Battery group DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 357 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐTHERMOSTAT
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
Allgasoline powered modelsare equipped with
On-Board Diagnostics for certain cooling system com-
ponents. Refer to On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) in the
Diagnosis section of this group for additional infor-
mation. If the powertrain control module (PCM)
detects low engine coolant temperature, it will record
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in the PCM mem-
ory. Do not change a thermostat for lack of heat as
indicated by the instrument panel gauge or by poor
heater performance unless a DTC is present. Refer to
the Diagnosis section of this group for other probable
causes.
The DTC can also be accessed through the
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedures information for diagnos-
tic information and operation of the DRBIIItscan
tool.
REMOVAL
WARNING: DO NOT LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE COOLING SYSTEM HOT
AND PRESSURIZED. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE
COOLANT CAN OCCUR.Do not waste reusable coolant. If the solution is
clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
If the thermostat is being replaced, be sure that
the replacement is the specified thermostat for the
vehicle model and engine type.
Factory installed thermostat housings on 5.9L
engine is installed on a gasket with an anti-stick
coating. This will aid in gasket removal and clean-up.
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Drain the cooling system until the coolant level
is below the thermostat (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Air Conditioned vehicles: Remove the support
bracket (generator mounting bracket-to-intake mani-
fold) located near the rear of the generator (Fig. 17).
NOTE: On air conditioning equipped vehicles, the
generator must be partially removed.
(4) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL) (Fig. 18).
(5) Remove the generator mounting bolts. Do not
remove any of the wiring at the generator. If
equipped with 4WD, unplug the 4WD indicator lamp
wiring harness (located near rear of generator).
(6) Remove the generator. Position the generator
to gain access for the thermostat gasket removal.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP. ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN
SERVICING CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
Fig. 16 Thermostat - 5.7L/5.9L Gas Powered
Engines
1 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
2 - GASKET
3 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
4 - THERMOSTAT
5 - MACHINED GROOVE
Fig. 17 Generator Support Bracket ± 5.9L Engine
1 - IDLER PULLEY BUSHING
2 - A/C AND/OR GENERATOR MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - IDLER PULLEY
4 - SCREW AND WASHER
7 - 42 ENGINEDR
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT- 5.7L (Continued)
Page 359 of 2627

(7) Air Conditioned vehicles; Install the generator.
Tighten the bolts to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.).
(8) Install the support bracket (generator mount-
ing bracket-to-intake manifold). (Fig. 17). Tighten the
bolts to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install the accessory drive belt (Fig. 18)(Refer
to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE
BELTS - INSTALLATION).
(10) Fill the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING
- STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(11) Connect battery negative cable.
(12) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
ENGINE COOLANT
THERMOSTAT - 3.7L/4.7L
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: Do not operate the engine without a ther-
mostat, except for servicing or testing.
A pellet-type thermostat controls the operating
temperature of the engine by controlling the amount
of coolant flow to the radiator. On all engines the
thermostat is closed below 195ÉF (90ÉC). Above this
temperature, coolant is allowed to flow to the radia-
tor. This provides quick engine warm up and overall
temperature control. On the 3.7L4.7L engine the
thermostat is designed to block the flow of the cool-
ant bypass journal by 50% instead of completely
blocking the flow. This design controls coolant tem-
perature more accurately (Fig. 23).The same thermostat is used for winter and sum-
mer seasons. An engine should not be operated with-
out a thermostat, except for servicing or testing.
Operating without a thermostat causes other prob-
lems. These are: longer engine warmup time, unreli-
able warmup performance, increased exhaust
emissions and crankcase condensation. This conden-
sation can result in sludge formation.
OPERATION
The wax pellet is located in a sealed container at
the spring end of the thermostat. When heated, the
pellet expands, overcoming closing spring tension
and water pump pressure to force the valve to open.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐTHERMOSTAT
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
Allgasoline powered modelsare equipped with
On-Board Diagnostics for certain cooling system com-
ponents. Refer to On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) in the
Diagnosis section of this group for additional infor-
mation. If the powertrain control module (PCM)
detects low engine coolant temperature, it will record
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in the PCM mem-
ory. Do not change a thermostat for lack of heat as
Fig. 21 Thermostat PositionÐ5.9L EnginesFig. 22 Belt Routing ± 5.9L Engines
1 - IDLER PULLEY
2 - GENERATOR PULLEY
3 - A/C COMPRESSOR PULLEY
4 - IF W/OUT A/C
5 - POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY
6 - WATER PUMP PULLEY
7 - CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
8 - AUTOMATIC TENSIONER
7 - 44 ENGINEDR
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT- 5.7L (Continued)
Page 360 of 2627

indicated by the instrument panel gauge or by poor
heater performance unless a DTC is present. Refer to
the Diagnosis section of this group for other probable
causes.
The DTC can also be accessed through the
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedures information for diagnos-
tic information and operation of the DRBIIItscan
tool.
REMOVAL
WARNING: DO NOT LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE COOLING SYSTEM HOT
AND PRESSURIZED. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE
COOLANT CAN OCCUR.Do not waste reusable coolant. If the solution is
clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
If the thermostat is being replaced, be sure that
the replacement is the specified thermostat for the
vehicle model and engine type.
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Raise and support the vehicle.
(4) Remove the splash shield.
(5) Remove the lower radiator hose clamp and the
lower radiator hose at the thermostat housing.
(6) Remove the thermostat housing mounting
bolts, thermostat housing and thermostat (Fig. 24).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean the mating areas of the timing chain
cover and the thermostat housing.
(2) Install the thermostat (spring side down) into
the recessed machined groove on the timing chain
cover (Fig. 24).
(3) Position the thermostat housing on the timing
chain cover.
(4) Install the housing-to-timing chain cover bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 13 N´m (112 in. lbs.).
CAUTION: The housing must be tightened evenly
and the thermostat must be centered into the
recessed groove in the timimg chain cover. If not, it
may result in a cracked housing, damaged timing
chain cover threads or coolant leaks.
(5) Install the lower radiator hose on the thermo-
stat housing.
(6) Install the splash shield.
(7) Lower the vehicle.
(8) Fill the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING
- STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(9) Connect negative battery cable.
(10) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
Fig. 23 Thermostat Cross Section View 3.7L/4.7L
1 - FROM HEATER AND DEGAS CONTAINER
2 - FROM RADIATOR
3 - TO WATER PUMP
4- THERMOSTAT
DRENGINE 7 - 45
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - 3.7L/4.7L (Continued)
Page 437 of 2627
(4) Inspect the battery thermal guard (if equipped)
for tears, cracks, deformation or other damage.
Replace any battery thermal guard that has been
damaged.
(5) Inspect the battery built-in test indicator sight
glass (if equipped) for an indication of the battery
condition. If the battery is discharged, charge as
required. Refer to Standard Procedures for the
proper battery built-in indicator test procedures. Also
refer to Standard Procedures for the proper battery
charging procedures.
SPECIFICATIONS
The battery Group Size number, the Cold Cranking
Amperage (CCA) rating, and the Reserve Capacity
(RC) rating or Ampere-Hours (AH) rating can be
found on the original equipment battery label. Be
certain that a replacement battery has the correct
Group Size number, as well as CCA, and RC or AH
ratings that equal or exceed the original equipment
specification for the vehicle being serviced. Battery
sizes and ratings are discussed in more detail below.
²Group Size- The outside dimensions and ter-
minal placement of the battery conform to standards
established by the Battery Council International
(BCI). Each battery is assigned a BCI Group Size
number to help identify a correctly-sized replace-
ment.
²Cold Cranking Amperage- The Cold Crank-
ing Amperage (CCA) rating specifies how much cur-
rent (in amperes) the battery can deliver for thirty
seconds at -18É C (0É F). Terminal voltage must not
fall below 7.2 volts during or after the thirty second
discharge period. The CCA required is generally
higher as engine displacement increases, depending
also upon the starter current draw requirements.
²Reserve Capacity- The Reserve Capacity (RC)
rating specifies the time (in minutes) it takes for bat-
tery terminal voltage to fall below 10.5 volts, at a
discharge rate of 25 amperes. RC is determined with
the battery fully-charged at 26.7É C (80É F). This rat-
ing estimates how long the battery might last after a
charging system failure, under minimum electrical
load.
²Ampere-Hours- The Ampere-Hours (AH) rat-
ing specifies the current (in amperes) that a battery
can deliver steadily for twenty hours, with the volt-
age in the battery not falling below 10.5 volts. This
rating is also sometimes identified as the twenty-
hour discharge rating.
BATTERY CLASSIFICATIONS & RATINGS
Part NumberBCI Group Size
ClassificationCold Cranking
AmperageReserve
CapacityAmpere -
HoursLoad Test
Amperage
56029449AB 65 600 120 Minutes 66 300
56029451AB 65 750 150 Minutes 75 375
56028450AA 65 600 120 Minutes 66 300
56028452AA 65 750 150 Minutes 75 375
56028452AB 65 700 130 Minutes 70 350
56029396AA 65 700 130 Minutes 70 350
56029382AA 65 700 130 Minutes 70 350
Fig. 3 Clean Battery Terminal Post - Typical
1 - TERMINAL BRUSH
2 - BATTERY CABLE
3 - BATTERY
8F - 6 BATTERY SYSTEMDR
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 438 of 2627
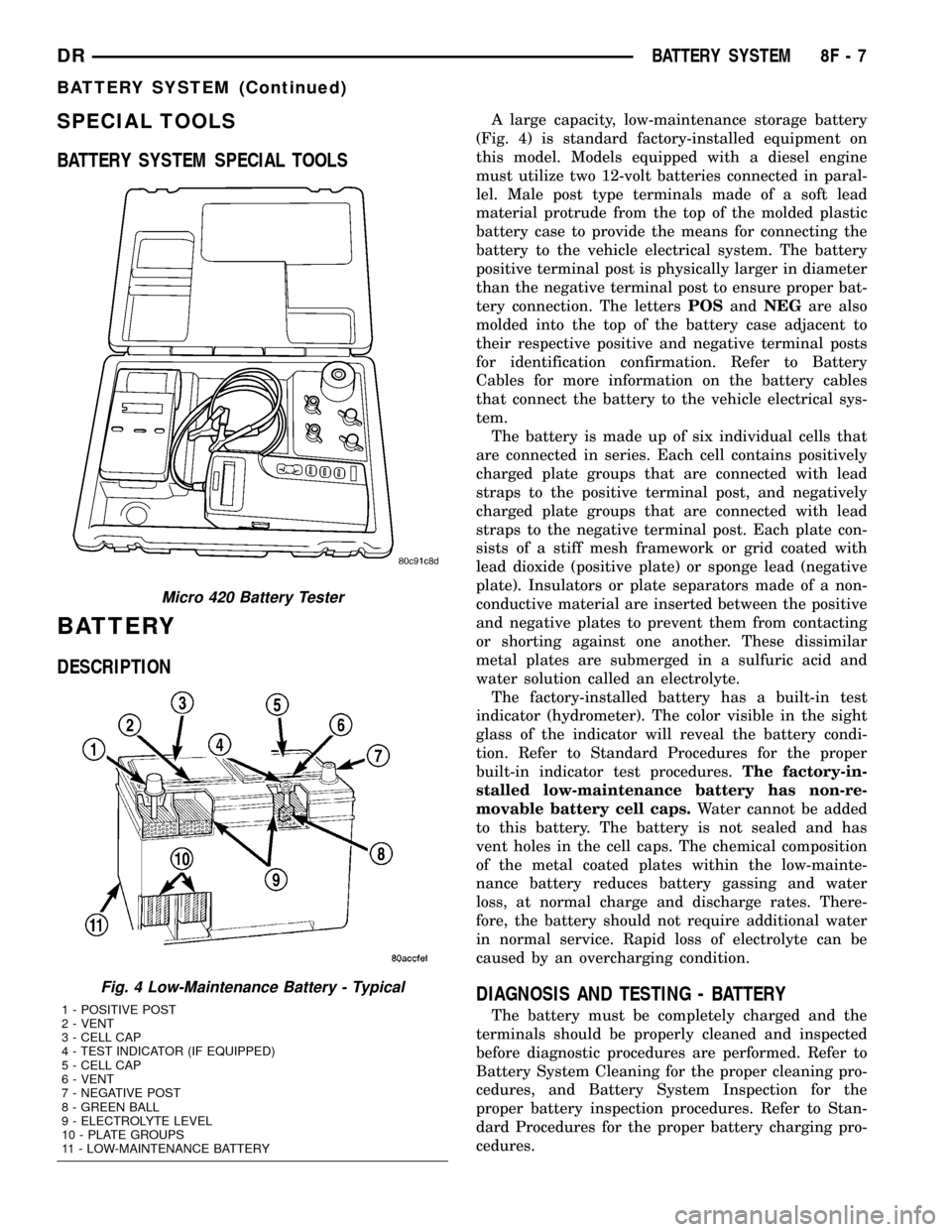
SPECIAL TOOLS
BATTERY SYSTEM SPECIAL TOOLS
BATTERY
DESCRIPTION
A large capacity, low-maintenance storage battery
(Fig. 4) is standard factory-installed equipment on
this model. Models equipped with a diesel engine
must utilize two 12-volt batteries connected in paral-
lel. Male post type terminals made of a soft lead
material protrude from the top of the molded plastic
battery case to provide the means for connecting the
battery to the vehicle electrical system. The battery
positive terminal post is physically larger in diameter
than the negative terminal post to ensure proper bat-
tery connection. The lettersPOSandNEGare also
molded into the top of the battery case adjacent to
their respective positive and negative terminal posts
for identification confirmation. Refer to Battery
Cables for more information on the battery cables
that connect the battery to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem.
The battery is made up of six individual cells that
are connected in series. Each cell contains positively
charged plate groups that are connected with lead
straps to the positive terminal post, and negatively
charged plate groups that are connected with lead
straps to the negative terminal post. Each plate con-
sists of a stiff mesh framework or grid coated with
lead dioxide (positive plate) or sponge lead (negative
plate). Insulators or plate separators made of a non-
conductive material are inserted between the positive
and negative plates to prevent them from contacting
or shorting against one another. These dissimilar
metal plates are submerged in a sulfuric acid and
water solution called an electrolyte.
The factory-installed battery has a built-in test
indicator (hydrometer). The color visible in the sight
glass of the indicator will reveal the battery condi-
tion. Refer to Standard Procedures for the proper
built-in indicator test procedures.The factory-in-
stalled low-maintenance battery has non-re-
movable battery cell caps.Water cannot be added
to this battery. The battery is not sealed and has
vent holes in the cell caps. The chemical composition
of the metal coated plates within the low-mainte-
nance battery reduces battery gassing and water
loss, at normal charge and discharge rates. There-
fore, the battery should not require additional water
in normal service. Rapid loss of electrolyte can be
caused by an overcharging condition.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY
The battery must be completely charged and the
terminals should be properly cleaned and inspected
before diagnostic procedures are performed. Refer to
Battery System Cleaning for the proper cleaning pro-
cedures, and Battery System Inspection for the
proper battery inspection procedures. Refer to Stan-
dard Procedures for the proper battery charging pro-
cedures.
Micro 420 Battery Tester
Fig. 4 Low-Maintenance Battery - Typical
1 - POSITIVE POST
2 - VENT
3 - CELL CAP
4 - TEST INDICATOR (IF EQUIPPED)
5 - CELL CAP
6 - VENT
7 - NEGATIVE POST
8 - GREEN BALL
9 - ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
10 - PLATE GROUPS
11 - LOW-MAINTENANCE BATTERY
DRBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 7
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 448 of 2627

(2) Disconnect and isolate the remote battery neg-
ative cable terminal.
(3) Remove the battery from the vehicle. Refer to
the procedure in this group.
(4) One at a time, trace the battery cable retaining
pushpins, fasteners and routing clips until the cable
is free from the vehicle.
(5) Remove the battery cable from the engine com-
partment.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the battery cable in the engine com-
partment.
(2) One at a time, install the battery cable retain-
ing pushpins, fasteners and routing clips until the
cable is installed exactly where it was in the vehicle.
Refer to Wiring for illustrations.
(3) Install the battery in the vehicle. Refer to the
procedure in this group.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable terminal.
BATTERY TRAY
DESCRIPTION
The molded plastic tray battery tray is located in
the left front corner of the engine compartment. On
this model, the battery tray also provides an anchor
point for the anti-lock brake controller, cruise control
servo (if equipped) and the integrated power module
(Fig. 15). The battery hold down hardware is con-
tained within the battery tray. A hole in the bottom
of the battery tray is fitted with a battery tempera-
ture sensor. Refer to Charging System for more infor-
mation on the battery temperature sensor.
OPERATION
The battery tray and the battery hold down hard-
ware combine to secure and stabilize the battery in
the engine compartment, which prevents battery
movement during even the most extreme vehicle
operation. Unrestrained battery movement during
vehicle operation could result in damage to the vehi-
cle, the battery, or both.
REMOVAL
LEFT SIDE
(1) Remove the battery from the battery tray
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BAT-
TERY - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the integrated power module (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER DISTRIBUTION/INTEL-
LIGENT POWER MODULE - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the wire harness retainers from the
battery tray assembly.
(4) Remove the anti-lock brake controller (if
equipped) retaining bolts and support the brake con-
troller with mechanics wire. It is not necessary to
completely remove the anti-lock brake control unit.
(5) Remove the left front wheelhouse splash shiel-
d(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/LF WHEEL-
HOUSE SPLASH SHIELD - REMOVAL).
(6) Mark the location of the cruise servo (if
equipped) and remove the retaining screws. Position
the servo out of the way.
(7) Remove the battery temperature sensor from
the battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/CHARG-
ING/BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR -
REMOVAL).
(8) Disconnect the purge solenoid from its mount-
ing bracket.
(9) Disconnect the left front fender ground wire.
(10) Remove the remaining battery tray retaining
bolts (Fig. 16).
(11) Remove the battery tray from the vehicle.
RIGHT SIDE
(1) Remove the battery from the battery tray
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BAT-
TERY - REMOVAL).
Fig. 15 DR Battery Tray
1 - BATTERY TRAY ASSEMBLY
2 - BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
3 - ANTI-LOCK BRAKE CONTROLLER MOUNTING LOCATION
4 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE MOUNTING SANCTION
DRBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 17
BATTERY CABLES (Continued)
Page 451 of 2627

²a faulty or improperly adjusted switch that
allows a lamp to stay on. Refer to Ignition-Off Draw
Test in 8, Battery for more information.
INSPECTION
The PCM (Powertrain Control Module), or ECM
(Diesel) monitors critical input and output circuits of
the charging system, making sure they are opera-
tional. A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is assigned
to each input and output circuit monitored by the
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) system. Some charging
system circuits are checked continuously, and some
are checked only under certain conditions.
Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes in; Powertrain
Control Module; Electronic Control Modules for more
DTC information. This will include a complete list of
DTC's including DTC's for the charging system.
To perform a complete test of the charging system,
refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures service manual and the DRBtscan tool. Per-
form the following inspections before attaching the
scan tool.
(1) Inspect the battery condition. Refer to 8, Bat-
tery for procedures.(2) Inspect condition of battery cable terminals,
battery posts, connections at engine block, starter
solenoid and relay. They should be clean and tight.
Repair as required.
(3) Inspect all fuses in both the fuseblock and
Power Distribution Center (PDC) for tightness in
receptacles. They should be properly installed and
tight. Repair or replace as required.
(4) Inspect generator mounting bolts for tightness.
Replace or tighten bolts if required. Refer to the Gen-
erator Removal/Installation section of this group for
torque specifications.
(5) Inspect generator drive belt condition and ten-
sion. Tighten or replace belt as required. Refer to
Belt Tension Specifications in 7, Cooling System.
(6) Inspect automatic belt tensioner (if equipped).
Refer to 7, Cooling System for information.
(7) Inspect generator electrical connections at gen-
erator field, battery output, and ground terminal (if
equipped). Also check generator ground wire connec-
tion at engine (if equipped). They should all be clean
and tight. Repair as required.
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERATOR RATINGS
TYPE PART NUMBER RATED SAE AMPS ENGINES
DENSO 56029700AA 136 3.7L / 4.7L
BOSCH 56041120AC 136 3.7L / 4.7L
DENSO 56028696AA 136 5.7L Gas/5.9L Diesel
BOSCH 56028699AA 136 5.7L Gas/5.9L Diesel
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - GENERATOR /
CHARGING SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Generator Mounting Bolts
- 5.7L41 30 -
Generator Support
Bracket Bolt/Nuts - 5.7L41 30 -
Generator Upper Mounting
Bolt - 5.9L Diesel Engine41 30 -
Generator Vertical
Mounting Bolt - 3.7L / 4.7L
Engines55 40 -
Generator (long)
Horizontal Mounting Bolt -
3.7L / 4.7L Engines55 40 -
8F - 20 CHARGINGDR
CHARGING (Continued)
Page 453 of 2627

The stator winding connections deliver the induced
alternating current to 3 positive and 3 negative
diodes for rectification. From the diodes, rectified
direct current is delivered to the vehicle electrical
system through the generator battery terminal.
Although the generators appear the same exter-
nally, different generators with different output rat-
ings are used on this vehicle. Be certain that the
replacement generator has the same output rating
and part number as the original unit. Refer to Gen-
erator Ratings in the Specifications section at the
back of this group for amperage ratings and part
numbers.
Noise emitting from the generator may be caused
by: worn, loose or defective bearings; a loose or defec-
tive drive pulley; incorrect, worn, damaged or misad-
justed fan drive belt; loose mounting bolts; a
misaligned drive pulley or a defective stator or diode.
REMOVAL
3.7L / 4.7L
WARNING: DISCONNECT NEGATIVE CABLE FROM
BATTERY BEFORE REMOVING BATTERY OUTPUT
WIRE (B+ WIRE) FROM GENERATOR. FAILURE TO
DO SO CAN RESULT IN INJURY OR DAMAGE TO
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Remove generator drive belt. Refer to 7, Cool-
ing System for procedure.
(3) Unsnap plastic insulator cap from B+ output
terminal (Fig. 2).
(4) Remove B+ terminal mounting nut at rear of
generator (Fig. 2). Disconnect terminal from genera-
tor.
(5) Disconnect field wire connector at rear of gen-
erator (Fig. 2) by pushing on connector tab.
(6) Remove 1 rear vertical generator mounting bolt
(Fig. 3).
(7) Remove 2 front horizontal generator mounting
bolts (Fig. 3).
(8) Remove generator from vehicle.
5.7L
WARNING: DISCONNECT NEGATIVE CABLE FROM
BATTERY BEFORE REMOVING BATTERY OUTPUT
WIRE (B+ WIRE) FROM GENERATOR. FAILURE TO
DO SO CAN RESULT IN INJURY OR DAMAGE TO
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Remove generator drive belt. Refer to 7, Cool-
ing System for procedure.(3) Unsnap plastic insulator cap from B+ output
terminal.
(4) Remove B+ terminal mounting nut at rear of
generator. Disconnect terminal from generator.
(5) Disconnect field wire connector at rear of gen-
erator by pushing on connector tab.
Fig. 2 GENERATOR CONNECTORS - 3.7L / 4.7L
1 - GENERATOR
2-B+NUT
3 - PLASTIC INSULATOR CAP
4 - FIELD WIRE CONNECTOR
Fig. 3 REMOVE / INSTALL GENERATOR - 3.7L / 4.7L
1 - LOWER BOLTS
2 - REAR BOLT
3 - GENERATOR
8F - 22 CHARGINGDR
GENERATOR (Continued)
Page 457 of 2627

STARTING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STARTING
DESCRIPTION.........................26
OPERATION...........................26
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTING
SYSTEM............................27
SPECIFICATIONS
STARTING SYSTEM...................31
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - STARTING
SYSTEM............................32
STARTER MOTOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER
MOTOR .............................32REMOVAL.............................33
INSTALLATION.........................34
STARTER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................36
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER RELAY . 36
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................37
STARTING
DESCRIPTION
The starting system consists of:
²Starter relay
²Starter motor (including an integral starter sole-
noid)
Other components to be considered as part of start-
ing system are:
²Battery
²Battery cables
²Ignition switch and key lock cylinder
²Clutch pedal position switch (manual transmis-
sion)
²Park/neutral position switch (automatic trans-
mission)
²Wire harnesses and connections.
The Battery, Starting, and Charging systems oper-
ate in conjunction with one another, and must be
tested as a complete system. For correct operation of
starting/charging systems, all components used in
these 3 systems must perform within specifications.
When attempting to diagnose any of these systems, it
is important that you keep their interdependency in
mind.
The diagnostic procedures used in each of these
groups include the most basic conventional diagnostic
methods, to the more sophisticated On-Board Diag-
nostics (OBD) built into the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM). Use of an induction-type milliampere
ammeter, volt/ohmmeter, battery charger, carbon pile
rheostat (load tester), and 12-volt test lamp may be
required.Certain starting system components are monitored
by the PCM and may produce a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC). Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes in
Emission Control for a list of codes.
OPERATION
The starting system components form two separate
circuits. A high-amperage feed circuit that feeds the
starter motor between 150 and 350 amperes (700
amperes - diesel engine), and a low-amperage control
circuit that operates on less than 20 amperes. The
high-amperage feed circuit components include the
battery, the battery cables, the contact disc portion of
the starter solenoid, and the starter motor. The low-
amperage control circuit components include the igni-
tion switch, the clutch pedal position switch (manual
transmission), the park/neutral position switch (auto-
matic transmission), the starter relay, the electro-
magnetic windings of the starter solenoid, and the
connecting wire harness components.
If the vehicle is equipped with a manual transmis-
sion, it has a clutch pedal position switch installed in
series between the ignition switch and the coil bat-
tery terminal of the starter relay. This normally open
switch prevents the starter relay from being ener-
gized when the ignition switch is turned to the Start
position, unless the clutch pedal is depressed. This
feature prevents starter motor operation while the
clutch disc and the flywheel are engaged. The starter
relay coil ground terminal is always grounded on
vehicles with a manual transmission.
8F - 26 STARTINGDR
Page 588 of 2627

SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
A self-diagnostic test is built-in to the module to
determine that the electronics module is operating
properly, and that all the J1850 PCI data bus mes-
sages are being received for proper operation. To per-
form the self-diagnostic test proceed as follows:
(1) With the ignition switch in the Off position,
simultaneously depress and hold theSTEP and
RESET buttons.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
(3) Following completion of the test, the electronics
module will display one of the following messages:
a.Pass Self Test (EVIC only), PASS (CMTC)-
The electronics module is working properly.
b.Failed Self Test (EVIC only), FAIL (CMTC)-
The electronics module has an internal failure. The
electronics module is faulty and must be replaced.
c.Failed J1850 Communication (EVIC only),
BUS (CMTC)- The electronics module is not receiv-
ing proper message input through the J1850 PCI
data bus circuit. This can result from one or more
faulty electronic modules in the vehicle, or from a
faulty PCI data bus. The use of a DRB IIItscan tool
and the proper Diagnostic Procedures manual are
required for further diagnosis.
NOTE: If the compass functions, but accuracy is
suspect, it may be necessary to perform a variation
adjustment. This procedure allows the compass
unit to accommodate variations in the earth's mag-
netic field strength, based on geographic location.
Refer to Compass Variation Adjustment in the Stan-
dard Procedures section of this group.
NOTE: If the compass reading displays dashes, and
only ªCALº appears in the display, demagnetizing
may be necessary to remove excessive residual
magnetic fields from the vehicle. Refer to Compass
Demagnetizing in the Standard Procedures section
of this group.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - READING/
COURTESY LAMP REPLACEMENT
(1) Open hood, disconnect and isolate the negative
battery cable.
(2) Remove the reading/courtesy lamp lens. Using
a trim stick, gently pry the forward edge of the read-
ing/courtesy lamp lens outward.
(3) Remove the reading/courtesy lamp socket from
the overhead console. Rotate the reading/courtesy
lamp socket one quarter turn counter clockwise.
(4) Remove the lamp and socket assembly.(5) Reverse the above procedure to install.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MODULE LENS
REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove the overhead console (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CONSOLE -
REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the electronics module from the over-
head console. Refer to the procedure later in this sec-
tion.
(3) Unsnap the lens from the module and replace
lens as necessary.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MODULE LAMP
REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove the overhead console (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CONSOLE -
REMOVAL).
(2) Using a flat blade screwdriver twist out socket/
lamp (Fig. 2).
(3) Replace lamp(s) as necessary.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPASS
CALIBRATION
CAUTION: Do not place any external magnets, such
as magnetic roof mount antennas, in the vicinity of
the compass. Do not use magnetic tools when ser-
vicing the overhead console.
Fig. 2 Top of Overhead Console
1 - OVERHEAD CONSOLE HOUSING
2 - EVIC/CMTC MODULE
3 - ILLUMINATION LAMPS
4 - MODULE RETAINING SCREWS
DRMESSAGE SYSTEMS 8M - 3
OVERHEAD CONSOLE (Continued)