seats DODGE NEON 2000 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 22 of 1285

For more information on the description and oper-
ation of an individual component, refer to the appli-
cable component heading in this section.
STRUT ASSEMBLY (FRONT)
A Macpherson type design strut assembly is used
in place of the front suspension upper control arm
and upper ball joint (Fig. 1). The bottom of the strut
mounts directly to the steering knuckle using 2
attaching bolts and nuts going through the strut cle-
vis bracket and steering knuckle. The top of the strut
mounts directly to the strut tower of the vehicle
using the three threaded studs on the strut assem-
blies upper mount. During steering maneuvers, the
strut assembly (through a pivot bearing in the upper
strut mount) and steering knuckle (through the lower
ball joint) turn as an assembly. The strut assembly is
used to dampen the front suspension and smooth the
ride of the vehicle.
The strut assembly includes the following compo-
nents: A rubber isolated upper mount, an upper
spring seat and bearing, a dust shield, a jounce
bumper, a coil spring, a lower spring isolator and a
strut (Fig. 1). Each component is serviced by remov-
ing the strut assembly from the vehicle and disas-
sembling it.
COIL SPRING
The strut and front suspension of the vehicle is
supported by coil springs positioned around the
upper half of each strut. The springs are contained
between the upper and the lower seats of the strut
assembly.
Coil springs are rated separately for each corner or
side of the vehicle depending on optional equipment
and type of vehicle service. During service procedures
of the strut assembly, if both springs are removed,
mark the springs to ensure installation in its original
position.
NOTE: If a coil spring requires replacement, be
sure that it is replaced with a spring meeting the
correct load rating for the vehicle and its specific
options.
STEERING KNUCKLE
The steering knuckle is a single casting with legs
machined for attachment to the front strut assembly
on the top and the lower control arm ball joint on the
bottom (Fig. 1). The steering knuckle also has
machined abutments on the casting to support and
align the front brake caliper assembly.
WHEEL BEARING AND HUB
The knuckle also supports the wheel bearing and
hub (Fig. 1). The wheel hub is pressed into a sealed
for life wheel bearing that is pressed into the steer-
ing knuckle. A retainer plate also holds it in place.
The hub supports the driveshaft outer constant veloc-
ity (C/V) joint. Each is splined and meshes in the
center of the hub. The outer C/V joint is retained to
the hub using a nut. The nut is held on the outer C/V
stub shaft using a nut retainer and cotter pin.
The wheel bearing is a Unit 1 type cartridge bear-
ing that requires no maintenance. The wheel bearing
is serviced separately from the hub.
LOWER CONTROL ARM
There is one lower control arm on each side of the
vehicle. Each lower control arm is a stamped steel
unit using rubber isolated pivot bushings to isolate it
from the front suspension crossmember and frame of
the vehicle (Fig. 1). The rear bushing can be serviced
separately.
The front of the lower control arm is bolted to the
front crossmember using a bolt through the center of
the rubber pivot bushing. The rear of the lower con-
trol arm is mounted to both the front crossmember
and the frame rail of the vehicle using a thru-bolt.
The thru-bolt goes through both the crossmember
and rear lower control arm bushing, threading
directly into the frame rail of the vehicle.
The left and right lower control arms are intercon-
nected through a linked rubber isolated stabilizer
bar.
The outboard end of each lower control arm con-
nects to the steering knuckle using a ball joint.
1 ± VEHICLE STRUT TOWER
2 ± OUTER TIE ROD
3 ± STEERING GEAR
4 ± STRUT ASSEMBLY
5 ± JAM NUT
6 ± LOWER CONTROL ARM
7 ± CROSSMEMBER
8 ± BALL JOINT
9 ± STABILIZER BAR
10 ± STABILIZER BAR CUSHION AND RETAINER11 ± STABILIZER BAR LINK
12 ± HUB
13 ± KNUCKLE
14 ± STRUT
15 ± LOWER SPRING ISOLATOR
16 ± COIL SPRING
17 ± JOUNCE BUMPER
18 ± DUST SHIELD
19 ± SPRING SEAT AND BEARING
20 ± UPPER MOUNT
PLSUSPENSION 2 - 11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 82 of 1285

The power brake vacuum booster assembly mounts
on the engine side of the dash panel. The booster
input push rod connects to the brake pedal. A vac-
uum line connects the power booster to the intake
manifold. The master cylinder is bolted to the front
of the power brake booster.
MASTER CYLINDER
The base brakes on a vehicle not equipped with
ABS use a standard compensating port master cylin-
der, while vehicles equipped with ABS use a center
valve design master cylinder. The information pro-
vided here applies only to the non-ABS master cylin-
der. For information on the master cylinder used on
vehicles with ABS, refer to the ANTILOCK BRAKE
SYSTEM section in this service manual group.
The non-ABS master cylinder is a four-outlet
design with two screw-in proportioning valves. One is
attached directly to the inboard side of the master
cylinder housing while the other is attached to the
bottom (Fig. 3). Vehicles equipped with rear drum
brakes use a master cylinder with a 22.23 mm (0.875
in.) bore diameter, while vehicles equipped with rear
disc brakes use a 23.82 mm (0.937 in.) bore diameter
master cylinder.
The master cylinder body is an anodized aluminum
casting. It has a machined bore to accept the master
cylinder piston and also has threaded ports with
seats for hydraulic brake line connections.
The master cylinder's primary outlet ports supply
hydraulic pressure to the right front and left rearbrakes while the secondary outlet ports supply
hydraulic pressure to the left front and right rear
brakes (Fig. 3).
BRAKE FLUID RESERVOIR
The master cylinder has the brake fluid reservoir
mounted on top of it which gravity feeds brake fluid
to the master cylinder when it is required. The res-
ervoir is made of see-through plastic and it houses
the brake fluid level switch.
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
The brake fluid level switch is located in the brake
fluid reservoir on the master cylinder (Fig. 1). It
senses the level of the brake fluid within the reser-
voir and when the level drops below an acceptable
level, the switch closes and completes the ground cir-
cuit for the red BRAKE warning lamp. This turns on
the red BRAKE warning lamp. For additional infor-
mation, refer to RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP also
in this section.
PROPORTIONING VALVE
NOTE: Only vehicles without antilock brakes have
proportioning valves. Vehicles with antilock brakes
have electronic brake distribution that is built into
the integrated control unit.
Fig. 2 Power Brake Booster
1 ± MOUNTING STUD
2 ± PARTS IDENTIFICATION TAG
3 ± MASTER CYLINDER MOUNTING STUDS
4 ± VACUUM CHECK VALVE
Fig. 3 Non-ABS Master Cylinder
1 ± RIGHT FRONT BRAKE TUBE
2 ± LEFT FRONT BRAKE TUBE
3 ± LEFT REAR BRAKE TUBE
4 ± REAR PROPORTIONING VALVES
5 ± RIGHT REAR BRAKE TUBE
PLBRAKES 5 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 86 of 1285

The adapter is used to mount the brake caliper to the
vehicle (Fig. 9). The adapter has two machined abut-
ments, which are used to position and align the cal-
iper and brake pads for movement inboard and
outboard. The adapter also mounts the parking brake
shoes and actuating cables to the vehicle.
PARKING BRAKES
The parking brakes (Fig. 4) consist of the following
components:
²Hand-operated park brake lever - automatic-ad-
justing
²Parking brake cables
²Actuation levers and struts
²Duo-servo parking brake assembly (rear disc
only)
PARKING BRAKE LEVER
All vehicles are equipped with a center-mounted,
hand-operated parking brake lever mounted between
the front seats (Fig. 10). This lever is an automatic-
adjusting type that continuously applies minimal
tension to the parking brake cables to keep them in
adjustment at all times. Due to this feature, the
parking brake cable system does not require adjust-
ment. Proper parking brake system adjustment is
obtained by proper drum brake or drum-in-hat brake
shoe adjustment. When service is needed, the lever
auto-adjust mechanism must be reloaded and locked
out before service can be performed.
The parking brake lever has a short output cable
with an equalizer bracket attached to it that connects
to the parking brake cables (Fig. 10). The output
cable can only be serviced as part of the parking
brake lever.PARKING BRAKE CABLES
There is an individual parking brake cable for each
rear wheel that joins a parking cable equalizer,
attached to the parking brake lever, to the rear park-
ing brakes. The parking brake cables are made of
flexible steel cable. Both drum rear brakes and disc
rear brakes use the same parking brake cable config-
uration, but the cables are different.
PARKING BRAKES
On vehicles equipped with rear drum brakes, the
rear wheel service brakes also act as the vehicle's
parking brakes. The rear drum brake shoes, when
acting as parking brakes, are mechanically operated
using an internal actuating lever and strut connected
to the flexible steel parking brake cable.
The parking brakes on vehicles equipped with rear
disc brakes consist of a small duo-servo brake assem-
bly mounted to the disc brake caliper adapter (Fig.
11). The hat (center) section of the rear brake rotor
serves as the braking surface (drum) for the parking
brakes (Fig. 12). This parking brake application uses
the same operating cable configuration as the drum
brake equipped vehicles, but different cables.
Fig. 10 Parking Brake Lever
1 ± PARKING BRAKE LEVER
2 ± PARKING BRAKE WARNING LAMP SWITCH
3 ± OUTPUT CABLEFig. 11 Parking Brake Assembly With Rear Disc
Brakes
1 ± DISC BRAKE ADAPTER
2 ± PARKING BRAKE BRAKE SHOES
3 ± HUB/BEARING ASSEMBLY
4 ± BRAKING DISC STONE SHIELD
5 ± PARKING BRAKE ACTUATING STRUT
PLBRAKES 5 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 175 of 1285
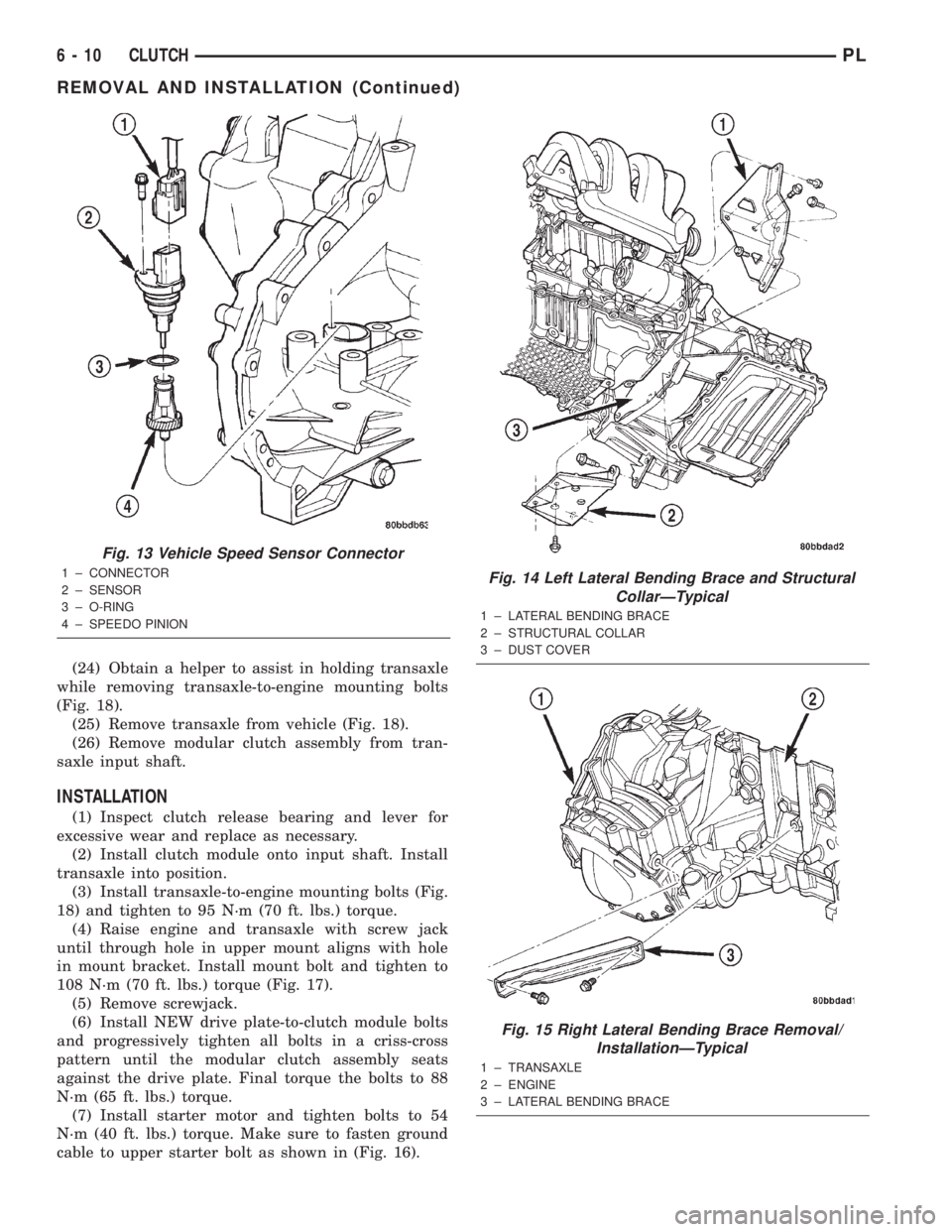
(24) Obtain a helper to assist in holding transaxle
while removing transaxle-to-engine mounting bolts
(Fig. 18).
(25) Remove transaxle from vehicle (Fig. 18).
(26) Remove modular clutch assembly from tran-
saxle input shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Inspect clutch release bearing and lever for
excessive wear and replace as necessary.
(2) Install clutch module onto input shaft. Install
transaxle into position.
(3) Install transaxle-to-engine mounting bolts (Fig.
18) and tighten to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Raise engine and transaxle with screw jack
until through hole in upper mount aligns with hole
in mount bracket. Install mount bolt and tighten to
108 N´m (70 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig. 17).
(5) Remove screwjack.
(6) Install NEW drive plate-to-clutch module bolts
and progressively tighten all bolts in a criss-cross
pattern until the modular clutch assembly seats
against the drive plate. Final torque the bolts to 88
N´m (65 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Install starter motor and tighten bolts to 54
N´m (40 ft. lbs.) torque. Make sure to fasten ground
cable to upper starter bolt as shown in (Fig. 16).
Fig. 13 Vehicle Speed Sensor Connector
1 ± CONNECTOR
2 ± SENSOR
3 ± O-RING
4 ± SPEEDO PINIONFig. 14 Left Lateral Bending Brace and Structural
CollarÐTypical
1 ± LATERAL BENDING BRACE
2 ± STRUCTURAL COLLAR
3 ± DUST COVER
Fig. 15 Right Lateral Bending Brace Removal/
InstallationÐTypical
1 ± TRANSAXLE
2 ± ENGINE
3 ± LATERAL BENDING BRACE
6 - 10 CLUTCHPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 254 of 1285

INSTRUMENT CLUSTER LAMPS
WARNINGS/INDICATORS
The instrument cluster warning/indicator lamps
are all serviceable Light Emitting Diodes (LED's).
The instrument cluster must first be removed, refer
to Instrument Cluster Removal and Installation in
this section, and then the defective LED just turns
out with needle nose pliers.
ILLUMINATION LAMPS
The high beam indicator, turn signals, and illumi-
nation bulbs are also serviceable. The instrument
cluster must first be removed, refer to Instrument
Cluster Removal and Installation in this section, and
then the defective bulb and socket turns out. The
bulb locations are printed on the back cover of the
instrument cluster.
INSTRUMENT PANEL ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable (Fig. 6).
(2) Push seats back to their full back position.
(3) Using a trim stick (special tool #C-4755), gently
pry out on left and right A-pillar trim moldings and
remove.
(4) Remove top cover. Refer to Top Cover Removal
and Installation in this section.
(5) Gently pull up on cluster bezel and remove
from vehicle.
(6) Gently pull rearward on left lower instrument
panel cover and remove from vehicle.
CAUTION: Lock the steering wheel in the straight
ahead position. This will prevent clockspring dam-
age when the steering wheel rotates freely.
(7) Remove steering column. Refer to Group 19
Steering, Steering Column Removal and Installation.
(8) Remove left and right instrument panel end-
caps.
(9) Remove left and right cowl side panels.
(10) Remove center console. Refer to Group 23
Body, Center Console Removal and Installation.
(11) Depress the sides of the Data Link Connector
(DLC) and remove from instrument panel reinforce-
ment.
(12) Remove four bulkhead instrument panel
retaining screws.
(13) Remove two bolts on top of the brake pedal
support bracket.
(14) Remove two center support mounting bolts.
(15) Remove left and right A-pillar mounting bolts,
two on each side.(16) Disconnect right side antenna connector.
(17) Remove left and right A-pillar door harness
connectors (Fig. 10).
(18) Disconnect two harness connectors to hvac at
right top instrument panel (Fig. 11).
Fig. 10 A-Pillar Door Harness Connector
1 ± INSTRUMENT PANEL HARNESS CONNECTOR
2 ± DOOR CHECK STRAP
3 ± DOOR HARNESS CONNECTOR
Fig. 11 Instrument Panel to HVAC Harness Connectors
1 ± HVAC HARNESS CONNECTORS
PLINSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEMS 8E - 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 735 of 1285
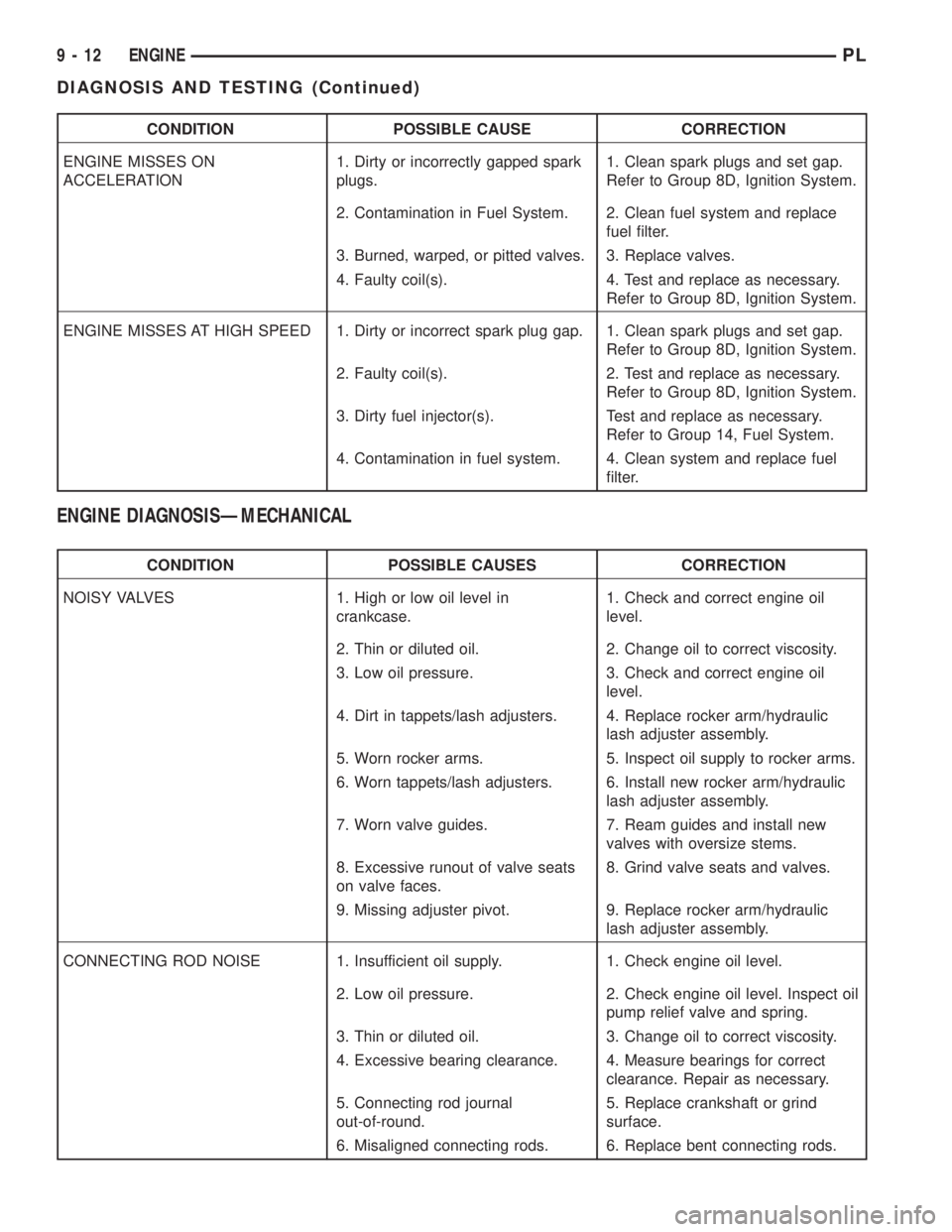
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.1. Clean spark plugs and set gap.
Refer to Group 8D, Ignition System.
2. Contamination in Fuel System. 2. Clean fuel system and replace
fuel filter.
3. Burned, warped, or pitted valves. 3. Replace valves.
4. Faulty coil(s). 4. Test and replace as necessary.
Refer to Group 8D, Ignition System.
ENGINE MISSES AT HIGH SPEED 1. Dirty or incorrect spark plug gap. 1. Clean spark plugs and set gap.
Refer to Group 8D, Ignition System.
2. Faulty coil(s). 2. Test and replace as necessary.
Refer to Group 8D, Ignition System.
3. Dirty fuel injector(s). Test and replace as necessary.
Refer to Group 14, Fuel System.
4. Contamination in fuel system. 4. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐMECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. Check and correct engine oil
level.
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil to correct viscosity.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check and correct engine oil
level.
4. Dirt in tappets/lash adjusters. 4. Replace rocker arm/hydraulic
lash adjuster assembly.
5. Worn rocker arms. 5. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms.
6. Worn tappets/lash adjusters. 6. Install new rocker arm/hydraulic
lash adjuster assembly.
7. Worn valve guides. 7. Ream guides and install new
valves with oversize stems.
8. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.8. Grind valve seats and valves.
9. Missing adjuster pivot. 9. Replace rocker arm/hydraulic
lash adjuster assembly.
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary.
5. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.5. Replace crankshaft or grind
surface.
6. Misaligned connecting rods. 6. Replace bent connecting rods.
9 - 12 ENGINEPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 739 of 1285

CRANKSHAFT
A nodular cast iron crankshaft is used. The engine
has five main bearings. The number three main is
flanged to control thrust. The mains and connecting
rod journals have undercut fillet radiuses that are
deep rolled for added strength. To optimize bearing
loading, eight counterweights are used. Hydrody-
namic seals provide end sealing, where the crank-
shaft exits the block. Anaerobic gasket material is
used for parting line sealing. A sintered iron timing
belt sprocket is mounted on the crankshaft nose. This
sprocket transmits crankshaft movement, via timing
belt to the camshaft sprocket providing timed valve
actuation.
PISTONS
The engineDOES NOThave provision for a free
wheeling valve train. Non free wheeling valve train
means, in the event of a broken timing belt pistons
will contact the valves. The engine uses pressed-in
piston pins to attach forged powdered metal connect-
ing rods. The connecting rods are a cracked cap
design and are not repairable. Hex head cap screw
are used to provide alignment and durability in the
assembly. Pistons and connecting rods are serviced as
an assembly.
PISTON RINGS
The piston rings include a molybdenum faced top
ring for reliable compression sealing and a taper
faced intermediate ring for additional cylinder pres-
sure control. Oil Control Ring Package consist of two
steel rails and an expander spacer.
CYLINDER HEAD
The aluminum cylinder head features a Single
Over Head Camshaft (SOHC), four-valves per cylin-
der, cross flow design. The valves are arranged in
two inline banks, with the two intake per cylinder
facing toward the radiator. The exhaust valves facing
toward the dash panel. Rocker arm shafts mount
directly to the cylinder head. It incorporates powder
metal valve guides and seats. The hollow rocker arm
shafts supplies oil to the hydraulic lash adjusters,
camshaft and valve mechanisms.
CAMSHAFT
The nodular iron camshaft has five bearing jour-
nals and three cam lobes per cylinder. Provision for a
cam position sensor is provided on the camshaft at
the rear of cylinder head which also acts as thrust
plate. A hydrodynamic oil seal is used for oil control
at the front of the camshaft.
VALVES
Four valves per cylinder are actuated by roller
rocker arms/hydraulic lash adjusters assemblies
which pivot on rocker arm shafts. All valves have
chrome plated valve stems. Viton rubber valve stem
seals are integral with spring seats. Valve springs,
spring retainers, and locks are conventional design.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
The intake manifold is a molded plastic composi-
tion, attached to the cylinder head with five fasten-
ers. This long branch design enhances low and mid-
range torque.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
The exhaust manifold is made of nodular cast iron
for strength and high temperatures. Exhaust gasses
exit the manifold into an articulated joint connection
and exhaust pipe.
COMPONENT REPLACEMENT
If any of the following parts have been changed or
replaced:
²Camshaft
²Camshaft Position Sensor
²Camshaft Position Sensor Target Magnet
²Cylinder Block
²Cylinder Head
²Water Pump
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Timing Belt and Timing Belt Tensioner
The camshaft and crankshaft timing relearn proce-
dure must be performed. Refer to the component
Removal and Installation procedure in this section.
9 - 16 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 762 of 1285

(2) Apply MopartGasket Sealant (aerosol can) to
both sides of the new cylinder head gasket.
(3) Position a new cylinder head gasket on the
locating dowels.
(4) Position crankshaft sprocket to TDC, then
rotate crankshaft until mark is three teeth before
TDC (Fig. 59). This will ensure that no piston-to-
valve contact occurs upon installation of cylinder
head in the event of camshaft rotation.
(5) Position the cylinder head onto the cylinder
block. Make sure the cylinder head seats fully over
the locating dowels.
(6) Before installing cylinder head bolts, the
threads should be oiled with engine oil. The 4 shorter
bolts 164 mm (6.45 in.), are to be installed in posi-
tions 7, 8, 9, and 10 (Fig. 60).
(7) Tighten the cylinder head bolts in the sequence
shown in (Fig. 60). Using the 4 step torque method,
tighten according to the following values:²First All to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.)
²Second All to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
²Third All to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
²Fourth Turn an additional 1/4 Turn.Do not use
a torque wrench for this step.
(8) Install cylinder head cover.
(9) Install heater hose to thermostat housing con-
nector.
(10) Install heater tube to cylinder head attaching
fasteners.
(11) Connect cam sensor and coolant temperature
electrical connectors.
(12) Connect Crankcase Closed Ventilation (CCV)
hose to cylinder head cover.
Fig. 56 Checking Cylinder Head Flatness
1 ± FEELER GAUGE
2 ± STRAIGHT EDGE
Fig. 57 Checking Bolts for Stretching (Necking)
1 ± STRETCHED BOLT
2 ± THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 ± THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 ± UNSTRETCHED BOLT
Fig. 58 Proper Tool Usage for Surface Preparation
1 ± ABRASIVE PAD
2 ± 3M ROLOCYBRISTLE DISC
3 ± PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
Fig. 59 Crankshaft Sprocket Position
1 ± TDC MARK
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 39
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 784 of 1285
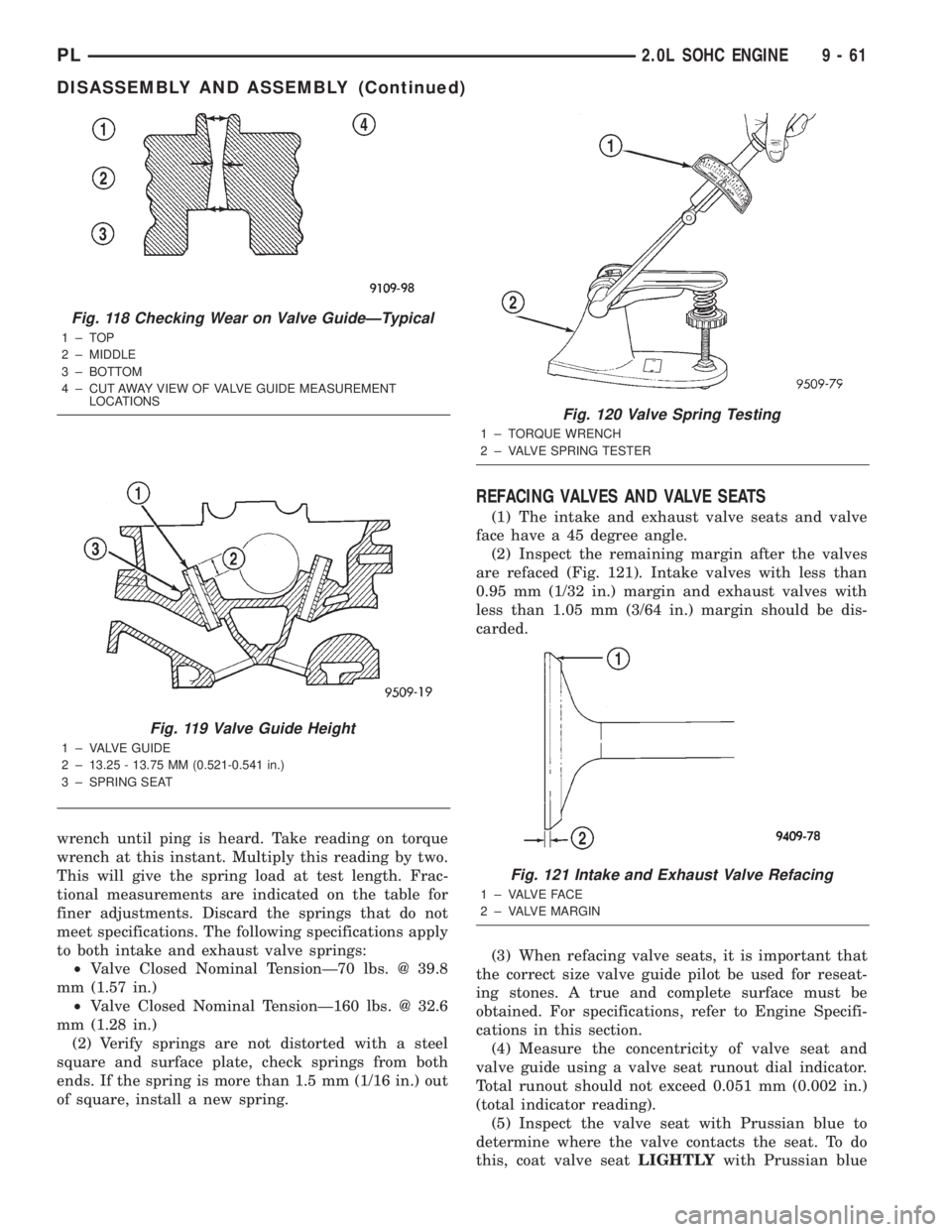
wrench until ping is heard. Take reading on torque
wrench at this instant. Multiply this reading by two.
This will give the spring load at test length. Frac-
tional measurements are indicated on the table for
finer adjustments. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications. The following specifications apply
to both intake and exhaust valve springs:
²Valve Closed Nominal TensionÐ70 lbs. @ 39.8
mm (1.57 in.)
²Valve Closed Nominal TensionÐ160 lbs. @ 32.6
mm (1.28 in.)
(2) Verify springs are not distorted with a steel
square and surface plate, check springs from both
ends. If the spring is more than 1.5 mm (1/16 in.) out
of square, install a new spring.
REFACING VALVES AND VALVE SEATS
(1) The intake and exhaust valve seats and valve
face have a 45 degree angle.
(2) Inspect the remaining margin after the valves
are refaced (Fig. 121). Intake valves with less than
0.95 mm (1/32 in.) margin and exhaust valves with
less than 1.05 mm (3/64 in.) margin should be dis-
carded.
(3) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be
obtained. For specifications, refer to Engine Specifi-
cations in this section.
(4) Measure the concentricity of valve seat and
valve guide using a valve seat runout dial indicator.
Total runout should not exceed 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
(total indicator reading).
(5) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seatLIGHTLYwith Prussian blue
Fig. 118 Checking Wear on Valve GuideÐTypical
1±TOP
2 ± MIDDLE
3 ± BOTTOM
4 ± CUT AWAY VIEW OF VALVE GUIDE MEASUREMENT
LOCATIONS
Fig. 119 Valve Guide Height
1 ± VALVE GUIDE
2 ± 13.25 - 13.75 MM (0.521-0.541 in.)
3 ± SPRING SEAT
Fig. 120 Valve Spring Testing
1 ± TORQUE WRENCH
2 ± VALVE SPRING TESTER
Fig. 121 Intake and Exhaust Valve Refacing
1 ± VALVE FACE
2 ± VALVE MARGIN
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 61
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 785 of 1285

then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to top edge of the valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15 degrees stone. If the blue is transferred to
the bottom edge of valve face raise valve seat with a
65 degrees stone.
(6) Valve seats which are worn or burned can be
reworked, provided that correct angle and seat width
are maintained. The intake valve seat must be ser-
viced when the valve seat width is 2.0 mm (0.079 in.)
or greater. The exhaust valve seat must be serviced
when the valve seat width is 2.5 mm (0.098 in.) or
greater. Otherwise the cylinder head must be
replaced.
(7) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake and exhaust seats should be 0.75±1.25 mm
(0.030±0.049 in.) (Fig. 122).
(8) Check valve tip to spring seat dimensions A
after grinding the valve seats or faces. Grind valve
tip until within specifications. Measure from valve
tip to spring seat when installed in the head (mea-
surement A) (Fig. 123). For specifications, refer to
Engine Specifications in this section. The valve tip
chamfer may need to be reground to prevent seal
damage when the valve is installed.
CLEANING
Clean all valve guides, valves and valve spring
assemblies thoroughly with suitable cleaning solution
before reassembling.
VALVE INSTALLATION
(1) Coat valve stems with clean engine oil and
insert in cylinder head.
(2) Install new valve stem seals on all valves using
a valve stem seal tool (Fig. 124). The valve stem
seals should be pushed firmly and squarely over
valve guide.CAUTION: If oversize valves are used, there is only
one oversize valve available. The same stem seal is
used on both the standard and oversize valve.
(3) Install valve springs and retainers. Compress
valve springs only enough to install locks, taking
care not to misalign the direction of compression.
Nicked valve stems may result from misalignment of
the valve spring compressor.
CAUTION: When depressing the valve spring
retainers with valve spring compressor the locks
can become dislocated. Check to make sure both
locks are in their correct location after removing
tool.
(4) Check the valve spring installed height after
refacing the valve and seat (measurment B) (Fig.
123). Make sure measurements are taken from top of
spring seat to the bottom surface of spring retainer.
If height is greater than 40.18 mm (1.58 in.), install
Fig. 122 Valve Seat Refacing
Fig. 123 Spring Installed Height and Valve Tip to
Spring Seat Dimensions
1 ± GARTER SPRING
2 ± VALVE SPRING SEAT
3 ± CYLINDER HEAD SURFACE
Fig. 124 Valve Stem Oil Seal Tool
1 ± VALVE SEAL TOOL
2 ± VALVE STEM
9 - 62 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)