ECU DODGE TRUCK 1993 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1993, Model line: TRUCK, Model: DODGE TRUCK 1993Pages: 1502, PDF Size: 80.97 MB
Page 21 of 1502

0 - 2
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
• Commercial service
When a vehicle is continuously subjected to severe
driving conditions, lubricate:
• Body components
• All the driveline coupling joints
• Steering linkage More often than normal driving conditions
DUSTY
AREAS
With this type of severe driving condition, special
care should be given to the:
• Engine air cleaner filter
• PCV filter
• Crankcase ventilation system
• Brake booster control valve air filter. Verify that the filters and the associated compo
nents are clean. Also verify that they are functioning
effectively. This will minimize the amount of abra sive particles that enter the engine.
OFF-ROAD
(4WD)
OPERATION
After off-road (4WD) operation, inspect the under
side of the vehicle. Inspect the:
• Tires
• Body structure
• Steering components
• Suspension components • Exhaust system
• Threaded fasteners
HARSH
SURFACE ENVIRONMENTS
After extended operation in harsh environments,
the brake drums, brake linings, and rear wheel bear ings should be inspected and cleaned. This will pre
vent wear and erratic brake action.
ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
The following routine maintenance is recommended
on a monthly basis: TIRES—Inspect the tires for unusual wear/damage.
Determine if the inflation pressure is adequate for
the vehicle load. BATTERY—Inspect and clean the terminals.
Tighten the terminals if necessary. FLUIDS—Determine if the component fluid levels
are acceptable. Add fluid, if necessary. LIGHTS/ELECTRICAL—Test all the electrical sys
tems in the vehicle for proper operation. It is also recommended that the engine oil and the
washer fluid level be determined at each fuel fill-up.
VEHICLE
NOISE CONTROL
Vehicles with a GVWR of 4 535 kg (10,000 lbs), or
more, are required to comply with Federal Exterior Noise Regulations (Fig. 2).
VEHICLE
NOISE
EMISSION
CONTROL INFORMATION
DATE
OF
VEHICLE
MANUFACTURE
THIS
VEHICLE CONFORMS
TO
U.S. EPA REGULATIONS FOR NOISE EMISSION
APPLICABLE
TO
MEDIUM
AND HEAVY
DUTY
TRUCKS. THE
FOLLOWING
ACTS OR THE CAUSING THEREOF BY ANY PERSON ARE PROHIBITED BY THE NOISE CONTROL ACT
OF 1972. (A) THE
REMOVAL
OR
RENDERING
INOPERATIVE, OTHER
THAN
FOR
PURPOSES
OF
MAINTENANCE,
REPAIR.
OR REPLACEMENT, OF ANY NOISE CONTROL DEVICE OR ELEMENT OF
DESIGN
(LISTED
IN
THE
OWNERS
MANUAL)
INCORPORATED
INTO
THIS
VEHICLE
IN COMPLIANCE
WITH
THE NOISE CONTROL
ACT:
(B) THE
USE
OF
THIS
VEHICLE
AFTER SUCH DEVICE
OR
ELEMENT
OF
DESIGN HAS BEEN REMOVED
OR
RENDERED
INOPERATIVE.
PU626D
Fig.
2 Vehicle
Noise
Emission
Control Information
Label
UNAUTHORIZED
DEFEAT
OF
NOISE
CONTROL COMPONENTS
Federal law prohibits removal, altering or other
wise defeating any noise control component. This in
cludes before or after the vehicle is in use. Federal
law also prohibits the use of a vehicle after a noise
control component is defeated.
REQUIRED MAINTENANCE/SERVICE
FOR
NOISE
CONTROL
The following maintenance is required after each
6-month or 9 600 km (6,000 miles) interval. This will
ensure that the vehicle noise control components are
operating properly.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
Inspect exhaust system for exhaust leaks and dam
aged components. The exhaust hangers, clamps and
U-bolts should be attached and in good condition.
Burned or ruptured mufflers, damaged exhaust pipes should be replaced. Refer to Group 11—Exhaust Sys
tem/Intake Manifold for service information.
AIR
FILTER
HOUSING/CANISTER
Inspect the air filter assembly for proper fit. Verify
the cover is securely attached to the housing/canis
ter. Inspect all the air filter housing hoses for con nections. The gasket between the air filter housing and throttle body must be in good condition. The air
filter element should be clean and serviced according
to the maintenance schedule.
FUEL
REQUIREMENTS
GASOLINE
ENGINES
All engines require the use of unleaded gasoline to
reduce the effects of lead to the environment. Also unleaded fuel is necessary to prevent damage to the
catalytic converter/02 sensor. The fuel must have a
minimum octane rating of 87 based on the (R + M)/2
calculation method.
Page 30 of 1502
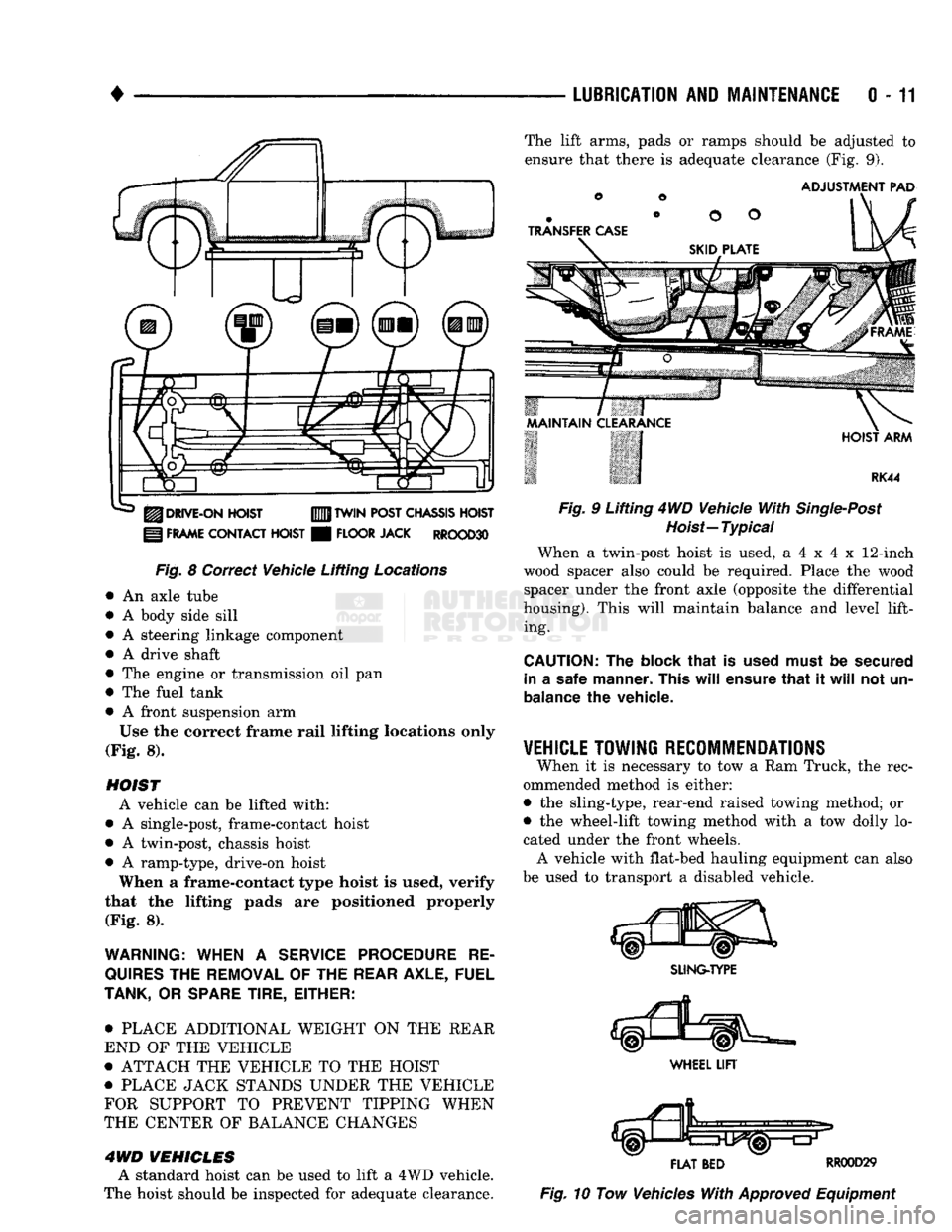
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
0-11
J
DRIVE-ON
HOIST
I
FRAME
CONTACT
HOIST
TWIN
POST
CHASSIS
HOIST
FLOOR
JACK
RROOD30
Fig.
8 Correct Vehicle Lifting
Locations
An axle tube
A body side sill
A steering linkage component
A drive shaft
The engine or transmission oil pan
The fuel tank
• A front suspension arm Use the correct frame rail lifting locations only
(Fig. 8).
HOIST A vehicle can be lifted with:
• A single-post, frame-contact hoist
• A twin-post, chassis hoist
• A ramp-type, drive-on hoist
When a frame-contact type hoist is used, verify
that the lifting pads are positioned properly (Fig. 8).
WARNING:
WHEN
A
SERVICE
PROCEDURE
RE
QUIRES
THE
REMOVAL
OF
THE
REAR
AXLE,
FUEL
TANK,
OR
SPARE
TIRE,
EITHER:
• PLACE ADDITIONAL WEIGHT ON THE REAR
END OF THE VEHICLE
« ATTACH THE VEHICLE TO THE HOIST
« PLACE JACK STANDS UNDER THE VEHICLE
FOR SUPPORT TO PREVENT TIPPING WHEN
THE CENTER OF BALANCE CHANGES
4WD VEHICLES A standard hoist can be used to lift a 4WD vehicle.
The hoist should be inspected for adequate clearance. The lift arms, pads or ramps should be adjusted to
ensure that there is adequate clearance (Fig. 9).
ADJUSTMENT
PAD
ii 7
MAINTAIN
CLEARANCE
HOIST
ARM
RK44
Fig.
9 Lifting 4WD Vehicle
With
Single-Post
Hoist—
Typical
When a twin-post hoist is used, a 4 x 4 x 12-inch
wood spacer also could be required. Place the wood spacer under the front axle (opposite the differential
housing). This will maintain balance and level lift ing.
CAUTION:
The
block
that
is
used must
be
secured in
a
safe manner. This
will
ensure
that
it
will
not un
balance
the
vehicle.
VEHICLE
TOWING
RECOMMENDATIONS
When it is necessary to tow a Ram Truck, the rec
ommended method is either:
• the sling-type, rear-end raised towing method; or
• the wheel-lift towing method with a tow dolly lo
cated under the front wheels. A vehicle with flat-bed hauling equipment can also
be used to transport a disabled vehicle.
SLING-TYPE
FLAT
BED
RR0OD29
Fig.
10 Tow Vehicles
With
Approved
Equipment
Page 31 of 1502

0 - 12
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
• A vehicle equipped with SAE approved sling-type
towing equipment can be used (Fig. 10). However,
many vehicles are equipped with air dams, spoilers, and/or ground effect panels. In this case a wheel-lift
towing vehicle or a flat-bed hauling vehicle is recom mended (Fig. 10). If a flat bed device is used, the ap
proach angle should not exceed 15 degrees.
GROUND CLEARANCE The lifted wheels of the disabled vehicle should be
a minimum of 10 cm (4 in.) off the ground. Make
sure there is enough clearance at the opposite end.
This is critical when towing over rough terrain. If necessary, the rear ground clearance can be increased by removing the wheels from the lifted end
and then towing with the lifted end closer to the
ground. If the rear wheels are removed, secure the
brake drums. A 20 cm (8 in.) ground clearance must
be maintained between brake drums or rotors and the ground.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS The following safety precautions must be consid
ered when preparing for and during a vehicle towing operation:
• Remove exhaust pipe tips that interfere with the
tow sling and crossbar • Padding should be placed between the tow sling/
crossbar and any painted surfaces
• If the vehicle is damaged, secure the loose and pro
truding parts
• Always use a safety chain system that is indepen dent of the lifting and towing equipment
• When placing tow hooks on the rear axle, position them so they do not damage the brake tubing or
hoses
• Do not allow any of the towing equipment to con
tact the fuel tank
• Do not tow the vehicle by connecting to the front
or rear shock absorbers
• The operator should not go under a vehicle while
it is lifted by the towing equipment. The vehicle
should first be supported by safety stands
• Do not allow passengers in a vehicle being towed
• Observe all state and local laws involving warning signals, night illumination, speed, etc.
• Do not exceed a towing speed of 48 km/h (30 mph)
• Avoid towing distances of more than 24 km (15
miles) whenever possible • Do not attach tow chains or a tow sling to a
bumper, the steering linkage, the universal joints, or a drive shaft
REAR-END RAISED TOWING It is recommended that the rear-end raised towing
method be used. Vehicles can be towed with the front
wheels on the ground for extended distances at speeds not exceeding 48 km/h (30 mph) (Fig. 11). (1) Attach the J-hooks around the axle shaft tubes
outboard of the rear springs. (2) Position and center the sling under and for
ward of the rear bumper. (3) Attach safety chains (with pads) at each end of
the rear bumper.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the OFF position to
unlock the steering wheel. (5) Clamp the steering wheel with the front wheels
in the straight ahead position.
CAUTION:
Do not use the steering
column
lock
to
secure
front
wheel
in the straight-ahead
position.
(6) Shift the transmission to NEUTRAL.
POSITION CENTER BAR FORWARD
OF
BUMPER
-
/
J-HOOKS OUTBOARD
OF
SPRINGS
RN967A
Fig. 11 Rear-End
Raised
Towing
FRONT'END RAISED TOWING If a vehicle cannot be towed from the rear, the
front-end raised towing method normally can be
used (Fig. 12). (1) Center the sling with the bumper and position
it at the frame front crossmember.
CAUTION:
Use tow
chains
with
J-hooks
for
con
necting
to the
disabled
vehicle's
lower
suspension
arms.
Never use
T-hooks.
(2) Route the J-hooks and tow chains over the
steering linkage outboard of the coil spring.
(3) Attach the J-hooks to the outer end of the
lower suspension arms.
(4) Raise the vehicle.
(5.) Attach the safety chains to the disabled vehicle
at the frame rails.
Vehicles equipped with a MANUAL TRANSMIS
SION can be towed with the rear wheels on the
Page 58 of 1502

•
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 5 (4) Front wheels for excessive radial, lateral
runout and unbalance. Refer to Group 22, Wheels and Tires for diagnosis information.
(5) Suspension components for wear and noise. Check
components for correct torque. Refer to Groups 2 and 3, Suspension and Axle for additional information.
WHEEL
ALIGNMENT
MEASUREMENTS/ADJUSTMENTS
The front wheel alignment positions must be set to
the specified limits. This will prevent abnormal tire
tread wear. The equipment manufacturer's recommenda
tions for use of their
equipment
should always
be followed. All
damaged
front suspension sys
tem components
should
be replaced. Do not at tempt to straighten any
bent
component.
CAMBER AND CASTER-2WD VEHICLES Camber and caster angle adjustments involve repo
sitioning the upper suspension arm cam adjustment
bolts (Fig. 2). Alignment adjustments are accom
plished by loosening the nuts and changing the posi
tion of the cam bolt.
(1) Remove all foreign material from the adjust
ment bolt threads.
(2) Record the camber and caster measurements
before loosening the adjustment bolt nuts.
(3) The camber angle should be adjusted as near as
possible to the preferred angle. The caster should be
the same at both sides of the vehicle. Refer to the Specifications chart.
CAMBER AND CASTER—4WD VEHICLES For 4WD vehicles, the correct wheel camber (verti
cal tilt) angle is factory preset at zero degree (0°).
Camber cannot be altered by adjustment.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to
adjust
the
camber
an
gle by
heating
or bending the axle or any
suspen
sion
component. If camber angle is
incorrect,
the
component(s)
causing
an
incorrect
angle must be replaced.
(1) It is important that the camber (vertical tilt)
angle be the same for both front wheels.
(2) The camber angle should be measured with ac
curate wheel alignment equipment. The acceptable
range is -1° to +1°. Refer to the Specifications chart.
Road test the vehicle and observe the steering
wheel return-to-center position. Before road testing,
check
and
correct
the tire
inflation pressures. Inflate
both
of the front tires
with exactly the
same
pressure.
During the road test, make vehicle turns to both
the left and right. If the steering wheel returns to
ward the center position unassisted, the caster angle is correct. However, if the steering wheel does not re turn toward the center position unassisted, an incor
rect caster angle is probable.
(1) The caster angle is factory preset at positive
two degrees
(
+
2°).
The acceptable range is +1/2° to +
3
1/2°.
(2) The caster angle should be measured with ac
curate wheel alignment equipment.
(3) Caster angle can be adjusted by installing ta
pered shims between the front axle pads and the spring brackets. The caster angle should be adjusted
as near as possible to the preferred angle.
(4) Record the caster measurement before remov
ing the original shims from the spring pads.
(5) The caster should be the same at both sides of
the vehicle. Refer to the Specifications chart.
RN1030
Fig.
2 Caster &
Camber
Adjustment Location—2WD
Vehicles
WHEEL TOE POSITION The wheel toe position adjustment should be the fi
nal front wheel alignment adjustment. In all in stances, follow the equipment manufacturer's
recommended procedure.
(1) Secure the steering wheel with the front wheels
in the straight-ahead position. For vehicles equipped
with power steering, start the engine before straight ening the wheels.
With power steering, the engine should be op
erating during the wheel toe position adjust
ment.
(2) Loosen the tie rod adjustment sleeve clamp
bolts (Fig. 3).
(3) Adjust the wheel toe position by rotating the
tie rod adjustment sleeve (Fig. 3). Rotate each tie-rod end in the direction of
sleeve rotation during the adjustment (Fig. 3).
This will ensure that both tie-rod ends are at the center of their travel.
(4) If applicable, turn the ignition switch off.
Page 62 of 1502
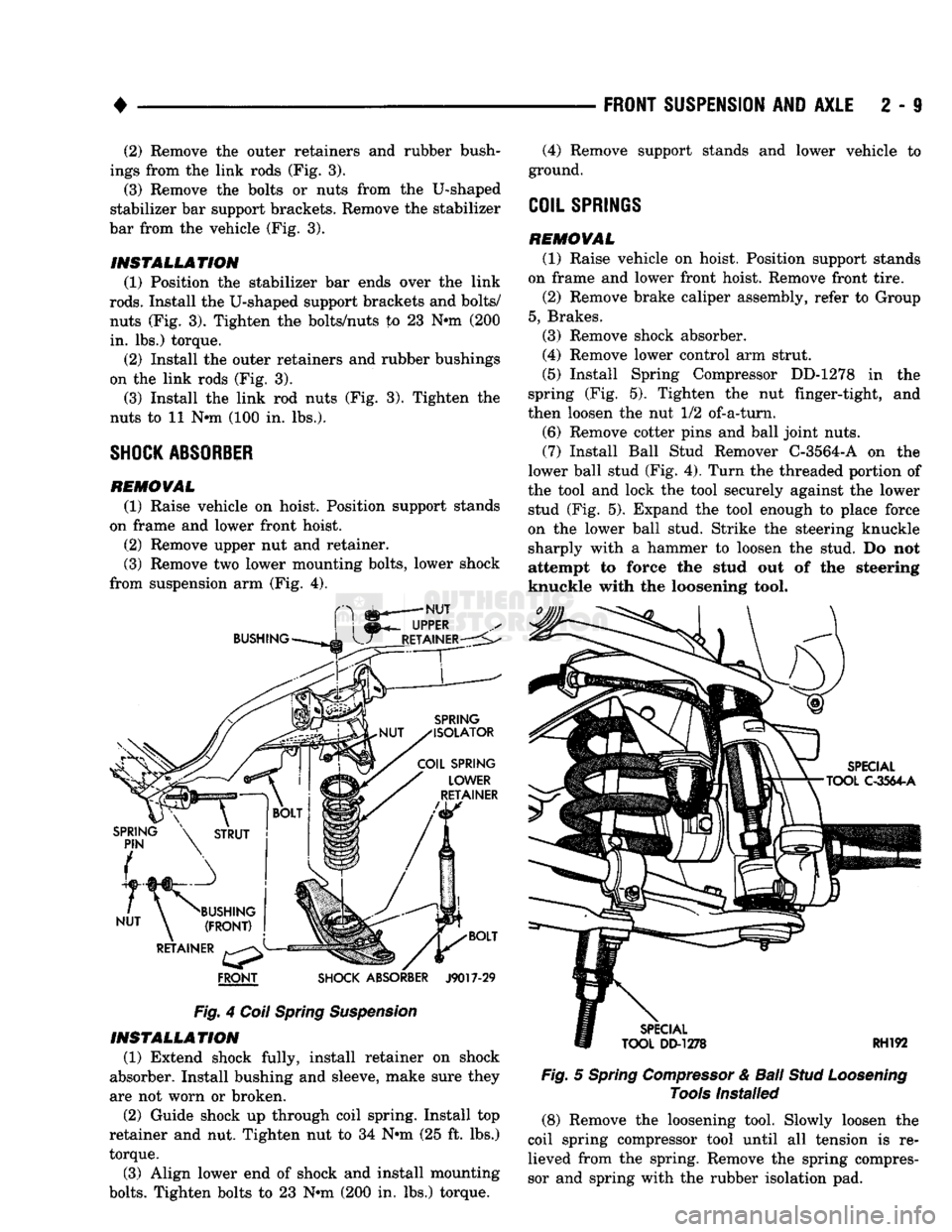
4
FRONT
SHOCK ABSORBER
J9017-29
Fig.
4
Coil Spring Suspension INSTALLATION
(1) Extend shock fully, install retainer on shock
absorber. Install bushing and sleeve, make sure they
are not worn or broken.
(2) Guide shock up through coil spring. Install top
retainer and nut. Tighten nut to 34 Nnn (25 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Align lower end of shock and install mounting
bolts.
Tighten bolts to 23 Nnn (200 in. lbs.) torque.
FRONT SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - i
Fig.
5
Spring Compressor
&
Ball
Stud Loosening
Tools
Installed (8) Remove the loosening tool. Slowly loosen the
coil spring compressor tool until all tension is re lieved from the spring. Remove the spring compres
sor and spring with the rubber isolation pad.
(2) Remove the outer retainers and rubber bush
ings from the link rods (Fig. 3).
(3) Remove the bolts or nuts from the U-shaped
stabilizer bar support brackets. Remove the stabilizer
bar from the vehicle (Fig. 3).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the stabilizer bar ends over the link
rods.
Install the U-shaped support brackets and bolts/ nuts (Fig. 3). Tighten the bolts/nuts to 23 Nnn (200
in.
lbs.) torque. (2) Install the outer retainers and rubber bushings
on the link rods (Fig. 3).
(3) Install the link rod nuts (Fig. 3). Tighten the
nuts to 11 Nnn (100 in. lbs.).
SHOCK ABSORBER
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist. Position support stands
on frame and lower front hoist.
(2) Remove upper nut and retainer.
(3) Remove two lower mounting bolts, lower shock
from suspension arm (Fig. 4). (4) Remove support stands and lower vehicle to
ground.
COIL
SPRINGS
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist. Position support stands
on frame and lower front hoist. Remove front tire. (2) Remove brake caliper assembly, refer to Group
5, Brakes. (3) Remove shock absorber.
(4) Remove lower control arm strut.
(5) Install Spring Compressor DD-1278 in the
spring (Fig. 5). Tighten the nut finger-tight, and
then loosen the nut 1/2 of-a-turn.
(6) Remove cotter pins and ball joint nuts.
(7) Install Ball Stud Remover C-3564-A on the
lower ball stud (Fig. 4). Turn the threaded portion of
the tool and lock the tool securely against the lower stud (Fig. 5). Expand the tool enough to place force
on the lower ball stud. Strike the steering knuckle sharply with a hammer to loosen the stud. Do not
attempt to force the stud out of the steering
knuckle with the loosening tool.
Page 64 of 1502

•
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 11 (2) Position the seal over the ball stud (if neces
sary, use a replacement seal). Force portion of the
seal downward on the ball stud housing with an ap
propriate size socket wrench until it is securely locked in place.
(3) Install lower suspension arm using procedure
under Lower Suspension Arm Installation.
LOWER SUSPENSION
ARM
BUSHING
REMOVAL (1) Follow procedure under Coil Spring and Lower
Suspension Arm Removal.
(2) Use an arbor press and an appropriate size
sleeve to force the original bushing from the lower
suspension arm bore.
INSTALLATION (1) Use an arbor press and an appropriate size
sleeve to force the replacement bushing into the
lower suspension arm bore. Ensure that it is com
pletely seated in the bore.
(2) Install the lower suspension arm according to in
structions provided within the installation procedure.
UPPER SUSPENSION
ARM REMOVAL (1) Raise the vehicle. Position support stands un
der the frame rail and lower the front of the hoist.
Remove the wheel/tire.
(2) Remove shock absorber, refer to above proce
dures.
(3) Install Spring Compressor DD-1278 (Fig. 5).
Tighten the nut finger-tight and then loosen it 1/2 of- a-turn.
(4) Remove the cotter pins and the ball stud nuts.
(5) Install Ball Stud Remover C^3564-A (Fig. 8).
Turn the threaded portion of the tool to lock it se curely against the upper ball stud (Fig. 8). Spread
the tool enough to apply force against the upper ball stud. Strike the steering knuckle sharply with a
hammer to loosen the upper ball stud. Do not at
tempt to force the ball stud out of the steering knuckle bore with the loosening tool.
(6) Remove the loosening tool. Remove the nuts,
eccentric (cam) bolts and suspension arm from the
vehicle (Fig. 9).
INSTALLATION (1) Position the suspension arm and install the ec
centric (cam) bolts (Fig. 9). and nuts finger-tight.
(2) Install upper ball stud into steering knuckle.
Install nuts on the ball studs. Tighten to 142 N« (105
ft. lbs.) torque. Install replacement cotter pins.
(3) Remove the spring compressor tool (Fig. 5).
Fig.
8
Ball
Stud
Loosening
Tool Installed
(4) Install the shock absorber. Tighten nut to 34
N*m (25 ft. lbs.) torque and lower bolts to 23 N*m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install the wheel/tire. Raise the vehicle, remove
the support stands and lower the vehicle to the surface.
(6) Adjust the caster and camber angles. Tighten
the eccentric (cam) nuts to 95 N*m (70 ft. lbs.)
torque.
UPPER BALL STUD
INSPECTION (1) Position a floor jack under the lower suspension
arm. Raise the wheel and allow the tire to lightly
contact the floor (vehicle weight relieved from the
tire).
(2) Grasp the top of the tire and apply force in and
out. Look for any movement at the ball joints be
tween the upper suspension arm and steering knuckle.
(3) If any lateral movement is evident, replace the
ball joint.
REMOVAL (1) Position a support under the outer end of the
lower suspension arm. Lower the vehicle so that the
support compresses the coil spring.
(2) Remove the wheel/tire.
(3) Remove the ball stud nuts. Use Ball Stud Re
mover C-3564-A to loosen the upper ball stud (Fig.
8).
(4) Use Wrench C-3561 to un-thread the upper ball
stud from the upper suspension arm.
Page 66 of 1502
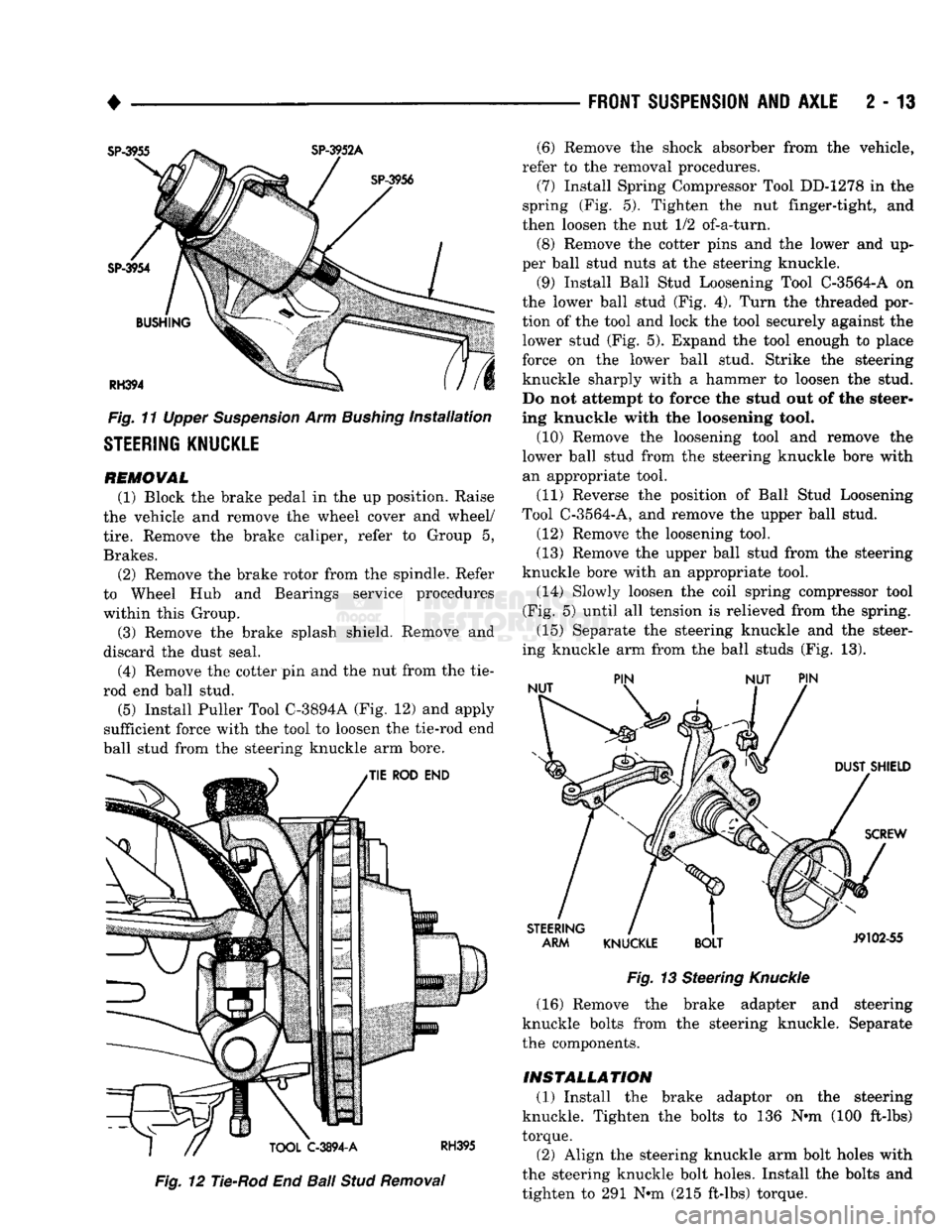
•
Fig.
11 Upper Suspension Arm Bushing installation
STEERING KNUCKLE
REMOVAL
(1) Block the brake pedal in the up position. Raise
the vehicle and remove the wheel cover and wheel/
tire.
Remove the brake caliper, refer to Group 5,
Brakes. (2) Remove the brake rotor from the spindle. Refer
to Wheel Hub and Bearings service procedures
within this Group.
(3) Remove the brake splash shield. Remove and
discard the dust seal.
(4) Remove the cotter pin and the nut from the tie-
rod end ball stud.
(5)
Install Puller Tool C-3894A (Fig. 12) and apply
sufficient force with the tool to loosen the tie-rod end
ball stud from the steering knuckle arm bore.
Fig.
12 Tie-Rod End
Ball
Stud
Removal
FRONT SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 13
Fig.
13 Steering
Knuckle
(16) Remove the brake adapter and steering
knuckle bolts from the steering knuckle. Separate
the components.
INSTALLATION (1) Install the brake adaptor on the steering
knuckle. Tighten the bolts to 136 Nnn (100 ft-lbs)
torque.
(2) Align the steering knuckle arm bolt holes with
the steering knuckle bolt holes. Install the bolts and
tighten to 291 Nnn (215 ft-lbs) torque. (6) Remove the shock absorber from the vehicle,
refer to the removal procedures. (7) Install Spring Compressor Tool DD-1278 in the
spring (Fig. 5). Tighten the nut finger-tight, and
then loosen the nut 1/2 of-a-turn.
(8) Remove the cotter pins and the lower and up
per ball stud nuts at the steering knuckle.
(9) Install Ball Stud Loosening Tool C-3564-A on
the lower ball stud (Fig. 4). Turn the threaded por
tion of the tool and lock the tool securely against the lower stud (Fig. 5). Expand the tool enough to place
force on the lower ball stud. Strike the steering
knuckle sharply with a hammer to loosen the stud.
Do not attempt to force the stud out of the steer
ing knuckle with the loosening tool.
(10) Remove the loosening tool and remove the
lower ball stud from the steering knuckle bore with an appropriate tool.
(11) Reverse the position of Ball Stud Loosening
Tool C-3564-A, and remove the upper ball stud.
(12) Remove the loosening tool.
(13) Remove the upper ball stud from the steering
knuckle bore with an appropriate tool. (14) Slowly loosen the coil spring compressor tool
(Fig. 5) until all tension is relieved from the spring.
(15) Separate the steering knuckle and the steer
ing knuckle arm from the ball studs (Fig. 13).
Page 72 of 1502
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 19
DRAIN
AND
REFILL
(1) Drive the vehicle until the gear lubricant
reaches normal operating temperature. (2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove the lubricant fill hole plug from the
differential housing cover.
(4) Remove the differential housing cover. Allow
the original lubricant to completely drain from the
housing and axle shaft tubes.
(5) With standard differential, clean the differen
tial and the housing cavity with a flushing oil (or light engine oil). This will remove the residual lubricant and foreign matter. Do not use water, steam,
kerosene or gasoline for flushing. (6) Scrape the residual gasket from the housing
and cover mating surfaces. Clean the mating sur
faces with mineral spirits. Install a new cover gas ket. Apply a bead of MOPAR® Silicone Rubber Sealant on the housing cover (Fig. 2). Allow the
sealant to cure for a few minutes.
SEALING
SURFACE
CONTOUR
OF
BEAD
BEAD
THICKNESS
6.35mm
(1/4")
J9302-30
Fig.
2 Sealant On
Housing
Cover
Install the housing cover within 5 minutes af
ter applying the sealant. If not installed the seal ant must be removed and another bead applied.
(7) Install the cover on the differential with the
bolts.
Install the identification tag. Tighten the cover
bolts to 47 Nnn (35 ft. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION:
Overfilling the
differential
can result in
the lubricant
foaming
and overheating.
(8) Refill the differential housing with the speci
fied quantity of MOPAR® Hypoid Gear Lubricant.
(9) Install the fill hole plug and tighten to 34 N#m
(25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(10) Road test the vehicle.
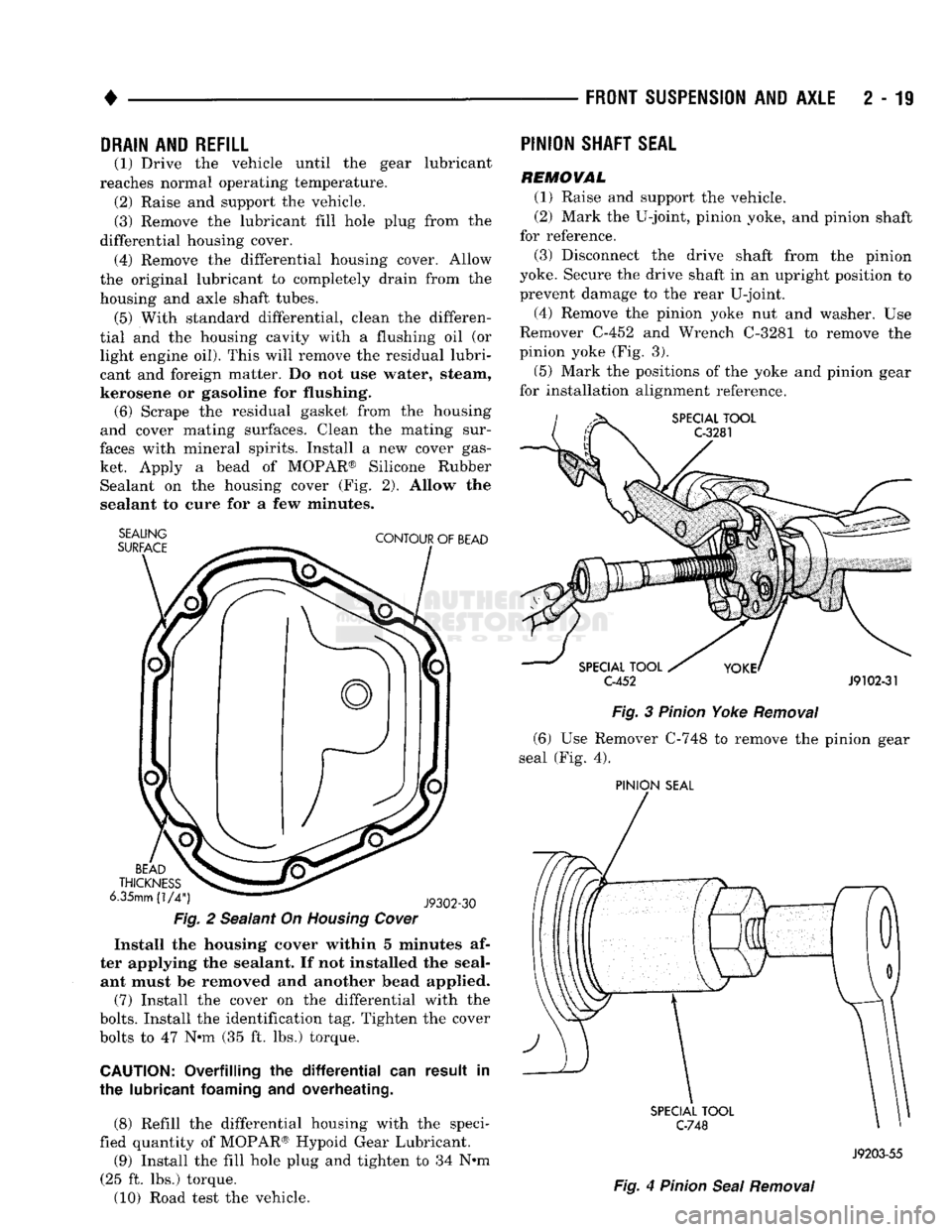
PINION
SHAFT
SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Mark the U-joint, pinion yoke, and pinion shaft
for reference.
(3) Disconnect the drive shaft from the pinion
yoke. Secure the drive shaft in an upright position to prevent damage to the rear U-joint.
(4) Remove the pinion yoke nut and washer. Use
Remover C-452 and Wrench C-3281 to remove the
pinion yoke (Fig. 3).
(5) Mark the positions of the yoke and pinion gear
for installation alignment reference.
SPECIAL
TOOL
C-3281
SPECIAL
TOOL
C-452
J9102-31
Fig.
3
Pinion
Yoke
Removal
(6) Use Remover C-748 to remove the pinion gear
seal (Fig. 4).
PINION
SEAL
SPECIAL
TOOL
C-748
Fig.
4
Pinion
Seal
Removal
J9203-55
Page 143 of 1502
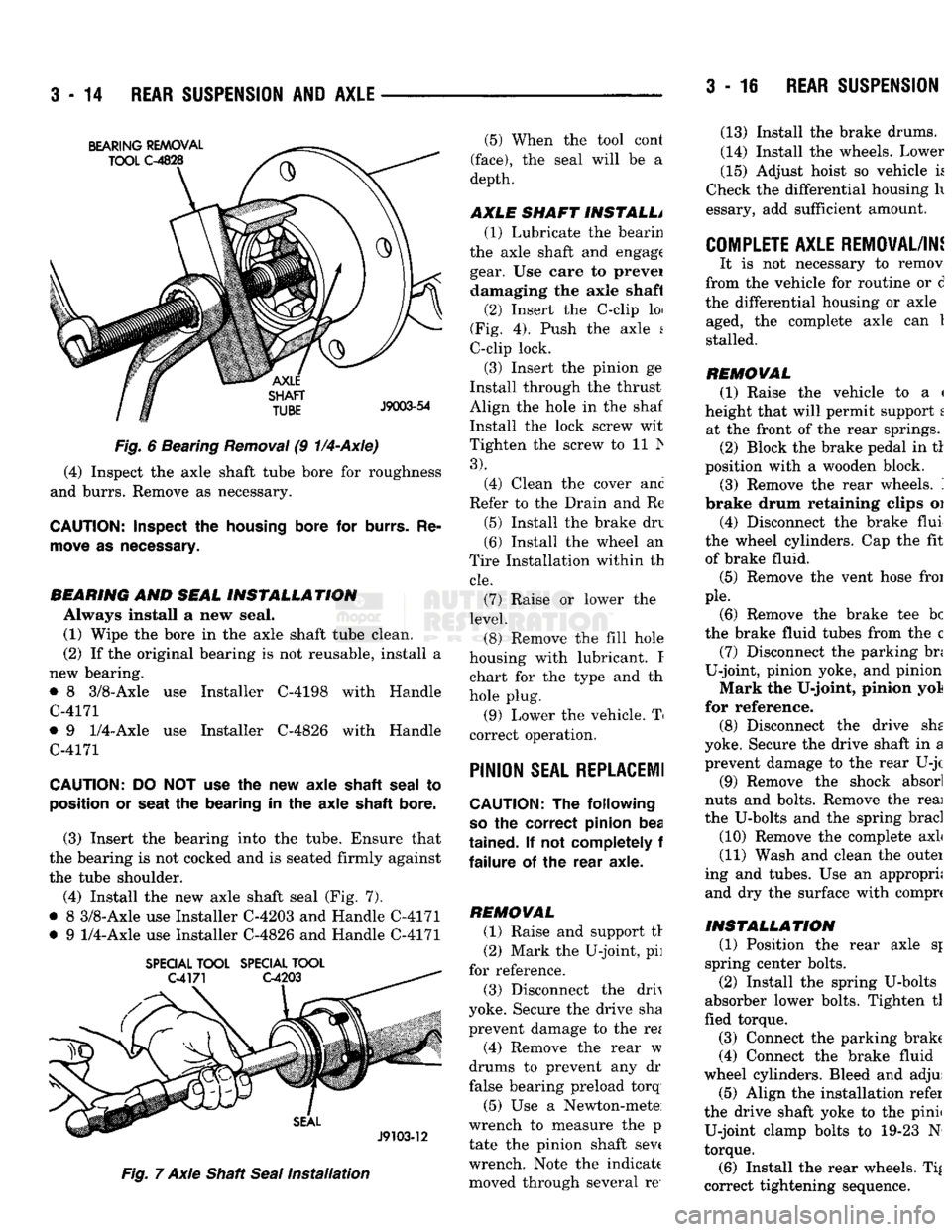
3
- 14
REAR SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
3
- 18
REAR SUSPENSION Fig.
6 Bearing
Removal
(9
1/4-Axle)
(4) Inspect the axle shaft tube bore for roughness
and burrs. Remove as necessary.
CAUTION:
Inspect
the
housing
bore for
burrs.
Re
move
as
necessary.
BEARING
AND
SEAL
INSTALLATION
Always install a new seal. (1) Wipe the bore in the axle shaft tube clean.
(2) If the original bearing is not reusable, install a
new bearing.
• 8 3/8-Axle use Installer C-4198 with Handle
C-4171
• 9
1/4-Axle
use Installer C-4826 with Handle
C-4171
CAUTION:
DO NOT use the new axle
shaft
seal
to
position
or
seat
the bearing in the axle
shaft
bore.
(3) Insert the bearing into the tube. Ensure that
the bearing is not cocked and is seated firmly against
the tube shoulder.
(4) Install the new axle shaft seal (Fig. 7).
• 8 3/8-Axle use Installer C-4203 and Handle C-4171
• 9
1/4-Axle
use Installer C-4826 and Handle C-4171
SPECIAL
TOOL
SPECIAL
TOOL
Fig.
7 Axle Shaft
Seal
Installation
(5) When the tool cont
(face),
the seal will be a
depth.
AXLE SHAFT INSTALL* (1) Lubricate the bearin
the axle shaft and engage gear. Use care to prevei damaging the axle shaft
(2) Insert the C-clip loi
(Fig. 4). Push the axle s
C-clip lock.
(3) Insert the pinion ge
Install through the thrust
Align the hole in the shaf
Install the lock screw wit
Tighten the screw to 11 Is
3).
(4) Clean the cover anc
Refer to the Drain and Re
(5) Install the brake drv
(6) Install the wheel an
Tire Installation within th
cle.
(7) Raise or lower the
level.
(8) Remove the fill hole
housing with lubricant. I chart for the type and th
hole plug.
(9) Lower the vehicle. T
correct operation.
PINION
SEAL REPLACE!!
CAUTION:
The following
so
the correct pinion bea
tained.
If not completely f
failure
of the rear axle.
REMOVAL (1) Raise and support tr
(2) Mark the U-joint, pi]
for reference.
(3) Disconnect the drh
yoke. Secure the drive sha
prevent damage to the re*
(4) Remove the rear w
drums to prevent any dr
false bearing preload torq
(5) Use a Newton-mete
wrench to measure the p
tate the pinion shaft sev( wrench. Note the indicate moved through several re' (13) Install the brake drums.
(14) Install the wheels. Lower
(15) Adjust hoist so vehicle k
Check the differential housing h
essary, add sufficient amount.
COMPLETE AXLE REMOVAL/IN!
It is not necessary to remov
from the vehicle for routine or d
the differential housing or axle aged, the complete axle can 1
stalled.
REMOVAL (1) Raise the vehicle to a <
height that will permit support t at the front of the rear springs. (2) Block the brake pedal in tl
position with a wooden block. (3) Remove the rear wheels. '.
brake drum retaining clips oi
(4) Disconnect the brake flui
the wheel cylinders. Cap the fit of brake fluid.
(5) Remove the vent hose froi
pie.
(6) Remove the brake tee be
the brake fluid tubes from the c (7) Disconnect the parking bn
U-joint, pinion yoke, and pinion
Mark the U-joint, pinion yol
for reference. (8) Disconnect the drive she
yoke. Secure the drive shaft in a prevent damage to the rear U-jc
(9) Remove the shock absorl
nuts and bolts. Remove the reai
the U-bolts and the spring brad
(10) Remove the complete axL
(11) Wash and clean the outei
ing and tubes. Use an appropri; and dry the surface with comprc
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the rear axle sj
spring center bolts.
(2) Install the spring U-bolts
absorber lower bolts. Tighten tl
fled torque.
(3) Connect the parking brake
(4) Connect the brake fluid
wheel cylinders. Bleed and adjui (5) Align the installation refer
the drive shaft yoke to the pinii U-joint clamp bolts to 19-23 N
torque.
(6) Install the rear wheels. Ti|
correct tightening sequence.
Page 158 of 1502

•
REAR
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
3 - 31
LUBRICANT
Hypoid gear lubricant, as defined by MIL-L-2105-B
and API GL 5 is the specified lube. MOPAR Hypoid
Gear Lubricant conforms with both of these specifica
tions and is highly recommended.
CAUTION:
If a
rear
axle
is
submerged
in
water,
the
axle
lubricant
must
be
replaced
immediately,
DRAIN
AND
REFILL
(1) Drive the vehicle until the gear lubricant
reaches normal operating temperature. (2) Raise and support the vehicle. (3) Remove the lubricant fill hole plug from the
differential housing cover. (4) Remove the differential housing cover. Allow
the lubricant to completely drain from the housing and axle shaft tubes. (5) Flush the differential and the housing cavity
with a flushing oil to remove residual lubricant and
foreign matter. Do not use water,
steam,
kerosene
or
gasoline for
flushing,
(6) Scrape the residual gasket from the housing
and cover mating surfaces. Clean the mating sur
faces with mineral spirits. Install a new cover gas
ket. Apply a bead of MOPAR® Silicone Rubber Sealant on the housing cover (Fig. 2). Allow the seal
ant to cure for a few minutes.
SEALING
SURFACE
CONTOUR
OF
BEAD
BEAD
THICKNESS
6.35mm
(1/4")
J9302-30
Fig.
2 Sealant On Housing Cower
Install
the
housing
cover
within 5
minutes
af
ter
applying
the
sealant.
If not
installed,
the
sealant
must be
removed
and another
bead
ap
plied.
(7) Install the cover on the differential. Install the
identification tag. Tighten the cover bolts to 47 Nem (35 ft. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION:
Overfilling
the differential" can
result
in
the
lubricant
foaming
and
overheating.
(8) Refill the differential housing with the speci
fied quantity of MOPAR® Hypoid Gear Lubricant.
With Trac-Lok differentials, add a container of Trac-
Lok Lubricant additive.
(9) Install the fill hole plug. Tighten to 34 N-m (25
ft. lbs.) torque.
(10) Road test the vehicle. Drive the vehicle and
make 10 to 12 slow, figure-eight turns. This maneu
ver will pump lubricant through clutch discs.
PINION
SHAFT
SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Mark the U-joint, pinion yoke, and pinion shaft
for reference.
(3) Disconnect the drive shaft from the pinion
yoke. Secure the drive shaft in an upright position to
prevent damage to the rear U-joint.
(4) Remove the pinion yoke nut and washer. Use
Remover C-452 and Wrench C-3281 to remove the
pinion yoke (Fig. 3).
(5) Mark the positions of the yoke and pinion gear
for installation alignment reference.
SPECIAL
TOOL
C-3281
SPECIAL
TOOL
C-452
J9102-31
Fig.
3 Pinion Yoke
Removal
(6) Use Remover C-748 to remove the pinion gear
seal (Fig. 4).
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on the
lip of pinion seal. Install the new seal (Fig. 5);
• Model 60 use Installer C-3719-A and Handle C-4735
• Model 70 use Installer C-359 and Handle C-4735 (2) Align the installation reference marks and po-