Electronic DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 551 of 2627

cator is electronically disabled. The upshift indicator
consists of an upward pointed arrow icon, which
appears on the right side of the electronic gear selec-
tor indicator Vacuum Fluorescent Display (VFD)
unit. The VFD is soldered onto the cluster electronic
circuit board and is visible through a window with a
smoked clear lens located on the lower edge of the
speedometer gauge dial face of the cluster overlay.
The dark lens over the VFD prevents the indicator
from being clearly visible when it is not illuminated.
The icon appears in a blue-green color and at the
same lighting level as the odometer/trip odometer
information when it is illuminated by the instrument
cluster electronic circuit board. The upshift indicator
is serviced as a unit with the instrument cluster.
OPERATION
The upshift indicator gives an indication to the
vehicle operator when the manual transmission
should be shifted to the next highest gear in order to
achieve the best fuel economy. This indicator is con-
trolled by the instrument cluster circuit board based
upon cluster programming and electronic messages
received by the cluster from the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) on vehicles with a gasoline engine, or
from the Engine Control Module (ECM) on vehicles
with a diesel engine over the Programmable Commu-
nications Interface (PCI) data bus. The upshift indi-
cator is completely controlled by the instrument
cluster logic circuit, and that logic will only allow
this indicator to operate when the instrument cluster
receives a battery current input on the fused ignition
switch output (run-start) circuit. Therefore, the indi-
cator will always be off when the ignition switch is in
any position except On or Start. The indicator only
illuminates when it is switched to ground by the
instrument cluster circuitry. The instrument cluster
will turn on the upshift indicator for the following
reasons:
²Upshift Lamp-On Message- Each time the
cluster receives an upshift lamp-on message from the
PCM or ECM indicating the engine speed and load
conditions are right for a transmission upshift to
occur, the upshift indicator is illuminated. The indi-
cator remains illuminated until the cluster receives
an upshift lamp-off message from the PCM or ECM,
or until the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion, whichever occurs first. The PCM or ECM will
normally send an upshift lamp-off message three to
five seconds after a lamp-on message, if an upshift is
not performed. The indicator will then remain off
until the vehicle stops accelerating and is brought
back into the range of indicator operation, or until
the transmission is shifted into another gear.
²Actuator Test- Each time the cluster is put
through the actuator test, the upshift indicator willbe turned on, then off again during the VFD portion
of the test to confirm the functionality of the VFD
and the cluster control circuitry.
On vehicles with a gasoline engine, the PCM con-
tinually monitors the engine speed and load condi-
tions to determine the proper fuel and ignition
requirements. On vehicles with a diesel engine, the
ECM continually monitors the engine speed and load
conditions to determine the proper fuel requirements.
The PCM or ECM then sends the proper upshift indi-
cator lamp-on and lamp-off messages to the instru-
ment cluster. For further diagnosis of the upshift
indicator or the instrument cluster circuitry that con-
trols the indicator, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IN-
STRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). For proper diagnosis of the PCM, the
ECM, the PCI data bus, or the electronic message
inputs to the instrument cluster that control the
upshift indicator, a DRBIIItscan tool is required.
Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
VOLTAGE GAUGE
DESCRIPTION
A voltage gauge is standard equipment on all
instrument clusters. The voltage gauge is located in
the upper left quadrant of the instrument cluster,
above the fuel gauge. The voltage gauge consists of a
movable gauge needle or pointer controlled by the
instrument cluster circuitry and a fixed 90 degree
scale on the cluster overlay that reads left-to-right
from ªLº (or Low) to ªHº (or High) for gasoline
engines. On vehicles with a diesel engine, the scale
reads from ª8º to ª18º volts. An International Control
and Display Symbol icon for ªBattery Charging Con-
ditionº is located on the cluster overlay, directly
below the right end of the gauge scale (Fig. 34). The
voltage gauge graphics are black against a white
field except for a single red graduation at each end of
the gauge scale, making them clearly visible within
the instrument cluster in daylight. When illuminated
from behind by the panel lamps dimmer controlled
cluster illumination lighting with the exterior lamps
turned On, the black graphics appear blue and the
red graphics still appear red. The orange gauge nee-
dle is internally illuminated. Gauge illumination is
provided by replaceable incandescent bulb and bulb
holder units located on the instrument cluster elec-
tronic circuit board. The voltage gauge is serviced as
a unit with the instrument cluster.
Fig. 34 Battery Charging Condition Icon
8J - 42 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERDR
UPSHIFT INDICATOR (Continued)
Page 552 of 2627

OPERATION
The voltage gauge gives an indication to the vehi-
cle operator of the electrical system voltage. This
gauge is controlled by the instrument cluster circuit
board based upon cluster programming and elec-
tronic messages received by the cluster from the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) on vehicles
equipped with a gasoline engine, or from the Engine
Control Module (ECM) on vehicles equipped with a
diesel engine over the Programmable Communica-
tions Interface (PCI) data bus. The voltage gauge is
an air core magnetic unit that receives battery cur-
rent on the instrument cluster electronic circuit
board through the fused ignition switch output (run-
start) circuit whenever the ignition switch is in the
On or Start positions. The cluster is programmed to
move the gauge needle back to the left end of the
scale after the ignition switch is turned to the Off
position. The instrument cluster circuitry controls
the gauge needle position and provides the following
features:
²System Voltage Message- Each time the clus-
ter receives a system voltage message from the PCM
or ECM indicating the system voltage is between
about 9.5 volts and about 15 volts, the gauge needle
is moved to the relative voltage position on the gauge
scale.
²System Voltage Low (Charge Fail) Message
- Each time the cluster receives three consecutive
messages from the PCM or ECM indicating the elec-
trical system voltage is less than about 9 volts
(charge fail condition), the gauge needle is moved to
the graduation on the far left end of the gauge scale
and the check gauges indicator is illuminated. The
gauge needle remains at the far left end of the gauge
scale and the check gauges indicator remains illumi-
nated until the cluster receives a single message
from the PCM or ECM indicating the electrical sys-
tem voltage is greater than about 9.5 volts (but less
than about 15.5 volts), or until the ignition switch is
turned to the Off position, whichever occurs first. On
vehicles equipped with the optional diesel engine, the
ECM is programmed to restrict the voltage gauge
needle to a position above the graduation on the far
left end of the gauge scale and suppress the check
engine indicator operation until after the engine
intake manifold air heater has completed a pre-heat
or post-heat cycle.²System Voltage High Message- Each time
the cluster receives three consecutive messages from
the PCM or ECM indicating the electrical system
voltage is greater than about 15.5 volts, the gauge
needle is moved to the graduation on the far right
end of the gauge scale and the check gauges indica-
tor is illuminated. The gauge needle remains at the
right end of the gauge scale and the check gauges
indicator remains illuminated until the cluster
receives a message from the PCM or ECM indicating
the electrical system voltage is less than about 15.0
volts (but greater than about 9.5 volts), or until the
ignition switch is turned to the Off position, which-
ever occurs first.
²Communication Error- If the cluster fails to
receive a system voltage message, it will hold the
gauge needle at the last indication for about five sec-
onds or until the ignition switch is turned to the Off
position, whichever occurs first. After five seconds,
the cluster will move the gauge needle to the far left
end of the gauge scale.
²Actuator Test- Each time the cluster is put
through the actuator test, the voltage gauge needle
will be swept to several calibration points on the
gauge scale in a prescribed sequence in order to con-
firm the functionality of the gauge and the cluster
control circuitry.
On vehicles with a gasoline engine, the PCM con-
tinually monitors the system voltage to control the
generator output. On vehicles with a diesel engine,
the ECM continually monitors the system voltage to
control the generator output. The PCM or ECM then
sends the proper system voltage messages to the
instrument cluster. For further diagnosis of the volt-
age gauge or the instrument cluster circuitry that
controls the gauge, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IN-
STRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING). If the instrument cluster turns on the check
gauges indicator due to a charge fail or voltage high
condition, it may indicate that the charging system
requires service. For proper diagnosis of the charging
system, the PCM, the ECM, the PCI data bus, or the
electronic message inputs to the instrument cluster
that control the voltage gauge, a DRBIIItscan tool is
required. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation.
DRINSTRUMENT CLUSTER 8J - 43
VOLTAGE GAUGE (Continued)
Page 553 of 2627

WAIT-TO-START INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION
A wait-to-start indicator is only found in the
instrument clusters for vehicles equipped with an
optional diesel engine (Fig. 35). The wait-to-start
indicator is located near the lower edge of the instru-
ment cluster, between the tachometer and the speed-
ometer. The wait-to-start indicator consists of stencil-
like cutout of the International Control and Display
Symbol icon for ªDiesel Preheatº in the opaque layer
of the instrument cluster overlay. The dark outer
layer of the overlay prevents the indicator from being
clearly visible when it is not illuminated. An amber
Light Emitting Diode (LED) behind the cutout in the
opaque layer of the overlay causes the icon to appear
in amber through the translucent outer layer of the
overlay when the indicator is illuminated from
behind by the LED, which is soldered onto the
instrument cluster electronic circuit board. The wait-
to-start indicator is serviced as a unit with the
instrument cluster.
OPERATION
The wait-to-start indicator gives an indication to
the vehicle operator when the air temperature within
the diesel engine intake manifold is too cool for effi-
cient and reliable engine starting, and that the
intake air heater grids are energized in their pre-
heat operating mode. This indicator is controlled by a
transistor on the instrument cluster circuit board
based upon cluster programming and electronic mes-
sages received by the cluster from the Engine Control
Module (ECM) over the Programmable Communica-
tions Interface (PCI) data bus. The wait-to-start indi-
cator Light Emitting Diode (LED) is completely
controlled by the instrument cluster logic circuit, and
that logic will only allow this indicator to operate
when the instrument cluster receives a battery cur-
rent input on the fused ignition switch output (run-
start) circuit. Therefore, the LED will always be off
when the ignition switch is in any position except On
or Start. The LED only illuminates when it is pro-
vided a path to ground by the instrument cluster
transistor. The instrument cluster will turn on the
wait-to-start indicator for the following reasons:
²Wait-To-Start Lamp-On Message- Each time
the cluster receives a wait-to-start lamp-on message
from the ECM indicating that the air temperature
within the intake manifold is too cool for efficient
and reliable engine starting, the wait-to-start indica-
tor will be illuminated. The indicator remains illumi-nated until the cluster receives a wait-to-start lamp-
off message, until the ECM detects that the engine is
running or until the ignition switch is turned to the
Off position, whichever occurs first.
²Actuator Test- Each time the cluster is put
through the actuator test, the wait-to-start indicator
will be turned on, then off again during the bulb
check portion of the test to confirm the functionality
of the LED and the cluster control circuitry.
The ECM continually monitors the engine intake
air temperature sensor to determine when the intake
air heater grids should be energized in their pre-heat
operating mode. The ECM then sends the proper
wait-to-start lamp-on and lamp-off messages to the
instrument cluster. For further diagnosis of the wait-
to-start indicator or the instrument cluster circuitry
that controls the indicator, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). For proper diagnosis of the engine intake
air temperature sensor, the intake air heater grid
control circuits, the ECM, the PCI data bus, or the
electronic message inputs to the instrument cluster
that control the wait-to-start indicator, a DRBIIIt
scan tool is required. Refer to the appropriate diag-
nostic information.
WASHER FLUID INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION
A washer fluid indicator is standard equipment on
all instrument clusters. The washer fluid indicator
consists of the words ªLOW WASHº, which appear in
the lower portion of the odometer/trip odometer Vac-
uum-Fluorescent Display (VFD) unit (Fig. 36). The
VFD is soldered onto the cluster electronic circuit
board and is visible through a window with a smoked
clear lens located on the lower edge of the tachome-
ter gauge dial face of the cluster overlay. The dark
lens over the VFD prevents the indicator from being
clearly visible when it is not illuminated. The ªLOW
WASHº text appears in an amber color and at the
same lighting level as the odometer/trip odometer
information when it is illuminated by the instrument
cluster electronic circuit board. The washer fluid
indicator is serviced as a unit with the VFD in the
instrument cluster.
OPERATION
The washer fluid indicator gives an indication to
the vehicle operator that the fluid level in the washer
Fig. 35 Wait-To-Start Indicator
Fig. 36 Washer Fluid Indicator
8J - 44 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERDR
Page 554 of 2627

reservoir is low. This indicator is controlled by the
instrument cluster circuit board based upon cluster
programming and electronic messages received by
the cluster from the Front Control Module (FCM)
over the Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) data bus. The washer fluid indicator is com-
pletely controlled by the instrument cluster logic cir-
cuit, and that logic will only allow this indicator to
operate when the instrument cluster receives a bat-
tery current input on the fused ignition switch out-
put (run-start) circuit. Therefore, the indicator will
always be off when the ignition switch is in any posi-
tion except On or Start. The indicator only illumi-
nates when it is switched to ground by the
instrument cluster circuitry. The instrument cluster
will turn on the washer fluid indicator for the follow-
ing reasons:
²Washer Fluid Indicator Lamp-On Message-
Each time the cluster receives a washer fluid indica-
tor lamp-on message from the FCM indicating that a
low washer condition has been detected for sixty con-
secutive seconds, the washer fluid indicator is illumi-
nated and a single chime tone is sounded. The
indicator remains illuminated until the cluster
receives a washer fluid indicator lamp-off message
for sixty consecutive seconds from the FCM or until
the ignition switch is turned to the Off position,
whichever occurs first. The chime tone feature will
only repeat during the same ignition cycle if the
washer fluid indicator is cycled off and then on again
by the appropriate washer fluid lamp messages from
the FCM.
²Actuator Test- Each time the cluster is put
through the actuator test, the washer fluid indicator
will be turned on, then off again during the VFD por-
tion of the test to confirm the functionality of the
VFD and the cluster control circuitry.
The FCM continually monitors the washer fluid
level switch in the washer reservoir to determine the
level of the washer fluid. The FCM then sends the
proper washer fluid indicator lamp-on and lamp-off
messages to the instrument cluster. For further diag-
nosis of the washer fluid indicator or the instrument
cluster circuitry that controls the indicator, (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAG-
NOSIS AND TESTING). For proper diagnosis of the
washer fluid level switch, the FCM, the PCI data
bus, or the electronic message inputs to the instru-
ment cluster that control the washer fluid indicator,
a DRBIIItscan tool is required. Refer to the appro-
priate diagnostic information.WATER-IN-FUEL INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION
A water-in-fuel indicator is only found in the
instrument clusters for vehicles equipped with an
optional diesel engine (Fig. 37). The water-in-fuel
indicator is located near the lower edge of the instru-
ment cluster, between the tachometer and the speed-
ometer. The water-in-fuel indicator consists of stencil-
like cutout of the International Control and Display
Symbol icon for ªWater In Fuelº in the opaque layer
of the instrument cluster overlay. The dark outer
layer of the overlay prevents the indicator from being
clearly visible when it is not illuminated. A red Light
Emitting Diode (LED) behind the cutout in the
opaque layer of the overlay causes the icon to appear
in red through the translucent outer layer of the
overlay when the indicator is illuminated from
behind by the LED, which is soldered onto the
instrument cluster electronic circuit board. The
water-in-fuel indicator is serviced as a unit with the
instrument cluster.
OPERATION
The water-in-fuel indicator gives an indication to
the vehicle operator when there is excessive water in
the fuel system. This indicator is controlled by a
transistor on the instrument cluster circuit board
based upon the cluster programming and electronic
messages received by the cluster from the Engine
Control Module (ECM) over the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus. The water-in-
fuel indicator Light Emitting Diode (LED) is
completely controlled by the instrument cluster logic
circuit, and that logic will only allow this indicator to
operate when the instrument cluster receives a bat-
tery current input on the fused ignition switch out-
put (run-start) circuit. Therefore, the LED will
always be off when the ignition switch is in any posi-
tion except On or Start. The LED only illuminates
when it is provided a path to ground by the instru-
ment cluster transistor. The instrument cluster will
turn on the water-in-fuel indicator for the following
reasons:
²Bulb Test- Each time the ignition switch is
turned to the On position the water-in-fuel indicator
is illuminated for about two seconds as a bulb test.
²Water-In-Fuel Lamp-On Message- Each time
the cluster receives a water-in-fuel lamp-on message
from the ECM indicating that there is excessive
Fig. 37 Water-In-Fuel Indicator
DRINSTRUMENT CLUSTER 8J - 45
WASHER FLUID INDICATOR (Continued)
Page 555 of 2627

water in the diesel fuel system, the water-in-fuel
indicator will be illuminated. The indicator remains
illuminated until the cluster receives a water-in-fuel
lamp-off message, or until the ignition switch is
turned to the Off position, whichever occurs first.
²Actuator Test- Each time the cluster is put
through the actuator test, the water-in-fuel indicator
will be turned on, then off again during the bulb
check portion of the test to confirm the functionality
of the LED and the cluster control circuitry.
The ECM continually monitors the water-in-fuel
sensor to determine whether there is excessive water
in the diesel fuel system. The ECM then sends theproper water-in-fuel lamp-on and lamp-off messages
to the instrument cluster. For further diagnosis of
the water-in-fuel indicator or the instrument cluster
circuitry that controls the indicator, (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING). For proper diagnosis of the
water-in-fuel sensor, the ECM, the PCI data bus, or
the electronic message inputs to the instrument clus-
ter that control the water-in-fuel indicator, a
DRBIIItscan tool is required. Refer to the appropri-
ate diagnostic information.
8J - 46 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERDR
WATER-IN-FUEL INDICATOR (Continued)
Page 563 of 2627
(2) Install the lamp back plate onto the tail lamp
unit.
(3) Install the tail lamp unit (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/TAIL
LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION).
(4) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION - WITHOUT CARGO BOX
(1) Install the backup lamp bulb into the backup
lamp socket by pushing inward and rotating it clock-
wise.
NOTE: Install the tail lamp lens with the clear por-
tion (back-up lens) at the top of the housing. Make
sure that the gasket is correctly in place and not
twisted or torn.
(2) Position the tail lamp lens and gasket onto the
tail lamp unit.
NOTE: Do not overtighten the tail lamp lens screws
or damage to the tail lamp lens may result.
(3) Install the four screws that secure the tail
lamp lens to the tail lamp unit. Tighten the screws
securely.
(4) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
BACKUP LAMP SWITCH
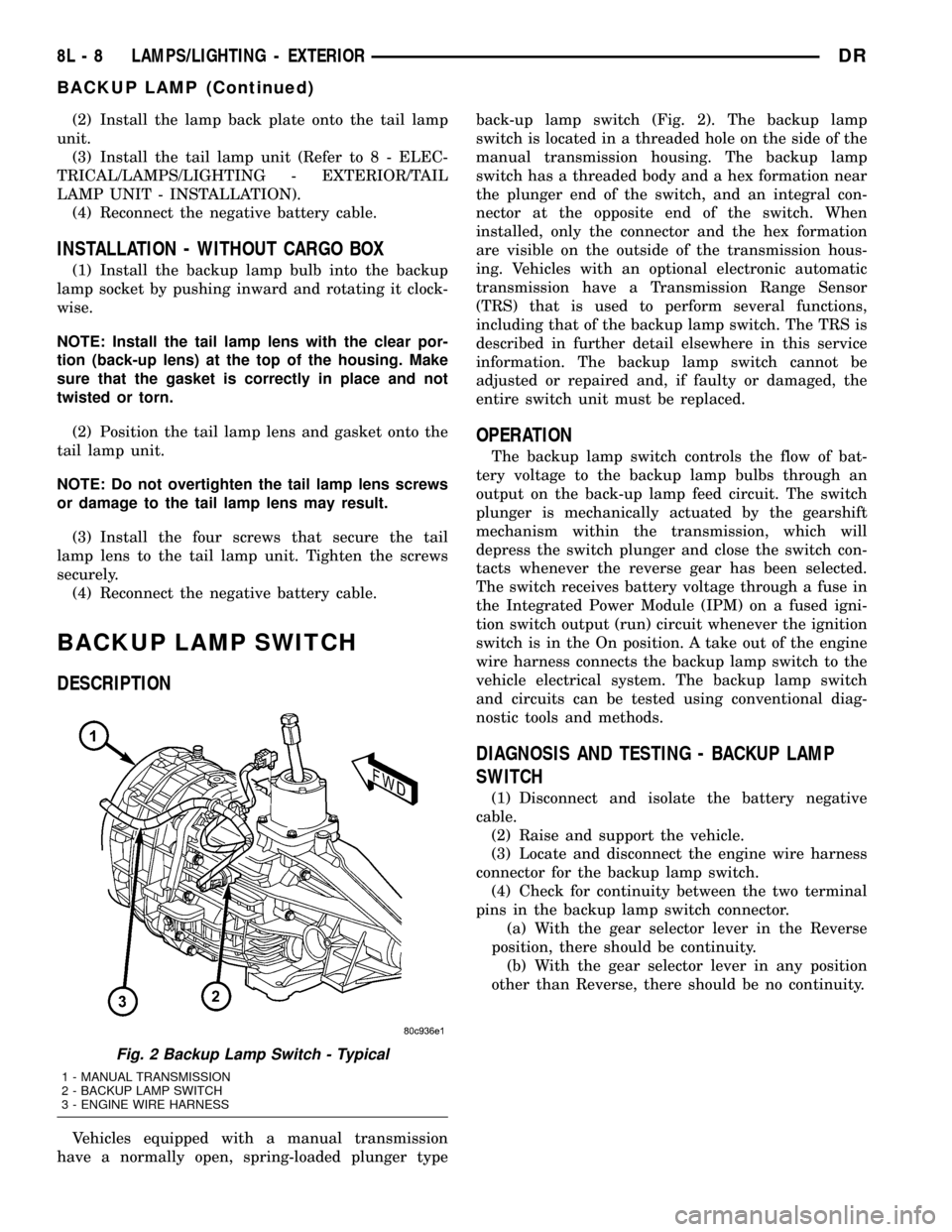
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with a manual transmission
have a normally open, spring-loaded plunger typeback-up lamp switch (Fig. 2). The backup lamp
switch is located in a threaded hole on the side of the
manual transmission housing. The backup lamp
switch has a threaded body and a hex formation near
the plunger end of the switch, and an integral con-
nector at the opposite end of the switch. When
installed, only the connector and the hex formation
are visible on the outside of the transmission hous-
ing. Vehicles with an optional electronic automatic
transmission have a Transmission Range Sensor
(TRS) that is used to perform several functions,
including that of the backup lamp switch. The TRS is
described in further detail elsewhere in this service
information. The backup lamp switch cannot be
adjusted or repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the
entire switch unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The backup lamp switch controls the flow of bat-
tery voltage to the backup lamp bulbs through an
output on the back-up lamp feed circuit. The switch
plunger is mechanically actuated by the gearshift
mechanism within the transmission, which will
depress the switch plunger and close the switch con-
tacts whenever the reverse gear has been selected.
The switch receives battery voltage through a fuse in
the Integrated Power Module (IPM) on a fused igni-
tion switch output (run) circuit whenever the ignition
switch is in the On position. A take out of the engine
wire harness connects the backup lamp switch to the
vehicle electrical system. The backup lamp switch
and circuits can be tested using conventional diag-
nostic tools and methods.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BACKUP LAMP
SWITCH
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Locate and disconnect the engine wire harness
connector for the backup lamp switch.
(4) Check for continuity between the two terminal
pins in the backup lamp switch connector.
(a) With the gear selector lever in the Reverse
position, there should be continuity.
(b) With the gear selector lever in any position
other than Reverse, there should be no continuity.
Fig. 2 Backup Lamp Switch - Typical
1 - MANUAL TRANSMISSION
2 - BACKUP LAMP SWITCH
3 - ENGINE WIRE HARNESS
8L - 8 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORDR
BACKUP LAMP (Continued)
Page 582 of 2627

(4) Push the right side of the lamp in the head-
liner opening and push the lamp lens up into the
lamp to secure (Fig. 1).
DOOR AJAR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The door ajar switches are integral to the door
latches on each door. The switches close a path to
ground for the Instrument Cluster when a door is
opened.
The door ajar switches cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, the door latch unit must be
replaced. Refer to the Body section under Doors for
the removal and installation procedure.
OPERATION
The door ajar switches close a path to ground for
the Instrument Cluster when a door is opened. The
passenger front door is connected in a parallel-series
circuit between ground and the Instrument Cluster,
while the driver side front door ajar switch is con-
nected in series between ground and the Instrument
Cluster to provide a unique input. The Instrument
Cluster reads the switch status, then sends the
proper switch status messages to other electronic
modules over the Programmable Communications
Interface (PCI) data bus network. The door ajar
switches can be diagnosed using conventional diag-
nostic tools and methods. Refer to the Body section
under Doors for the Removal and Installation proce-
dures.
GLOVE BOX LAMP/SWITCH
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the glove box from the instrument
panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
GLOVE BOX - REMOVAL) for the procedures.
(3) Reach through the glove box opening and
behind the glove box lamp and switch mounting
bracket to access the instrument panel wire harness
connector on the glove box lamp and switch (Fig. 3).
(4) Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector from the connector receptacle on the back
of the glove box lamp and switch unit.
(5) Reach through the glove box opening and
behind the glove box lamp and switch mounting
bracket to depress the retaining tabs on the top and
bottom of the glove box lamp and switch housing.
(6) While holding the retaining tabs depressed,
push the glove box lamp and switch unit out through
the hole in the mounting bracket on the instrument
panel glove box opening upper reinforcement.
(7) Remove the glove box lamp and switch unit
from the instrument panel.
Fig. 2 Dome Lamp
1 - SLIDE LAMP
Fig. 3 Glove Box Lamp and Switch Remove/Install
1 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
2 - DASH BOARD
3 - GLOVE BOX SWITCH/LIGHT
DRLAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR 8L - 27
DOME LAMP (Continued)
Page 586 of 2627
MESSAGE SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
OVERHEAD CONSOLE
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - OVERHEAD
CONSOLE............................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - READING/
COURTESY LAMP REPLACEMENT.........3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MODULE LENS
REPLACEMENT.......................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MODULE LAMP
REPLACEMENT.......................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPASS
CALIBRATION.........................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPASS
DEMAGNETIZING......................4
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPASS
VARIATION ADJUSTMENT................5
REMOVAL
OVERHEAD CONSOLE REMOVAL.........6
INSTALLATION..........................6
COMPASS/MINI-TRIP COMPUTER
DESCRIPTION..........................6
OPERATION............................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMPASS
MINI-TRIP COMPUTER..................6
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................6
ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFO CENTER
DESCRIPTION..........................7OPERATION............................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ELECTRONIC
VEHICLE INFORMATION CENTER.........8
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ELECTRONIC
VEHICLE INFORMATION CENTER
PROGRAMMING.......................8
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION..........................9
AMBIENT TEMP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................10
OPERATION...........................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR...............10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT........10
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
UNIVERSAL TRANSMITTER
DESCRIPTION.........................11
OPERATION...........................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - UNIVERSAL
TRANSMITTER.......................11
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ERASING
TRANSMITTER CODES.................12
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SETTING
TRANSMITTER CODES.................12
REMOVAL.............................12
OVERHEAD CONSOLE
DESCRIPTION
Two different overhead consoles are available on
DR models. The Electronic Vehicle Information Cen-
ter (EVIC) (Fig. 1) or Compass Mini-Trip Computer
(CMTC). All consoles are equipped with two reading/
courtesy lamps. The overhead console is mounted
with screws and two snap clips to a molded plastic
retainer bracket located above the headliner.
COMPASS DISPLAY
All the available overhead consoles on this model
include Compass information. While in the compass/
temperature mode, the compass will display the
direction in which the vehicle is pointed using the
eight major compass headings (Examples: north is N,
northeast is NE). The self-calibrating compass unit
requires no adjusting in normal use. The only cali-
bration that may prove necessary is to drive the vehi-
cle at 5 to 8 kilometers-per-hour (3 to 5 miles-per-
hour), on level ground in a square shaped pattern.
This will reorient the compass unit to its vehicle.
DRMESSAGE SYSTEMS 8M - 1
Page 587 of 2627

The compass unit also will compensate for magne-
tism the body of the vehicle may acquire during nor-
mal use. However, avoid placing anything magnetic
directly on the roof of the vehicle. Magnetic mounts
for an antenna, a repair order hat, or a funeral pro-
cession flag can exceed the compensating ability of
the compass unit if placed on the roof panel. Mag-
netic bit drivers used on the fasteners that hold the
overhead console assembly to the roof header can
also affect compass operation. If the vehicle roof
should become magnetized, the demagnetizing and
calibration procedures found in this section may be
required to restore proper compass operation.
TEMPERATURE DISPLAY
All the available overhead consoles on this model
include Temperature information. The temperature
displays the outside ambient temperature in whole
degrees. The temperature display can be toggled
from Fahrenheit to Celsius by selecting the desired
U.S./Metric option from the customer programmable
features. The displayed temperature is not an instant
reading of conditions, but an average temperature. It
may take the temperature display several minutes to
respond to a major temperature change, such as driv-
ing out of a heated garage into winter temperatures.
When the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion, the last displayed temperature reading stays in
the electronic control modules, (CMTC, EVIC) mem-
ory. When the ignition switch is turned to the On
position again, the electronic module will display the
memory temperature for one minute; then update the
display to the current average temperature reading
within five minutes.The temperature function is supported by an ambi-
ent temperature sensor. This sensor is mounted out-
side the passenger compartment near the front and
center of the vehicle, and is hard wired to the Front
Control Module (FCM). The FCM sends temperature
status messages to the module over the J1850 PCI
data bus circuit. For more information on the ambi-
ent temperature sensor, refer to Ambient Tempera-
ture Sensor later in this section.
Following are general descriptions of the major
components used in the overhead console. Refer to
Wiring Diagrams for complete circuit schematics.
OPERATION
Refer to the vehicle Owner's Manual for specific
operation of each overhead console and its systems.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - OVERHEAD
CONSOLE
If the problem with the overhead console is an
inaccurate or scrambled display, refer toSELF-DI-
AGNOSTIC TESTlater in this text. If the problem
with the overhead console is incorrect Vacuum Fluo-
rescent Display (VFD) dimming levels, use a DRB
IIItscan tool and the proper Diagnostic Procedures
manual to test for the correct dimming message
inputs being received from the Body Control Module
(BCM) or Front Control Module (FCM) over the
J1850 Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) data bus circuit. If the problem is a no-display
condition, use the following procedure. For complete
circuit diagrams, refer toOverhead Consolein the
Wiring Diagrams section of the service manual.
(1) Remove the overhead console from the head-
liner (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CON-
SOLE - REMOVAL).
(2) Check for battery voltage at the overhead con-
sole electrical connector. Refer to Wiring for connec-
tor information. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, Check
for battery voltage at the appropriate B(+) fuse in the
integrated power module, repair the open fused B(+)
circuit as required.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check the fused ignition switch output circuit(s) at
the overhead console electrical connector. If OK, go to
Step 4. If not OK, repair the open or shorted circuit
as required.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Check for continuity between the ground circuit cav-
ity of the overhead console electrical connector and a
good ground. There should be continuity. If OK, refer
toSELF-DIAGNOSTIC TESTbelow for further
diagnosis of the electronics module and the J1850
PCI data bus circuit. If not OK, repair the open
ground circuit as required.
Fig. 1 DR OVERHEAD CONSOLE ± EVIC
8M - 2 MESSAGE SYSTEMSDR
OVERHEAD CONSOLE (Continued)
Page 588 of 2627

SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
A self-diagnostic test is built-in to the module to
determine that the electronics module is operating
properly, and that all the J1850 PCI data bus mes-
sages are being received for proper operation. To per-
form the self-diagnostic test proceed as follows:
(1) With the ignition switch in the Off position,
simultaneously depress and hold theSTEP and
RESET buttons.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
(3) Following completion of the test, the electronics
module will display one of the following messages:
a.Pass Self Test (EVIC only), PASS (CMTC)-
The electronics module is working properly.
b.Failed Self Test (EVIC only), FAIL (CMTC)-
The electronics module has an internal failure. The
electronics module is faulty and must be replaced.
c.Failed J1850 Communication (EVIC only),
BUS (CMTC)- The electronics module is not receiv-
ing proper message input through the J1850 PCI
data bus circuit. This can result from one or more
faulty electronic modules in the vehicle, or from a
faulty PCI data bus. The use of a DRB IIItscan tool
and the proper Diagnostic Procedures manual are
required for further diagnosis.
NOTE: If the compass functions, but accuracy is
suspect, it may be necessary to perform a variation
adjustment. This procedure allows the compass
unit to accommodate variations in the earth's mag-
netic field strength, based on geographic location.
Refer to Compass Variation Adjustment in the Stan-
dard Procedures section of this group.
NOTE: If the compass reading displays dashes, and
only ªCALº appears in the display, demagnetizing
may be necessary to remove excessive residual
magnetic fields from the vehicle. Refer to Compass
Demagnetizing in the Standard Procedures section
of this group.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - READING/
COURTESY LAMP REPLACEMENT
(1) Open hood, disconnect and isolate the negative
battery cable.
(2) Remove the reading/courtesy lamp lens. Using
a trim stick, gently pry the forward edge of the read-
ing/courtesy lamp lens outward.
(3) Remove the reading/courtesy lamp socket from
the overhead console. Rotate the reading/courtesy
lamp socket one quarter turn counter clockwise.
(4) Remove the lamp and socket assembly.(5) Reverse the above procedure to install.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MODULE LENS
REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove the overhead console (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CONSOLE -
REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the electronics module from the over-
head console. Refer to the procedure later in this sec-
tion.
(3) Unsnap the lens from the module and replace
lens as necessary.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MODULE LAMP
REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove the overhead console (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CONSOLE -
REMOVAL).
(2) Using a flat blade screwdriver twist out socket/
lamp (Fig. 2).
(3) Replace lamp(s) as necessary.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPASS
CALIBRATION
CAUTION: Do not place any external magnets, such
as magnetic roof mount antennas, in the vicinity of
the compass. Do not use magnetic tools when ser-
vicing the overhead console.
Fig. 2 Top of Overhead Console
1 - OVERHEAD CONSOLE HOUSING
2 - EVIC/CMTC MODULE
3 - ILLUMINATION LAMPS
4 - MODULE RETAINING SCREWS
DRMESSAGE SYSTEMS 8M - 3
OVERHEAD CONSOLE (Continued)