weight DODGE DURANGO 1998 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: DURANGO, Model: DODGE DURANGO 1998 1.GPages: 193, PDF Size: 5.65 MB
Page 132 of 193
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
PISTON PIN
Clearance in Piston 0.00635 ± 0.01905 mm
(0.00025 ± 0.00075 in.)
Diameter 24.996 ± 25.001 mm
(0.9841 ± 0.9843 in.)
End Play NONE
Length 75.946 ± 76.454 mm
(2.990 ± 3.010 in.)
PISTON RINGS
Ring Gap
Compression Rings 0.254 ± 0.508 mm
(0.010 ± 0.020 in.)
Oil Control (Steel Rails) 0.254 ± 1.270 mm
(0.010 ± 0.050 in.)
Ring Side Clearance
Compression Rings 0.038 ± 0.076 mm
(0.0015 ± 0.0030 in.)
Oil Ring (Steel Rails) 0.06 ± 0.21 mm
(0.002 ± 0.008 in.)
Ring Width
Compression rings 1.971 ± 1.989 mm
(0.0776 ± 0.0783 in.)
Oil Ring (Steel Rails) ±
Max.3.848 ± 3.975 mm
(0.1515 ± 0.1565 in.)
VALVE TIMING
Exhaust Valve
Closes (ATDC) 21É
Opens (BBDC) 60É
Duration 264É
Intake Valve
Closes (ATDC) 61É
Opens (BBDC) 10É
Duration 250É
Valve Overlap 31ÉOVERSIZE AND UNDERSIZE ENGINE
COMPONENT MARKINGS CHART
U/S-O/S Item Identification Identification
Location
U/S Rod/ R or M R-1-4
ect.Milled flat on
No.8
.0254
mmMain (indicating
No. 1crankshaft
(0.001
in.)Journal and 4
connectingcounterweight.
rod journal)
and/or
M-2-3 ect.
(indicating
No. 2
and 3 main
bearing
journal)
O/S HydrauliclDiamond-
shaped
.2032
mmTappets stamp top pad
-
(.008 in.) front of engine
and flat
ground
on outside
surface of
each
O/S tappet
bore.
O/S Valve X Milled pad
.127 mm Stems adjacent to
two
(.005 in.) tapped holes
(3/8 in.) on
each
end of
cylinder
head.
DN5.2L ENGINE 9 - 131
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 137 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE
DESCRIPTION
The 5.9 Liter (360 CID) eight-cylinder engine is a
V-Type lightweight, single cam, overhead valve
engine with hydraulic roller tappets. This engine is
designed for unleaded fuel.
The engine lubrication system consists of a rotor
type oil pump and a full flow oil filter.
The cylinders are numbered from front to rear; 1,
3, 5, 7 on the left bank and 2, 4, 6, 8 on the right
bank. The firing order is 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2 (Fig. 1).
The engine serial number is stamped into a
machined pad located on the left, front corner of the
cylinder block. When component part replacement is
necessary, use the engine type and serial number for
reference (Fig. 2).
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
A gear-type positive displacement pump (Fig. 3) is
mounted at the underside of the rear main bearing
cap. The pump uses a pick-up tube and screen
assembly to gather engine oil from the oil pan.
OPERATION
The pump draws oil through the screen and inlet
tube from the sump at the rear of the oil pan. The oil
is driven between the drive and idler gears and
pump body, then forced through the outlet to the
block. An oil gallery in the block channels the oil to
the inlet side of the full flow oil filter. After passing
through the filter element, the oil passes from the
center outlet of the filter through an oil gallery that
channels the oil up to the main gallery, which
extends the entire length on the right side of the
block. The oil then goes down to the No. 1 main bear-
ing, back up to the left side of the block, and into the
oil gallery on the left side of the engine.
Galleries extend downward from the main oil gal-
lery to the upper shell of each main bearing. The
crankshaft is drilled internally to pass oil from the
main bearing journals to the connecting rod journals.
Each connecting rod bearing has half a hole in it, oil
passes through the hole when the rods rotate and the
hole lines up, oil is then thrown off as the rod
rotates. This oil throwoff lubricates the camshaft
lobes, distributor drive gear, cylinder walls, and pis-
ton pins.
Fig. 1 Firing Order
Fig. 2 Engine Identification Number
Fig. 3 Positive Displacement Oil PumpÐTypical
1 ± INNER ROTOR AND SHAFT
2 ± BODY
3 ± DISTRIBUTOR DRIVESHAFT (REFERENCE)
4 ± COTTER PIN
5 ± RETAINER CAP
6 ± SPRING
7 ± RELIEF VALVE
8 ± LARGE CHAMFERED EDGE
9 ± BOLT
10 ± COVER
11 ± OUTER ROTOR
9 - 136 5.9L ENGINEDN
Page 142 of 193
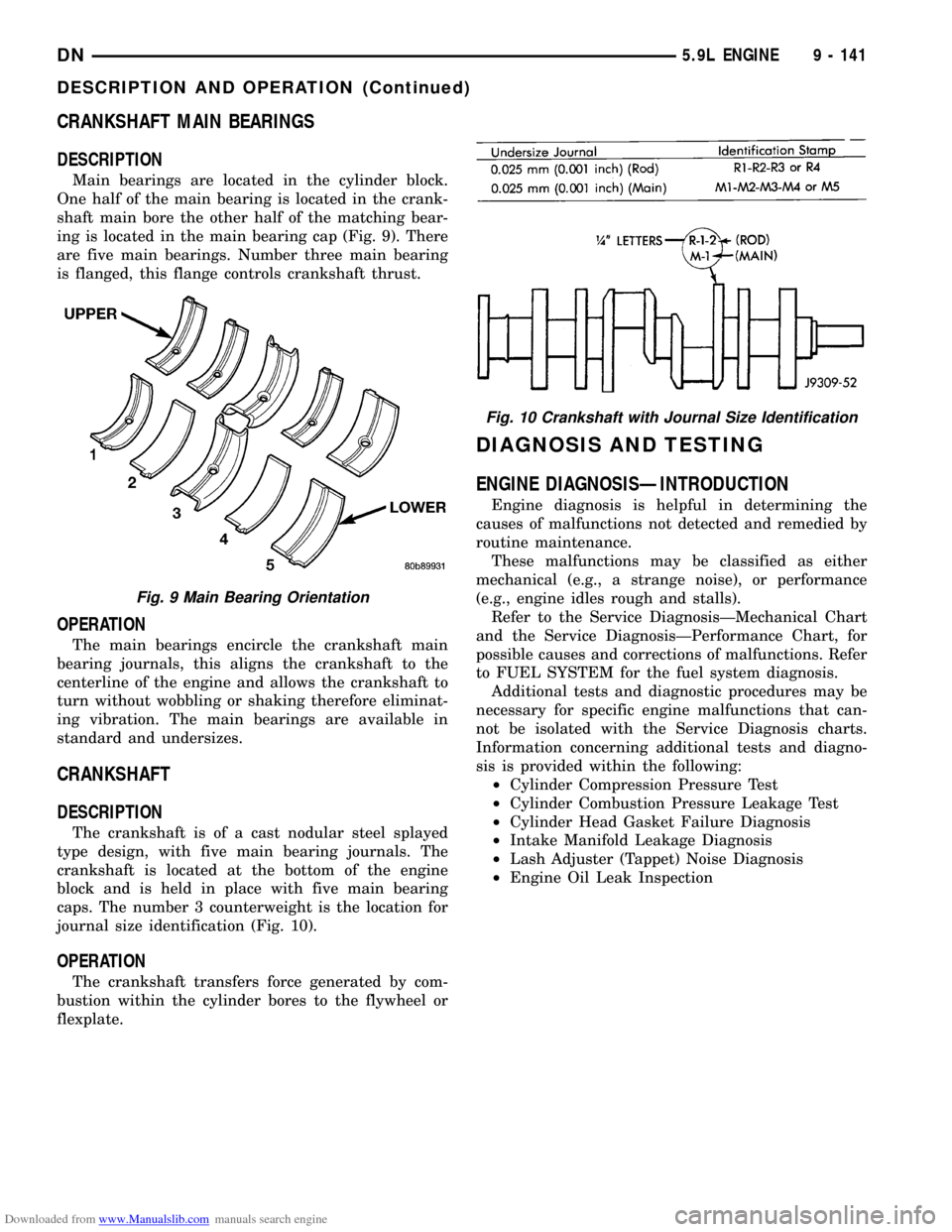
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
DESCRIPTION
Main bearings are located in the cylinder block.
One half of the main bearing is located in the crank-
shaft main bore the other half of the matching bear-
ing is located in the main bearing cap (Fig. 9). There
are five main bearings. Number three main bearing
is flanged, this flange controls crankshaft thrust.
OPERATION
The main bearings encircle the crankshaft main
bearing journals, this aligns the crankshaft to the
centerline of the engine and allows the crankshaft to
turn without wobbling or shaking therefore eliminat-
ing vibration. The main bearings are available in
standard and undersizes.
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft is of a cast nodular steel splayed
type design, with five main bearing journals. The
crankshaft is located at the bottom of the engine
block and is held in place with five main bearing
caps. The number 3 counterweight is the location for
journal size identification (Fig. 10).
OPERATION
The crankshaft transfers force generated by com-
bustion within the cylinder bores to the flywheel or
flexplate.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐINTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
Refer to the Service DiagnosisÐMechanical Chart
and the Service DiagnosisÐPerformance Chart, for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions. Refer
to FUEL SYSTEM for the fuel system diagnosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
²Lash Adjuster (Tappet) Noise Diagnosis
²Engine Oil Leak Inspection
Fig. 9 Main Bearing Orientation
Fig. 10 Crankshaft with Journal Size Identification
DN5.9L ENGINE 9 - 141
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 149 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, check the oil pressure. If vehicle
has no oil pressure gauge, install a reliable gauge at
the pressure sending-unit. The pressure should be
between 207-552 kPa (30-80 psi) at 3,000 RPM.
Check the oil level after the engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Allow 5 minutes to stabilize
oil level, check dipstick. The oil level in the pan
should never be above the FULL mark or below the
ADD OIL mark on dipstick. Either of these two con-
ditions could be responsible for noisy tappets.
OIL LEVEL
HIGH
If oil level is above the FULL mark, it is possible
for the connecting rods to dip into the oil. With the
engine running, this condition could create foam in
the oil pan. Foam in oil pan would be fed to the
hydraulic tappets by the oil pump causing them to
lose length and allow valves to seat noisily.
LOW
Low oil level may allow oil pump to take in air.
When air is fed to the tappets, they lose length,
which allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on
intake side of oil pump through which air can be
drawn will create the same tappet action. Check the
lubrication system from the intake strainer to the
pump cover, including the relief valve retainer cap.
When tappet noise is due to aeration, it may be
intermittent or constant, and usually more than one
tappet will be noisy. When oil level and leaks have
been corrected, operate the engine at fast idle. Run
engine for a sufficient time to allow all of the air
inside the tappets to be bled out.
TAPPET NOISE DIAGNOSIS
(1) To determine source of tappet noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed.
(2) Feel each valve spring or rocker arm to detect
noisy tappet. The noisy tappet will cause the affected
spring and/or rocker arm to vibrate or feel rough in
operation.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is
the case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
(3) Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger, or by theplunger partially sticking in the tappet body cylinder.
The tappet should be replaced. A heavy click is
caused by a tappet check valve not seating, or by for-
eign particles wedged between the plunger and the
tappet body. This will cause the plunger to stick in
the down position. This heavy click will be accompa-
nied by excessive clearance between the valve stem
and rocker arm as valve closes. In either case, tappet
assembly should be removed for inspection and clean-
ing.
(4) The valve train generates a noise very much
like a light tappet noise during normal operation.
Care must be taken to ensure that tappets are mak-
ing the noise. If more than one tappet seems to be
noisy, it's probably not the tappets.
LEAK-DOWN TEST
After cleaning and inspection, test each tappet for
specified leak-down rate tolerance to ensure zero-lash
operation (Fig. 11).
Swing the weighted arm of the hydraulic valve tap-
pet tester away from the ram of the Universal Leak-
Down Tester.
(1) Place a 7.925-7.950 mm (0.312-0.313 inch)
diameter ball bearing on the plunger cap of the tap-
pet.
(2) Lift the ram and position the tappet (with the
ball bearing) inside the tester cup.
(3) Lower the ram, then adjust the nose of the ram
until it contacts the ball bearing. DO NOT tighten
the hex nut on the ram.
(4) Fill the tester cup with hydraulic valve tappet
test oil until the tappet is completely submerged.
(5) Swing the weighted arm onto the push rod and
pump the tappet plunger up and down to remove air.
When the air bubbles cease, swing the weighted arm
away and allow the plunger to rise to the normal
position.
(6) Adjust the nose of the ram to align the pointer
with the SET mark on the scale of the tester and
tighten the hex nut.
(7) Slowly swing the weighted arm onto the push
rod.
(8) Rotate the cup by turning the handle at the
base of the tester clockwise one revolution every 2
seconds.
(9) Observe the leak-down time interval from the
instant the pointer aligns with the START mark on
the scale until the pointer aligns with the 0.125
mark. A normally functioning tappet will require
20-110 seconds to leak-down. Discard tappets with
leak-down time interval not within this specification.
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure sending unit.
9 - 148 5.9L ENGINEDN
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 150 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine (2) Install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool
C-3292. Start engine and record pressure. Refer to
Oil Pressure in Engine Specifications for the proper
pressures.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS
There are several places where form-in-place gas-
kets are used on the engine.DO NOT use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Care
must be taken when applying form-in-place gaskets.
Bead size, continuity and location are of great impor-
tance. Too thin a bead can result in leakage while too
much can result in spill-over. A continuous bead of
the proper width is essential to obtain a leak-free
joint.
Two types of form-in-place gasket materials are
used in the engine area (Mopar Silicone Rubber
Adhesive Sealant and Mopar Gasket Maker). Each
have different properties and cannot be used inter-
changeably.
MOPAR SILICONE RUBBER ADHESIVE SEALANT
Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant, normally
black in color, is available in 3 ounce tubes. Moisture
in the air causes the sealant material to cure. This
material is normally used on flexible metal flanges.
It has a shelf life of a year and will not properly cure
if over aged. Always inspect the package for the expi-
ration date before use.
MOPAR GASKET MAKER
Mopar Gasket Maker, normally red in color, is
available in 6 cc tubes. This anaerobic type gasket
material cures in the absence of air when squeezed
between smooth machined metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. DO NOT use
on flexible metal flanges.
SURFACE PREPARATION
Parts assembled with form-in-place gaskets may be
disassembled without unusual effort. In some
instances, it may be necessary to lightly tap the part
with a mallet or other suitable tool to break the seal
between the mating surfaces. A flat gasket scraper
may also be lightly tapped into the joint but care
must be taken not to damage the mating surfaces.
Scrape or wire brush all gasket surfaces to remove
all loose material. Inspect stamped parts to ensure
gasket rails are flat. Flatten rails with a hammer on
a flat plate, if required. Gasket surfaces must be free
of oil and dirt. Make sure the old gasket material is
removed from blind attaching holes.
GASKET APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care.
Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant should be
applied in a continuous bead approximately 3 mm
(0.12 inch) in diameter. All mounting holes must be
circled. For corner sealing,a3or6mm(1/8 or 1/4
inch) drop is placed in the center of the gasket con-
tact area. Uncured sealant may be removed with a
shop towel. Components should be torqued in place
while the sealant is still wet to the touch (within 10
minutes). The use of a locating dowel is recom-
mended during assembly to prevent smearing the
material off location.
Mopar Gasket Maker should be applied sparingly
to one gasket surface. The sealant diameter should
be 1.00 mm (0.04 inch) or less. Be certain the mate-
rial surrounds each mounting hole. Excess material
can easily be wiped off. Components should be
torqued in place within 15 minutes. The use of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing the material off location.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
It is important that the vehicle is operating to its
optimum performance level to maintain fuel economy
and the lowest emission levels. If vehicle is not oper-
ating to these standards, refer to Engine Diagnosis
outlined in this section. The following procedures can
assist in achieving the proper engine diagnosis.
(1) Test cranking amperage draw. Refer to Electri-
cal Group 8B, Cold Cranking Test.
Fig. 11 Leak-Down Tester
1 ± POINTER
2 ± WEIGHTED ARM
3 ± RAM
4 ± CUP
5 ± HANDLE
6 ± PUSH ROD
DN5.9L ENGINE 9 - 149
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 158 of 193
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine CONNECTING ROD BEARINGSÐFITTING
Fit all rods on a bank until completed. DO NOT
alternate from one bank to another, because connect-
ing rods and pistons are not interchangeable from
one bank to another.
The bearing caps are not interchangeable and
should be marked at removal to ensure correct
assembly.
Each bearing cap has a small V-groove across the
parting face. When installing the lower bearing shell,
make certain that the V-groove in the shell is in line
with the V-groove in the cap. This provides lubrica-
tion of the cylinder wall in the opposite bank.The bearing shells must be installed so that the
tangs are in the machined grooves in the rods and
caps.
Limits of taper or out-of-round on any crankshaft
journals should be held to 0.025 mm (0.001 inch).
Bearings are available in 0.025 mm (0.001 inch),
0.051 mm (0.002 inch), 0.076 mm (0.003 inch), 0.254
mm (0.010 inch) and 0.305 mm (0.012 inch) under-
size.Install the bearings in pairs. DO NOT use a
new bearing half with an old bearing half. DO
NOT file the rods or bearing caps.
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGSÐFITTING
Bearing caps are not interchangeable and should
be marked at removal to ensure correct assembly.
Upper and lower bearing halves are NOT inter-
changeable. Lower main bearing halves of No.2 and 4
are interchangeable.
PISTON MEASUREMENT CHART
PISTON A DIA = PISTON BORE
SIZE DIAMETER DIAMETER
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX.
mm
(in.)mm
(in.)mm
(in.)mm (in.)
AÐÐÐ Ð
B101.580 101.592 101.605 101.618
(3.9992) (3.9997) (4.0002) (4.0007)
C101.592 101.605 101.618 101.630
(3.9997) (4.0002) (4.0007) (4.0012)
D101.605 101.618 101.630 101.643
(4.0002) (4.0007) (4.0012) (4.0017)
EÐÐÐ Ð
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
PISTON PIN BORE 25.007 - 25.015 mm
(.9845 -.9848 in.)
RING GROOVE
HEIGHT
OIL RAIL 4.033 - 4.058 mm
(.1588 -.1598 in.)
COMPRESSION
RAIL1.529 - 1.554 mm
(.0602 -.0612 in.)
TOTAL FINISHED 470.862 grams
WEIGHT (16.6076.0706 ounces)
Fig. 27 Second Compression Ring Identification
(Typical)
1 ± SECOND COMPRESSION RING (BLACK CAST IRON)
2 ± CHAMFER
3 ± TWO DOTS
Fig. 28 Top Compression Ring Identification
(Typical)
1 ± TOP COMPRESSION RING (GRAY IN COLOR)
2 ± CHAMFER
3 ± ONE DOT
DN5.9L ENGINE 9 - 157
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 177 of 193
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine INSTALLATION
(1) Be sure that compression ring gaps are stag-
gered so that neither is in-line with oil ring rail gap.
(2) Before installing the ring compressor, make
sure the oil ring expander ends are butted and the
rail gaps located properly (Fig. 70).
(3) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil. Slide Piston Ring Compressor Tool C-385
over the piston and tighten with the special wrench
(part of Tool C-385).Be sure position of rings
does not change during this operation.
(4) Install connecting rod bolt protectors on rod
bolts, the long protector should be installed on the
numbered side of the connecting rod.
(5) Rotate crankshaft so that the connecting rod
journal is on the center of the cylinder bore. Be sure
connecting rod and cylinder bore number are the
same. Insert rod and piston into cylinder bore and
guide rod over the crankshaft journal.
(6) Tap the piston down in cylinder bore, using a
hammer handle. At the same time, guide connecting
rod into position on crankshaft journal.
(7) The notch or groove on top of piston must be
pointing toward front of engine. The larger chamfer
of the connecting rod bore must be installed toward
crankshaft journal fillet.
(8) Install rod caps. Be sure connecting rod, con-
necting rod cap and cylinder bore number are the
same. Install nuts on cleaned and oiled rod bolts and
tighten nuts to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install the oil pan.
(10) Install the cylinder head.
(11) Install the engine into the vehicle.
CRANKSHAFT
A crankshaft which has undersize journals will be
stamped with 1/4 inch letters on the milled flat on
the No.3 crankshaft counterweight (Fig. 71).
FOR EXAMPLE:R2 stamped on the No.3 crank-
shaft counterweight indicates that the No.2 rod jour-
nal is 0.025 mm (0.001 in) undersize. M4 indicates
that the No.4 main journal is 0.025 mm (0.001 in)
undersize. R3 M2 indicates that the No.3 rod journal
and the No.2 main journal are 0.025 mm (0.001 in)
undersize.
When a crankshaft is replaced, all main and con-
necting rod bearings should be replaced with new
bearings. Therefore, selective fitting of the bearings
is not required when a crankshaft and bearings are
replaced.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the oil pan.
(2) Remove the oil pump from the rear main bear-
ing cap.
(3) Remove the vibration damper.
(4) Remove the timing chain cover.
(5) Identify bearing caps before removal. Remove
bearing caps and bearings one at a time.
(6) Lift the crankshaft out of the block.
Fig. 70 Proper Ring Installation
1 ± OIL RING SPACER GAP
2 ± SECOND COMPRESSION RING GAP OIL RING RAIL GAP
(TOP)
3 ± OIL RING RAIL GAP (BOTTOM)
4 ± TOP COMPRESSION RING GAP
Fig. 71 Location of Crankshaft Identification
1 ± 1/4º LETTERS
2 ± (ROD)
3 ± (MAIN)
CRANKSHAFT IDENTIFICATION MARK
LOCATION CHART
UNDERSIZE JOURNAL IDENTIFICATION
STAMP
0.025 mm (0.001 in.)
(ROD)R1-R2-R3 or R4
0.025 mm (0.001 in.)
(MAIN)M1-M2-M3-M4 or M5
9 - 176 5.9L ENGINEDN
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 184 of 193
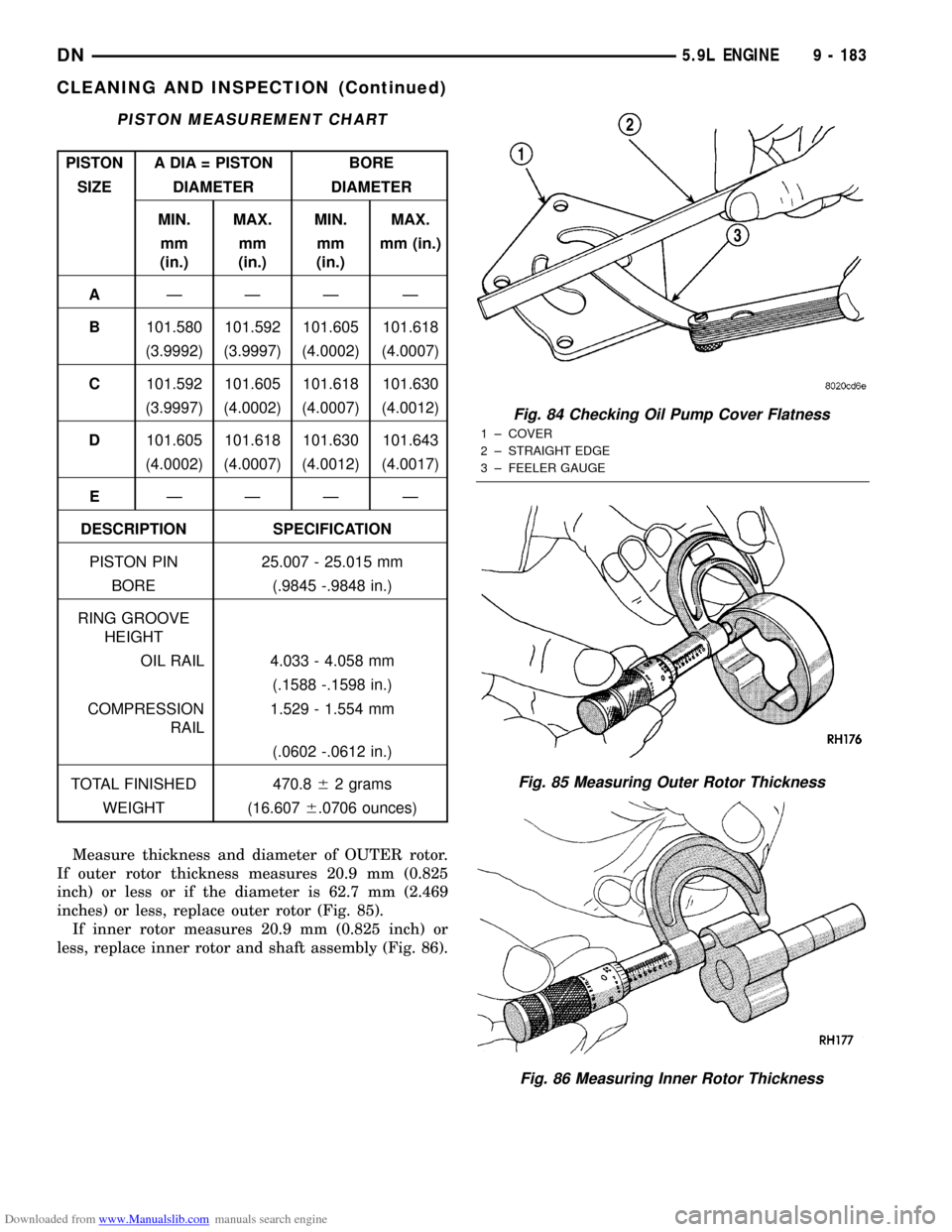
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Measure thickness and diameter of OUTER rotor.
If outer rotor thickness measures 20.9 mm (0.825
inch) or less or if the diameter is 62.7 mm (2.469
inches) or less, replace outer rotor (Fig. 85).
If inner rotor measures 20.9 mm (0.825 inch) or
less, replace inner rotor and shaft assembly (Fig. 86).
PISTON MEASUREMENT CHART
PISTON A DIA = PISTON BORE
SIZE DIAMETER DIAMETER
MIN. MAX. MIN. MAX.
mm
(in.)mm
(in.)mm
(in.)mm (in.)
AÐÐÐ Ð
B101.580 101.592 101.605 101.618
(3.9992) (3.9997) (4.0002) (4.0007)
C101.592 101.605 101.618 101.630
(3.9997) (4.0002) (4.0007) (4.0012)
D101.605 101.618 101.630 101.643
(4.0002) (4.0007) (4.0012) (4.0017)
EÐÐÐ Ð
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
PISTON PIN 25.007 - 25.015 mm
BORE (.9845 -.9848 in.)
RING GROOVE
HEIGHT
OIL RAIL 4.033 - 4.058 mm
(.1588 -.1598 in.)
COMPRESSION
RAIL1.529 - 1.554 mm
(.0602 -.0612 in.)
TOTAL FINISHED 470.862 grams
WEIGHT (16.6076.0706 ounces)
Fig. 84 Checking Oil Pump Cover Flatness
1 ± COVER
2 ± STRAIGHT EDGE
3 ± FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 85 Measuring Outer Rotor Thickness
Fig. 86 Measuring Inner Rotor Thickness
DN5.9L ENGINE 9 - 183
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 189 of 193

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
PISTONS
Clearance at Top of Skirt 0.013 ± 0.038 mm
(0.0005 ± 0.0015 in.)
Land Clearance (Diam.) 0.508 ± 0.660 mm
(0.020 ± 0.026 in.)
Piston Length 81.03 mm (3.19 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
DepthÐ
#1&2 4.761 ± 4.912 mm
(0.187 ± 0.193 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
DepthÐ
#3 3.996 ± 4.177 mm
(0.157 ± 0.164 in.)
Weight 582 ± 586 grams
(20.53 ± 20.67 oz.)
PISTON PINS
Clearance in Piston 0.006 ± 0.019 mm
(0.00023 ± 0.00074 in.)
Diameter 25.007 ± 25.015 mm
(0.9845 ± 0.9848 in.)
End Play NONE
Length 67.8 ± 68.3 mm
(2.67 ± 2.69 in.)
PISTON RINGS
Ring Gap
Compression Ring (Top) 0.30 ± 0.55 mm
(0.012 ± 0.022 in.)
Compression Ring (2nd) 0.55 ± 0.80 mm
(0.022 ± 0.031 in.)
Oil Control (Steel Rails) 0.381 ± 1.397 mm
(0.015 ± 0.055 in.)
Ring Side Clearance
Compression Rings 0.040 ± 0.085 mm
(0.0016 ± 0.0033 in.)
Oil Ring (Steel Rails) 0.05 ± 0.21 mm
(0.002 ± 0.008 in.)
Ring Width
Compression rings 1.530 ± 1.555 mm
(0.060 ± 0.061 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Oil Ring (Steel Rails) ±
Max.0.447 ±0.473 mm
(0.018 ± 0.019 in.)
VALVE TIMING
Exhaust Valve
Closes (ATDC) 33É
Opens (BBDC) 56É
Duration 269É
Intake Valve
Closes (ATDC) 62É
Opens (BBDC) 7É
Duration 249É
Valve Overlap 41É
OVERSIZE AND UNDERSIZE ENGINE
COMPONENT MARKINGS CHART
ITEM U/S
(O/S)IDENTI-
FICATIONIDENTI-
FICATION
LOCATION
Crank-
shaft
Journals0.0254
mm
(0.001
in.) U/SR or M M-2-3
ect.
(indicating
No. 2 and 3
main bearing
journal)
and/or R-1-4
ect.
(indicating
No. 1 and 4
connecting
rod journal)Milled flat on
No. 8
crankshaft
counterweight.
Hydraulic
Tappets0.2032
mm
(0.008
in.)
(O/S)lDiamond-
shaped stamp
top pad - front
of engine and
flat ground on
outside
surface of
each O/S
tappet bore.
Valve
Stems0.127
mm
(0.005
in.)
(O/S)X Milled pad
adjacent to
two tapped
holes (3/8 in.)
on each end
of cylinder
head.
9 - 188 5.9L ENGINEDN
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)