check engine DATSUN 510 1968 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1968, Model line: 510, Model: DATSUN 510 1968Pages: 252, PDF Size: 12.2 MB
Page 59 of 252

54
CHAP1ER
SIX
2
Set
the
valve
spnng
seat
m
position
on
the
top
of
the
block
and
over
the
valve
stem
3
Place
the
oil
seal
over
the
valve
stem
4
Place
the
mner
and
outer
valve
spnngs
over
the
valve
stem
S
Place
the
spnng
retamer
over
the
springs
compress
spnngs
With
spring
compressor
Figure
55
and
mstall
valve
collets
around
valve
stem
so
that
they
lock
onto
stem
6
Release
spnng
compressor
If
collets
are
firm
ly
locked
onto
the
groove
m
the
valve
stem
assembly
IS
complete
7
Install
the
rocker
guIde
on
top
of
the
valve
stem
when
assemblmg
the
rocker
pivot
assembly
VaIve
Rocker
Pivot
Assembly
1
Thread
lock
nut
onto
valve
rocker
pivOt
and
place
rocker
retaIner
over
the
valve
rocker
pivOt
2
Thread
the
above
assembly
mto
the
rocker
bushIng
protrudIng
from
the
head
Camshaft
Assembly
1
Mount
the
locatIng
plate
on
the
front
of
the
head
as
shown
m
FJgIlI
1
56
2
From
the
back
of
the
head
carefully
InSert
the
camshaft
through
the
four
camshaft
beanngs
being
ca
efu1
not
to
move
or
damage
the
bear
ings
NOTE
Install
the
CQJ7IShaft
sprocket
onto
the
camshaft
so
that
the
three
locating
holes
are
at
the
top
left
and
bottom
h
1
3
Install
the
camshaft
sprocket
and
fuel
pump
cam
onto
the
front
of
the
camshaft
and
torque
to
specificatIon
4
Check
the
camshaft
for
end
play
using
a
feeler
gauge
as
preViously
described
Rocker
Pivot
Assembly
1
Push
down
on
valve
spnng
with
screwdriver
and
insert
rocker
piVOt
arm
between
camshaft
and
valve
stem
Insert
rocker
valve
guide
onto
top
of
valve
stem
at
this
time
2
Install
valve
rocker
springs
over
top
of
rocker
pivot
arm
Piston
and
Connecting
Rod
Assembly
1
Assemble
the
four
pistons
pms
and
connect
mg
rods
Secure
piston
pm
The
connecting
rod
IS
press
fitted
onto
the
pISton
pin
With
from
1
to
3
tons
of
force
NOTE
The
pistons
are
marked
with
an
F
which
should
point
toward
the
front
of
the
engine
The
connecting
rods
must
be
installed
so
that
the
011
Jet
In
the
large
end
IS
positioned
to
ward
the
right
Side
of
the
tnglne
The
center
of
the
piston
pin
IS
oD
set
In
relation
to
the
center
of
the
piston
so
correct
assembly
is
cntical
2
Use
a
nng
expander
to
install
the
rings
onto
the
pistons
Install
the
top
and
rmddle
nngs
with
the
marks
up
3
Lubncate
the
rod
bearings
hghtly
and
mstall
them
into
their
respective
connectIng
rods
and
rod
caps
Page 60 of 252

ENGINE
55
Cylinder
Block
Assembly
1
PositIon
all
crankshaft
parts
on
a
work
bench
ThIS
mcludes
the
crankshaft
main
beanngs
rear
011
seal
woodruff
keys
crankshaft
gear
011
pump
gear
011
thrower
bolts
and
bearing
caps
Figure
57
shows
the
arrangement
@
2
Insert
maIO
beanngs
mto
appropnate
cy1m
der
block
holders
NOTE
The
center
No
3
beanng
IS
the
only
flanged
type
of
thrust
bear
Ing
Bearings
No
2
and
No
4
are
Identical
No
1
and
No
5
Jaring
ap
pear
identical
but
No
1
as
an
011
hole
All
bearings
except
No
1
are
Interchangeable
as
to
upper
and
lower
half
3
LIghtly
lubncate
the
crankshaft
and
beanng
matmg
surfaces
then
mstall
beanngs
10
mam
beanng
caps
4
Install
the
crankshaft
5
Install
mam
beanng
caps
over
crankshaft
msert
mam
cap
bolts
and
tighten
hghtly
The
mam
beanng
caps
have
an
arrow
marked
on
each
one
These
must
pomt
to
the
front
of
the
engme
6
Gently
move
the
crankshaft
10
an
aXIal
drrec
don
toward
the
front
of
the
engme
to
venfy
that
the
mam
beanng
caps
are
properly
alIgned
and
seated
7
Use
a
torque
wrench
to
tighten
the
cap
bolts
to
the
hmlts
speCIfied
The
t1ghtenmg
operatIon
should
be
done
gradually
10
three
or
four
sep
arate
stages
starting
10
the
center
and
workmg
outward
to
each
end
8
Rotate
the
crankshaft
to
make
certain
it
isn
t
bmding
9
Use
a
feeler
gauge
to
check
the
end
play
at
the
center
No
3
beanng
Figure
58
10
Install
the
SIde
oll
seals
into
the
rear
mam
cap
and
cy1mder
block
as
shown
10
Figure
59
@
11
Install
the
rear
011
seal
WIth
Datsun
tool
ST49370000
or
equIvalent
12
Install
the
rear
end
plate
13
Install
the
flywheel
WIth
proper
bolts
and
lock
washers
and
torque
as
specified
Page 61 of 252
56
CHAPTER
SIX
NOTE
Lubncate
the
cylinder
walls
with
new
engine
oil
prior
to
insertIOn
of
pistOns
Make
certain
that
the
ring
gaps
are
not
In
line
wIth
one
another
Place
the
gaps
180
degrees
from
each
other
and
not
posltloned
either
front
to
back
or
dIrectly
in
line
with
the
piston
pIns
CAUTION
Use
extreme
care
when
Inserting
pzs
tons
so
as
to
avoId
crankshaft
damage
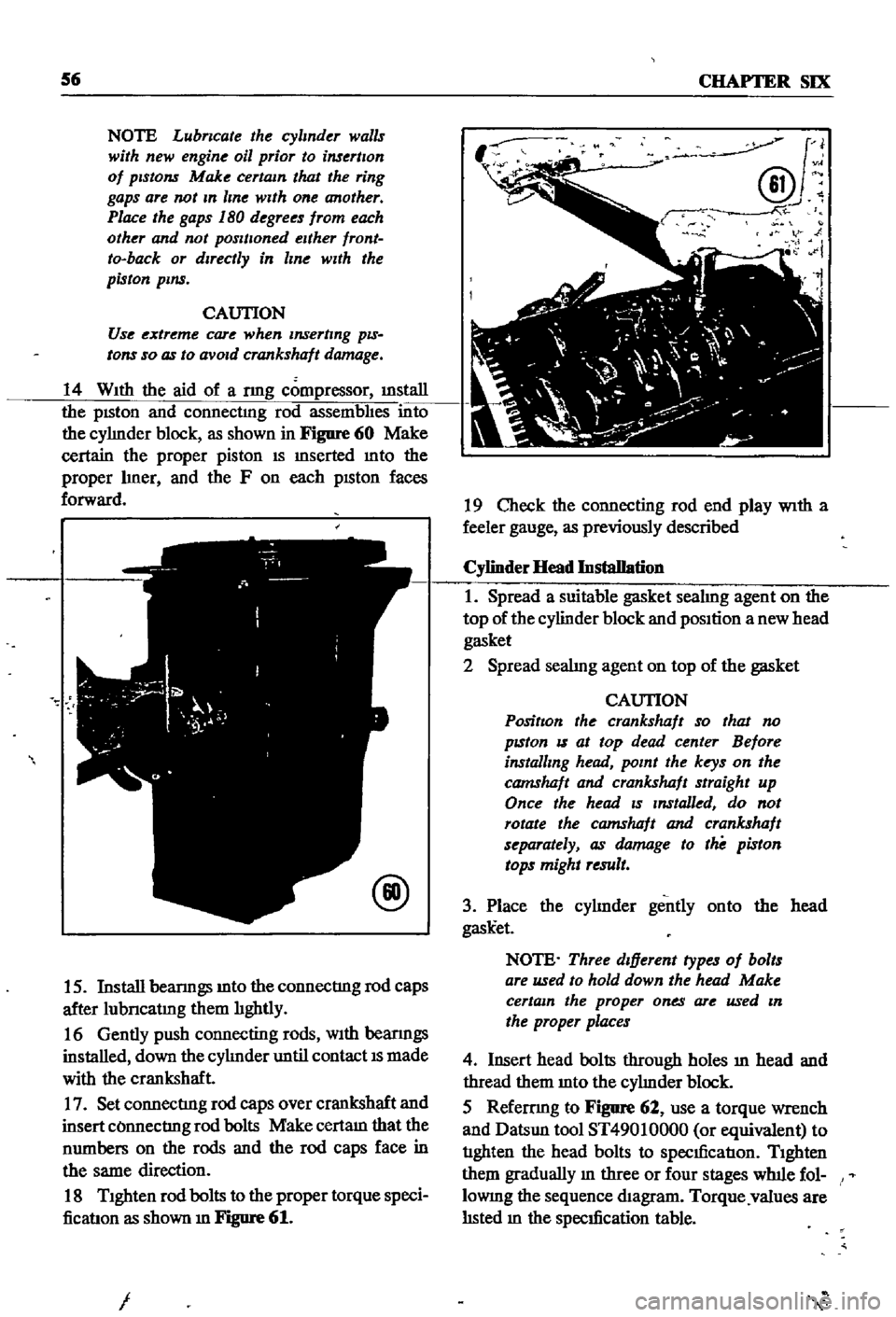
14
With
the
aid
of
a
nng
compressor
illStaIl
the
pISton
and
connectmg
rod
assembhes
into
the
cyhnder
block
as
shown
in
Figure
60
Make
certain
the
proper
piston
IS
mserted
mto
the
proper
hner
and
the
F
on
each
pISton
faces
forward
@
15
Install
beanngs
mto
the
connectIng
rod
caps
after
lubncatmg
them
hghtly
16
Gently
push
connecting
rods
With
beanngs
installed
down
the
cyhnder
until
contact
IS
made
with
the
crankshaft
17
Set
connectIng
rod
caps
over
crankshaft
and
insert
COnnectIng
rod
bolts
Make
certam
that
the
numbers
on
the
rods
and
the
rod
caps
face
in
the
same
direction
18
Tighten
rod
bolts
to
the
proper
torque
speci
ficatIon
as
shown
m
Figure
61
I
J
@v
N
i
19
Check
the
connecting
rod
end
play
With
a
feeler
gauge
as
previously
described
Cylinder
Head
Installation
1
Spread
a
suitable
gasket
seahng
agent
on
the
top
of
the
cylinder
block
and
position
a
new
head
gasket
2
Spread
seahng
agent
on
top
of
the
gasket
CAUTION
PositIon
the
crankshaft
so
that
no
pzston
IS
at
top
dead
center
Before
installing
head
point
the
keys
on
the
camshaft
and
crankshaft
straight
up
Once
the
head
zs
Installed
do
not
rotate
the
camshaft
and
crankshaft
separately
as
damage
to
the
piston
tops
might
result
3
Place
the
cyhnder
gently
onto
the
head
gask
et
NOTE
Three
dIfferent
types
of
bolts
are
used
to
hold
down
the
head
Make
certain
the
proper
ones
are
used
In
the
proper
places
4
Insert
head
bolts
through
holes
ill
head
and
thread
them
mto
the
cyhnder
block
5
Refemng
to
Figure
62
use
a
torque
wrench
and
Datsun
tool
ST49010000
or
equivalent
to
tIghten
the
head
bolts
to
specIficatIon
Tighten
them
gradually
m
three
or
four
stages
wlnle
fol
lOWIng
the
sequence
diagram
Torque
values
are
hsted
m
the
specIfication
table
Page 76 of 252

FUEL
SYSTEM
71
Dash
Pot
Adjustment
The
adjustment
of
the
dash
pot
IS
done
by
warmmg
up
the
engme
properly
and
checkIng
If
the
throttle
lever
touches
th
dash
pot
stem
as
the
engine
reaches
1
800
and
2
000
rpm
under
no
load
conditIons
Proper
contact
between
the
throttle
lever
and
the
dash
pot
stem
produces
a
normal
dash
pot
performance
Should
a
normal
mcrease
m
engme
speed
not
occur
adjust
the
dash
pot
as
follows
1
Loosen
the
dash
pot
locknuts
2
Rotate
the
dash
pot
nght
and
then
left
3
Adjust
the
dash
pot
so
that
the
throttle
lever
hIts
the
stem
between
1
800
and
2
000
rpm
4
Fasten
the
lock
nuts
securely
5
The
clearance
between
the
throttle
valve
and
the
throttle
chamber
wall
should
be
0
0709
m
0
8mm
or
10
degrees
In
throttle
valve
angle
MAJOR
CARBURETOR
SERVICE
PROCEDURES
A
carburetor
m
good
operatIng
condition
will
delIver
the
pr
per
gasolme
and
aIr
ratIos
for
all
engme
runnmg
speeds
A
gradual
declme
In
smoothness
response
and
power
Will
occur
as
the
carburetor
slIps
from
adjustment
and
Its
delI
cate
parts
become
dirty
and
worn
Overhaul
should
only
be
attempted
by
an
expenenced
mechanic
Accurate
calIbratIon
of
passages
and
dIS
charge
hole
reqUIre
that
extreme
care
be
taken
In
dISassembly
cleanmg
and
reassembly
Use
only
a
hIgh
grade
carburetor
cleaner
and
com
pressed
arr
to
clean
parts
and
passages
Never
use
wire
or
other
pOInted
Instruments
for
clean
ing
CalIbratIon
of
the
carburetor
will
be
af
fected
The
procedures
below
are
generally
true
for
all
models
As
an
aId
Figures
13
and
14
are
typIcal
examples
of
the
carburetors
used
Carburetor
Removal
1
Remove
the
au
cleaner
by
dIsconnectIng
all
hoses
attached
to
It
remoVmg
the
two
bolts
holdmg
the
aIr
cleaner
to
the
support
and
loos
enmg
the
band
bolt
at
the
base
of
the
aIr
cleaner
2
DIsconnect
fuellme
vacuum
Ime
and
choke
wire
u
eqUIpped
from
the
carburetor
3
Remove
the
throttle
lever
4
Remove
four
nuts
and
washers
holdmg
car
buretor
to
manIfold
5
Lift
carburetor
off
of
manuold
6
Remove
and
dIscard
carburetor
to
manuold
gasket
7
Place
carburetor
on
clean
workbench
Carburetor
Disassembly
1
The
maIn
Jets
slow
Jets
and
needle
valves
on
both
the
pnmary
and
secondary
systenIS
are
accessIble
from
outsIde
the
carburetor
Refer
to
FIgures
13
and
14
for
locatI
n
2
The
choke
chamber
can
be
detached
by
re
mOVIng
the
connectIng
rod
pump
connectIng
rod
return
sprmg
stop
pm
and
the
set
screws
I
that
hold
It
in
place
3
The
pnmary
and
secondary
emulSIon
tubes
can
be
disassembled
by
remOVIng
the
mam
air
bleeds
on
the
respectIve
SIdes
4
To
check
the
accelerator
pump
remove
the
cylInder
cover
Be
careful
not
to
lose
the
return
spnng
and
Inlet
valve
at
the
lower
part
of
the
pIston
durmg
dIsassembly
5
Detach
the
throttle
chamber
from
the
float
chamber
by
remOVIng
the
rod
lInkIng
the
dia
phragm
WIth
the
secondary
throttle
valve
and
the
four
screws
that
hold
It
However
It
IS
preferable
to
leave
the
throttle
valve
mtact
unless
absolutely
reqUired
If
It
IS
necessary
to
dlS
assemble
the
valve
It
should
be
Installed
so
that
the
secondary
throttle
valve
will
be
gap
free
OtherwIse
stable
Idle
and
good
slow
speed
performance
will
suffer
is
To
check
the
float
the
float
chamber
cover
must
be
removed
I
7
The
dIaphragm
IS
dIsassembled
by
removing
the
set
screws
holdmg
the
dIaphragm
chamber
cover
In
reassemblIng
the
diaphragm
be
careful
not
to
turn
the
edge
of
the
dIaphragm
up
8
In
dlsassemblmg
and
reassembling
the
mter
lockIng
lInks
take
care
so
that
each
lInkage
has
a
smooth
actIon
and
that
parts
are
not
forced
mto
pOSItIon
9
For
vehIcles
equipped
With
an
automatIc
choke
remove
the
brmetal
case
by
releasmg
the
set
screws
The
bimetal
1l
extremely
senSItIve
Page 94 of 252

COOLING
SYSTEM
89
FAN
CLUTCH
Fan
Clutch
Operation
and
Inspection
Figure
6
shows
a
typICal
fan
clutch
dISas
sembled
Check
the
umt
whenever
the
water
pump
IS
removed
or
whenever
troubles
are
suspected
m
the
assembly
OperatIon
of
the
fan
clutch
should
be
observed
when
the
vehIcle
is
at
nmning
temperature
Operation
plate
Dust
cover
Drum
o9
Q
SpIder
assembly
LIning
CD
1
Warm
up
the
engme
2
MaIntam
engIne
speed
at
2
500
rpm
3
Usmg
a
thermometer
measure
the
temper
ature
close
to
the
fan
clutch
assembly
on
the
fan
4
The
clutch
should
engage
when
the
temp
erature
reaches
17
degrees
F
65
degrees
C
Conversely
the
clutch
should
deenergIze
when
the
temperature
drops
to
97
degrees
F
54
de
grees
C
5
Take
the
measurements
at
least
twice
SInce
the
thermostat
has
somewhat
of
a
tlme
lag
6
If
the
fan
clutch
falls
to
operate
properly
It
should
be
dIsassembled
and
servIced
Fan
Clutch
Disassembly
1
Follow
the
mstructIons
as
prevIOusly
gIven
to
remove
the
fan
and
clutch
assembly
from
the
water
pump
2
Refer
to
the
appropnate
exploded
illustratIon
for
your
model
and
to
Figure
7
which
shows
a
typiCal
fan
clutch
assembly
3
DIsassemble
unit
and
mspect
all
parts
for
signs
of
wear
or
breakage
4
To
check
the
operatIon
of
the
fan
clutch
thermostat
submerge
the
operatIon
plate
With
the
thermostat
In
hot
water
of
126
degrees
F
70
degrees
C
for
two
to
three
mmutes
Replace
if
It
faIls
to
operate
5
Assemble
the
fan
clutch
m
the
reverse
order
o
dIsassembly
THERMOSTAT
The
system
thermostat
IS
located
inside
the
water
outlet
elbow
on
the
upper
left
hand
por
bon
of
the
cylInder
head
The
temperature
sens
Ing
deVice
IS
threaded
Into
the
base
of
the
therm
ostat
housmg
and
IS
connected
electrlcally
to
the
temperature
gauge
WIthIn
the
vehIcle
dash
board
The
wax
pellet
m
the
thermostat
expands
when
heated
and
contracts
when
cold
The
pellet
IS
connected
through
a
pIston
to
a
valve
Expan
sion
pressure
IS
exerted
agalUst
a
rubber
dIa
phragm
which
forces
the
valve
to
open
and
per
rrut
coolant
to
flow
through
the
entIre
system
As
the
pellet
cools
contractIOn
allows
a
spnng
to
close
the
valve
Thermostat
Removal
1
Open
the
draIn
cock
on
the
bottom
of
the
radiator
and
dram
out
enough
coolant
so
that
the
level
In
the
radIator
IS
below
the
bottom
of
the
upper
radIator
hose
2
DIsconnect
the
upper
radIator
hose
from
the
water
outlet
elbow
3
Remove
the
two
nuts
holdIng
the
water
outlet
elbow
to
the
thermostat
housmg
4
Remove
the
gasket
and
thermostat
from
the
housmg
as
shown
m
FIgure
7
Thermostat
Inspection
and
Replacement
Submerge
the
thermostat
In
a
pan
of
water
Heat
the
water
and
momtor
the
temperature
2
The
thermostat
should
start
to
open
at
1796
1
27
degrees
F
82
1
1
5
degrees
C
Max
Imum
opemng
should
occur
at
203
degrees
F
95
Page 100 of 252

ENGINE
ELECI
RlCAL
SYSTEM
9S
@
@
4
Test
the
COIls
for
shorts
by
unsoldermg
the
connectIons
of
each
coIl
and
repeatlng
the
test
given
m
step
3
If
a
defectIve
coil
IS
found
It
must
be
replaced
BRUSHES
AND
BRUSH
LEAD
WIRE
1
Check
condItIon
of
the
brush
contact
surface
and
general
wear
of
the
brush
If
the
brush
is
worn
to
under
02362
In
60mm
m
length
replace
It
Inspect
all
connectIons
carefully
for
looseness
or
cracks
Replace
or
reparr
as
re
qUIred
2
Check
the
connectIon
of
the
lead
clIp
and
WIre
3
Check
brush
holders
and
sprmg
clIps
for
damage
Replace
1f
they
will
not
hold
the
brushes
agaInst
the
commutator
properly
Clean
all
brushes
aIld
brush
holders
thoroughly
4
Check
brush
sprmg
tenSIon
WIth
a
spnng
scale
as
shown
m
Figure
14
The
reading
should
be
1
76
Ibs
0
8
kg
Replace
the
spnng
if
the
tenSIon
IS
under
1
54
Ibs
0
7
kg
@
ARMATURE
ASSEMBLY
1
Check
external
appearance
of
the
armature
and
commutator
2
Use
a
dIal
gauge
Figure
15
to
measure
the
armature
shaft
for
bend
Replace
the
armature
shaft
1f
the
bend
exceeds
0
001
in
0
08mm
@
3
Inspect
the
commutator
If
the
surface
IS
rough
sand
It
With
No
500
emery
paper
untIl
smooth
Use
a
dIal
gauge
to
check
the
commu
tator
If
out
of
round
IS
more
than
00079
In
0
2mm
or
the
depth
of
the
Insulatlng
mica
is
less
than
0
0079
In
0
2mm
from
the
commu
tator
surface
the
commutator
should
be
turned
on
a
lathe
Out
of
round
should
be
less
than
o
0020
in
0
05mm
Insulatmg
mica
should
be
undercut
as
shown
m
Figure
16
to
a
depth
of
from
0
0197
to
0
0315
in
0
5
to
0
8mm
4
Inspect
the
soldered
connectIon
of
the
arma
ture
lead
and
the
commutator
If
the
connection
is
loose
resolder
It
5
Usmg
a
clrcmt
tester
test
the
armature
for
Page 102 of 252
ENGINE
ELECI
RlCAL
SYSTEM
97
No
Load
Lock
Torque
Test
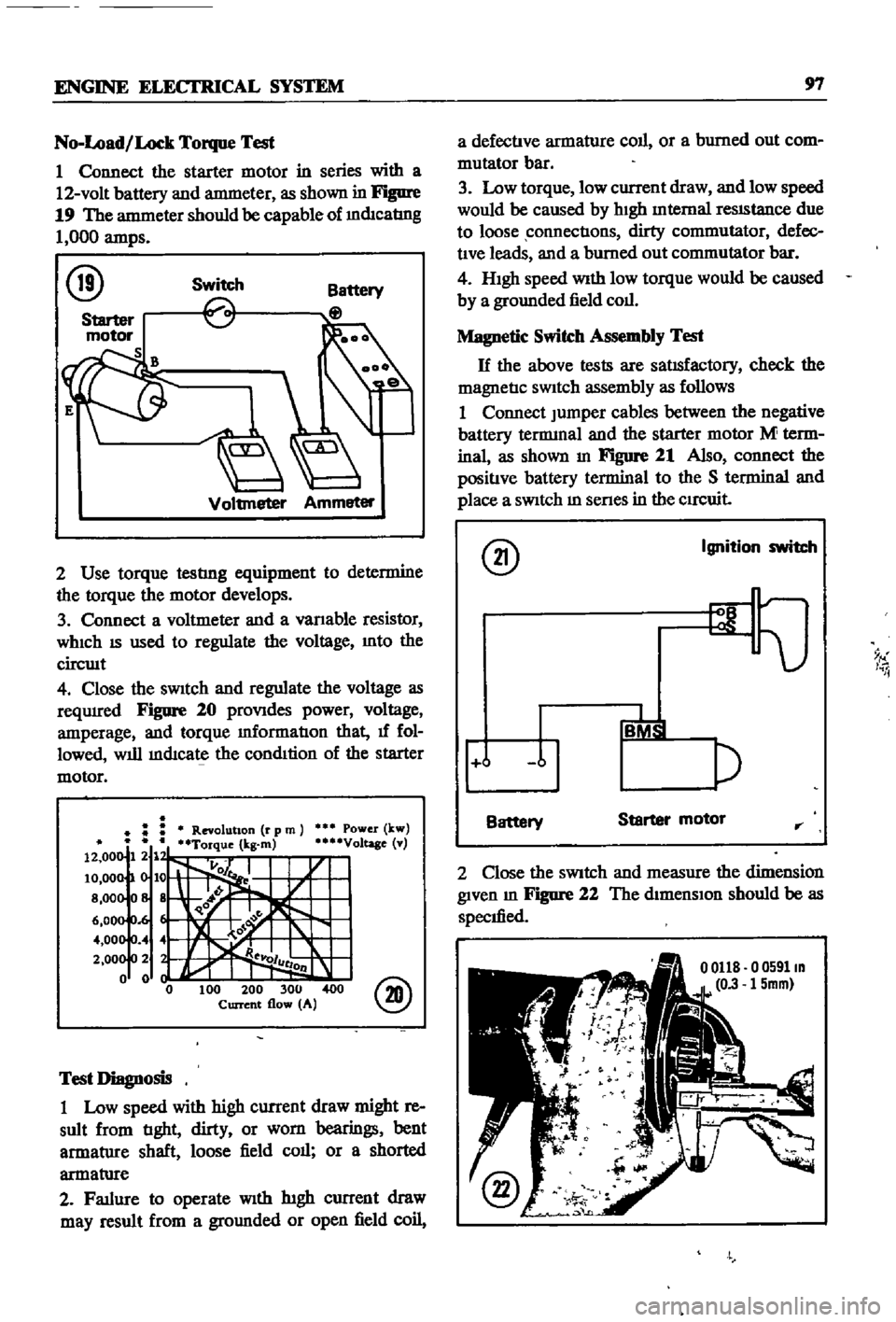
1
Connect
the
starter
motor
in
series
with
a
12
volt
battery
and
antmeter
as
shown
in
Figure
19
The
antmeter
should
be
capable
of
mdIcatIng
1
000
amps
@
Switch
Voltmeter
Ammeter
2
Use
torque
testlng
equipment
to
determine
the
torque
the
motor
develops
3
Connect
a
voltmeter
and
a
vanable
resistor
WhICh
IS
used
to
regulate
the
voltage
Into
the
circwt
4
Close
the
sWitch
and
regulate
the
voltage
as
reqUIred
Figure
20
proVIdes
power
voltage
amperage
and
torque
mformatIon
that
1f
fol
lowed
will
mdIcate
the
condItion
of
the
starter
motor
Power
kw
Voltage
v
@
Test
Diagnosis
1
Low
speed
with
high
current
draw
might
re
sult
from
tIght
dirty
or
worn
bearings
bent
armatlIre
shaft
loose
field
call
or
a
shorted
armatlIre
2
Fatlure
to
operate
With
htgh
current
draw
may
result
from
a
gromlded
or
open
field
coil
a
defectIve
armature
coll
or
a
burned
out
com
mutator
bar
3
Low
torque
low
current
draw
and
low
speed
would
be
caused
by
hIgh
Internal
reSIStance
due
to
loose
connectIons
dirty
commutator
defec
tIve
leads
and
a
burned
out
commutator
bar
4
HIgh
speed
With
low
torque
would
be
caused
by
a
grounded
field
coll
Magnetic
Switch
Assembly
Test
H
the
above
tests
are
satIsfactory
check
the
magnetIc
SWitch
assembly
as
follows
1
Connect
Jumper
cables
between
the
negative
battery
tennmal
and
the
starter
motor
M
term
inal
as
shown
In
Figure
21
Also
connect
the
positIve
battery
terminal
to
the
S
terminal
and
place
a
SWitch
m
senes
in
the
CIrCuit
@
Ignition
switch
9
I
i
j
Battery
Starter
motor
rr
2
Close
the
SWitch
and
measure
the
dimension
given
m
Figure
22
The
dimensIon
should
be
as
specIfied
o
0591m
15mm
Page 108 of 252
ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
103
2
Check
the
lead
Wires
of
the
armature
coil
Includmg
the
neutral
wire
for
ground
as
shown
In
Figure
42
HIgh
reSIStance
no
current
flow
indicates
gqod
condItion
If
not
the
stator
must
be
replaced
DIODE
INSPECTION
The
diodes
can
be
inspected
through
the
use
of
a
lamp
and
battery
or
with
a
tester
The
lamp
and
battery
test
can
be
made
Without
disassembl
ing
the
alternator
wh1le
the
tester
should
be
used
when
the
dIodes
are
dIrectly
acceSSIble
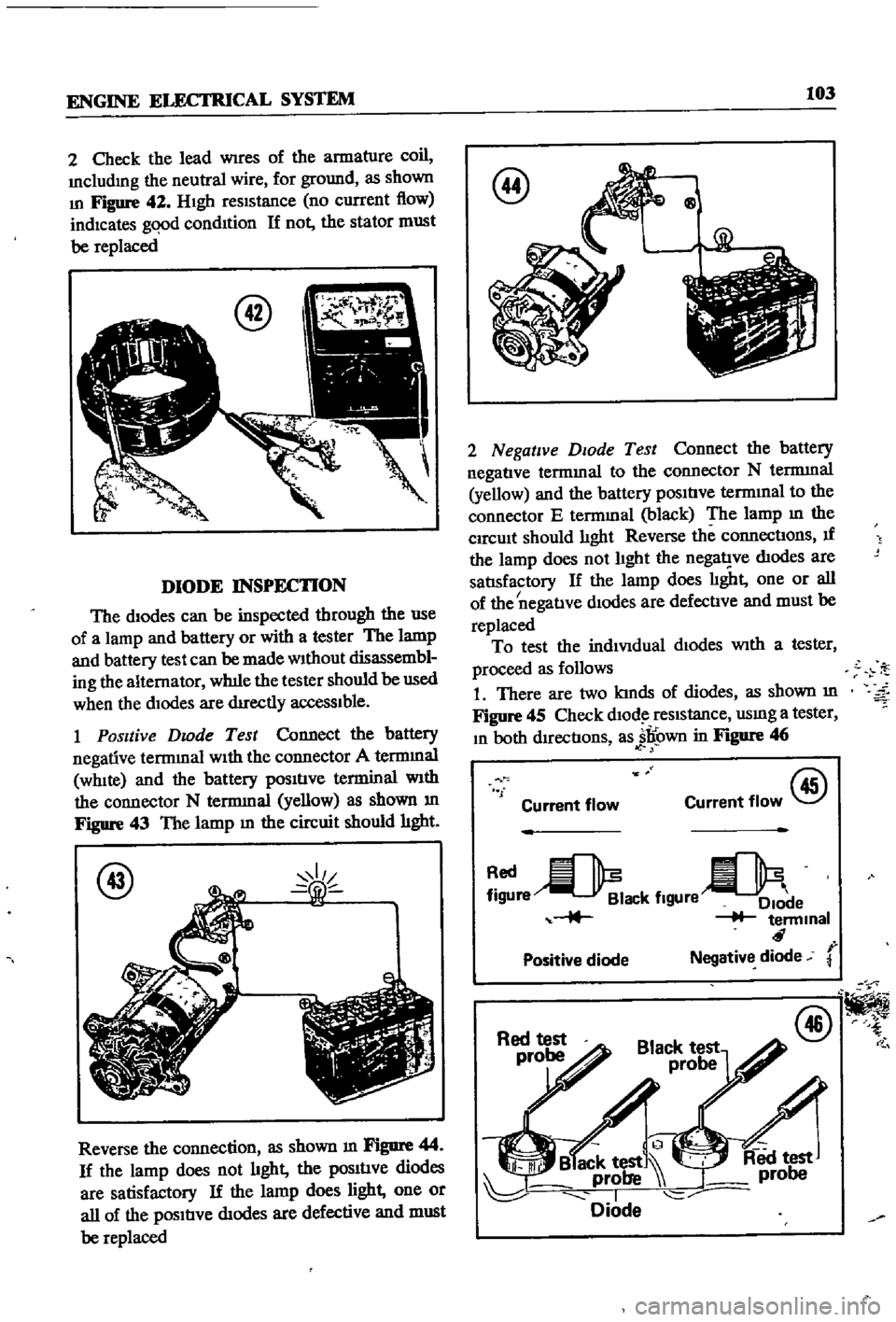
1
Positive
Dwde
Test
Connect
the
battery
negative
terrmnal
WIth
the
connector
A
terrmnal
WhIte
and
the
battery
pOSItIve
terminal
With
the
connector
N
terrmnal
yellow
as
shown
m
Figure
43
The
lamp
m
the
circuit
should
hght
@
Reverse
the
connection
as
shown
m
Figure
44
If
the
lamp
does
not
hght
the
pOSItIve
diodes
are
satisfactory
If
the
lamp
does
light
one
or
all
of
the
pOSItIve
dIodes
are
defective
and
must
be
replaced
@
Qg
2
Negative
DIOde
Test
Connect
the
battery
negatIve
termmal
to
the
connector
N
terrmnal
yellow
and
the
battery
pOSItIve
termInal
to
the
connector
E
termmal
black
The
lamp
m
the
CIrcUit
should
lIght
Reverse
the
connectIons
If
the
lamp
does
not
lIght
the
nega1
ve
dIodes
are
satlsfactory
If
the
lamp
does
lIght
one
or
all
I
of
the
negatIve
dIodes
are
defectIve
and
must
be
replaced
To
test
the
indiVIdual
dIodes
With
a
tester
proceed
as
follows
1
There
are
two
kInds
of
diodes
as
shown
m
Figure
45
Check
dlOd
reSIstance
usmg
a
tester
In
both
dIrectIons
as
jl
own
in
Figure
46
f
Current
flow
@
Current
flow
re
ack
flgUre
e
terminal
r
Positive
diode
Negative
diode
@
Page 111 of 252
106
CHAPTER
NINE
@
Igmtlon
switch
IgnItion
plug
engine
Condenser
IgnItIon
cod
@
II
9
ft
O
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTMENT
foreIgn
matenal
or
cracks
Qean
the
cap
thor
oughly
Replace
it
If
cracks
are
found
Inspect
the
hIgh
tensIon
cables
to
see
that
all
connectIons
are
firmly
made
and
that
the
cables
are
not
cracked
Replace
any
defective
cables
Do
not
try
to
tape
or
mend
them
Cap
and
Rotor
Head
The
cap
and
the
rotor
head
must
always
be
kept
clean
to
prevent
lugh
voltage
leaks
Inspect
the
cap
penod1cally
for
SIgnS
of
carbon
bwldup
Page 119 of 252

CHAPTER
TEN
EMISSION
CONTROL
SYSTEM
ThIs
chapter
covers
emission
control
and
exhaust
systems
The
emission
devices
used
in
clude
crankcase
ermssion
controls
an
exhaust
ermssion
system
and
evaporative
emission
con
trols
EXHAUST
EMISSION
CONTROL
SYSTEM
Two
methods
of
exhaust
emission
control
are
used
on
the
Datsun
One
is
an
aIr
injection
system
the
other
consists
of
engine
modifica
tIons
Datsuns
were
equipped
With
the
air
injec
tIon
system
only
through
1970
SInce
then
all
models
have
combined
aIr
mjection
with
engine
modIficatIons
EmisSIon
servicing
IS
complex
and
should
be
left
to
qualIfied
professionals
Figure
1
Illustrates
the
system
used
through
model
year
1969
Figure
2
IS
the
system
used
after
1970
Figures
3
through
7
offer
detaIls
of
various
emission
components
Maintenance
and
Testing
Penodlc
mspection
and
service
should
be
done
every
12
months
or
12
000
miles
The
engine
must
be
in
good
working
order
to
main
tain
a
low
level
of
harmful
emissions
There
fore
perform
a
general
tune
up
as
spec1fied
in
Chapter
Four
before
followmg
the
procedures
below
CRANKCASE
EMISSION
CONTROL
SYSTEM
The
crankcase
emission
control
system
is
shown
in
FlgDre
8
It
IS
a
closed
system
that
pre
vents
crankcase
gases
from
escaping
to
the
at
mosphere
Blowby
gases
are
dIrected
to
the
intake
manifold
through
the
ventilation
control
valve
Normally
capacity
of
the
valve
is
suffi
cient
to
handle
the
blowby
gas
plus
a
small
amount
of
ventIlating
air
drawn
from
the
air
cleaner
through
a
tube
leading
to
the
crankcase
Under
fun
throttle
condItIons
manifold
vacuum
is
Insufficient
to
draw
the
blowby
through
the
valve
When
this
happens
b10wby
flows
through
the
system
In
the
reverse
dIrection
General
1
Start
the
engine
and
bring
up
to
operating
temperature
2
Check
hoses
and
hose
connections
for
leaks
3
Examine
the
hoses
for
signs
of
cracks
or
de
terioraoon
Replace
as
required
Crankcase
Ventilation
Control
Valve
1
Start
the
engme
2
Remove
the
ventIlator
hose
from
the
crank
case
ventilatIon
control
valve
A
htssmg
nOISe