wheel DODGE POWER WAGON 2006 2.G Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2006, Model line: POWER WAGON, Model: DODGE POWER WAGON 2006 2.GPages: 467, PDF Size: 1.93 MB
Page 251 of 467
CAUTION!
Reduced tire pressure increases the risk of tire dam-
age and may cause tire unseating with total loss of
air pressure. To reduce the risk of tire unseating,
while at a reduced tire pressure, drive at slower
speeds and avoid sharp turns or abrupt maneuvers.
Vehicle Recovery
If you drive off-road, you may encounter a situation
where you will need to recover your vehicle. Vehicle
recovery should always be given consideration before
attempting a questionable obstacle. You should never go
off-road driving without the ability to recover your
vehicle from a situation. Having another vehicle with
you usually works best for most situations. The first
thing to do is assess the situation. Why are you stuck?
Are you hung up on something? Would it be easier to go
forward or to go backward? Can you still move thevehicle? Is there an anchor point to winch to? Are you
alone or do you have another vehicle to help? Is there
high risk of vehicle damage during the recovery process?
Answering these questions will help you determine the
best method of recovery. If you can still move the vehicle
slightly and the only issue is slick ground, then rock
cycling your vehicle would be the first choice. If you have
ample room, an additional vehicle and there is low risk of
vehicle impingement on the surroundings, then using a
tow strap to the vehicle tow hooks would be fast and
easy. If the vehicle is severely hung up or in a situation
where great care needs to be taken during the recovery,
then nothing can do the job better than a winch. If you are
severely hung up on something you should jack the
vehicle up and stack something under the wheels to
allow the vehicle to roll off the object without causing
further damage. This should be tried before attempting
any recovery method.
STARTING AND OPERATING 251
5
Page 252 of 467
CAUTION!
Pulling the vehicle off an obstacle, without first
clearing the object, may result in additional under-
body damage.
•Rock Cycling Your Vehicle– Rock cycling your ve-
hicle is one of the easiest, fastest and most commonly
used methods. This simply involves shifting your
vehicle from drive to reverse, while applying throttle
after each shift. During this process, for additional
traction, try turning your steering wheel quickly back
and forth no more than a
1�4turn. If you are stuck in
mud, sand, or snow try spinning your tires during this
process to clean the debris from the tread and improve
the traction. You want to create a rocking motion with
the vehicle. This helps build vehicle momentum,
which hopefully gets you out. Remember to ease off
and on the accelerator before and after the shift. If aftera few rock cycles your vehicle is not free, stop and try
another method of recovery. Continuous rock cycling
will only cause unnecessary damage to your vehicle
and the environment.
CAUTION!
Damage can occur when spinning your tires at an
excessive high speed. Do not spin your tires faster
than an indicated 35 mph
•Using The Tow Hooks With A Tow Strap–Tow
straps are a quick and easy way to recover your
vehicle from minor situations if you have a secondary
vehicle which is not stuck. The tow hooks on your
vehicle are designed to take the abusive force gener-
ated during vehicle recovery. Do not use the bumper
or any other vehicle component as an attachment
point. Using tow straps requires coordination between
252 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 255 of 467

WARNING!
Winch cables are under high tension when in use
and can become a projectile if they fail. Never stand
over or straddle the winch cable. Never jerk or
overload the winch cable. Never stand in front of the
vehicle while winching. Failure to follow these in-
structions can result in serious or fatal injury.
After Driving Off-Road
Off-road operation puts more stress on your vehicle than
does most on-road driving. After driving off-road, it is
always a good idea to check for damage.
•Completely inspect the underbody of your vehicle.
Check tires, body structure, steering, suspension, and
exhaust system for damage.
•Check threaded fasteners for looseness, particularly on
the chassis, drivetrain components, steering, and sus-
pension. Retighten them, if required, and torque to the
values specified in the Service Manual.
•Check for accumulations of plants or brush. These
things could be a fire hazard, or they might hide
damage to fuel lines, brake hoses, axle pinion seals,
and propeller shafts.
•After extended operation in mud, sand, water, or
similar dirty conditions, have brake drums and rotors,
brake linings, and axle yokes inspected and cleaned as
soon as possible.
•If you experience unusual vibration after driving in
mud, slush or similar conditions, check the wheels for
packed material. Packed foreign material can cause a
wheel imbalance and cleaning the wheels will correct
the situation.
STARTING AND OPERATING 255
5
Page 266 of 467
CAUTION!
Always be certain the anchor you select will with-
stand the load.
NOTE: How to choose an anchor point:A secure
anchor is critical to winching operations. An anchor must
be strong enough to hold while winching. Natural an-
chors include trees, stumps and rocks. Hook the cable as
low as possible. If no natural anchors are available when
recovering another vehicle, your vehicle becomes the
anchor point. In this case, be sure to put the transmission
in neutral, apply the hand brake and block its wheels to
prevent your vehicle from moving. Ideally, you’ll want
an anchor point that will enable you to pull straight in the
direction the vehicle will move. This allows the wire rope
to wind tightly and evenly onto the spooling drum. An
anchor point as far away as possible will provide the
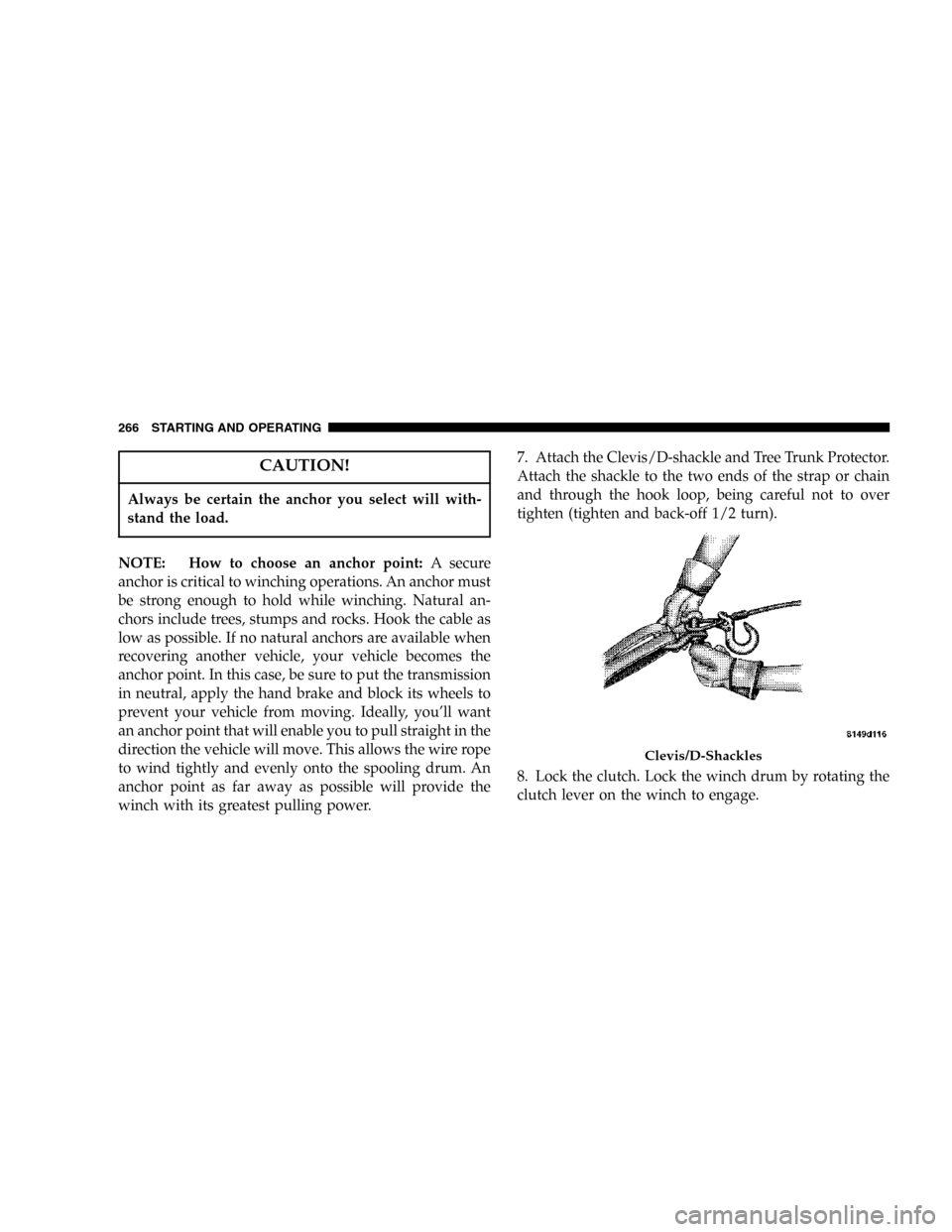
winch with its greatest pulling power.7. Attach the Clevis/D-shackle and Tree Trunk Protector.
Attach the shackle to the two ends of the strap or chain
and through the hook loop, being careful not to over
tighten (tighten and back-off 1/2 turn).
8. Lock the clutch. Lock the winch drum by rotating the
clutch lever on the winch to engage.
Clevis/D-Shackles
266 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 276 of 467

LOCK
Locks the automatic transmission shift control into the
PARK position. It also engages the steering wheel lock (if
equipped) when the steering wheel is turned.
NOTE: This vehicle is equipped with a transmission
shift interlocking system. The brake pedal must be
depressed to shift out of Park (P).
OFF
Unlocks the steering wheel (if equipped with locking
wheel) and the automatic transmission shift control with
engine off.
ON
This is the normal running position.
START
Starts the engine. When the engine starts, release the key.
The ignition key will return to the ON position for
normal driving.
ACC
Allows the electrical accessories to be used when the
engine is not running.
276 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 280 of 467
TRANSMISSION SHIFTING
Automatic Transmission with Overdrive
The gear shift selector display, located in the instrument
panel cluster, indicates the transmission gear range (the
selector is illuminated for night driving). The selector
lever is mounted on the right side of the steering column.
You must depress the brake pedal, to pull the selector
lever out of park (P) position (Brake Interlock System). To
drive, move the selector lever from Park or Neutral to the
desired drive position. Pull the selector lever toward you
when shifting into Reverse, Second, First or Park, or
when shifting out of Park.
Gear Ranges
DO NOT race the engine when shifting from Park or
Neutral position into another gear range.“P” Park
This gear position supplements the parking brake by
locking the transmission. The engine can be started in
this range. Never use Park while the vehicle is in motion.
Apply the parking brake when leaving the vehicle in this
range. Always apply parking brake first, then place the
selector in Park position. On 4-wheel-drive vehicles be
sure that the transfer case is in a drive position!
WARNING!
Never use Park position on an automatic transmis-
sion as a substitute for the parking brake. Always
apply parking brake fully when parked to guard
against vehicle movement and possible injury or
damage.
280 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 287 of 467
CAUTION!
When descending a hill, be very careful to downshift
one gear at a time to prevent overspeeding the
engine which can cause valve damage.
FOUR-WHEEL- DRIVE OPERATION
Manually Shifted Transfer Case Operating
Information/Precautions
The transfer case provides 4 mode positions-2(rear)-
wheel-drive high range, 4-wheel-drive high range, neu-
tral, and 4-wheel-drive low range.
This transfer case is intended to be driven in the 2-wheel-
drive position (2H) for normal street and highway con-
ditions such as dry hard surfaced roads.
When additional traction is required the transfer case 4H
and 4L positions can be used to lock the front and reardriveshafts together and force the front and rear wheels
to rotate at the same speed. This is accomplished by
simply moving the shift lever to the desired positions.
The 4H and 4L positions are intended for loose, slippery
road surfaces only. Driving in the 4H and 4L positions on
dry hard surfaced roads may cause increased tire wear
and damage to the driveline components.
The 4-wheel drive high (4WD) and 4–wheel drive low
(4WDLOW) lights, located in the instrument cluster, alert
the driver that the vehicle is either in 4-wheel drive high
or 4–wheel drive low and that the front and rear drive-
shafts are locked together. There are no lights for the 2H
or N (Neutral) positions.
When operating your vehicle in 4L, the engine speed is
approximately three times that of the 2H or 4H positions
at a given road speed. Take care not to overspeed the
engine and do not exceed 25 mph (40 km/h).
STARTING AND OPERATING 287
5
Page 288 of 467
Proper operation of 4-wheel-drive vehicles depends on
tires of equal size, type and circumference on each wheel.
Any difference will adversely affect shifting and can
cause damage to the transfer case.
NOTE:Do not attempt to make a shift while only the
front or rear wheels are spinning. The transfer case is not
equipped with a synchronizer and therefore the front and
rear driveshaft speeds must be equal for the shift to take
place. Shifting while only the front or rear wheels are
spinning can cause damage to the transfer case.
Because 4-wheel drive provides improved traction, there
is a tendency to exceed safe turning and stopping speeds.
Do not go faster than road conditions permit.
NOTE:Delayed shifts out of four-wheel drive may be
experienced due to uneven tire wear, low or uneven tire
pressures, excessive vehicle loading, or cold tempera-
tures.WARNING!
You or others could be injured if you leave the
vehicle unattended with the transfer case in the
Neutral (N) position without first fully engaging the
parking brake. The transfer case Neutral (N) position
disengages both the front and rear driveshafts from
the powertrain and will allow the vehicle to move
regardless of the transmission position. The parking
brake should always be applied when the driver is
not in the vehicle.
For additional information on the appropriate use of each
transfer case mode position see the information below:
2H
Rear Wheel Drive High Range - Normal street and
highway driving. Dry hard surfaced roads.
288 STARTING AND OPERATING
Page 289 of 467

4H
4-Wheel-Drive High Range - Locks the front and rear
driveshafts together. Forces the front and rear wheels to
rotate at the same speed. Additional traction for loose,
slippery road surfaces only.
N
Neutral - Disengages both the front and rear driveshafts
from the powertrain. To be used for flat towing behind
another vehicle. See Recreational Towing for more infor-
mation.
4L
4-Wheel-Drive Low Range - Low speed 4-wheel-drive.
Locks the front and rear driveshafts together. Forces the
front and rear wheels to rotate at the same speed.
Additional traction and maximum pulling power for
loose, slippery road surfaces only. Do not exceed 25 mph
(40 km/h).
Shifting Procedure - Manually Shifted Transfer
Case
2H⇔4H
Shifting between 2H and 4H can be made with the
vehicle stopped or in motion. If the vehicle is in motion,
shifts can be made up to 55 mph (88 km/h). With the
Manual Transfer Case Shifter
STARTING AND OPERATING 289
5
Page 290 of 467

vehicle in motion, the transfer case will engage / disen-
gage faster if you momentarily release the accelerator
pedal after completing the shift. Apply a constant force
when shifting the transfer case lever.
2H or 4H⇔4L
With the vehicle rolling at 2 to 3 mph (3 to 5 km/h), shift
an automatic transmission to N (Neutral) or depress the
clutch on a manual transmission. While the vehicle is
coasting at 2 to 3 mph (3 to 5 km/h), shift the transfer
case lever firmly to the desired position. Do not pause in
transfer case N (Neutral).
NOTE:Pausing in transfer case N (Neutral) in vehicles
equipped with an automatic transmission may require
shutting the engine OFF to avoid gear clash while
completing the shift. If difficulty occurs, shift automatic
transmission to N (Neutral), hold foot on brake, and turn
engine OFF. Make shift to the desired mode.NOTE:Shifting into or out of 4L is possible with the
vehicle completely stopped, however difficulty may oc-
cur due to the mating clutch teeth not being properly
aligned. Several attempts may be required for clutch
teeth alignment and shift completion to occur. The pre-
ferred method is with the vehicle rolling 2 to 3 mph (3 to
5 km/h). Avoid attempting to engage or disengage 4L
with the vehicle moving faster than 2 to 3 mph (3 to 5
km/h).
NOTE:Do not attempt to shift to or from 4L while the
transmission is in gear or clutch is engaged.
Transfer Case Reminder Light
The four-wheel-drive operating light (4WD), located in
the instrument cluster, is used to alert the driver that the
front axle is fully engaged and all four wheels are
driving.
290 STARTING AND OPERATING