boot DATSUN 610 1969 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1969, Model line: 610, Model: DATSUN 610 1969Pages: 171, PDF Size: 10.63 MB
Page 50 of 171
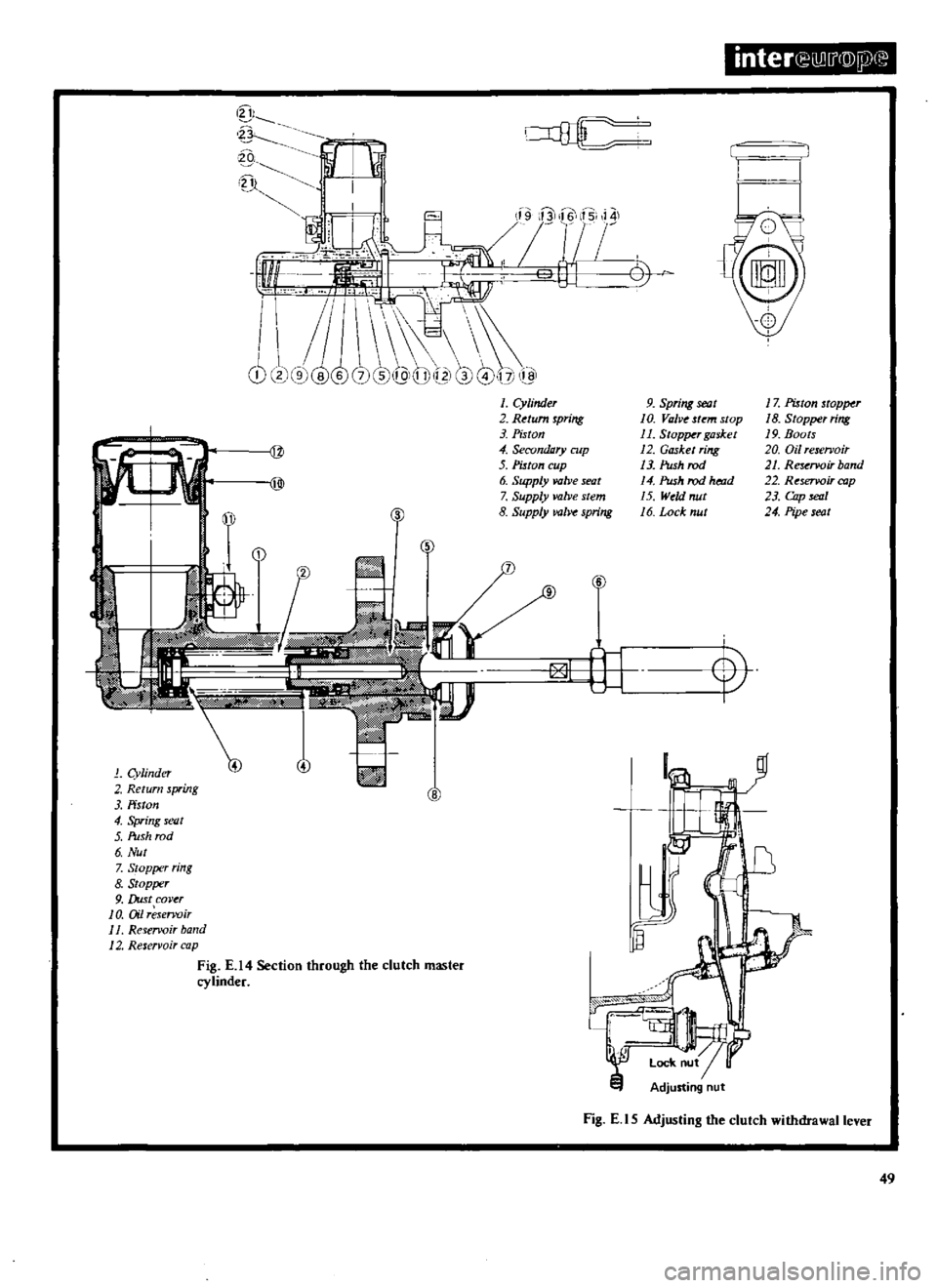
inter
lliJ
j
flDlJ
l
Jl
iO
n
cxB
L
of
lii
t
hl
9
q
6
15
1
r
8t
r
L
L
I
i
1
2
9
@
7
5I1
9
QlIf12
12J
J
7
ll
I
I
o
Q
1
Cylinder
2
Return
spring
3
Piston
4
Secondary
cup
5
Piston
cup
6
Supply
valve
seat
7
Supply
valve
stem
8
Supply
lIOlve
spring
9
Spring
seat
10
Va
ve
stem
stop
11
Stopper
gasket
12
Gasket
ring
13
Push
rod
14
Push
rod
ht
lld
15
Wdd
nut
16
Lock
nut
17
Piston
stopper
18
Stopper
ring
19
Boots
20
Oil
reservoir
21
Rese1l
Oir
band
22
Reservoir
cop
23
Cap
24
Pipe
seat
J
J
5
9
a
ID
1
Cylinder
2
Return
spring
C1
3
Piston
4
Spring
seat
5
Push
rod
6
Nut
7
Stopper
ring
8
Stopper
9
Dust
cover
10
on
reservoir
1
J
Reservoir
balld
12
Reservoir
cap
Fig
E
14
Section
through
the
clutch
master
cylinder
Adjusting
nut
Fig
E
l
S
Adjusting
the
clutch
withdrawal
lever
49
Page 76 of 171

Rear
Axle
Rear
SuspensIon
DESCRIPTION
REAR
AXLE
AND
SUSPENSION
Removal
Saloons
COIL
SPRINGS
Saloons
REAR
SHOCK
ABSORBERS
Saloons
REAR
SUSPENSION
ARM
Saloons
DESCRIPTION
Saloon
models
are
fitted
with
independent
rear
suspension
with
semi
trailing
arms
suspension
arms
coil
springs
and
telescopic
hydraulic
double
acting
shock
absorbers
The
differ
ential
gear
carrier
and
suspension
member
is
mounted
directly
onto
the
body
structure
via
rubber
mountings
See
Fig
H
I
Estate
cars
and
1800
ce
Vans
are
fitted
with
a
semi
floating
rear
axle
with
semi
elliptic
leaf
springs
and
telescopic
hydraulic
shock
absorbers
mounted
on
rubrer
bushes
See
Fig
H
2
REAR
AXLE
AND
SUSPENSION
Removal
Saloon
models
I
Jack
up
the
rear
of
the
vehicle
and
support
it
on
stands
2
Remove
the
road
wheels
disconnect
the
hand
brake
linkage
and
the
return
spring
Fig
H
3
3
Remove
the
exhaust
tail
pipe
and
silencer
4
Disconnect
the
brake
hoses
and
plug
the
openings
to
prevent
the
ingress
of
dirt
5
Remove
the
propeller
shaft
assembly
as
described
in
the
relevant
section
after
marking
the
propeller
rear
flange
and
differential
pinion
flange
6
Jack
up
the
suspension
ann
and
remove
the
shock
absorber
lower
mountings
taking
care
not
to
lose
the
rubber
bushings
7
Place
ajack
under
the
centre
of
the
suspension
member
and
differential
carrier
and
remove
the
nuts
securing
the
suspension
member
to
the
body
7
in
Fig
H
3
Remove
the
differential
mounting
nuts
8
8
Carefully
lower
and
remove
the
suspension
assembly
REAR
SUSPENSION
Inspection
Saloons
Examine
all
parts
for
wear
and
damage
paying
particular
attention
to
the
rubber
bushes
in
the
suspension
arms
and
the
bump
rubbers
Check
the
condition
of
the
spring
rubber
insulators
in
the
suspension
member
and
differential
mounting
memrer
The
rubber
insulators
must
be
replaced
if
the
dimension
A
in
Fig
H
4
is
less
than
5mm
0
2
in
REAR
AXLE
SHAFTS
BEARINGS
AND
SEALS
Saloons
DRNE
SHAFTS
REAR
AXLE
Removal
Estate
cars
and
Vans
REAR
SPRING
Estate
cars
and
Vans
REAR
SHOCK
ABSORBERS
Estate
cars
and
Vans
REAR
SUSPENSION
Installation
Saloons
Installation
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedures
noting
the
following
points
Ensure
that
the
suspension
member
and
differential
mount
ing
member
are
correctly
aligned
as
shown
in
Fig
U
5
and
insert
the
rubber
insulators
from
the
underside
of
the
vehicle
Tighten
the
differential
mounting
member
the
suspension
member
and
lower
shock
absorber
nuts
to
the
specified
tighten
ing
torques
COIL
SPRINGS
Removal
Saloons
Jack
up
the
rear
of
the
vehicle
and
support
it
on
stands
2
Remove
the
road
wheels
and
disconnect
the
handbrake
linkage
and
return
spring
3
Remove
the
drive
shaft
flange
nuts
at
the
wheel
side
Fig
H
6
and
the
bump
rubber
securing
nuts
4
Place
ajack
under
the
suspension
ann
and
remove
the
shock
absorber
from
the
lower
mounting
bracket
Carefully
lower
the
jack
and
remove
the
coil
spring
spring
scat
and
bump
rubber
Fig
H7
COIL
SPRINGS
Installation
Saloons
Oleck
the
coil
springs
for
signs
of
deformation
or
cracks
Test
the
spring
for
its
free
length
and
height
under
load
and
compare
the
figures
obtained
with
the
information
in
Technical
Data
Inspect
all
rubber
parts
and
replace
any
which
are
damaged
or
deformed
Installation
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedure
making
sure
that
the
flat
face
of
the
spring
is
at
the
top
REAR
SHOCK
ABSORBERS
Removal
and
Installation
Saloons
Remove
the
trim
in
the
boot
trunk
and
take
off
the
two
nuts
securing
the
upper
shock
absorber
mounting
See
Fig
H
S
Detach
the
shock
absorber
from
the
lower
mounting
bracket
The
shock
absorber
should
be
tested
and
the
fIgUres
com
pared
with
the
specifications
in
Technical
Data
Cbeck
for
oil
leaks
and
cracks
Make
sure
that
the
shaft
is
straight
and
that
the
rubber
bushes
are
not
damaged
or
defonned
Renew
all
unsatis
75
Page 80 of 171

factory
parts
Installation
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedure
REAR
SUSPENSION
ARM
Removal
and
Installation
Saloon
I
J
ad
up
the
car
at
the
rear
and
support
it
on
stands
2
Remove
the
road
wheel
and
brake
drum
as
described
in
the
section
BRAKES
3
Disconnect
the
drive
shaft
from
the
axle
shaft
4
Disconnect
the
handbrake
cable
from
the
equalizer
bracket
and
the
wheel
cylinder
lever
Disconnect
the
brake
hose
from
the
brake
line
by
removing
the
lock
spring
and
then
withdrawing
through
the
connector
Plug
the
end
of
the
brake
line
to
avoid
loss
of
fluid
and
ingress
of
dirt
5
Remove
the
wheel
bearing
locknut
Fig
H
9
the
rear
axle
shaft
wheel
bearings
and
oil
seal
Remove
the
rear
brake
assembly
from
the
suspension
ann
See
section
BRAKES
6
Jack
up
the
suspension
arm
to
relieve
the
tension
on
the
shock
absorber
and
disconnect
the
shock
absorber
from
the
lower
mounting
Lower
the
jack
gradually
and
remove
the
coil
spring
seat
and
bump
rubber
7
Remove
the
bolts
securing
the
suspension
arm
to
the
suspension
member
Fig
H
IO
and
withdraw
the
suspension
arm
The
rubber
bushes
can
be
drawn
out
of
the
suspension
arm
if
necessary
using
the
special
tool
ST
38280000
Fig
H
Il
O1eck
the
suspension
arm
for
distortion
or
cracks
and
inspect
the
rubber
bushes
for
signs
of
wear
or
damage
Renew
any
part
which
is
unsatisfactory
Installation
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedure
Tighten
all
the
suspension
arm
mounting
bolts
with
the
weight
of
the
vehicle
resting
on
the
rear
wheels
The
self
locking
nuts
must
be
renewed
at
each
overhaul
REAR
AXLE
SHAFTS
BEARINGS
AND
SEALS
Saloon
Removal
and
Dismantling
I
Raise
the
vehicle
at
the
rear
and
place
stands
under
the
body
member
2
Remove
the
road
wheel
and
brake
drum
3
Disconnect
the
drive
shaft
from
the
axle
shaft
and
remove
the
wheel
bearing
locknut
The
special
wrench
ST
38060001
can
be
used
to
hold
the
flange
as
shownin
Fig
H
12
4
Withdraw
the
axle
shaft
assembly
as
shown
in
Fig
H
13
using
the
special
tool
ST
07640000
and
sliding
hammer
ST
36230000
Remove
the
rear
axle
drive
flange
5
Use
a
suitable
drift
or
special
tool
ST
37750000
See
Fig
H
14
to
drive
out
the
inner
bearing
and
oil
seal
F
6
Remove
the
grease
retainer
and
withdraw
the
outer
bearing
with
a
conventional
puller
DO
NOT
re
use
this
outer
bearing
REAR
AXLE
SHAFTS
BEARINGS
AND
SEALS
Saloon
Assembly
and
Installation
Oleck
the
axle
shaft
for
straightness
make
sure
that
it
is
not
cracked
or
damaged
in
any
way
00
NOT
heat
the
shaft
if
attempting
to
re
straighten
Make
sure
that
the
lip
of
the
oil
seal
is
not
damaged
or
distorted
Check
the
bearing
for
excessive
wear
and
damage
Oean
the
wheel
bearings
the
oil
seal
and
the
inside
of
the
axle
housing
When
installing
the
wheel
bearings
the
sealed
side
of
the
outer
bearing
should
face
the
wheel
and
the
sealed
side
of
the
inner
bearing
should
face
the
differential
See
Fig
H
IS
Pressure
must
be
applied
to
the
inner
race
when
fitting
When
replacing
the
suspension
arm
check
that
the
distance
piece
is
0
05
mm
0
002
in
shorter
than
the
length
of
the
housing
dimension
LI
See
Fig
H
16
The
distance
piece
and
axle
housing
code
markings
must
coincide
The
wheel
bearing
grease
must
be
replaced
every
50
000
km
30
000
miles
Pack
the
wheel
bearings
with
grease
at
the
positions
shown
in
Fig
H
IS
and
coat
the
lip
of
the
oil
seal
Renew
the
locknut
and
oil
seal
at
each
overhaul
Wheel
bearing
adjustment
Tighten
the
locknut
to
the
specified
torque
reading
of
25
33
kgm
181
239
lb
ft
and
check
that
the
rear
axle
shaft
end
play
does
not
exceed
0
15
mm
0
006
in
with
a
turning
torque
of
less
than
7
kg
em
6
11b
in
for
the
1400
and
1600cc
models
510
series
or
4
5
kg
em
3
91b
in
for
the
1800cc
610
series
If
the
correct
end
play
or
turning
torque
cannot
be
obtained
it
will
be
necessary
to
change
the
distance
piece
See
above
DRIVE
SHAFTS
Removal
and
Dismantlill8
Disconnect
the
end
flanges
and
remove
the
shaft
See
Fig
H
17
The
drive
shaft
should
only
be
dismantled
to
lubricate
the
splines
This
operation
will
only
be
necessary
every
two
years
or
50
000
km
30
000
miles
Remove
the
universal
joint
spider
at
the
differential
side
Refer
to
the
propeller
shaft
section
Remove
the
snap
ring
securiilg
the
sleeve
yoke
plug
and
take
out
the
plug
Compress
the
drive
shaft
and
remove
the
snap
ring
and
stopper
Fig
H
17
Disconnect
the
boot
and
split
the
shaft
Make
sure
that
the
balls
and
spacers
are
retained
DRIVE
SHAFTS
Inspection
and
Assembly
The
drive
shaft
should
be
replaced
as
an
assembly
if
any
part
is
found
to
be
defective
Check
the
shaft
for
straightness
damage
or
wear
Old
79
Page 82 of 171

the
steel
balls
and
the
sleeve
yoke
for
damage
or
wear
Renew
the
boots
and
the
sleeve
yoke
plug
0
ring
if
necessary
Renew
the
universal
joint
jf
faulty
Check
the
play
in
the
drive
shaft
using
a
dial
gauge
as
shown
in
Fig
H
18
The
measurement
taken
with
the
dri
le
shaft
fully
compressed
should
not
exceed
O
lmm
0
004
in
Renew
the
drive
shaft
as
embly
if
the
specified
value
is
not
obtained
Oean
the
old
grease
from
the
sleeve
yoke
and
the
drive
shaft
ball
grooves
and
lubricate
with
oil
Asse
bly
of
the
drive
shaft
is
a
reversal
of
the
dismantling
procedure
noting
the
following
points
Align
the
yokes
and
make
sure
that
the
steel
balls
and
spacers
are
fitted
in
the
correct
order
Select
a
snap
ring
which
will
adjust
the
axial
play
of
the
universaIjoints
to
within
0
02mm
0
0008
in
Snap
rings
are
available
in
four
thicknesses
of
1
49
1
52
1
55
and
1
58
mm
0
0587
0
0598
0
0610
0
0622
in
Apply
a
generous
quantity
of
multi
purpose
grease
to
the
ball
groove
and
the
area
shown
in
Fig
H
19
REAR
AXLE
Removal
See
Fig
H
2
Estate
car
and
Van
Jack
up
the
vehicle
at
the
rear
and
support
it
on
stands
Remove
the
road
wheels
and
brake
drums
I
3
Disconnect
the
brake
hose
from
the
brake
pipe
Plug
the
end
of
the
hose
to
prevent
the
ingress
of
foreign
matter
4
Disconnect
the
handbrake
rear
cable
from
the
balance
lever
assembly
5
Disconnect
the
propeller
shaft
from
the
differential
flange
Release
the
lower
shock
absorber
self
locking
nuts
and
slide
the
mounting
eyes
of
the
shock
absorber
from
the
rear
spring
seat
pivot
6
Support
the
rear
axle
with
ajack
loosen
the
U
bolts
and
remove
the
nuts
from
the
rear
spring
shackles
Withdraw
the
shackles
from
the
spring
eyes
7
Remove
the
V
bolt
lock
nuts
completely
and
lower
the
jack
to
withdraw
the
rear
axle
assembly
REAR
AXLE
Dismailtling
and
Inspection
Disconnect
the
brake
pipes
from
the
wheel
cylinders
and
remove
the
brake
pipe
and
three
way
connector
Remove
the
cross
rod
clamp
and
the
balance
lever
from
the
rear
axle
case
Remove
both
cross
rod
ends
from
the
wheel
cylinder
lever
assembly
Unscrew
the
oil
drain
plug
and
drain
the
oil
from
the
axle
case
into
a
clean
container
The
oil
may
be
re
used
if
it
is
in
good
condition
Remove
the
nuts
securing
the
brake
backplate
to
the
axle
case
and
draw
out
the
axle
shaft
assembly
with
the
backpl
te
and
grease
catcher
A
sliding
hammer
ST
36230000
should
be
used
for
this
operation
as
shown
in
Fig
H
2Q
The
bearing
collar
can
be
removed
with
a
press
or
by
cutting
with
a
cold
chisel
and
the
bearing
withdrawn
with
the
puller
ST
3712001
as
shown
in
Fig
H
2t
Remove
the
brake
backplate
and
withdraw
the
gear
carrier
from
the
axle
case
Check
the
axle
shafts
for
straightness
wear
and
cracks
00
NOT
attempt
to
straighten
a
bent
shaft
by
heating
Check
the
oil
seal
lips
for
signs
of
damage
or
distortion
Make
sure
that
the
bearing
is
not
worn
or
damaged
REAR
AXLE
Assembly
and
Installation
Assembly
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedure
noting
the
following
points
Thoroughly
clean
all
parts
and
fit
a
new
gasket
between
the
axle
case
and
gear
carrier
Tighten
the
nuts
in
a
diagonal
pattern
and
to
the
specified
torque
readings
Fit
the
grease
catcher
bearing
spacer
bearing
and
new
bearing
collar
onto
the
axle
shaft
A
load
of
4
5
tons
will
be
required
to
press
the
bearing
onto
the
shaft
Insert
the
wheel
bearing
with
the
seal
side
facing
the
wheel
and
ensure
that
the
oil
seal
lips
are
coated
with
wheel
bearing
grease
prior
to
fitting
Check
and
adjust
the
axial
play
between
the
wheel
bearing
and
the
axle
housing
using
a
dial
gauge
as
shown
in
Fig
H
22
The
axial
play
should
be
adjusted
to
within
0
3
0
5mm
0
0118
0
0197
in
on
the
1400
and
1600cc
models
and
to
within
O
lmm
0
0039
in
on
the
1800cc
models
Fill
the
rear
axle
with
the
specified
amount
of
oil
and
bleed
and
adjust
the
brake
system
as
described
in
the
appropriate
section
REAR
SPRING
Removal
and
Inspection
Estate
cars
aud
Vans
The
rear
springs
can
be
removed
in
the
following
manner
Jack
up
the
vehicle
at
the
rear
until
the
wheels
are
clear
of
the
ground
and
place
stands
under
the
rear
frame
Disconnect
the
shock
absorber
from
the
spring
seat
Fig
H
21a
and
support
the
rear
axle
housing
with
ajack
3
Take
off
the
locknuts
and
remove
the
U
bolts
shown
arrowed
in
Fig
H
2t
the
spring
seat
location
plates
and
seat
pads
4
Remove
the
nuts
securing
the
front
bracket
to
the
body
remove
the
bracket
from
the
spring
eye
and
car
body
and
withdraw
the
rear
spring
5
Remove
the
upper
and
lower
rear
shackle
nuts
Fig
H
23
and
remove
the
rear
spring
from
the
vehicle
Clean
the
spring
leaves
thoroughly
and
examine
them
for
fractures
or
cracks
Renew
the
assembly
if
necessary
Check
the
front
pin
shackle
U
boIts
and
spring
seat
for
signs
of
wear
cracks
and
damaged
threads
Renew
the
components
as
required
REAR
SPRING
Installation
Installation
of
the
rear
spring
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedure
noting
the
following
points
The
front
bracket
pin
front
bracket
bushing
shackle
pin
and
shackle
bushing
should
be
coated
with
a
soapy
solution
prior
to
assembly
Tighten
the
front
pin
securing
nut
and
the
shock
absorber
lower
securing
nut
with
the
vehicle
weight
resting
on
the
rear
wheels
Ensure
that
the
flange
of
the
shackle
bushing
is
clamped
evenly
on
both
sides
The
tightening
torque
values
can
be
found
on
the
page
entitled
TIGHTENING
TORQUES
81
Page 102 of 171

BRAKE
WARNING
UGHT
SWITCH
A
hydraulically
operated
warning
light
switch
is
located
in
the
engine
compartment
Fig
LA
The
front
and
rear
brake
systems
of
the
dual
circuit
are
connected
to
the
switch
which
provides
a
warning
via
the
warning
light
on
the
instrument
panel
when
a
pressure
difference
of
13
17
kg
sq
cm
185
242Ib
sq
in
occurs
between
the
front
and
rear
brake
systems
The
switch
cannot
be
repaired
and
must
be
renewed
if
faulty
FRONT
DRUM
BRAKE
Removal
1
Jack
up
the
front
of
the
vehicle
and
support
it
on
stands
2
Remove
the
brake
drum
and
the
hub
cap
and
hub
assembly
3
Disconnect
the
brake
pipe
at
the
bracket
on
the
front
suspension
strut
as
previously
described
in
the
section
FRONT
SUSPENSION
4
Unhook
the
two
return
springs
shown
in
Fig
L
5
and
remove
the
brake
shoes
5
Disconnect
the
bridge
pipe
3
in
Fig
L
6
and
remove
the
two
wheel
cylinders
6
Take
out
the
installation
bolts
and
withdraw
the
brake
backplate
from
the
spindle
FRONT
DRUM
BRAKE
Inspection
and
Overhaul
Examine
the
brake
drums
for
scoring
and
out
of
round
The
maximum
permissible
inner
diameter
of
the
drums
must
not
exceed
228
6mm
9
00
in
and
out
of
round
should
be
below
0
02mm
0
0008in
The
brake
shoe
linings
must
re
renewed
when
worn
down
to
a
thickness
of
1
5mm
0
06
in
or
below
Renew
the
linings
if
they
are
contaminated
in
any
way
or
incorrectly
seated
The
complete
set
of
linings
must
be
replaced
if
any
single
lining
is
unsatisfactory
O1eck
the
shoe
return
springs
and
if
they
have
become
weakened
replace
them
Withdraw
the
pistons
and
springs
from
the
wheel
cylinders
and
inspect
the
bore
of
the
cylinders
for
signs
of
wear
corrosion
or
damage
Renew
the
cylinder
and
the
piston
if
the
clearance
between
the
two
exceeds
O
15mm
0
006
in
Renew
the
rubber
boots
and
cups
FRONT
DRUM
BRAKE
Assembly
and
Installation
Assembly
and
installation
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
and
dismantling
procedure
noting
the
fOllowing
points
Apply
a
thin
layer
of
special
grease
to
the
piston
cup
and
other
rubber
parts
when
assembling
the
wheel
cylinder
The
internal
components
of
the
cylinder
should
be
dipped
in
brake
fluid
and
assembled
whilst
still
wet
Install
the
wheel
cylinders
on
the
brake
backplate
and
smear
the
cylinder
backplate
and
cylinder
lever
fulcrum
with
grease
Fig
L
8
Tighten
the
backplate
mounting
bolts
to
a
torque
reading
of
2
7
3
7
kgm
19
5
26
71b
ft
Adjust
the
brake
shoes
and
bleed
the
hydraulic
system
as
described
under
the
appropriate
headings
REAR
DRUM
BRAKE
REMOVAL
Fig
L
IO
Jack
up
the
vehicle
at
the
rear
and
support
it
on
stands
Remove
the
road
wheel
2
Release
the
handbrake
remove
the
clevis
pin
3
from
the
rear
wheel
cylinder
lever
4
see
Fig
L
9
Disconnect
the
handbrake
cable
2
and
remove
the
return
spring
I
3
Remove
the
brake
drum
Remove
the
shoe
retainers
the
return
springs
and
brake
shoes
Fig
L
II
4
Disconnect
the
fluid
line
from
the
wheel
cylinders
and
plug
the
opened
end
to
prevent
to
loss
of
fluid
5
Remove
the
dust
cover
adjusting
shims
and
plates
then
remove
the
wheel
cylinder
from
the
backplate
6
The
brake
backplate
and
axle
shaft
assembly
can
be
with
drawn
if
necessary
by
taking
out
the
four
flange
bolts
and
removing
the
assembly
as
described
in
the
section
REAR
AXLE
AND
REAR
SUSPENSION
REAR
DRUM
BRAKE
Inspection
and
Overhaul
The
inspection
and
overhaul
procedures
fpr
the
rear
drum
brakes
are
similar
to
those
previously
described
for
the
front
drum
brakes
Tighten
the
brake
backplate
mounting
bolts
to
a
torque
reading
of
3
9
5
3
kgm
28
38Ib
ft
FRONT
DRUM
BRAKE
Adjusting
Jack
up
the
vehicle
and
pump
the
brake
pedal
several
times
With
the
brake
drum
installed
turn
one
of
the
adjusting
cams
clockwise
until
the
brake
shoe
is
in
contact
with
the
drum
This
operation
is
carried
out
from
the
rear
of
the
backplate
When
the
brake
shoe
contacts
the
drum
turn
the
cam
in
the
opposite
direction
until
the
shoe
is
just
clear
and
the
brake
drum
can
be
rotated
freely
by
hand
Repeat
the
operation
on
the
other
adjusting
cam
and
then
depress
the
brake
pedal
to
make
sure
that
the
brakes
are
working
correctly
The
adjusters
must
be
released
slightly
if
the
brake
drum
binds
when
turned
by
hand
Fig
L
12
shows
the
adjusting
cams
REAR
DRUM
BRAKE
Adjusting
Jack
up
the
vehicle
at
the
rear
and
pump
the
brake
pedal
several
times
Turn
the
brake
shoe
adjuster
Fig
L
13
until
the
101
Page 150 of 171

The
type
D3034C
carburettor
has
certain
additional
features
These
include
a
power
valve
mechanism
to
improve
the
performance
at
high
speed
a
fuel
cut
off
valve
which
cuts
the
fuel
supply
when
the
ignition
key
is
turned
to
the
off
position
and
an
idling
limiter
to
maintain
the
emissions
below
a
certain
level
Sectional
views
of
the
two
types
of
pumps
are
shown
in
Figs
8
1
and
B
2
An
EP
3
electrical
fuel
pump
is
located
in
the
centre
of
the
spare
wheel
housing
in
the
boot
Fig
B
3
shows
a
sectional
view
of
the
pump
with
its
contact
the
pump
mechanisms
solenoid
relay
and
built
in
filter
The
air
cleaner
uses
a
viscous
paper
type
element
which
should
be
replaced
every
40
000
km
24
000
miles
Cleaning
is
not
required
and
should
not
be
attempted
The
cartridge
type
fuel
strainer
incorporates
a
fibre
clement
which
should
be
renewed
at
inervals
not
exceeding
40
000
km
24
000
miles
Fit
B
4
shows
a
sectional
view
of
the
assembly
The
fuel
lines
should
not
be
disconnected
from
the
strainer
when
the
fuel
tank
is
full
unless
absolutely
necessary
as
the
strainer
is
below
the
fuel
level
FUEL
PUMP
Testing
Disconnect
the
fuel
hose
from
the
pump
outlet
Connect
a
hose
with
an
inner
diameter
of
approximately
6
mm
0
024
in
to
the
pump
outlet
and
place
a
container
under
the
end
of
the
pipe
Note
that
the
inner
diameter
of
the
pipe
must
not
be
too
small
or
the
pipe
will
be
incapable
of
delivering
the
correct
quantity
of
fuel
when
testing
Hold
the
end
of
the
hose
above
the
level
of
the
pump
and
operate
the
pump
for
more
than
IS
seconds
to
check
the
delivery
capacity
The
capacity
should
be
I
400
cc
3
24
U
S
pts
in
one
minute
or
less
The
pump
must
be
removed
from
the
vehicle
if
it
does
not
operate
or
if
a
reduced
quantity
of
fuel
flows
from
the
end
of
the
hose
Remove
the
pump
from
the
vehicle
and
test
as
follows
Connect
the
pump
to
a
fully
charged
battery
If
the
pump
now
operates
and
discharges
fuel
correctly
the
fault
does
not
lie
in
the
pump
but
may
be
attributed
to
any
of
the
following
causes
Battery
voltage
drop
poor
battery
earth
loose
wiring
loose
connections
blocked
hoses
or
a
faulty
carburettor
If
the
pump
does
not
operate
and
discharge
fuel
when
connected
to
the
battery
then
the
pump
itself
is
faulty
and
must
be
checked
as
follows
First
make
sure
that
current
is
flowing
This
will
be
indica
ted
by
sparking
at
the
tenninals
If
current
flows
the
trouble
is
caused
by
a
sticking
pump
plunger
or
piston
The
pump
must
be
dismantled
in
this
case
and
the
parts
thoroughly
cleaned
in
petrol
If
the
current
does
not
flow
a
coil
or
lead
wire
is
broken
and
the
pump
must
be
renewed
A
reduced
fuel
flow
is
caused
by
a
faulty
pump
inlet
or
discharged
valve
or
blocked
filter
mesh
The
pump
must
of
course
be
dismantled
and
serviced
as
necessary
FUEL
PUMP
Removing
and
Dismantling
Remove
the
bolts
attaching
the
fuel
pump
cover
to
the
floor
panel
see
Fig
B
S
Remove
the
bolts
attaching
the
pump
to
the
cover
2
Disconnect
the
cable
and
fuel
hoses
Withdraw
the
pump
Dismantle
as
follows
Slacken
the
locking
band
screws
and
remove
the
strainer
strainer
spring
filter
strainer
seal
and
locking
band
Remove
the
snap
ring
Withdraw
the
four
screws
from
the
yoke
and
remove
the
electromagnetic
ulJ
it
Press
the
plunger
down
and
withdraw
the
inlet
vaive
the
packing
and
the
cylinder
and
plunger
assembly
A
defective
eledrical
unit
cannot
be
dismantled
as
it
is
sealed
and
must
be
renewed
as
a
complete
unit
FUEL
PUMP
Inspection
and
Assembly
Wash
the
strainer
filter
and
gasket
in
petrol
and
dry
using
compressed
air
Renew
the
filter
and
gasket
if
necessary
Note
that
the
filter
should
be
cleaned
every
40
000
km
24
000
miles
Wash
the
plunger
piston
and
inlet
valve
in
petrol
and
make
sure
the
piston
moves
smoothly
in
the
cylinder
Replace
the
parts
if
found
to
be
defective
Insert
the
plunger
assembly
into
the
cylinder
of
the
electri
cal
unit
and
move
the
assembly
up
and
down
to
make
sure
tha
t
the
contacts
are
operated
If
the
contacts
do
not
operate
the
electrical
unit
is
faulty
and
must
be
renewed
Assembly
is
a
reversal
of
the
dismantling
procedures
tak
ing
care
to
renew
the
gaskets
as
necessary
CARBURETIOR
Idling
Adjustment
The
D3034C
carburettor
fitted
to
engines
equipped
with
an
emission
control
system
must
be
adjusted
as
described
under
the
heading
IGNITION
TIMING
AND
IDLING
SPEED
in
the
section
EMISSION
CONTROL
SYSTEM
Reference
should
be
made
to
carburettor
idling
adjustment
procedures
for
the
L14
L16
and
LI8
engines
when
adjusting
the
type
DAK
340
carburettor
fitted
to
the
G
18
engine
A
smooth
engine
speed
of
approximately
550
rpm
should
be
attained
in
this
case
FUEL
lEVEL
Adjustment
DAK
340earburettor
A
constant
fuellevcl
in
the
float
chamber
is
maintained
by
the
float
and
needle
valve
See
Fig
8
6
If
the
fuel
level
does
not
correspond
with
the
level
gauge
line
it
will
be
necessary
to
care
fully
bend
the
float
seat
until
the
float
upper
position
is
correctly
set
The
clearance
H
between
valve
stem
and
float
seat
should
be
I
5
mm
0
0059
in
with
the
float
fully
lifted
Adjustment
can
be
carried
out
by
carefully
bending
the
float
stopper
3
FUEL
lEVEL
Adjustment
D3034Ccarburettnr
The
fuel
level
should
correspond
with
the
level
gauge
line
Adjustment
can
be
carried
out
if
necessary
by
changing
the
gaskets
between
the
float
chamber
body
and
needle
valve
seat
The
gaskets
are
shown
as
item
4
in
Fig
B
7
When
correctly
adjusted
there
should
be
a
clearance
of
approximately
7
mm
0
027
in
between
float
and
chamber
as
indicated
STARTING
INTERLOCK
VALVE
OPENING
The
choke
valve
at
its
fully
closed
position
automatically
opens
the
throttle
valve
to
an
optimum
angle
of
14
degrees
on
the
type
DAK
340
carburettor
and
13
5
degrees
on
the
D3034C
carburettor
With
the
choke
valve
fully
closed
the
clearance
G
I
in
Fig
8
should
be
1
I
mm
0
0433
in
This
clearance
S19
Page 157 of 171
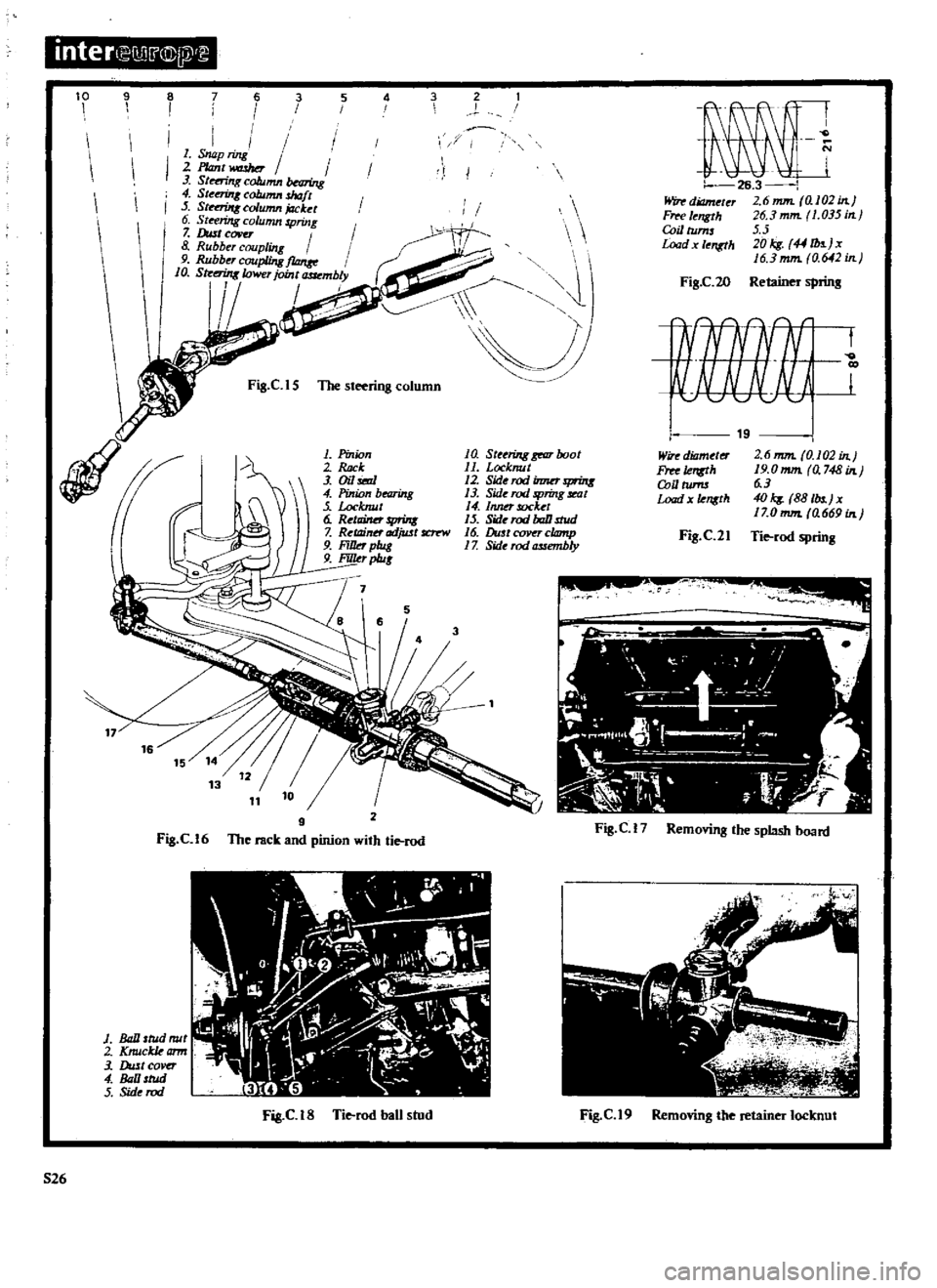
inter
Il
l
@
l
10
9
8
7
6
3
5
4
I
i
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
1
Snap
ring
I
2
P
antwashor
I
3
St
ng
column
bNring
4
S
eerinK
column
shaft
5
Str
nUIx
column
jacket
6
St
riJrg
column
spring
7
Dust
covu
I
8
Rubber
coupling
9
Rubber
coupling
f10nre
I
10
Str
t
rin8lcwer
joint
mbly
I
I
1
Z
I
1
J
Fig
ClS
1be
steering
column
lfj
II
J
1
Pinion
2
ck
3
Oil
i6d
4
Pinion
bearing
Locknut
6
RetlliMr
print
7
Ret11inn
adjwt
fC1
r
W
9
FiIJd
plug
9
FiJILr
p1u
1
a
Steering
gear
boot
11
Locknut
12
Sid
rodinmr
f1fUtl
13
Side
rod
5
Jring
seat
4
Inner
socket
15
Sid
rod
baD
stud
16
DustceJVqclomp
1
Z
Side
rod
assembly
7
5
2
Fig
Cl6
9
The
rack
and
pinion
with
tie
rod
I
1
il
1
W
y
o
Ol
l
r
I
J
I
t4
I
J
Z
i
I
i
r
t
I
1
Ball
stud
mil
2
Knuckkamr
3
DultCOver
4
lll
tud
5
Sid
rod
Fig
C
IS
Tie
rod
ban
stud
526
J
1
26
3
Windiameler
2
6mm
al02in
Fffl
I
ngth
J6
3
mm
1
035
in
CoillUms
5
5
Load
I
ngth
JOkg
44
b
jx
16
3
mm
0
642
in
FiS
C
20
Retainer
sprins
t
Wire
diameter
Free
Ie
Q
U
tums
Load
x
1ensth
Fig
C
21
Fig
C
17
Removing
the
splash
board
Fig
C
19
Removing
the
retainer
locknut
Page 158 of 171

Gean
all
parts
thoroughly
and
renew
if
damaged
If
the
column
shaft
or
jacket
is
excessively
damaged
the
steering
gear
housing
must
be
checked
A
damaged
bearing
must
be
replaced
together
with
the
column
jacket
assembly
Assembly
is
a
reversal
of
the
dismantling
procedures
The
column
shaft
journal
should
be
lubricated
with
multipurpose
grease
which
can
also
be
used
to
fill
up
the
dust
cover
Grease
the
needle
bearing
when
assembling
the
universal
joint
Use
the
tightest
snap
ring
available
when
fitting
the
needle
bearing
Snap
rings
are
supplied
in
oversizes
of
0
95
mm
05
mm
and
1
5
mm
0
0374
0
0413
and
0
0453
in
Installation
of
the
column
assembly
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedures
Tighten
the
rubber
coupling
bolts
to
a
torque
reading
of
I
S
to
1
8
kgm
I
0
8
to
13
0
Ib
ft
Refit
the
steering
wheel
and
tighten
the
nut
to
a
reading
of
4
0
to
5
0
kgm
28
9
to
36
2Ib
ft
RACK
AND
PINION
AND
TIE
ROD
Removing
and
Dismantling
1
Jack
up
the
vehicle
and
support
it
on
stands
Remove
the
road
wheels
2
Slacken
the
bolts
connecting
the
pinion
to
the
steering
lower
joint
See
Figs
C
16
3
Remove
the
bolts
from
the
steering
column
rubber
coupl
ing
See
Fig
C
15
and
remove
the
splash
board
Fig
C
17
4
Remove
the
tie
rod
ball
stud
nut
and
disconnect
the
tie
rod
from
the
knuckle
arm
Fig
C
I8
5
Lift
the
engine
slightly
with
suitable
tackle
but
take
care
not
to
damage
the
accelerator
or
remote
control
linkage
Remove
the
bolts
securing
the
steering
gear
housing
to
the
suspension
member
Withdraw
the
rack
and
pinion
assem
bly
Dismantle
as
follows
Detach
the
steering
lower
joint
from
the
rack
and
pinion
assembly
Clamp
the
unit
in
a
vice
taking
care
not
to
damage
the
steering
gear
housing
Refer
to
Fig
C
16
and
take
off
the
dust
cover
and
boot
clamps
at
both
sides
Slacken
the
stopper
nut
remove
the
tie
rod
inner
socket
and
disconnect
the
tie
rods
from
the
rack
Withdraw
the
spring
seat
and
tie
rod
spring
Take
off
the
steering
gear
boots
at
both
sides
Slacken
the
locknut
and
disconnect
the
tie
rod
outer
socket
from
the
ball
Slacken
the
locknut
remove
the
retainer
adjusting
screw
and
withdraw
the
steering
gear
retainer
See
Fig
C
19
Take
off
the
oil
seal
remove
the
snap
ring
and
withdraw
the
pinion
Remove
the
snap
ring
and
withdraw
the
bearing
from
the
pinion
Remove
the
filler
plug
and
take
out
the
rack
Remove
the
grease
reservoir
Clcan
all
parts
thoroughly
and
replace
any
which
show
signs
of
wear
or
damage
Check
the
axial
play
of
the
inner
and
outer
ball
joints
The
play
should
be
0
06
mm
0
0024
in
for
the
inner
ball
joint
and
from
0
1
to
0
5
mm
0
0039
to
0
0197
in
for
the
outer
joints
Use
a
spring
balance
to
check
the
force
required
to
swing
the
ball
joints
this
should
be
between
0
8
to
LS
kgm
5
8
to
10
8Ib
ft
Renew
the
oil
seal
Examine
the
retainer
and
tie
rod
springs
and
compare
them
with
the
values
given
in
Figs
C
20
and
c
n
RACK
AND
PINION
AND
TIE
ROD
Assembling
and
Adjusting
Press
the
bearing
on
to
the
pinion
gear
and
fi
t
the
tigh
test
snap
ring
available
Snap
rings
are
supplied
in
the
following
over
sizes
Snap
Ring
Thicknesses
1
04
to
1
09
mm
0
0409
to
0
0429
in
1
09
to
I
14
mm
0
0429
to
0
0449
in
1
14toI19mm
0
0449toO
0469in
Ll9
to
1
24
mm
0
0469
to
0
0488
in
1
24
to
1
29
mm
0
0488
to
0
0502
in
Clamp
the
steering
gear
housing
in
a
vice
Grease
the
teeth
and
friction
surfaces
of
the
rack
with
multipurpose
grease
Lubricate
the
gear
housing
from
the
pinion
housing
side
Ensure
that
the
rack
projects
by
an
equal
amount
of
96
mm
3
8
in
in
both
ends
of
the
housing
with
the
rack
teeth
directed
towards
the
pinion
shaft
Grease
the
pinion
teeth
end
bushing
and
pinion
bearing
Engage
the
tccth
of
the
pinion
with
the
rack
and
insert
the
pinion
Make
sure
that
the
bushing
does
not
become
damaged
The
rack
must
project
from
the
housing
by
an
equal
amount
at
each
side
with
the
groove
on
the
pinion
serration
facing
upwards
Fit
the
snap
ring
into
the
housing
groove
to
hold
the
bearing
outer
race
in
position
The
snap
ring
must
fit
tightly
and
can
be
selected
from
the
following
oversizes
Snap
Ring
Thicknesses
LS5
to
1
60
mm
0
0610
to
0
0630
in
1
60
to
1
65
mm
0
0630
to
0
0650
in
1
65
to
I
70
mm
0
0650
to
0
0669
in
1
70
to
I
75
mm
0
0669
to
0
0689
in
Fit
the
oil
seal
Use
a
dial
gauge
as
shown
in
Fig
C
22
to
check
the
thrust
play
of
the
pinion
The
play
should
be
less
than
0
09mm
0
0035
in
Grease
the
retainer
and
insert
it
with
the
spring
Tighten
the
retainer
adjusting
screw
fully
then
back
it
off
by
20
to
25
degrees
Tighten
the
locknut
to
a
torque
reading
of
4
0
to
6
0
kgm
28
9
to
43
4lb
ft
Coat
the
locknut
with
liquid
pack
ing
Three
Bond
When
the
rack
and
pinion
is
assembled
measure
the
force
required
to
rotate
the
pinion
and
also
the
preload
of
the
rack
Use
a
spring
balance
as
shown
in
Figs
C
23
and
C
24
and
check
that
the
pinion
torque
is
8
to
20
kg
cm
7
to
17
Ib
in
and
the
rack
preload
is
from
8
to
18
kg
17
6
to
39
7Ibs
Take
care
to
slide
the
assembly
over
the
complete
range
of
the
stroke
Fit
a
dust
cover
clamp
at
each
end
of
the
housing
Install
the
stop
nut
on
the
threads
of
the
rack
Liberally
grease
the
ball
joint
friction
area
of
the
tie
rod
assembly
Assemble
the
spring
and
ball
seat
and
fit
the
inner
socket
part
of
the
tie
rod
assembly
to
the
rack
Make
sure
the
boot
is
positioned
at
the
ball
stud
end
Note
that
the
left
hand
tie
rod
is
marked
with
an
L
the
right
hand
rod
is
not
marked
527
Page 159 of 171
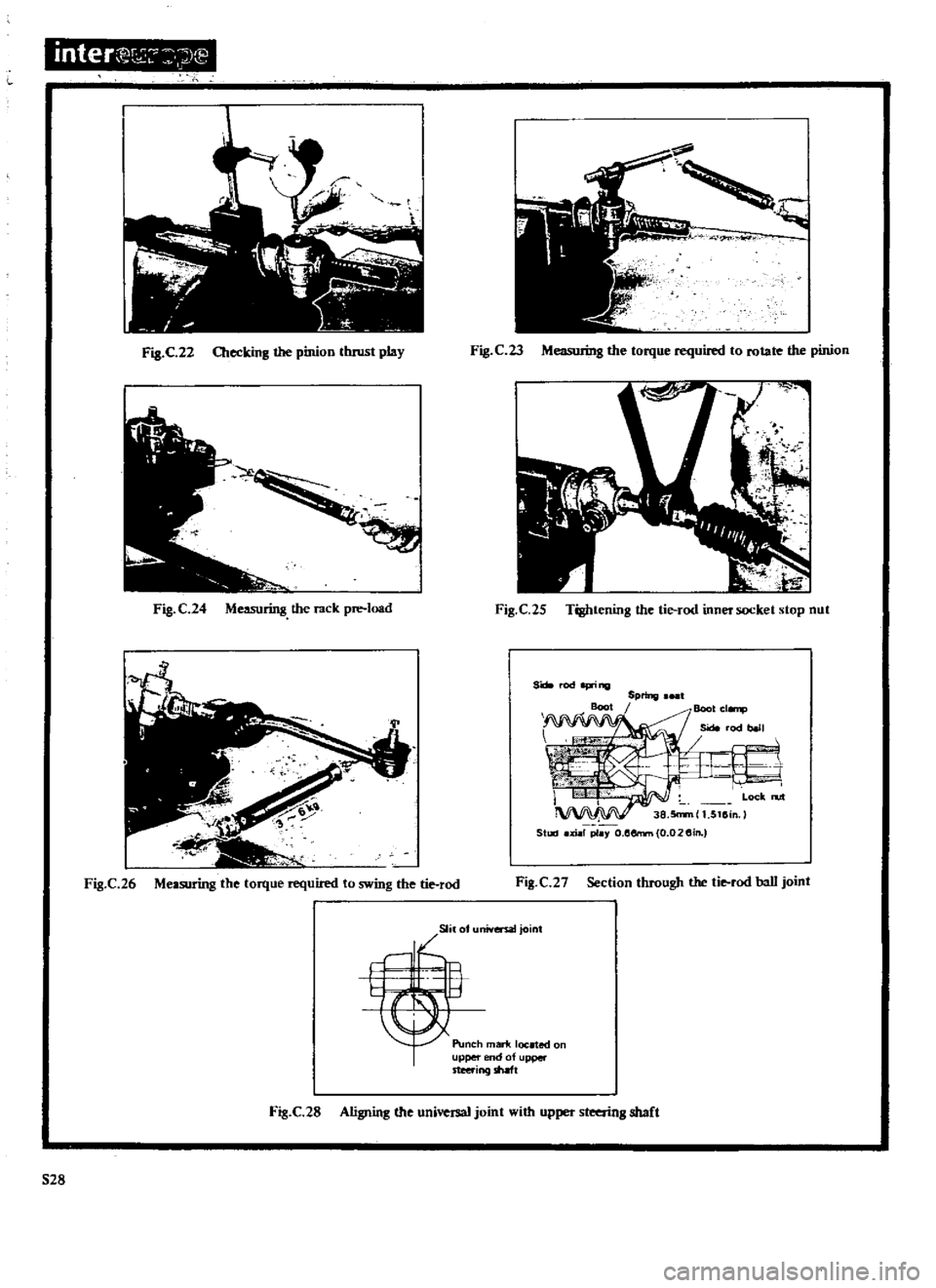
inter
C
7
j
l
l
IJ
Fig
C
22
Checking
the
pinion
tluust
play
Fig
C23
ML
Io
b
the
torque
required
to
rotate
the
pinion
Fig
C
24
Measuring
the
rack
pre
load
Fig
C
25
Tightening
the
tie
rod
inner
socket
stop
nut
S
rod
I
p
ing
Boot
Spring
I
Boot
cl
np
Side
rod
1
t
I
I
Lock
n
rt
38
5n
m
1
5115in
Staaj
xial
p1
Y
o
l5errm
0
02
5in
Fig
C
26
Measuring
the
torque
required
to
swing
the
tie
rod
Fig
C
2
Section
through
the
tie
rod
ball
joint
Slila
niversatjoint
Punch
marif
located
on
upper
nd
of
upper
steering
shaft
Fig
C
28
Aligning
the
universal
joint
with
upper
steering
shaft
528
Page 160 of 171

Tighten
the
inner
socket
until
the
ball
seat
is
at
the
rack
end
then
back
off
the
socket
by
30
to
40
degrees
and
tighten
the
stop
nut
to
a
torque
reading
of
8
0
to
10
0
kgm
57
8
to
72
3
Ib
ft
as
shown
in
Fig
C
25
With
the
tie
rod
assembled
measure
the
force
required
to
swing
the
tie
rod
Hook
a
spring
balance
at
the
end
of
the
rod
as
shown
in
Fig
C
26
and
check
that
the
force
is
from
3
0
to
6
0
kgm
6
6
to
13
2
lb
Measure
the
stroke
of
the
rack
which
should
be
73
0
mm
2
874
in
Fit
grease
nipples
at
both
ends
of
the
rack
and
pinion
housing
Apply
multipurpose
ase
to
each
joint
until
a
small
quantity
of
grease
appears
at
the
out
let
hole
in
the
boot
Do
not
use
an
excessive
amount
of
grease
The
pinion
housing
should
be
lubricated
until
a
small
quantity
of
grease
appears
between
rack
and
housing
Remove
the
grease
nipple
and
fit
the
plug
Fit
the
boot
Fill
the
grease
reseIVoir
with
grease
and
attach
it
to
the
rack
housing
Adjust
the
length
of
the
tie
rods
at
both
sides
as
des
ribed
under
FRONT
WHEEL
ALIGNMENT
Assemble
the
steering
lower
joint
to
the
rack
and
pinion
and
tighten
the
lower
joint
bolt
to
a
torque
reading
of
4
0
to
5
0
kgm
29
0
to
36
0
Ib
ft
Installation
of
the
rack
and
pinion
assembly
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedure
COLLAPSIBLE
STEERING
Removi
8
and
Dismantti
8
The
steering
coluJllfl
See
Fig
C
3
can
be
removed
in
a
similar
manner
to
the
standard
type
of
column
Take
care
not
to
drop
the
column
when
it
is
removed
from
the
vehicle
or
the
shaft
may
collapse
Do
not
exert
any
pressure
on
the
column
or
the
bellows
may
be
defonned
To
dismantle
proceed
as
follows
Remove
the
retaining
wire
and
pull
out
the
lower
shaft
Disconnect
the
control
linkage
if
the
vehicle
is
fitted
with
auto
matic
transmission
Slide
the
steering
shaft
bracket
away
With
draw
the
screws
and
separate
the
upper
and
lower
tubes
Assembly
is
a
reversal
of
the
dismantling
procedure
Note
that
the
slot
in
the
universal
joint
must
be
aligned
with
the
punch
mark
at
the
top
of
the
upper
steering
shaft
as
shown
in
Fig
C
28
When
installing
the
column
make
sure
that
the
bellows
do
not
become
bent
of
twisted
as
the
clamp
and
bottom
plate
bolts
are
tightened
TechnICal
Data
TYP
Gear
I1ltio
Rack
and
pinion
17
8
I
Steerin
column
shaft
spring
Wire
diameter
Freelenath
CoiltW
llJ
Load
length
Retainer
sprinJ
dimension
Wire
diameter
F
CoilturnJ
l
oadxlensth
Side
rod
SPrina
dimeruion
Wire
diameter
Fn
elenath
Coil
turns
Load
x
lensth
Side
rod
inner
ball
joint
ax
ia
I
play
Side
rod
outer
ball
joint
uiaJ
play
Pinion
thrultplay
Retainer
float
play
Rack
moke
Side
rod
inner
ball
joint
swinsinl
torque
Side
rod
uter
ball
joint
swingina
torque
Pinion
oration
torque
Rack
pre1
d
Wheel
alipment
1IIl1a
a
ondition
Cut
c
m
Kinl
pin
inclination
Toe
in
S
In
teerinlan
eOut
10
40
8005
12
15
mm
0
47
0
59
in
38024
35036
2
9
mm
0
11
2
in
36
5
mm
1
4370
in
3
25q
551
18mm
0
7087
2
6
mm
1
102in
26
3
mm
1
035
in
5
5
20
kl
lbs
16
3
mm
0
642
in
26
mm
0
102
in
19
0
mm
0
748
in
6
3
40
q
88Ibs
17
0
mm
0
669
in
0
06
mm
0
002
m
0
1
0
5
mm
0
0039
0
0197
in
less
than
0
3
mm
0
0118
in
0
09
mm
0
0035
in
73
mm
t
2
87
in
0
8
1
5
q
m
5
8
10
8Ib
n
0
8
J
S
kg
m
5
8
JO
8Ib
ft
8
20q
7
17
lb
in
8
18
q
l7
6
39
7Ibs
Strut
DlelDbly
Strut
outer
Ilia
50
8
mm
2
0
in
Piston
rod
di
a
20
mm
0
787
in
Cylinder
inner
dia
30mm
I
181
in
Dampinl
force
at
pistonlpeed
0
3
m
I
1
08
ft
I
Expansion
67
IOq
I47
7
221bs
Compression
25
4kl
55
1
8
81bs
Shock
absorber
inner
cylinderlcngth
IOmm
16
1
in
R
IlD
vchicle
LH
D
ehide
CoiIsprina
LIi
IlIi
OOIh
Wire
diameter
mm
in
12
0
472
12
0
472
12
0
472
Coil
diameter
mm
in
130
5
12
130
5
12
130
5
12
Coil
Ium
S
Coil
effective
turnl
6
5
6
5
6
5
Free
lenJth
mm
in
371
5
14
6
386
5
15
2
371
5
14
6
Installed
hei
ht
load
mmq
180
270
200
270
180
270
in
lb
7
1
594
7
9
594
7
1
594
SpriDgCOfl
ltant
ka
mm
1
45
US
1
45
529
1