instrument panel DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: NUBIRA, Model: DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 253 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 7
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
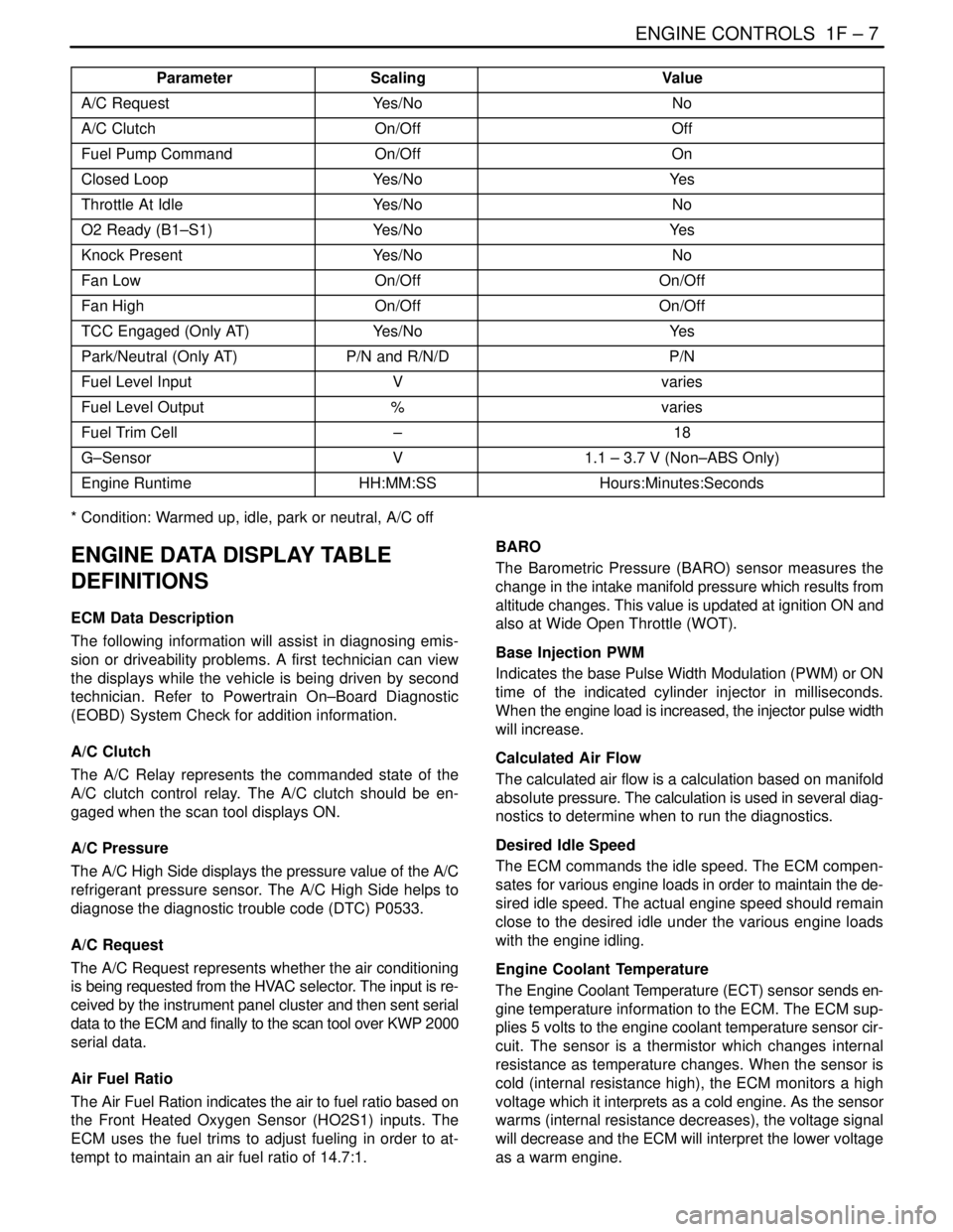
Parameter ValueScaling
A/C RequestYes/NoNo
A/C ClutchOn/OffOff
Fuel Pump CommandOn/OffOn
Closed LoopYes/NoYe s
Throttle At IdleYes/NoNo
O2 Ready (B1–S1)Yes/NoYe s
Knock PresentYes/NoNo
Fan LowOn/OffOn/Off
Fan HighOn/OffOn/Off
TCC Engaged (Only AT)Yes/NoYe s
Park/Neutral (Only AT)P/N and R/N/DP/N
Fuel Level InputVvaries
Fuel Level Output%varies
Fuel Trim Cell–18
G–SensorV1.1 – 3.7 V (Non–ABS Only)
Engine RuntimeHH:MM:SSHours:Minutes:Seconds
* Condition: Warmed up, idle, park or neutral, A/C off
ENGINE DATA DISPLAY TABLE
DEFINITIONS
ECM Data Description
The following information will assist in diagnosing emis-
sion or driveability problems. A first technician can view
the displays while the vehicle is being driven by second
technician. Refer to Powertrain On–Board Diagnostic
(EOBD) System Check for addition information.
A/C Clutch
The A/C Relay represents the commanded state of the
A/C clutch control relay. The A/C clutch should be en-
gaged when the scan tool displays ON.
A/C Pressure
The A/C High Side displays the pressure value of the A/C
refrigerant pressure sensor. The A/C High Side helps to
diagnose the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0533.
A/C Request
The A/C Request represents whether the air conditioning
is being requested from the HVAC selector. The input is re-
ceived by the instrument panel cluster and then sent serial
data to the ECM and finally to the scan tool over KWP 2000
serial data.
Air Fuel Ratio
The Air Fuel Ration indicates the air to fuel ratio based on
the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) inputs. The
ECM uses the fuel trims to adjust fueling in order to at-
tempt to maintain an air fuel ratio of 14.7:1.BARO
The Barometric Pressure (BARO) sensor measures the
change in the intake manifold pressure which results from
altitude changes. This value is updated at ignition ON and
also at Wide Open Throttle (WOT).
Base Injection PWM
Indicates the base Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) or ON
time of the indicated cylinder injector in milliseconds.
When the engine load is increased, the injector pulse width
will increase.
Calculated Air Flow
The calculated air flow is a calculation based on manifold
absolute pressure. The calculation is used in several diag-
nostics to determine when to run the diagnostics.
Desired Idle Speed
The ECM commands the idle speed. The ECM compen-
sates for various engine loads in order to maintain the de-
sired idle speed. The actual engine speed should remain
close to the desired idle under the various engine loads
with the engine idling.
Engine Coolant Temperature
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor sends en-
gine temperature information to the ECM. The ECM sup-
plies 5 volts to the engine coolant temperature sensor cir-
cuit. The sensor is a thermistor which changes internal
resistance as temperature changes. When the sensor is
cold (internal resistance high), the ECM monitors a high
voltage which it interprets as a cold engine. As the sensor
warms (internal resistance decreases), the voltage signal
will decrease and the ECM will interpret the lower voltage
as a warm engine.
Page 255 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 9
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Spark Advance
This is a display of the spark advance Ignition Coil (IC) cal-
culation which the ECM is programming in the ignition sys-
tem. It computes the desired spark advance using data
such as engine temperature, rpm, engine load, vehicle
speed and operating mode.
TCC Engaged
When the brake pedal is applied, the Torque Converter
Clutch (TCC) brake switch sends a signal to the ECM to
disengage the TCC and disable the cruise control.
Total Misfire Current Counter
Indicates the total number of misfires that have been de-tected in all the cylinders after 100 engine cycles. One
cycle equals one complete 4 stroke cycle. The total misfire
only increments during the steady state cruise conditions.
TP Sensor
The ECM uses the TP Sensor in order to determine the
amount of the throttle demanded by the vehicle’s operator.
The TP Sensor reads between 0.36–0.96 volts at idle to
above 4 volts at WOT.
Vehicle Speed
The vehicle speed sensor signal is converted into mph or
km/h for display. The vehicle speed output from the ECM
is 4000 pulses per mile. The scan tool uses the KWP 2000
serial data from the ECM to obtain vehicle speed, while the
Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC), cruise control module and
the chime alarm module use the 4000 ppm output.
Page 305 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 59
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
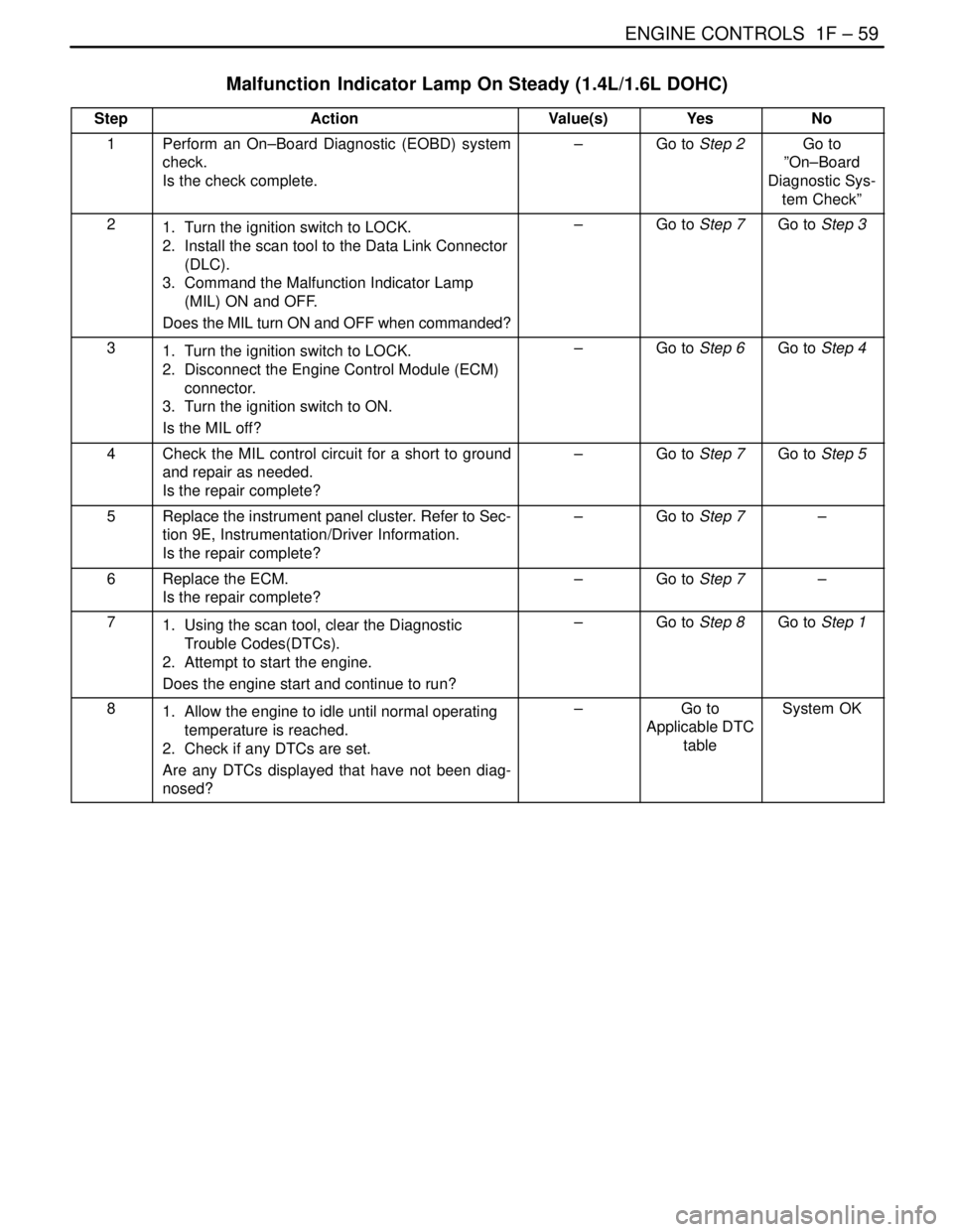
Malfunction Indicator Lamp On Steady (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) system
check.
Is the check complete.–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Install the scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
3. Command the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) ON and OFF.
Does the MIL turn ON and OFF when commanded?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the Engine Control Module (ECM)
connector.
3. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Is the MIL off?–Go to Step 6Go to Step 4
4Check the MIL control circuit for a short to ground
and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 5
5Replace the instrument panel cluster. Refer to Sec-
tion 9E, Instrumentation/Driver Information.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 7–
6Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 7–
71. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes(DTCs).
2. Attempt to start the engine.
Does the engine start and continue to run?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 1
81. Allow the engine to idle until normal operating
temperature is reached.
2. Check if any DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 307 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 61
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
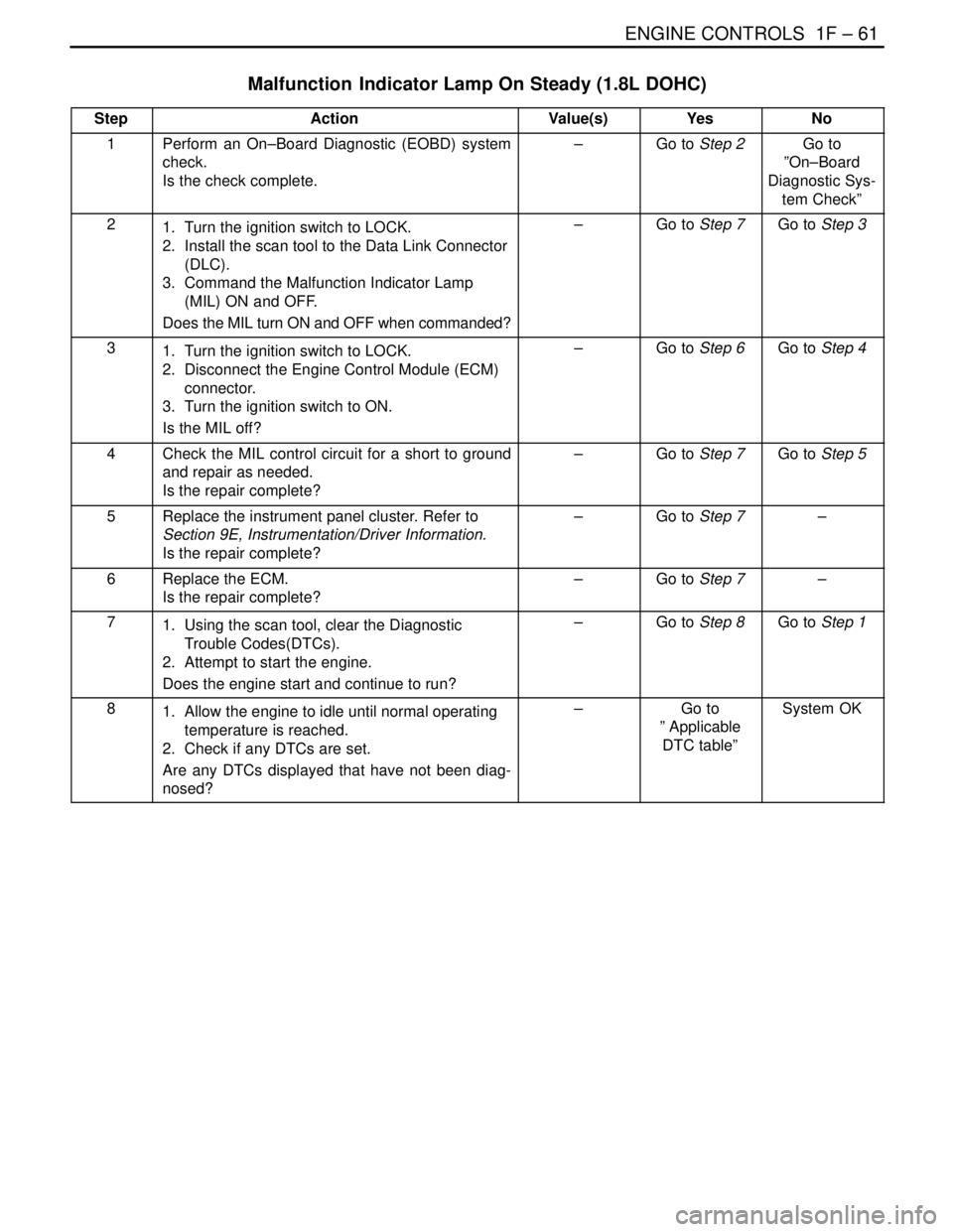
Malfunction Indicator Lamp On Steady (1.8L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) system
check.
Is the check complete.–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Install the scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
3. Command the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) ON and OFF.
Does the MIL turn ON and OFF when commanded?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the Engine Control Module (ECM)
connector.
3. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Is the MIL off?–Go to Step 6Go to Step 4
4Check the MIL control circuit for a short to ground
and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 5
5Replace the instrument panel cluster. Refer to
Section 9E, Instrumentation/Driver Information.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 7–
6Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 7–
71. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes(DTCs).
2. Attempt to start the engine.
Does the engine start and continue to run?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 1
81. Allow the engine to idle until normal operating
temperature is reached.
2. Check if any DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
” Applicable
DTC table”System OK
Page 352 of 2643

1F – 106IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DATA LINK CONNECTOR DIAGNOSIS (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The provision for communicating with the Engine Control
Module (ECM) is the Data Link Connector (DLC). It is lo-
cated under the instrument panel. The DLC is used to con-
nect the scan tool. Battery power and ground is supplied
for the scan tool through the DLC. The Keyword 2000 seri-
al data circuit to the DLC allows the ECM to communicate
with the scan tool. A Universal Asynchronous Receiver
Transmitter (UART) serial data line is used to communi-
cate with the other modules such as the Electronic Brake
Control Module (EBCM), the Supplemental Inflatable Re-
straint (SIR) system. and the Instrument Panel Cluster.
Diagnostic Aids
Ensure that the correct application (model line, car year,
etc.) has been selected on the scan tool. If communication
still cannot be established, try the scan tool on another ve-
hicle to ensure that the scan tool or cables are not the
cause of the condition.
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed through wire insulation, or a broken wire inside the
insulation.
Any circuitry that is suspected of causing an intermittent
complaint should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions:
S Backed–out terminals.S Improper mating of terminals.
S Broken locks.
S Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
S Poor terminal–to–wiring connection.
S Physical damage to the wiring harness.
S Corrosion.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. Unlike the UART serial data circuit, the only time a
Class II serial data circuit has any voltage on it is
when a scan tool asks the ECM for information and
sends the information out.
5. Locate and repair any shorts that may have caused
the fuse to open before replacement, if the no volt-
age condition was due to an open fuse.
10. The scan tool or associated cables could be mal-
functioning. Refer to the scan tool’s manual for re-
pair information.
Page 354 of 2643

1F – 108IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DATA LINK CONNECTOR DIAGNOSIS (1.8L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The provision for communicating with the Engine Control
Module (ECM) is the Data Link Connector (DLC). It is lo-
cated under the instrument panel. The DLC is used to con-
nect the scan tool. Battery power and ground is supplied
for the scan tool through the DLC. The Keyword 2000 seri-
al data circuit to the DLC allows the ECM to communicate
with the scan tool. A Universal Asynchronous Receiver
Transmitter (UART) serial data line is used to communi-
cate with the other modules such as the Electronic Brake
Control Module (EBCM), the Supplemental Inflatable Re-
straint (SIR) system. and the Instrument Panel Cluster.
Diagnostic Aids
Ensure that the correct application (model line, car year,
etc.) has been selected on the scan tool. If communication
still cannot be established, try the scan tool on another ve-
hicle to ensure that the scan tool or cables are not the
cause of the condition.
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed through wire insulation, or a broken wire inside the
insulation.
Any circuitry that is suspected of causing an intermittent
complaint should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions:
S Backed–out terminals.S Improper mating of terminals.
S Broken locks.
S Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
S Poor terminal–to–wiring connection.
S Physical damage to the wiring harness.
S Corrosion.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. Unlike the UART serial data circuit, the only time a
Class II serial data circuit has any voltage on it is
when a scan tool asks the ECM for information and
sends the information out.
5. Locate and repair any shorts that may have caused
the fuse to open before replacement, if the no volt-
age condition was due to an open fuse.
10. The scan tool or associated cables could be mal-
functioning. Refer to the scan tool’s manual for re-
pair information.
Page 503 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 257
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0501
VEHICLE SPEED NO SIGNAL (M/T ONLY)
Circuit Description
Vehicle speed information is provided to the engine control
module (ECM) by the voltage speed sensor (VSS) is a per-
manent magnet generator that is mounted in the transaxle
and produces a pulsing voltage whenever vehicle speed
is over 3 mph (5km/h). The A/C voltage level and the num-
ber of pulses increase with vehicle speed. The ECM con-
verts the pulsing voltage into mph (km/h) and than sup-
plies the necessary signal to the instrument panel for
speedometer/ odometer operation and to the cruise con-
trol module and multi–function alarm module operation.
The Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will detect if vehicle
speed is reasonable according to engine rpm and load.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Vehicle speed is not change at least 25 seconds.
S Engine speed is greater than 2,500rpm.
S MAF is greater than 180mg/tdc.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S Coolant fan turns on.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S Using the scan tool can clear DTC(s).
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
An Intermittent problem may be caused by a poor connec-
tion, rubbed through wire insulation, or wire that is broken
inside the insulation.
VSS signal circuit should be thoroughly checked for the
following conditions
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
Page 744 of 2643

1F – 498IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0502
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR NO SIGNAL (ENGINE SIDE)
Circuit Description
Vehicle speed information is provided to the Engine Con-
trol Module (ECM) by the Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS).
The VSS is a permanent magnet generator that is
mounted in the transaxle and produces a pulsing voltage
whenever vehicle speed is over 3 mph (5 km/h). The Alter-
nating Current (AC) voltage level and the number of
pulses increases with vehicle speed. The ECM converts
the pulsing voltage into mph (km/h) and then supplies the
necessary signal to the instrument panel for speedometer/
odometer operation and to the cruise control module and
multi–function alarm module operation. This Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) will detect if vehicle speed is reason-
able according to engine rpm and load.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Vehicle speed is less than 5 km/h (3.1 mph) for
Power and Decel test.
S Engine is running.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is greater than
60 °C (140 °F).
S Ignition voltage is between 11–16 volts.
S Power Test
S The rpm is between 1200 and 4000.S Throttle Position (TP) sensor is between 25%
and 60%.
S MAP is greater than 60 kPa (8.7 psi).
S Deceleration Test
S Generator compensated Manifold Absolute
Pressure (MAP) is less than 30 kPa (4.4 psi)
S Change in rpm per cycle is less than 50 rpm/
cycle.
S Throttle Position (TP) sensor is less than 0.8%.
S The rpm is between 1800 and 6000.
S DTC(s) P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204,
P0300, P0351, P0352, P0402, P0404, P1404,
P0405, and P0406 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
Page 877 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 631
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S Barometric Pressure (BARO)
S Intake Air Temperature (IAT)
S Throttle Position (TP)
S High canister purge
S Fuel trim
S A/C on
Trip
Technically, a trip is a key–on run key–off cycle in which all
the enable criteria for a given diagnostic are met, allowing
the diagnostic to run. Unfortunately, this concept is not
quite that simple. A trip is official when all the enable crite-
ria for a given diagnostic are met. But because the enable
criteria vary from one diagnostic to another, the definition
of trip varies as well. Some diagnostics are run when the
vehicle is at operating temperature, some when the ve-
hicle first starts up; some require that the vehicle be cruis-
ing at a steady highway speed, some run only when the
vehicle is at idle; some diagnostics function with the
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) disabled. Some run only
immediately following a cold engine startup.
A trip then, is defined as a key–on run key–off cycle in
which the vehicle was operated in such a way as to satisfy
the enables criteria for a given diagnostic, and this diag-
nostic will consider this cycle to be one trip. However,
another diagnostic with a different set of enable criteria
(which were not met) during this driving event, would not
consider it a trip. No trip will occur for that particular diag-
nostic until the vehicle is driven in such a way as to meet
all the enable criteria
Diagnostic Information
The diagnostic charts and functional checks are designed
to locate a faulty circuit or component through a process
of logical decisions. The charts are prepared with the re-
quirement that the vehicle functioned correctly at the time
of assembly and that there are not multiple faults present.
There is a continuous self–diagnosis on certain control
functions. This diagnostic capability is complimented by
the diagnostic procedures contained in this manual. The
language of communicating the source of the malfunction
is a system of diagnostic trouble codes. When a malfunc-
tion is detected by the control module, a diagnostic trouble
code is set and the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) is illu-
minated.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) is required by On–
Board Diagnostics (EOBD) that it illuminates under a strict
set of guide lines.
Basically, the MIL is turned on when the engine control
module (ECM) detects a DTC that will impact the vehicle
emissions.The MIL is under the control of the Diagnostic Executive.
The MIL will be turned on if an emissions–related diagnos-
tic test indicates a malfunction has occurred. It will stay on
until the system or component passes the same test, for
three consecutive trips, with no emissions related faults.
Extinguishing the MIL
When the MIL is on, the Diagnostic Executive will turn off
the MIL after three consecutive trips that a ”test passed”
has been reported for the diagnostic test that originally
caused the MIL to illuminate. Although the MIL has been
turned off, the DTC will remain in the ECM memory (both
Freeze Frame and Failure Records) until forty (40) warm–
up cycles after no faults have been completed.
If the MIL was set by either a fuel trim or misfire–related
DTC, additional requirements must be met. In addition to
the requirements stated in the previous paragraph, these
requirements are as follows:
S The diagnostic tests that are passed must occur
with 375 rpm of the rpm data stored at the time the
last test failed.
S Plus or minus ten percent of the engine load that
was stored at the time the last test failed. Similar
engine temperature conditions (warmed up or
warming up) as those stored at the time the last
test failed.
Meeting these requirements ensures that the fault which
turned on the MIL has been corrected.
The MIL is on the instrument panel and has the following
functions:
S It informs the driver that a fault that affects vehicle
emission levels has occurred and that the vehicle
should be taken for service as soon as possible.
S As a system check, the MIL will come on with the
key ON and the engine not running. When the en-
gine is started, the MIL will turn OFF.
S When the MIL remains ON while the engine is run-
ning, or when a malfunction is suspected due to a
driveability or emissions problem, an EOBD System
Check must be performed. The procedures for
these checks are given in EOBD System Check.
These checks will expose faults which may not be
detected if other diagnostics are performed first.
Data Link Connector (DLC)
The provision for communicating with the control module
is the Data Link Connector (DLC). The DLC is used to con-
nect to a scan tool. Some common uses of the scan tool
are listed below:
S Identifying stored DTCs.
S Clearing DTCs.
S Performing output control tests.
S Reading serial data.
Page 893 of 2643
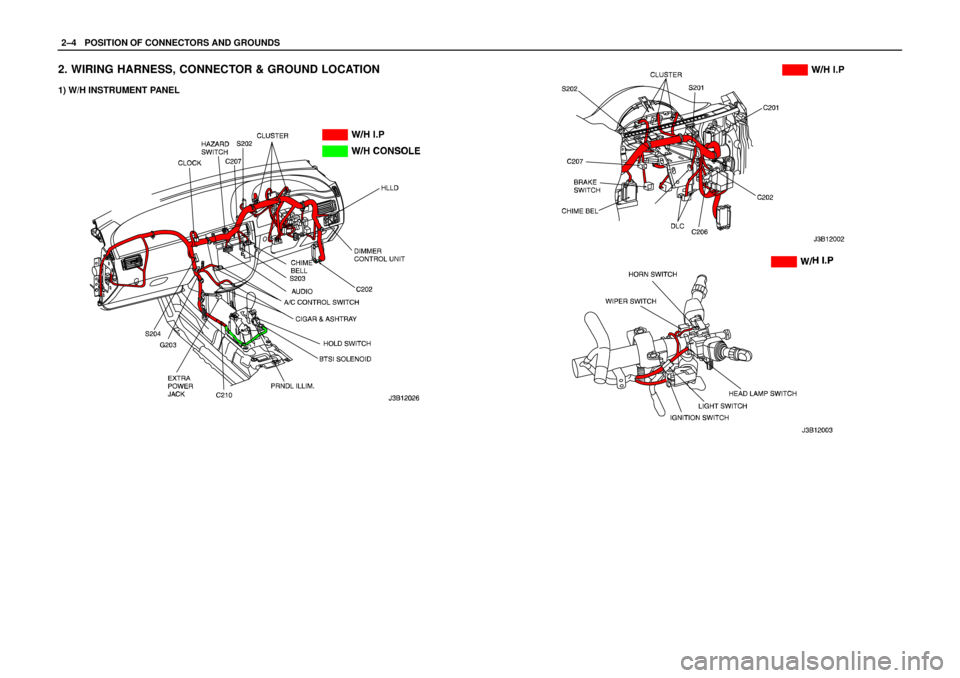
2–4WPOSITION OF CONNECTORS AND GROUNDS
2. WIRING HARNESS, CONNECTOR & GROUND LOCATION
1) W/H INSTRUMENT PANEL