brake light DATSUN B110 1973 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1973, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1973Pages: 513, PDF Size: 28.74 MB
Page 11 of 513
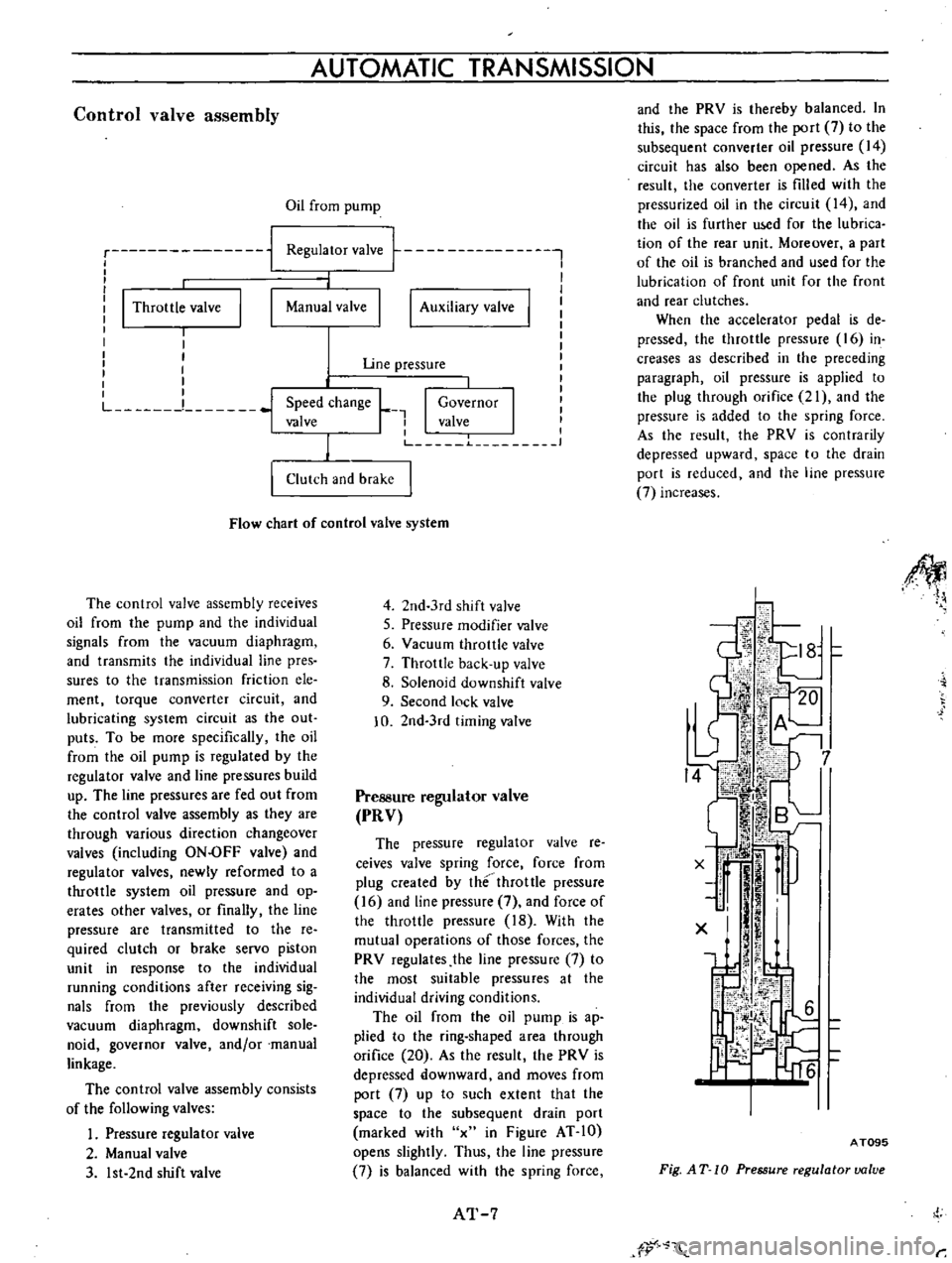
Control
valve
assembly
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
Oil
from
pump
ru
nn
i
I
I
I
Throttle
valve
I
I
1
m
nn
I
Auxiliary
valve
I
Regulator
valve
j
Manual
valve
I
Uoe
pressure
Speed
change
L
I
Governor
valve
I
I
valve
J
1
1
Clutch
and
brake
Flow
chart
of
control
valve
system
The
control
valve
assembly
receives
oil
from
the
pump
and
the
individual
signals
from
the
vacuum
diaphragm
and
transmits
the
individual
line
pres
sures
to
the
transmission
friction
ele
ment
torque
converter
circuit
and
lubricating
system
circuit
as
the
out
puts
To
be
more
specifically
the
oil
from
the
oil
pump
is
regulated
by
the
regulator
valve
and
line
pressures
build
up
The
line
pressures
are
fed
out
from
the
control
valve
assembly
as
they
are
through
various
direction
changeover
valves
including
ON
OFF
valve
and
regulator
valves
newly
reformed
to
a
throttle
system
oil
pressure
and
op
crates
other
valves
or
finally
the
line
pressure
are
transmitted
to
the
re
quired
clutch
or
brake
servo
piston
unit
in
response
to
the
individual
running
conditions
after
receiving
sig
nals
from
the
previously
described
vacuum
diaphragm
downshift
sole
noid
governor
valve
and
or
manual
linkage
The
control
valve
assembly
consists
of
the
following
valves
Pressure
regulator
valve
2
Manual
valve
3
1st
2nd
shift
valve
4
2nd
3rd
shift
valve
S
Pressure
modifier
valve
6
Yacuum
throttle
valve
7
Throttle
back
up
valve
8
Solenoid
downshift
valve
9
Second
lock
valve
0
2nd
3rd
timing
valve
Pressure
regulator
valve
PRV
The
pressure
regulator
valve
re
ceives
valve
spring
force
force
from
plug
created
by
the
throttle
pressure
16
and
line
pressure
7
and
force
of
the
throttle
pressure
18
With
the
mutual
operations
of
those
forces
the
PRY
regulates
the
line
pressure
7
to
the
most
suitable
pressures
at
the
individual
driving
conditions
The
oil
from
the
oil
pump
is
ap
plied
to
the
ring
shaped
area
through
orifice
20
As
the
result
the
PRY
is
depressed
downward
and
moves
from
port
7
up
to
such
extent
that
the
space
to
the
subsequent
drain
port
marked
with
x
in
Figure
AT
10
opens
slightly
Thus
the
line
pressure
7
is
balanced
with
the
spring
force
AT
7
and
the
PRY
is
thereby
balanced
In
this
the
space
from
the
port
7
to
the
subsequent
converter
oil
pressure
14
circuit
has
also
been
opened
As
the
result
the
converter
is
filled
with
the
pressurized
oil
in
the
circuit
14
and
the
oil
is
further
u
d
for
the
Iubrica
tion
of
the
rear
unit
Moreover
a
part
of
the
oil
is
branched
and
used
for
the
lubrication
of
front
unit
for
the
front
and
rear
clutches
When
the
accelerator
pedal
is
de
pressed
the
throttle
pressure
16
in
creases
as
described
in
the
preceding
paragraph
oil
pressure
is
applied
to
the
plug
through
orifice
21
and
the
pressure
is
added
to
the
spring
force
As
the
result
the
PRY
is
contrarily
depressed
upward
space
to
the
drain
port
is
reduced
and
the
line
pressure
7
increases
Afl
II
Jwi
06
A
J
L
I
7
I
tf
Iij
BL
i
il
J
jti
r
x
r
1
J
I
l
I
X
6
C
l
o
ii
J
f
A
T09S
Fig
AT
10
Pressure
regulator
value
tr
r
Page 38 of 513
Fig
A
T
49
Torque
converter
aligning
cut
3
When
connecting
torque
con
verter
to
transmission
measure
dis
tance
A
to
be
certain
that
they
are
correctly
assembled
See
Figure
AT
50
Distance
A
More
than
16
5
IllIll
0
650
in
A
AT117
Fig
A
T
50
Installing
torque
converter
CHASSIS
4
Bolt
converter
to
drive
plate
Tightening
torque
0
8
to
1
0
kg
Ill
5
8
to
7
2
ft
Ib
Note
Align
chalk
marks
painted
a
cross
both
parts
during
disas
sembling
processes
5
After
converter
is
installed
rotate
crankshaft
several
turns
and
check
to
be
sure
that
transmission
rotates
freely
without
binding
6
Pour
recommended
automatic
transmission
fluid
up
to
correct
level
through
oil
charge
pipe
7
Connect
manual
lever
to
shift
rod
Operation
should
be
carried
out
with
manual
and
selector
levers
in
N
8
Connect
inhibitor
switch
wires
Notes
a
Refer
to
covering
topic
under
Checking
and
adjusting
inhibitor
switch
on
page
AT
51
b
Inspect
and
adjust
switch
as
above
whenever
it
has
to
be
removed
for
service
9
Check
inhibitor
switch
for
op
eration
AT
34
Starter
should
be
brought
into
op
eration
only
when
selector
lever
is
in
P
and
N
positions
it
should
not
be
started
when
lever
is
in
D
2
1
and
R
positions
Back
up
lamp
should
also
light
when
selector
lever
is
placed
in
R
position
10
Check
level
of
oil
in
transmis
sion
For
detailed
procedure
see
page
AT
49
II
Move
selector
lever
through
all
positions
to
be
sure
that
transmission
operates
correctly
With
hand
brake
applied
rotate
engine
at
idling
Without
disturbing
the
above
setting
move
selector
lever
through
N
to
D
to
2
to
I
and
to
R
A
slight
shock
should
be
felt
by
hand
gripping
selector
each
time
transmission
is
shifted
Note
See
page
AT
50
for
checking
enigne
idling
12
Check
to
be
sure
that
line
pres
sure
is
correct
To
do
this
refer
to
relative
topic
under
Testing
line
pres
sure
on
page
AT
53
13
Perform
stall
test
as
per
the
instructions
on
page
AT
51
Page 48 of 513
Assembly
I
Prior
10
assemlbing
dip
all
parts
in
clean
automatic
transmission
fluid
Reverse
disassembly
procedure
to
assemble
brake
2
Use
extreme
care
to
avoid
dam
aging
rubber
ring
when
installing
seal
lace
3
Blow
under
pressure
air
from
apply
side
of
piston
to
lislen
for
defi
nite
piston
operation
as
shown
in
Figure
AT
93
4
With
appIy
side
of
piston
plugged
with
thumb
blow
air
under
pressure
into
cylinder
from
release
side
as
shown
in
Figure
AT
94
If
retainer
is
raised
a
little
it
is
an
indication
that
attaching
bolts
are
loosened
calling
for
retightening
Governor
Disassembly
l
Separate
governor
from
oil
dis
tributor
by
unscrewing
attaching
bolts
2
To
disassemble
secondary
gover
nor
remove
spring
seat
spring
and
secondary
governor
valve
from
valve
body
in
this
written
order
as
shown
in
Figure
AT
95
3
If
primary
governor
is
to
be
dis
assembled
for
any
purpose
remove
spring
seat
primary
governor
valve
spring
and
spring
eal
CHASSIS
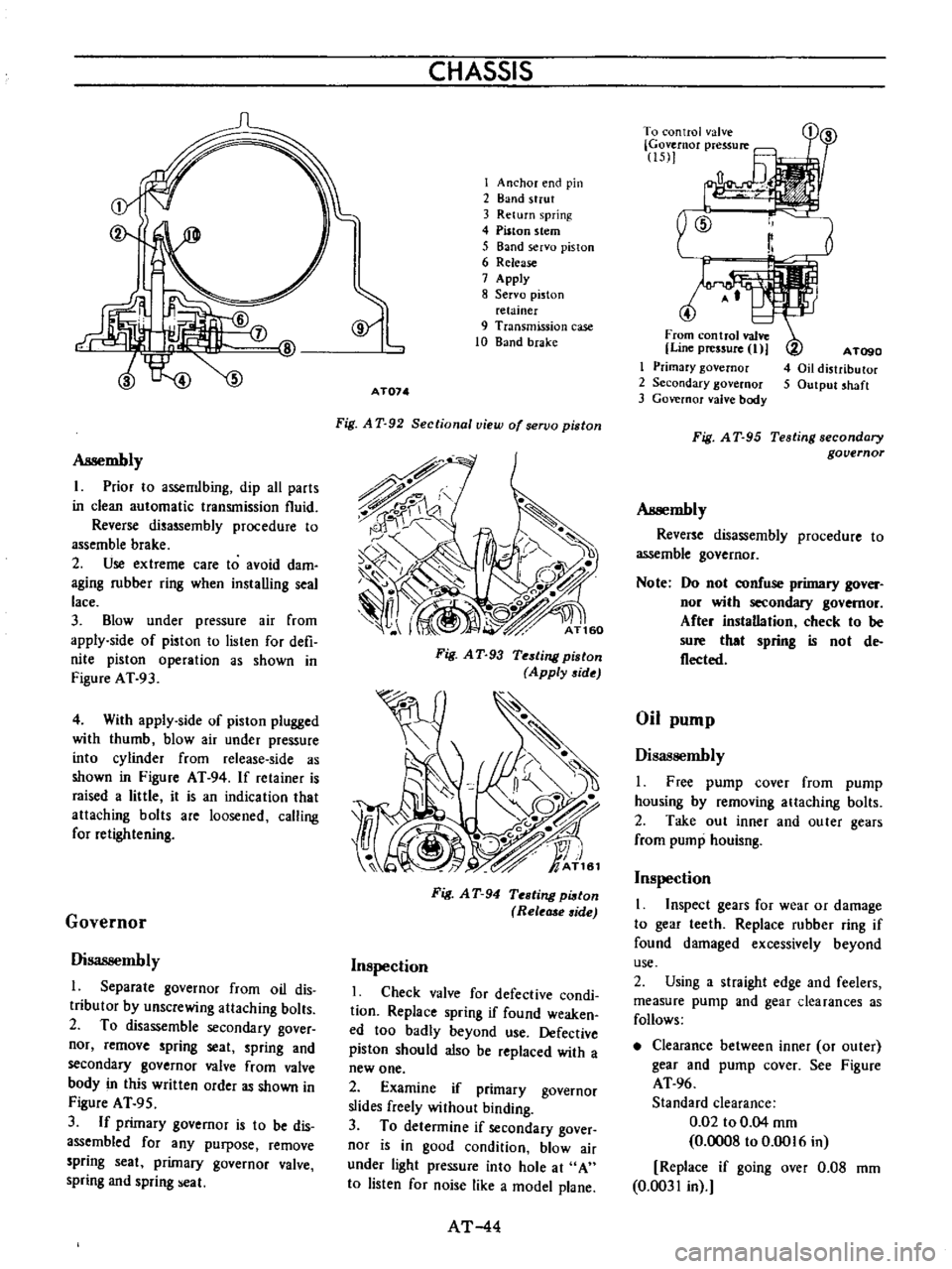
I
Anchor
end
pin
2
Band
strut
3
Return
spring
4
Piston
stem
5
Band
servo
piston
6
Release
7
Apply
8
Servo
piston
relainer
9
Transmission
case
10
Band
brake
AT074
Fig
A
T
92
Sectional
view
of
servo
piston
Fig
A
T
93
Testing
piston
Apply
side
Fig
A
T
94
Testing
pi8ton
Rele
side
Inspection
I
Check
valve
for
defective
condi
tion
Replace
spring
if
found
weaken
ed
too
badly
beyond
use
Defective
piston
should
also
be
replaced
with
a
new
one
2
Examine
if
primary
governor
slides
freely
without
binding
3
To
determine
if
secondary
gover
nor
is
in
good
condition
blow
air
under
light
pressure
into
hole
at
A
to
listen
for
noise
like
a
model
plane
AT
44
r
To
control
valve
Governor
pressure
15
1
4
From
control
valve
Line
pressure
I
I
Primary
governor
2
Secondary
governor
3
Governor
valve
body
A
TogO
4
Oil
distributor
5
Output
shaft
Fig
A
T
95
Testing
secondary
governor
Assembly
Reverse
disassembly
procedure
to
assemble
governor
Note
Do
nol
confuse
primary
gover
nor
wilh
secondary
governor
After
instaDation
check
to
be
sure
that
spring
is
nol
de
flecled
Oil
pump
Disassembly
I
Free
pump
cover
from
pump
housing
by
removing
attaching
bolts
2
Take
out
inner
and
outer
gears
from
pump
houisng
Inspection
1
Inspect
gears
for
wear
or
damage
to
gear
leeth
Replace
rubber
ring
if
found
damaged
excessively
beyond
use
2
Using
a
straight
edge
and
feelers
measure
pump
and
gear
clearances
as
follows
Clearance
between
inner
or
outer
gear
and
pump
cover
See
Figure
AT
96
Standard
clearance
0
02
to
0
04
mm
0
0008
to
0
0016
in
Replace
if
going
over
0
08
mm
0
0031
in
Page 55 of 513

c
Inspection
and
adJu
Stmenf
trouble
first
check
the
linhge
f
no
1
i
jI
fect
is
found
in
the
lin1
age
check
of
manu
a
l
liiiJ
i
the
inhibitor
switch
Th
d
1F
aI
S
t
th
I
I
f
e
a
JU
i
J
u
epara
e
e
range
se
eet
ever
rom
Iy
important
ii
s3
ns
etion
of
oil
the
lower
shift
rod
and
turn
the
range
1
level
for
the
automatiC
tran
smission
select
lever
to
N
Therefore
great
care
should
be
exer
Note
In
the
position
N
the
slot
of
cised
because
defective
adjustment
will
the
manual
shaft
is
vertical
result
in
the
breakdown
of
the
trans
By
the
use
of
the
tester
check
the
two
bIack
yellow
BY
wires
from
the
inhibitor
switch
in
the
ranges
N
and
P
and
the
two
red
bIack
RB
wires
in
the
range
R
for
continuity
Turn
range
select
lever
to
both
directions
from
each
lever
set
position
and
check
each
continuity
range
It
is
normal
if
the
electricity
is
on
while
the
lever
is
within
an
angle
of
about
3
0
on
both
sides
from
each
lever
set
line
How
ever
if
its
continuity
range
is
obvi
ously
unequal
on
both
sides
the
adjustment
is
required
f
any
malfunction
is
found
un
screw
the
fastening
nut
of
the
range
selector
lever
and
two
fastening
bolts
of
the
switch
body
and
then
remove
the
machine
screw
under
the
switch
body
Adjust
the
manual
shaft
correct
ly
to
the
position
N
by
means
of
the
selector
lever
When
the
slot
of
the
shaft
becomes
vertical
the
detent
works
to
position
the
shaft
correctly
with
a
click
sound
Move
the
switch
slightly
aside
so
that
the
screw
hole
will
be
aligned
with
the
pin
hole
of
the
internal
rotor
combined
with
the
manual
shaft
and
check
their
alignment
by
inserting
a
1
5
0101
0
0591
in
diameter
pin
into
the
holes
If
the
alignment
is
made
correct
1
5ten
the
switch
body
with
the
bolts
pull
out
the
pin
and
tighten
up
the
screw
again
into
the
hole
and
fasten
the
selector
lever
as
before
Check
over
again
the
continuity
with
the
tester
If
the
malfunction
still
remains
replace
the
inhibitor
switch
mission
Inspection
Pull
the
selector
lever
toward
you
and
turn
it
so
far
as
p
to
1
range
where
clicks
will
be
felt
by
hand
This
is
the
detent
of
manual
valve
in
the
body
and
indicates
the
correct
posi
tion
of
the
lever
Inspect
whether
the
pointer
of
selector
dial
corresponds
to
this
point
and
also
whether
the
lever
comes
in
alignment
with
the
stepping
of
posi
tion
plate
when
it
is
released
Adjustment
This
procedure
can
be
accom
plished
by
referring
to
Removal
and
nstallation
Checking
and
adjusting
inhibitor
switch
The
inhibitor
switch
serves
to
light
the
reverse
lamp
in
the
range
R
of
the
transmission
operation
and
also
to
rotate
the
starter
motor
in
the
ranges
N
and
P
j
r@
I
If
r
f
B
@
I
Jt
@
@
c
v@
i
r
fji
AT109
1
Inhibitor
switch
2
Manual
shaft
3
Washer
4
Nut
5
Manual
plate
Fig
AT
II
0
Con
truction
of
inhibitor
witch
6
Washer
7
Nut
8
Inhibitor
switch
9
Range
select
lever
Check
whether
the
reverse
lamp
and
the
starter
motor
operate
normal
ly
in
these
ranges
If
there
is
any
t
ki
A
mm
ATIC
TRANSMISSION
STALL
TEST
The
purpose
of
this
test
is
to
check
the
transmission
and
engine
for
trou
ble
by
measuring
the
maximwn
num
bers
of
revolutions
of
the
engine
while
vehicle
is
held
in
a
stalled
condition
and
the
carburetor
is
in
full
throttle
operation
with
the
selector
lever
in
AT
51
rang
s
D
2
and
I
respectively
and
by
com
pairing
the
measured
re
sults
with
the
standard
values
Standard
stall
revolution
1
750
to
2
000
rpm
Components
to
be
tested
and
test
items
1
Clutches
brake
and
band
in
trans
mission
for
slipping
2
Torque
converter
for
function
3
Engine
for
overall
property
Stall
test
procedures
Before
testing
check
the
enigne
oil
and
torque
converter
oil
warm
up
the
engine
cooling
water
to
the
suitable
temperature
by
warming
up
ope
ration
at
1
200
rpm
with
the
selector
lever
in
the
range
P
for
several
minutes
and
warm
up
the
torque
converter
oil
to
the
suitable
temperature
60
to
IOOoC
140
to
2120F
1
Mount
the
engine
tachometer
at
a
location
that
allows
good
visibility
from
the
driver
s
seat
and
put
a
mark
on
specified
revolutions
on
the
meter
2
Secure
the
front
and
rear
wheels
completely
with
chocks
and
apply
the
hand
brake
Be
sure
to
depress
the
brake
pedal
firmly
with
the
left
foot
before
depressing
down
the
accelerator
pedal
3
Throw
the
selector
lever
into
the
range
D
4
Slowly
depress
the
accelerator
pedal
down
till
the
throttle
valve
is
fully
opened
Quickly
read
and
record
the
engine
revolution
when
the
engine
begins
to
rotate
steadily
and
then
release
the
accelerator
pedal
5
Turn
the
selector
lever
into
N
and
operate
the
enigne
at
approxi
mately
1
200
rpm
for
more
than
one
minute
to
cool
down
the
torque
con
verter
oil
and
coolant
6
Make
similar
stall
tests
in
the
ranges
2
I
and
R
Note
The
stall
test
operation
as
spec
ified
in
the
item
4
should
be
made
within
five
seconds
If
it
takes
too
long
the
oil
deterio
rates
and
the
clutches
brake
Page 92 of 513
CHASSIS
Tightening
torque
of
front
suspension
cross
member
and
body
is
3
2
to
4
0
kg
m
23
1
to
28
9
ft
Ib
5
Tightening
torque
of
bolt
used
to
secure
the
upper
portion
of
the
strut
assembly
on
the
body
is
1
6
to
2
1
kg
m
11
6
to
15
2ft
lb
FRONT
AXLE
Removal
I
Jack
up
the
vehicle
remove
the
wheel
and
discon
nect
the
brake
hose
at
the
strut
outer
casing
bracket
unit
For
details
see
Removal
of
front
axle
and
suspension
assembly
2
Remove
the
brake
caliper
installation
bolts
and
remove
the
caliper
assembly
Disc
type
brake
3
Remove
the
brake
druOL
Drum
type
brake
4
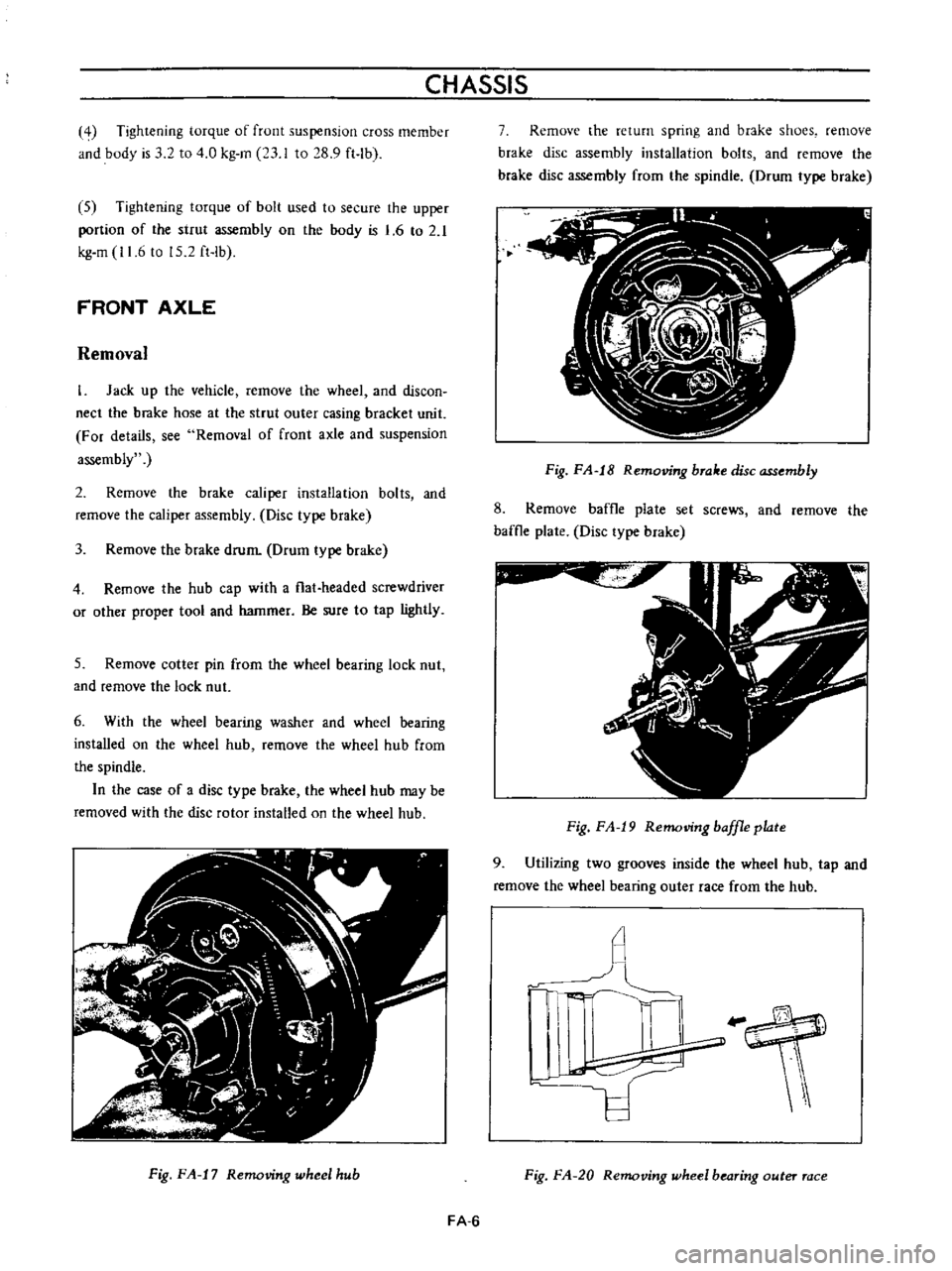
Remove
the
hub
cap
with
a
flal
headed
screwdriver
or
other
proper
tool
and
hammer
Be
sure
to
tap
lightly
5
Remove
cotter
pin
from
the
wheel
bearing
lock
nut
and
remove
the
lock
nut
6
With
the
wheel
bearing
washer
and
wheel
bearing
installed
on
the
wheel
hub
remove
the
wheel
hub
from
the
spindle
In
the
case
of
a
disc
type
brake
the
wheel
hub
may
be
removed
with
the
disc
rotor
installed
on
the
wheel
hub
Fig
FA
17
Removing
wheel
hub
7
Remove
the
return
spring
and
brake
shoes
remove
brake
disc
assembly
installation
bolts
and
remove
the
brake
disc
assembly
from
the
spindle
Drum
type
brake
Fig
FA
IS
Removing
brake
disc
a
ssembly
8
Remove
baffle
plate
set
screws
and
remove
the
baffle
plate
Disc
type
brake
Fig
FA
19
Removingbaffleplate
9
Utilizing
two
grooves
inside
the
wheel
hub
tap
and
remove
the
wheel
bearing
outer
race
from
the
hub
Fig
FA
20
Removing
wheel
bearing
outer
race
FA
6
Page 112 of 513
Vehicle
pulls
to
right
or
left
When
driving
with
hands
off
the
steering
wheel
over
a
flat
road
the
vehicle
gently
swerves
to
right
or
left
Note
A
defective
rear
suspension
may
also
be
the
cause
of
this
trouble
and
therefore
see
also
the
chapter
dealing
with
the
rear
suspension
Instability
of
vehicle
Stiff
steering
wheel
checking
up
procedure
Jack
up
front
wheels
detach
the
steering
gear
and
operate
the
steering
wheel
and
If
it
is
light
check
steering
linkage
and
suspension
groups
If
it
is
heavy
check
steering
gear
and
steering
colunm
groups
CHASSIS
Malfunction
of
shock
absorber
inside
the
strut
or
loose
installation
bolts
Unbalance
of
vehicle
level
Improper
air
pressure
of
tire
or
insuf
ficient
tightening
of
wheel
nuts
Difference
in
height
of
right
and
left
tire
treads
Incorrect
adjustment
or
abrasion
of
front
wheel
bearing
Collapsed
or
twisted
front
spring
Incorrect
wheel
alignment
Incorrect
brake
adjustment
binding
Worn
rubber
bushings
for
transverse
link
and
tension
rod
Deformed
steering
linkage
and
suspension
link
Unbalanced
vehicle
level
Improper
air
pressure
of
tire
Worn
rubber
bushings
for
transverse
link
and
tension
rod
Incorrect
wheel
alignment
Worn
or
deformed
steering
linkage
and
suspension
link
Incorrect
adjustment
of
steering
gear
Deformed
unbalanced
wheel
Improper
air
pressure
of
tire
Insufficient
lubricants
or
mixing
im
purities
in
steering
linkage
or
excessively
worn
steering
linkage
Stiff
or
damaged
suspension
ball
joint
or
lack
of
grease
Worn
or
incorrectly
adjusted
wheel
bearing
Worn
damaged
steering
gear
and
bearing
FA
26
Replace
or
retighten
Correct
the
unbalance
Adjust
or
tighten
Replace
tires
Adjust
or
replace
Replace
Adjust
Adjust
Replace
Replace
Correct
the
unbalance
Adjust
Adjust
Adjust
Replace
Adjust
Correct
or
replace
Adjust
Repl
nish
grease
or
re
place
the
part
Replace
Replace
or
adjust
Replace
Page 116 of 513
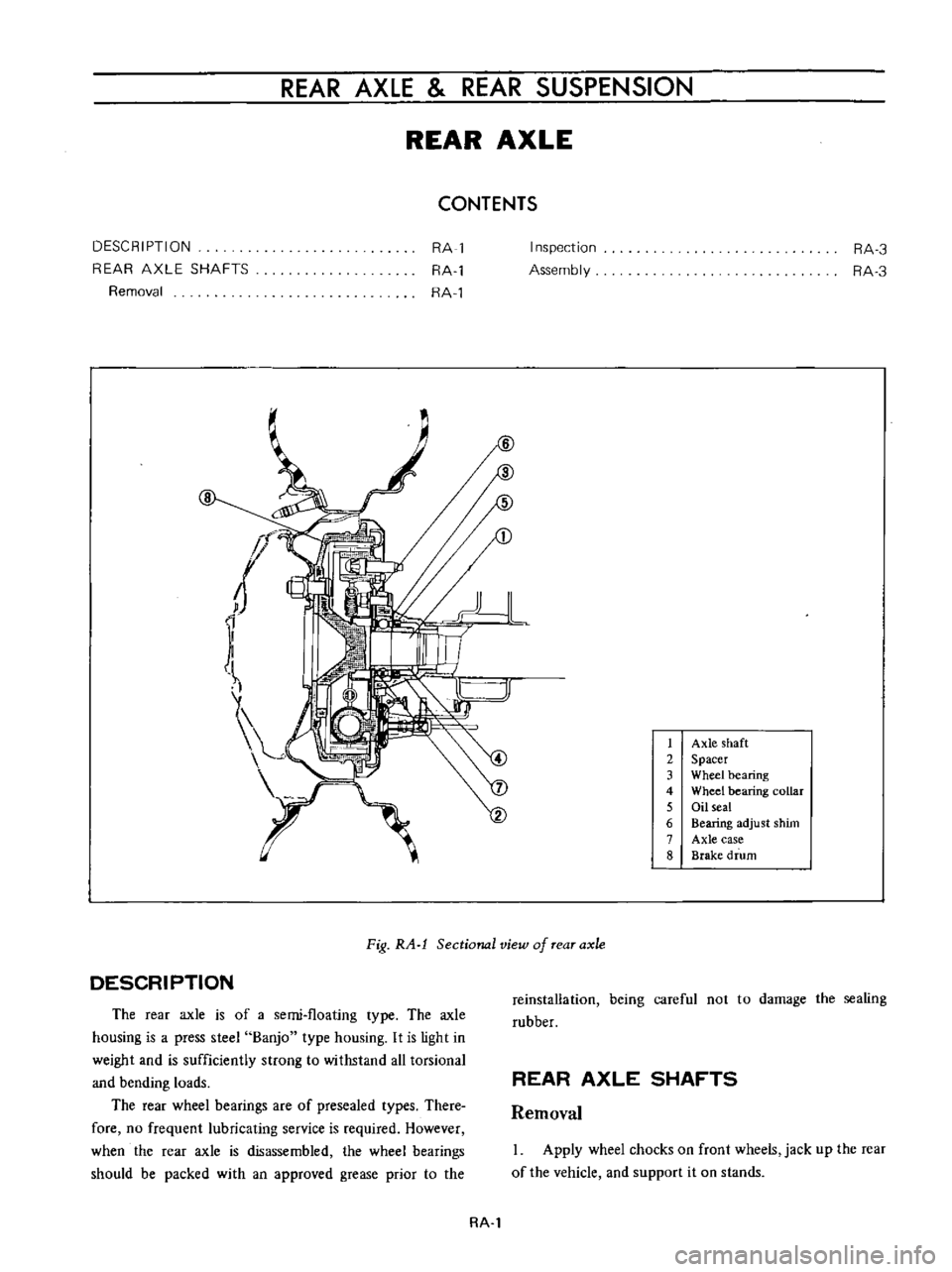
REAR
AXLE
REAR
SUSPENSION
REAR
AXLE
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION
REAR
AXLE
SHAFTS
Removal
RA
1
RA
l
RA
l
8
Inspection
Assembly
RA
3
RA
3
1
Axle
shaft
2
Spacer
3
Wheel
bearing
4
Wheel
bearing
collar
5
Oil
seal
6
Bearing
adjust
shim
7
Axle
case
8
Brake
drum
DESCRIPTION
Fig
RA
l
Sectional
view
of
rear
axle
The
rear
axle
is
of
a
semi
floating
type
The
axle
housing
is
a
press
steel
Banjo
type
housing
It
is
light
in
weight
and
is
sufficiently
strong
to
withstand
all
torsional
and
bending
loads
The
rear
wheel
bearings
are
of
presea1ed
types
There
fore
no
frequent
lubricating
service
is
required
However
when
the
rear
axle
is
disassembled
the
wheel
bearings
should
be
packed
with
an
approved
grease
prior
io
the
reinstallation
being
careful
not
to
damage
the
sealing
rubber
REAR
AXLE
SHAFTS
Removal
Apply
wheel
chocks
on
front
wheels
jack
up
the
rear
of
the
vehicle
and
support
it
on
stands
RA
l
Page 125 of 513
DESCRIPTION
BRAKE
PEDAL
Removal
Inspection
Reinstallation
TANDEM
MASTER
CYLINDER
Removal
Disassembly
Inspection
Reassembly
Reinstallation
SINGLE
MASTER
CYLINDER
Removal
and
disassembly
Inspection
Reassembly
and
reinstallation
BRAKE
LINE
Removal
Inspection
Reinstallation
Brake
line
pressure
differential
warning
light
switch
FRONT
DRUM
BRAKE
cr
I
1
0
I
I
CD
BRAKE
BRAKE
CONTENTS
BR
2
BR
2
BR
2
BR
2
BR
2
BR
3
BR
3
BR
3
BR
3
BR
4
BR
4
BR
4
BR
5
BR
5
BR
5
BR
5
BR
5
BR
6
BR
6
BR
7
BR
8
Removal
and
disassembly
Inspection
Reassembly
and
reinstallation
FRONT
DISC
BRAKE
Brake
pad
Caliper
assembly
Reassembly
Reinstallation
REAR
BRAKE
Removal
and
disassembly
Inspection
Reassembly
and
reinstallation
HAND
8RAKE
Removal
Inspection
Reinstallation
ADJUSTMENT
Brake
shoe
clearance
Brake
pedal
height
Hand
brake
Bleeding
hydraulic
system
@
7
o
i
1
Brake
hose
2
Brake
master
cylinder
3
3
way
connector
4
Hand
brake
lever
5
Brake
hose
6
3
way
connector
7
Hanger
strap
8
Turn
buckle
Fig
BR
l
Brake
system
BR
BR
8
BR
9
BR
9
BR
lO
BR
Il
BR
12
BR
14
BR
16
BR
16
BR
17
BR
17
BR
18
BR
18
BR
19
BR
19
BR
20
BR
20
BR
20
BR
21
BR
21
BR
22
Page 128 of 513
CHASSIS
Ii
t
L
1
J
rJ
I
e
i
L
rubber
parts
und
alcohol
long
than
30
seconds
After
the
parts
are
cleaned
dry
them
with
com
pressed
air
Check
the
cylinder
and
piston
for
damage
and
uneven
wear
on
the
sliding
surface
and
for
other
defective
conditions
Replace
as
required
2
Replace
if
the
cylinder
and
piston
clearance
is
more
than
0
15
mm
0
006
in
3
In
principle
replace
the
piston
cup
packing
and
valves
with
new
ones
whenever
the
master
cylinder
is
disassembled
Be
sure
to
replace
if
damaged
worn
weakened
or
expanded
4
Check
the
return
springs
for
wear
damage
and
other
defective
conditions
and
replace
as
required
5
Replace
others
if
deformed
damaged
or
defective
Reassembly
Assemble
the
master
cylinder
in
reverse
sequence
of
SINGLE
MASTER
CYLINDER
s
m
e
disassembly
noting
the
following
matters
Apply
brake
fluid
to
the
component
parts
such
as
cylinder
bore
piston
etc
and
carry
out
the
operations
carefully
so
that
the
component
parts
are
not
damaged
or
no
dust
and
other
foreign
matters
enter
the
cylinder
and
brake
fluid
reselVoir
Moreover
for
rubber
parts
such
as
piston
cup
etc
apply
rubber
grease
slightly
Tightening
torque
Valve
cap
2
5
to
3
5
kg
m
I8
to
25
3
ft
Ib
Bleeder
screw
0
5
kg
m
3
6
ft
lb
Stopper
bolt
0
5
to
0
3
kg
m
l
I
to
2
2ft
lb
Reinstallation
Reinstall
the
master
cylinder
in
reverse
sequence
of
removal
After
air
bleeding
make
sure
that
no
brake
fluid
leaks
from
the
circuit
For
the
pedal
height
adjustment
refer
to
lhe
paragraph
pedal
adjustment
r
11L
y
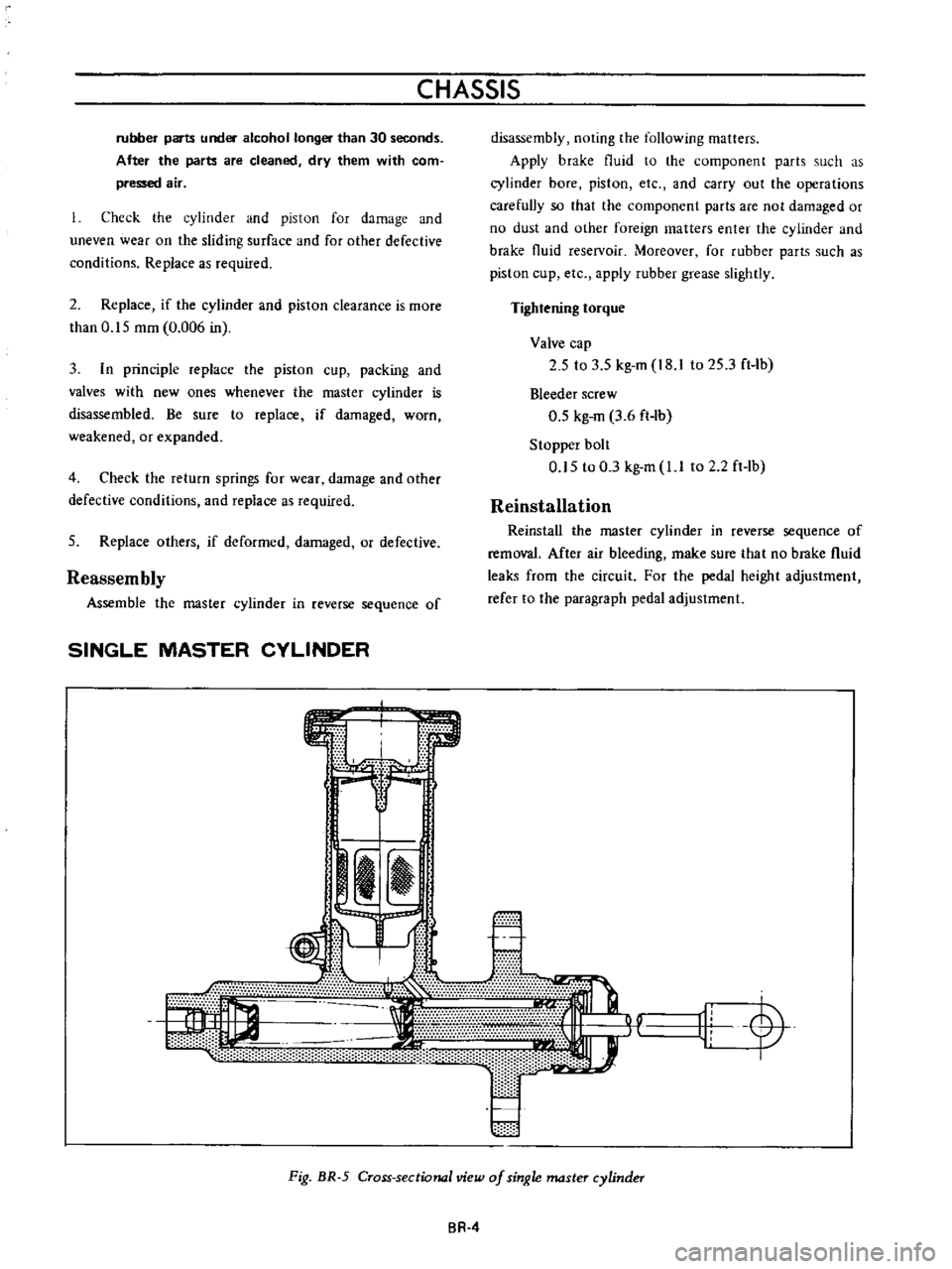
Fig
BR
5
Cross
sectional
view
of
single
master
cylinder
BR
4
Page 131 of 513
Tightening
torque
3
way
connector
1
5
to
1
8
kg
m
10
8
to
13
0
ft
lh
1
5
to
1
8
kg
m
10
8
to
13
0
ft
lh
1
5
to
1
8
kg
m
10
8
to
13
0
ft
lb
0
7
to
0
9
kg
m
5
1
to
6
5
ft
1b
Master
cylinder
Brake
hose
Air
bleeder
5
Fill
the
master
cylinder
brake
fluid
reservoir
with
brake
fluid
and
perform
air
bleeding
complele1y
Note
a
Do
not
use
brake
fluid
other
than
specified
b
The
specified
brake
fluid
is
used
for
both
single
and
tandem
type
master
cylinders
6
Upon
completion
of
air
bleeding
make
sure
that
the
brake
operates
correctly
and
check
the
brake
tube
and
hose
connectors
for
fluid
leaking
Fully
depress
the
brake
pedal
continue
to
depress
the
brake
pedal
for
several
seconds
and
make
sure
that
no
brake
fluid
leaks
from
any
part
of
the
brake
line
Replace
defective
part
if
required
Brake
line
pressure
differential
warning
light
switch
A
warning
light
is
located
on
the
instrument
panel
to
warn
the
driver
when
a
pressure
difference
of
13
to
17
kg
cm2
185
to
2421bJsq
in
exists
between
the
front
and
rear
b
rake
systems
A
hydraulically
actuated
warning
light
switch
is
located
in
the
engine
compartment
Both
front
and
rear
brake
systems
are
connected
to
this
switch
assembly
When
a
pressure
difference
of
13
to
17
kgJcm2
185
to
242
lbJsq
in
occurs
between
the
front
and
rear
brake
systems
the
valves
will
shuttle
toward
the
side
with
the
low
pressure
The
valve
contacts
with
the
switch
terminal
BRAKE
the
ground
circuit
for
the
warning
light
is
completed
and
thus
the
warning
light
lights
In
this
case
correct
the
hydraulic
brake
problem
and
bleed
the
brakes
Check
the
warning
light
switch
assembly
for
a
proper
operation
Check
the
switch
assembly
for
fluid
leakage
Note
Do
not
attempt
to
repair
switch
for
any
reason
replace
switch
assembly
completely
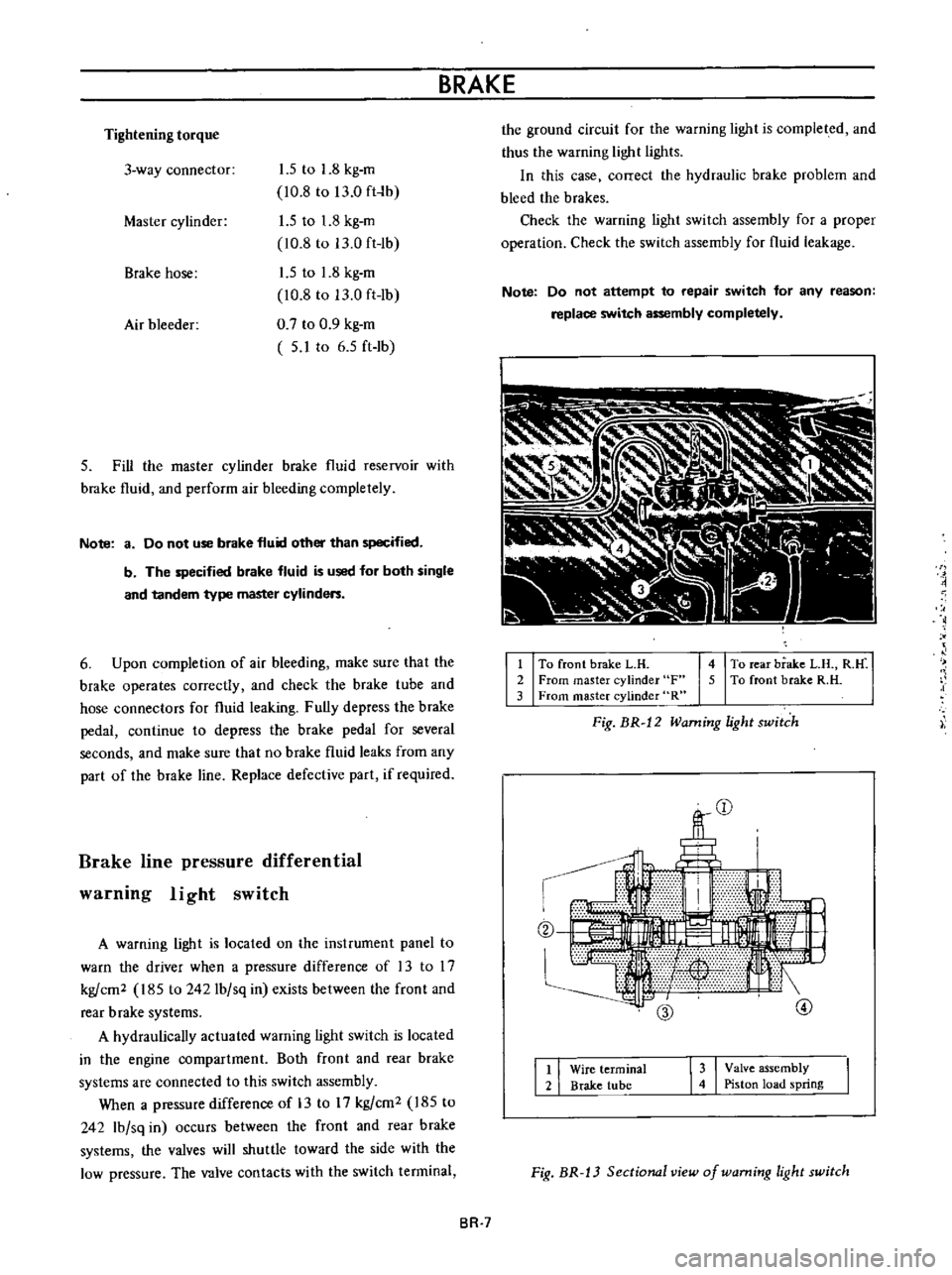
1
To
front
brake
L
H
2
From
master
cylinder
F
3
From
master
cylinder
R
4
To
rear
brake
L
B
R
M
5
To
front
brake
R
H
Fig
BR
12
Warning
light
switch
r
I
@
I
I
3
I
Valve
assembly
4
Piston
load
spring
Wire
terminal
Brake
tube
Fig
BR
13
Sectional
view
of
warning
light
switch
BR
7