transfer DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 1901 of 2627

GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The governor pressure sensor measures output
pressure of the governor pressure solenoid valve (Fig.
77).
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate is designed to supply transmis-
sion line pressure to the governor pressure solenoid
valve and to return governor pressure.
The governor pressure solenoid valve is mounted in
the governor body. The body is bolted to the lower
side of the transfer plate (Fig. 77).
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
There are four governor pressure curves pro-
grammed into the transmission control module. The
different curves allow the control module to adjust
governor pressure for varying conditions. One curve
is used for operation when fluid temperature is at, or
below, ±1ÉC (30ÉF). A second curve is used when fluid
temperature is at, or above, 10ÉC (50ÉF) during nor-
mal city or highway driving. A third curve is used
during wide-open throttle operation. The fourth curve
is used when driving with the transfer case in low
range.
OPERATION
Compensation is required for performance varia-
tions of two of the input devices. Though the slope of
the transfer functions is tightly controlled, offset may
vary due to various environmental factors or manu-
facturing tolerances.
The pressure transducer is affected by barometric
pressure as well as temperature. Calibration of the
zero pressure offset is required to compensate for
shifting output due to these factors.
Normal calibration will be performed when sump
temperature is above 50 degrees F, or in the absenceof sump temperature data, after the first 10 minutes
of vehicle operation. Calibration of the pressure
transducer offset occurs each time the output shaft
speed falls below 200 RPM. Calibration shall be
repeated each 3 seconds the output shaft speed is
below 200 RPM. A 0.5 second pulse of 95% duty cycle
is applied to the governor pressure solenoid valve
and the transducer output is read during this pulse.
Averaging of the transducer signal is necessary to
reject electrical noise.
Under cold conditions (below 50 degrees F sump),
the governor pressure solenoid valve response may
be too slow to guarantee 0 psi during the 0.5 second
calibration pulse. Calibration pulses are continued
during this period, however the transducer output
valves are discarded. Transducer offset must be read
at key-on, under conditions which promote a stable
reading. This value is retained and becomes the off-
set during the9cold9period of operation.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The inlet side of the solenoid valve is exposed to
normal transmission line pressure. The outlet side of
the valve leads to the valve body governor circuit.
The solenoid valve regulates line pressure to pro-
duce governor pressure. The average current sup-
plied to the solenoid controls governor pressure. One
amp current produces zero kPa/psi governor pres-
sure. Zero amps sets the maximum governor pres-
sure.
The powertrain control module (PCM) turns on the
trans control relay which supplies electrical power to
the solenoid valve. Operating voltage is 12 volts
(DC). The PCM controls the ground side of the sole-
noid using the governor pressure solenoid control cir-
cuit.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The sensor output signal provides the necessary
feedback to the PCM. This feedback is needed to ade-
quately control governor pressure.
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate channels line pressure to the
solenoid valve through the governor body. It also
channels governor pressure from the solenoid valve
to the governor circuit. It is the solenoid valve that
develops the necessary governor pressure.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
LOW TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE
When the transmission fluid is cold the conven-
tional governor can delay shifts, resulting in higher
than normal shift speeds and harsh shifts. The elec-
tronically controlled low temperature governor pres-
Fig. 77 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
21 - 198 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1902 of 2627

sure curve is higher than normal to make the
transmission shift at normal speeds and sooner. The
PCM uses a temperature sensor in the transmission
oil sump to determine when low temperature gover-
nor pressure is needed.
NORMAL OPERATION
Normal operation is refined through the increased
computing power of the PCM and through access to
data on engine operating conditions provided by the
PCM that were not available with the previous
stand-alone electronic module. This facilitated the
development of a load adaptive shift strategy - the
ability to alter the shift schedule in response to vehi-
cle load condition. One manifestation of this capabil-
ity is grade9hunting9prevention - the ability of the
transmission logic to delay an upshift on a grade if
the engine does not have sufficient power to main-
tain speed in the higher gear. The 3-2 downshift and
the potential for hunting between gears occurs with a
heavily loaded vehicle or on steep grades. When
hunting occurs, it is very objectionable because shifts
are frequent and accompanied by large changes in
noise and acceleration.
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE OPERATION
In wide-open throttle (WOT) mode, adaptive mem-
ory in the PCM assures that up-shifts occur at the
preprogrammed optimum speed. WOT operation is
determined from the throttle position sensor, which
is also a part of the emission control system. The ini-
tial setting for the WOT upshift is below the opti-
mum engine speed. As WOT shifts are repeated, the
PCM learns the time required to complete the shifts
by comparing the engine speed when the shifts occur
to the optimum speed. After each shift, the PCM
adjusts the shift point until the optimum speed is
reached. The PCM also considers vehicle loading,
grade and engine performance changes due to high
altitude in determining when to make WOT shifts. It
does this by measuring vehicle and engine accelera-
tion and then factoring in the shift time.
TRANSFER CASE LOW RANGE OPERATION
On four-wheel drive vehicles operating in low
range, the engine can accelerate to its peak more
rapidly than in Normal range, resulting in delayed
shifts and undesirable engine9flare.9The low range
governor pressure curve is also higher than normal
to initiate upshifts sooner. The PCM compares elec-
tronic vehicle speed signal used by the speedometer
to the transmission output shaft speed signal to
determine when the transfer case is in low range.REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Remove transmission fluid pan and filter.
(3) Disengage wire connectors from pressure sen-
sor and solenoid (Fig. 78).
(4) Remove screws holding pressure solenoid
retainer to governor body.
(5) Separate solenoid retainer from governor (Fig.
79).
Fig. 78 Governor Solenoid And Pressure Sensor
1 - PRESSURE SENSOR
2 - PRESSURE SOLENOID
3 - GOVERNOR
Fig. 79 Pressure Solenoid Retainer
1 - PRESSURE SOLENOID RETAINER
2 - GOVERNOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 199
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1908 of 2627
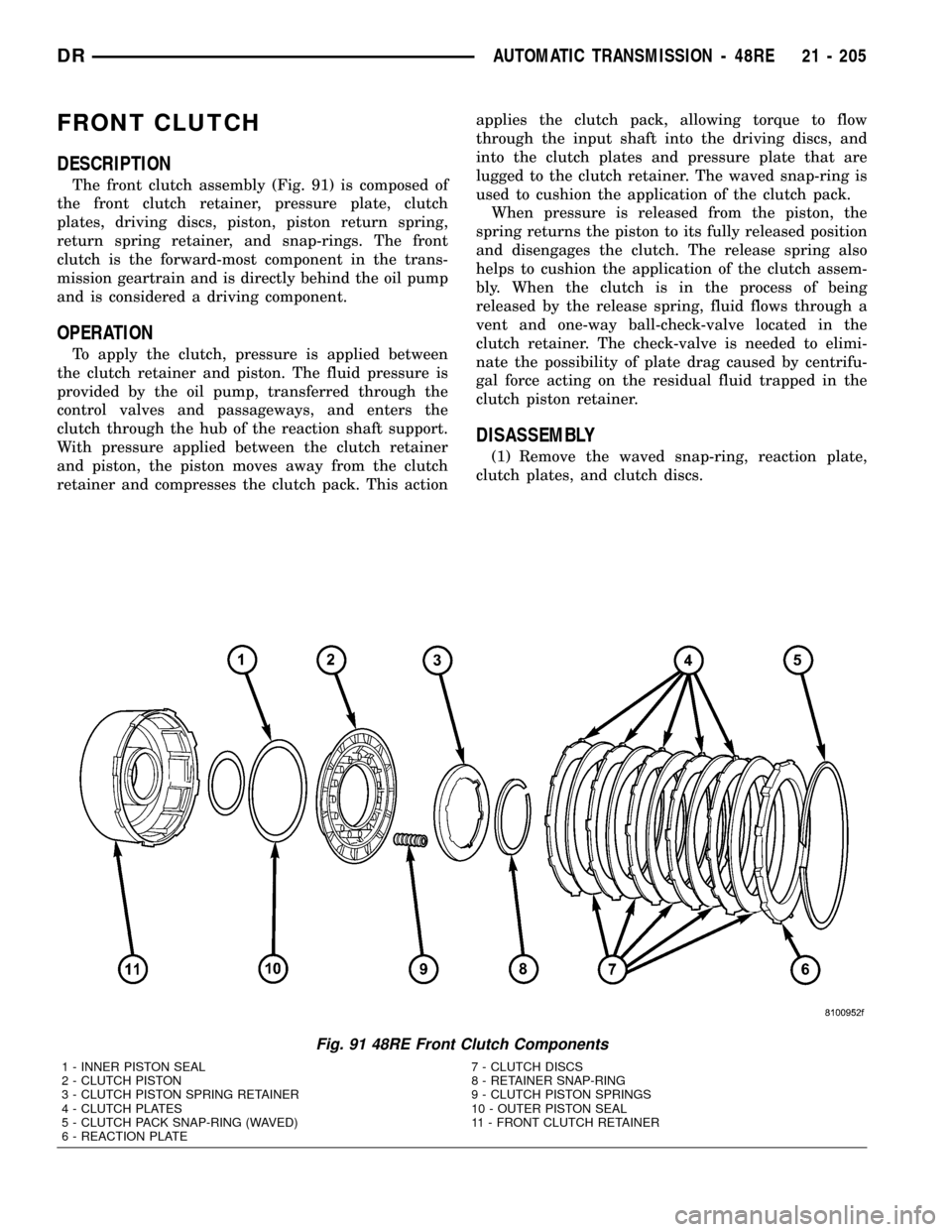
FRONT CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The front clutch assembly (Fig. 91) is composed of
the front clutch retainer, pressure plate, clutch
plates, driving discs, piston, piston return spring,
return spring retainer, and snap-rings. The front
clutch is the forward-most component in the trans-
mission geartrain and is directly behind the oil pump
and is considered a driving component.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the clutch retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through the hub of the reaction shaft support.
With pressure applied between the clutch retainer
and piston, the piston moves away from the clutch
retainer and compresses the clutch pack. This actionapplies the clutch pack, allowing torque to flow
through the input shaft into the driving discs, and
into the clutch plates and pressure plate that are
lugged to the clutch retainer. The waved snap-ring is
used to cushion the application of the clutch pack.
When pressure is released from the piston, the
spring returns the piston to its fully released position
and disengages the clutch. The release spring also
helps to cushion the application of the clutch assem-
bly. When the clutch is in the process of being
released by the release spring, fluid flows through a
vent and one-way ball-check-valve located in the
clutch retainer. The check-valve is needed to elimi-
nate the possibility of plate drag caused by centrifu-
gal force acting on the residual fluid trapped in the
clutch piston retainer.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove the waved snap-ring, reaction plate,
clutch plates, and clutch discs.
Fig. 91 48RE Front Clutch Components
1 - INNER PISTON SEAL 7 - CLUTCH DISCS
2 - CLUTCH PISTON 8 - RETAINER SNAP-RING
3 - CLUTCH PISTON SPRING RETAINER 9 - CLUTCH PISTON SPRINGS
4 - CLUTCH PLATES 10 - OUTER PISTON SEAL
5 - CLUTCH PACK SNAP-RING (WAVED) 11 - FRONT CLUTCH RETAINER
6 - REACTION PLATE
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 205
Page 1920 of 2627
INSTALLATION
(1) Place replacement bearing in position in hous-
ing.
(2) Using a suitable driver, drive bearing into
housing until the snap-ring groove is visible.
(3) Install snap-ring to hold bearing into housing
(Fig. 116).
(4) Install overdrive geartrain into housing.
(5) Install overdrive unit in vehicle.
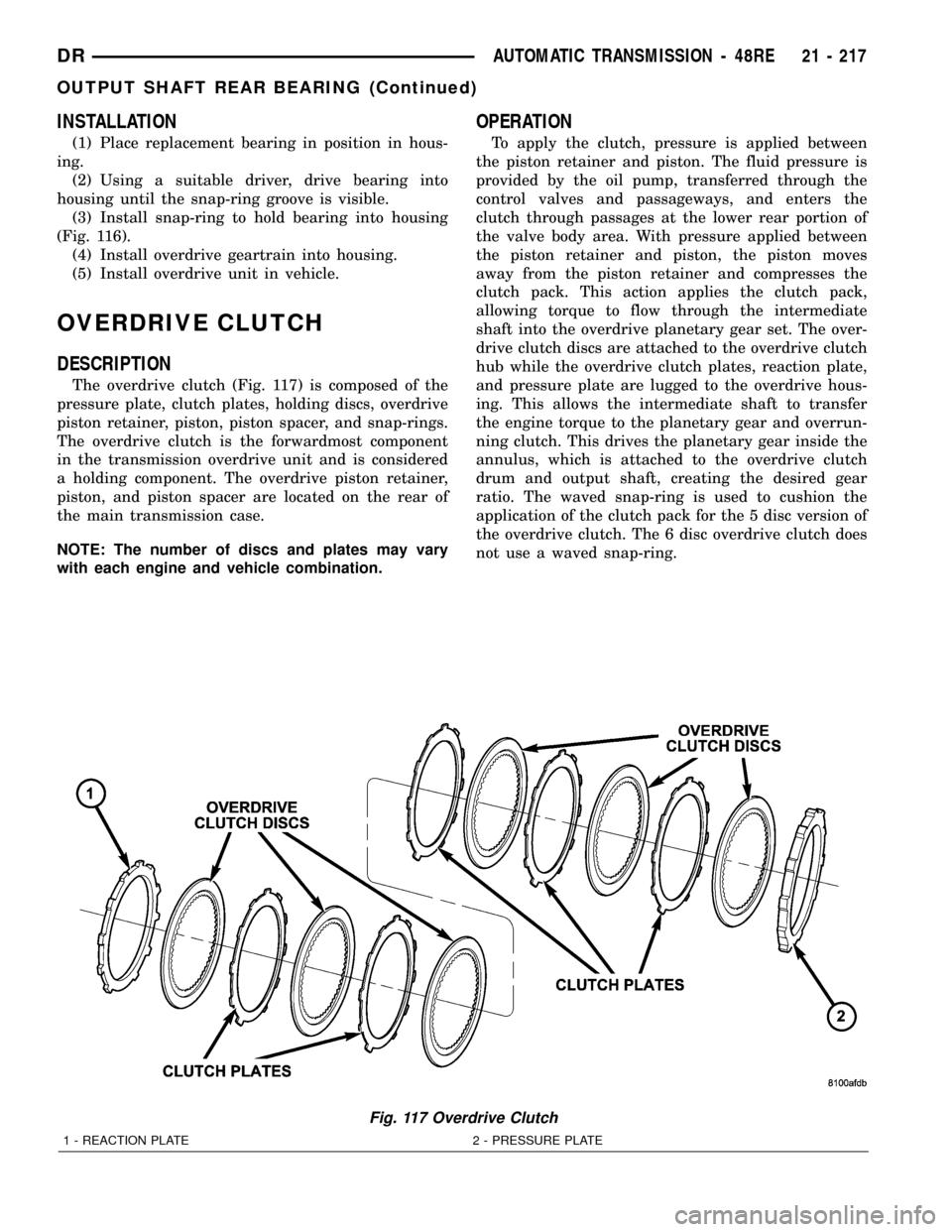
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The overdrive clutch (Fig. 117) is composed of the
pressure plate, clutch plates, holding discs, overdrive
piston retainer, piston, piston spacer, and snap-rings.
The overdrive clutch is the forwardmost component
in the transmission overdrive unit and is considered
a holding component. The overdrive piston retainer,
piston, and piston spacer are located on the rear of
the main transmission case.
NOTE: The number of discs and plates may vary
with each engine and vehicle combination.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the piston retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through passages at the lower rear portion of
the valve body area. With pressure applied between
the piston retainer and piston, the piston moves
away from the piston retainer and compresses the
clutch pack. This action applies the clutch pack,
allowing torque to flow through the intermediate
shaft into the overdrive planetary gear set. The over-
drive clutch discs are attached to the overdrive clutch
hub while the overdrive clutch plates, reaction plate,
and pressure plate are lugged to the overdrive hous-
ing. This allows the intermediate shaft to transfer
the engine torque to the planetary gear and overrun-
ning clutch. This drives the planetary gear inside the
annulus, which is attached to the overdrive clutch
drum and output shaft, creating the desired gear
ratio. The waved snap-ring is used to cushion the
application of the clutch pack for the 5 disc version of
the overdrive clutch. The 6 disc overdrive clutch does
not use a waved snap-ring.
Fig. 117 Overdrive Clutch
1 - REACTION PLATE 2 - PRESSURE PLATE
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 217
OUTPUT SHAFT REAR BEARING (Continued)
Page 1921 of 2627
OVERDRIVE UNIT
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into PARK.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove transfer case, if equipped.
(4) Mark propeller shaft universal joint(s) and axle
pinion yoke, or the companion flange and flange
yoke, for alignment reference at installation, if neces-
sary.
(5) Disconnect and remove the rear propeller shaft,
if necessary. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIV-
ELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(6) Remove transmission oil pan, remove gasket,
drain oil and reinstall pan.
(7) If overdrive unit had malfunctioned, or if fluid
is contaminated, remove entire transmission. If diag-
nosis indicated overdrive problems only, remove just
the overdrive unit.
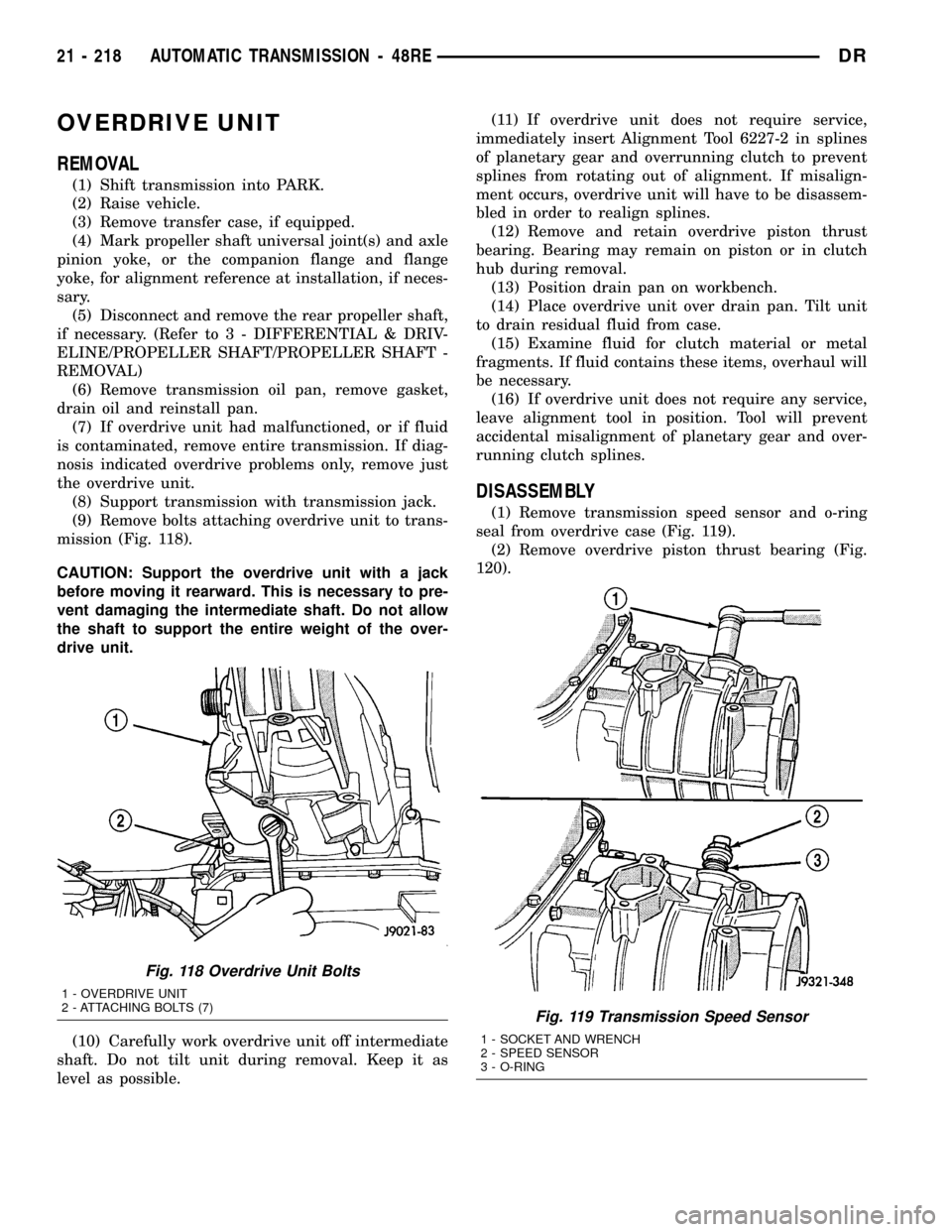
(8) Support transmission with transmission jack.
(9) Remove bolts attaching overdrive unit to trans-
mission (Fig. 118).
CAUTION: Support the overdrive unit with a jack
before moving it rearward. This is necessary to pre-
vent damaging the intermediate shaft. Do not allow
the shaft to support the entire weight of the over-
drive unit.
(10) Carefully work overdrive unit off intermediate
shaft. Do not tilt unit during removal. Keep it as
level as possible.(11) If overdrive unit does not require service,
immediately insert Alignment Tool 6227-2 in splines
of planetary gear and overrunning clutch to prevent
splines from rotating out of alignment. If misalign-
ment occurs, overdrive unit will have to be disassem-
bled in order to realign splines.
(12) Remove and retain overdrive piston thrust
bearing. Bearing may remain on piston or in clutch
hub during removal.
(13) Position drain pan on workbench.
(14) Place overdrive unit over drain pan. Tilt unit
to drain residual fluid from case.
(15) Examine fluid for clutch material or metal
fragments. If fluid contains these items, overhaul will
be necessary.
(16) If overdrive unit does not require any service,
leave alignment tool in position. Tool will prevent
accidental misalignment of planetary gear and over-
running clutch splines.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove transmission speed sensor and o-ring
seal from overdrive case (Fig. 119).
(2) Remove overdrive piston thrust bearing (Fig.
120).
Fig. 118 Overdrive Unit Bolts
1 - OVERDRIVE UNIT
2 - ATTACHING BOLTS (7)
Fig. 119 Transmission Speed Sensor
1 - SOCKET AND WRENCH
2 - SPEED SENSOR
3 - O-RING
21 - 218 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
Page 1938 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Be sure overdrive unit Alignment Tool 6227-2
is fully seated before moving unit. If tool is not
seated and gear splines rotate out of alignment, over-
drive unit will have to be disassembled in order to
realign splines.
(2) If overdrive piston retainer was not removed
during service and original case gasket is no longer
reusable, prepare new gasket by trimming it.
(3) Cut out old case gasket around piston retainer
with razor knife (Fig. 176).
(4) Use old gasket as template and trim new gas-
ket to fit.
(5) Position new gasket over piston retainer and
on transmission case. Use petroleum jelly to hold
gasket in place if necessary. Do not use any type of
sealer to secure gasket. Use petroleum jelly only.
(6) Install selective spacer on intermediate shaft, if
removed. Spacer goes in groove just rearward of
shaft rear splines (Fig. 177).
(7) Install thrust bearing in overdrive unit sliding
hub. Use petroleum jelly to hold bearing in position.
CAUTION: Be sure the shoulder on the inside diam-
eter of the bearing is facing forward.(8) Verify that splines in overdrive planetary gear
and overrunning clutch hub are aligned with Align-
ment Tool 6227-2. Overdrive unit cannot be installed
if splines are not aligned. If splines have rotated out
of alignment, unit will have to be disassembled to
realign splines.
(9) Carefully slide Alignment Tool 6227-2 out of
overdrive planetary gear and overrunning clutch
splines.
(10) Raise overdrive unit and carefully slide it
straight onto intermediate shaft. Insert park rod into
park lock reaction plug at same time. Avoid tilting
overdrive during installation as this could cause
planetary gear and overrunning clutch splines to
rotate out of alignment. If this occurs, it will be nec-
essary to remove and disassemble overdrive unit to
realign splines.
(11) Work overdrive unit forward on intermediate
shaft until seated against transmission case.
(12) Install bolts attaching overdrive unit to trans-
mission unit. Tighten bolts in diagonal pattern to 34
N´m (25 ft-lbs).
(13) Connect the transmission speed sensor and
overdrive wiring connectors.
(14) Install the transfer case, if equipped.
(15) Align and install rear propeller shaft, if nec-
essary. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/
PROPELLER SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT -
INSTALLATION)
Fig. 176 Trimming Overdrive Case Gasket
1 - GASKET
2 - SHARP KNIFE
Fig. 177 Intermediate Shaft Selective Spacer
Location
1 - SELECTIVE SPACER
2 - SPACER GROOVE
3 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 235
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1951 of 2627

OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the clutch retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through the hub of the reaction shaft support.
With pressure applied between the clutch retainer
and piston, the piston moves away from the clutch
retainer and compresses the clutch pack. This action
applies the clutch pack, allowing torque to flow
through the input shaft into the driving discs, and
into the clutch plates and pressure plate that are
lugged to the clutch retainer. The waved spring is
used to cushion the application of the clutch pack.
The snap-ring is selective and used to adjust clutch
pack clearance.
When pressure is released from the piston, the
spring returns the piston to its fully released position
and disengages the clutch. The release spring also
helps to cushion the application of the clutch assem-
bly. When the clutch is in the process of being
released by the release spring, fluid flows through a
vent and one-way ball-check-valve located in the pis-
ton. The check-valve is needed to eliminate the pos-
sibility of plate drag caused by centrifugal force
acting on the residual fluid trapped in the clutch pis-
ton retainer.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove fiber thrust washer from forward side
of clutch retainer.
(2) Remove input shaft front and rear seal rings.
(3) Remove selective clutch pack snap-ring (Fig.
214).
(4) Remove the reaction plate, clutch discs, steel
plates, pressure plate, wave spring, spacer ring, and
piston spring (Fig. 214).
(5) Remove clutch piston with rotating motion.
(6) Remove and discard piston seals.
(7) Remove input shaft retaining ring. It may be
necessary to press the input shaft in slightly to
relieve tension on the retaining ring
(8) Press input shaft out of retainer with shop
press and suitable size press tool. Use a suitably
sized press tool to support the retainer as close to the
input shaft as possible.
CLEANING
Clean the clutch components with solvent and dry
them with compressed air. Do not use rags or shop
towels to dry any of the clutch parts. Lint from such
materials will adhere to component surfaces and
could restrict or block fluid passages after assembly.
INSPECTION
Replace the clutch discs if warped, worn, scored,
burned/charred, the lugs are damaged, or if the fac-
ing is flaking off. Replace the top and bottom pres-
sure plates if scored, warped, or cracked. Be sure the
driving lugs on the pressure and clutch plates are
also in good condition. The lugs must not be bent,
cracked or damaged in any way.
Replace the piston spring and wave spring if either
part is distorted, warped or broken.
Check the lug grooves in the clutch retainer. The
clutch and pressure plates should slide freely in the
slots. Replace the retainer if the grooves are worn or
damaged. Also check action of the check balls in the
retainer and piston. Each check ball must move
freely and not stick.
Replace the retainer bushing if worn, scored, or
doubt exists about bushing condition.
Inspect the piston and retainer seal surfaces for
nicks or scratches. Minor scratches can be removed
with crocus cloth. However, replace the piston and/or
retainer if the seal surfaces are seriously scored.
Check condition of the fiber thrust washer and
metal output shaft thrust washer. Replace either
washer if worn or damaged.
Check condition of the seal rings on the input shaft
and clutch retainer hub. Replace the seal rings only
if worn, distorted, or damaged. The input shaft front
seal ring is teflon with chamfered ends. The rear ring
is metal with interlocking ends.
Check the input shaft for wear, or damage. Replace
the shaft if worn, scored or damaged in any way.
21 - 248 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1957 of 2627

ADJUSTMENTS - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
A correctly adjusted throttle valve cable will cause
the throttle lever on the transmission to move simul-
taneously with the throttle body lever from the idle
position. Proper adjustment will allow simultaneous
movement without causing the transmission throttle
lever to either move ahead of, or lag behind the lever
on the throttle body.
ADJUSTMENT VERIFICATION
(1) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
(2) Remove air cleaner.
(3) Verify that lever on throttle body is at curb idle
position (Fig. 224). Then verify that the transmission
throttle lever (Fig. 225) is also at idle (fully forward)
position.
(4) Slide cable off attachment stud on throttle body
lever.
(5) Compare position of cable end to attachment
stud on throttle body lever:
²Cable end and attachment stud should be
aligned (or centered on one another) to within 1 mm
(0.039 in.) in either direction (Fig. 226).
²If cable end and attachment stud are misaligned
(off center), cable will have to be adjusted as
described in Throttle Valve Cable Adjustment proce-
dure.
Fig. 225 Throttle Valve Cable at Transmission
1 - TRANSMISSION SHIFTER CABLE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
3 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFTER CABLE
4 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFTER CABLE BRACKET RETAINING
BOLT(1OR2)
5 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE BRACKET RETAINING BOLT
6 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
7 - TRANSMISSION FLUID LINES
Fig. 226 Throttle Valve Cable at Throttle Linkage
1 - THROTTLE LINKAGE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE LOCKING CLIP
3 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
Fig. 224 Throttle Valve Cable Attachment - At
Engine
1 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
2 - CABLE BRACKET
3 - THROTTLE BODY LEVER
4 - ACCELERATOR CABLE
5 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
21 - 254 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE (Continued)
Page 1961 of 2627

STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 230) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 231).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 232) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is
natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impeller
and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston was added to the turbine, and a friction mate-
rial was added to the inside of the front cover to pro-
vide this mechanical lock-up.
Fig. 230 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 231 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 232 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
21 - 258 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1962 of 2627

OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 233) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in a direction
that would tend to slow it down.
Fig. 233 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 259
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)