Front Differential DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 17 of 2627

tic and soften solder. The increased temperature can
result in engine detonation. In addition, 100 percent
ethylene-glycol freezes at -22ÉC (-8ÉF).
50/50 Ethylene-Glycol and Water-Is the recom-
mended mixture, it provides protection against freez-
ing to -37ÉC (-34ÉF). The antifreeze concentration
must alwaysbe a minimum of 44 percent, year-
round in all climates. If percentage is lower, engine
parts may be eroded by cavitation. Maximum protec-
tion against freezing is provided with a 68 percent
antifreeze concentration, which prevents freezing
down to -67.7ÉC (-90ÉF). A higher percentage will
freeze at a warmer temperature. Also, a higher per-
centage of antifreeze can cause the engine to over-
heat because specific heat of antifreeze is lower than
that of water.
CAUTION: Richer antifreeze mixtures cannot be
measured with normal field equipment and can
cause problems associated with 100 percent ethyl-
ene-glycol.
COOLANT SELECTION AND ADDITIVES
NOTE: Refer to the vehicle's coolant bottle to iden-
tify HOAT or Non-HOAT coolant. Non-HOAT coolant
is green in color.
The use of aluminum cylinder blocks, cylinder
heads and water pumps requires special corrosion
protection. Only MopartAntifreeze/Coolant, 5
Year/100,000 Mile Formula (glycol base coolant with
corrosion inhibitors called HOAT, for Hybrid Organic
Additive Technology) is recommended. This coolant
offers the best engine cooling without corrosion when
mixed with 50% distilled water to obtain to obtain a
freeze point of -37ÉC (-35ÉF). If it loses color or
becomes contaminated, drain, flush, and replace with
fresh properly mixed coolant solution.
CAUTION: Do not use coolant additives that are
claimed to improve engine cooling.
DESCRIPTION - TRANSFER CASE
Recommended lubricant for the NV241 GENII,
NV271, NV243, NV244 GENII, and NV273 transfer
cases is MopartATF +4, Automatic Transmission
Fluid.
DESCRIPTION - AXLE
NOTE: DaimlerChrysler recommends using MoparT
lubricants or lubricants of equal quality.
FRONT AXLE
²C205F - MopartGear Lubricant 75W-90
²9 1/4 AA - MopartSynthetic Gear Lubricant
75W-90
REAR AXLE
²9 1/4 - MopartSynthetic Gear Lubricant 75W-
140
²10 1/2 AA - MopartSynthetic Gear Lubricant
75W-90
²11 1/2 AA - MopartSynthetic Gear Lubricant
75W-90
NOTE: Trac-LokTdifferentials require Limited Slip
Additive in the lubricant. Trac-RiteŸ differentials
DO NOT require Limited Slip Additive.
DESCRIPTION - MANUAL TRANSMISSION
NOTE: DaimlerChrysler recommends using MoparT
lubricants or lubricants of equal quality.
²NV3500 - MopartManual Transmission Lubri-
cant
²NV4500 - MopartSynthetic 75W85 Manual
Transmission Lubricant
²NV5600 - MopartManual Transmission Lubri-
cant
DESCRIPTION - AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
FLUID
NOTE: Refer to Service Procedures in this group for
fluid level checking procedures.
MopartATF +4, Automatic Transmission Fluid is
the recommended fluid for DaimlerChrysler auto-
matic transmissions.
Dexron II fluid IS NOT recommended. Clutch
chatter can result from the use of improper
fluid.
MopartATF +4, Automatic Transmission Fluid
when new is red in color. The ATF is dyed red so it
can be identified from other fluids used in the vehicle
such as engine oil or antifreeze. The red color is not
permanent and is not an indicator of fluid condition.
As the vehicle is driven, the ATF will begin to look
darker in color and may eventually become brown.
This is normal.ATF+4 also has a unique odor that
may change with age. Consequently, odor and color
cannot be used to indicate the fluid condition or the
need for a fluid change.
0 - 4 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEDR
FLUID TYPES (Continued)
Page 82 of 2627

DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PROPELLER SHAFT......................1
HALF SHAFT...........................20
FRONT AXLE - C205F....................27
FRONT AXLE - 9 1/4 AA...................54REAR AXLE-91/4.......................80
REAR AXLE - 10 1/2 AA..................112
REAR AXLE - 11 1/2 AA..................140
PROPELLER SHAFT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PROPELLER SHAFT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................1
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................3
SPECIFICATIONS........................6
SPECIAL TOOLS........................6
PROPELLER SHAFT- LD FRONT
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................7
PROPELLER SHAFT - HD FRONT
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................7
REAR PROPELLER SHAFT
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION..........................8CENTER BEARING
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION..........................9
ADJUSTMENTS.........................9
SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS
DISASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY - WITH SNAP RINGS......10
DISASSEMBLY - WITH INJECTED RINGS . . . 11
ASSEMBLY
ASSEMBLY - WITH SNAP RINGS.........12
ASSEMBLY - WITH INJECTED RINGS......13
DOUBLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS
DISASSEMBLY.........................16
ASSEMBLY............................17
PROPELLER SHAFT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
PROPELLER SHAFT VIBRATION
Out-of-round tires or wheels that are out of bal-
ance, will cause a low frequency vibration.
Driveline vibration can also caused by loose or
damaged engine mounts.Propeller shaft vibration increases with vehicle
speed. A vibration that occurs at a specific speed
range, is not usually caused by an out of balance pro-
peller shaft. Defective universal joints or an incorrect
propeller shaft angle are usually the cause of such a
vibration.
DRDIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE 3 - 1
Page 101 of 2627

HALF SHAFT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION.............................20
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................20
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................21
SPECIFICATIONS.......................21
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................21CV JOINT-OUTER
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................23
CV JOINT-INNER
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION
CAUTION:: Never grasp half shaft assembly by the
boots. This may cause the boot to pucker or crease
and reduce the service life of the boot.
Avoid over angulating or stroking the C/V joints
when handling the half shaft.
Half shafts exposed to battery acid, transmission
fluid, brake fluid, differential fluid or gasoline may
cause the boots to deteriorate. Failure to heed cau-
tion may result in damage.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Check inboard and outboard C/V joint for leaking
grease. This is a sign of boot or boot clamp damage.
NOISE/VIBRATION IN TURNS
A clicking noise or vibration in turns could be
caused by a damaged outer C/V or inner tripod joint
seal boot or seal boot clamps. This will result in the
loss/contamination of the joint grease, resulting in
inadequate lubrication of the joint. Noise could also
be caused by another component of the vehicle com-
ing in contact with the half shafts.
CLUNKING NOISE DURING ACCELERATION
This noise may be a damaged or worn C/V joint. A
torn boot or loose/missing clamp on the inner/outer
joint which has allowed the grease to be lost will
damage the C/V joint.
SHUDDER/VIBRATION DURING ACCELERATION
This could be a worn/damaged inner tripod joint or
a sticking tripod joint. Improper wheel alignment
may also cause a shudder or vibration.
VIBRATION AT HIGHWAY SPEEDS
This problem could be a result of out of balance
front tires or tire/wheel runout. Foreign material
(mud, etc.) packed on the backside of the wheel(s)
will also cause a vibration.
REMOVAL
(1) With vehicle in neutral, position vehicle on
hoist.
(2) Remove half shaft hub nut.
(3) Remove brake caliper and rotor.
(4) Position hydraulic jack under lower suspension
arm and raise jack to unload rebound bumper.
(5) Remove lower shock absorber bolt.
(6) Remove upper ball joint nut and seperate ball
with Remover 8677 (Fig. 1).
(7) Disengage inner C/V joint from axle shaft with
two pry bars between the C/V housing and axle hous-
ing.
Fig. 1 UPPER BALL JOINT SEPARATION
1 - UPPER CONTROL ARM
2 - REMOVER
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
3 - 20 HALF SHAFTDR
Page 108 of 2627

FRONT AXLE - C205F
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FRONT AXLE - C205F
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................27
REMOVAL.............................31
INSTALLATION.........................31
ADJUSTMENTS........................32
SPECIFICATIONS.......................39
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................40
AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................43
AXLE SHAFT SEALS
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION.........................43
AXLE BEARINGS
REMOVAL.............................43INSTALLATION.........................44
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................45
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL.............................46
DISASSEMBLY.........................47
ASSEMBLY............................47
INSTALLATION.........................48
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS
REMOVAL.............................48
INSTALLATION.........................48
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR
REMOVAL.............................49
INSTALLATION.........................51
FRONT AXLE - C205F
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, tooth contact, worn/damaged
gears or the carrier housing not having the proper
offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast, or constant load.
When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly check for:
²Insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. The side gears are loaded dur-
ing turns. They usually do not cause noise during
straight-ahead driving when the gears are unloaded.
A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a snapping
or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearingshave a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Differential bearingsusually produce a low pitch
noise. Differential bearing noise is similar to pinion
bearing noise. The pitch of differential bearing noise
is also constant and varies only with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearingsproduce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 m.p.h.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by:
²Worn U-joints/CV joint.
²Worn side-gear thrust washers.
²Worn pinion shaft bore.
DRFRONT AXLE - C205F 3 - 27
Page 110 of 2627
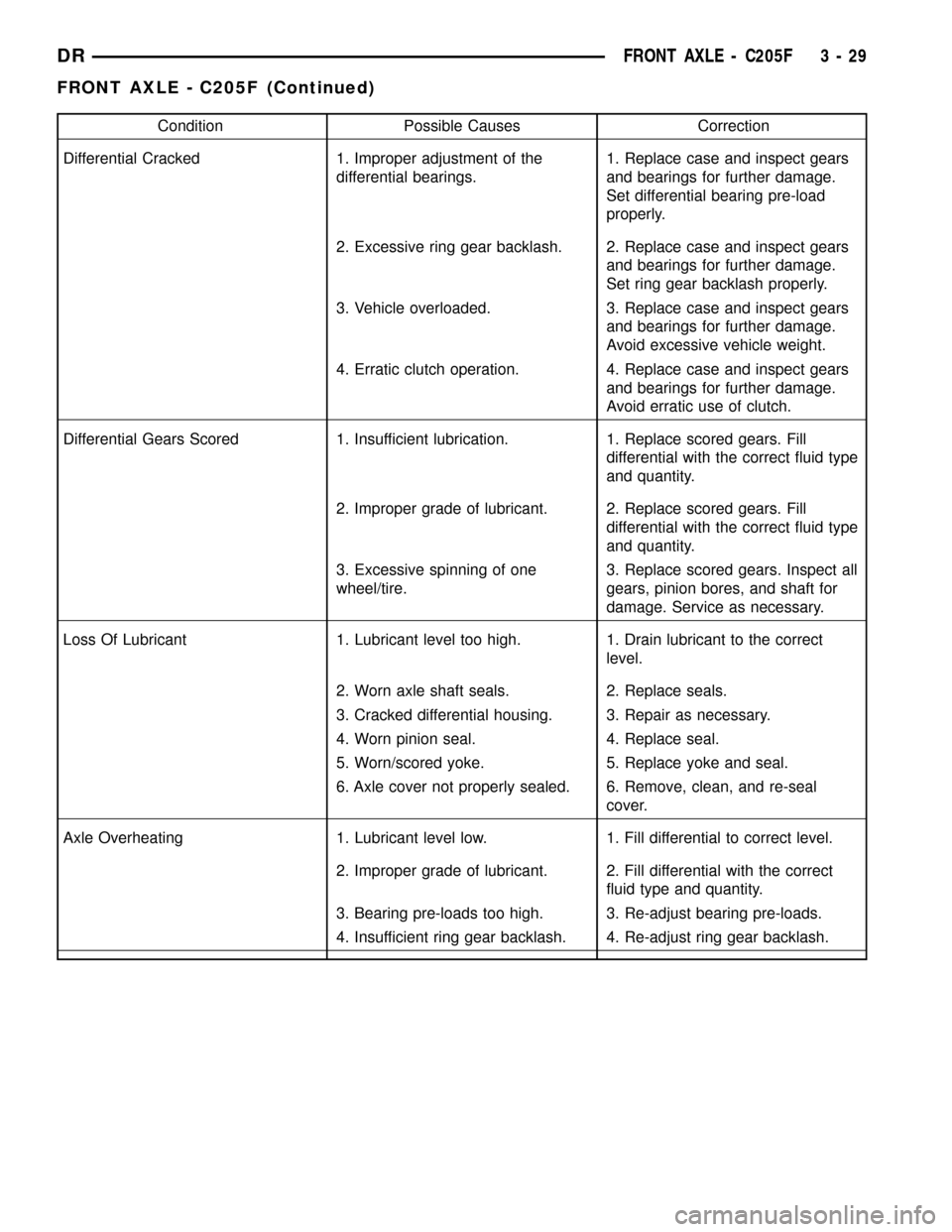
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal
cover.
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
DRFRONT AXLE - C205F 3 - 29
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)
Page 111 of 2627
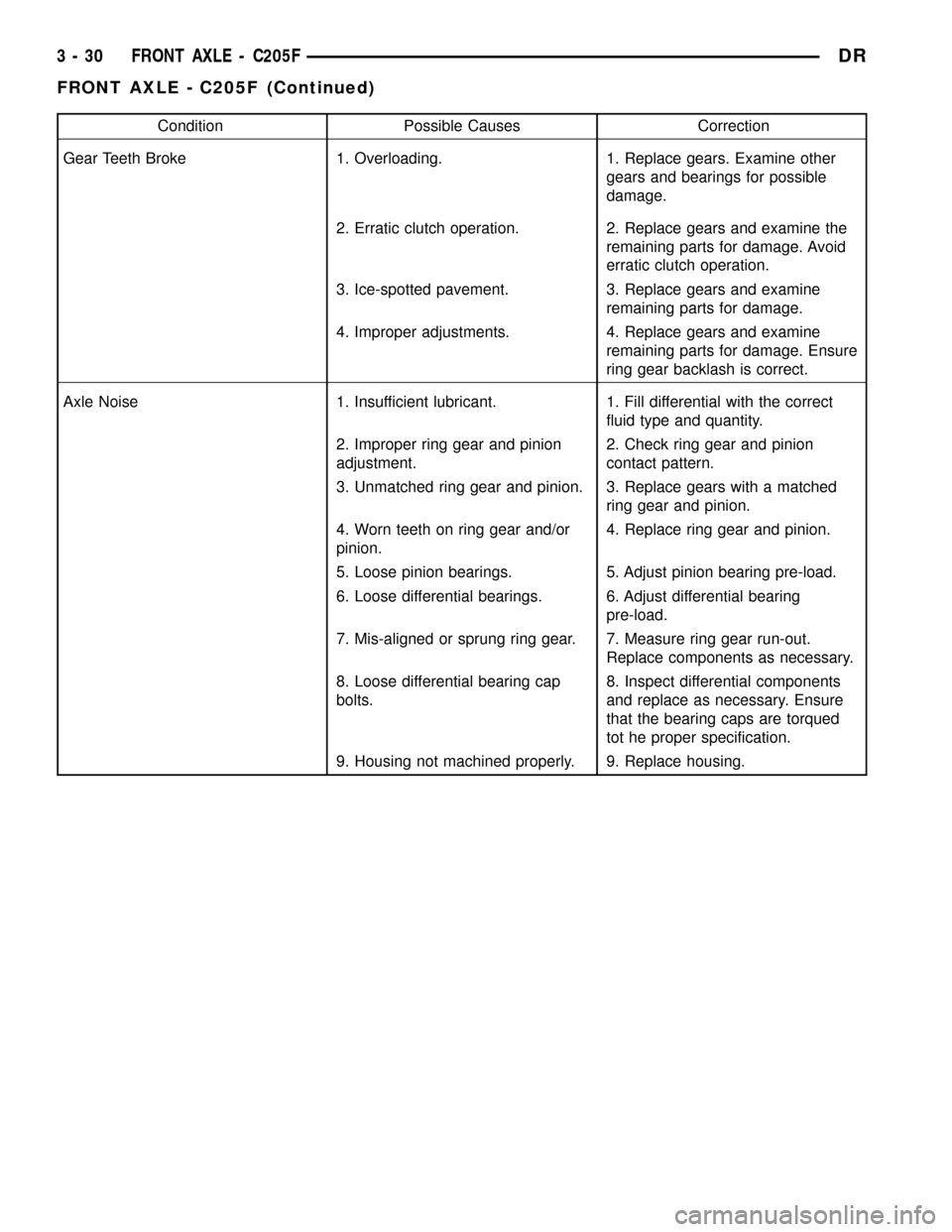
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
3 - 30 FRONT AXLE - C205FDR
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)
Page 112 of 2627

REMOVAL
(1) With vehicle in neutral, position vehicle on
hoist.
(2) Remove axle half shafts.
(3) Remove exhaust crossover.
(4) Mark front propeller shaft and remove shaft.
(5) Remove suspension crossmember mounting
bolts (Fig. 1) and remove crossmember.
(6) Support axle with hydraulic jack.
(7) Remove axle housing pinion mounting bolts
(Fig. 2).
(8) Remove axle shaft tube mounting bolts (Fig. 3).
(9) Remove differential housing mounting bolts
(Fig. 4).
(10) Lower axle from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Raise axle into position.
(2) Install axle mounting bolts and tighten nuts to
95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install suspension crossmember and bolts.
Tighten crossmember nuts to 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install front propeller shaft with reference
marks aligned (Fig. 5) and tighten bolts to 115 N´m
(85 ft. lbs.).
(5) Install exhaust crossover.
(6) Install axle half shafts.
Fig. 1 SUSPENSION CROSSMEMBER
1 - PINION FLANGE
2 - AXLE TUBE MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - CROSSMEMBER BOLTS
Fig. 2 HOUSING PINION MOUNTING BOLTS
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS
2 - PINION FLANGE
Fig. 3 AXLE TUBE MOUNT
1 - MOUNTING
2 - BOLTS
DRFRONT AXLE - C205F 3 - 31
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)
Page 113 of 2627

ADJUSTMENTS
Ring gear and pinion are supplied as a matched
sets. Identifying numbers for the ring gear and pin-
ion are painted onto the pinion gear shaft and the
side of the ring gear. A plus (+) number, minus (±)
number or zero (0) along with the gear set sequence
number (01 to 99) is on each gear. This first number
is the amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth
varies from the standard depth setting of a pinion
marked with a (0). The next two numbers are the
sequence number of the gear set. The standard depth
provides the best teeth contact pattern.
Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with select shims located between the rear
pinion bearing cone and pinion gear head (Fig. 6).
If installing a new gear, note the depth variance
number of the original and replacement pinion. Add
or subtract this number from the original depth
shim/oil slinger to compensate for the difference in
the depth variances. The numbers represent thou-
sands of an inch deviation from the standard. If the
number is negative, add that value to the required
thickness of the depth shims. If the number is posi-
tive, subtract that value from the thickness of the
depth shim.
Pinion Gear Depth Variance Chart: Note where
Old and New Pinion Marking columns intersect.
Intersecting figure represents plus or minus the
amount needed.
Fig. 4 DIFFERENTIAL MOUNT
1 - DIFFERENTIAL MOUNT
2 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
3 - MOUNTING BOLTS
Fig. 5 COMPANION FLANGE
1 - COMPANION FLANGE
2 - PROPELLER SHAFT
3 - FLANGE YOKE
4 - REFERENCE MARK
Fig. 6 ADJUSTMENT SHIM
1 - PINION GEAR DEPTH SHIM
2 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD SHIM
3 - RING GEAR
4 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD SHIM
5 - COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
3 - 32 FRONT AXLE - C205FDR
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)
Page 114 of 2627

PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
Original Pinion
Gear Depth
VarianceNew Pinion Gear Depth Variance
24232221 0 +1 +2 +3 +4
+4+0.008 +0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 0
+3+0.007 +0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.001
+2+0.006 +0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.002
+1+0.005 +0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.003
0+0.004 +0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.004
21+0.003 +0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.005
22+0.002 +0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.006
23+0.001 020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.00620.007
24020.00120.00220.00320.00420.00520.00620.00720.008
PINION DEPTH MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
Measurements are taken with pinion cups and pin-
ion bearings installed in housing. Take measure-
ments with a Pinion Gauge Set, Pinion Block 8177,
Arbor Discs 8541 and Dial Indicator C-3339 (Fig. 7).(1) Assemble Pinion Height Block 6739, Pinion
Block 8177 and rear pinion bearing onto Screw 6741
(Fig. 7).
(2) Insert assembled height gauge components,
rear bearing and screw into the housing through the
pinion bearing cups (Fig. 8).
(3) Install front pinion bearing and Cone-Nut 6740
onto the screw. Tighten cone-nut until Torque To
Rotate the screw is 2.0 N´m (18 in. lbs.) (Fig. 7).
(4) Place Arbor Discs 8541 on Arbor D-115-3 in
position in the housing side bearing cradles (Fig. 9).
Install differential bearing caps on arbor discs and
tighten cap bolts to specification.
(5) Assemble Dial Indicator C-3339 into Scooter
Block D-115-2 and secure set screw.
Fig. 7 PINION GEAR DEPTH GAUGE
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - ARBOR
3 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
4 - CONE
5 - SCREW
6 - PINION BLOCK
7 - SCOOTER BLOCK
8 - ARBOR DISC
Fig. 8 PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
1 - PINION BLOCK
2 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
DRFRONT AXLE - C205F 3 - 33
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)
Page 115 of 2627

(6) Place Scooter Block/Dial Indicator in position
in the housing so dial probe and scooter block are
flush against the surface of the pinion height block.
Hold scooter block in place and zero the dial indica-
tor. Tighten dial indicator face lock screw.
(7) Slide the dial indicator probe across the gap
between the pinion height block and the arbor bar
with the scooter block against the pinion height block
(Fig. 10). Slide the dial probe to the crest of the arbor
bar and record the highest reading.
(8) Select a shim equal to the dial indicator read-
ing plus the drive pinion gear depth variance number
marked on the shaft of the pinion gear using the
opposite sign on the variance number. For example, if
the depth variance is ±2, add +0.002 in. to the dial
indicator reading.
(9) Remove the pinion depth gauge components
from the housing
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD AND GEAR
BACKLASH
Differential side bearing preload and gear backlash
is achieved by selective shims inserted between the
bearing cup and the housing. The proper shim thick-
ness can be determined using slip-fit Dummy Bear-
ings 8398 in place of the differential side bearings
and a Dial Indicator C-3339. Before measuring differ-
ential bearing preload and gear backlash, measure
pinion gear depth and prepare pinion for installation.Pinion gear depth is essential to establishing gear
backlash and tooth contact patterns. After measuring
shim thickness to take up differential side play,
install pinion and measure gear backlash shim thick-
ness. Overall shim thickness is the dial indicator
reading and preload specification added together. The
gear backlash measurement determines the shim
thickness used on the ring gear side of the differen-
tial case. Subtract gear backlash shim thickness from
overall shim thickness to determine shim thickness
for pinion gear side of the differential (Fig. 11).
Fig. 9 PINION GAUGE TOOLS
1 - ARBOR DISC
2 - PINION BLOCK
3 - ARBOR
4 - PINION HEIGHT BLOCK
Fig. 10 PINION GEAR DEPTH MEASUREMENT
1 - ARBOR
2 - SCOOTER BLOCK
3 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 11 ADJUSTMENT SHIM
1 - PINION GEAR DEPTH SHIM
2 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD SHIM
3 - RING GEAR
4 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD SHIM
5 - COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
3 - 34 FRONT AXLE - C205FDR
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)