ignition DODGE RAM 2002 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 1009 of 2255

RADIO C1 - GRAY 7 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1- -
2 X55 18BR/RD LEFT FRONT DOOR SPEAKER (-)
3 X56 18DB/RD RIGHT FRONT DOOR SPEAKER (-)
4 E17 18YL/BK DAY BRIGHTNESS SENSE
5 E2 22OR PANEL LAMPS FEED
6 X12 16RD/WT FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN-ACC)
7 M1 22PK FUSED B(+)
RADIO C2 - BLACK 7 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 X16 22LG ANTENNA RELAY OUTPUT
2 X51 18BR/YL LEFT REAR SPEAKER (+)
3 X52 18DB/WT RIGHT REAR SPEAKER (+)
4 X53 18DG LEFT FRONT DOOR SPEAKER (+)
5 X54 18VT RIGHT FRONT DOOR SPEAKER (+)
6 X57 18BR/LB LEFT REAR SPEAKER (-)
7 X58 18DB/OR RIGHT REAR SPEAKER (-)
RADIO C3-2WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 D1 20VT/BR CCD BUS (+)
2 D2 20WT/BK CCD BUS (-)
RADIO CHOKE RELAY - BLACK 4 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 X60 16DG/RD FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN-ACC)
2 X13 16BK/RD RADIO CHOKE RELAY OUTPUT
3 X16 22LG ANTENNA RELAY OUTPUT
4 Z9 16BK/VT GROUND
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (ABS)-2WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 B114 20WT/VT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (-)
2 B113 20RD/VT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (+)
8W - 80 - 74 8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTSBR/BE
Page 1016 of 2255
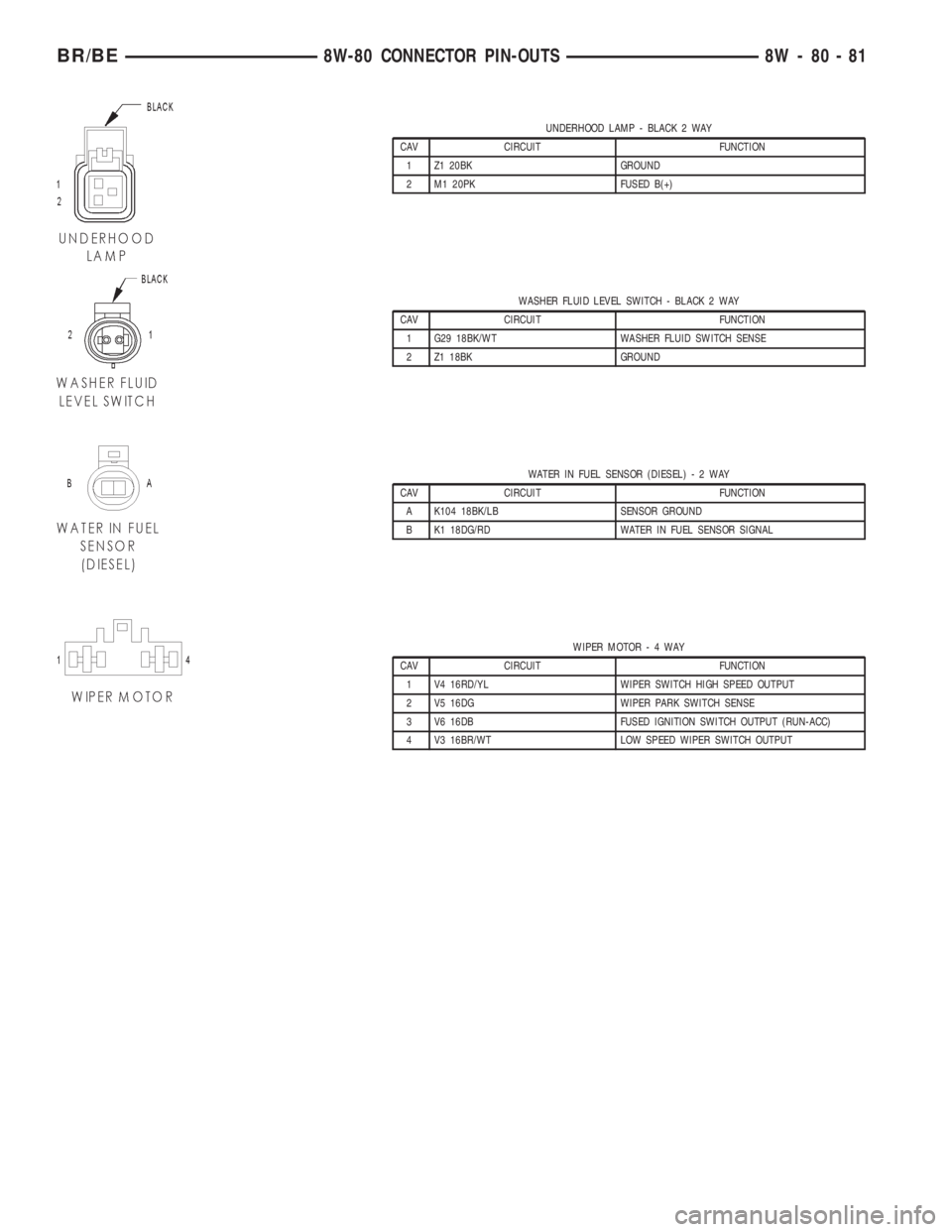
UNDERHOOD LAMP - BLACK 2 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 Z1 20BK GROUND
2 M1 20PK FUSED B(+)
WASHER FLUID LEVEL SWITCH - BLACK 2 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 G29 18BK/WT WASHER FLUID SWITCH SENSE
2 Z1 18BK GROUND
WATER IN FUEL SENSOR (DIESEL)-2WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
A K104 18BK/LB SENSOR GROUND
B K1 18DG/RD WATER IN FUEL SENSOR SIGNAL
WIPER MOTOR-4WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 V4 16RD/YL WIPER SWITCH HIGH SPEED OUTPUT
2 V5 16DG WIPER PARK SWITCH SENSE
3 V6 16DB FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN-ACC)
4 V3 16BR/WT LOW SPEED WIPER SWITCH OUTPUT
BR/BE8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTS 8W - 80 - 81
Page 1021 of 2255

CONNECTOR NAME/
NUMBERCOLOR LOCATION FIG.
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor
(V8)BK Near Distributor 5
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor
(V10)Near Oil Filter 8
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor
(Diesel)Left Side of Engine 15
Fuel Heater (Diesel) Left Side of Engine 13
Fuel Injection Pump (Diesel) Left Side of Engine, Below ECM 13
Fuel Injector No.1 BK At Fuel Injector 7
Fuel Injector No. 2 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 3 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 4 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 5 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 6 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 7 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 8 BK At Fuel Injector 7, 8
Fuel Injector No. 9 BK At Fuel Injector 8
Fuel Injector No. 10 BK At Fuel Injector 8
Fuel Pump Module (Gas) LTGY At Frame Rail 29
Fuel Tank Module (Diesel) LTGY At Frame Rail N/S
Fuel Transfer Pump (Diesel) Left Rear of Engine Bottom of Pump 13
Generator BK Front of Engine 10, 11
Glove Box Lamp At Glove Box 30
Headlamp Switch C1 BK Left Side of Instrument Panel 30, 34
Headlamp Switch C2 Left Side of Instrument Panel 30, 34
Heated Mirror Switch Center of Instrument Panel 33
High Note Horn BK Front Bumper Right Support 22
Idle Air Control Motor BK On Throttle Body 12
Ignition Coil (5.9L) GY Right Front of Engine 7, 12
Ignition Coil 4 Pack (8.0L) BK Right Side of Engine 12
Ignition Coil 6 Pack (8.0L) BK Right Side of Engine 12
Ignition Switch C1 BK Steering Column 32
Ignition Switch C2 GY Steering Column 32
Instrument Cluster C1 Rear of Instrument Cluster 30
Instrument Cluster C2 Rear of Instrument Cluster 30
Intake Air Heater Relay
(Diesel)Left Fender Side Shield 21
Intake Air Temperature
Sensor (Diesel)Left Rear of Engine 13
Intake Air Temperature
Sensor (Gas)BK On Intake Manifold 7, 8
Joint Connector No. 1 In Power Distribution Center N/S
Joint Connector No. 2 In Power Distribution Center N/S
8W - 91 - 4 8W-91 CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATIONBR/BE
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION (Continued)
Page 1037 of 2255
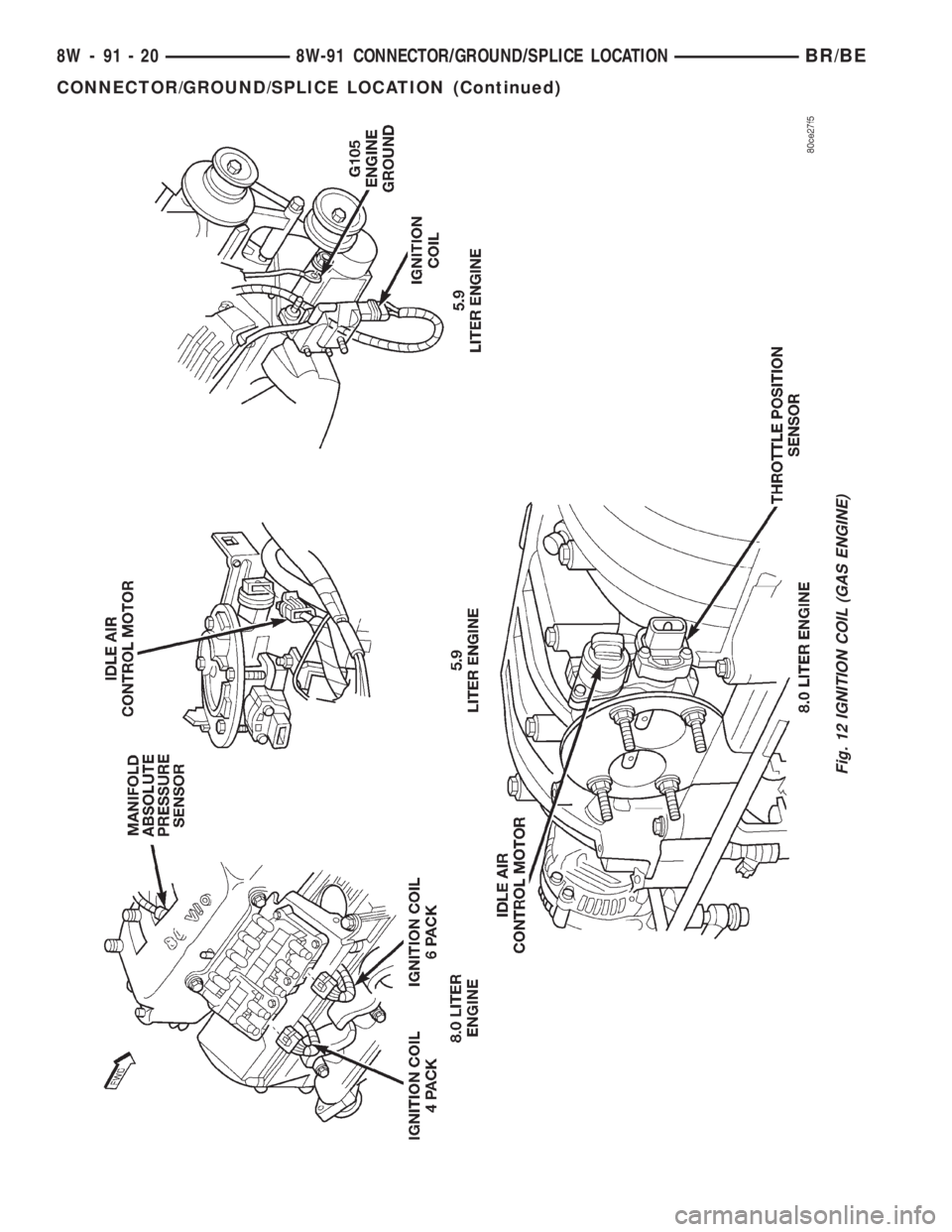
Fig. 12 IGNITION COIL (GAS ENGINE)
8W - 91 - 20 8W-91 CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATIONBR/BE
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION (Continued)
Page 1061 of 2255

tribution points for the electrical current required to
operate all of the many standard and optional facto-
ry-installed electrical and electronic powertrain,
chassis, safety, security, comfort and convenience sys-
tems. At the same time, the power distribution sys-
tem was designed to provide ready access to these
electrical distribution points for the vehicle techni-
cian to use when conducting diagnosis and repair of
faulty circuits. The power distribution system can
also prove useful for the sourcing of additional elec-
trical circuits that may be required to provide the
electrical current needed to operate many accessories
that the vehicle owner may choose to have installed
in the aftermarket.
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION
A cigar lighter is standard equipment on this
model. The cigar lighter is installed in the instru-
ment panel next to the ash receiver, which is located
near the center of the instrument panel, below the
radio. The cigar lighter base is secured by a snap fit
within the instrument panel.
The cigar lighter knob and heating element unit,
and the cigar lighter receptacle unit are available for
service. These components cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, they must be replaced.
OPERATION
The cigar lighter consists of two major components:
a knob and heating element unit, and the cigar
lighter base or receptacle shell. The receptacle shell
is connected to ground, and an insulated contact in
the bottom of the shell is connected to battery cur-
rent. The cigar lighter receives battery voltage from afuse in the junction block only when the ignition
switch is in the Accessory or On positions.
The knob and heating element are encased within
a spring-loaded housing, which also features a sliding
protective heat shield. When the knob and heating
element are inserted in the receptacle shell, the heat-
ing element resistor coil is grounded through its
housing to the receptacle shell. If the cigar lighter
knob is pushed inward, the heat shield slides up
toward the knob exposing the heating element, and
the heating element extends from the housing toward
the insulated contact in the bottom of the receptacle
shell.
Two small spring-clip retainers are located on
either side of the insulated contact inside the bottom
of the receptacle shell. These clips engage and hold
the heating element against the insulated contact
long enough for the resistor coil to heat up. When the
heating element is engaged with the contact, battery
current can flow through the resistor coil to ground,
causing the resistor coil to heat.
When the resistor coil becomes sufficiently heated,
excess heat radiates from the heating element caus-
ing the spring-clips to expand. Once the spring-clips
expand far enough to release the heating element,
the spring-loaded housing forces the knob and heat-
ing element to pop back outward to their relaxed
position. When the cigar lighter knob and element
are pulled out of the receptacle shell, the protective
heat shield slides downward on the housing so that
the heating element is recessed and shielded around
its circumference for safety.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CIGAR LIGHTER
OUTLET
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toCigar
Lighterin Wiring Diagrams.
WARNING: REFER TO THE PASSIVE RESTRAINT
SECTION OF THE SERVICE MANUAL BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Check the fused ignition switch output (run/ac-
cessory) fuse in the junction block. If OK, go to Step
2. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or component
as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check for battery voltage at the fused ignition switch
output (run/accessory) fuse in the junction block. If
OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the open fused
Terminal Pick Kit 6680
8W - 97 - 2 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONBR/BE
POWER DISTRIBUTION (Continued)
Page 1062 of 2255

ignition switch output (run/accessory) circuit to the
ignition switch as required.
(3) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Remove the cigar lighter knob and element from the
cigar lighter receptacle. Check for continuity between
the inside circumference of the cigar lighter recepta-
cle and a good ground. There should be continuity. If
OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, go to Step 5.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check for battery voltage at the insulated contact
located at the back of the cigar lighter receptacle. If
OK, replace the faulty cigar lighter knob and ele-
ment. If not OK, go to Step 5.
(5) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Remove the cigar lighter receptacle from the instru-
ment panel and disconnect the wire harness connec-
tor. Check for continuity between the ground circuit
cavity of the cigar lighter wire harness connector and
a good ground. There should be continuity. If OK, go
to Step 6. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit to
ground as required.
(6) Connect the battery negative cable. Turn the
ignition switch to the On position. Check for battery
voltage at the fused ignition switch output (run/ac-
cessory) circuit cavity of the cigar lighter wire har-
ness connector. If OK, replace the faulty cigar lighter
receptacle. If not OK, repair the open fused ignition
switch output (run/accessory) circuit to the junction
block fuse as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Pull the cigar lighter knob and element out of
the cigar lighter receptacle base, or unsnap the pro-
tective cap from the power outlet receptacle base
(Fig. 1).
(3) Look inside the cigar lighter or power outlet
receptacle base and note the position of the rectangu-
lar retaining bosses of the mount that secures the
receptacle base to the instrument panel (Fig. 2).
(4) Insert a pair of external snap ring pliers into
the cigar lighter or power outlet receptacle base and
engage the tips of the pliers with the retaining
bosses of the mount.
(5) Squeeze the pliers to disengage the mount
retaining bosses from the receptacle base and, using
a gentle rocking motion, pull the pliers and the
receptacle base out of the mount.
(6) Pull the receptacle base away from the instru-
ment panel far enough to access the instrument
panel wire harness connector.
(7) Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector from the cigar lighter or power outlet
receptacle base connector receptacle.
Fig. 1 Cigar Lighter and Power Outlet - Typical
1 - RECEPTACLE BASE
2 - KNOB & ELEMENT
3 - MOUNT
4 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
5 - POWER OUTLET
Fig. 2 Cigar Lighter and Power Outlet Remove/
Install
1 - KNOB AND ELEMENT
2 - RETAINING BOSSES-ENGAGE PLIERS HERE
3 - BASE
4 - PARTIALLY REMOVED
5 - EXTERNAL SNAP-RING PLIERS
6 - MOUNT
7 - BASE
BR/BE8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 3
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET (Continued)
Page 1064 of 2255

to service. Refer toCharging Systemin the index of
this service manual for the charging system diagnos-
tic procedures.
(1) Position the generator cartridge fuse onto the
two B(+) terminal stud bus bars within the PDC.
(2) Install and tighten the two screws that secure
the generator cartridge fuse to the two B(+) terminal
stud bus bars within the PDC. Tighten the screws to
3.4 N´m (30 in. lbs.).Be certain that both screws
are tightened to the proper torque value.
(3) Install and latch the cover onto the PDC.
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
IOD FUSE
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles are equipped with an Ignition-Off
Draw (IOD) fuse (Fig. 3) that is disconnected within
the Junction Block when the vehicle is shipped from
the factory. Dealer personnel are to reconnect the
IOD fuse in the junction block as part of the prepa-
ration procedures performed just prior to new vehicle
delivery.
The left end of the instrument panel cover has a
snap-fit fuse access panel that can be removed to pro-
vide service access to the fuses in the junction block.
A finger recess is molded into the access panel for
easy removal. An adhesive-backed fuse layout map issecured to the instrument panel side of the access
panel to ensure proper fuse identification. The IOD
fuse is a 10 ampere mini blade-type fuse. The fuse is
secured within a black molded plastic fuse holder
and puller unit that serves both as a tool for discon-
necting and reconnecting the fuse in its junction
block cavity, and as a fuse holder that conveniently
stores the fuse in the same junction block cavity after
it has been disconnected.
CIRCUITS INCLUDED WITH IOD FUSE
²Cargo Lamp
²CHMSL
²Diagnostic Connector
²Dome Lamp
²Glove Box Lamp
²Map/Reading Lamps
²Power Mirrors
²Radio
²Under Hood Lamp
OPERATION
The term ignition-off draw identifies a normal con-
dition where power is being drained from the battery
with the ignition switch in the Off position. The IOD
fuse feeds the memory and sleep mode functions for
some of the electronic modules in the vehicle as well
as various other accessories that require battery cur-
rent when the ignition switch is in the Off position,
including the clock. The only reason the IOD fuse is
disconnected is to reduce the normal IOD of the vehi-
cle electrical system during new vehicle transporta-
tion and pre-delivery storage to reduce battery
depletion, while still allowing vehicle operation so
that the vehicle can be loaded, unloaded and moved
as needed by both vehicle transportation company
and dealer personnel.
The IOD fuse is disconnected from JB fuse cavity
12 when the vehicle is shipped from the assembly
plant. Dealer personnel must reconnect the IOD fuse
when the vehicle is being prepared for delivery in
order to restore full electrical system operation. Once
the vehicle is prepared for delivery, the IOD function
of this fuse becomes transparent and the fuse that
has been assigned the IOD designation becomes only
another Fused B(+) circuit fuse. The IOD fuse serves
no useful purpose to the dealer technician in the ser-
vice or diagnosis of any vehicle system or condition,
other than the same purpose as that of any other
standard circuit protection device.
The IOD fuse can be used by the vehicle owner as
a convenient means of reducing battery depletion
when a vehicle is to be stored for periods not to
exceed about thirty days. However, it must be
remembered that disconnecting the IOD fuse will not
eliminate IOD, but only reduce this normal condition.
Fig. 3 Ignition-Off Draw Fuse
1 - JUNCTION BLOCK
2 - IGNITION-OFF DRAW FUSE AND HOLDER
3 - LEFT INSTRUMENT PANEL END BRACKET
BR/BE8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 5
GENERATOR CARTRIDGE FUSE (Continued)
Page 1065 of 2255

If a vehicle will be stored for more than about thirty
days, the battery negative cable should be discon-
nected to eliminate normal IOD; and, the battery
should be tested and recharged at regular intervals
during the vehicle storage period to prevent the bat-
tery from becoming discharged or damaged. Refer to
theBatterysection of the service manual for the
location of additional service information covering
the battery.
REMOVAL
The Ignition-Off Draw (IOD) fuse is disconnected
from Junction Block (JB) fuse cavity 12 when the
vehicle is shipped from the assembly plant. Dealer
personnel must reconnect the IOD fuse when the
vehicle is being prepared for delivery in order to
restore full electrical system operation.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
(2) Remove the fuse access panel by unsnapping it
from the left outboard end of the instrument panel.
(3) Grasp the upper and lower tabs of the IOD
fuse holder unit in fuse cavity 12 (Fig. 4) of the JB
between the thumb and forefinger and pull the unit
firmly outward.
(4) Install the fuse access panel by snapping it
onto the left outboard end of the instrument panel.
INSTALLATION
The Ignition-Off Draw (IOD) fuse is disconnected
from Junction Block (JB) fuse cavity 12 when the
vehicle is shipped from the assembly plant. Dealer
personnel must reconnect the IOD fuse when the
vehicle is being prepared for delivery in order to
restore full electrical system operation.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
(2) To install the IOD fuse, use a thumb to press
the IOD fuse holder unit in fuse cavity 12 firmly into
the JB.
(3) Install the fuse access panel by snapping it
onto the left outboard end of the instrument panel.
JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
An electrical Junction Block (JB) is concealed
behind the left outboard end of the instrument panel
cover (Fig. 5). The JB combines the functions previ-
ously provided by a separate fuseblock module and
relay center, serves to simplify and centralize numer-
ous electrical components, and to distribute electrical
current to many of the accessory systems in the vehi-
cle. It also eliminates the need for numerous splice
connections and serves in place of a bulkhead connec-
Fig. 4 Ignition-Off Draw Fuse
1 - JUNCTION BLOCK
2 - IGNITION-OFF DRAW FUSE AND HOLDER
3 - LEFT INSTRUMENT PANEL END BRACKETFig. 5 Junction Block Location
1 - JUNCTION BLOCK
2 - FUSE ACCESS PANEL
8W - 97 - 6 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONBR/BE
IOD FUSE (Continued)
Page 1073 of 2255

contained within a small, rectangular, molded plastic
housing and is connected to all of the required inputs
and outputs by five integral male spade-type termi-
nals that extend from the bottom of the relay base.
Relays cannot be adjusted or repaired and, if faulty
or damaged, the unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
A micro-relay is an electromechanical switch that
uses a low current input from one source to control a
high current output to another device. The movable
common feed contact point is held against the fixed
normally closed contact point by spring pressure.
When the relay coil is energized, an electromagnetic
field is produced by the coil windings. This electro-
magnetic field draws the movable relay contact point
away from the fixed normally closed contact point,
and holds it against the fixed normally open contact
point. When the relay coil is de-energized, spring
pressure returns the movable contact point back
against the fixed normally closed contact point. A
resistor is connected in parallel with the relay coil in
the relay, and helps to dissipate voltage spikes and
electromagnetic interference that can be generated as
the electromagnetic field of the relay coil collapses.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MICRO-RELAY
(1) Remove the relay from its mounting location.
(2) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 67.5 - 82.5 ohms. If OK, go to
Step 4. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(4) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, reinstall the relay and use a DRBIIIt
scan tool to perform further testing. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the relay by grasping it firmly and
pulling it straight out from its receptacle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Align the micro-relay terminals with the termi-
nal cavities in the receptacle.(2) Push firmly and evenly on the top of the relay
until the terminals are fully seated in the terminal
cavities in the receptacle.
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
A relay is an electromechanical device that
switches fused battery current to a electrical compo-
nent when the ignition switch is turned to the Acces-
sory or Run positions, or when controlled by a
electronic module. The relays are located in the junc-
tion block or power distribution center (Fig. 17).
The relay is a International Standards Organiza-
tion (ISO) relay. Relays conforming to the ISO speci-
fications have common physical dimensions, current
capacities, terminal patterns, and terminal functions.
A relay cannot be repaired or adjusted and, if
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor and three (two fixed and one movable) elec-
trical contacts. The movable (common feed) relay con-
tact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When the elec-
tromagnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable
contact away from the normally closed fixed contact,
and holds it against the other (normally open) fixed
contact.
When the electromagnetic coil is de-energized,
spring pressure returns the movable contact to the
normally closed position. The resistor is connected in
parallel with the electromagnetic coil in the relay,
and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that are pro-
duced when the coil is de-energized.
Fig. 17 TYPE 1 RELAY
8W - 97 - 14 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONBR/BE
MICRO-RELAY (Continued)
Page 1074 of 2255

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RELAY
The relays are located in the junction block or
power distribution center. For complete circuit dia-
grams, refer toWiring Diagrams.
(1) Remove the relay from its mounting location.
(2) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 60.7 - 80.3 ohms. If OK, go to
Step 4. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(4) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, perform the Relay Circuit Test that
follows. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) of
the junction block or power distribution center is con-
nected to battery voltage and should be hot at all
times. Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) cir-
cuit cavity in the junction block receptacle for the
relay. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the fused
B(+) circuit to the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
fuse as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to the common feed terminal (30) in the ener-
gized position. This terminal supplies battery voltage
to the fused B(+) fuse in the junction block that feedsthe accessory when the relay is energized by the igni-
tion switch. There should be continuity between the
junction block cavity for relay terminal 87 and the
fused B(+) fuse in the junction block at all times. If
OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open fused
B(+) circuit to the junction block fuse as required.
(4) The coil ground terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It receives battery
feed to energize the relay when the ignition switch is
in the Accessory or Run positions. Turn the ignition
switch to the On position. Check for battery voltage
at the fused ignition switch output (acc/run) circuit
cavity for relay terminal 85 in the junction block
receptacle for the relay. If OK, go to Step 5. If not
OK, repair the open fused ignition switch output
(acc/run) circuit to the ignition switch as required.
(5) The coil battery terminal (86) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. The junction block
cavity for this terminal should have continuity to
ground at all times. If not OK, repair the open
ground circuit to ground as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the relay by grasping it firmly and
pulling it straight out from its receptacle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the relay to the proper receptacle.
(2) Align the relay terminals with the terminal
cavities in the receptacle.
(3) Push firmly and evenly on the top of the relay
until the terminals are fully seated in the terminal
cavities in the receptacle.
BR/BE8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 15
RELAY (Continued)