltage Too High
(Engine Side) 1F–515. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0601 ECM Checksum Fault
(Engine Side) 1F–517. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0602 ECM Reprogrom Error 1F–518. . . . . . . .
DTC P0607 Lower Power Counter Error 1F–519. . . .
DTC P0700 Transaxle Control Module
Malfunction 1F–520. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1106 Manifold Abosolute Pressure
Intermittent High Voltage 1F–522. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1107 Manifold Abosolute Pressure
Intermittent Low Voltage 1F–524. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1111 Intake Air Temperature Intermittent
High Voltage 1F–526. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1112 Intake Air Temperature Intermittent
Low Voltage 1F–529. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1114 Engine Coolant Temperature
Intermittent Low Voltage 1F–531. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1115 Engine Coolant Temperature
Intermittent High Voltage 1F–533. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1121 Throttle Position Sensor Intermittent
High Voltage 1F–535. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1122 Throttle Position Sensor Intermittent
Low Voltage 1F–537. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1133 Front Heated Oxyzen Sensor
(HO2S1) Too Few Transitions 1F–539. . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1134 Front Heated Oxyzen Sensor
(HO2S1) Transitions Ratio 1F–543. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1167 Front Heated Oxyzen Sensor
(HO2S1) Rich in Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) 1F–546
DTC P1171 Fuel Trim System Lean During Power
Enrichment 1F–548. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1336 58X Crank Position Tooth Error Not
Learned 1F–550. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1391 G Sensor Rough Road Rationality 1F–552
DTC P1392 G Sensor Rough Low Voltage 1F–555. .
DTC P1393 G Sensor Rough High Voltage 1F–558. .
DTC P1396 ABS WSS Signal Variation 1F–561. . . . .
DTC P1397 ABS WSS No Signal 1F–563. . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1404 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Closed
Valve Pintle Error 1F–565. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1601 SPI Communications Between
ECM and TCM 1F–568. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1607 Lower Power Counter Reset 1F–569. . .
DTC P1626 Immobilizer No Response 1F–570. . . . . .
DTC P1631 Immobilizer Invalid Response 1F–571. .
DTC P1650 SPI Communications Between Error
with SIDM Chip 1F–572. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1655 SPI Communications Between Error
with PSVI Chip 1F–573. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 253 of 2643
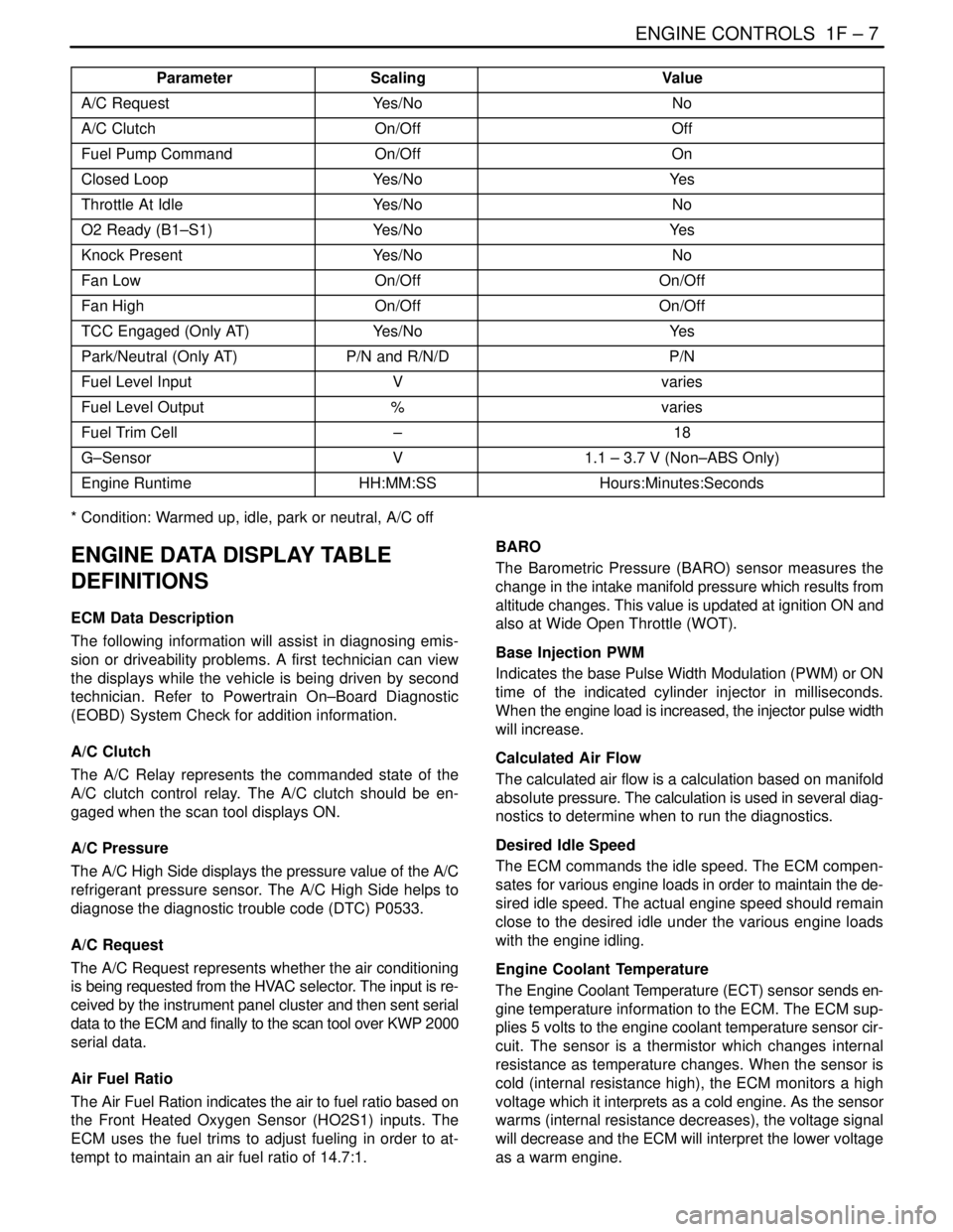
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 7
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Parameter ValueScaling
A/C RequestYes/NoNo
A/C ClutchOn/OffOff
Fuel Pump CommandOn/OffOn
Closed LoopYes/NoYe s
Throttle At IdleYes/NoNo
O2 Ready (B1–S1)Yes/NoYe s
Knock PresentYes/NoNo
Fan LowOn/OffOn/Off
Fan HighOn/OffOn/Off
TCC Engaged (Only AT)Yes/NoYe s
Park/Neutral (Only AT)P/N and R/N/DP/N
Fuel Level InputVvaries
Fuel Level Output%varies
Fuel Trim Cell–18
G–SensorV1.1 – 3.7 V (Non–ABS Only)
Engine RuntimeHH:MM:SSHours:Minutes:Seconds
* Condition: Warmed up, idle, park or neutral, A/C off
ENGINE DATA DISPLAY TABLE
DEFINITIONS
ECM Data Description
The following information will assist in diagnosing emis-
sion or driveability problems. A first technician can view
the displays while the vehicle is being driven by second
technician. Refer to Powertrain On–Board Diagnostic
(EOBD) System Check for addition information.
A/C Clutch
The A/C Relay represents the commanded state of the
A/C clutch control relay. The A/C clutch should be en-
gaged when the scan tool displays ON.
A/C Pressure
The A/C High Side displays the pressure value of the A/C
refrigerant pressure sensor. The A/C High Side helps to
diagnose the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0533.
A/C Request
The A/C Request represents whether the air conditioning
is being requested from the HVAC selector. The input is re-
ceived by the instrument panel cluster and then sent serial
data to the ECM and finally to the scan tool over KWP 2000
serial data.
Air Fuel Ratio
The Air Fuel Ration indicates the air to fuel ratio based on
the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) inputs. The
ECM uses the fuel trims to adjust fueling in order to at-
tempt to maintain an air fuel ratio of 14.7:1.BARO
The Barometric Pressure (BARO) sensor measures the
change in the intake manifold pressure which results from
altitude changes. This value is updated at ignition ON and
also at Wide Open Throttle (WOT).
Base Injection PWM
Indicates the base Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) or ON
time of the indicated cylinder injector in milliseconds.
When the engine load is increased, the injector pulse width
will increase.
Calculated Air Flow
The calculated air flow is a calculation based on manifold
absolute pressure. The calculation is used in several diag-
nostics to determine when to run the diagnostics.
Desired Idle Speed
The ECM commands the idle speed. The ECM compen-
sates for various engine loads in order to maintain the de-
sired idle speed. The actual engine speed should remain
close to the desired idle under the various engine loads
with the engine idling.
Engine Coolant Temperature
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor sends en-
gine temperature information to the ECM. The ECM sup-
plies 5 volts to the engine coolant temperature sensor cir-
cuit. The sensor is a thermistor which changes internal
resistance as temperature changes. When the sensor is
cold (internal resistance high), the ECM monitors a high
voltage which it interprets as a cold engine. As the sensor
warms (internal resistance decreases), the voltage signal
will decrease and the ECM will interpret the lower voltage
as a warm engine.
Page 254 of 2643

1F – 8IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
EGR Desired Position
The desired exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) position is
the commanded EGR position. The ECM calculates the
desired EGR position. The higher the percentage, the lon-
ger the ECM is commanding the EGR valve ON.
Engine Load
Indicates engine load based on manifold absolute pres-
sure. The higher the percentage, the more load the engine
is under.
Engine Run Time
The engine run time is a measure of how long the engine
has been running. When the engine stops running, the tim-
er resets to zero.
Engine Speed
Engine Speed is computed by the ECM from the fuel con-
trol reference input. It should remain close to desired idle
under the various engine loads with the engine idling.
Fan
The Fan Control (FC) Relay is commanded by the ECM.
The FC Relay displays the command as ON or OFF.
Fuel Level Sensor
The Fuel Level Sensor monitors the fuel level in the tank.
The Fuel Level Sensor monitors the rate of change of the
air pressure in the EVAP system. Several of the Enhanced
EVAP System diagnostics are dependent upon the correct
fuel level.
Fuel System Status
The Closed Loop is displayed indicating that the ECM is
controlling the fuel delivery according to the Front Heated
Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) voltage as close to an air/fuel ra-
tio of 14.7 to 1 as possible.
IAC Position
The scan tool displays the ECM command for the Idle Air
Control (IAC) pintle position in counts. The higher the
number of counts, the greater the commanded idle speed
reads. The Idle Air Control responds to changes in the en-
gine load in order to maintain the desired idle rpm.
Ignition 1 (Voltage)
The ignition volts represent the system voltage measured
by the ECM at the ignition feed circuit.
Intake Air Temperature
The ECM converts the resistance of the Intake Air Tem-
perature (IAT) sensor to degrees in the same manner as
the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor. In take air
temperature is used by the ECM to adjust fuel delivery and
spark timing according to incoming air density.Knock Present
The KS Noise Channel indicates when the ECM detects
the KS signal. The ECM should display NO at idle.
Long Term FT
The Long Term Fuel Trim (FT) is derived from the short
term fuel trim value. The Long Term FT is used for the long
term correction of the fuel delivery. A value of 128 counts
(0%) indicates that the fuel delivery requires no com-
pensation in order to maintain a 14.7:1 air to fuel ratio. A
value below 128 counts means that the fuel system is too
rich and the fuel delivery is being reduced. The ECM is de-
creasing the injector pulse width. A value above 128
counts indicates that a lean condition exists for which the
ECM is compensating.
MAP
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the change in the intake manifold pressure which results
from engine load and speed changes. As the intake man-
ifold pressure increases, the air density in the intake also
increases and the additional fuel is required.
Misfire History #1–4
Indicates the number of misfires that have occurred after
195 current misfires have been counted. The current mis-
fire counter will add its misfires to the history misfire count-
er after 195 total misfires have taken place. If 1 cylinder is
misfiring, the misfiring current counter will have 195 mis-
fires counted before adding to its history counter. If 2 cylin-
ders are misfiring, the misfiring current counter will add to
their history counters after 97 misfires. The counter incre-
ments only after a misfire diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
has been set.
Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
The pre–converter Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1) reading represents the exhaust oxygen sensor
output voltage. This voltage will fluctuate constantly be-
tween 100 mv (lean exhaust) and 900 mv (rich exhaust)
when the system is operating in a Closed Loop.
Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
The post–converter Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2) represents the exhaust oxygen output voltage
past the catalytic converter. This voltage remains inactive,
or the voltage will appear lazy within a range of 100 mv
(lean exhaust) and 900 mv (rich exhaust) when operating
in a Closed Loop.
Short Term FT
The Short Term FT represents a short term correction to
fuel delivery by the ECM in response to the amount of time
the oxygen sensor voltage spends above or below the 450
mv threshold. If the oxygen sensor has mainly been below
450 mv, indicating a lean air/fuel mixture, short term fuel
trim will increase to tell the ECM to add fuel. If the oxygen
sensor voltage stays mainly above the threshold, the ECM
will reduce fuel delivery to compensate for the indicated
rich condition.