fuel gage DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 1647 of 2627

(6) Install injector into cylinder head with male
connector port facing the intake manifold. Push down
on fuel injector mounting flange to engage o-ring and
seat injector.
(7) Tightening Sequence:
(a) Install fuel injector holdown clamp (mount-
ing flange) bolts.Do a preliminary tightening
of these bolts to 5 N´m (44 in. lbs.) torque.
This preliminary tightening insures the fuel
injector is seated and centered.
(b) After tightening, relieve bolt torque, but
leave both bolts threaded in place.
(c) Install high-pressure connector and retaining
nut. Do a preliminary tightening to 15 N´m (11 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(d) Alternately tighten injector holdown bolts to
10 N´m (89 in. lbs.) torque.
(e) Do a final tightening of the high-pressure
connector and retaining nut. Tighten to 50 N´m (37
ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Connect injector solenoid wires and nuts to top
of injectors (Fig. 18). Tighten connector nuts to 1.25
N´m (11 in. lbs.) torque.Be very careful not to
overtighten these nuts as damage to fuel injec-
tor will occur.
(9) Install exhaust rocker arm assembly. Refer to
Engine.
(10) Set exhaust valve lash. Refer to Engine.
(11) Install high pressure fuel line. Refer to Torque
Specifications.Be sure to use a secondary
back-up wrench on the connector nut (fitting)
while torquing fuel line fitting.Refer to Fuel Line
Installation for additional information.
(12) Install valve cover. Refer to Engine.
(13) Install breather assembly.
(14) Connect negative battery cables to both bat-
teries.
FUEL INJECTOR RAIL
DESCRIPTION
The fuel injector rail is bolted to the top of the
intake manifold.
OPERATION
The fuel rail is used as a distribution device to
supply high-pressure fuel to the high-pressure fuel
lines.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Cleanliness cannot be overemphasized
when handling or replacing diesel fuel system com-
ponents. This especially includes the fuel injectors,
high-pressure fuel lines and fuel injection pump.Very tight tolerances are used with these parts. Dirt
contamination could cause rapid part wear and pos-
sible plugging of fuel injector nozzle tip holes. This
in turn could lead to possible engine misfire.
Always wash/clean any fuel system component
thoroughly before disassembly and then air dry.
Cap or cover any open part after disassembly.
Before assembly, examine each part for dirt, grease
or other contaminants and clean if necessary. When
installing new parts, lubricate them with clean
engine oil or clean diesel fuel only.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries. Isolate ends of both cables.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector at fuel pressure
sensor.
(3) Remove banjo bolt at fuel limiting valve.
(4) Disconnect necessary wiring harness retention
clips from intake manifold.
(5) Lift 2 rubber covers to gain access to positive
(+), intake heater cable nuts. Remove 2 nuts and
remove 2 cables from studs.
(6) Carefully remove 4 high-pressure fuel lines
from top of injector rail engine. Note position of each
line while removing.Do not bend lines while
removing.
CAUTION: WHEN LOOSENING OR TIGHTENING
HIGH-PRESSURE LINES ATTACHED TO A SEPA-
RATE FITTING, USE A BACK-UP WRENCH ON FIT-
TING. DO NOT ALLOW FITTING TO ROTATE.
DAMAGE TO BOTH FUEL LINE AND FITTING WILL
RESULT.
(7) Carefully remove 2 high-pressure fuel lines at
each end of injector rail. Note position of each line
while removing.Do not bend lines while remov-
ing.
(8) Remove fuel line connecting injector pump to
fuel rail.
(9) Remove 3 injector rail mounting bolts (Fig. 22).
(10) Remove rail from top of intake manifold.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean any dirt/debris from top of intake mani-
fold and bottom of fuel rail.
(2) Position fuel rail to top of manifold and install
3 mounting bolts. Refer to Torque Specifications.
(3) Install all high-pressure lines to rail. Refer to
Fuel Lines for procedures.
(4) Reposition wiring harness to intake manifold
and install new tie wraps.
(5) Install and tighten fuel limiting valve banjo
bolt. Refer to Torque Specifications.
(6) Connect electrical connector to fuel pressure
sensor.
(7) Position 2 positive (+) cables to intake heater
studs. Install 2 nuts.
14 - 78 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELDR
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1654 of 2627

Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Not Mounted To Engine
(1) Attach cable to Accelerator Pedal Position Sen-
sor (APPS). Refer to APPS (Diesel) Removal / Instal-
lation.
(2) Push cable housing into rubber grommet and
through opening in dash panel.
(3) From inside vehicle, install clip holding cable
to dashpanel (Fig. 35).
(4) From inside vehicle, slide throttle cable core
wire into opening in top of pedal arm.
(5) Push cable retainer (clip) into pedal arm open-
ing until it snaps in place.
(6) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
(7) If necessary, use DRB IIItScan Tool to erase
any APPS Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) from
Engine Control Module (ECM).
PTO SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
This Engine Control Module (ECM) input is used
only on models equipped with aftermarket Power
Take Off (PTO) units.
OPERATION
This input is used only to tell the PCM (non-die-
sel), or ECM (diesel) that the aftermarket PTO
(Power Take Off) unit has been engaged. The PCM
(or ECM) will disable (temporarily shut down) cer-
tain OBD II diagnostic trouble codes when the PTO
unit is engaged.
Fig. 35 ACCELERATOR PEDAL MOUNTING
1 - ACCELERATOR CABLE
2 - PLASTIC RETAINER (CLIP)
3 - THROTTLE PEDAL ARM
4 - PEDAL / BRACKET ASSEMBLY
5 - CABLE CLIP
DRFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 85
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE (Continued)
Page 1837 of 2627

IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan gas-
ket surface (Fig. 2). Refer to this information when
ordering replacement parts.
GEAR RATIOS
The 48RE gear ratios are:
1st.................................2.45:1
2nd................................1.45:1
3rd................................1.00:1
4th.................................0.69:1
Rev.................................2.20:1
OPERATION
The application of each driving or holding compo-
nent is controlled by the valve body based upon the
manual lever position, throttle pressure, and gover-
nor pressure. The governor pressure is a variable
pressure input to the valve body and is one of the
signals that a shift is necessary. First through fourth
gear are obtained by selectively applying and releas-
ing the different clutches and bands. Engine power is
thereby routed to the various planetary gear assem-
blies which combine with the overrunning clutch
assemblies to generate the different gear ratios. The
torque converter clutch is hydraulically applied and
is released when fluid is vented from the hydraulic
circuit by the torque converter control (TCC) solenoid
on the valve body. The torque converter clutch is con-
trolled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The
torque converter clutch engages in fourth gear, and
in third gear under various conditions, such as when
the O/D switch is OFF, when the vehicle is cruising
on a level surface after the vehicle has warmed up.
The torque converter clutch can also be engaged in
the MANUAL SECOND gear position if high trans-
mission temperatures are sensed by the PCM. The
torque converter clutch will disengage momentarily
when an increase in engine load is sensed by the
PCM, such as when the vehicle begins to go uphill or
the throttle pressure is increased. The torque con-
verter clutch feature increases fuel economy and
reduces the transmission fluid temperature.
Since the overdrive clutch is applied in fourth gear
only and the direct clutch is applied in all ranges
except fourth gear, the transmission operation for
park, neutral, and first through third gear will be
described first. Once these powerflows are described,
the third to fourth shift sequence will be described.
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER 10 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
2 - INPUT SHAFT 11 - DIRECT CLUTCH
3 - OIL PUMP 12 - PLANETARY GEAR
4 - FRONT BAND 13 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
5 - FRONT CLUTCH 14 - OVERDRIVE OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
6 - REAR CLUTCH 15 - DIRECT CLUTCH SPRING
7 - PLANETARIES 16 - OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER
8 - REAR BAND 17 - OIL PAN
9 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH 18 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 2 Transmission Part Number And Serial
Number Location
1 - PART NUMBER
2 - BUILD DATE
3 - SERIAL NUMBER
21 - 134 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1958 of 2627
(6) Reconnect cable end to attachment stud. Then
with aid of a helper, observe movement of transmis-
sion throttle lever and lever on throttle body.
²If both levers move simultaneously from idle to
half-throttle and back to idle position, adjustment is
correct.
²If transmission throttle lever moves ahead of, or
lags behind throttle body lever, cable adjustment will
be necessary. Or, if throttle body lever prevents
transmission lever from returning to closed position,
cable adjustment will be necessary.
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
(2) Remove air cleaner if necessary.
(3) Disconnect cable end from attachment stud.
Carefully slide cable off stud. Do not pry or pull
cable off.
(4) Verify that transmission throttle lever is in
fully closed position. Then be sure lever on throttle
body is at curb idle position.
(5) Pry the T.V. cable lock (A) into the UP position
(Fig. 226). This will unlock the cable and allow for
readjustment.
(6) Apply just enough tension on the T.V. cable (B)
to remove any slack in the cable.Pulling too tight
will cause the T.V. lever on the transmission to
move out of its idle position, which will result
in an incorrect T.V. cable adjustment.Slide the
sheath of the T.V. cable (D) back and forth until the
centerlines of the T.V. cable end (B) and the throttle
bell crank lever (C) are aligned within one millimeter
(1mm) (Fig. 226).
(7) While holding the T.V. cable in the set position
push the T.V. cable lock (A) into the down position
(Fig. 226). This will lock the present T.V. cable
adjustment.
NOTE: Be sure that as the cable is pulled forward
and centered on the throttle lever stud, the cable
housing moves smoothly with the cable. Due to the
angle at which the cable housing enters the spring
housing, the cable housing may bind slightly and
create an incorrect adjustment.
(8) Reconnect the T.V. cable (B) to the throttle
bellcrank lever (C).
(9) Check cable adjustment. Verify transmission
throttle lever and lever on throttle body move simul-
taneously.
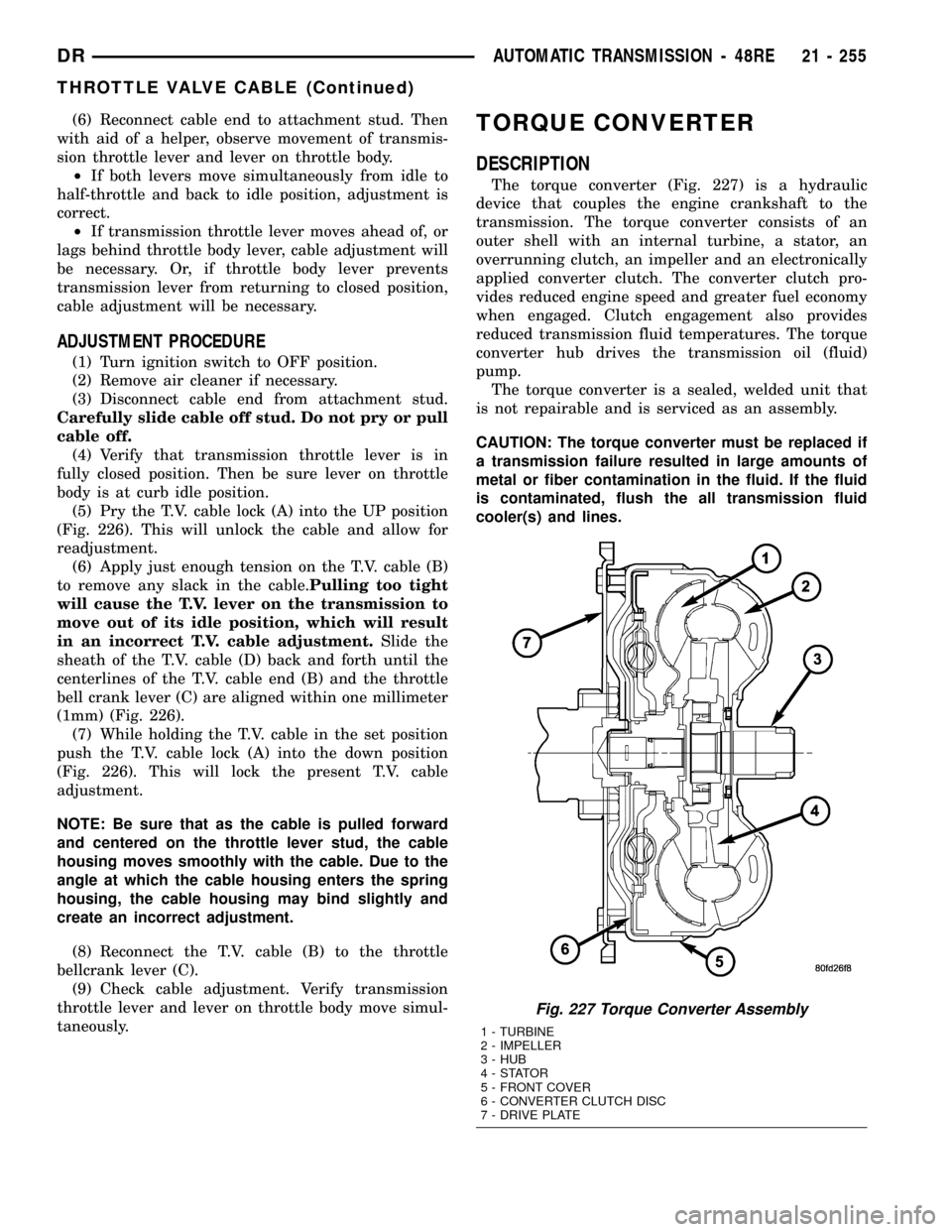
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 227) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The torque
converter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid)
pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid. If the fluid
is contaminated, flush the all transmission fluid
cooler(s) and lines.
Fig. 227 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - FRONT COVER
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
7 - DRIVE PLATE
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 255
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE (Continued)
Page 2102 of 2627

A solenoid can also be described by the method by
which it is controlled. Some of the possibilities
include variable force, pulse-width modulated, con-
stant ON, or duty cycle. The variable force and pulse-
width modulated versions utilize similar methods to
control the current flow through the solenoid to posi-
tion the solenoid plunger at a desired position some-
where between full ON and full OFF. The constant
ON and duty cycled versions control the voltage
across the solenoid to allow either full flow or no flow
through the solenoid's valve.
OPERATION
When an electrical current is applied to the sole-
noid coil, a magnetic field is created which produces
an attraction to the plunger, causing the plunger to
move and work against the spring pressure and the
load applied by the fluid the valve is controlling. The
plunger is normally directly attached to the valve
which it is to operate. When the current is removed
from the coil, the attraction is removed and the
plunger will return to its original position due to
spring pressure.
The plunger is made of a conductive material and
accomplishes this movement by providing a path for
the magnetic field to flow. By keeping the air gap
between the plunger and the coil to the minimum
necessary to allow free movement of the plunger, the
magnetic field is maximized.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 117) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, anoverrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The torque
converter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid)
pump and contains an o-ring seal to better control oil
flow.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid.
Fig. 117 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE ASSEMBLY
2-STATOR
3 - CONVERTER HUB
4 - O-RING
5 - IMPELLER ASSEMBLY
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH PISTON
7 - TURBINE HUB
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 399
SOLENOIDS (Continued)