service schedule DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY 2001 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: TOWN AND COUNTRY, Model: DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY 2001Pages: 2321, PDF Size: 68.09 MB
Page 42 of 2321

LUBRICANTS AND GREASES
Lubricating grease is rated for quality and usage
by the NLGI. All approved products have the NLGI
symbol (Fig. 4) on the label. At the bottom NLGI
symbol is the usage and quality identification letters.
Wheel bearing lubricant is identified by the letter
ªGº. Chassis lubricant is identified by the latter ªLº.
The letter following the usage letter indicates the
quality of the lubricant. The following symbols indi-
cate the highest quality.
SPECIALIZED LUBRICANTS AND OILS
Some maintenance or repair procedures may
require the use of specialized lubricants or oils. Con-
sult the appropriate sections in this manual for the
correct application of these lubricants.
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COOLANT
WARNING: ANTIFREEZE IS AN ETHYLENE GLYCOL
BASE COOLANT AND IS HARMFUL IF SWAL-
LOWED OR INHALED. IF SWALLOWED, DRINK
TWO GLASSES OF WATER AND INDUCE VOMIT-
ING. IF INHALED, MOVE TO FRESH AIR AREA.
SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION IMMEDIATELY. DO NOT
STORE IN OPEN OR UNMARKED CONTAINERS.
WASH SKIN AND CLOTHING THOROUGHLY AFTER
COMING IN CONTACT WITH ETHYLENE GLYCOL.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN. DISPOSE OF
GLYCOL BASE COOLANT PROPERLY, CONTACT
YOUR DEALER OR GOVERNMENT AGENCY FOR
LOCATION OF COLLECTION CENTER IN YOUR
AREA. DO NOT OPEN A COOLING SYSTEM WHEN
THE ENGINE IS AT OPERATING TEMPERATURE OR
HOT UNDER PRESSURE, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT. AVOID RADIATOR COOLING FAN WHEN
ENGINE COMPARTMENT RELATED SERVICE IS
PERFORMED, PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: Use of Propylene Glycol based coolants
is not recommended, as they provide less freeze
protection and less boiling protection.The cooling system is designed around the coolant.
The coolant must accept heat from engine metal, in
the cylinder head area near the exhaust valves and
engine block. Then coolant carries the heat to the
radiator where the tube/fin radiator can transfer the
heat to the air.
The use of aluminum cylinder blocks, cylinder
heads, and water pumps requires special corrosion
protection. MopartAntifreeze/Coolant, 5
Year/100,000 Mile Formula (MS-9769), or the equiva-
lent ethylene glycol base coolant with hybrid organic
corrosion inhibitors (called HOAT, for Hybrid Organic
Additive Technology) is recommended. This coolant
offers the best engine cooling without corrosion when
mixed with 50% Ethylene Glycol and 50% distilled
water to obtain a freeze point of -37ÉC (-35ÉF). If it
loses color or becomes contaminated, drain, flush,
and replace with fresh properly mixed coolant solu-
tion.
The green coolantMUST NOT BE MIXEDwith
the orange or magenta coolants. When replacing cool-
ant the complete system flush must be performed
before using the replacement coolant.
CAUTION: MoparTAntifreeze/Coolant, 5
Year/100,000 Mile Formula (MS-9769) may not be
mixed with any other type of antifreeze. Doing so
will reduce the corrosion protection and may result
in premature water pump seal failure. If non-HOAT
coolant is introduced into the cooling system in an
emergency, it should be replaced with the specified
coolant as soon as possible.DESCRIPTION - AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
FLUID
NOTE: Refer to the maintenance schedules for the
recommended maintenance (fluid/filter change)
intervals for this transaxle.
NOTE: For fluid level checking procedures, (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
31TH/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
NOTE: The 31TH transaxle has a common transmis-
sion and differential sump. Filling the transaxle
accommodates the differential as well.
TRANSMISSION FLUID
MopartATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid-
Type 9602) is required in this transaxle. Substitute
fluids can induce torque converter clutch shudder.
Fig. 4 NLGI Symbol
1 - WHEEL BEARINGS
2 - CHASSIS LUBRICATION
3 - CHASSIS AND WHEEL BEARINGS
RGLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE - RG - 2.5 L TURBO DIESEL0a-3
FLUID TYPES (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 44 of 2321

FLUID FILL/CHECK
LOCATIONS
DESCRIPTION
The fluid check/fill points and lubrication locations
are located in each applicable service manual section.
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES - DIESEL ENGINE
There are two maintenance schedules that show
proper service for the vehicle.
First is ScheduleªAº. It lists all the scheduled
maintenance to be performed under ªnormalº operat-
ing conditions.
Second is ScheduleªBº. It is a schedule for vehi-
cles that are operated under the conditions listed at
the beginning of the schedule.
Use the schedule that best describes the driving
conditions.
Where time and mileage are listed, follow the
interval that occurs first.
At Each Stop for Fuel
²Check the engine oil level, add as required.
²Check the windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
Once a Month
²Check the tire pressure and look for unusual
wear or damage.
²Inspect the battery and clean and tighten termi-
nals as required.
²Check the fluid levels of coolant reservoir, brake
master cylinder, power steering and transaxle and
add as needed.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
²Check the rubber seals on each side of the radi-
ator for proper fit.
At Each Oil Change
²Replace the engine oil filter at each oil change.
²Inspect exhaust system.
²Inspect brake hoses
²Inspect the CV joints and front suspension com-
ponents
²Rotate the tires at each oil change interval
shown on schedule ªAº 20 000 km or every other
interval shown on schedule ªBº 20 000 km.
²Check the coolant level, hoses, and clamps.
²Inspect brake linings, hoses and calipers.
²Inspect engine accessory drive belts.
²Inspect for presence of water in fuel filter/water
separator, drain if necessary.
SCHEDULE ªAº
20 000 km (12 000 miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element. Replace as necessary.
40 000 km (24 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
60 000 km (37 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element. Replace as necessary.
80 000 km (49 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
100 000 km (62 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element. Replace as necessary.
120 000 km (75 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
140 000 km (86 000 miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element. Replace as necessary.
Fig. 6 Engine Oil Viscosity Recommendation ±
Diesel Engines
RGLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE - RG - 2.5 L TURBO DIESEL0a-5
FLUID TYPES (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 45 of 2321

160 000 km (100 000 miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
²Flush and replace engine coolant. (3)
180 000 km (110 000 miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element. Replace as necessary.
IMPORTANT: Inspection and service should also
be performed any time a malfunction is observed or
suspected. Retain all receipts.
²Change oil every 12 months regardless of mile-
age.
²The fuel filter/water separator element should
be replaced once a year if the vehicle is driven less
than 40 000 km annually or if power loss from fuel
starvation is detected.
²
Flush and replace engine coolant every 60 months
even if the vehicle is driven less than 160 000 km.
SCHEDULE ªBº
Follow this schedule if the vehicle is operated
under one or more of the following conditions.
²Day or night temperatures are below 0É C
(32É F).
²Stop and go driving.
²Extensive engine idling.
²Driving in dusty conditions.
²Short trips of less than 16.2 km (10 miles).
²More than 50% of driving is at sustained high
speeds during hot weather, above 32É C (90É F).
²Trailer towing.
²Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).
10 000 km (6 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element.
20 000 km (12 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
30 000 km (18 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element.
40 000 km (24 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
²Change manual transaxle fluid.
50 000 km (31 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element.
60 000 km (37 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
70 000 km (43 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element.
80 000 km (49 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
²Change manual transaxle fluid.
90 000 km (55 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element.
100 000 km (62 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
110 000 km (68 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect air filter element.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element. (2)
²Check alignment.
120 000 km (74 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Change manual transaxle fluid.
130 000 km (80 000 Miles)
²Change engine oil. (1)
²Replace engine oil filter.
0a - 6 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE - RG - 2.5 L TURBO DIESELRG
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 285 of 2321

A refractometer will test the amount of glycol in a
coolant mixture by measuring the amount a beam of
light bends as it passes through the fluid.
Some coolant manufactures use other types of gly-
cols into their coolant formulations. Propylene glycol
is the most common new coolant. However, propylene
glycol based coolants do not provide the same freez-
ing protection and corrosion protection and is not rec-
ommended.
CAUTION: Do not mix types of coolantÐcorrosion
protection will be severely reduced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT SERVICE
For engine coolant recommended service schedule,
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAIN-
TENANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION).
COOLANT RECOVERY
CONTAINER
DESCRIPTION
The coolant recovery/reserve system container is
mounted in the engine compartment (Fig. 2). The
container is made of plastic.
OPERATION
The coolant recovery system works with the radia-
tor pressure cap to use thermal expansion and con-
traction of the coolant to keep the coolant free of
trapped air. Provides a convenient and safe method
for checking coolant level and adjusting level at
atmospheric pressure without removing the radiator
pressure cap. It also provides some reserve coolant to
cover deaeration, evaporation, or boiling losses.
Fig. 1 Temperature Gauge Indications
7 - 18 ENGINERS
COOLANT (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 322 of 2321

100 Percent Ethylene-GlycolÐShould Not Be Used in
Chrysler Vehicles
Use of 100 percent ethylene-glycol will cause for-
mation of additive deposits in the system, as the cor-
rosion inhibitive additives in ethylene-glycol require
the presence of water to dissolve. The deposits act as
insulation, causing temperatures to rise to as high as
149 deg. C (300 deg. F). This temperature is hot
enough to melt plastic and soften solder. The
increased temperature can result in engine detona-
tion. In addition, 100 percent ethylene-glycol freezes
at -22 deg. C (-8 deg. F ).
Propylene-glycol FormulationsÐShould Not Be Used in
Chrysler Vehicles
Propylene-glycol formulations do not meet
Chrysler coolant specifications.It's overall effec-
tive temperature range is smaller than that of ethyl-
ene-glycol. The freeze point of 50/50 propylene-glycol
and water is -32 deg. C (-26 deg. F). 5 deg. C higher
than ethylene-glycol's freeze point. The boiling point
(protection against summer boil-over) of propylene-
glycol is 125 deg. C (257 deg.F)at96.5 kPa (14 psi),
compared to 128 deg. C (263 deg. F) for ethylene-gly-
col. Use of propylene-glycol can result in boil-over or
freeze-up in Chrysler vehicles, which are designed for
ethylene-glycol. Propylene glycol also has poorer heat
transfer characteristics than ethylene glycol. This
can increase cylinder head temperatures under cer-
tain conditions.
Propylene-glycol/Ethylene-glycol MixturesÐShould Not Be
Used in Chrysler Vehicles
Propylene-glycol/ethylene-glycol Mixtures can
cause the destabilization of various corrosion inhibi-
tors, causing damage to the various cooling system
components. Also, once ethylene-glycol and propy-
lene-glycol based coolants are mixed in the vehicle,
conventional methods of determining freeze point will
not be accurate. Both the refractive index and spe-
cific gravity differ between ethylene glycol and propy-
lene glycol.
CAUTION: Richer antifreeze mixtures cannot be
measured with normal field equipment and can
cause problems associated with 100 percent ethyl-
ene-glycol.DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLANT
CONCENTRATION TESTING
Coolant concentration should be checked when any
additional coolant was added to system or after a
coolant drain, flush and refill. The coolant mixture
offers optimum engine cooling and protection against
corrosion when mixed to a freeze point of -37ÉC
(-34ÉF) to -59ÉC (-50ÉF). The use of a hydrometer or a
refractometer can be used to test coolant concentra-
tion.
A hydrometer will test the amount of glycol in a
mixture by measuring the specific gravity of the mix-
ture. The higher the concentration of ethylene glycol,
the larger the number of balls that will float, and
higher the freeze protection (up to a maximum of
60% by volume glycol).
A refractometer will test the amount of glycol in a
coolant mixture by measuring the amount a beam of
light bends as it passes through the fluid.
Some coolant manufactures use other types of gly-
cols into their coolant formulations. Propylene glycol
is the most common new coolant. However, propylene
glycol based coolants do not provide the same freez-
ing protection and corrosion protection and is not rec-
ommended.
CAUTION: Do not mix types of coolantÐcorrosion
protection will be severely reduced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT SERVICE
For engine coolant recommended service schedule,
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAIN-
TENANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ADDING
ADDITIONAL COOLANT
The pressure/vent cap should not be removed
from the coolant recovery pressure container.
When additional coolant is needed to maintain this
level, it should be added to the coolant recovery pres-
sure container (Fig. 1). Use only 50/50 mix of ethyl-
ene glycol type antifreeze and distilled water. For the
recommeded antifreeze/coolant type (Refer to LUBRI-
CATION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
CAUTION: Do not use well water, or suspect water
supply in cooling system. A 50/50 ethylene glycol
and distilled water mix is recommended. For the
recommeded antifreeze/coolant type (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
RGENGINE7a-15
COOLANT (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 389 of 2321

BATTERY SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
A single 12-volt battery system is standard factory-
installed equipment on this model. All of the compo-
nents of the battery system are located within the
engine compartment of the vehicle. The service infor-
mation for the battery system in this vehicle covers
the following related components, which are covered
in further detail elsewhere in this service manual:
²Battery- The storage battery provides a reli-
able means of storing a renewable source of electrical
energy within the vehicle.
²Battery Cable- The battery cables connect the
battery terminal posts to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem.
²Battery Holddown- The battery holddown
hardware secures the battery in the battery tray in
the engine compartment.
²Battery Thermoguard- The battery thermo-
guard insulates the battery to protect it from engine
compartment temperature extremes.
²Battery Tray- The battery tray provides a
secure mounting location in the vehicle for the bat-
tery and an anchor point for the battery holddown
hardware.
For battery system maintenance schedules and
jump starting procedures, see the owner's manual in
the vehicle glove box. Optionally, refer to Lubrication
and Maintanance for the recommended battery main-
tenance schedules and for the proper battery jump
starting procedures. While battery charging can be
considered a maintenance procedure, the battery
charging procedures and related information are
located in the standard procedures section of this ser-
vice manual. This was done because the battery must
be fully-charged before any battery system diagnosis
or testing procedures can be performed. Refer to
Standard procedures for the proper battery charging
procedures.
OPERATION
The battery system is designed to provide a safe,
efficient, reliable and mobile means of delivering and
storing electrical energy. This electrical energy is
required to operate the engine starting system, as
well as to operate many of the other vehicle acces-sory systems for limited durations while the engine
and/or the charging system are not operating. The
battery system is also designed to provide a reserve
of electrical energy to supplement the charging sys-
tem for short durations while the engine is running
and the electrical current demands of the vehicle
exceed the output of the charging system. In addition
to delivering, and storing electrical energy for the
vehicle, the battery system serves as a capacitor and
voltage stabilizer for the vehicle electrical system. It
absorbs most abnormal or transient voltages caused
by the switching of any of the electrical components
or circuits in the vehicle.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY SYSTEM
The battery, starting, and charging systems in the
vehicle operate with one another and must be tested
as a single complete system. In order for the engine
to start and the battery to charge properly, all of the
components that are used in these systems must per-
form within specifications. It is important that the
battery, starting, and charging systems be thoroughly
tested and inspected any time a battery needs to be
charged or replaced. The cause of abnormal battery
discharge, overcharging or early battery failure must
be diagnosed and corrected before a battery is
replaced and before a vehicle is returned to service.
The service information for these systems has been
separated within this service manual to make it eas-
ier to locate the specific information you are seeking.
However, when attempting to diagnose any of these
systems, it is important that you keep their interde-
pendency in mind.
The diagnostic procedures used for the battery,
starting, and charging systems include the most
basic conventional diagnostic methods, to the more
sophisticated On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) built into
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Use of an
induction-type milliampere ammeter, a volt/ohmme-
ter, a battery charger, a carbon pile rheostat (load
tester) and a 12-volt test lamp may be required. All
OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in elec-
tronic memory for any failure it detects. Refer to
Charging System for the proper charging system on-
board diagnostic test procedures.
8F - 2 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 392 of 2321
²A faulty or incorrect starting system component.
Refer to Starting System for the proper starting sys-
tem diagnosis and testing procedures.
²A faulty or incorrect battery. Refer to Standard
Procedures for the proper battery diagnosis and test-
ing procedures. Refer to Battery System Specifica-
tions for the proper specifications.
CLEANING
The following information details the recommended
cleaning procedures for the battery and related com-
ponents. In addition to the maintenance schedules
found in this service manual and the owner's man-
ual, it is recommended that these procedures be per-
formed any time the battery or related components
must be removed for vehicle service.
(1) Clean the battery cable terminal clamps of all
corrosion. Remove any corrosion using a wire brush
or a post and terminal cleaning tool, and a sodium
bicarbonate (baking soda) and warm water cleaning
solution (Fig. 1).
(2) Clean the battery tray and battery holddown
hardware of all corrosion. Remove any corrosion
using a wire brush and a sodium bicarbonate (baking
soda) and warm water cleaning solution. Paint any
exposed bare metal.
(3) If the removed battery is to be reinstalled,
clean the outside of the battery case and the top
cover with a sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) and
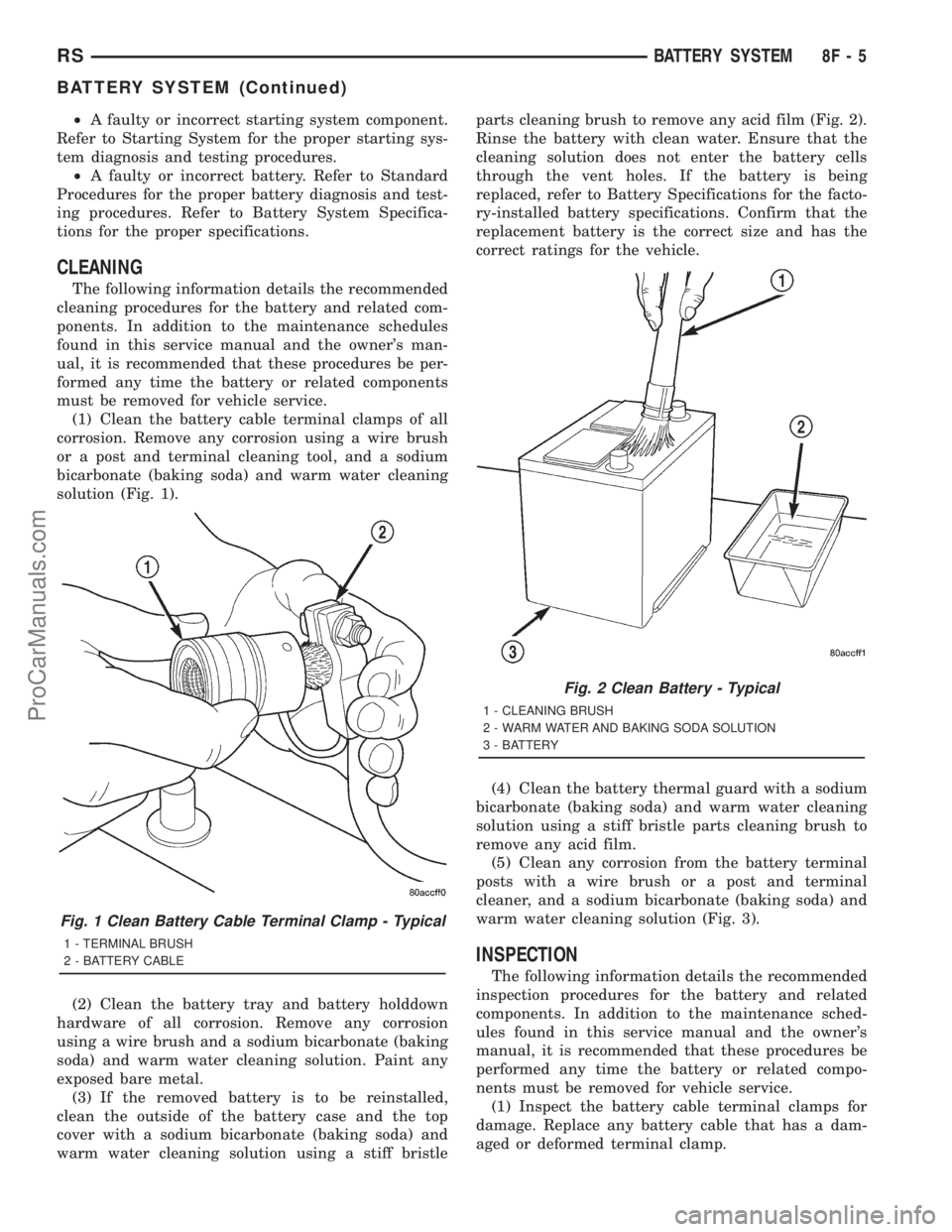
warm water cleaning solution using a stiff bristleparts cleaning brush to remove any acid film (Fig. 2).
Rinse the battery with clean water. Ensure that the
cleaning solution does not enter the battery cells
through the vent holes. If the battery is being
replaced, refer to Battery Specifications for the facto-
ry-installed battery specifications. Confirm that the
replacement battery is the correct size and has the
correct ratings for the vehicle.
(4) Clean the battery thermal guard with a sodium
bicarbonate (baking soda) and warm water cleaning
solution using a stiff bristle parts cleaning brush to
remove any acid film.
(5) Clean any corrosion from the battery terminal
posts with a wire brush or a post and terminal
cleaner, and a sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) and
warm water cleaning solution (Fig. 3).
INSPECTION
The following information details the recommended
inspection procedures for the battery and related
components. In addition to the maintenance sched-
ules found in this service manual and the owner's
manual, it is recommended that these procedures be
performed any time the battery or related compo-
nents must be removed for vehicle service.
(1) Inspect the battery cable terminal clamps for
damage. Replace any battery cable that has a dam-
aged or deformed terminal clamp.
Fig. 1 Clean Battery Cable Terminal Clamp - Typical
1 - TERMINAL BRUSH
2 - BATTERY CABLE
Fig. 2 Clean Battery - Typical
1 - CLEANING BRUSH
2 - WARM WATER AND BAKING SODA SOLUTION
3 - BATTERY
RSBATTERY SYSTEM8F-5
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 457 of 2321

INSTALLATION - 2.4L
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in front of the starter (Fig. 13).
(1) Install knock sensor. Tighten knock sensor to
10 N´m (7 ft. lbs.) torque.Over or under tighten-
ing effects knock sensor performance, possibly
causing improper spark control.
(2) Attach electrical connector to knock sensor.
INSTALLATION - 3.8L
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in the rear.
(1) Install knock sensor. Tighten knock sensor to
10 N´m (7 ft. lbs.) torque.Over or under tighten-
ing effects knock sensor performance, possibly
causing improper spark control.
(2) Attach electrical connector to knock sensor.
(3) On All Wheel Drive vehicles install the PTU
(Power Transfer Unit) for the rear wheels, refer to
the Transmission section for more information.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect the negative cable.
SPARK PLUG
DESCRIPTION - STANDARD 2.4L
All engines use resistor spark plugs. They have
resistance values ranging from 6,000 to 20,000 ohms
when checked with at least a 1000 volt spark plug
tester.
Do not use an ohm meter to check the resis-
tance of the spark plugs. This will give an inac-
curate reading.
Refer to the Specifications section for gap and type
of spark plug.
DESCRIPTION - PLATINUM 3.3/3.8L
These engines utilize platinum spark plugs. Refer
to the maintenance schedule.
All engines use resistor spark plugs. They have
resistance values ranging from 6,000 to 20,000 ohms
when checked with at least a 1000 volt spark plug
tester.
Do not use an ohm meter to check the resis-
tance of the spark plugs. This will give an inac-
curate reading.
The spark plugs are double platinum and have a
recommended service life of 100,000 miles for normal
driving conditions per schedule A in this manual. The
spark plugs have a recommended service life of
75,000 miles for severe driving conditions per sched-
ule B in this manual. A thin platinum pad is welded
to both electrode ends as show in (Fig. 14). Extreme
care must be used to prevent spark plug cross
threading, mis-gaping and ceramic insulator damage
during plug removal and installation.
Fig. 13 Knock Sensor
1 - GENERATOR
2 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
3 - KNOCK SENSOR
4-STARTER
Fig. 14 Platinum Pads
1 - APPLY ANTI-SEIZE COMPOUND HERE ONLY
2 - PLATINUM SPARK SURFACE
8I - 8 IGNITION CONTROLRS
KNOCK SENSOR (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1407 of 2321

The fuel filter is replaceable, it is mounted on the
outside and on top of the fuel tank. Refer to the
Maintenance Schedules in the Introduction section of
this manual for recommended fuel filter replacement
intervals.
FFV REPLACEMENT PARTS
Many components in a Flexible Fuel Vehicle (FFV)
are designed to be compatible with ethanol. Always
be sure that the vehicle is serviced with correct etha-
nol compatible parts.
CAUTION: Replacing fuel system components with
non-ethanol compatible components can damage
your vehicle and may void the warranty.
OPERATION
The fuel system is provided fuel pressure by an in-
tank pump module. The PCM controls the operation
of the fuel system by providing battery voltage to the
fuel pump through the fuel pump relay. The PCM
requires only three inputs and a good ground to oper-
ate the fuel pump relay. The three inputs are:
²Ignition voltage
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL DELIVERY
SYSTEM
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnositic Information)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE
(1) Remove Fuel Pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.(2) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(3) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(4) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
(5) Place a rag or towel below fuel line quick-con-
nect fitting at fuel rail.
(6) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(7) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRB IIItscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING FUEL
TANK
(1) Release fuel system pressure, refer to the Fuel
System Release Procedure in this section.
(2) Insert a 1/4 inch siphon (max. O. D. 5/16) hose
from a portable fuel siphoning tank through the fuel
filler neck opening into the fuel tank. Hose most
have a 30 degree angle cut on the end to bypass the
check valve in the end of the filler neck. Refer to the
siphoning tank's Manufacturing Instructions.
(3) Drain fuel from fuel tank into siphoning tank.
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
400 kpa634 kpa (58 psi65 psi)
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fuel Rail 2.4L 22 200
Fuel Rail 3.3/3.8L 11.8 105
Fuel Tank Strap 54 40
Fuel Tank T Strap 28.2 250
Fuel Filter Bolt 4.5 40
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERYRS
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1501 of 2321

(transmission fluid) this indicates that the Transmis-
sion differential carrier seal should be replaced. If
the fluid leaking is light brown (gear lube) this indi-
cates that the Power Transfer Unit input seal should
be replaced. For replacement of these seals refer to
Power Transfer Unit Service Procedures.
If fluid is leaking from weep hole B (Fig. 5) the
type of fluid leaking will determine which seal is
leaking. If the fluid leaking is red in color (transmis-
sion fluid) this indicates that the input shaft end seal
should be replaced. If the fluid leaking is light brown
(gear lube) this indicates that the half shaft innerseal and P.T.U. input shaft cover seal should be
replaced. For replacement of these seals refer to
Power Transfer Unit Service Procedures.
Before condemning any seal or gasket be sure that
the rear rocker arm cover on the engine is not the
cause of the oil leak. Oil leaking from the rocker arm
cover is easily mistaken for a leaking Power Transfer
Unit.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
INSPECTION
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove PTU inspection plug (Fig. 6).
(3) Fluid level should be within 3/16º from bottom
of inspection hole. Add Moparž Gear and Axle Lubri-
cant 80W-90 as necessary with suitable suction gun
(Fig. 7).
(4) Install inspection plug and torque to 20 N´m
(180 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Lower vehicle.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PTU FLUID CHANGE
NOTE: PTU Fluid should be changed upon servic-
ing the unit, or at the unit's regular scheduled inter-
val. (Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION)
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove PTU inspection plug (Fig. 8).
Fig. 3 Seal Location
1 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - OUTPUT SHAFT
3 - REAR COVER
4 - P.T.U. CASE
5 - INPUT SHAFT SEAL
Fig. 4 Seal Location
1 - P.T.U. INPUT SHAFT COVER SEAL
2 - HALF SHAFT INNER SEAL
3 - INSIDE VIEW OF P.T.U. END COVER
Fig. 5 Weep Hole Locations
1 - ENGINE OIL PAN
2 - WEEP HOLE ªAº
3 - TRANSAXLE CASE
4 - P.T.U.
5 - WEEP HOLE ªBº
21 - 4 POWER TRANSFER UNITRS
POWER TRANSFER UNIT (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com