fuse chart DODGE TRUCK 1993 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1993, Model line: TRUCK, Model: DODGE TRUCK 1993Pages: 1502, PDF Size: 80.97 MB
Page 325 of 1502

8A
- 4
ELECTRICAL
•
IGNITION
OFF
DRAW
(IOD)
Ignition off draw refers to power being drained
from the battery with the ignition turned off. A nor
mal vehicle electrical system will draw from 5 to 20
milliamps. A vehicle that has not been operated for
an extended period of time (approximately 20 days)
may discharge the battery to an inadequate level.
Battery drain should not exceed approximately 20
MA (20 milliamps = 0.020 amps). The 20 MA are needed to supply PCM memory,
digital clock memory, and ETR (electronically tuned
radio) memory. Excessive battery drain is caused by items left
turned on, internally shorted generator, or intermit
tent short in wiring.
If the IOD is excessive (over 20 milliamperes), the
defect must be found and corrected before replacing a
battery. In most cases the battery can be charged and returned to service.
TEST PROCEDURE Testing for higher amperage IOD must be per
formed first to prevent damage to most milliamp
meters.
Verify that all electrical accessories are OFF. Turn
off all lights, remove ignition key, and close all
doors.
If the vehicle is equipped with electronic acces
sories (illuminated entry, high line radio), allow the
systems to automatically shut off (time out), up to 3
minutes.
(1) After determining that the underhood lamp is
operating properly then disconnect bulb. (2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Connect a typical 12 volt test light (low watt
age bulb) between the negative cable clamp and the
battery negative terminal. The test light may light brightly for up to 3 min
utes or may not light at all (depending on the elec
trical equipment). The term brightly being used
throughout the following tests, implies the bright ness of the test light will be the same as if it were
connected across the battery.
The test light must be securely clamped to the neg
ative cable and battery terminal. If the test light be
comes disconnected during any of the IOD test, the electronic timer function will be activated and all
tests must be repeated.
(4) After 3 minutes, the test light should turn OFF
or be DIMLY lit (depending on the electrical equip
ment).
If the test light remains brightly lit do not
disconnect it. Remove each fuse or circuit breaker (refer to Group 8 - Wiring Diagrams) until test light
is either OFF or DIMLY lit. This will eliminate the
higher amperage draw.
If test light is still bright after disconnecting each
fuse and circuit breaker, disconnect the wiring har ness from the generator. Refer to Generator Testing
in this group. Do not disconnect the test light. After higher amperage IOD has been corrected, low
amperage IOD may be checked.
It is now safe to install milliamp meter to check for
low amperage IOD.
(5) With test light still connected, securely clamp
an ammeter between battery negative terminal and
negative battery cable.
If the test light or the milliamp meter circuit is
broken the various timer circuits will start. Do
not open any doors or turn on any electrical ac cessories with the test light disconnected or the
meter may be damaged.
(6) Disconnect test light. The current draw should
not exceed 0.020 amp. If it exceeds 20 milliamps iso
late each circuit by removing circuit breakers and
fuses.
The meter reading drops once the high current
problem is found. Repair this section of the circuit,
whether it is a wiring short or component failure.
BATTERY
OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TEST
A battery voltage (no load) test will indicate the
state of charge of a battery that will pass the Battery
Load Test described in this section. Before proceed
ing with this test or the Battery Load Test the
battery must be completely charged as de scribed in Battery Charging in this section. If a battery has a no load voltage reading of 12.4
volts or greater but will not endure a load test, it is
defective and should be replaced. Refer to Group 8B,
Battery/Starter Service for instructions. To test bat
tery no load voltage, perform the following operation: (1) Before measuring open circuit voltage, the sur
face charge must be removed from plates. Turn head lights on for 15 seconds then allow up to 5 minutes
for voltage to stabilize. (2) Remove both battery cables, negative first.
(3) Using a voltmeter connected to the battery
posts,
see instructions provided with voltmeter, mea sure open circuit voltage (Fig. 6). This voltage reading will indicate state of charge,
but will not reveal cranking capacity. Refer to Bat
tery Open Circuit Voltage chart.
BATTERY OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE
Open
Circuit
Volts
Percent
Chang©
11.7
volts
or
less
0%
12.0 25%
12.2 50%
12.4 75%
12.6
or more 100%
918A-3
Page 412 of 1502

•
HORNS
8G - 1
HORNS
CONTENTS
SERVICE
PROCEDURES
page
.. 3
TEST PROCEDURES
page
.. 1
GENERAL
INFORMATION plied from the fuse block and grounded in the horn The horn system consists of a horn switch, horn re- switch. When the horn switch on the steering column
lay (located on the fuse block), horns, and all their is pressed, the ground circuit is completed, energiz-
wiring and connections. The circuit voltage is sup- ing the relay, and supplying power to the horns.
TEST PROCEDURES
HORNS
WILL
NOT
SOUND
If the horns do not sound, check for a blown horn
fuse in cavity number 4 of the fuse block. If the fuse is blown, replace it with the same type fuse. If the
horns fail to sound and the newly replaced fuse blows
the horn switch is depressed, check for one of the fol lowing:
• a short circuit in the horn
• the horn wiring between the fuse terminal and the
horn is faulty. If the fuse is intact, unplug wire connector at horn.
Connect one lead of a test lamp to the wire connector and the other lead to a good body ground (Fig. 1).
Depress the horn switch. Should test lamp illuminate
the horn is ungrounded or faulty. Ground can be checked by using a jumper wire between horn
bracket (scratch through paint) and the battery neg ative terminal. If the horn still fails to sound with
the ground jumper wire still intact and the horn re connected, replace the horn. If the lamp fails to illuminate, check for a defective
horn relay by substituting a known good horn relay in the circuit. If the lamp illuminates when depress
ing the horn switch, the original relay is defective. If
the lamp fails to illuminate with a known good relay, unplug that relay. Connect a jumper wire from the
battery terminal to the horn terminal on the relay
terminal board. If the lamp, connected in place of the
horns, fails to illuminate, inspect for an open circuit
between the horn fuse and the horn terminal on the relay. Also check between relay terminal board and
the horn terminals. Should the lamp illuminate, a defective horn switch or an open circuit in the wiring
between the relay terminal and the horn switch is at fault.
HORNS SOUND CONTINUOUSLY
Should the horns sound continuously, unplug the
horn relay from the relay connector inside the pas-
HORN
TEST LAMP TO RELAY
AND
HORN
BUTTON
-
TO GOOD BODY GROUND HORN,
CONNECTOR
PR714
Fig.
1 Testing for Voltage
senger compartment (Fig. 2). Plug in a known good
relay. If the horns stop blowing, relay is defective and must be replaced. Should the horns still sound,
proceed with Horn Diagnosis Chart.
HORN RELAY
FUSE BLOCK
RB1359
Fig.
2
Horn
Relay
Remove steering wheel pad and disconnect wire
from horn switch. Repeat the above test and if the
test lamp still illuminates, wire is shorted and should be repaired. If test lamp does not illuminate,
horn switch is defective and must be replaced.
Page 435 of 1502

8K - 4
WINDSHIELD WIPER
AND
WASHER
SYSTEMS
•
PROCEDURE (1) Remove wiring harness. Connect jumper from
Terminal P2 to terminal "L" of wiper motor (Fig, 4).
TERMINALS
Fig. 4 Om Jumper Wire Between Terminal "P2" and
"L".
One Jumper Wire Between Terminal "P1" and "B+" (2) Connect second jumper from terminal "PI" to
battery. If motor runs to PARK position and stops,
wiper switch is faulty. If motor keeps running and
does not park, replace motor assembly.
CONDITION Motor will stop wherever it is, when column
switch is put in OFF position. (Wipers do not
continue running to PARK position).
PROCEDURE
(1) Remove motor wiring connector and clean ter
minals. Reconnect connector and test motor. If prob lem persists, proceed to step No. 2.
(2) Put wiper switch to OFF and ignition switch to
ACC position. Disconnect motor wiring connector. Connect a voltmeter or test lamp to the motor
ground strap. Connect the other lead to terminal
"PI"
of wiring connector.
(a) If voltage is not present, check for an open
circuit in the wiring harness or wiper control
switch or fuse. (b) If voltage is present, proceed to step (3).
(3) Remove wiper motor from vehicle and connect
an ohmmeter or continuity tester between terminals
"L"
and "P2" (Fig. 5).
(a) If there is continuity between these termi
nals,
the problem is a defective motor. Fig. 5 Ohmmeter Between Terminal "L" and "P2"
(b) If there is no continuity, the problem is an
open circuit in the wiper control switch or wiring
harness.
MULTIFUNCTION
(TWO
SPEED WIPER) SWITCH
TESTING PROCEDURES
The multifunction switch contains circuitry for:
• turn signal
• hazard warning
• headlamp beam select
• headlamp optical horn
• windshield wiper
• pulse wipe
• and windshield washer switching. This integrated switch assembly is mounted to the
left-hand side of the steering column. Should any
function of the switch fail, the entire switch assem
bly must be replaced. To test the switch: (1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove tilt lever (Tilt column only).
(3)
Remove upper and lower column covers to gain
access to the switch connector (Fig. 6). (4) Remove lower fixed column cover.
(5) Loosen steering column upper bracket nuts. Do
Not remove nuts.
(6)
Move upper fixed column cover to gain access
to rear of multifunction switch.
(7)
Remove switch connector (Figs. 7 and 8).
(8)
Using an ohmmeter, test for continuity (no re
sistance) between the terminals of the switch as
shown in the following continuity chart (Fig. 9).
(9)
Refer to Service Procedures for assembly.
Page 476 of 1502
•
WIRING DIAGRAMS
8W
- 1
CONTENTS
page page
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION
.............
9
SPLICE LOCATIONS
29
GENERAL
INFORMATION
1
WIRING DIAGRAMS AD-BODY
37
GENERAL
INFORMATION
INDEX
page
Circuit
Identification
2
Component
Identification
3
Connectors
3
Fusible Links
3
Harness
Repair
3
Locating
A
System
or
Component
2
page
Secondary
Ignition
Wiring
1
Splice Locations
3
Symbols
and
Fuses
5
Troubleshooting
Wiring
Problems
3
Wire Code
Identification
2
Wiring
Diagram Sheets
and
Indexes
1
The wiring diagrams contain
the
latest information
available
at
time
of
publication. Throughout
out
this
group references
may
be
made
to a
particular vehicle
by letter
or
number designation.
A
chart showing
the
breakdown
of
these designations
is
included
in the
Introduction Section
of
this service manual.
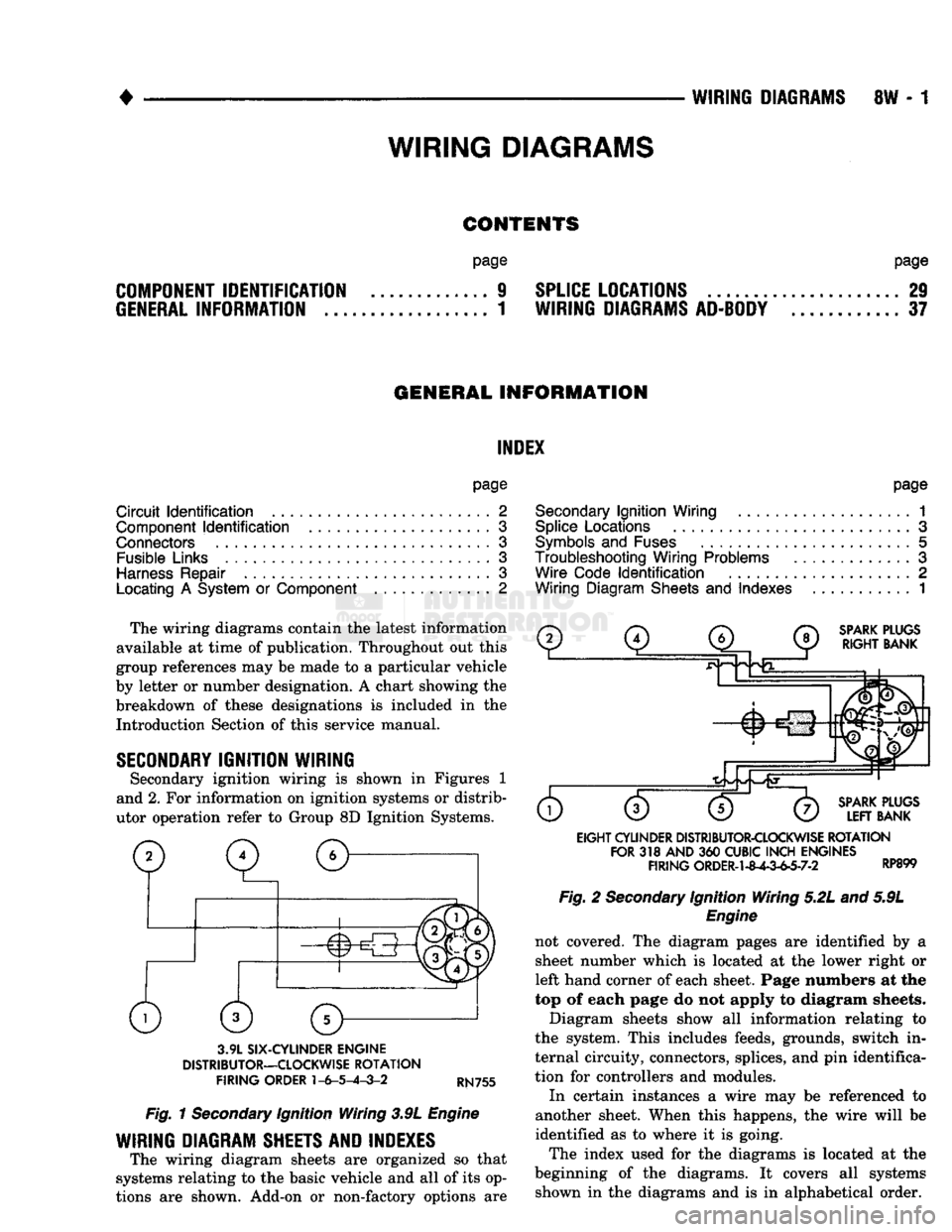
SECONDARY
IGNITION WIRING
Secondary ignition wiring
is
shown
in
Figures
1
and 2.
For
information
on
ignition systems
or
distrib
utor operation refer
to
Group
8D
Ignition Systems.
SPARK
PLUGS
RIGHT
BANK
3.9L
SIX-CYLINDER
ENGINE
DISTRIBUTOR—CLOCKWISE
ROTATION
FIRING
ORDER
1-6-5-4-3-2
RN755
Fig.
1
Secondary
Ignition Wiring 3.9L
Engine
WIRING DIAGRAM SHEETS AND INDEXES
The wiring diagram sheets
are
organized
so
that
systems relating
to the
basic vehicle
and all of
its op
tions
are
shown. Add-on
or
non-factory options
are
SPARK
PLUGS
LEFT
BANK
EIGHT
CYLINDER
DISTRIBUTOR-CLOCKWISE
ROTATION
FOR
318
AND
360
CUBIC
INCH
ENGINES
FIRING
ORDER-1-8^-3-63-7-2 RP899 Fig.
2
Secondary
Ignition Wiring 5.2L and 5.9L
Engine
not covered.
The
diagram pages
are
identified
by a
sheet number which
is
located
at the
lower right
or
left hand corner
of
each sheet. Page numbers
at the
top
of
each page
do not
apply
to
diagram sheets.
Diagram sheets show
all
information relating
to
the system. This includes feeds, grounds, switch
in
ternal circuity, connectors, splices,
and
pin
identifica
tion
for
controllers
and
modules.
In certain instances
a
wire
may be
referenced
to
another sheet. When this happens,
the
wire will
be
identified
as to
where
it is
going.
The index used
for the
diagrams
is
located
at the
beginning
of the
diagrams.
It
covers
all
systems shown
in the
diagrams
and is in
alphabetical order.
WIRING
DIAGRAMS
Page 477 of 1502

8W
- 2
WIRING
DIAGRAMS
•
WIRE CODE
IDENTIFICATION
Each wire shown in the diagrams contains a code
(Fig. 3) which identifies the main circuit, part of the
main circuit, gauge of wire, and color. The color is shown as a two letter code which can be identified by
referring to the Wire Color Code Chart (Fig. 4). If
the wire has a tracer and it is a standard color an asterisk will follow the main wire color. If the tracer
is non-standard the main wire color will have a slash (/) after it followed by the tracer color. 18
LB/YL*
COLOR
OF
WIRE
(Light
Blue
with
Yellow
Tracer)
.
GAUGE
OF
WIRE
(18
Gauge)
PART
OF
AAAIN CIRCUIT
(Varies
Depending
on
Equipment)
AAAIN CIRCUIT
IDENTIFICATION
918W-16
Fig.
3
Wire
Color
Code
Identification
CIRCUIT IDENTIFICATION
All circuits in the diagrams use an alpha/numeric
code to identify the, wire and its function. To identify
which circuit code applies to a system, refer to the
Circuit Identification Code Chart. This chart shows
the main circuits only and does not show the second ary codes that may apply to some models.
COLOR
CODE COLOR
STANDARD
TRACER
COLOR COLOR
CODE
COLOR
STANDARD
TRACER
CODE
BL BLUE WT
OR ORANGE
BK
BK
BLACK
WT PK
PINK
BK
OR WT
BR
BROWN
WT RD
RED WT
DB DARK
BLUE WT
TN
TAN WT
DG DARK
GREEN WT
VT
VIOLET
WT
GY GRAY
BK
WT
WHITE
BK
LB
LIGHT
BLUE
BK
YL YELLOW
BK
LG
LIGHT
GREEN
BK
*
WITH
TRACER
918W-136
Fig.
4
Wire
Color
Code
Chart
LOCATING
A
SYSTEM
OR
COMPONENT
To locate a system or component in the diagrams,
refer to the alphabetical index at the front of the di agrams. Determine the diagram sheet number. Sheet
numbers are located at the lower right or left hand
corner of each sheet. Page numbers at the top of
the page do not apply to diagram sheets. The diagram index identifies the main system and
all components that relate to that system. There are
also sections of the index that identify specific com
ponents only (for example modules, lamps, etc.). Re-
MAIN
CIRCUIT IDENTIFICATION
CIRCUIT
DESCRIPTION
CIRCUIT
DESCRIPTION
A
Battery
Feed: Fused and Unfused
P
Power
Assist
System:
Locks,
Mirrors
B
ABS
System Q Power
Assist
System: Windows
C
Air Conditioning System
R
Airbag System
D
CCD
(+),
CCD
(-)
S
Air Suspension, Automatic Load Leveling
E
Interior
Lamp
Illumination
T Electronic Automatic Transaxle
F
Battery
Feed: Fused and Unfused
V
Windshield Wipers and Washers,
G
Sensors,
Sending Units, Switches Vehicle Speed Control System
K
Powertrain
Central
Module W Power
Assist
System: Windows
L
Exterior
Lighting, Stop Lamp Switch
X
Horn, Radio, Radio Speakers, Power Locks
M
Interior
Lamps
Z
Ground Circuits: Includes power and signal
Interior
Lamps
grounds
for PCM
938W-17
Page 478 of 1502

•
WIRING
DIAGRAMS
8W - 3 fer to a components name in the index if you are
unclear as to what a system may be called.
Diagram pages are arranged starting with the bat
tery and fuses. Then working into charging, starting, and ignition systems. After this they start at the
front of the vehicle and work to rear of the vehicle.
The diagrams end with connector identification
pages.
COMPONENT
IDENTIFICATION
To find a components actual location on the vehicle
refer to the wiring and components section index. This section shows the wire harness routing and the compo
nents location in the vehicle. When using this section
refer to the wiring diagrams for the general location of
the component. Then use the component identification index to locate the proper figure number.
SPLICE
LOCATIONS
Splices are indicated in the wiring diagrams by a
diamond with splice circuit code within it (Fig. 5 ex ample 1). If there is more than one splice per circuit
splice code a small box will be connected to the dia
mond with the splice number in it (Fig. 5 example 2). To locate a splice in the wire harness determine
the splice number from the wiring diagrams, then re
fer to the splice location index. This section shows
the general location of the splice in the harness.
EXAMPLE
1
EXAMPLE
2 918W-18
Fig.
5 Wiring
Splice
Examples
CONNECTORS
The connectors shown in the diagram are viewed from
the terminal end unless otherwise specified. For view ing bulkhead and engine controller connectors refer to
the back of the wiring diagrams. This area shows major connectors for pin and cavity identification.
TROUBLESHOOTING
WIRING
PROBLEMS
When troubleshooting wiring problems there are
six steps which can aid in the procedure. The steps
are listed and explained below. (1) Verify the problem.
(2) Verify any related symptoms. Perform opera
tional checks on components in the same circuit as the problem area. Refer to the wiring diagram fuse
application chart for circuit information. (3) Analyze the symptoms. Use the wiring dia
grams to determine what the circuit is doing, where
the problem most likely is occurring and where the diagnosis will continue. (4) Isolate the problem area. (5) Repair the problem.
(6) Verify proper operation. For this step check for
proper operation of all items on the circuit repaired. Refer to the wiring diagram fuse application chart.
FUSIBLE
LINKS
Vehicle wiring harnesses are equipped with fusible
links.
For protection against harness damage in the
event of a short. Fusible links are color coded as to
wire gauge size. Refer to the fusible link chart for color and gauge identification (Fig. 6).
Wire and
Gauge
Color
Code
Color
12 Ga.
BK
Black
14 Ga.
RD
Red
16 Ga.
DB
Dark
Blue
18 Ga.
GY
Gray
20 Ga.
OR
Orange
22 Ga.
WT
White
918W-19
Fig.
6 Fusible
Link
Chart
HARNESS
REPAIR
FUSIBLE
LINK
REPLACEMENT
CAUTION:
Do not replace blown fusible
links
with
a
standard
wire.
Only
use fusible type
wire
with
hyp-
alon
insulation or
damage
to the electrical
system
could
occur.
Also
make
sure
correct
gauge
of
wir
ing
is
used.
Refer to the wiring
diagrams
for proper
gauge
and
color.
When a fusible link blows it is important to find
out what the problem is. They are placed in the elec
trical system for protection against shorts to ground
that can be caused by a component or various wiring
failures. Do not just replace the fusible link to correct the problem.
When diagnosing a faulty fusible link it is impor
tant to check the wire carefully. In some instances
the link may be blown and it will not show through the insulation, the wire should be checked over its
entire length for internal breaks.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Cut out the blown portion of the fusible link.
(3) Strip 1 inch of insulation from each end of the
existing fusible link.
(4) Place a piece of heat shrink tubing over one
side of the fusible link. Make sure the tubing will be
long enough to cover and seal the entire repair area.
(5) Cut a replacement piece of fusible link approx
imately two inches longer than the piece removed. (6) Remove one inch of insulation from each end of
the replacement fusible link.
Page 480 of 1502
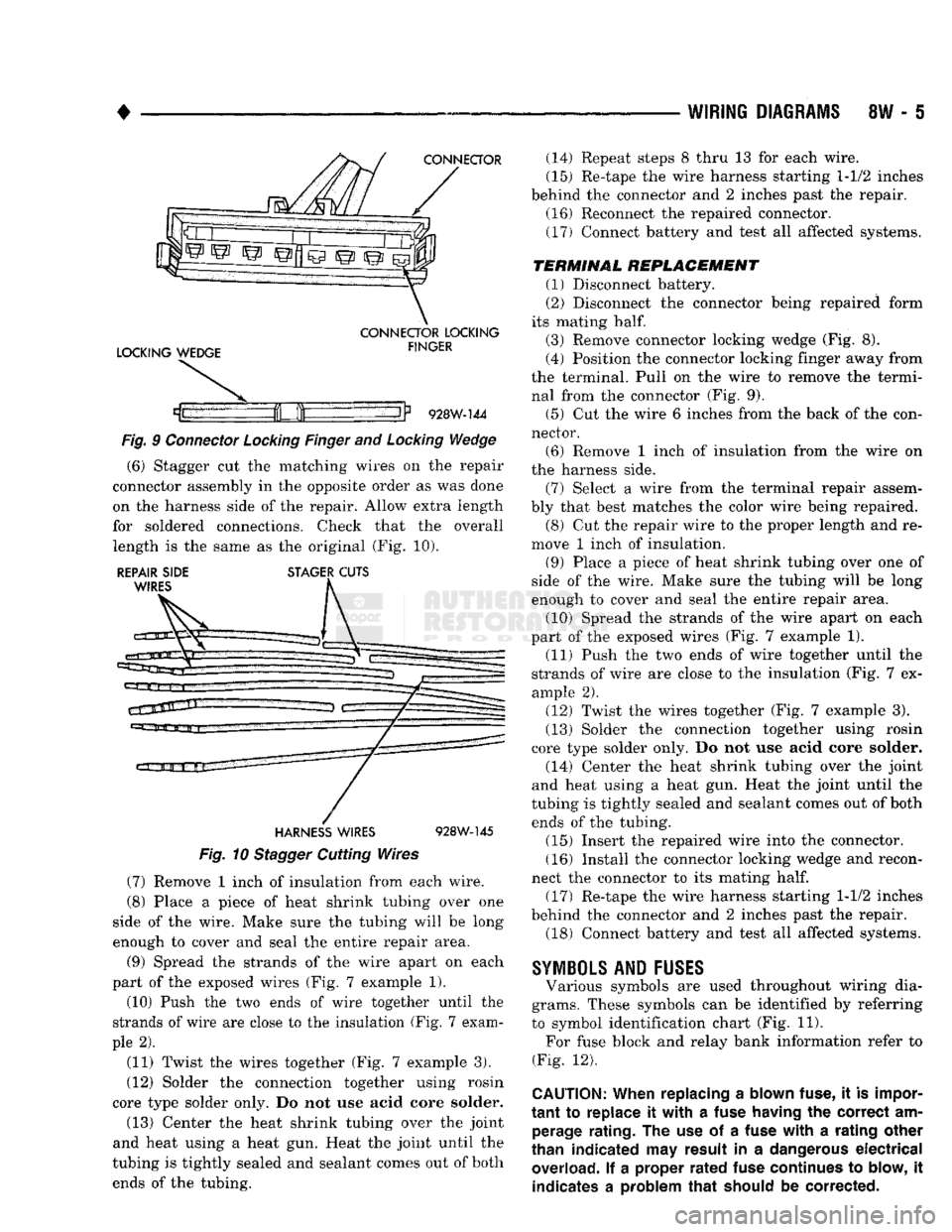
WIRING DIAGRAMS
SW - 5
CONNECTOR
LOCKING WEDGE
CONNECTOR
LOCKING
FINGER
If
928W-144
Fig.
9
Connector
Locking
Finger
and
Locking
Wedge
(6) Stagger cut the matching wires on the repair
connector assembly in the opposite order as was done
on the harness side of the repair. Allow extra length
for soldered connections. Check that the overall length is the same as the original (Fig. 10).
REPAIR SIDE STAGER CUTS WIRES
HARNESS
WIRES
928W-145
Fig.
10
Stagger
Cutting Wires (7) Remove 1 inch of insulation from each wire.
(8) Place a piece of heat shrink tubing over one
side of the wire. Make sure the tubing will be long
enough to cover and seal the entire repair area.
(9) Spread the strands of the wire apart on each
part of the exposed wires (Fig. 7 example 1).
(10) Push the two ends of wire together until the
strands of wire are close to the insulation (Fig. 7 exam
ple 2).
(11) Twist the wires together (Fig. 7 example 3).
(12) Solder the connection together using rosin
core type solder only. Do not use acid core solder.
(13) Center the heat shrink tubing over the joint
and heat using a heat gun. Heat the joint until the
tubing is tightly sealed and sealant comes out of both ends of the tubing. (14) Repeat steps 8 thru 13 for each wire.
(15) Re-tape the wire harness starting 1-1/2 inches
behind the connector and 2 inches past the repair. (16) Reconnect the repaired connector.
(17) Connect battery and test all affected systems.
TERMINAL
REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect battery.
(2) Disconnect the connector being repaired form
its mating
half.
(3) Remove connector locking wedge (Fig. 8).
(4) Position the connector locking finger away from
the terminal. Pull on the wire to remove the termi nal from the connector (Fig. 9).
(5) Cut the wire 6 inches from the back of the con
nector. (6) Remove 1 inch of insulation from the wire on
the harness side.
(7) Select a wire from the terminal repair assem
bly that best matches the color wire being repaired. (8) Cut the repair wire to the proper length and re
move 1 inch of insulation.
(9) Place a piece of heat shrink tubing over one of
side of the wire. Make sure the tubing will be long
enough to cover and seal the entire repair area.
(10) Spread the strands of the wire apart on each
part of the exposed wires (Fig. 7 example 1). (11) Push the two ends of wire together until the
strands of wire are close to the insulation (Fig. 7 ex
ample 2).
(12) Twist the wires together (Fig. 7 example 3).
(13) Solder the connection together using rosin
core type solder only. Do not use acid core solder.
(14) Center the heat shrink tubing over the joint
and heat using a heat gun. Heat the joint until the
tubing is tightly sealed and sealant comes out of both ends of the tubing.
(15) Insert the repaired wire into the connector.
(16) Install the connector locking wedge and recon
nect the connector to its mating
half.
(17) Re-tape the wire harness starting 1-1/2 inches
behind the connector and 2 inches past the repair. (18) Connect battery and test all affected systems.
SYMBOLS
AND
FUSES
Various symbols are used throughout wiring dia
grams. These symbols can be identified by referring
to symbol identification chart (Fig. 11). For fuse block and relay bank information refer to
(Fig. 12).
CAUTION:
When replacing
a
blown fuse,
it is
impor
tant
to
replace
it
with
a
fuse having
the
correct
am
perage rating.
The use of a
fuse
with
a
rating other
than indicated
may
result
in a
dangerous
electrical
overload.
If a
proper
rated
fuse continues
to
blow,
it
indicates
a
problem
that
should
be
corrected.
Page 513 of 1502

8W
- 38
WIRING
DIAGRAMS
• Wiring Diagram Name Sheet Number
EMCC
Relay
11
EMCC
Solenoid
11
Ground
11
EMCC
Relay
with Gas
Engine
11,16
EMCC
Solenoid
with Gas
Engine
11,12
Engine
Oil
Pressure Sending
Unit
.27,28
Engine
Starter
Motor
7,9
Engine
Starter
Relay
.7,9
Engine
Starter
System 1,7,8,9 Back-Up Lamp
Switch
.7,9
Bypass
Jumper
(Clutch
Pedal
Position)
8
Clutch
Pedal
Position
Switch
8
Fuse
. 7,9
Motor
7,9
Park/Neutral
Position
Switch
. .7,9
Relay
7,9
Engine Temp Sending
Unit
.
.27,28
Flasher-Hazard Warning
.56
Flasher-Turn Signal
56
Four Wheel
Drive
Indicator
Lamp
13
Front
End
Lighting
. .
.43,44
Front
End
Lighting
(Canada) 45,46
Fuel
Gauge
81,82
Fuel
Tank Gauge
Level
Sending
Unit
Diesel Engine
77
Fuel
Tank Gauge
Level
Sending
Unit
with Gas
Engine
78
Fuel
Heater
Diesel Engine
24
Fuel
Solenoid Diesel Engine
.24
Fuse
Application
Chart
1,2
Fuse
Block Module
and
Relay Bank
82
Fuses
Fuse
1 2,36
Fuse
2
.........
2,10,12,13,14,58,77,78
Fuse
3
2,7,9,10,39
Fuse
4
1,30,47
Fuse
5
1,77,78
Fuse
6
......
.1,73
Fuse
7
1,10,52
Fuse
8
.2,10,61,63
Fuse
9
.2,10,31,33,56
Fuse
10
.2,10,54,55
Fuse
11
2,10,66,67,69
Fuse
12
2,10,71
Fuse
13 1,56
Fuse
14
1,47,52,61,63
Fuse
15
1,49,51,52,61,63,75
Fusible Links 1,2,3,4,5,6,21
Gas
Engine
Wiring
Connector
89
Gauge-Fuel .77,78
Generator
.4,6
Glove
Box
Lamp
Switch
52
Hazard Warning System
. .56
Headlamp Dimmer
Switch
47
Headlamp
Switch
1,47
Headlamp
Switch
Controlled
Interior
Lamps
Headlamps 43,44,
Heated
Rear Window
(Sport
Utility)
Heater
Motor
Resistor
Heater
System Wiring Diagram Name Sheet Number
Horn System
30
Identification
Lamps-Dual Rear Wheels
41,42
Identification
Lamps-Roof Mounted
. 40
Ignition
Coil
.16
Ignition
Switch
.2,10
Ignition
Switch
System
10
Ignition
System (Gas Engine)
.........
.15,16,17,18,19,20
Automatic
Shut Down Relay
.16
Camshaft
Position
Sensor
20
Crankshaft
Position
Sensor
.18
Data
Link
Connector
* . . .17
Engine Coolant Temp
Sensor
20
EVAP
Purge Solenoid
16
Exhaust Gas
Recirculation
Solenoid
16
Fuel
Pump Relay
.16
Heated
Oxygen
Sensor
. . . 17
Idle
Air
Control
Motor
.19
Ignition
Coil
.15
Injectors
.15
Intake
Air
Temp
Sensor
. .20
Map
Sensor
. .20
Powertrain
Control
Module .15,16,17,18,19,20
Throttle
Position
(Sensor)
.18
Vehicle
Speed
Sensor
.20
Ignition
Time
Delay Relay
49
Injectors
.15 Intermittent
Wiper
System .53,54
Control
Unit
.54 Intermittent
Windshield
Wiper
Motor
54
Windshield
Washer Pump
Motor
53
Wiper
Switch
53
Key-In
Switch
49
Key-In Warning Buzzer 77,78
Lamps
Air-Conditioning
and
Heater
Switch
Lamp
48
Ash
Receiver .48,52 Back-Up Lamps
......
79,80,81
Cargo Lamp
.
.49,50 Clearance Lamps-Dual Rear Wheels .41,42
Clearance Lamps Roof Mounted
.40
Cluster
Illumination
Lamps
.
.57,58,59
Dome Lamp
50,51
Four Wheel
Drive
Indicator
.13
Glove
Box
Lamp
52
Headlamp-Left
43,45 Headlamp-Right 44,46
Headlamp
Switch
Controlled
Interior
Lamps
. 48
Heater
Switch
Lamp
.48
High Beam
Indicator
Lamp
.59
Identification
Lamp
.
.40,41
Ignition
Switch
Lamp
.49
Instrument
Panel
Illumination
Lamps
.
.57,58,59
License Lamp
. . . 80
.
.48 Low
Engine
Oil
Pressure Lamp
59
45,46
Map
Lamp
49
.
.39
Parking
Lamp-Left
Front
43,45
66,67 Parking Lamp-Right
Front
44,46 .
.66
Rear
End
Lighting
System .79,80,81
Page 517 of 1502
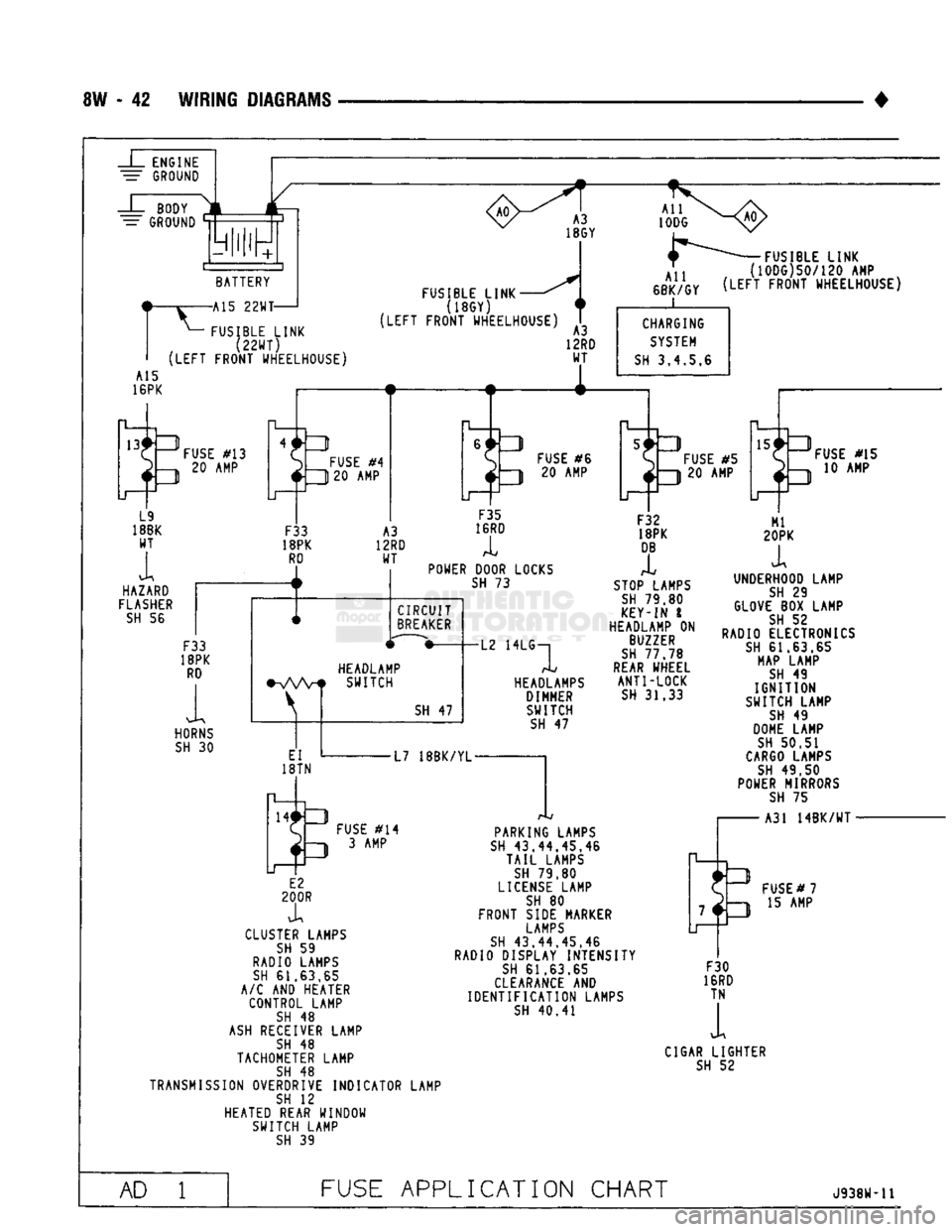
8W
- 42
WIRING DIAGRAMS
-J_
ENGINE
=
GROUND
BODY
—
GROUND
BATTERY
-A
15
22WT-
^—
FUSIBLE LINK
(22WT)
(LEFT
FRONT WHEELHOUSE) FUSIBLE LINK
(18GY)
(LEFT
FRONT WHEELHOUSE)
All
6BK/GY FUSIBLE LINK
{1000)50/120 AMP
(LEFT
FRONT WHEELHOUSE) A15
16PK
13#-ZI
L9
18BK WT
i
HAZARD
FLASHER
SH
56
IT-
FUSE
#13
20 AMP
O
FUSE
#4
|
ft 20 AMP
F33
18PK
RD
A3
12RD WT A3
12RD WT
4-
CHARGING
SYSTEM
SH
3,4,5.6
FUSE
#6 20 AMP
FUSE
#5
J—1| 20 AMP
F33
18PK
RD
HORNS
SH
30
POWER DOOR LOCKS
SH
73
CIRCUIT
BREAKER
HEADLAMP
•VWf
SWITCH
EI
18TN
SH
47
-L2 HEADLAMPS
DIMMER SWITCH
SH
47
F32
18PK
DB
I
STOP LAMPS
SH
79,80
KEY-IN
I
HEADLAMP
ON
BUZZER
SH
77.78
REAR
WHEEL ANTI-LOCK
SH
31.33
FUSE
#15
10 AMP
L7
18BK/YL-
3
FUSE
#14
D 3AMP
E2
200R
X
CLUSTER LAMPS
SH
59
RADIO LAMPS
SH
61.63.65
A/C
AND
HEATER CONTROL LAMP
SH
48
ASH
RECEIVER LAMP
SH
48
TACHOMETER LAMP
SH
48
TRANSMISSION OVERDRIVE INDICATOR LAMP
SH
12
HEATED REAR WINDOW SWITCH LAMP
SH
39
PARKING LAMPS
SH
43.44.45,46
TAIL
LAMPS
SH
79.80
LICENSE
LAMP
SH
80
FRONT SIDE MARKER
LAMPS
SH
43.44.45.46
RADIO DISPLAY INTENSITY
SH
61.63.65
CLEARANCE
AND
IDENTIFICATION
LAMPS
SH
40.41
UNDERHOOD LAMP
SH
29
GLOVE
BOX
LAMP
SH
52
RADIO ELECTRONICS
SH
61.63.65
MAP LAMP
SH
49
IGNITION
SWITCH LAMP
SH
49
DOME LAMP
SH
50.51
CARGO
LAMPS
SH
49.50
POWER MIRRORS
SH
75
A31
14BK/WT
-
7*3
LI FUSE
#7
2h-i
15 AMP
F30
16RD TN
1
CIGAR LIGHTER
SH
52
AD
1
FUSE
APPLICATION CHART
J938W-U
Page 518 of 1502
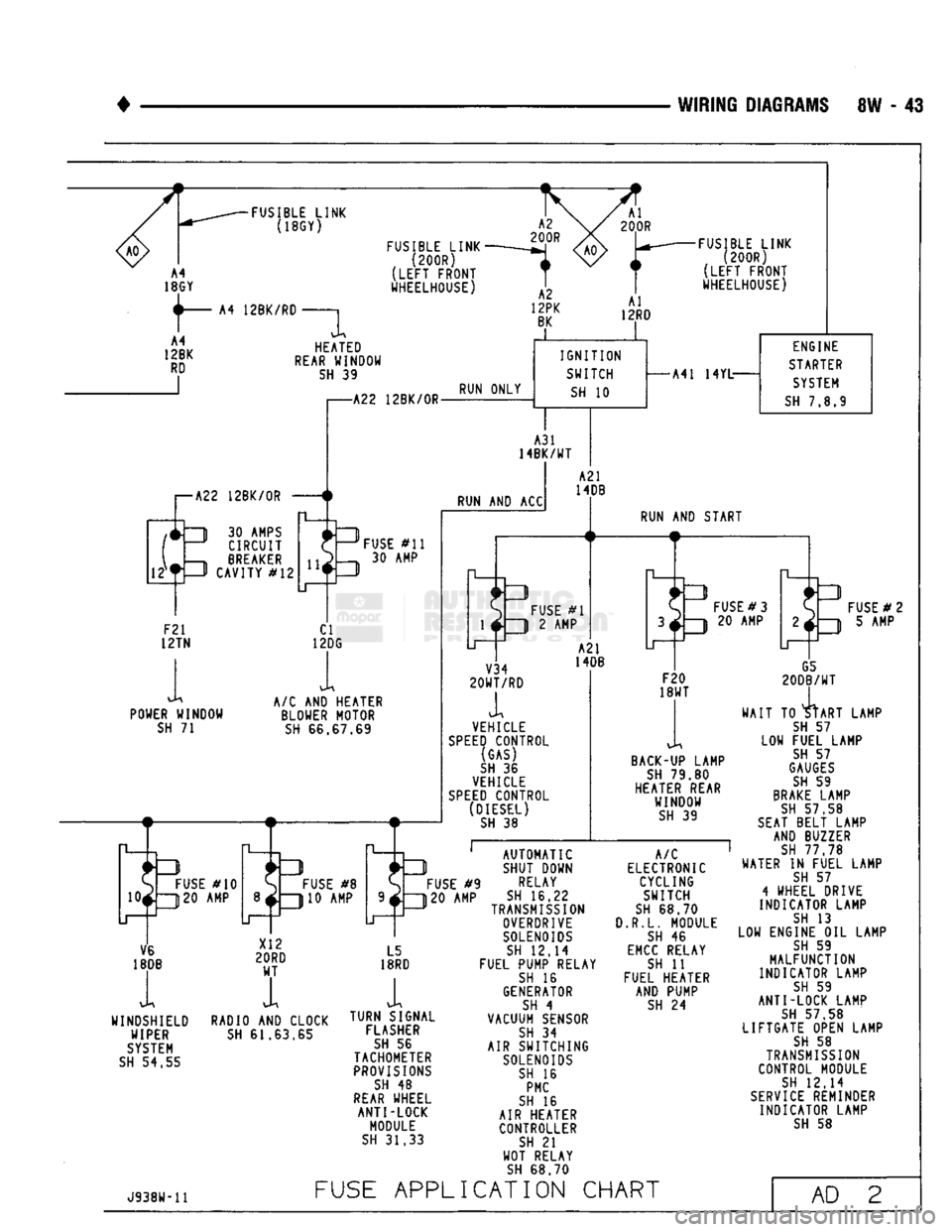
WIRING
DIAGRAMS
8W - 43
FUSIBLE
LINK
(18GY)
12BK/RD
FUSIBLE
LINK
(200R)
(LEFT
FRONT
WHEELHOUSE) HEATED
REAR
WINDOW
SH
39
FUSIBLE
LINK
(200R)
(LEFT
FRONT
WHEELHOUSE)
I—A22
12BK/0R
IT
1
30
AMPS
J CIRCUIT
,—h BREAKER —P CAVITY
#12
-A22
12BK/0R-
RUN ONLY
IGNITION
SWITCH
SH
10
A31
14BK/WT
RUN
AND ACC
F21
12TN
POWER WINDOW
SH
71
FUSE
#11
30 AMP
CI
12DG
A/C
AND
HEATER BLOWER MOTOR
SH
66.67.69
S
FUSE
#10
10*ZJ20
AMP
O
FUSE
#8
310 AMP
-A41
14YL-
ENGINE
STARTER
SYSTEM
SH
7.8.9
A21
14DB
FUSE
#1
3
2 AMP
RUN
AND
START
V34
20WT/RD
A2I
14DB
VEHICLE
SPEED
CONTROL (GAS)
SH
36
VEHICLE
SPEED
CONTROL (DIESEL)
SH
38
FUSE
#3
20 AMP
F20
18WT
BACK-UP
LAMP
SH
79.80
HEATER REAR WINDOW
SH
39
G5
20DB/WT
TO
4tART
D
FUSE
# 2
3
5 AMP
LAMP LOW
FUSE
#9
120 AMP
V6
18DB
WINDSHIELD WIPER
SYSTEM
SH
54.55
RADIO
AND
CLOCK
SH
61.63.65
L5
18RD
i
TURN SIGNAL FLASHER
SH
56
TACHOMETER
PROVISIONS
SH
48
REAR
WHEEL ANTI-LOCK
MODULE
SH
31.33
AUTOMATIC
SHUT DOWN
RELAY
SH
16.22
TRANSMISSION
OVERDRIVE
SOLENOIDS
SH
12.14
FUEL PUMP RELAY
SH
16
GENERATOR
SH
4
VACUUM SENSOR
SH
34
AIR SWITCHING
SOLENOIDS
SH
16
PMC
SH
16
AIR HEATER CONTROLLER
SH
21
WOT RELAY
SH
68.70
A/C
ELECTRONIC CYCLING SWITCH
SH
68.70
3.R.L.
MODULE
SH
46
EMCC
RELAY
SH
11
FUEL HEATER AND PUMP
SH
24
WAIT
TO
START
SH
57
FUEL LAMP
SH
57
GAUGES
SH
59
BRAKE
LAMP
SH
57.58
SEAT
BELT LAMP AND BUZZER
SH
77 78
WATER
IN
FUEL LAMP
SH
57
4
WHEEL DRIVE
INDICATOR LAMP
SH
13
LOW ENGINE
OIL
LAMP
SH
59
MALFUNCTION
INDICATOR LAMP
SH
59
ANTI-LOCK LAMP
SH
57 58
LIFTGATE OPEN LAMP
SH
58
TRANSMISSION
CONTROL MODULE
SH
12.14
SERVICE
REMINDER INDICATOR LAMP
SH
58
J938W-11
FUSE
APPLICATION
CHART
AD
2