bulb DODGE RAM 2001 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 281 of 2889
(4) Have helper press and hold brake pedal to floor
and observe warning light.
(a) If warning light illuminates, switch is operat-
ing correctly.
(b) If light fails to illuminate, check circuit fuse,
bulb, and wiring. The parking brake switch can be
used to aid in identifying whether or not the brake
light bulb and fuse is functional. Repair or replace
parts as necessary and test differential pressure
switch operation again.
(5) If warning light still does not illuminate,
switch is faulty. Replace combination valve assembly,
bleed brake system and verify proper switch and
valve operation.
REMOVAL
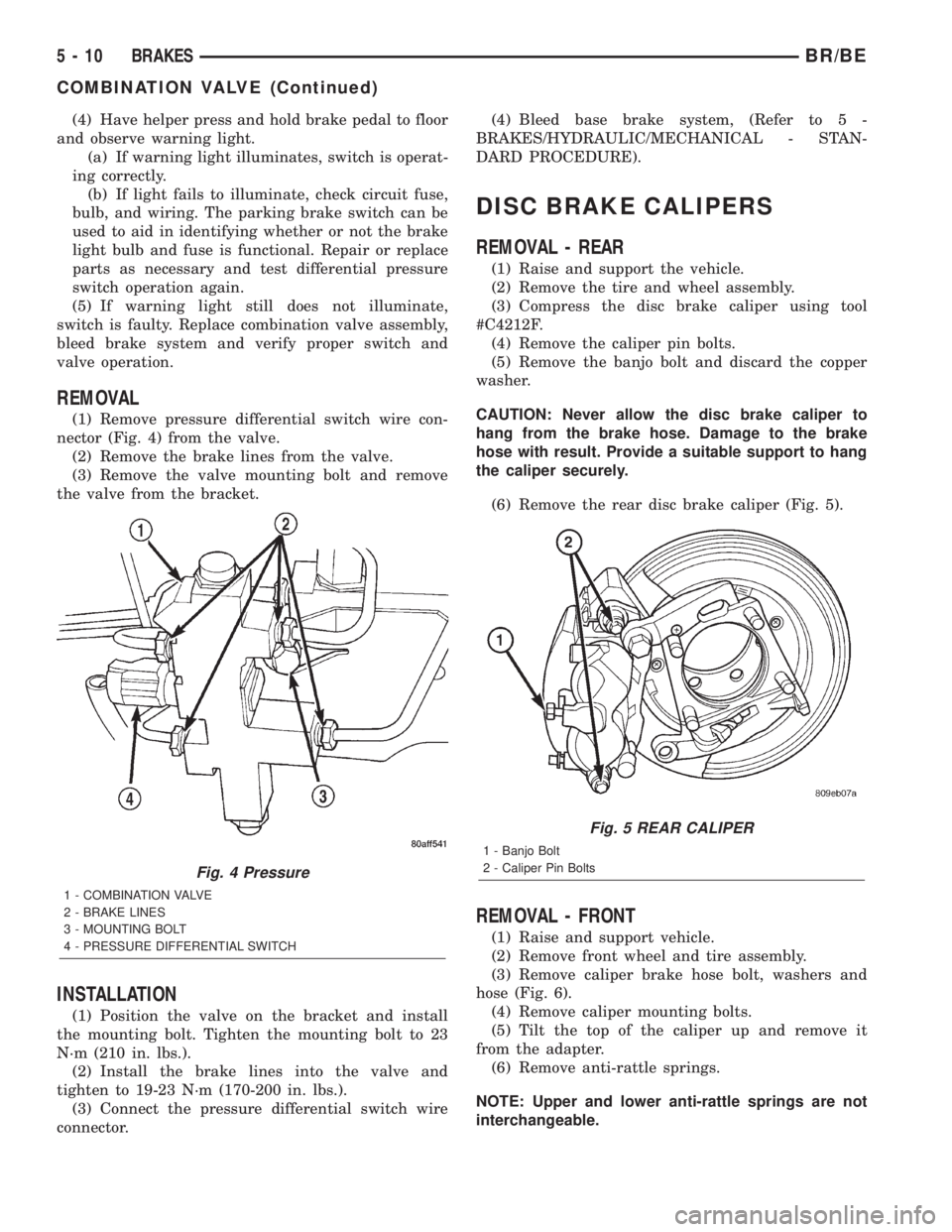
(1) Remove pressure differential switch wire con-
nector (Fig. 4) from the valve.
(2) Remove the brake lines from the valve.
(3) Remove the valve mounting bolt and remove
the valve from the bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the valve on the bracket and install
the mounting bolt. Tighten the mounting bolt to 23
N´m (210 in. lbs.).
(2) Install the brake lines into the valve and
tighten to 19-23 N´m (170-200 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the pressure differential switch wire
connector.(4) Bleed base brake system, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS
REMOVAL - REAR
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the tire and wheel assembly.
(3) Compress the disc brake caliper using tool
#C4212F.
(4) Remove the caliper pin bolts.
(5) Remove the banjo bolt and discard the copper
washer.
CAUTION: Never allow the disc brake caliper to
hang from the brake hose. Damage to the brake
hose with result. Provide a suitable support to hang
the caliper securely.
(6) Remove the rear disc brake caliper (Fig. 5).
REMOVAL - FRONT
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove front wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove caliper brake hose bolt, washers and
hose (Fig. 6).
(4) Remove caliper mounting bolts.
(5) Tilt the top of the caliper up and remove it
from the adapter.
(6) Remove anti-rattle springs.
NOTE: Upper and lower anti-rattle springs are not
interchangeable.
Fig. 4 Pressure
1 - COMBINATION VALVE
2 - BRAKE LINES
3 - MOUNTING BOLT
4 - PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL SWITCH
Fig. 5 REAR CALIPER
1 - Banjo Bolt
2 - Caliper Pin Bolts
5 - 10 BRAKESBR/BE
COMBINATION VALVE (Continued)
Page 483 of 2889

²Clear or Bright- Indicates a low battery elec-
trolyte level. The electrolyte level in the battery is
below the built-in indicator. A maintenance-free bat-
tery with non-removable cell caps must be replaced if
the electrolyte level is low. Water must be added to a
low-maintenance battery with removable cell caps
before it is charged. Refer to Standard Procedures for
the proper battery filling procedures. A low electro-
lyte level may be caused by an overcharging condi-
tion. Refer to Charging System for the proper
charging system diagnosis and testing procedures.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROMETER TEST
The hydrometer test reveals the battery state-of-
charge by measuring the specific gravity of the elec-
trolyte.This test cannot be performed on
maintenance-free batteries with non-removable
cell caps.If the battery has non-removable cell caps,
refer to Diagnosis and Testing for alternate methods
of determining the battery state-of-charge.
Specific gravity is a comparison of the density of the
battery electrolyte to the density of pure water. Pure
water has a specific gravity of 1.000, and sulfuric acid
has a specific gravity of 1.835. Sulfuric acid makes up
approximately 35% of the battery electrolyte by
weight, or 24% by volume. In a fully-charged battery
the electrolyte will have a temperature-corrected spe-
cific gravity of 1.260 to 1.290. However, a specific grav-
ity of 1.235 or above is satisfactory for the battery to
be load tested and/or returned to service.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF
FREEZING, LEAKING OR LOOSE POSTS, DO NOT
TEST, ASSIST-BOOST, OR CHARGE. THE BATTERY
MAY ARC INTERNALLY AND EXPLODE. PERSONAL
INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: EXPLOSIVE HYDROGEN GAS FORMS IN
AND AROUND THE BATTERY. DO NOT SMOKE,
USE FLAME, OR CREATE SPARKS NEAR THE BAT-
TERY. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT.WARNING: THE BATTERY CONTAINS SULFURIC
ACID, WHICH IS POISONOUS AND CAUSTIC. AVOID
CONTACT WITH THE SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING.
IN THE EVENT OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER
AND CALL A PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT
OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY IS EQUIPPED WITH
REMOVABLE CELL CAPS, BE CERTAIN THAT EACH
OF THE CELL CAPS IS IN PLACE AND TIGHT
BEFORE THE BATTERY IS RETURNED TO SER-
VICE. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT FROM LOOSE OR MISSING
CELL CAPS.
Before testing, visually inspect the battery for any
damage (a cracked case or cover, loose posts, etc.)
that would cause the battery to be faulty. Then
remove the battery cell caps and check the electrolyte
level. Add distilled water if the electrolyte level is
below the top of the battery plates. Refer to Battery
System Cleaning for the proper battery inspection
procedures.
See the instructions provided by the manufacturer
of the hydrometer for recommendations on the cor-
rect use of the hydrometer that you are using.
Remove only enough electrolyte from the battery cell
so that the float is off the bottom of the hydrometer
barrel with pressure on the bulb released. To read
the hydrometer correctly, hold it with the top surface
of the electrolyte at eye level (Fig. 10).
CAUTION: Exercise care when inserting the tip of
the hydrometer into a battery cell to avoid damag-
ing the plate separators. Damaged plate separators
can cause early battery failure.
Hydrometer floats are generally calibrated to indi-
cate the specific gravity correctly only at 26.7É C (80É
F). When testing the specific gravity at any other
temperature, a correction factor is required. The cor-
rection factor is approximately a specific gravity
value of 0.004, which may also be identified as four
points of specific gravity. For each 5.5É C above 26.7É
C (10É F above 80É F), add four points. For each 5.5É
C below 26.7É C (10É F below 80É F), subtract four
points. Always correct the specific gravity for temper-
ature variation.
EXAMPLE:A battery is tested at -12.2É C (10É F)
and has a specific gravity of 1.240. Determine the
actual specific gravity as follows:
(1) Determine the number of degrees above or
below 26.7É C (80É F):26.6É C - -12.2É C = 38.8É C
(80É F - 10É F = 70É F)
(2) Divide the result from Step 1 by 5.5É C (10É
F):38.8É C45.5ÉC=7(70É F410ÉF=7)
Fig. 9 Built-In Indicator Sight Glass Chart
8F - 12 BATTERY SYSTEMBR/BE
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 484 of 2889

(3) Multiply the result from Step 2 by the temper-
ature correction factor (0.004):7 X 0.004 = 0.028
(4) The temperature at testing was below 26.7É C
(80É F); therefore, the temperature correction factor
is subtracted:1.240 - 0.028 = 1.212
(5) The corrected specific gravity of the battery cell
in this example is 1.212.
Test the specific gravity of the electrolyte in each
battery cell. If the specific gravity of all cells is above
1.235, but the variation between cells is more than
fifty points (0.050), the battery should be replaced. If
the specific gravity of one or more cells is less than
1.235, charge the battery at a rate of approximately
five amperes. Continue charging the battery until
three consecutive specific gravity tests, taken at one-
hour intervals, are constant. If the cell specific grav-
ity variation is more than fifty points (0.050) at the
end of the charge period, replace the battery.
When the specific gravity of all cells is above 1.235,
and the cell variation is less than fifty points (0.050),
the battery may be load tested to determine its
cranking capacity. Refer to Standard Procedures for
the proper battery load test procedures.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OPEN-CIRCUIT
VOLTAGE TEST
A battery open-circuit voltage (no load) test will
show the approximate state-of-charge of a battery.
This test can be used in place of the hydrometer test
when a hydrometer is not available, or for mainte-
nance-free batteries with non-removable cell caps.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF
FREEZING, LEAKING OR LOOSE POSTS, DO NOT
TEST, ASSIST-BOOST, OR CHARGE. THE BATTERY
MAY ARC INTERNALLY AND EXPLODE. PERSONAL
INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: EXPLOSIVE HYDROGEN GAS FORMS IN
AND AROUND THE BATTERY. DO NOT SMOKE,
USE FLAME, OR CREATE SPARKS NEAR THE BAT-
TERY. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: THE BATTERY CONTAINS SULFURIC
ACID, WHICH IS POISONOUS AND CAUSTIC. AVOID
CONTACT WITH THE SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING.
IN THE EVENT OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER
AND CALL A PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT
OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY IS EQUIPPED WITH
REMOVABLE CELL CAPS, BE CERTAIN THAT EACH
OF THE CELL CAPS IS IN PLACE AND TIGHT
BEFORE THE BATTERY IS RETURNED TO SER-
VICE. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT FROM LOOSE OR MISSING
CELL CAPS.
Before proceeding with this test, completely charge
the battery. Refer to Standard Procedures for the
proper battery charging procedures.
(1) Before measuring the open-circuit voltage, the
surface charge must be removed from the battery.
Turn on the headlamps for fifteen seconds, then
allow up to five minutes for the battery voltage to
stabilize.
(2) Disconnect and isolate both battery cables, neg-
ative cable first.
(3) Using a voltmeter connected to the battery
posts (see the instructions provided by the manufac-
turer of the voltmeter), measure the open-circuit volt-
age (Fig. 11).
Fig. 10 Hydrometer - Typical
1 - BULB
2 - SURFACE COHESION
3 - SPECIFIC GRAVITY READING
4 - TEMPERATURE READING
5 - HYDROMETER BARREL
6 - FLOAT
BR/BEBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 13
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 487 of 2889

A vehicle that has not been operated for approxi-
mately twenty days, may discharge the battery to an
inadequate level. When a vehicle will not be used for
twenty days or more (stored), remove the IOD fuse
from the Power Distribution Center (PDC). This will
reduce battery discharging.
Excessive IOD can be caused by:
²Electrical items left on.
²Faulty or improperly adjusted switches.
²Faulty or shorted electronic modules and compo-
nents.
²An internally shorted generator.
²Intermittent shorts in the wiring.If the IOD is over thirty-five milliamperes, the
problem must be found and corrected before replac-
ing a battery. In most cases, the battery can be
charged and returned to service after the excessive
IOD condition has been corrected.
(1) Verify that all electrical accessories are off.
Turn off all lamps, remove the ignition key, and close
all doors. If the vehicle is equipped with an illumi-
nated entry system or an electronically tuned radio,
allow the electronic timer function of these systems
to automatically shut off (time out). This may take
up to three minutes. See the Electronic Module Igni-
tion-Off Draw Table for more information.
ELECTRONIC MODULE IGNITION-OFF DRAW (IOD) TABLE
ModuleTime Out?
(If Yes, Interval And Wake-Up Input)IODIOD After Time
Out
Radio No1to3
milliamperesN/A
Audio Power
AmplifierNoup to 1
milliampereN/A
Central Timer Module
(CTM)No4.75
milliamperes
(max.)N/A
Powertrain Control
Module (PCM)No 0.95 milliampere N/A
ElectroMechanical
Instrument Cluster
(EMIC)No 0.44 milliampere N/A
Combination Flasher No 0.08 milliampere N/A
(2) Determine that the underhood lamp is operat-
ing properly, then disconnect the lamp wire harness
connector or remove the lamp bulb.
(3) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(4) Set an electronic digital multi-meter to its
highest amperage scale. Connect the multi-meter
between the disconnected battery negative cable ter-
minal clamp and the battery negative terminal post.
Make sure that the doors remain closed so that the
illuminated entry system is not activated. The multi-
meter amperage reading may remain high for up to
three minutes, or may not give any reading at all
while set in the highest amperage scale, depending
upon the electrical equipment in the vehicle. The
multi-meter leads must be securely clamped to the
battery negative cable terminal clamp and the bat-
tery negative terminal post. If continuity between the
battery negative terminal post and the negative cable
terminal clamp is lost during any part of the IOD
test, the electronic timer function will be activated
and all of the tests will have to be repeated.(5) After about three minutes, the high-amperage
IOD reading on the multi-meter should become very
low or nonexistent, depending upon the electrical
equipment in the vehicle. If the amperage reading
remains high, remove and replace each fuse or circuit
breaker in the Power Distribution Center (PDC) and
then in the Junction Block (JB), one at a time until
the amperage reading becomes very low, or nonexist-
ent. Refer to the appropriate wiring information in
this service manual for complete PDC and JB fuse,
circuit breaker, and circuit identification. This will
isolate each circuit and identify the circuit that is the
source of the high-amperage IOD. If the amperage
reading remains high after removing and replacing
each fuse and circuit breaker, disconnect the wire
harness from the generator. If the amperage reading
now becomes very low or nonexistent, refer to Charg-
ing System for the proper charging system diagnosis
and testing procedures. After the high-amperage IOD
has been corrected, switch the multi-meter to pro-
gressively lower amperage scales and, if necessary,
repeat the fuse and circuit breaker remove-and-re-
8F - 16 BATTERY SYSTEMBR/BE
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 520 of 2889

HEATED SEAT SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION............................5
OPERATION.............................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................6
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM..................6
DRIVER SEAT HEATER SWITCH
DESCRIPTION............................7
OPERATION.............................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................8
HEATED SEAT SWITCH...................8
REMOVAL...............................9
INSTALLATION............................9
HEATED SEAT ELEMENT
DESCRIPTION...........................10
OPERATION.............................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................11HEATED SEAT ELEMENT & SENSOR.......11
HEATED SEAT RELAY
DESCRIPTION...........................11
OPERATION.............................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................12
HEATED SEAT RELAY...................12
REMOVAL..............................13
INSTALLATION...........................13
PASSENGER SEAT HEATER SWITCH
DESCRIPTION...........................13
OPERATION.............................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................14
HEATED SEAT SWITCH..................14
REMOVAL..............................15
INSTALLATION...........................16
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
Individually controlled electrically heated front
seats are available factory-installed optional equip-
ment on the Ram quad cab models that are also
equipped with the optional SLT Plus (leather) trimpackage. Vehicles with this option can be visually
identified by the two separate heated seat switches
mounted in a bezel located in the lower right corner
of the instrument cluster bezel, next to the radio
receiver (Fig. 1). The heated seat system allows the
front seat driver and passenger to select from two
different levels of supplemental electrical seat heat-
ing, or no seat heating to suit their individual com-
fort requirements. The heated seat system for this
vehicle includes the following major components:
²The heated seat switches, including two heated
seat Light-Emitting Diode (LED) indicator lamps and
an incandescent back lighting bulb for each switch.
²The heated seat module, also referred to as the
Seat Heat Interface Module (SHIM), which contains
the solid state electronic control and diagnostic logic
circuitry for the heated seat system. Refer to the
Electronic Control Modules section of the service
manual for heated seat module information.
²The heated seat elements and sensors, which
are integral to the individual front seat cushion and
front seat back trim covers.
²The heated seat relay, which controls the avail-
ability of battery current to the heated seat module
or SHIM.
Following are general descriptions of the major
components in the heated seat system. See the own-
er's manual in the vehicle glove box for more infor-
mation on the features, use and operation of the
heated seat system. Refer toPower Seatin the
index of this service manual for the location of com-
plete heated seat system wiring diagrams.
Fig. 1 Heated Seat System Switches
1 - RADIO RECEIVER
2 - HEATED SEAT SWITCHES
BR/BEHEATED SEAT SYSTEM 8G - 5
Page 522 of 2889

²If both indicator lamps for a heated seat switch
operate, but the heated seat elements do not heat,
refer toHeated Seat Modulein Electronic Control
Modules for the location of the proper heated seat
module diagnosis and testing procedures. Also refer
to the Body Diagnostic Manual for additional diagno-
sis and testing procedures.
²If none of the indicator lamps for both heated
seat switches will operate and the heated seat ele-
ments for both seats do not heat, refer toHeated
Seat Relayin this section for the location of the
proper heated seat relay diagnosis and testing proce-
dures.
²If the an indicator lamp on either heated seat
switch remains illuminated after the heated seat has
been turned Off, refer toHeated Seat Modulein
Electronic Control Modules for the location of the
proper heated seat module diagnosis and testing pro-
cedures. Also refer to the Body Diagnostic Manual for
additional diagnosis and testing procedures.
DRIVER SEAT HEATER
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The heated seat switches used on vehicles with
this option are both mounted in a heated seat switch
bezel (Fig. 2), which replaces the standard equipmentcubby bin located in the lower right corner of the
instrument cluster bezel next to the radio receiver.
The two switches are snapped into the mounting
holes of the heated seat switch bezel, and the heated
seat switch bezel is secured with three screws to the
instrument panel. The mounts for the heated seat
switch bezel are concealed behind the instrument
cluster bezel. The two heated seat switches are iden-
tical in appearance and construction, except for the
location of a keyway in the single connector recepta-
cle on the back of each switch. The instrument panel
wire harness connectors for the heated seat switches
are keyed to match the connector receptacles on the
switches so that the two heated seat switches can
only be connected to the proper heated seat.
The momentary, bidirectional rocker-type heated
seat switch provides a resistor-multiplexed signal to
the heated seat module. Each switch has a center
neutral position and momentary Low and High posi-
tions so that both the driver and the front seat pas-
senger can select a preferred seat heating mode.
Each heated seat switch has two Light-Emitting
Diode (LED) indicator lamps, which indicate the
selected mode (Low or High) of the seat heater for
each seat and to provide diagnostic feedback for the
heated seat system. Each switch also has an incan-
descent bulb, which provides panel lamps dimmer
controlled back lighting of the switch nomenclature
when the headlamps or park lamps are turned on.
The two LED indicator lamps and the incandescent
bulb in each heated seat switch cannot be repaired. If
the indicator lamps or back lighting bulb are faulty
or damaged, the individual heated seat switch unit
must be replaced.
OPERATION
The heated seat switches receive battery current
through a fused ignition switch output (run) circuit
when the ignition switch is in the On position.
Depressing the heated seat switch rocker to its
momentary High or Low position provides a hard-
wired resistor multiplexed voltage request signal to
the heated seat module to power the heated seat ele-
ment of the selected seat and maintain the requested
temperature setting. If the heated seat switch is
depressed to a different position (Low or High) than
the currently selected state, the heated seat module
will change states to support the new selection. If a
heated seat switch is depressed a second time to the
same position as the currently selected state, the
heated seat module interprets the second input as a
request to turn the seat heater off. The heated seat
module will then turn the heated seat elements for
that seat off.
Fig. 2 Heated Seat Switches
1 - DRIVER SIDE SWITCH
2 - PASSENGER SIDE SWITCH
3 - INDICATOR LAMPS
4 - HEATED SEAT SWITCH BEZEL
BR/BEHEATED SEAT SYSTEM 8G - 7
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 523 of 2889

The indicator lamps in the heated seat switches
receive battery current through a fused ignition
switch output (run) circuit when the ignition switch
is in the On position. The ground side of each indi-
cator lamp is controlled by a separate (high or low/
driver or passenger) indicator lamp driver circuit by
the heated seat module. The heated seat module con-
trol of the switch indicator lamps also allows the
module to provide diagnostic feedback to the vehicle
operator to indicate monitored heated seat system
faults by flashing the indicator lamps on and off. One
side of the incandescent back lighting bulb in each
heated seat switch is connected to ground at all
times. The other side of the incandescent bulb is con-
nected to the fused panel lamps dimmer switch sig-
nal circuit. These bulbs are energized when the park
lamps or headlamps are turned on, and their illumi-
nation intensity is controlled by the panel lamps dim-
mer switch.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SWITCH
Refer toWiring Diagramsfor the location of com-
plete heated seat system wiring diagrams.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) If the problem being diagnosed involves inoper-
ative heated seat switch back lighting and the cluster
illumination lamps operate, go to Step 2. If the prob-
lem being diagnosed involves inoperative heated seat
switch back lighting and the cluster illumination
lamps are also inoperative, refer toInstrument
Clusterin the index of this service manual for the
proper cluster illumination lamps diagnosis and test-
ing procedures. If the problem being diagnosed
involves inoperative heated seat switch indicator
lamps and the heated seat elements do not heat,
refer to Step 4. If the problem being diagnosed
involves inoperative heated seat switch indicator
lamps and the heated seat elements do heat, go to
Step 8. If the problem being diagnosed involves a
heated seat switch indicator lamp that remains illu-minated after the heated seat has been turned Off,
refer toHeated Seat Modulein Electronic Control
Modules for the location of the proper heated seat
module diagnosis and testing procedures. Also refer
to the Body Diagnostic Manual for additional diagno-
sis and testing procedures.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the heated seat switch and bezel unit
from the instrument panel. Disconnect the instru-
ment panel wire harness connector from the connec-
tor receptacle on the back of the heated seat switch
to be tested. Check for continuity between the ground
circuit cavity of the instrument panel wire harness
connector for the heated seat switch and a good
ground. There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step
3. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground
as required.
(3) Reconnect the battery negative cable. Turn the
park lamps on with the headlamp switch. Rotate the
panel lamps dimmer thumbwheel on the headlamp
switch upward to just before the interior lamps
detent. Check for battery voltage at the fused panel
lamps dimmer switch signal circuit cavity of the
instrument panel wire harness connector for the
heated seat switch. If OK, replace the faulty heated
seat switch. If not OK, repair the open fused panel
lamps dimmer switch signal circuit to the fuse in the
Junction Block (JB) as required.
(4) Check the fused ignition switch output (run)
fuse in the Junction Block (JB). If OK, go to Step 5.
If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or component as
required and replace the faulty fuse.
(5) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check for battery voltage at the fused ignition switch
output (run) fuse in the JB. If OK, go to Step 6. If
not OK, repair the open fused ignition switch output
(run) circuit to the ignition switch as required.
(6) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the heated seat switch and bezel unit
from the instrument panel. Disconnect the instru-
ment panel wire harness connector from the connec-
tor receptacle on the back of the heated seat switch
to be tested. Reconnect the battery negative cable.
Turn the ignition switch to the On position. Check
for battery voltage at the fused ignition switch out-
put (run) circuit cavity of the instrument panel wire
harness connector for the heated seat switch. If OK,
go to Step 7. If not OK, repair the open fused ignition
switch output (run) circuit to the JB fuse as required.
(7) Check the continuity and resistance values of
the heated seat switch in the Neutral, Low and High
positions as shown in the Heated Seat Switch Conti-
nuity chart (Fig. 3). If OK, refer toHeated Seat
Modulein Electronic Control Modules for the loca-
tion of the proper heated seat module diagnosis and
testing procedures. Also refer to the Body Diagnostic
8G - 8 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMBR/BE
DRIVER SEAT HEATER SWITCH (Continued)
Page 529 of 2889

The momentary, bidirectional rocker-type heated
seat switch provides a resistor-multiplexed signal to
the heated seat module. Each switch has a center
neutral position and momentary Low and High posi-
tions so that both the driver and the front seat pas-
senger can select a preferred seat heating mode.
Each heated seat switch has two Light-Emitting
Diode (LED) indicator lamps, which indicate the
selected mode (Low or High) of the seat heater for
each seat and to provide diagnostic feedback for the
heated seat system. Each switch also has an incan-
descent bulb, which provides panel lamps dimmer
controlled back lighting of the switch nomenclature
when the headlamps or park lamps are turned on.
The two LED indicator lamps and the incandescent
bulb in each heated seat switch cannot be repaired. If
the indicator lamps or back lighting bulb are faulty
or damaged, the individual heated seat switch unit
must be replaced.
OPERATION
The heated seat switches receive battery current
through a fused ignition switch output (run) circuit
when the ignition switch is in the On position.
Depressing the heated seat switch rocker to its
momentary High or Low position provides a hard-
wired resistor multiplexed voltage request signal to
the heated seat module to power the heated seat ele-
ment of the selected seat and maintain the requestedtemperature setting. If the heated seat switch is
depressed to a different position (Low or High) than
the currently selected state, the heated seat module
will change states to support the new selection. If a
heated seat switch is depressed a second time to the
same position as the currently selected state, the
heated seat module interprets the second input as a
request to turn the seat heater off. The heated seat
module will then turn the heated seat elements for
that seat off.
The indicator lamps in the heated seat switches
receive battery current through a fused ignition
switch output (run) circuit when the ignition switch
is in the On position. The ground side of each indi-
cator lamp is controlled by a separate (high or low/
driver or passenger) indicator lamp driver circuit by
the heated seat module. The heated seat module con-
trol of the switch indicator lamps also allows the
module to provide diagnostic feedback to the vehicle
operator to indicate monitored heated seat system
faults by flashing the indicator lamps on and off. One
side of the incandescent back lighting bulb in each
heated seat switch is connected to ground at all
times. The other side of the incandescent bulb is con-
nected to the fused panel lamps dimmer switch sig-
nal circuit. These bulbs are energized when the park
lamps or headlamps are turned on, and their illumi-
nation intensity is controlled by the panel lamps dim-
mer switch.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SWITCH
Refer toWiring Diagramsfor the location of com-
plete heated seat system wiring diagrams.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) If the problem being diagnosed involves inoper-
ative heated seat switch back lighting and the cluster
illumination lamps operate, go to Step 2. If the prob-
lem being diagnosed involves inoperative heated seat
switch back lighting and the cluster illumination
lamps are also inoperative, refer toInstrument
Fig. 9 Heated Seat Switches
1 - DRIVER SIDE SWITCH
2 - PASSENGER SIDE SWITCH
3 - INDICATOR LAMPS
4 - HEATED SEAT SWITCH BEZEL
8G - 14 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMBR/BE
PASSENGER SEAT HEATER SWITCH (Continued)
Page 562 of 2889

²Check Gauges Indicator
²Cruise Indicator (Odometer VFD)
²Four-Wheel Drive Indicator
²High Beam Indicator
²Low Fuel Indicator
²Washer Fluid Indicator
²Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
²Overdrive-Off Indicator
²Seatbelt Indicator
²Service Reminder Indicator (SRI)
²Transmission Overtemp Indicator
²Turn Signal (Right and Left) Indicators
²Upshift Indicator
²Wait-To-Start Indicator (Diesel Only)
²Water-In-Fuel Indicator (Diesel Only)
Some of these indicators are either programmable
or automatically configured when the EMIC is con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system. This feature
allows those indicators to be activated or deactivated
for compatibility with certain optional equipment.
The EMIC also includes a provision for mounting the
automatic transmission gear selector indicator in the
lower right corner of the cluster. The spring-loaded,
cable driven, mechanical gear selector indicator gives
an indication of the transmission gear that has been
selected with the automatic transmission gear selec-
tor lever. The gear selector indicator pointer is easily
visible through an opening provided in the front of
the cluster overlay, and is also lighted by the cluster
illumination lamps for visibility at night. Models
equipped with a manual transmission have a block-
out plate installed in place of the gear selector indi-
cator.
Cluster illumination is accomplished by adjustable
incandescent back lighting, which illuminates the
gauges for visibility when the exterior lighting is
turned on. The EMIC high beam indicator, turn sig-
nal indicators, and wait-to-start indicator are also
illuminated by dedicated incandescent bulbs. The
remaining indicators in the EMIC are each illumi-
nated by a dedicated Light Emitting Diode (LED)
that is soldered onto the electronic circuit board.
Each of the incandescent bulbs is secured by an inte-
gral bulb holder to the electronic circuit board from
the back of the cluster housing.
Hard wired circuitry connects the EMIC to the
electrical system of the vehicle. These hard wired cir-
cuits are integral to several wire harnesses, which
are routed throughout the vehicle and retained by
many different methods. These circuits may be con-
nected to each other, to the vehicle electrical system
and to the EMIC through the use of a combination of
soldered splices, splice block connectors, and many
different types of wire harness terminal connectors
and insulators. Refer to the appropriate wiring infor-
mation. The wiring information includes wiring dia-grams, proper wire and connector repair procedures,
further details on wire harness routing and reten-
tion, as well as pin-out and location views for the
various wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
The EMIC modules for this model are serviced only
as complete units. The EMIC module cannot be
adjusted or repaired. If a gauge, an LED indicator,
the VFD, the electronic circuit board, the circuit
board hardware, the cluster overlay, or the EMIC
housing are damaged or faulty, the entire EMIC mod-
ule must be replaced. The cluster lens and hood unit,
the rear cluster housing cover, the automatic trans-
mission gear selector indicator, and the incandescent
lamp bulbs with holders are available for individual
service replacement.
OPERATION
The ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC)
is designed to allow the vehicle operator to monitor
the conditions of many of the vehicle components and
operating systems. The gauges and indicators in the
EMIC provide valuable information about the various
standard and optional powertrains, fuel and emis-
sions systems, cooling systems, lighting systems,
safety systems and many other convenience items.
The EMIC is installed in the instrument panel so
that all of these monitors can be easily viewed by the
vehicle operator when driving, while still allowing
relative ease of access for service. The microproces-
sor-based EMIC hardware and software uses various
inputs to control the gauges and indicators visible on
the face of the cluster. Some of these inputs are hard
wired, but most are in the form of electronic mes-
sages that are transmitted by other electronic mod-
ules over the Chrysler Collision Detection (CCD) data
bus network. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELEC-
TRONIC CONTROL MODULES/COMMUNICATION
- OPERATION).
The EMIC microprocessor smooths the input data
using algorithms to provide gauge readings that are
accurate, stable and responsive to operating condi-
tions. These algorithms are designed to provide
gauge readings during normal operation that are con-
sistent with customer expectations. However, when
abnormal conditions exist, such as low/high battery
voltage, low oil pressure, or high coolant tempera-
ture, the algorithm drives the gauge pointer to an
extreme position and the microprocessor turns on the
Check Gauges indicator to provide a distinct visual
indication of a problem to the vehicle operator. The
instrument cluster circuitry may also generate a
hard wired chime tone request to the Central Timer
Module (CTM) when it monitors certain conditions or
inputs, in order to provide the vehicle operator with
an audible alert.
BR/BEINSTRUMENT CLUSTER 8J - 3
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)
Page 564 of 2889

The VFD is diagnosed using the EMIC self-diag-
nostic actuator test. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IN-
STRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). Proper testing of the CCD data bus and
the data bus message inputs to the EMIC that con-
trol some of the VFD functions requires the use of a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic information. Specific operation details for the
odometer and trip odometer functions of the VFD
may be found elsewhere in this service manual.
INDICATORS
Indicators are located in various positions within
the EMIC and are all connected to the EMIC circuit
board. The four-wheel drive indicator, high beam
indicator, washer fluid indicator, turn signal indica-
tors, and wait-to-start indicator are hard wired. The
brake indicator is controlled by CCD data bus mes-
sages from the Controller Anti-lock Brake (CAB) and
the hard wired park brake switch input to the EMIC.
The seatbelt indicator is controlled by the EMIC pro-
gramming, CCD data bus messages from the Airbag
Control Module (ACM), and the hard wired seat belt
switch input to the EMIC. The Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) is normally controlled by CCD data bus
messages from the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM); however, if the EMIC loses CCD data bus
communications, the EMIC circuitry will automati-
cally turn the MIL on, and flash the odometer VFD
on and off repeatedly until CCD data bus communi-
cation is restored. The EMIC uses CCD data bus
messages from the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM), the diesel engine only Engine Control Module
(ECM), the ACM, and the CAB to control all of the
remaining indicators. Different indicators are con-
trolled by different strategies; some receive fused
ignition switch output from the EMIC circuitry clus-
ter and have a switched ground, while others are
grounded through the EMIC circuitry and have a
switched battery feed.
In addition, certain indicators in this instrument
cluster are programmable or configurable. This fea-
ture allows the programmable indicators to be acti-
vated or deactivated with a DRBIIItscan tool, while
the configurable indicators will be automatically
enabled or disabled by the EMIC circuitry for com-
patibility with certain optional equipment. The only
programmable indicator for this model is the upshift
indicator. The cruise indicator, four-wheel drive indi-
cator, overdrive-off indicator, service reminder indica-
tor, and the transmission overtemp indicator are
automatically configured, either electronically or
mechanically.The hard wired indicators are diagnosed using con-
ventional diagnostic methods. The EMIC and CCD
bus message controlled indicator lamps are diagnosed
using the EMIC self-diagnostic actuator test. (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT CLUSTER -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). Proper testing of the
CCD data bus and the data bus message inputs to
the EMIC that control each indicator lamp require
the use of a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appro-
priate diagnostic information. Specific operation
details for each indicator may be found elsewhere in
this service manual.
CLUSTER ILLUMINATION
The EMIC has several illumination lamps that are
illuminated when the exterior lighting is turned on
with the headlamp switch. The illumination bright-
ness of these lamps is adjusted by the panel lamps
dimmer rheostat when the headlamp switch thumb-
wheel is rotated (down to dim, up to brighten). The
illumination lamps receive battery current through
the panel lamps dimmer rheostat and a fuse in the
JB on a fused panel lamps dimmer switch signal cir-
cuit. The illumination lamps are grounded at all
times.
In addition, an analog/digital (A/D) converter in
the EMIC converts the analog panel lamps dimmer
rheostat input from the headlamp switch to a digital
dimming level signal for controlling the lighting level
of the VFD. The EMIC also broadcasts this digital
dimming information as a message over the CCD
data bus for use by the Compass Mini-Trip Computer
(CMTC) in synchronizing the lighting level of its
VFD with that of the EMIC. The headlamp switch
thumbwheel also has a Parade position to provide a
parade mode. The EMIC monitors the request for
this mode through a hard wired day brightness sense
circuit input from the headlamp switch. In this mode,
the EMIC will override the selected panel dimmer
switch signal and send a message over the CCD data
bus to illuminate all vacuum fluorescent displays at
full brightness for easier visibility when driving in
daylight with the exterior lighting turned on. The
parade mode has no effect on the incandescent bulb
illumination intensity.
The hard wired cluster illumination lamps are
diagnosed using conventional diagnostic methods.
Proper testing of the VFD dimming level and the
CCD data bus dimming level message functions
requires the use of a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information.
BR/BEINSTRUMENT CLUSTER 8J - 5
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)