transmission oil DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 1955 of 2627

SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION
The gear shift mechanism provides six shift posi-
tions which are:
²PARK (P)
²REVERSE (R)
²NEUTRAL (N)
²DRIVE (D)
²Manual SECOND (2)
²Manual LOW (1)
OPERATION
Manual LOW (1) range provides first gear only.
Overrun braking is also provided in this range. Man-
ual SECOND (2) range provides first and second gear
only.
DRIVE range provides first, second, third, and
overdrive fourth gear ranges. The shift into overdrive
fourth gear range occurs only after the transmission
has completed the shift into D third gear range. No
further movement of the shift mechanism is required
to complete the 3-4 shift.
The fourth gear upshift occurs automatically when
the overdrive selector switch is in the ON position.
No upshift to fourth gear will occur if any of the fol-
lowing are true:
²The transmission fluid temperature is below 10É
C (50É F) or above 121É C (250É F).
²The shift to third is not yet complete.
²Vehicle speed is too low for the 3-4 shift to occur.
²Battery temperature is below -5É C (23É F).
SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The typical electrical solenoid used in automotive
applications is a linear actuator. It is a device that
produces motion in a straight line. This straight line
motion can be either forward or backward in direc-
tion, and short or long distance.
A solenoid is an electromechanical device that uses
a magnetic force to perform work. It consists of a coil
of wire, wrapped around a magnetic core made from
steel or iron, and a spring loaded, movable plunger,
which performs the work, or straight line motion.
The solenoids used in transmission applications
are attached to valves which can be classified asnor-
mally openornormally closed. Thenormally
opensolenoid valve is defined as a valve which
allows hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is
applied to the solenoid. Thenormally closedsole-
noid valve is defined as a valve which does not allow
hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is applied
to the solenoid. These valves perform hydraulic con-trol functions for the transmission and must there-
fore be durable and tolerant of dirt particles. For
these reasons, the valves have hardened steel pop-
pets and ball valves. The solenoids operate the valves
directly, which means that the solenoids must have
very high outputs to close the valves against the siz-
able flow areas and line pressures found in current
transmissions. Fast response time is also necessary
to ensure accurate control of the transmission.
The strength of the magnetic field is the primary
force that determines the speed of operation in a par-
ticular solenoid design. A stronger magnetic field will
cause the plunger to move at a greater speed than a
weaker one. There are basically two ways to increase
the force of the magnetic field:
1. Increase the amount of current applied to the
coil or
2. Increase the number of turns of wire in the coil.
The most common practice is to increase the num-
ber of turns by using thin wire that can completely
fill the available space within the solenoid housing.
The strength of the spring and the length of the
plunger also contribute to the response speed possi-
ble by a particular solenoid design.
A solenoid can also be described by the method by
which it is controlled. Some of the possibilities
include variable force, pulse-width modulated, con-
stant ON, or duty cycle. The variable force and pulse-
width modulated versions utilize similar methods to
control the current flow through the solenoid to posi-
tion the solenoid plunger at a desired position some-
where between full ON and full OFF. The constant
ON and duty cycled versions control the voltage
across the solenoid to allow either full flow or no flow
through the solenoid's valve.
OPERATION
When an electrical current is applied to the sole-
noid coil, a magnetic field is created which produces
an attraction to the plunger, causing the plunger to
move and work against the spring pressure and the
load applied by the fluid the valve is controlling. The
plunger is normally directly attached to the valve
which it is to operate. When the current is removed
from the coil, the attraction is removed and the
plunger will return to its original position due to
spring pressure.
The plunger is made of a conductive material and
accomplishes this movement by providing a path for
the magnetic field to flow. By keeping the air gap
between the plunger and the coil to the minimum
necessary to allow free movement of the plunger, the
magnetic field is maximized.
21 - 252 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
Page 1958 of 2627
(6) Reconnect cable end to attachment stud. Then
with aid of a helper, observe movement of transmis-
sion throttle lever and lever on throttle body.
²If both levers move simultaneously from idle to
half-throttle and back to idle position, adjustment is
correct.
²If transmission throttle lever moves ahead of, or
lags behind throttle body lever, cable adjustment will
be necessary. Or, if throttle body lever prevents
transmission lever from returning to closed position,
cable adjustment will be necessary.
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
(2) Remove air cleaner if necessary.
(3) Disconnect cable end from attachment stud.
Carefully slide cable off stud. Do not pry or pull
cable off.
(4) Verify that transmission throttle lever is in
fully closed position. Then be sure lever on throttle
body is at curb idle position.
(5) Pry the T.V. cable lock (A) into the UP position
(Fig. 226). This will unlock the cable and allow for
readjustment.
(6) Apply just enough tension on the T.V. cable (B)
to remove any slack in the cable.Pulling too tight
will cause the T.V. lever on the transmission to
move out of its idle position, which will result
in an incorrect T.V. cable adjustment.Slide the
sheath of the T.V. cable (D) back and forth until the
centerlines of the T.V. cable end (B) and the throttle
bell crank lever (C) are aligned within one millimeter
(1mm) (Fig. 226).
(7) While holding the T.V. cable in the set position
push the T.V. cable lock (A) into the down position
(Fig. 226). This will lock the present T.V. cable
adjustment.
NOTE: Be sure that as the cable is pulled forward
and centered on the throttle lever stud, the cable
housing moves smoothly with the cable. Due to the
angle at which the cable housing enters the spring
housing, the cable housing may bind slightly and
create an incorrect adjustment.
(8) Reconnect the T.V. cable (B) to the throttle
bellcrank lever (C).
(9) Check cable adjustment. Verify transmission
throttle lever and lever on throttle body move simul-
taneously.
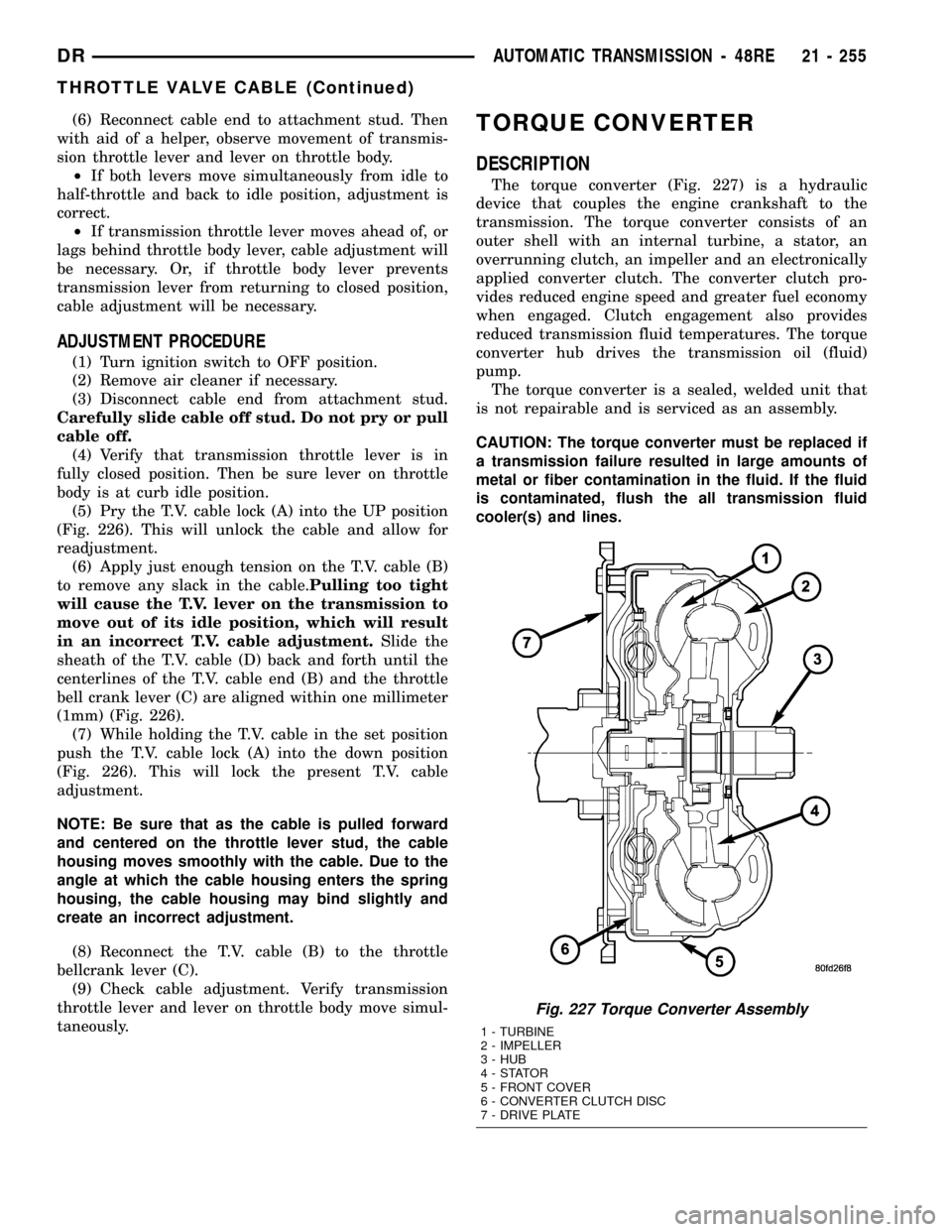
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 227) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The torque
converter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid)
pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid. If the fluid
is contaminated, flush the all transmission fluid
cooler(s) and lines.
Fig. 227 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - FRONT COVER
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
7 - DRIVE PLATE
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 255
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE (Continued)
Page 1959 of 2627

IMPELLER
The impeller (Fig. 228) is an integral part of the
converter housing. The impeller consists of curved
blades placed radially along the inside of the housing
on the transmission side of the converter. As the con-
verter housing is rotated by the engine, so is the
impeller, because they are one and the same and are
the driving members of the system.
Fig. 228 Impeller
1 - ENGINE FLEXPLATE 4 - ENGINE ROTATION
2 - OIL FLOW FROM IMPELLER SECTION INTO TURBINE
SECTION5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - IMPELLER VANES AND COVER ARE INTEGRAL
21 - 256 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1960 of 2627

TURBINE
The turbine (Fig. 229) is the output, or driven,
member of the converter. The turbine is mounted
within the housing opposite the impeller, but is not
attached to the housing. The input shaft is inserted
through the center of the impeller and splined into
the turbine. The design of the turbine is similar to
the impeller, except the blades of the turbine are
curved in the opposite direction.
Fig. 229 Turbine
1 - TURBINE VANE 4 - PORTION OF TORQUE CONVERTER COVER
2 - ENGINE ROTATION 5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - INPUT SHAFT 6 - OIL FLOW WITHIN TURBINE SECTION
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 257
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1961 of 2627

STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 230) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 231).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 232) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is
natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impeller
and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston was added to the turbine, and a friction mate-
rial was added to the inside of the front cover to pro-
vide this mechanical lock-up.
Fig. 230 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 231 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 232 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
21 - 258 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1963 of 2627

STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 234).
Under stall conditions the turbine is stationary and
the oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of
the stator blades and tries to rotate them in a coun-
terclockwise direction. When this happens the over-
running clutch of the stator locks and holds the
stator from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil
strikes the stator blades and is redirected into a
ªhelpingº direction before it enters the impeller. This
circulation of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to
stator, and stator to impeller, can produce a maxi-
mum torque multiplication of about 1.75:1. As the
turbine begins to match the speed of the impeller, the
fluid that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The torque converter clutch is hydraulically
applied or released when fluid is feed or vented from
the hydraulic circuit by the torque converter control
(TCC) solenoid on the valve body. The torque con-
verter clutch is controlled by the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The torque converter clutch engages
in FOURTH gear, and in THIRD gear under various
conditions, such as when the O/D switch is OFF, orwhen the vehicle is cruising on a level surface after
the vehicle has warmed up. The torque converter
clutch can also be engaged in the MANUAL SEC-
OND gear position if high transmission temperatures
are sensed by the PCM. The torque converter clutch
may disengage momentarily when an increase in
engine load is sensed by the PCM, such as when the
vehicle begins to go uphill or the throttle pressure is
increased.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
Fig. 234 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
21 - 260 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1976 of 2627
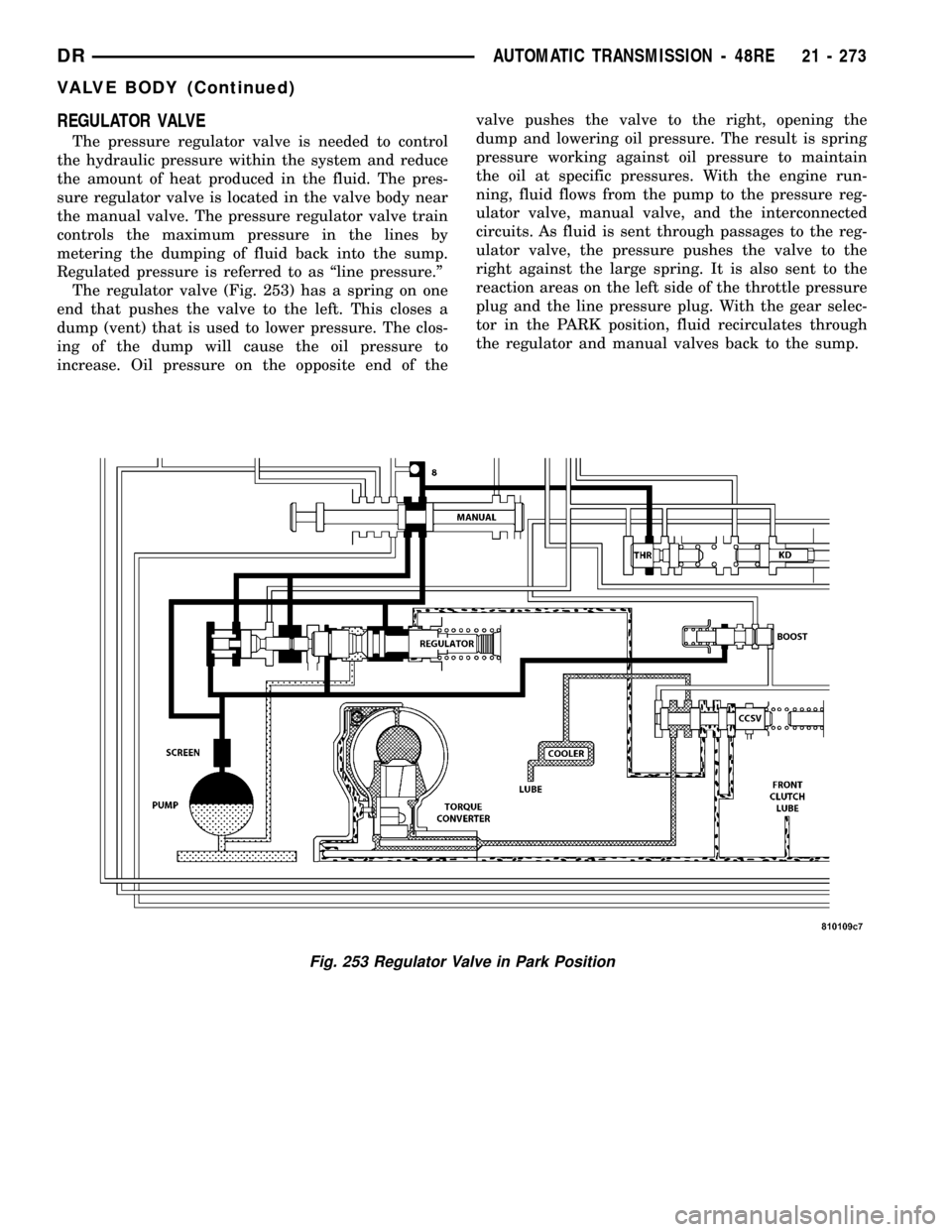
REGULATOR VALVE
The pressure regulator valve is needed to control
the hydraulic pressure within the system and reduce
the amount of heat produced in the fluid. The pres-
sure regulator valve is located in the valve body near
the manual valve. The pressure regulator valve train
controls the maximum pressure in the lines by
metering the dumping of fluid back into the sump.
Regulated pressure is referred to as ªline pressure.º
The regulator valve (Fig. 253) has a spring on one
end that pushes the valve to the left. This closes a
dump (vent) that is used to lower pressure. The clos-
ing of the dump will cause the oil pressure to
increase. Oil pressure on the opposite end of thevalve pushes the valve to the right, opening the
dump and lowering oil pressure. The result is spring
pressure working against oil pressure to maintain
the oil at specific pressures. With the engine run-
ning, fluid flows from the pump to the pressure reg-
ulator valve, manual valve, and the interconnected
circuits. As fluid is sent through passages to the reg-
ulator valve, the pressure pushes the valve to the
right against the large spring. It is also sent to the
reaction areas on the left side of the throttle pressure
plug and the line pressure plug. With the gear selec-
tor in the PARK position, fluid recirculates through
the regulator and manual valves back to the sump.
Fig. 253 Regulator Valve in Park Position
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 273
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1987 of 2627
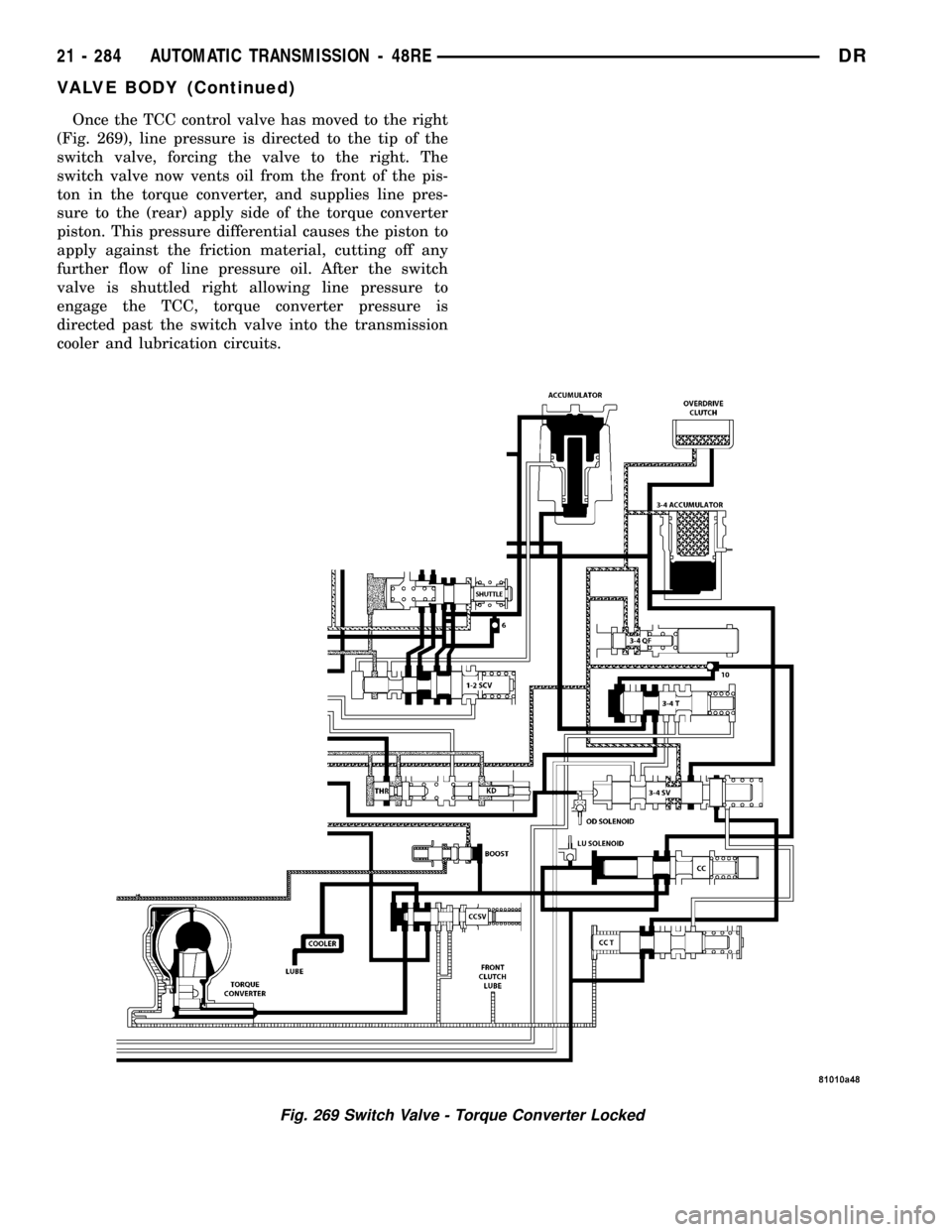
Once the TCC control valve has moved to the right
(Fig. 269), line pressure is directed to the tip of the
switch valve, forcing the valve to the right. The
switch valve now vents oil from the front of the pis-
ton in the torque converter, and supplies line pres-
sure to the (rear) apply side of the torque converter
piston. This pressure differential causes the piston to
apply against the friction material, cutting off any
further flow of line pressure oil. After the switch
valve is shuttled right allowing line pressure to
engage the TCC, torque converter pressure is
directed past the switch valve into the transmission
cooler and lubrication circuits.
Fig. 269 Switch Valve - Torque Converter Locked
21 - 284 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1989 of 2627
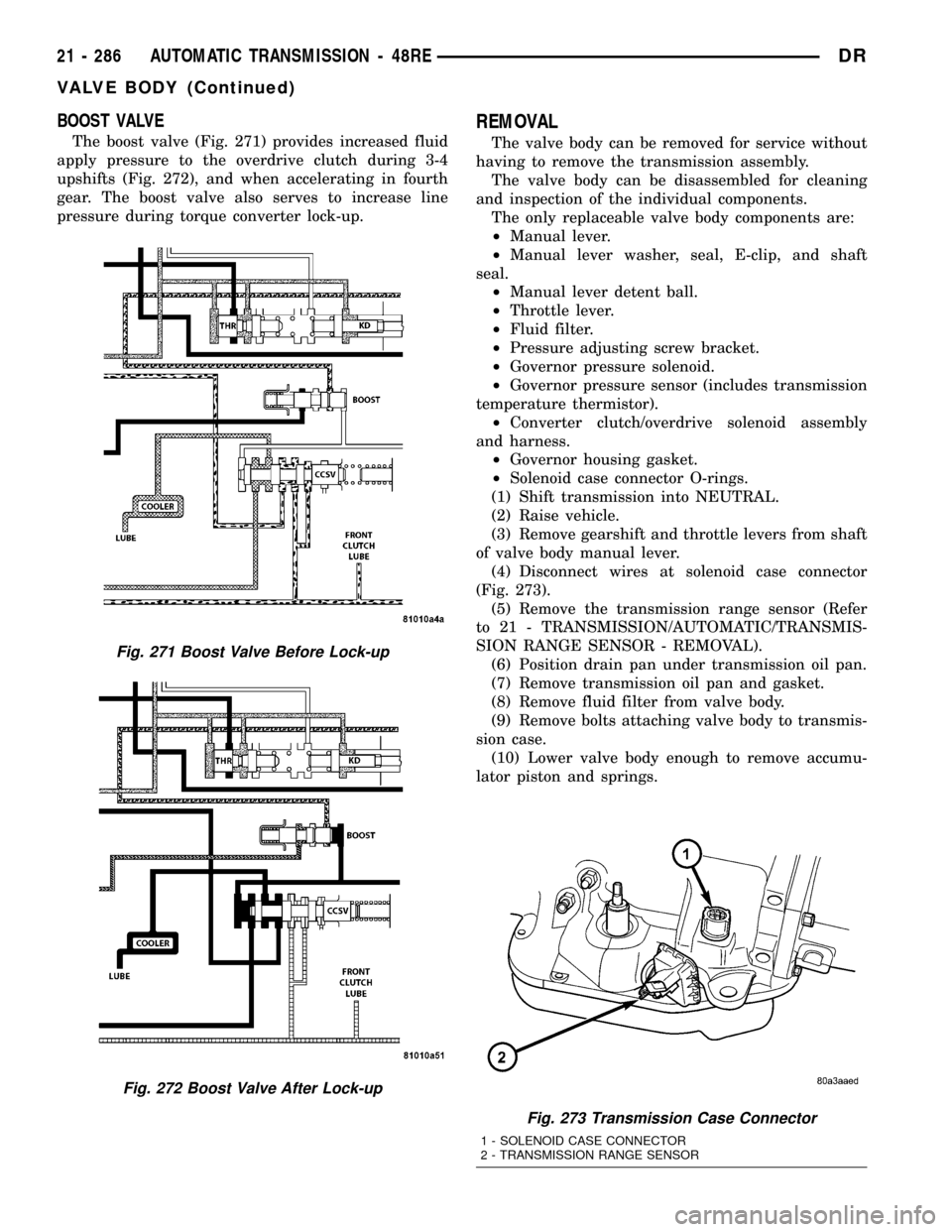
BOOST VALVE
The boost valve (Fig. 271) provides increased fluid
apply pressure to the overdrive clutch during 3-4
upshifts (Fig. 272), and when accelerating in fourth
gear. The boost valve also serves to increase line
pressure during torque converter lock-up.
REMOVAL
The valve body can be removed for service without
having to remove the transmission assembly.
The valve body can be disassembled for cleaning
and inspection of the individual components.
The only replaceable valve body components are:
²Manual lever.
²Manual lever washer, seal, E-clip, and shaft
seal.
²Manual lever detent ball.
²Throttle lever.
²Fluid filter.
²Pressure adjusting screw bracket.
²Governor pressure solenoid.
²Governor pressure sensor (includes transmission
temperature thermistor).
²Converter clutch/overdrive solenoid assembly
and harness.
²Governor housing gasket.
²Solenoid case connector O-rings.
(1) Shift transmission into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove gearshift and throttle levers from shaft
of valve body manual lever.
(4) Disconnect wires at solenoid case connector
(Fig. 273).
(5) Remove the transmission range sensor (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/AUTOMATIC/TRANSMIS-
SION RANGE SENSOR - REMOVAL).
(6) Position drain pan under transmission oil pan.
(7) Remove transmission oil pan and gasket.
(8) Remove fluid filter from valve body.
(9) Remove bolts attaching valve body to transmis-
sion case.
(10) Lower valve body enough to remove accumu-
lator piston and springs.
Fig. 273 Transmission Case Connector
1 - SOLENOID CASE CONNECTOR
2 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
Fig. 271 Boost Valve Before Lock-up
Fig. 272 Boost Valve After Lock-up
21 - 286 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 2001 of 2627

3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
(1) Remove end plate from housing.
(2) Remove piston spring.
(3) Remove piston. Remove and discard piston
seals (Fig. 304).
CLEANING
Clean the valve housings, valves, plugs, springs,
and separator plates with a standard parts cleaning
solution only. Do not use gasoline, kerosene, or any
type of caustic solution.
Do not immerse any of the electrical components in
cleaning solution. Clean the governor solenoid and
sensor and the dual solenoid and harness assembly
by wiping them off with dry shop towels only.
Dry all except the electrical parts with compressed
air. Make sure all passages are clean and free from
obstructions.Do not use rags or shop towels to
dry or wipe off valve body components. Lint
from these materials can stick to valve body
parts, interfere with valve operation, and clog
filters and fluid passages.
Wipe the governor pressure sensor and solenoid
valve with dry, lint free shop towels only. The O-rings
on the sensor and solenoid valve are the only service-
able components. Be sure the vent ports in the sole-
noid valve are open and not blocked by dirt or debris.
Replace the valve and/or sensor only when DRB scan
tool diagnosis indicates this is necessary. Or, if eitherpart has sustained physical damage (dented,
deformed, broken, etc.).
CAUTION: Do not turn the small screw at the end of
the solenoid valve for any reason. Turning the
screw in either direction will ruin solenoid calibra-
tion and result in solenoid failure. In addition, the
filter on the solenoid valve is NOT serviceable. Do
not try to remove the filter as this will damage the
valve housing.
INSPECTION
Inspect the throttle and manual valve levers and
shafts. Do not attempt to straighten a bent shaft or
correct a loose lever. Replace these components if
worn, bent, loose or damaged in any way.
Inspect all of the valve body mating surfaces for
scratches, nicks, burrs, or distortion. Use a straight-
edge to check surface flatness. Minor scratches may
be removed with crocus cloth using only very light
pressure.
Minor distortion of a valve body mating surface
may be corrected by smoothing the surface with a
sheet of crocus cloth. Position the crocus cloth on a
surface plate, sheet of plate glass or equally flat sur-
face. If distortion is severe or any surfaces are
heavily scored, the valve body will have to be
replaced.
CAUTION: Many of the valves and plugs, such as
the throttle valve, shuttle valve plug, 1-2 shift valve
and 1-2 governor plug, are made of coated alumi-
num. Aluminum components are identified by the
dark color of the special coating applied to the sur-
face (or by testing with a magnet). Do not sand alu-
minum valves or plugs under any circumstances.
This practice could damage the special coating
causing the valves/plugs to stick and bind.
Inspect the valves and plugs for scratches, burrs,
nicks, or scores. Minor surface scratches on steel
valves and plugs can be removed with crocus cloth
butdo not round off the edges of the valve or
plug lands.Maintaining sharpness of these edges is
vitally important. The edges prevent foreign matter
from lodging between the valves and plugs and the
bore.
Inspect all the valve and plug bores in the valve
body. Use a penlight to view the bore interiors.
Replace the valve body if any bores are distorted or
scored. Inspect all of the valve body springs. The
springs must be free of distortion, warpage or broken
coils.
Fig. 304 3-4 Accumulator and Housing
1 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
2 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
3 - TEFLON SEALS
4 - PISTON SPRING
5 - COVER PLATE AND SCREWS
21 - 298 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
VALVE BODY (Continued)