fuel cap release DODGE RAM 2002 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 1087 of 2255

(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Recover refrigerant from a/c system, if
equipped (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Remove the a/c condenser, if equipped (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
A/C CONDENSER - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the transmission oil cooler (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/TRANSMISSION/TRANS COOLER -
REMOVAL).
(6) Remove the washer bottle from the fan shroud.
(7) Remove the viscous fan/drive (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR - REMOVAL).
(9) Remove the upper crossmember and top core
support.
(10) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).(11) Remove the A/C compressor with the lines
attached. Secure compressor out of the way.
(12) Remove generator assembly (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR - REMOV-
AL).
(13) Remove the air cleaner resonator and duct
work as an assembly.
(14) Disconnect the throttle linkage (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/THROTTLE
CONTROL CABLE - REMOVAL).
(15) Remove throttle body (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/THROTTLE BODY -
REMOVAL).
(16) Remove the intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL).
(17) Remove the distributor cap and wiring.
(18) Disconnect the heater hoses.
(19) Disconnect the power steering hoses, if
equipped.
(20) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release
procedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(21) Disconnect the fuel supply line (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/QUICK CON-
NECT FITTING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(22) On Manual Transmission vehicles, remove the
shift lever (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/MANUAL/SHIFT COVER - REMOVAL).
(23) Raise and support the vehicle on a hoist and
drain the engine oil.
(24) Remove engine front mount thru-bolt nuts.
(25) Disconnect the transmission oil cooler lines
from their retainers at the oil pan bolts.
(26) Disconnect exhaust pipe at manifolds.
(27) Disconnect the starter wires. Remove starter
motor (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/STARTING/
STARTER MOTOR - REMOVAL).
(28) Remove the dust shield and transmission
inspection cover.
(29) Remove drive plate to converter bolts (Auto-
matic transmission equipped vehicles).
(30) Remove transmission bell housing to engine
block bolts.
(31) Lower the vehicle.
(32) Install an engine lifting fixture.
(33) Separate engine from transmission, remove
engine from vehicle, and install engine assembly on a
repair stand.
INSTALLATION
(1) Remove engine from the repair stand and posi-
tion in the engine compartment. Position the thru-
bolt into the support cushion brackets.
(2) Install engine lifting device.
Fig. 3 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
1 - CROSSHATCH PATTERN
2 - INTERSECT ANGLE
9 - 12 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
ENGINE 5.9L (Continued)
Page 1096 of 2255

OPERATION
OPERATIONÐCYLINDER HEAD
The cylinder head closes the combustion chamber
allowing the pistons to compress the air fuel mixture
to the correct ratio for ignition. The valves located in
the cylinder head open and close to either allow clean
air into the combustion chamber or to allow the
exhaust gases out, depending on the stroke of the
engine.
OPERATION - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
GASKET
The steel-backed silicone gasket is designed to seal
the cylinder head cover for long periods of time
through extensive heat and cold, without failure. The
gasket is designed to be reusable.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET FAILURE
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
²Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
²Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test in this
section. An engine cylinder head gasket leaking
between adjacent cylinders will result in approxi-
mately a 50±70% reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove the air cleaner resonator and duct
work.
(4) Remove the intake manifold-to-generator
bracket support rod. Remove the generator.
(5) Remove closed crankcase ventilation system.
(6) Disconnect the evaporation control system.
(7) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release pro-
cedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-
ERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE). Disconnect the
fuel supply line (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FITTING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Disconnect accelerator linkage and if so
equipped, the speed control and transmission kick-
down cables.
(9) Remove distributor cap and wires.
(10) Disconnect the coil wires.
(11) Disconnect heat indicator sending unit wire.
(12) Disconnect heater hoses and bypass hose.
(13) Remove cylinder head covers and gaskets
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLIN-
DER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(14) Remove intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL) and throttle body as an assembly. Dis-
card the flange side gaskets and the front and rear
cross-over gaskets.
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 21
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1125 of 2255

(2) Position the oil pump cover onto the pump
body. Tighten cover bolts to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Install the relief valve and spring. Insert the
cotter pin.
(4) Tap on a new retainer cap.
(5) Prime oil pump before installation by filling
rotor cavity with engine oil.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install oil pump. During installation slowly
rotate pump body to ensure driveshaft-to-pump rotor
shaft engagement.
(2) Hold the oil pump base flush against mating
surface on No.5 main bearing cap. Finger tighten
pump attaching bolts. Tighten attaching bolts to 41
N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The aluminum intake manifold (Fig. 64) is a single
plane design with equal length runners and uses a
separate plenum, therefore the manifold does have a
plenum gasket. It also uses separate flange gaskets
and front and rear cross-over gaskets. Extreme care
must be used when sealing the gaskets to ensure
that excess sealant does not enter the intake runners
causing a restriction. Whenever the intake manifold
is removed inspect the plenum pan for evidence of
excess oil buildup, this condition indicates that the
plenum pan gasket is leaking.
OPERATION
The intake manifold, meters and delivers air to the
combustion chambers allowing the fuel delivered by
the fuel injectors to ignite, thus producing power.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐINTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKAGE
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS, OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water at the suspected
leak area.(3) If a change in RPMs occur, the area of the sus-
pected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove the A/C compressor (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C
COMPRESSOR - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the accessory drive bracket.
(6) Remove the air cleaner.
(7) Perform the Fuel System Pressure release pro-
cedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-
ERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE). Disconnect the
fuel lines (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FITTING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Disconnect the accelerator linkage (Refer to 14
- FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/THROTTLE
CONTROL CABLE - REMOVAL) and if so equipped,
the speed control and transmission kickdown cables.
(9) Remove the return spring.
(10) Remove the distributor cap and wires.
(11) Disconnect the coil wires.
(12) Disconnect the heat indicator sending unit
wire.
Fig. 64 Intake Manifold and Throttle BodyÐV-8 Gas
Engines Typical
1 - FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY
2 - FUEL RAIL MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - FUEL RAIL CONNECTING HOSES
9 - 50 ENGINE 5.9LBR/BE
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1151 of 2255

CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The alloy cast iron cylinder heads (Fig. 7) are held
in place by 12 bolts. The spark plugs are located in
the peak of the wedge between the valves.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET FAILURE
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
²Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
²Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test in this
section. An engine cylinder head gasket leaking
between adjacent cylinders will result in approxi-
mately a 50±70% reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove the heat shields (Fig. 8).
(4) Remove the intake manifold-to-generator
bracket support rod. Remove the generator (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR -
REMOVAL).
(5) Remove closed crankcase ventilation system.
(6) Disconnect the evaporation control system.
(7) Remove the air cleaner.
(8) Perform the Fuel System Pressure release pro-
cedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-
Fig. 7 Cylinder Head Assembly
1 - SPARK PLUG
2 - INTAKE VALVES
3 - SPARK PLUG
4 - INTAKE VALVES
5 - SPARK PLUG
6 - SPARK PLUG
7 - INTAKE VALVE
8 - SPARK PLUG
9 - EXHAUST VALVE
10 - EXHAUST VALVES
11 - EXHAUST VALVES
9 - 76 ENGINE 8.0LBR/BE
Page 1300 of 2255
FUEL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE...............1
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE..............28FUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL.................54
FUEL INJECTION - DIESEL................91
FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE
DESCRIPTION - FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM....2
OPERATION - FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM......2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL
PRESSURE LEAK DOWN TEST...........2
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE...................3
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE - GAS ENGINES..............3
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - FUEL
DELIVERY............................4
SPECIAL TOOLS
FUEL SYSTEM........................4
FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION..........................5
OPERATION............................5
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................7
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................7
OPERATION............................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL GAUGE
SENDING UNIT........................7
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................8
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION..........................8
FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION............................9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
CAPACITY TEST.......................9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
PRESSURE TEST......................9DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
AMPERAGE TEST.....................10
FUEL PUMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION.........................12
OPERATION...........................13
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
FUEL RAIL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 5.9L...................14
DESCRIPTION - 8.0L...................14
OPERATION
OPERATION - 5.9L....................14
OPERATION - 8.0L....................15
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 5.9L......................15
REMOVAL - 8.0L......................16
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 5.9L..................17
INSTALLATION - 8.0L..................18
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION.........................18
OPERATION...........................18
REMOVAL.............................18
INSTALLATION.........................20
FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE
DESCRIPTION.........................21
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................23
INLET FILTER
REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................23
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
DESCRIPTION.........................24
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK-CONNECT
FITTINGS...........................24
BR/BEFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 1
Page 1302 of 2255

(4) Connect the 0-414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure
test gauge (from Gauge Set 5069) to the test port on
the appropriate Adaptor Tool.The DRBtIII Scan
Tool along with the PEP module, the 500 psi
pressure transducer, and the transducer-to-test
port adapter may also be used in place of the
fuel pressure gauge.
The fittings on both tools must be in good
condition and free from any small leaks before
performing the proceeding test.
(5) Start engine and bring to normal operating
temperature.
(6) Observe test gauge. Normal operating pressure
should be 339 kPa +/±34 kPa (49.2 psi +/±5 psi).
(7) Shut engine off.
(8) Pressure should not fall below30 psi for five
minutes.
(9) If pressure falls below 30 psi, it must be deter-
mined if a fuel injector, the check valve within the
fuel pump module, or a fuel tube/line is leaking.
(10) Again, start engine and bring to normal oper-
ating temperature.
(11) Shut engine off.
(12)Testing for fuel injector or fuel rail leak-
age:Clamp off the rubber hose portion of Adaptor
Tool between the fuel rail and the test port ªTº on
Adapter Tool. If pressure now holds at or above 30
psi, a fuel injector or the fuel rail is leaking.
(13)Testing for fuel pump check valve, filter/
regulator check valve or fuel tube/line leakage:
Clamp off the rubber hose portion of Adaptor Tool
between the vehicle fuel line and test port ªTº on
Adapter Tool. If pressure now holds at or above 30
psi, a leak may be found at a fuel tube/line. If no
leaks are found at fuel tubes or lines, one of the
check valves in either the electric fuel pump or filter/
regulator may be leaking.
Note: A quick loss of pressure usually indicates a
defective check valve in the filter/regulator. A slow
loss of pressure usually indicates a defective check
valve in the electric fuel pump.
The electric fuel pump is not serviced separately.
Replace the fuel pump module assembly. The filter/
regulator may be replaced separately on certain
applications. Refer to Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Reg-
ulator Removal/Installation for additional informa-
tion.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE
Use following procedure if the fuel injector
rail is, or is not equipped with a fuel pressure
test port.
(1) Remove fuel fill cap.(2) Remove fuel pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.
(3) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(4) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(5) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
CAUTION: Steps 1, 2, 3 and 4 must be performed to
relieve high pressure fuel from within fuel rail. Do
not attempt to use following steps to relieve this
pressure as excessive fuel will be forced into a cyl-
inder chamber.
(6) Unplug connector from any fuel injector.
(7) Attach one end of a jumper wire with alligator
clips (18 gauge or smaller) to either injector terminal.
(8) Connect other end of jumper wire to positive
side of battery.
(9) Connect one end of a second jumper wire to
remaining injector terminal.
CAUTION: Powering an injector for more than a few
seconds will permanently damage the injector.
(10) Momentarily touch other end of jumper wire
to negative terminal of battery for no more than a
few seconds.
(11) Place a rag or towel below fuel line quick-con-
nect fitting at fuel rail.
(12) Disconnect quick-connect fitting at fuel rail.
Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(13) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(14) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRBtscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE -
GAS ENGINES
All Gasoline Powered Engines:339 kPa 34
kPa (49.2 psi 5 psi)
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 3
FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE (Continued)
Page 1308 of 2255

FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The electric fuel pump is located inside of the fuel
pump module. A 12 volt, permanent magnet, electric
motor powers the fuel pump. The electric fuel pump
is not a separate, serviceable component.
OPERATION
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay.
Fuel is drawn in through a filter at the bottom of
the module and pushed through the electric motor
gearset to the pump outlet.
Check Valve Operation:The pump outlet con-
tains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel flow back
into the tank and to maintain fuel supply line pres-
sure (engine warm) when pump is not operational. It
is also used to keep the fuel supply line full of gaso-
line when pump is not operational. After the vehicle
has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop to 0 psi
(cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will remain
in fuel supply line between the check valve and fuel
injectors.Fuel pressure that has dropped to 0
psi on a cooled down vehicle (engine off) is a
normal condition.Refer to the Fuel Pressure Leak
Down Test for more information.
The electric fuel pump is not a separate, service-
able component.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
CAPACITY TEST
Before performing this test, verify fuel pump
pressure. Refer to Fuel Pump Pressure Test.
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pres-
sure Leak Down Test.
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect fuel supply line at fuel rail. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings. Some engines may require
air cleaner housing removal before line disconnection.
(3) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(4) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose into disconnected fuel supply line.
Insert other end of Adaptor Tool Hose into a gradu-
ated container.
(5) Remove fuel fill cap.
(6) To activate fuel pump and pressurize system,
obtain DRBtscan tool and actuate ASD Fuel System
Test.(7) A good fuel pump will deliver at least 1/4 liter
of fuel in 7 seconds. Do not operate fuel pump for
longer than 7 seconds with fuel line disconnected as
fuel pump module reservoir may run empty.
(a) If capacity is lower than specification, but
fuel pump can be heard operating through fuel fill
cap opening, check for a kinked/damaged fuel sup-
ply line somewhere between fuel rail and fuel
pump module.
(b) If line is not kinked/damaged, and fuel pres-
sure is OK, but capacity is low, replace fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. The filter/regulator may be
serviced separately on certain applications. Refer
to Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal/In-
stallation for additional information.
(c) If both fuel pressure and capacity are low,
replace fuel pump module assembly. Refer to Fuel
Pump Module Removal/Installation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
PRESSURE TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Capacity Test, Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test and
Fuel Pump Amperage Test found elsewhere in this
group.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
All fuel systems are equipped with a fuel tank
module mounted, combination fuel filter/fuel pressure
regulator. The fuel pressure regulator is not con-
trolled by engine vacuum.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF. BEFORE DISCONNECTING FUEL LINE AT
FUEL RAIL, THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
REFER TO THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
RELEASE PROCEDURE.
(1) Remove protective cap at fuel rail test port.
Connect the 0±414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure gauge
(from gauge set 5069) to test port pressure fitting on
fuel rail (Fig. 11).The DRBtIII Scan Tool along
with the PEP module, the 500 psi pressure
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 9
Page 1312 of 2255
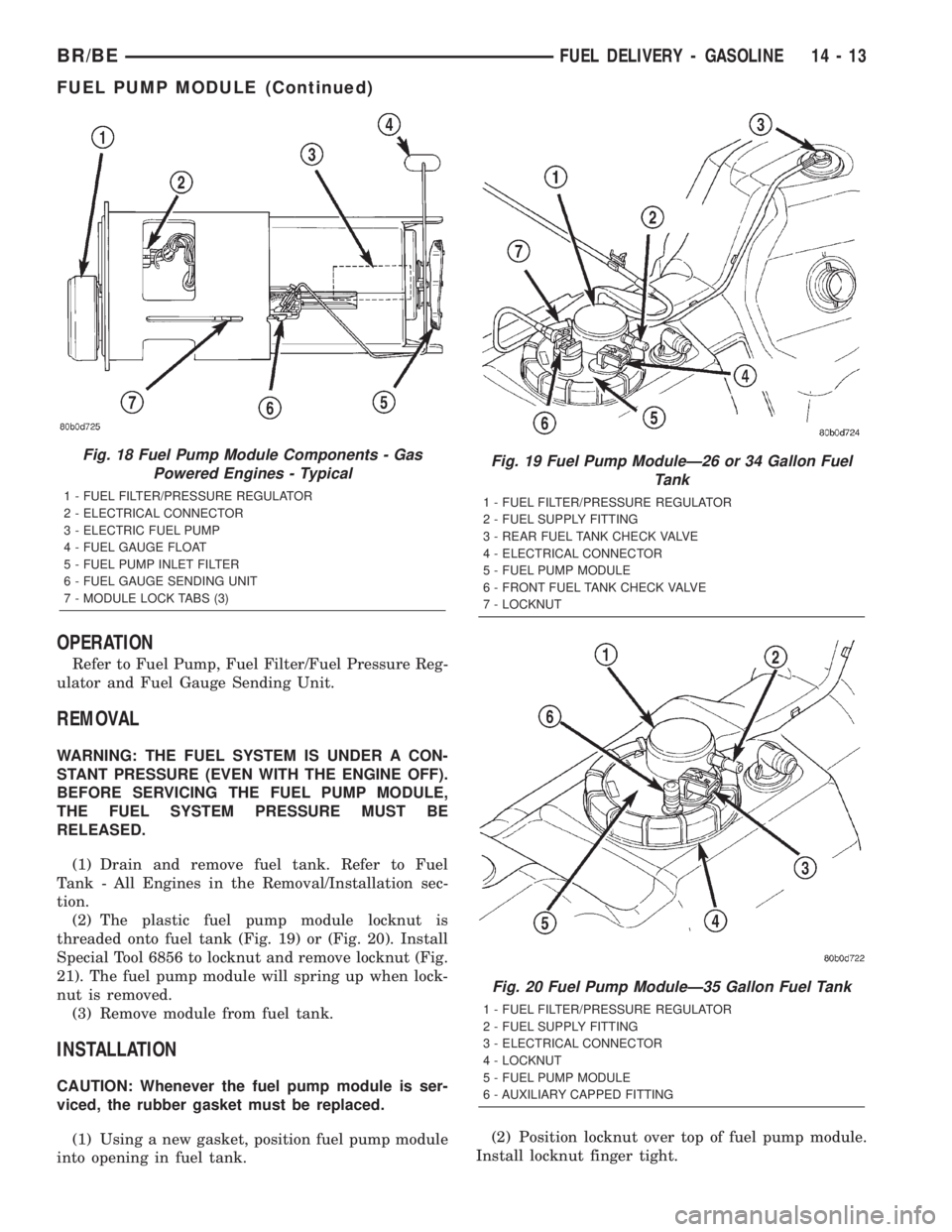
OPERATION
Refer to Fuel Pump, Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Reg-
ulator and Fuel Gauge Sending Unit.
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL PUMP MODULE,
THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE
RELEASED.
(1) Drain and remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel
Tank - All Engines in the Removal/Installation sec-
tion.
(2) The plastic fuel pump module locknut is
threaded onto fuel tank (Fig. 19) or (Fig. 20). Install
Special Tool 6856 to locknut and remove locknut (Fig.
21). The fuel pump module will spring up when lock-
nut is removed.
(3) Remove module from fuel tank.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Whenever the fuel pump module is ser-
viced, the rubber gasket must be replaced.
(1) Using a new gasket, position fuel pump module
into opening in fuel tank.(2) Position locknut over top of fuel pump module.
Install locknut finger tight.
Fig. 18 Fuel Pump Module Components - Gas
Powered Engines - Typical
1 - FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - ELECTRIC FUEL PUMP
4 - FUEL GAUGE FLOAT
5 - FUEL PUMP INLET FILTER
6 - FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
7 - MODULE LOCK TABS (3)
Fig. 19 Fuel Pump ModuleÐ26 or 34 Gallon Fuel
Tank
1 - FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - FUEL SUPPLY FITTING
3 - REAR FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE
4 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
6 - FRONT FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE
7 - LOCKNUT
Fig. 20 Fuel Pump ModuleÐ35 Gallon Fuel Tank
1 - FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - FUEL SUPPLY FITTING
3 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
4 - LOCKNUT
5 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
6 - AUXILIARY CAPPED FITTING
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 13
FUEL PUMP MODULE (Continued)
Page 1318 of 2255

Attach end of special test hose tool number 6541,
6539, 6631 or 6923 at fuel rail disconnection (tool
number will depend on model and/or engine applica-
tion). Position opposite end of this hose tool to an
approved gasoline draining station. Activate fuel
pump and drain tank until empty.
If electric fuel pump is not operating, tank must be
lowered for fuel draining. Refer to following proce-
dures.
(1) Remove fuel tank filler tube cap.
(2) Perform Fuel System Pressure Release proce-
dure as described in this group.
(3) Gasoline Engines: Disconnect negative battery
cable at battery. Diesel Engines: Disconnect both neg-
ative battery cables at both batteries.
(4) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(5) Certain models are equipped with a separate
grounding wire (strap) connecting the fuel fill tube
assembly to the body. Disconnect wire by removing
screw.
(6) Open fuel fill door and remove screws mount-
ing fuel filler tube assembly to body. Do not discon-
nect rubber fuel fill or vent hoses from tank at this
time.
(7) Place a transmission jack under center of fuel
tank. Apply a slight amount of pressure to fuel tank
with transmission jack.
(8) Remove fuel tank mounting strap nuts from
mounting strap studs (Fig. 32). If equipped, remove
fuel tank shield bolts.
(9) Lower fuel tank only enough to allow access to
top of tank. The 2 tank fittings (where rubber fuel fill
and vent hose connections are made) must be posi-
tioned above tank level. Rotate tank slightly to allow
these fittings to be above tank level.
WARNING: WRAP SHOP TOWELS AROUND HOSES
TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(10) While working over left rear tire/wheel, dis-
connect rubber fuel vent hose at fuel tank (Fig. 32)
(vent hose is the smallest of 2 hoses). Position fuel
siphoning/drain hose into this fitting at tank. Drain
fuel into an approved portable holding tank or a
properly labeled gasoline (or diesel fuel) safety con-
tainer.
(11) Disconnect rubber fuel fill hose at fuel tank
(Fig. 32).
(12)Gas Powered Engines:
(a) While working over left rear tire/wheel, dis-
connect wiring harness connector from electrical
connector at top of fuel pump module (Fig. 33) or
(Fig. 34).
(b) If equipped with 26 or 34 gallon fuel tank,
two EVAP lines are connected to the fuel tank
check valves. Disconnect EVAP line from check
valve at top of module (Fig. 33). Disconnect otherEVAP line from check valve near rear of tank (Fig.
33).
(c) If equipped with 35 gallon fuel tank, two
EVAP lines are connected to the fuel tank check
valves. Disconnect EVAP lines from check valves at
top-front and top-rear of fuel tank (Fig. 35).
(d) Disconnect fuel supply line at fuel filter/fuel
pressure regulator supply fitting (Fig. 33) or (Fig.
34). Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings for proce-
dures.
(13)Diesel Powered Engines:
(a) While working over left rear tire/wheel, dis-
connect wiring harness connector from electrical
connector at top of fuel tank module (Fig. 36).
(b) Disconnect fuel supply and fuel return lines
at the fuel tank module fittings (Fig. 36). Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings for procedures.
(14) Gasoline Engines: If fuel pump module
removal is necessary, refer to Fuel Pump Module
Removal/Installation in this group. Diesel Engines: If
fuel tank module removal is necessary, refer to Fuel
Tank Module Removal/Installation in this group.
Fig. 32 Fuel Tank MountingÐTypical
1 - STRAP MOUNTING STUDS (AT FRAME)
2 - FUEL FILL HOSE
3 - FUEL VENT HOSE
4 - STRAP MOUNTING NUTS (2)
5 - FUEL TANK STRAPS (2)
6 - FUEL TANK
7 - CLAMPS
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 19
FUEL TANK (Continued)
Page 1321 of 2255
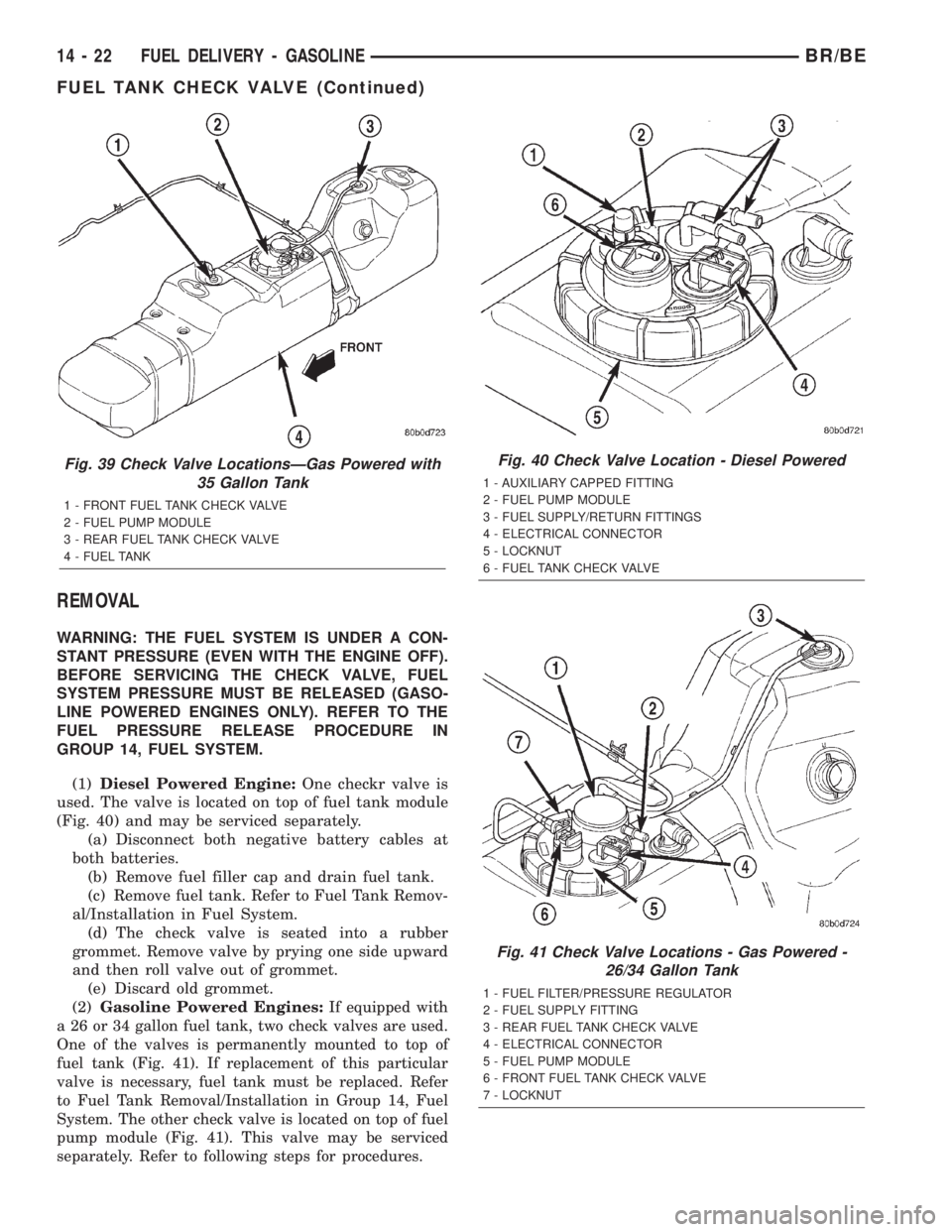
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING THE CHECK VALVE, FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED (GASO-
LINE POWERED ENGINES ONLY). REFER TO THE
FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
GROUP 14, FUEL SYSTEM.
(1)Diesel Powered Engine:One checkr valve is
used. The valve is located on top of fuel tank module
(Fig. 40) and may be serviced separately.
(a) Disconnect both negative battery cables at
both batteries.
(b) Remove fuel filler cap and drain fuel tank.
(c) Remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Remov-
al/Installation in Fuel System.
(d) The check valve is seated into a rubber
grommet. Remove valve by prying one side upward
and then roll valve out of grommet.
(e) Discard old grommet.
(2)Gasoline Powered Engines:
If equipped with
a 26 or 34 gallon fuel tank, two check valves are used.
One of the valves is permanently mounted to top of
fuel tank (Fig. 41). If replacement of this particular
valve is necessary, fuel tank must be replaced. Refer
to Fuel Tank Removal/Installation in Group 14, Fuel
System. The other check valve is located on top of fuel
pump module (Fig. 41). This valve may be serviced
separately. Refer to following steps for procedures.
Fig. 39 Check Valve LocationsÐGas Powered with
35 Gallon Tank
1 - FRONT FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE
2 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
3 - REAR FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE
4 - FUEL TANK
Fig. 40 Check Valve Location - Diesel Powered
1 - AUXILIARY CAPPED FITTING
2 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
3 - FUEL SUPPLY/RETURN FITTINGS
4 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - LOCKNUT
6 - FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE
Fig. 41 Check Valve Locations - Gas Powered -
26/34 Gallon Tank
1 - FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - FUEL SUPPLY FITTING
3 - REAR FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE
4 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
6 - FRONT FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE
7 - LOCKNUT
14 - 22 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL TANK CHECK VALVE (Continued)