oil FIAT 500 1963 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1963, Model line: 500, Model: FIAT 500 1963 1.GPages: 128, PDF Size: 9.01 MB
Page 91 of 128

RIGHT HAND TIE ROD
RELAY LEVER SUPPORTINTERMEDIATE TIE ROD!
STEERING BOX!
LEFT HAND TIE ROD
FIG 9 :1 Steering box, idler member and steering linkage arrangement on vehicle
FIG 9 : 2 Securing steering wheel mounting nut
Key
to Fig 9:2(Tightening torque: 29 to 36 Ib ft)
9 : 4 Steering box dismantling and reassembly
1 Remove the steering gear housing cover complete
with the adjusting screw and locking nut and drain the
oil from the unit.
2 Using Fiat puller A.4005.1.5 or a universal t w o leg
puller remove the pitman arm.
3 Remove the cotter pin from the lower thrust bearing
adjusting nut and unscrew this nut.
4 Remove the sealing ring at the sector shaft lower end
and using Fiat tool A.8065 loosen the eccentric bush
adjuster plate bolt and remove both the bolt and the
adjusting plate. Also remove the upper sealing ring.
98
5 Lift out the sector together with the upper thrust
washer and shims.
6 Remove the steering worm screw by pulling out from
below. The two bearing inner rings will remain on the
worm screw whilst the lower bearing outer ring will
remain in the housing.
7 Remove the oil seal using Fiat tool A.10110 followed
by the worm screw upper bearing outer ring using
Fiat tool A.66040 or a suitably sized drift.
Inspection:
1 Carefully inspect the sector teeth and the worm screw
threads to see that there are no signs of seizure,
indentations or scoring. Check that the contact faces
indicate that meshing between the two parts is taking
place at the centre.
2 Check the clearance between the eccentric bush 5
(see FIG 9 : 5) and the worm sector 11 which must not
exceed .0039 inch. These items have an initial
assembly clearance of .00 to .0016 inch. It should be
noted that if the eccentric bushing to sector shaft
clearance exceeds .0039 inch a new bushing should
be installed and its inner face reamed using Fiat
reamer U.0360.20.
3 Ensure that the worm screw is not distorted. The
permissible out of true is .0019 inch.
Adjustment:
1 If the backlash between the worm screw and the
sector is excessive it should be adjusted by first dis-
connecting the pitman arm and its relevant seal.
Remove the screw 7 (see FIG 9 : 5) fixing the abut-
ment plate 6. Rotate the eccentric bush 5 by the
adjustment plate and move the sector in towards the
worm screw. The adjustment plate should be secured
again using the second fixing hole.
Should the adjustment plate already be fixed in the
second hole remove the plate from the bush and
rotate one or more serrations and re-secure.
Page 92 of 128
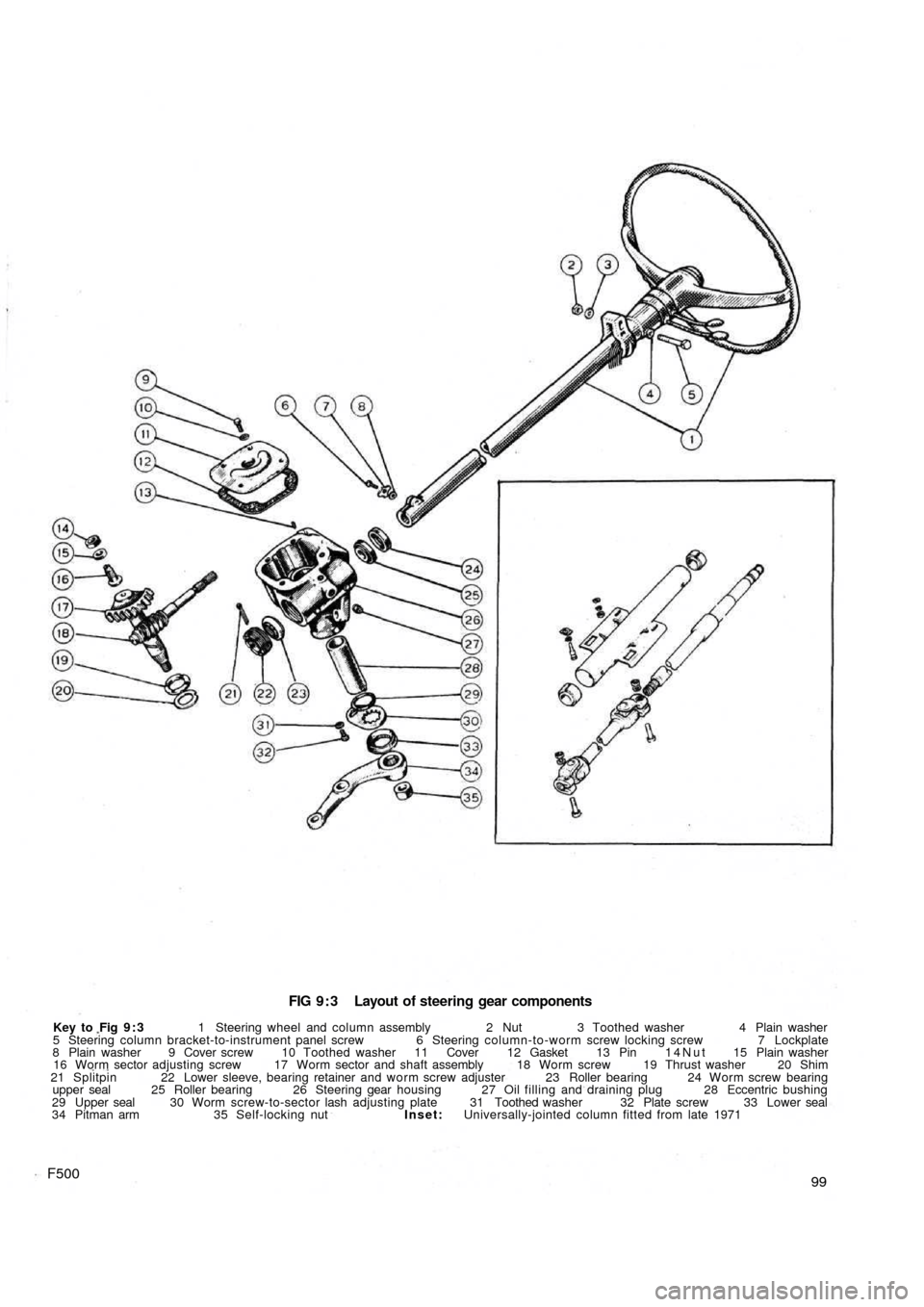
FIG 9 : 3 Layout of steering gear components
Key to Fig 9 : 3 1 Steering wheel and column assembly 2 Nut 3 Toothed washer 4 Plain washer
5 Steering column bracket-to-instrument panel screw 6 Steering column-to-worm screw locking screw 7 Lockplate
8 Plain washer 9 Cover screw 10 Toothed washer 11 Cover 12 Gasket 13 Pin 14Nut 15 Plain washer
16 Worm sector adjusting screw 17 Worm sector and shaft assembly 18 Worm screw 19 Thrust washer 20 Shim
21 Splitpin 22 Lower sleeve, bearing retainer and worm screw adjuster 23 Roller bearing 24 Worm screw bearing
upper seal 25 Roller bearing 26 Steering gear housing 27 Oil filling and draining plug 28 Eccentric bushing
29 Upper seal 30 Worm screw-to-sector lash adjusting plate 31 Toothed washer 32 Plate screw 33 Lower seal
34 Pitman arm 35 Self-locking nut Inset: Universally-jointed column fitted from late 1971
99F500
Page 93 of 128
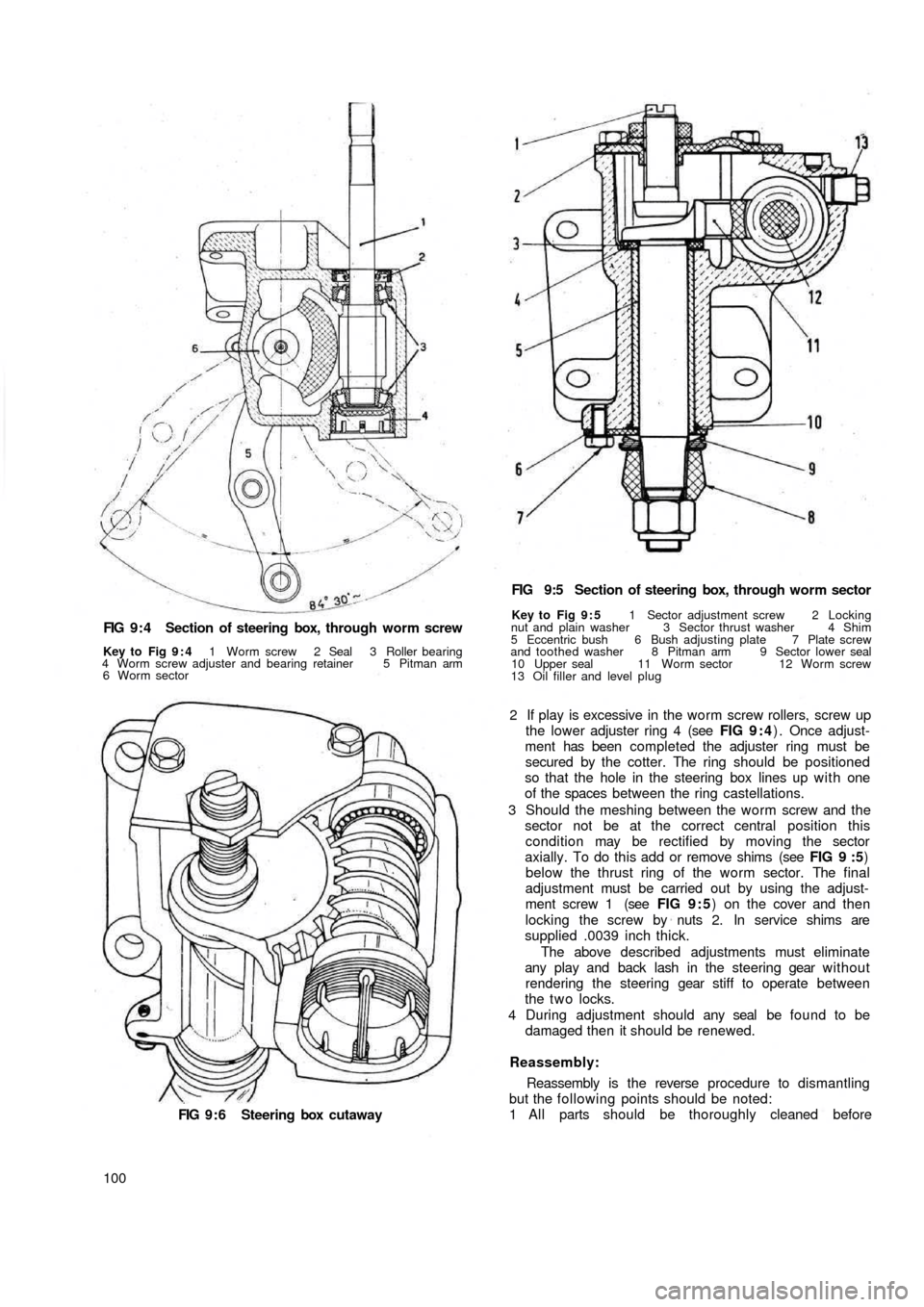
FIG 9 : 4 Section of steering box, through worm screw
Key to Fig 9 : 4 1 Worm screw 2 Seal 3 Roller bearing
4 Worm screw adjuster and bearing retainer 5 Pitman arm
6 Worm sector
FIG 9 : 6 Steering box cutaway
100FIG 9:5 Section of steering box, through worm sector
Key to Fig 9 : 5 1 Sector adjustment screw 2 Locking
nut and plain washer 3 Sector thrust washer 4 Shim
5 Eccentric bush 6 Bush adjusting plate 7 Plate screw
and toothed washer 8 Pitman arm 9 Sector lower seal
10 Upper seal 11 Worm sector 12 Worm screw
13 Oil filler and level plug
2 If play is excessive in the worm screw rollers, screw up
the lower adjuster ring 4 (see FIG 9 : 4) . Once adjust-
ment has been completed the adjuster ring must be
secured by the cotter. The ring should be positioned
so that the hole in the steering box lines up w i t h one
of the spaces between the ring castellations.
3 Should the meshing between the worm screw and the
sector not be at the correct central position this
condition may be rectified by moving the sector
axially. To do this add or remove shims (see FIG 9 :5)
below the thrust ring of the worm sector. The final
adjustment must be carried out by using the adjust-
ment screw 1 (see FIG 9 : 5) on the cover and then
locking the screw by nuts 2. In service shims are
supplied .0039 inch thick.
The above described adjustments must eliminate
any play and back lash in the steering gear without
rendering the steering gear stiff to operate between
the t w o locks.
4 During adjustment should any seal be found to be
damaged then it should be renewed.
Reassembly:
Reassembly is the reverse procedure to dismantling
but the following points should be noted:
1 All parts should be thoroughly cleaned before
Page 94 of 128
reassembling and during assembly liberally lubricated
using Fiat W90/M oil (SAE90 EP).
2 The pitman arm nut should be correctly positioned on
reassembly to the sector shaft and both are marked
with notches or a master tooth on the sector will mate
with a double tooth on the pitman arm which will
prevent incorrect reassembly.
3 The pitman arm nut must be tightened to a torque
wrench setting of 72 Ib/ft.
4 Fill the box up to the level and filler plug with SAE90 EP
gear oil.
Refitting the steering box:
To refit the steering box to the vehicle proceed as
follows:
1 Engage the w o r m screw f r o m the steering shaft by
gently manipulating the steering box.
2 Replace the steering box to body nuts and tighten to a
torque wrench setting of 14 to 18 Ib/ft.
3 Replace the t w o track rod pins in their seatings in the
pitman arm and tighten the self-locking nuts to a
torque wrench setting of 18 to 21 Ib/ft.
4 Replace the steering shaft to worm screw mounting
bolt, lock washer and nut.
9 :5 Relay lever and support
The steering idler arm is secured to the body by means
of a support bracket and a rubber bushed pivot bolt. This
is shown in FIG 9 : 7. When this unit is being serviced
the following points should be noted.
1 If there is excessive play between the pin and the
bushes the bushes must be renewed. Also check the
condition of the pin and if there are signs of excessive
wear it must be renewed.
2 To eliminate torsional stresses in the rubber bushes
during assembly the pin nut must be tightened to
torque wrench setting of 39 to 43 Ib/ft, once the
front wheel toe-in has been correctly adjusted w i t h the
wheels set in the straight ahead position.
3 The relay lever support to body mounting nuts must
be tightened to a torque wrench setting of 14 to 18
Ib/ft.
9 : 6 Steering rods (tie rods)
The steering rod is connected to the idler arm and the
drop arm by means of non-adjustable ball joints. The
track rods are connected to the right and left steering
arms by non-adjustable ball joints and comprise t w o
sleeves which are split and having internally threaded
ends. The ball joints are clamped to either end of the
sleeves. To facilitate adjustment one ball joint end has a
lefthand thread and the other a righthand thread.
Adjustment is made by loosening both the clamping bolts
and turning the central sleeve.
To remove the steering rods from the pitman arm, the
relay lever and knuckle arms Fiat pullers A.46006 and
A.6473 or universal ball joint removers should be used.
If excessive play is evident in the ball joint linkage or
the pin is damaged the complete ball joint assembly must
be renewed.
Upon reassembly the tie rod to ball pin knuckle arm
nuts must be tightened to a torque wrench setting of
18 to 21 Ib/ft.
F500101
FIG 9:7 Relay lever support section
FIG 9:8 Front wheel toe-in checking diagram
Key to Fig 9:8 A—B = 000 inch to .079 inch
It is important that all steering linkages are thoroughly
checked at regular intervals and if any parts are suspect
then they must be renewed.
9 : 7 Front wheel toe-in
To check and adjust the front wheel toe-in proceed as
follows:
1 Ensure that the tyres are inflated to the recommended
pressures. Ensure that the steering wheel is in its
Page 97 of 128
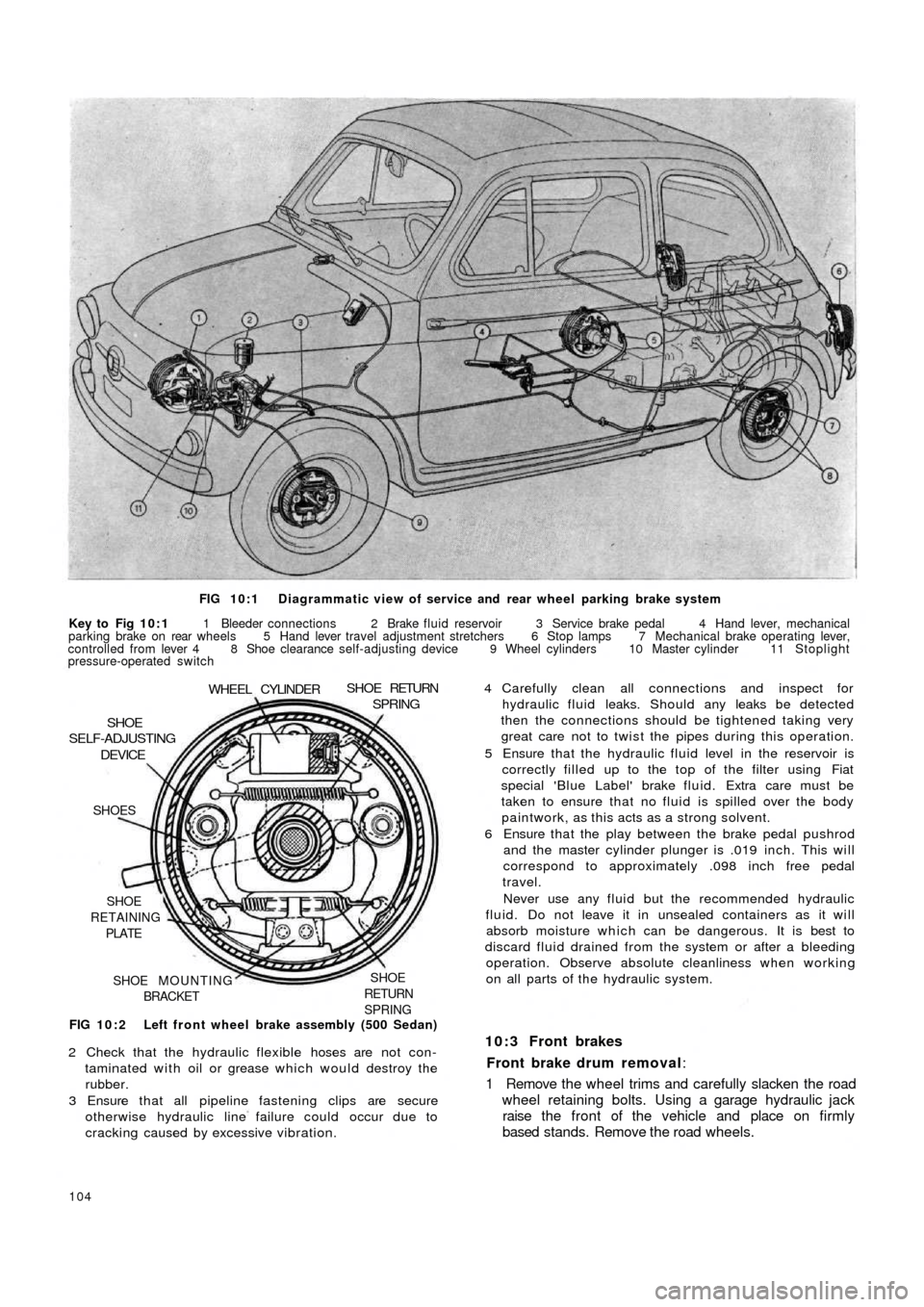
FIG 10:1 Diagrammatic view of service and rear wheel parking brake system
Key to Fig 10:1 1 Bleeder connections 2 Brake fluid reservoir 3 Service brake pedal 4 Hand lever, mechanical
parking brake on rear wheels 5 Hand lever travel adjustment stretchers 6 Stop lamps 7 Mechanical brake operating lever,
controlled from lever 4 8 Shoe clearance self-adjusting device 9 Wheel cylinders 10 Master cylinder 11 Stoplight
pressure-operated switch
FIG 10:2 Left front wheel brake assembly (500 Sedan)
SHOE
RETURN
SPRINGSHOE MOUNTING
BRACKET SHOE
RETAINING
PLATE SHOES
DEVICESHOE
SELF-ADJUSTING
WHEEL CYLINDERSHOE RETURNSPRING
2 Check that the hydraulic flexible hoses are not con-
taminated with oil or grease which would destroy the
rubber.
3 Ensure that all pipeline fastening clips are secure
otherwise hydraulic line failure could occur due to
cracking caused by excessive vibration.
104
4 Carefully clean all connections and inspect for
hydraulic fluid leaks. Should any leaks be detected
then the connections should be tightened taking very
great care not to twist the pipes during this operation.
5 Ensure that the hydraulic fluid level in the reservoir is
correctly filled up to the top of the filter using Fiat
special 'Blue Label' brake fluid. Extra care must be
taken to ensure that no fluid is spilled over the body
paintwork, as this acts as a strong solvent.
6 Ensure that the play between the brake pedal pushrod
and the master cylinder plunger is .019 inch. This will
correspond to approximately .098 inch free pedal
travel.
Never use any fluid but the recommended hydraulic
fluid. Do not leave it in unsealed containers as it will
absorb moisture which can be dangerous. It is best to
discard fluid drained from the system or after a bleeding
operation. Observe absolute cleanliness when working
on all parts of the hydraulic system.
10:3 Front brakes
Front brake drum removal:
1 Remove the wheel trims and carefully slacken the road
wheel retaining bolts. Using a garage hydraulic jack
raise the front of the vehicle and place on firmly
based stands. Remove the road wheels.
Page 98 of 128
2 Using Fiat puller A.46023 as shown in FIG 8 : 9
remove the wheel grease cap.
3 Using a universal t w o leg puller or Fiat puller A.40005
together w i t h items 1 and 9 remove the wheel hub/
drum assembly having first extracted the splitpin if
fitted and released the hub retaining nut (see FIG
8:10).
Dismantling brake unit:
1 Using a compressed air jet thoroughly clean all com-
ponents of the brake assembly.
2 Make a note of the location of the shoe return springs
and gently ease the shoes away from the brake
backplate (see FIG 10:2).
3 Disconnect the hydraulic line from the rear of t h e
wheel cylinder and remove the t w o cylinder retaining
bolts. Lift away the hydraulic cylinder.
Brake shoe lining:
Check the lining thickness and if found to be exces-
sively reduced service replacement shoes must be fitted.
The minimum allowable brake lining thickness is .059
inch.
Thoroughly check the linings for signs of oil or grease
which, if evident, the shoes must be renewed and the
drums and oil seals thoroughly inspected for the cause
of oil ingress and the cause remedied before reassembly.
Do not fit odd brake shoes and do not mix materials or
unbalanced braking will result.
Do not allow grease, oil or paint to contact the friction
linings.
Brake drums:
Whilst servicing the brakes, thoroughly inspect the
drums for scoring, ovality or distortion as well as inspect-
ing for minute hair line cracks. The drums may be refaced
by using a centre lathe and finally finishing by lapping
the drums to smooth out possible tool marks. The
maximum permissible oversize beyond the nominal drum
diameter of 6.702 to 6.712 inch is .039 inch. This limit
must never be exceeded otherwise the strength of the
drum will be impaired or a reduction in braking efficiency
caused by the increase of shoe expansion travel and the
consequent diminished contact pressure.
No brake adjustment will be required on the new 500
Saloon models after the drum has been reassembled as
the self-adjusting device will accommodate for the shoe
position to the new drum diameter during the first
operation of the brake pedal.
Reassembly of front brakes:
This is the reverse procedure to dismantling. Ensure
that the pull-off springs are correctly fitted to the holes in
the webs of the brake shoes and that the shoes register
correctly in the slotted ends of the pistons and the
side
mounting plate.
Upon assembly of the hub and brake drum assembly
liberally pack the space between the two bearings w i t h
Fiat MR grease, and remount the hub according to the
instructions in Chapter 8.
F500
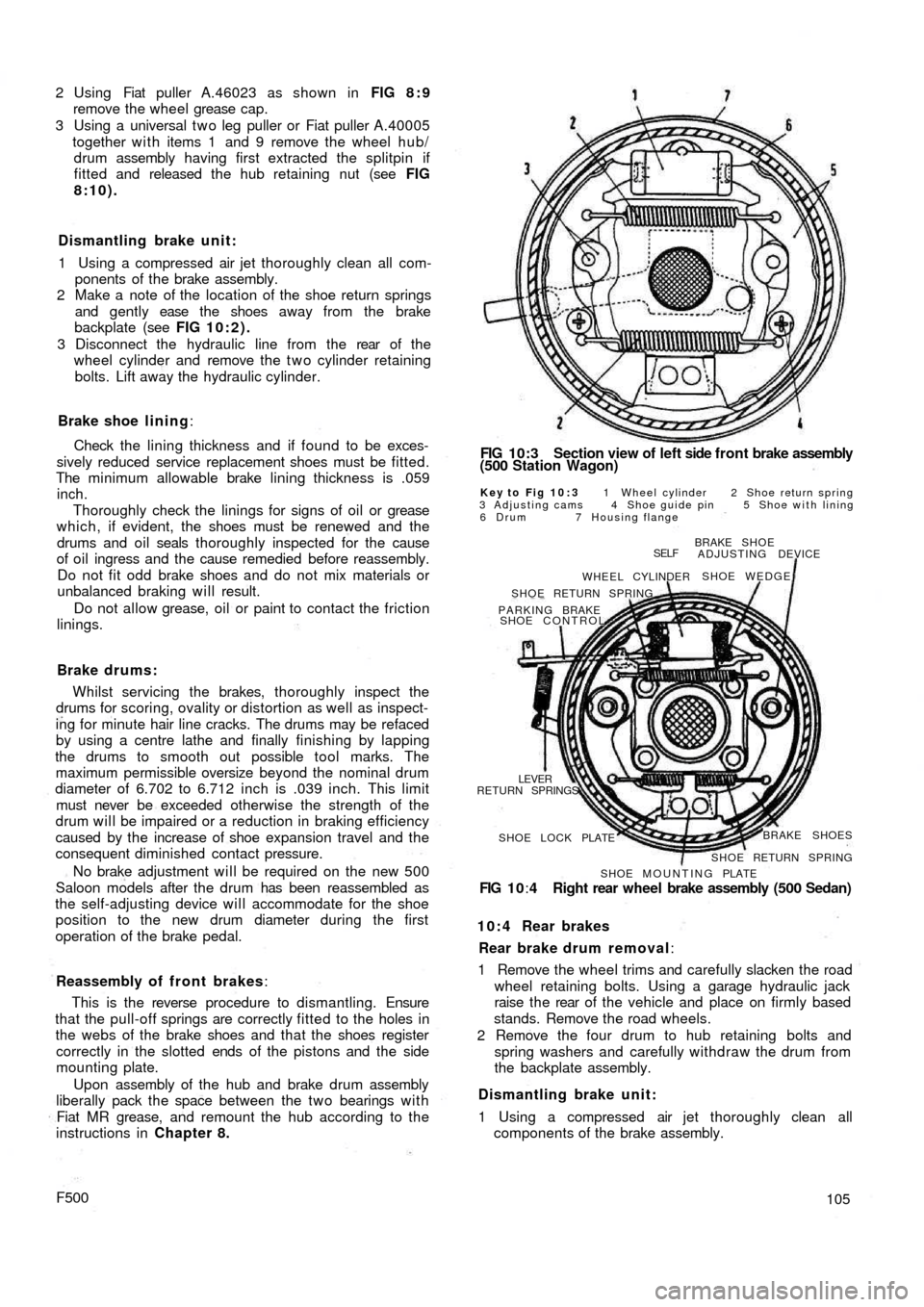
FIG 10:3 Section view of left side f r o n t brake assembly
(500 Station Wagon)
Key to Fig 10:3 1 Wheel cylinder 2 Shoe return spring
3 Adjusting cams 4 Shoe guide pin 5 Shoe with lining
6 Drum 7 Housing flange
BRAKE SHOE
ADJUSTING DEVICE
SHOE WEDGE
SELF
WHEEL CYLINDER
SHOE RETURN SPRING
PARKING BRAKE
SHOE CONTROL
RETURN SPRINGS
LEVER
SHOE LOCK PLATEBRAKE SHOES
SHOE RETURN SPRING
SHOE MOUNTING PLATE
FIG 1 0:4 Right rear wheel brake assembly (500 Sedan)
10:4 Rear brakes
Rear brake drum removal:
1 Remove the wheel trims and carefully slacken the road
wheel retaining bolts. Using a garage hydraulic jack
raise the rear of t h e vehicle and place on firmly based
stands. Remove the road wheels.
2 Remove the four drum to hub retaining bolts and
spring washers and carefully withdraw the drum from
the backplate assembly.
Dismantling brake unit:
1 Using a compressed air jet thoroughly clean all
components of the brake assembly.
105
Page 102 of 128
10:9 Brake fluid reservoir
The reservoir is located in the front compartment to the
side of the fuel tank as shown in FIG 10:9. Should it be
necessary to detach the fluid outlet line from the reservoir
the outlet hole must be blanked off using a tapered
wooden peg of suitable length so that the cap may be
replaced to prevent the ingress of foreign matter into
the reservoir and the absorbtion of moisture, oil or petrol
vapours which would alter the properties of the hydraulic
fluid.
A special filter is fitted into the top of the reservoir
through which all fluid used for topping-up the reservoir
must pass to ensure utmost inner cleanliness of the
hydraulic system.
10:10 Bleeding the system
This is not a routine maintenance operation and is only
necessary if air has entered the hydraulic system because
parts have been dismantled or because the f l u i d level in
the reservoir has dropped so low that air has been drawn
into the main feed pipe to the master cylinders.
1 Fill the reservoir w i t h Fiat 'Blue Label' hydraulic fluid.
During the bleeding operation fluid will be used and
constant topping-up of the supply reservoir will be
needed. If this is not done it is possible for air to enter
the master cylinder main feed pipe which will nullify
the operation and necessitate a fresh start.
2 Attach a length of rubber or plastic tubing to the
bleeder screw on the rear wheel cylinder furthermost
from the master cylinder. Immerse the free end of the
tube in a small volume of hydraulic brake fluid in a
clean jar.
3 Open the bleed screw one turn and get a second
operator to press down slowly on the brake pedal. After
a full stroke let the pedal return without assistance,
pause a moment and repeat the d o w n stroke. At first
there will be air bubbles issuing from the bleed tube,
but when fluid alone is ejected, hold the pedal firmly
down on the floor panel and tighten the bleed screw.
Repeat this operation on the other rear brake and then
repeat the operation on the two front brakes.
4 On completion, top-up the fluid in the reservoir to the
correct level. Discard all dirty fluid. If fluid is perfectly
clean, let it stand for twenty four hours to become
clear of air bubbles before using it again.
10:11 Hand parking brake
Normally with the new 500 Sedan model automatic
brake adjusting device, adjustment of the rear brakes
will take up excessive handbrake travel.
If there is excessive travel on the handbrake of the
Sedan model at any time, or in the case of Station Wagon
model even after the rear brakes have been manually
adjusted, suspect worn brake shoe linings or stretched
handbrake cables. Examine the linings and fit replace-
ment shoes if necessary. Check the action of the hand
parking brake again and if there is still too much travel
before the brakes are applied it is permissible to take up as
follows:
1 It is essential to ensure that the rear shoes are correctly
adjusted as described in Section 10:2.
2 Apply the hand parking brake lever until the pawl
engages with the ratchet at the second notch.
F500
FIG 10:11 An exploded view showing the components of
the tandem master cylinder
3 Jack up the rear of t h e vehicle and place on firmly
based stands.
4 Locate the cable adjusting nuts as shown in FIG
10:10 and adjust these until it is just possible to turn
the road wheels by heavy hand pressure. It is important
that both wheels offer the same resistance to turning
to obtain correctly balanced braking.
5 Return the lever to the OFF position and check that
both wheels are quite free to rotate. If a brake tends to
bind, remove the wheel and brake drum and check
the brake shoe pull-off spring is correctly fitted and
that the lever return spring and operating lever are
functioning correctly. Also check for suspected
seizure of the wheel cylinder. When the fault has
been rectified refit the drum. Readjust and recheck.
Removing the hand parking brake cable:
1 Chock the front wheels and release the handbrake.
Raise t h e rear of the vehicle and place on firmly based
stands.
2 Disconnect the cables from the operating levers on
each rear brake unit. Release each cable from its body
mounted bracket.
3 Inside the car, remove the rear seat and the seat belt
fitting from the floor. As necessary, remove the centre
console and the carpet to give access to the cover plate
on the centre tunnel and remove it.
4 Remove the handbrake lever assembly, detach the
cable compensator and pull the cables through the
holes in the box panel.
5 Reassembly is the reverse procedure to removal.
Ensure t h a t the cable is well lubricated and finally
readjust as previously described.
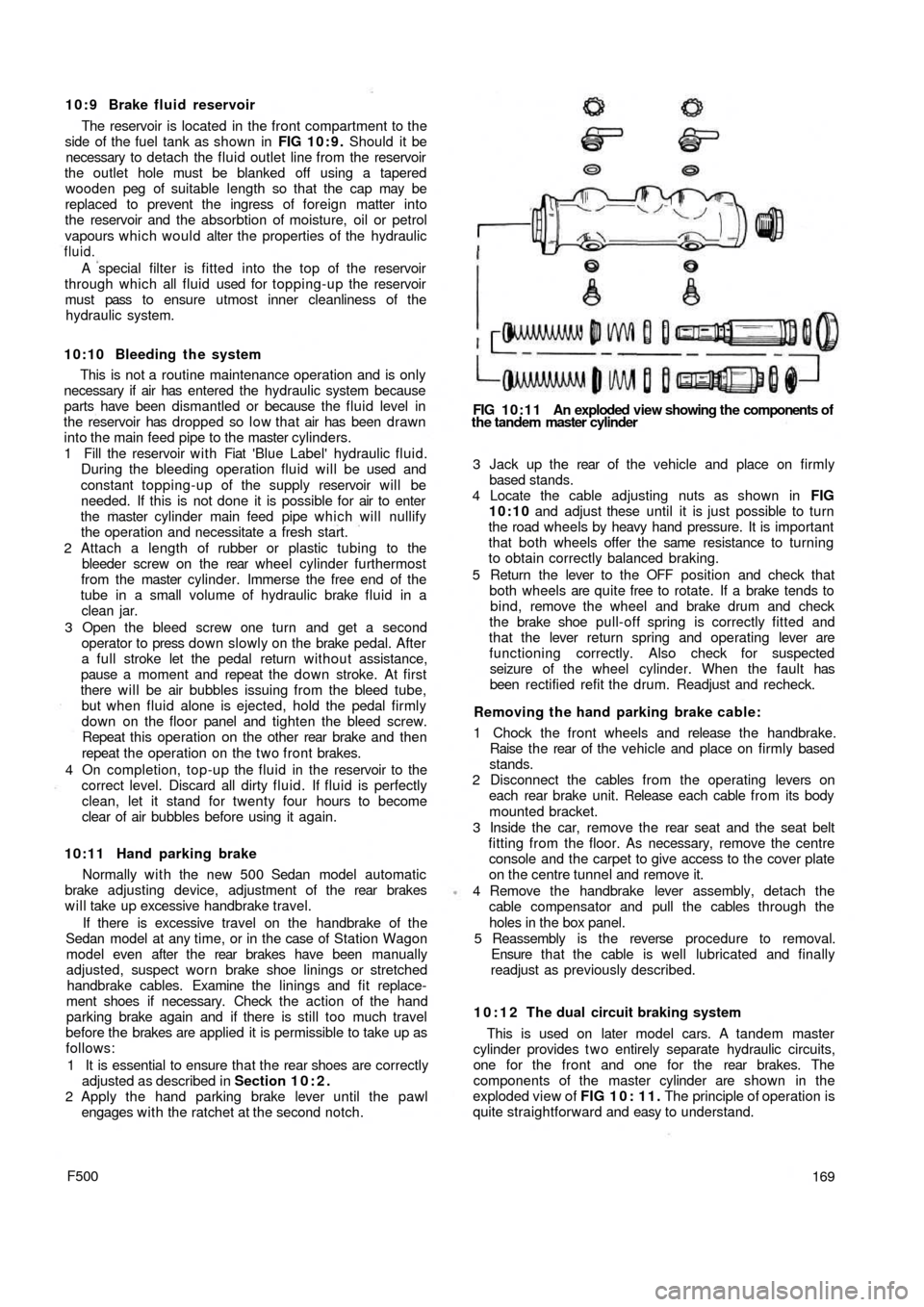
10:12 The dual circuit braking system
This is used on later model cars. A tandem master
cylinder provides t w o entirely separate hydraulic circuits,
one for the front and one for the rear brakes. The
components of the master cylinder are shown in the
exploded view of FIG 1 0 : 1 1 . The principle of operation is
quite straightforward and easy to understand.
169
Page 103 of 128

When the pedal is applied, it moves the rear (primary)
piston to pressurise the front brakes through the rear port.
This, in turn, forces the front (secondary) piston down the
bore to pressurise the rear brake circuit through the front
port. In the event of a failure in the primary circuit, the
primary piston moves into direct contact with the second-
ary piston and full braking is still available on the rear
wheels. If a leak occurs in the rear circuit, the secondary
piston is moved to the end of the bore, sealing off the out-
let port and full braking pressure is applied to the t w o front
brakes.
With two fluid reservoirs connected to the inlets 3 and 5
the two circuits are fully independent.
The remaining components in the braking system are
similar to those used in the earlier single circuit layout.
10:13 Fault diagnosis
(a) 'Spongy' pedal
1 Leak in t h e system
2 Worn master cylinder
3 Leaking wheel cylinders
4 Air in the system
5 Gaps between shoes and underside of linings
110
(b) Excessive pedal movement
1 Check 1 and 4 in (a)
2 Excessive lining wear
3 Very low fluid level in supply reservoir
4 Too much free movement of pedal
(c) Brakes grab or pull to one side
1 Brake backplate loose
2 Scored, cracked or distorted drum
3 High spots on drum
4 Unbalanced shoe adjustment
5 Wet or oily linings
6 Worn or loose spring fixings
7 Front suspension or rear suspension anchorages
loose
8 Worn steering connections
9 Mixed linings of different grades
10 Uneven tyre pressure
11 Broken shoe return springs
12 Seized handbrake cable
Page 104 of 128
CHAPTER 11
THE ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT
11:1 Description
11:2 Battery
11:3 The generator
11:4 The starter
11:5 The control box
1 1 : 6 Fuses
1 1 : 7 Flasher unit
11:1 Description
All models covered by this manual have 12 volts
electrical systems in which the negative battery terminal
is earthed. There are three units in the regulator box to
control the charging circuit; a cut-out, a current regulator
and a voltage regulator. These are adjustable but it must
be stressed that accurate moving coil meters are required
when checking or altering the settings. Cheap and
unreliable instruments will make accurate adjustments
impossible.
There are wiring diagrams in Technical Data at the end
of this manual to enable those with electrical experience
to trace and correct wiring faults.
For t h e U.K. Market the headlamps are of the double
filament dipping renewable bulb type with adjustments
for individual beam settings.
The battery is located in the front compartment
forward of the petrol tank and the fuses to the rear o f the
petrol tank.
Detailed instructions for servicing the electrical equip-
ment will be found in this chapter, but it must be pointed
out that it is not sensible to try to repair that which is
seriously defective, electrically or mechanically. Such
equipment should be replaced by new units which can
be obtained on an exchange basis.
F500111
11 :8 Windscreen wipers
1 1 : 9 The lighting system
11:10 Panel and warning lights
11:11 The horn
11:12 Lighting and flasher switch
1 1 : 1 3 Fault diagnosis
11.2 The battery
This of the 12-volt lead/acid type and has to meet
heavy demands for current particularly in the winter. To
maintain the performance of the battery at its maximum
it is essential to carry out the following operations.
Keep the top of the battery and surrounding parts dry
and clean, as dampness can cause leakage between the
securing clamps and the battery terminals. Clean off any
corrosion from the metal parts of the battery mounting
with diluted ammonia and paint them with an anti-
sulphuric paint. If the terminal posts are corroded,
remove the cables and clean w i t h diluted ammonia.
Smear the posts w i t h petroleum jelly before remaking the
connections and fit the terminals securely. High electrical
resistance due to corrosion at the terminal posts is often
responsible for lack of sufficient current to operate the
starter motor.
Ensure t h a t the filler plugs are in good condition and
show no signs of cracks. This may cause leakage of
electrolyte and consequent corrosion. Test the condition
of the cells after topping-up the electrolyte level with
distilled water to just above the tops of the separators as
shown in FIG 11 :2 . Never add neat acid. If it is
necessary to make a new electrolyte due to loss by
spillage add sulphuric acid to the
distilled water.
It is highly dangerous to add water to acid.
Page 105 of 128
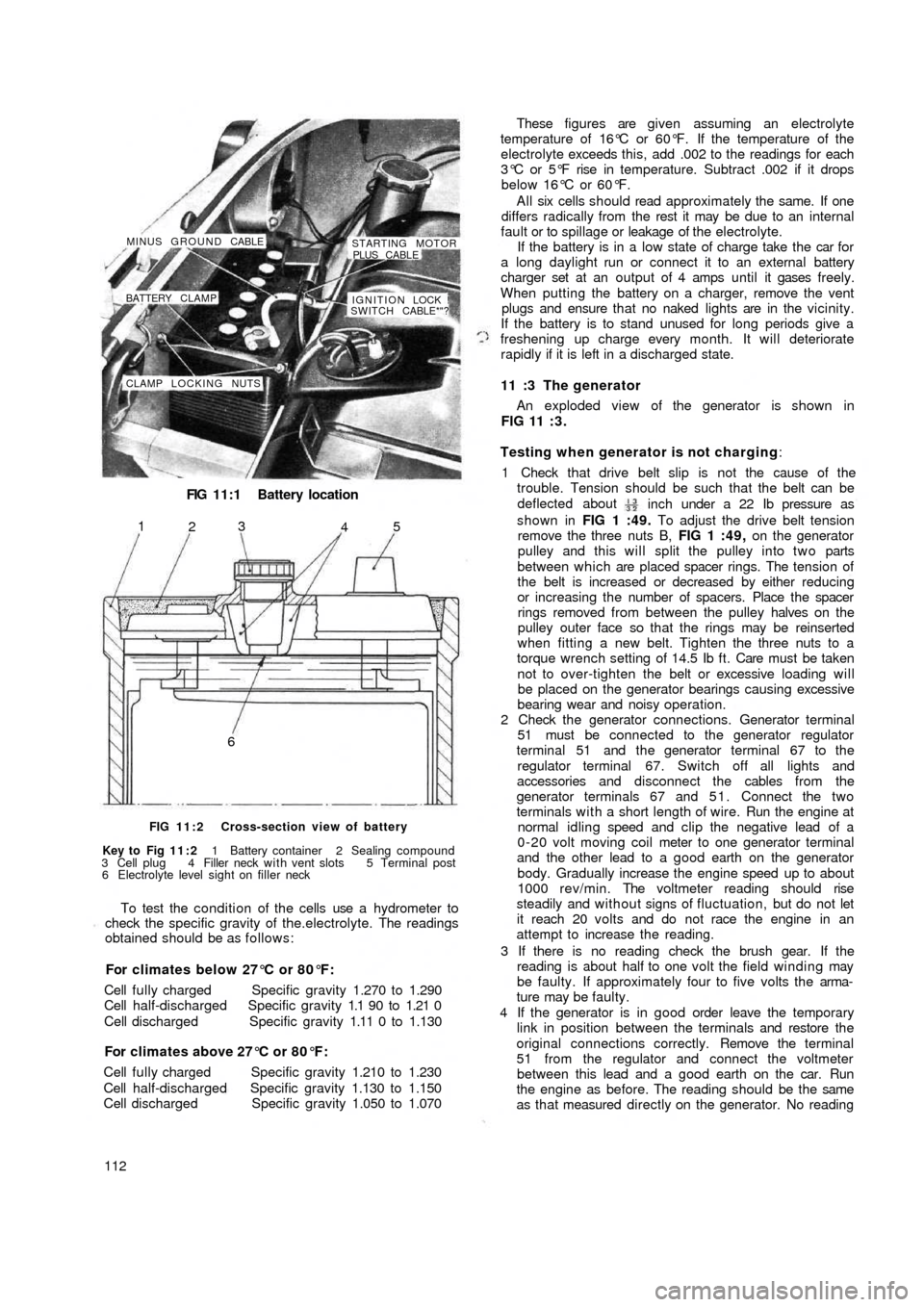
FIG 11:1 Battery location
CLAMP LOCKING NUTSIGNITION LOCK !
SWITCH CABLE*"? BATTERY CLAMP MINUS GROUND CABLE
STARTING MOTOR
PLUS CABLE
65
4 3
2 1
FIG 11:2 Cross-section view of battery
Key to Fig 11:2 1 Battery container 2 Sealing compound
3 Cell plug 4 Filler neck with vent slots 5 Terminal post
6 Electrolyte level sight on filler neck
To test the condition of the cells use a hydrometer to
check the specific gravity of the.electrolyte. The readings
obtained should be as follows:
For climates below 27°C or 80°F:
Cell fully charged Specific gravity 1.270 to 1.290
Cell half-discharged Specific gravity 1.1 90 to 1.21 0
Cell discharged Specific gravity 1.11 0 to 1.130
For climates above 27°C or 80°F:
Cell fully charged Specific gravity 1.210 to 1.230
Cell half-discharged Specific gravity 1.130 to 1.150
Cell discharged Specific gravity 1.050 to 1.070
112These figures are given assuming an electrolyte
temperature of 16°C or 60°F. If the temperature of the
electrolyte exceeds this, add .002 to the readings for each
3°C or 5°F rise in temperature. Subtract .002 if it drops
below 16°C or 60°F.
All six cells should read approximately the same. If one
differs radically from the rest it may be due to an internal
fault or to spillage or leakage of the electrolyte.
If the battery is in a low state of charge take the car for
a long daylight run or connect it to an external battery
charger set at an output of 4 amps until it gases freely.
When putting the battery on a charger, remove the vent
plugs and ensure that no naked lights are in the vicinity.
If the battery is to stand unused for long periods give a
freshening up charge every month. It will deteriorate
rapidly if it is left in a discharged state.
11 :3 The generator
An exploded view of the generator is shown in
FIG 11 : 3 .
Testing when generator is not charging:
1 Check that drive belt slip is not the cause of the
trouble. Tension should be such that the belt can be
deflected about
inch under a 22 Ib pressure as
shown in FIG 1 :49. To adjust the drive belt tension
remove the three nuts B, FIG 1 :49, on the generator
pulley and this will split the pulley into two parts
between which are placed spacer rings. The tension of
the belt is increased or decreased by either reducing
or increasing the number of spacers. Place the spacer
rings removed from between the pulley halves on the
pulley outer face so that the rings may be reinserted
when fitting a new belt. Tighten the three nuts to a
torque wrench setting of 14.5 Ib ft. Care must be taken
not to over-tighten the belt or excessive loading will
be placed on the generator bearings causing excessive
bearing wear and noisy operation.
2 Check the generator connections. Generator terminal
51 must be connected to the generator regulator
terminal 51 and the generator terminal 67 to the
regulator terminal 67. Switch off all lights and
accessories and disconnect the cables from the
generator terminals 67 and 5 1 . Connect the two
terminals with a short length of wire. Run the engine at
normal idling speed and clip the negative lead of a
0-20 volt moving coil meter to one generator terminal
and the other lead to a good earth on the generator
body. Gradually increase the
engine speed up to about
1000 rev/min. The voltmeter reading should rise
steadily and without signs of fluctuation, but do not let
it reach 20 volts and do not race the engine in an
attempt to increase the reading.
3 If there is no reading check the brush gear. If the
reading is about half to one volt the field winding may
be faulty. If approximately four to five volts the arma-
ture may be faulty.
4 If the generator is in good order leave the temporary
link in position between the terminals and restore the
original connections correctly. Remove the terminal
51 from the regulator and connect the voltmeter
between this lead and a good earth on the car. Run
the engine as before. The reading should be the same
as that measured directly on the generator. No reading