oil type DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY 2003 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2003, Model line: TOWN AND COUNTRY, Model: DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY 2003Pages: 2177, PDF Size: 59.81 MB
Page 1451 of 2177

If fluid is leaking from weep hole B (Fig. 5) the
type of fluid leaking will determine which seal is
leaking. If the fluid leaking is red in color (transmis-
sion fluid) this indicates that the input shaft end seal
should be replaced. If the fluid leaking is light brown
(gear lube) this indicates that the half shaft inner
seal and P.T.U. input shaft cover seal should be
replaced. For replacement of these seals refer to
Power Transfer Unit Service Procedures.
Before condemning any seal or gasket be sure that
the rear rocker arm cover on the engine is not the
cause of the oil leak. Oil leaking from the rocker arm
cover is easily mistaken for a leaking Power Transfer
Unit.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
INSPECTION
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove PTU inspection plug (Fig. 6).
Fig. 3 Seal Location
1 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - OUTPUT SHAFT
3 - REAR COVER
4 - P.T.U. CASE
5 - INPUT SHAFT SEAL
Fig. 4 Seal Location
1 - P.T.U. INPUT SHAFT COVER SEAL
2 - HALF SHAFT INNER SEAL
3 - INSIDE VIEW OF P.T.U. END COVER
Fig. 5 Weep Hole Locations
1 - ENGINE OIL PAN
2 - WEEP HOLE ªAº
3 - TRANSAXLE CASE
4 - P.T.U.
5 - WEEP HOLE ªBº
Fig. 6 Inspection Plug
1 - INSPECTION PLUG
21 - 4 POWER TRANSFER UNITRS
POWER TRANSFER UNIT (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1503 of 2177
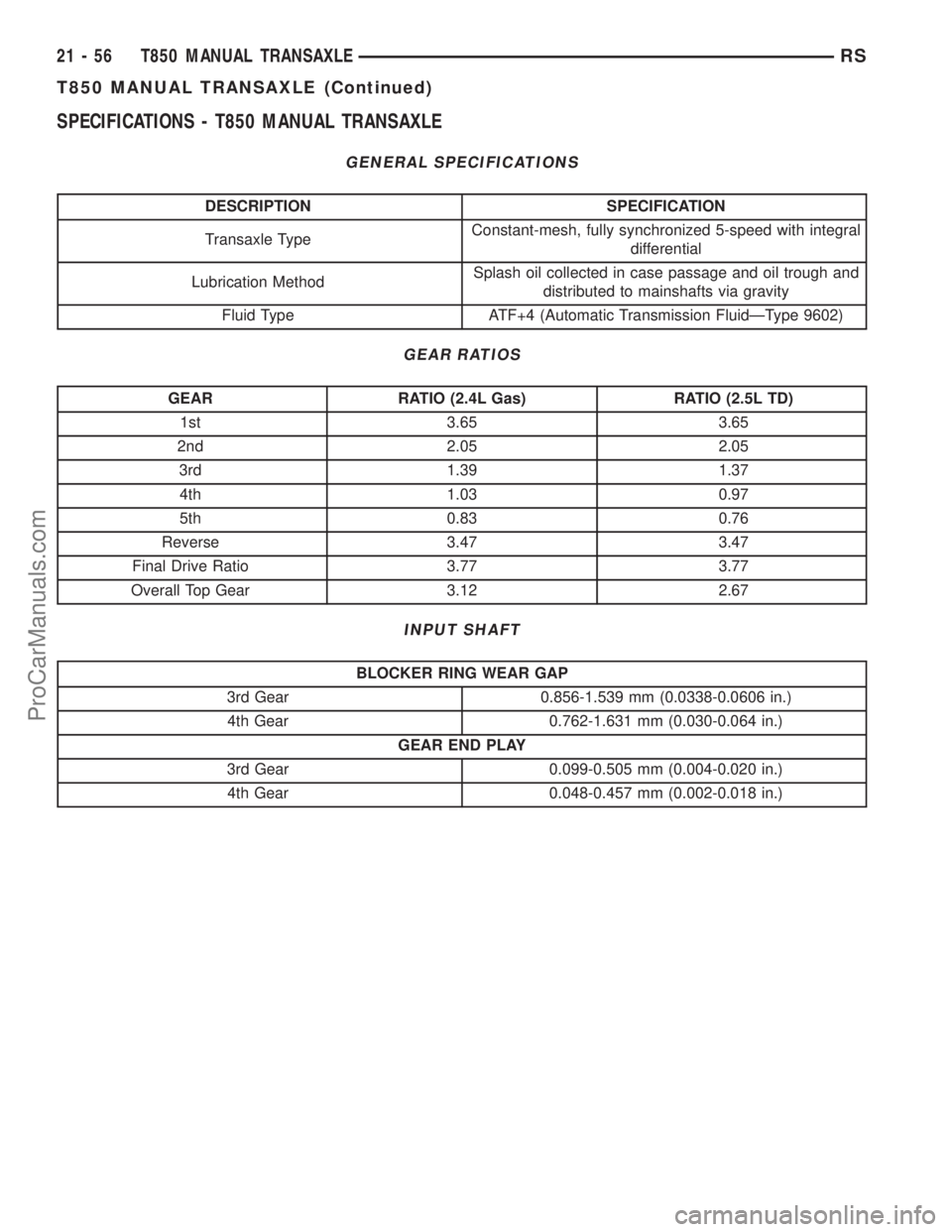
SPECIFICATIONS - T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Transaxle TypeConstant-mesh, fully synchronized 5-speed with integral
differential
Lubrication MethodSplash oil collected in case passage and oil trough and
distributed to mainshafts via gravity
Fluid Type ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission FluidÐType 9602)
GEAR RATIOS
GEAR RATIO (2.4L Gas) RATIO (2.5L TD)
1st 3.65 3.65
2nd 2.05 2.05
3rd 1.39 1.37
4th 1.03 0.97
5th 0.83 0.76
Reverse 3.47 3.47
Final Drive Ratio 3.77 3.77
Overall Top Gear 3.12 2.67
INPUT SHAFT
BLOCKER RING WEAR GAP
3rd Gear 0.856-1.539 mm (0.0338-0.0606 in.)
4th Gear 0.762-1.631 mm (0.030-0.064 in.)
GEAR END PLAY
3rd Gear 0.099-0.505 mm (0.004-0.020 in.)
4th Gear 0.048-0.457 mm (0.002-0.018 in.)
21 - 56 T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLERS
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1615 of 2177

(20) Connect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
(Fig. 166).
(21) Connect transmission range sensor connector
(Fig. 166).
(22) Connect input and output speed sensor con-
nectors (Fig. 166).
(23) Remove plugs and install transaxle oil cooler
line service splice kit. Refer to instructions included
with kit.
(24) Remove plug and Install fluid level indicator/
tube assembly.(25) Install coolant recovery bottle (Fig. 167).
(26) Install battery shield.
(27) Connect battery cables.
(28) Fill transaxle with suitable amount of ATF+4
(Automatic Transmission FluidÐType 9602). (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 166 Component Connector Location - Typical
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY. CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 167 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - UPPER BOLT ATTACHING TO BATTERY TRAY
2 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
3 - UPPER BOLT
4 - HOSE
5 - LOWER BOLT (QTY. 2)
6 - LEFT SIDE FRAME RAIL
21 - 168 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1628 of 2177

SPECIFICATIONS - 41TE TRANSAXLE
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Transaxle TypeFully adaptive, electronically controlled, four speed
automatic with torque converter and integral differential
Cooling Method Air-to-oil heat exchanger
Lubrication Pump (internal-external gear-type
GEAR RATIOS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
First Gear 2.84
Second Gear 1.57
Direct Gear 1.00
Overdrive Gear 0.69
Reverse Gear 2.21
BEARING SETTINGS (END PLAY & TURNING TORQUE)
DESCRIPTION METRIC STANDARD
Differential Assembly 0.6-2 N´m 5-18 in. lbs.
Output Hub 0.3-2 N´m 3-8 in. lbs.
Transfer Shaft (End Play) 0.051-0.102 mm 0.002-0.004 in.
Overall Drag At Output Hub 0.3-1.9 N´m 3-16 in. lbs.
CLUTCH CLEARANCES
DESCRIPTION METRIC STANDARD
Low/Rev Clutch (Select Reaction
Plate)0.89-1.47 mm 0.035-0.058 in.
Two/Four Clutch (No Selection) 0.76-2.64 mm 0.030-0.104 in.
Reverse Clutch (Select Snap Ring) 0.89-1.37 mm 0.035-0.054 in.
Overdrive Clutch (No Selection) 1.07-3.25 mm 0.042-0.128 in.
Underdrive Clutch (Select Pressure
Plate)0.94-1.50 mm 0.037-0.059 in.
OIL PUMP CLEARANCES
DESCRIPTION METRIC STANDARD
Outer Gear-to-Crescent 0.060-0.298 mm 0.0023-0.0117 in.
Inner Gear-to-Crescent 0.093-0.385 mm 0.0036-0.0151 in.
Outer Gear-to-Pocket 0.089-0.202 mm 0.0035-0.0079 in.
Outer Gear Side Clearance 0.020-0.046 mm 0.0008-0.0018 in.
Inner Gear Side Clearance 0.020-0.046 mm 0.0008-0.0018 in.
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 181
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1648 of 2177

PRELOAD ADJUSTMENT W/O SHIM
(1) Remove the bearing cup from the differential
bearing retainer using Miller special Tool 6062A.
(2) Remove existing shim from under bearing cup.
(3) Reinstall the bearing cup into the retainer
using Miller Special Tool 6061, and C-4171.
NOTE: Oil baffle is not required when making the
shim calculation.
(4) Install the bearing retainer into the case.
Torque bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(5) Position the transaxle assembly vertically on
the support stand and install Miller Special Tool
L-4436-A into the bearing retainer.
(6) Rotate the differential at least one full revolu-
tion to ensure the tapered roller bearings are fully
seated.
(7) Attach a dial indicator to the case and zero the
dial. Place the tip on the end of Special Tool
L-4436-A.
(8) Place a large screwdriver to each side of the
ring gear and lift. Check the dial indicator for the
amount of end play.
CAUTION: Do not damage the transaxle case and/or
differential retainer sealing surface.
(9) Using the end play measurement that was
determined, add 0.18mm (0.007 inch). This should
give you between 5-18 inch pounds of bearing pre-
load. Refer to the Differential Bearing Shim Chart to
determine which shim to use.
(10) Remove the differential bearing retainer.
Remove the bearing cup.
(11) Install the oil baffle. Install the proper shim
combination under the bearing cup.
(12) Install the differential bearing retainer. Seal
the retainer to the housing with MopartSilicone
Rubber Adhesive Sealant. Torque bolts to 28 N´m
(250 in. lbs.).
(13) Using Miller Special Tool L-4436-A and an
inch-pound torque wrench, check the turning torque
of the differential (Fig. 208). The turning torque
should be between 5-18 inch-pounds.
NOTE: If turning torque is too high install a 0.05mm
(0.002 inch) thicker shim. If the turning torque is too
low, install a 0.05mm (0.002 inch) thinner shim.
Repeat until 5-18 inch-pounds of turning torque is
obtained.
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK
NOTE: Only transmission fluid of the type labeled
Mopar ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid)
should be used in this transaxle.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
The transmission sump has a fluid level indicator
(dipstick) to check oil similar to most automatic
transmissions. It is located on the left side of the
engine. Be sure to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle
before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P Park and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in P Park
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate.The
engine should be running at idle speed for at
least one minute, with the vehicle on level
ground.At normal operating temperature 82É C
(180É F), the fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT
region on the oil level indicator (Fig. 209). The fluid
level should be within the COLD region of the dip-
stick at 27É C (80É F) fluid temperature.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK USING DRB
NOTE: Engine and Transaxle should be at normal
operating temperature before performing this proce-
dure.
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Hook up DRB scan tool and select transmis-
sion.
Fig. 209 Fluid Level Indicator
1 - FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 201
FINAL DRIVE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1650 of 2177

STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
SERVICE
NOTE: Refer to the maintenance schedules in
LUBRICATION and MAINTENANCE, or the vehicle
owner's manual, for the recommended maintenance
(fluid/filter change) intervals for this transaxle.
NOTE: Only fluids of the type labeled MoparTATF+4
(Automatic Transmission Fluid) should be used. A
filter change should be made at the time of the
transmission oil change. The magnet (on the inside
of the oil pan) should also be cleaned with a clean,
dry cloth.
NOTE: If the transaxle is disassembled for any rea-
son, the fluid and filter should be changed.
FLUID/FILTER SERVICE (RECOMMENDED)
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist. Refer to LUBRICA-
TION and MAINTENANCE for proper procedures.
Place a drain container with a large opening, under
transaxle oil pan.
(2) Loosen pan bolts and tap the pan at one corner
to break it loose allowing fluid to drain, then remove
the oil pan.
(3) Install a new filter and o-ring on bottom of the
valve body (Fig. 211).
(4) Clean the oil pan and magnet. Reinstall pan
using new Mopar Silicone Adhesive sealant. Tighten
oil pan bolts to 19 N´m (165 in. lbs.).(5) Pour four quarts of MopartATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission Fluid) through the dipstick opening.
(6) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position.
(7) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the lowest mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 212).
(8) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.). Refer
to Fluid Level and Condition Check for the proper
fluid fill procedure.
(9) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
DIPSTICK TUBE FLUID SUCTION METHOD
(ALTERNATIVE)
(1) When performing the fluid suction method,
make sure the transaxle is at full operating temper-
ature.
(2) To perform the dipstick tube fluid suction
method, use a suitable fluid suction device (VaculaŸ
or equivalent).
(3) Insert the fluid suction line into the dipstick
tube.
NOTE: Verify that the suction line is inserted to the
lowest point of the transaxle oil pan. This will
ensure complete evacuation of the fluid in the pan.
(4) Follow the manufacturers recommended proce-
dure and evacuate the fluid from the transaxle.
(5) Remove the suction line from the dipstick tube.
Fig. 211 Filter and O-Ring
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - O-RING
Fig. 212 Fluid Level Indicator
1 - FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 203
FLUID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1737 of 2177
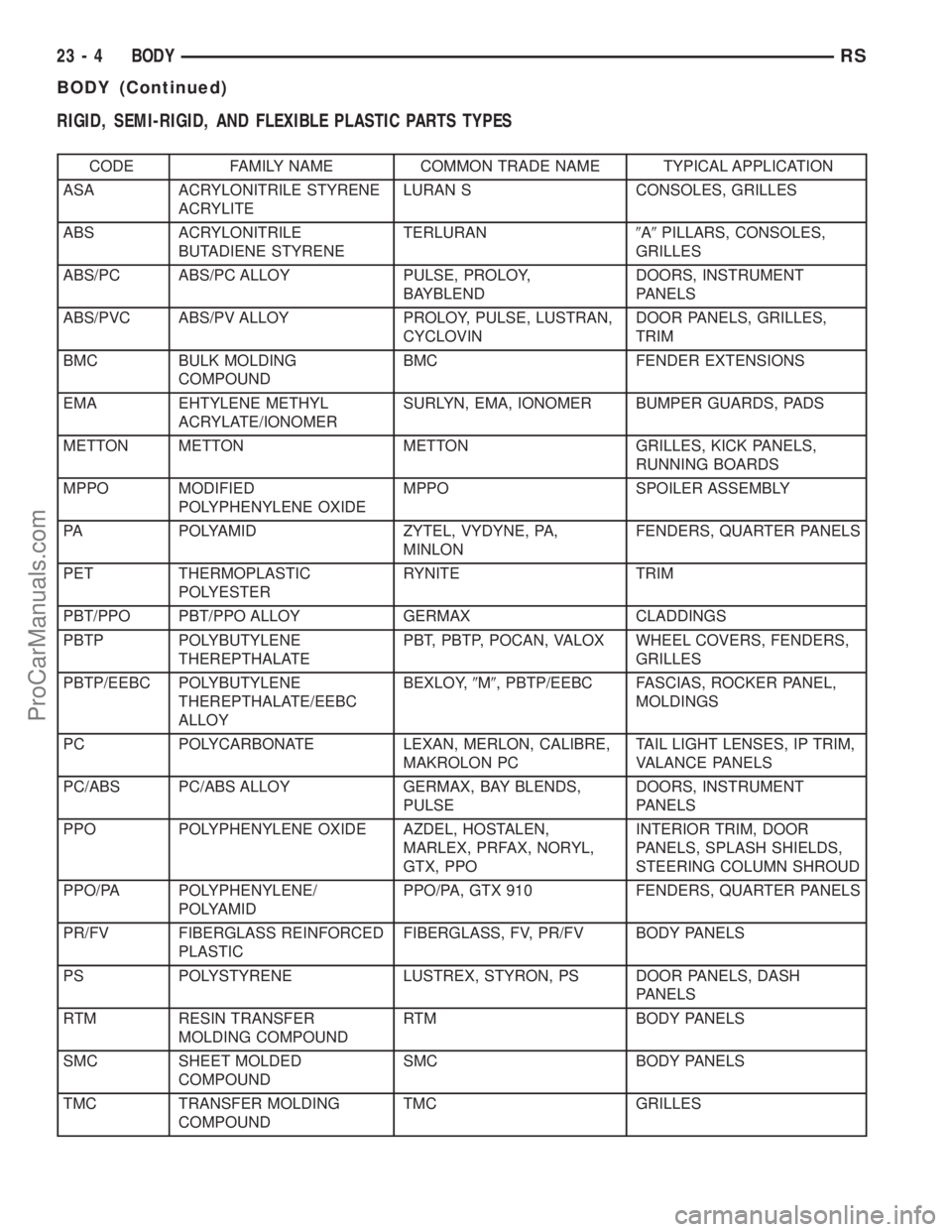
RIGID, SEMI-RIGID, AND FLEXIBLE PLASTIC PARTS TYPES
CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
ASA ACRYLONITRILE STYRENE
ACRYLITELURAN S CONSOLES, GRILLES
ABS ACRYLONITRILE
BUTADIENE STYRENETERLURAN9A9PILLARS, CONSOLES,
GRILLES
ABS/PC ABS/PC ALLOY PULSE, PROLOY,
BAYBLENDDOORS, INSTRUMENT
PANELS
ABS/PVC ABS/PV ALLOY PROLOY, PULSE, LUSTRAN,
CYCLOVINDOOR PANELS, GRILLES,
TRIM
BMC BULK MOLDING
COMPOUNDBMC FENDER EXTENSIONS
EMA EHTYLENE METHYL
ACRYLATE/IONOMERSURLYN, EMA, IONOMER BUMPER GUARDS, PADS
METTON METTON METTON GRILLES, KICK PANELS,
RUNNING BOARDS
MPPO MODIFIED
POLYPHENYLENE OXIDEMPPO SPOILER ASSEMBLY
PA POLYAMID ZYTEL, VYDYNE, PA,
MINLONFENDERS, QUARTER PANELS
PET THERMOPLASTIC
POLYESTERRYNITE TRIM
PBT/PPO PBT/PPO ALLOY GERMAX CLADDINGS
PBTP POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATEPBT, PBTP, POCAN, VALOX WHEEL COVERS, FENDERS,
GRILLES
PBTP/EEBC POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATE/EEBC
ALLOYBEXLOY,9M9, PBTP/EEBC FASCIAS, ROCKER PANEL,
MOLDINGS
PC POLYCARBONATE LEXAN, MERLON, CALIBRE,
MAKROLON PCTAIL LIGHT LENSES, IP TRIM,
VALANCE PANELS
PC/ABS PC/ABS ALLOY GERMAX, BAY BLENDS,
PULSEDOORS, INSTRUMENT
PANELS
PPO POLYPHENYLENE OXIDE AZDEL, HOSTALEN,
MARLEX, PRFAX, NORYL,
GTX, PPOINTERIOR TRIM, DOOR
PANELS, SPLASH SHIELDS,
STEERING COLUMN SHROUD
PPO/PA POLYPHENYLENE/
POLYAMIDPPO/PA, GTX 910 FENDERS, QUARTER PANELS
PR/FV FIBERGLASS REINFORCED
PLASTICFIBERGLASS, FV, PR/FV BODY PANELS
PS POLYSTYRENE LUSTREX, STYRON, PS DOOR PANELS, DASH
PANELS
RTM RESIN TRANSFER
MOLDING COMPOUNDRTM BODY PANELS
SMC SHEET MOLDED
COMPOUNDSMC BODY PANELS
TMC TRANSFER MOLDING
COMPOUNDTMC GRILLES
23 - 4 BODYRS
BODY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1740 of 2177

²Panel repair for both flexible and rigid panels
are basically the same. The primary difference
between flexible panel repair and rigid panel repair
is in the adhesive materials used (Fig. 5).
²The technician should first decide what needs to
be done when working on any type of body panel.
One should determine if it is possible to return the
damage part to its original strength and appearance
without exceeding the value of the replacement part.
²When plastic repairs are required, it is recom-
mended that the part be left on the vehicle when
every possible. That will save time, and the panel
will remain stationary during the repair. Misalign-
ment can cause stress in the repair areas and can
result in future failure.
VISUAL INSPECTION
Composite materials can mask the severity of an
accident. Adhesive bond lines, interior structure of
the doors, and steel structures need to be inspected
carefully to get a true damage assessment. Close
inspection may require partial removal of interior
trim or inner panels.
Identify the type of repair: Puncture or Crack -
Damage that has penetrated completely through the
panel. Damage is confined to one general area; a
panel section is not required. However, a backer
panel, open fiberglass tape, or matted material must
be bonded from behind (Fig. 7) (Fig. 6).
PANEL SURFACE PREPARATION
If a body panel has been punctured, cracked, or
crushed, the damaged area must be removed from
the panel to achieve a successful repair. All spider
web cracks leading away from a damaged area must
be stopped or removed. To stop a running crack in a
panel, drilla6mm(0.250 in.) hole at the end of the
crack farthest away from the damage. If spider web
cracks can not be stopped, the panel would require
replacement. The surfaces around the damaged area
should be stripped of paint and freed from wax and
oil. Scuff surfaces around repair area with 360 grit
wet/dry sandpaper, or equivalent, to assure adhesion
of repair materials.
PATCHING PANELS
An panel that has extensive puncture type damage
can be repaired by cutting out the damaged material
(Fig. 7). Use a suitable reciprocating saw or cut off
wheel to remove the section of the panel that is dam-
aged. The piece cut out can be used as a template to
shape the new patch. It is not necessary to have
access to the back of the panel to install a patch.
Bevel edges of cutout at 20 degrees to expose a larger
bonding area on the outer side. This will allow for an
increased reinforcement areas.
PANEL PATCH FABRICATIONS
A patch can be fabricated from any rigid fiberglass
panel that has comparable contour with the repair
area. Lift gates and fenders can be used to supply
patch material. If existing material is not available
or compatible, a patch can be constructed with adhe-
sive and reinforcement mesh (dry wall tape). Perform
the following operation if required:
Fig. 4 BEVELING ANGLE - 20 DEGREE
Fig. 5 FIBERGLASS TAPE
Fig. 6 DAMAGE COMPONENT
1 - PUNCTURE
RSBODY23-7
BODY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2010 of 2177

conditioner housing. Tighten the screws to 2 N´m (17
in. lbs.).
(6) Reinstall the silencer under the driver side end
of the instrument panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT PANEL
SILENCER - INSTALLATION).
(7) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(8) Perform the heater-A/C control calibration pro-
cedure. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/CONTROLS - FRONT/A/C-HEATER CONTROL
- STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEATER-A/C CON-
TROL CALIBRATION).
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The blower motor relay (Fig. 6) is a International
Standards Organization (ISO) mini-relay. Relays con-
forming to the ISO specifications have common phys-
ical dimensions, current capacities, terminal
patterns, and terminal functions. The ISO mini-relay
terminal functions are the same as a conventional
ISO relay. However, the ISO mini-relay terminal pat-
tern (or footprint) is different, the current capacity is
lower, and the physical dimensions are smaller than
those of the conventional ISO relay. The blower
motor relay is located in the Intelligent Power Mod-
ule (IPM), which is in the engine compartment near
the battery. See the fuse and relay layout map
molded into the inner surface of the IPM cover for
blower motor relay identification and location.The black, molded plastic case is the most visible
component of the blower motor relay. Five male
spade-type terminals extend from the bottom of the
base to connect the relay to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem, and the ISO designation for each terminal is
molded into the base adjacent to each terminal.
OPERATION
The blower motor relay is an electromechanical
switch that uses a low current input from the Front
Control Module (FCM) to control the high current
output to the blower motor resistor (manual heater-
A/C control) or blower power module (ATC control).
The movable common feed contact point is held
against the fixed normally closed contact point by
spring pressure. When the relay coil is energized, an
electromagnetic field is produced by the coil wind-
ings. This electromagnetic field draws the movable
relay contact point away from the fixed normally
closed contact point, and holds it against the fixed
normally open contact point. When the relay coil is
de-energized, spring pressure returns the movable
contact point back against the fixed normally closed
contact point. The resistor or diode is connected in
parallel with the relay coil in the relay, and helps to
dissipate voltage spikes and electromagnetic interfer-
ence that can be generated as the electromagnetic
field of the relay coil collapses.
The blower motor relay terminals are connected to
the vehicle electrical system through a receptacle in
the Intelligent Power Module (IPM). The inputs and
outputs of the blower motor relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from the battery through a B(+)
circuit at all times.
²The coil ground terminal (85) receives a ground
input through the front/rear blower motor relay con-
trol circuit only when the FCM electronically pulls
the control circuit to ground.
²The coil battery terminal (86) receives a battery
current input from the battery through a B(+) circuit
at all times.
²The normally open terminal (87) provides a bat-
tery current output to the blower motor resistor
(manual heater-A/C control) or blower power module
(automatic heater-A/C control) through a fuse in the
IPM on the fused front blower motor relay output cir-
cuit only when the blower motor relay coil is ener-
gized.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is not con-
nected to any circuit in this application, but provides
a battery current output only when the blower motor
relay coil is de-energized.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
Fig. 6 Blower Motor Relay
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
RSCONTROLS - FRONT24-13
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2015 of 2177

(3) Remove the serpentine drive belt. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
2.4L - REMOVAL) or (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCES-
SORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - 3.3/3.8L - REMOV-
AL).
(4) Disconnect the engine wire harness connector
for the compressor clutch coil from the clutch coil pig-
tail wire connector on the top of the compressor.
(5) On models with the 3.3L and 3.8L engines, dis-
engage the retainer on the engine wire harness com-
pressor clutch coil take out from the bracket on the
top of the compressor.
(6) On models with the 2.4L engine, remove all of
the compressor mounting screws except the upper
left (rear of the compressor) screw, which should only
be loosened. Allow the front (pulley end) of the com-
pressor to tilt downward far enough to access the
clutch for removal, then tighten the loosened upper
left compressor mounting screw.
(7) On models with the 3.3L and 3.8L engines,
remove the three screws and one nut that secure the
compressor to the engine. Disengage the mounting
ear at the front of the compressor from the stud on
the engine, allow the front (pulley end) of the com-
pressor to tilt downward far enough to access the
clutch for removal, then reinstall and tighten the
upper left compressor mounting screw.
(8) Remove the compressor shaft bolt (Fig. 12). If
necessary, a band-type oil filter wrench or a strap
wrench can be placed around the clutch plate to aid
in bolt removal.(9) Tap the clutch plate lightly with a plastic ham-
mer and remove the clutch plate and shim(s) from
the compressor shaft (Fig. 13).Be certain not to
lose the shim or shims.
CAUTION: Do not pry between the clutch plate unit
and the pulley to remove the clutch plate from the
compressor shaft as this may damage the clutch
plate.
(10) Using snap ring pliers (Special Tool C-4574 or
equivalent), remove the external snap ring that
secures the pulley to the front cover of the compres-
sor, then slide the pulley off of the compressor (Fig.
14).
(11) Remove the screw that secures the clutch coil
pigtail wire connector bracket and ground clip to the
top of the compressor housing.
(12) Using snap ring pliers (Special Tool C-4574 or
equivalent), remove the external snap ring that
secures the clutch coil to the front cover of the com-
pressor housing, then slide the clutch coil off of the
compressor (Fig. 15).
INSPECTION - COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL
Compressor clutch components should always be
inspected closely before they are reinstalled. The
clutch plate and clutch pulley are mated at the fac-
tory using a burnishing operation. No attempt should
be made to separately replace the compressor clutch
pulley or clutch plate. The clutch coil may be serviced
separately.
(1) Examine the friction surfaces of the clutch pul-
ley and the clutch plate for wear. The clutch pulley
and clutch plate should be replaced if there is exces-
sive wear or scoring.
Fig. 12 Compressor Shaft Bolt and Clutch Plate
1 - COMPRESSOR SHAFT BOLT
2 - COMPRESSOR CLUTCH PLATE
Fig. 13 Clutch Plate and Shim(s)
1 - COMPRESSOR SHAFT
2 - CLUTCH PLATE
3 - CLUTCH PLATE SHIM
24 - 18 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com