cooling FIAT 500 1973 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1973, Model line: 500, Model: FIAT 500 1973 1.GPages: 128, PDF Size: 9.01 MB
Page 44 of 128

indicates the condition inside the combustion chamber
and may be used as a guide to engine tuning.
Before the spark plugs are removed b l o w away any
loose dirt from the plug recesses using a compressed air
jet or tyre pump. Store the plugs in the order of removal
ready for inspection.
Examine the gaskets and if they are about half their
thickness they may be used again otherwise they must be
replaced.
Inspect the electrode end of the plugs and note the
type and colour of the deposit. Normally it should be
powdery and range from b r o w n to a greyish tan in colour.
There will also be slight wear of the electrodes and the
general effect described is one which comes from mixed
periods of high-speed and low-speed driving. Cleaning
and resetting the gap is all that will be necessary.
If the deposits are white or yellowish they indicate long
periods of constant-speed driving or much low-speed
city driving. Again, the treatment is straightforward.
Dry, black, fluffy deposits are usually the result of
running with too rich a mixture. Incomplete combustion
of the petrol air charge may also be a cause and this might
be traced to a defect in the ignition system or excessive
idling.
Overheated sparking plugs have a white blistered look
about the centre electrode and the side electrode may be
badly eroded. This may be caused by poor cooling, wrong
ignition timing or sustained high speeds under heavy load.
To clean the sparking plugs effectively they should be
cleaned using an abrasive blasting machine and tested
under pressure once the electrodes have been reset. File
these until they are clean, bright and the faces parallel and
set the gap to .019 to .023 inch. Do not try to bend the
centre electrode.
Before replacing the plugs use a wire brush to clean the
threads taking care that the electrodes are not touched.
Thoroughly clean the spark plug in petrol, and dry using a
compressed air jet or a tyre pump. If difficulty is found in
screwing the plugs into the cylinder head by hand run a
tap d o w n the threads to clear away any carbon. If a tap is
not available use an old sparking plug with crosscuts d o w nthe threads. Finally tighten the plugs to a torque wrench
setting of 18 to 21 Ib ft.
Sparking plug leads:
The spark plug leads and the lead from the coil to the
distributor cap must be regularly checked for cracking of
the insulation and also correct seating in the distributor
cap and coil top. It is recommended that silicone grease is
smeared around the sockets before the leads are replaced
to ensure no moisture may enter causing difficult starting.
3 : 9 The distributor driving spindle (sedan and
sports engine)
If for any reason, the driving spindle has been removed
from its housing in the crankcase, it must be correctly
meshed w i t h the camshaft gear otherwise it
will be impos-
sible to set the ignition timing.
3:10 Fault diagnosis
(a) Engine w i l l not fire
1 Battery discharged
2 Distributor contact points dirty, pitted or maladjusted
3 Distributor cap dirty, cracked or tracking
4 Carbon brush inside distributor cap not touching rotor
5 Faulty cable or loose connection in low-tension circuit
6 Distributor rotor arm cracked
7 Faulty coil
8 Broken contact breaker spring
9 Contact points stuck open
(b) Engine misfires
1 Check 2, 3, 4, and 7 in (a)
2 Weak contact breaker spring
3 High-tension plug and coil leads cracked or perished
4 Sparking plug(s) loose
5 Sparking plug insulation cracked
6 Sparking plug gap incorrectly set
7 Ignition timing too far advanced
Page 46 of 128

CHAPTER 4
THE COOLING SYSTEM
4:1
4:2
4:3Description
Air outlet thermostat and shutter
Tension adjustment4:4
4:5
4:6Heating system safety device
Maintenance
Fault diagnosis
4:1Description
Sedan:
A l l the Fiat new 500 models covered by this manual are
aircooled by the forced air circulation system from a
centrifugal blower which is mounted on the generator
output shaft. The blower fan has fourteen vanes which are
arranged at various angles to reduce operating noise
during high-speed operation. A specially designed
cowling as shown in FIGS 4 : 1 and 4:2 conveys the air
from the blower and distributes it to the various parts of
the exterior of the engine.
The main components of the air cooling system are as
follows:
1 Air intake compartment at the rear end of t h e body.
2 An elbow pipe for the admittance of incoming air.
3 A flexible air pipe connecting the elbow pipe to the
conveyor.
4 A spiral air conveyor which contains the centrifugal fan.
5 Distribution ducting for directing the air flow to various
parts of the engine.
6 A bellows type thermostat is fitted to the cowling which
operates a butterfly shutter controlling the air outlet
from the engine which ensures control of the engine
operating temperature.
F50053 When the shutter is in the open position, engine heated
air is allowed to disperse to the outside of the engine
cowling. With the shutter in its closed position, the air is
recirculated in the engine cowling so ensuring a quick
engine warm-up period.
It should be noted that by operating the heater lever
which is located on the centre tunnel at the rear seat,
warmed air flowing out from the engine cowling is passed
to the inside of the car for heating and demisting purposes.
Station wagon:
Refer to FIG 4 : 2 where it will be seen that as the engine
is located on its side underneath the luggage compartment
floor the ducting has been modified and the air intakes are
located at the rear of the side windows. A linear blower is
housed in the engine baffles and cowling and is attached
to the drive end of the generator.
The thermostat 'C' (see FIG 4 : 2) is located on the
righthand side of the engine cowling and should start
opening the engine heated air outlet shutter ' D ' when the
temperature of the air rises to 1 7 8 - 1 8 5 ° F and the shutter
should be wide open when the air is at a temperature of
196-207°F.
Page 47 of 128
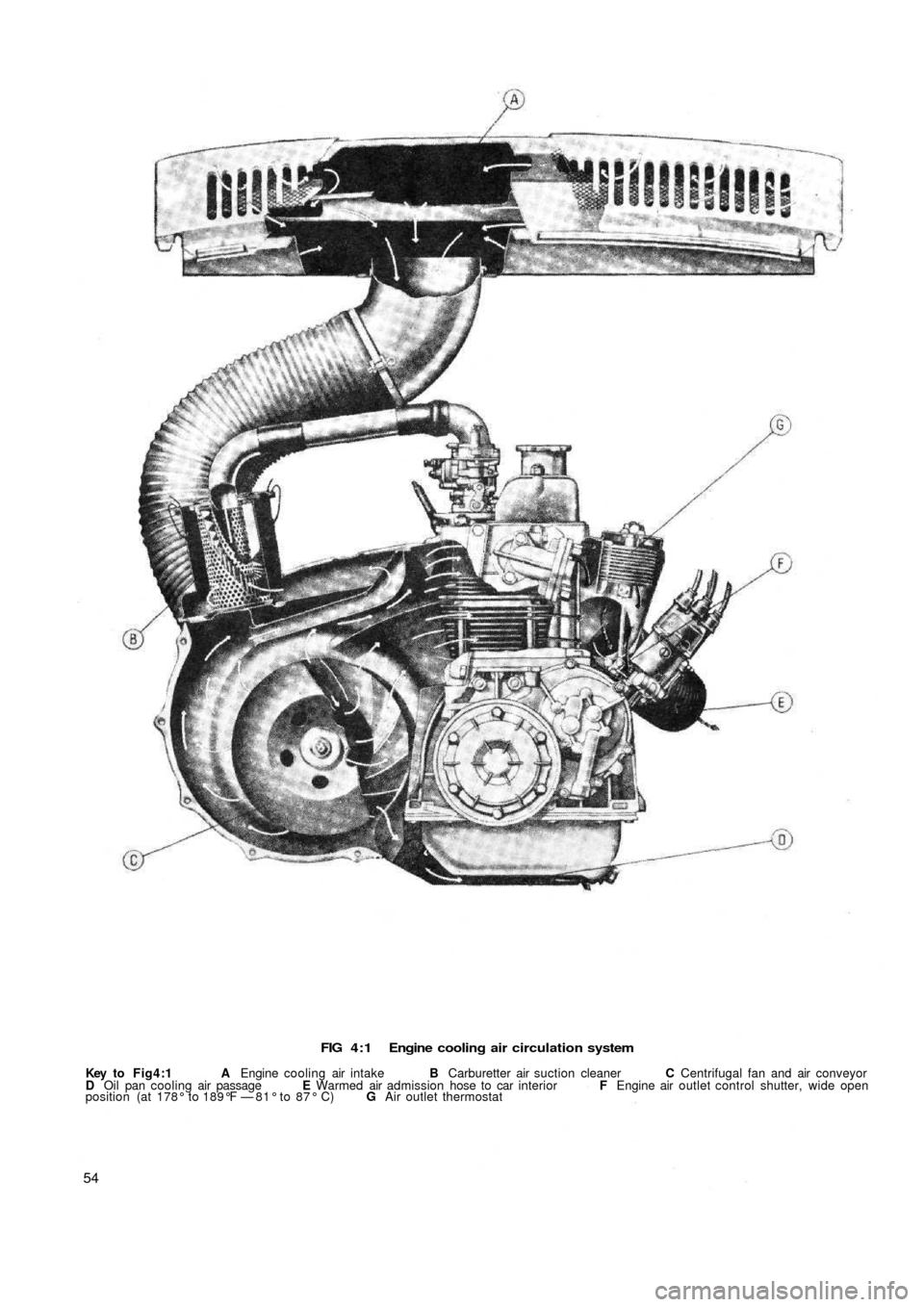
FIG 4 : 1 Engine cooling air circulation system
Key to Fig4:1 A Engine cooling air intake B Carburetter air suction cleaner C Centrifugal fan and air conveyor
D Oil pan cooling air passage E Warmed air admission hose to car interior F Engine air outlet control shutter, wide open
position (at 178° to 189°F — 81° to 87° C) G Air outlet thermostat
54
Page 48 of 128
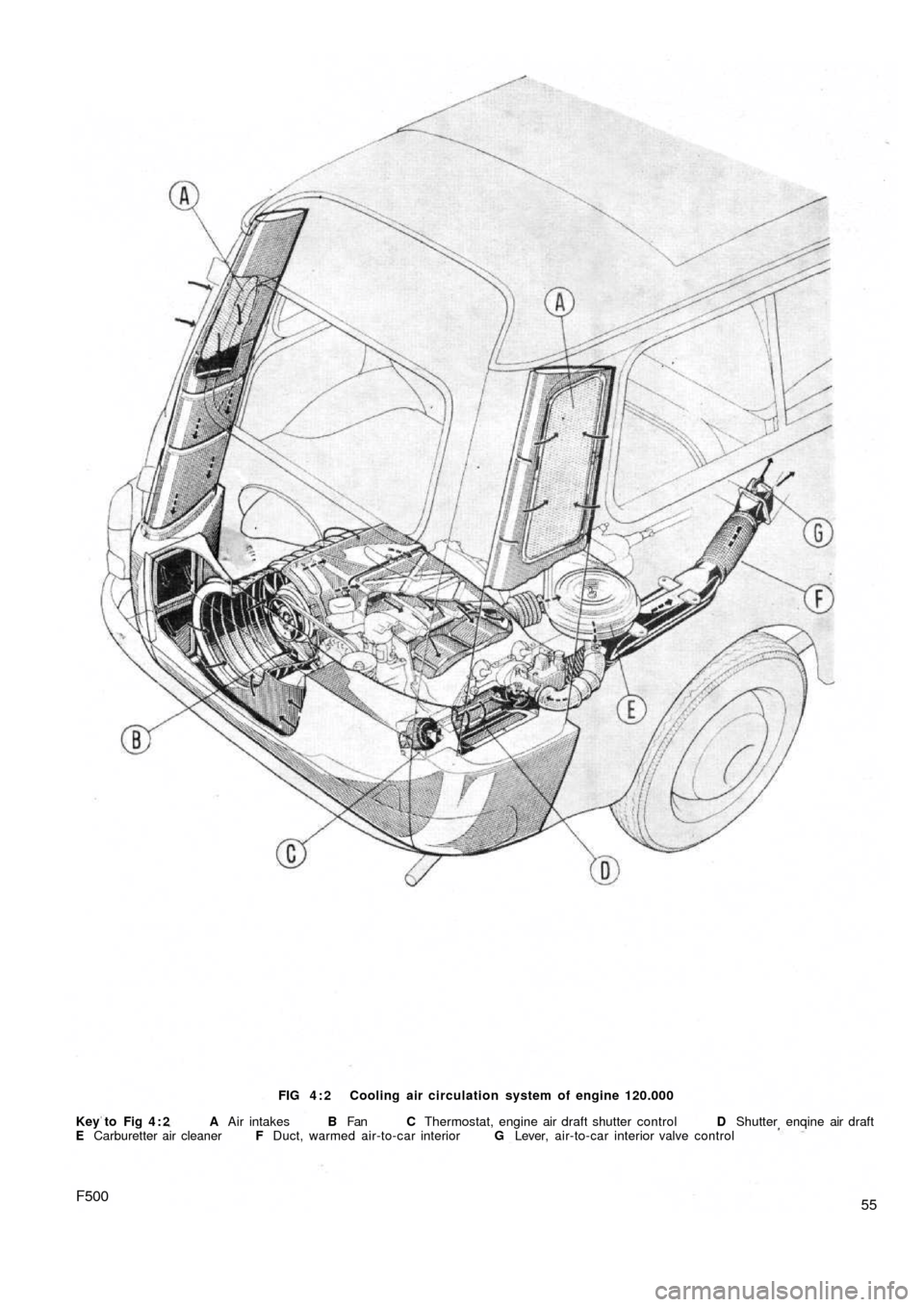
55F500
FIG 4 : 2 Cooling air circulation system of engine 120.000
Key to Fig 4 : 2 A Air intakes B Fan C Thermostat, engine air draft shutter control D Shutter enqine air draft
E Carburetter air cleaner F Duct, warmed air-to-car interior G Lever, air-to-car interior valve control
Page 49 of 128
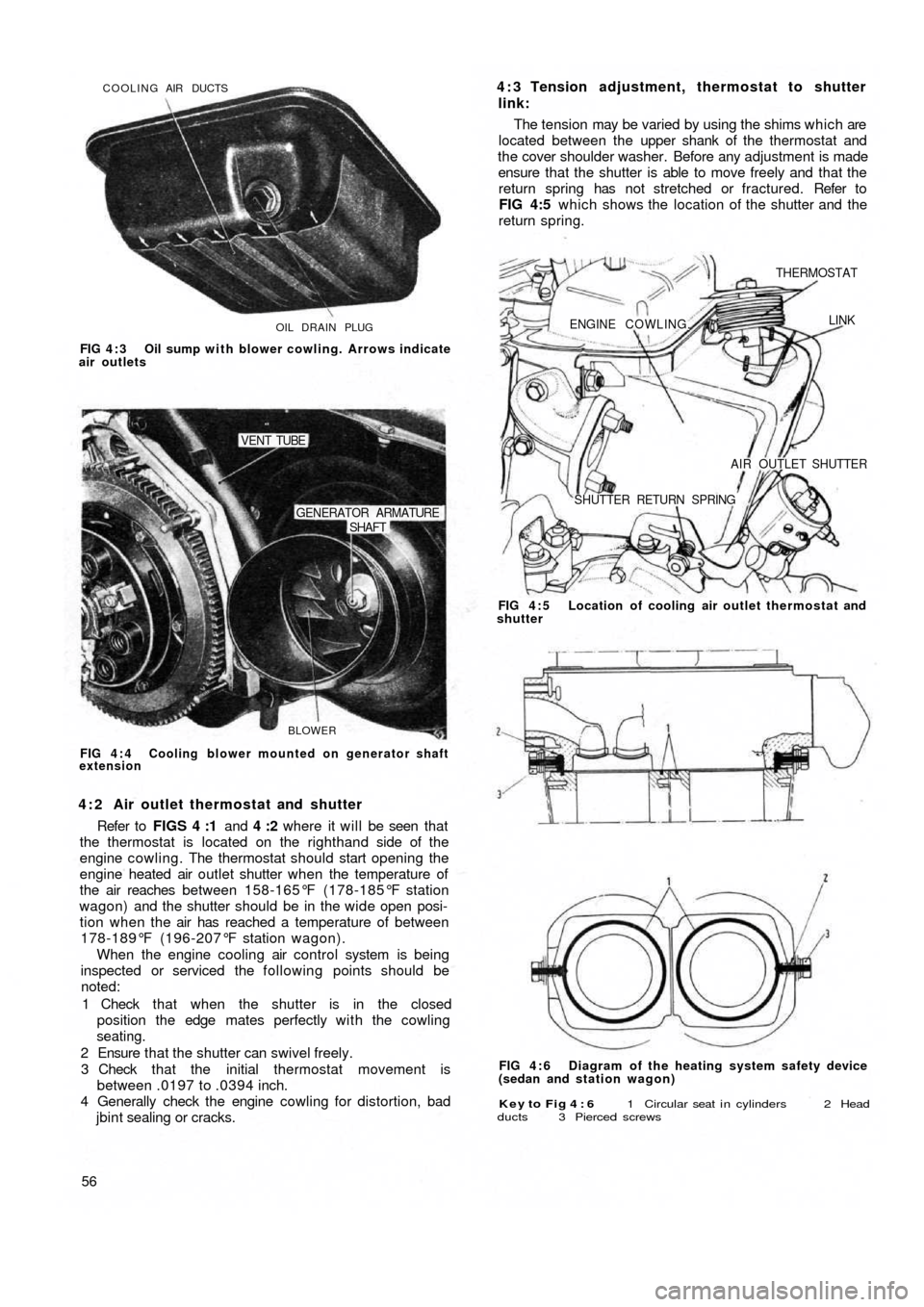
OIL DRAIN PLUG COOLING AIR DUCTS
FIG 4 : 3 Oil sump with blower cowling. Arrows indicate
air outlets
BLOWER
SHAFT GENERATOR ARMATURE
VENT TUBE
FIG 4 : 4 Cooling blower mounted on generator shaft
extension
4 : 2 Air outlet thermostat and shutter
Refer to FIGS 4 :1 and 4 :2 where it will be seen that
the thermostat is located on the righthand side of the
engine cowling. The thermostat should start opening the
engine heated air outlet shutter when the temperature of
the air reaches between 158-165°F (178-185°F station
wagon) and the shutter should be in the wide open posi-
tion when the air has reached a temperature of between
178-189°F (196-207°F station wagon).
When the engine cooling air control system is being
inspected or serviced the following points should be
noted:
1 Check that when the shutter is in the closed
position the edge mates perfectly with the cowling
seating.
2 Ensure that the shutter can swivel freely.
3 Check that the initial thermostat movement is
between .0197 to .0394 inch.
4 Generally check the engine cowling for distortion, bad
jbint sealing or cracks.
56
Key to Fig 4 : 6 1 Circular seat i n cylinders 2 Head
ducts 3 Pierced screws
FIG 4 : 6 Diagram of the heating system safety device
(sedan and station wagon) FIG 4 : 5 Location of cooling air outlet thermostat and
shutter
ENGINE COWLING.
THERMOSTAT
LINK
AIR OUTLET SHUTTER
SHUTTER RETURN SPRING
4 : 3 Tension adjustment, thermostat to shutter
link:
The tension may be varied by using the shims which are
located between the upper shank of the thermostat and
the cover shoulder washer. Before any adjustment is made
ensure that the shutter is able to move freely and that the
return spring has not stretched or fractured. Refer to
FIG 4:5 which shows the location of the shutter and the
return spring.
Page 50 of 128

4 : 4 Heating system safety device
110F series sedan engines and later station wagon
engines incorporate a modification to the cylinder head
designed so that in the event of cylinder head gasket
failure exhaust gases are expelled outside the engine and
not leaked into the heating system.
The safety device comprises a square section circular
seat 1 (see FIG 4 :6) which is formed in the upper face of
the cylinder, a special duct in the cylinder head and a
pierced screw 3 for each cylinder.
The system is so designed that the exhaust gases are
released to the atmosphere from the circular seat in the
cylinder via the duct 2 and the pierced screw 3. It should
be noted that the screw 3 is also used for securing the
conveyor.
4 : 5 Maintenance
Due to the simple design of the air cooling system
maintenance has been kept to an absolute minimum and
should consist of the following checks:1 Inspect all the air conveyor system joints and ensure
that all the joint nuts and bolts are tight and that there
is no distortion between two joint faces.
2 Check that the tension of the generator and fan drive
belt is correct: with a hand pressure of approximately
22 Ib the belt should sag 13/32 inch. Adjust if necessary
as detailed in Chapter 1.
3 Ensure that the shutter can swivel freely and that the
spring is in a serviceable condition.
4 : 6 Fault diagnosis
(a) Engine overheating
1 Generator and fan drive belt slipping
2 Shutter control thermostat defective
3 Shutter unable to swivel freely
4 Shutter return spring broken
5 Leaking joints in conveyor system
F50057
Page 106 of 128
indicates a break in the cable from the generator to
regulator. Repeat the test on terminal 67. Finally,
remove the temporary link from the generator. If the
readings are correct, test the regulator as described in
Section 11:5.
Removing generator:
1 Disconnect the leads from the generator.
2 Remove the drive belt as previously described.
3 Release t h e rear mounting bracket at the side of the
power unit.
4 Remove the air cooling ducting from around the fan
and generator area and lift away the unit.
5 Release the blower from the end of the armature shaft
and finally, the mounting bolts from the air ducting.
Dismantling generator:
1 Release the pulley self-locking nut and slide the pulley
off the armature shaft.
2 Remove the t w o Woodruff keys on armature shaft.
3 Unscrew the t w o through bolt nuts and pull out the
bolts.
4 Partially remove the commutator end head to the point
where the brushes are. s t i l l seating on the commutator.
Using a piece of hooked wire relieve the load of the
springs on the brushes by arranging the spring ends
on the brush sides. The brushes will be locked in their
holders and cannot be chipped by striking against the
armature shaft during the commutator end head
removal.
5 Gently ease the commutator and fan end heads apart
and, slide out the armature.
Servicing brushes:
Lift the brushes up in the boxes and hold them in that
position by letting each brush spring bear on the side of
its brush. Fit the commutator end bracket over the
commutator end of the armature shaft and release the
brushes by hooking up the springs using a thin screw
driver. Hold back each spring in turn and move the brush
by pulling gently on the flexible connector. If the brush
moves sluggishly remove it and polish the sides using a
smooth file. Before this operation is actually carried out it
is suggested that the brush is marked before removal so
that it is replaced in its original working position.
inch,The minimum permissible length of a brush is
so renew any t h a t are less than this figure. Test the brush
springs using a spring tension scale. New springs should
have a tension of 1.3 to 1.6 Ib. In service this value could
fall slightly before performance is affected. Always bed in
new brushes by wrapping fine sandpaper round the
commutator, pressing down on the brush and rotating
the commutator under it, or draw the paper t o o and f r o .
If new brushes are fitted always fit genuine Fiat replace-
ments.
Servicing the commutator:
A commutator in good condition should be smooth and
free from pitting or signs of the segments burning. Clean
with a rag moistened in petrol. If necessary, polish using
a fine glasspaper whilst rotating the armature. Never use
emerycloth.
If the commutator is badly worn it may be skimmed
using a centre lathe. Use a high rotational speed and take
F500113
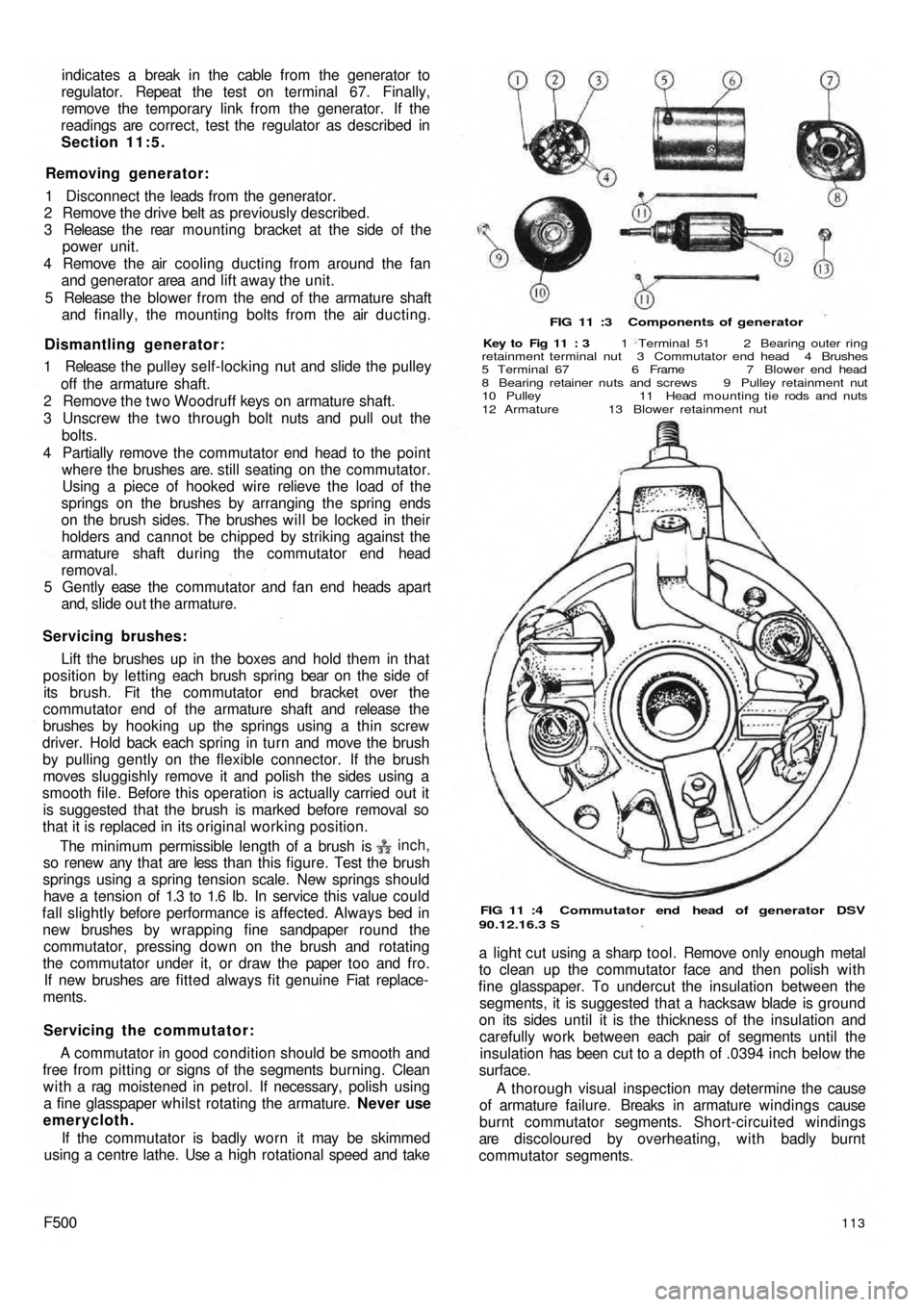
FIG 11 :3 Components of generator
Key to Fig 11 : 3 1 Terminal 51 2 Bearing outer ring
retainment terminal nut 3 Commutator end head 4 Brushes
5 Terminal 67 6 Frame 7 Blower end head
8 Bearing retainer nuts and screws 9 Pulley retainment nut
10 Pulley 11 Head mounting tie rods and nuts
12 Armature 13 Blower retainment nut
FIG 11 :4 Commutator end head of generator DSV
90.12.16.3 S
a light cut using a sharp tool. Remove only enough metal
to clean up the commutator face and then polish with
fine glasspaper. To undercut the insulation between the
segments, it is suggested that a hacksaw blade is ground
on its sides until it is the thickness of the insulation and
carefully work between each pair of segments until the
insulation has been cut to a depth of .0394 inch below the
surface.
A thorough visual inspection may determine the cause
of armature failure. Breaks in armature windings cause
burnt commutator segments. Short-circuited windings
are discoloured by overheating, with badly burnt
commutator segments.
Page 126 of 128

12:11 Folding top
The f ol di n g top assembly comprises the following
items:
1 Imitation leather top w i t h vinylite back window.
2 Front end frame complete with two handles and
catches. A movable bow which slides on the frame
guide rails.
3 Three stiffening bows fixed by chrome plated buttons
and tipped with rubber blocks.
4 Front mouldings for t o p mounting on frame.
5 Rear moulding on top mounting engine cooling air
intake body panel.
6 Retaining strap for the roller stop.
The removal of the folding top is straightforward but
care should be taken on reassembly to the vehicle and the
following points should be noted:
1 The t o p rear moulding is secured by ten screws
consisting of six self-tapping screws and four standard
screws which are located as follows:
(a) One long self-tapping screw at each end.
(b) Two standard screws at centre.
(c) Two standard screws next to the long screws.
(d) Four self-tapping screws, two on each side
between the standard screws.
These screws also secure the upper end of the engine
air intake panel to body.
2 Having fixed the rear moulding spread the top across
t h e o p e n i n g . Ensure t h e pivoting bow is located
between the second and third stiffening bows. Using
special screws fix the frame rails to the upper inner
ends of the body side panels.
12:12 Sunroof
The 'new 500' sunroof model differs from the con-
vertible model in the arrangement of the top. The sunroof
comprises a rear metal panel and a front imitation leather
covering which acts as a collapsible top.
The weather strip surrounded back window is
located
on t h e rear metal panel and the following items are
cemented in place; plastic lining, foam rubber strip at
upper front end, and two rubber welts located on the
sides to prevent water ingress.
FIG 12:14 Folded top retaining strap
F500
133 FOLDED TOP STRAP
FOLDED TOP
FIG 12:15 Arrangement of rolled top. This should be
done carefully to prevent damaging the vinylite back
window. Roll must never obstruct engine air intake slots
FOLDING TOP LOCKING HANDLES
FIG 12:16 Sun Roof top in locked position
The rear metal panel is secured to the body shell by
means of four screws, four plain washers and four spring
washers and at the rear by means of nine self-tapping
screws which provide a mounting for the engine air
intake grill and gutter.
The collapsible top comprises the following items:
1 Imitation leather lining.
2 Metal frame with a front crossmember onto which the
control handles and top front latch strikers are fitted.
A movable bow riveted to the top lining and fitted with
rubber pads which rest on t h e t o p of t h e body.
3 Front moulding for the top lining mounting onto the
framing crossmember. FOLDED TOP STRAP
Page 127 of 128
BOW
FIG 12:17 Sun Roof top in unlatched position
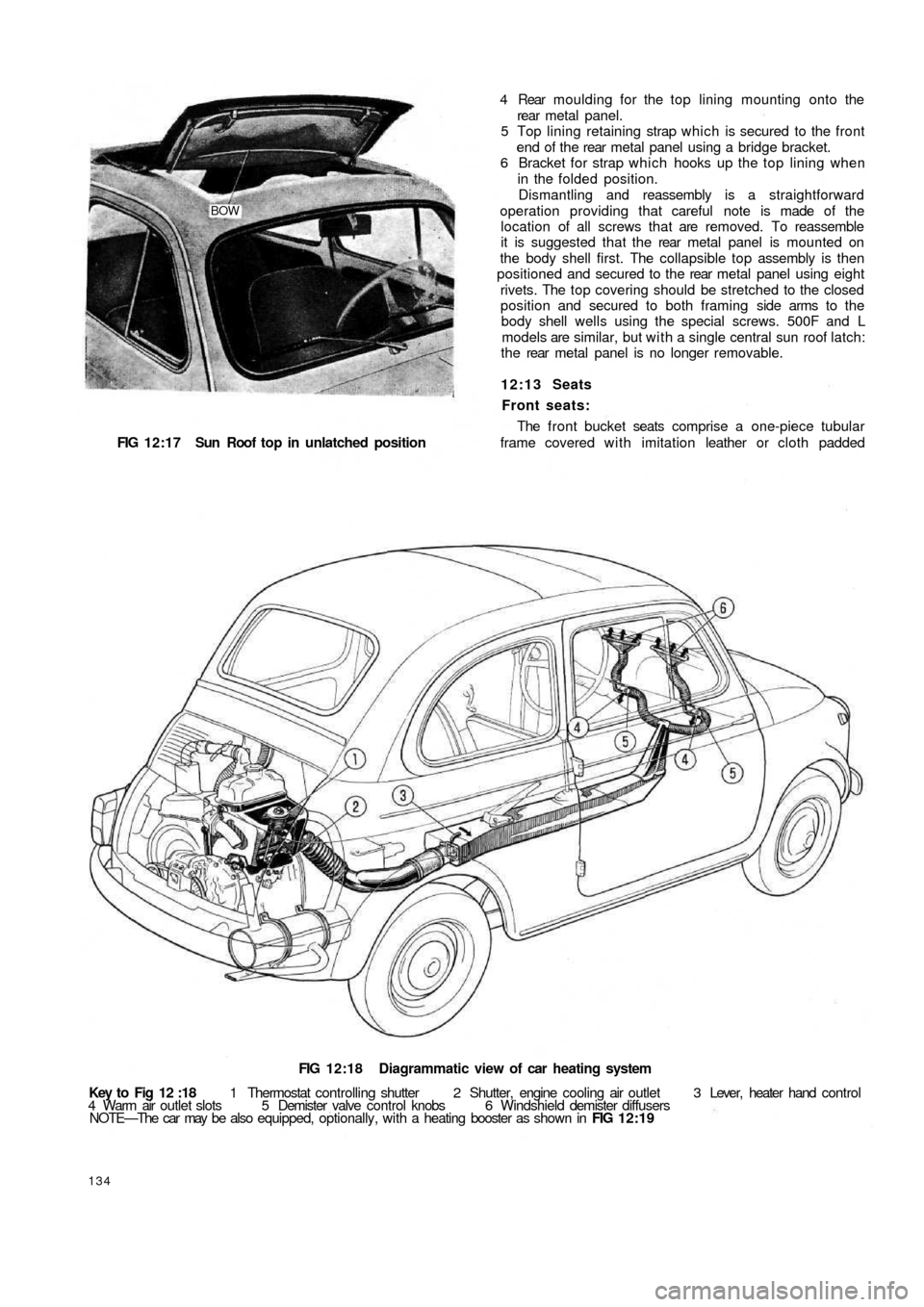
FIG 12:18 Diagrammatic view of car heating system
Key to Fig 12 :18 1 Thermostat controlling shutter 2 Shutter, engine cooling air outlet 3 Lever, heater hand control
4 Warm air outlet slots 5 Demister valve control knobs 6 Windshield demister diffusers
NOTE—The car may be also equipped, optionally, with a heating booster as shown in FIG 12:19
134
4 Rear moulding for the top lining mounting onto the
rear metal panel.
5 Top lining retaining strap which is secured to the front
end of t h e rear metal panel using a bridge bracket.
6 Bracket for strap which hooks up the top lining when
in the folded position.
Dismantling and reassembly is a straightforward
operation providing that careful note is made of the
location of all screws that are removed. To reassemble
it is suggested that the rear metal panel is mounted on
the body shell first. The collapsible top assembly is then
positioned and secured to the rear metal panel using eight
rivets. The top covering should be stretched to the closed
position and secured to both framing side arms to t h e
body shell wells using the special screws. 500F and L
models are similar, but with a single central sun roof latch:
t h e rear metal panel is no longer removable.
12:13 Seats
Front seats:
The front bucket seats comprise a one-piece tubular
frame covered with imitation leather or cloth padded
Page 128 of 128

cushion and back rest. A number of rubber straps are
hooked across the frame under the cushion and in a
sheath covering on the seat back.
The bottom of the front seat frame ends are provided
with sliding guides which run in guide rails attached to
the floor. The sliding guides are pivoted on the frame
tubes to allow for forward tilting of the seats giving better
access to the rear compartment. Two rubber pads
provide cushioning of the seat frame on the guide rails
as shown in FIG 12:11. The control lever for seat
adjustment is fitted in the frame righthand tube to permit
unlocking of the seats so that they may be adjusted to
individual drivers requirements.
Rear seats (Sedan):
The rear seat comprises of a foam rubber cushion and
back. The seat back is cemented to the rear floor and
body shell bulkhead. The rear seat lining is of fabric and
imitation leather. The seat lining is held in place by four
self-tapping screws, t w o of which secure the floor below
the back window and two the lining at the base of t h e
back rest. Included with the seat assembly is a masonite
floor which is fitted below the rear window.
Rear Seat (Station Wagon):
The rear seat back rest is pivoted at the base of its
frame so that it can be folded down to form a load plat-
form surface. In the upright position it is retained in place
by t w o brackets mounted on either side of the body below
the side
windows.
12:14 Interior heater
Description:
Interior heating is accomplished by recirculation of
warm air from the engine cooling system through engine
cowling. Referring to FIG 12:18 a hose conveys warmed
air from the engine cowling to the centre tunnel floor
where warm air flows out through two slots being cut on
the windshield delivery hoses. Air admission can be
adjusted by turning the control lever to the right which
operates the tunnel throttle valve at the rear seat.
The heating system may be fitted with a booster which
comprises a casing on the front exhaust pipe being
connected to the engine cowling and the warmed air
passage tunnel. Warm air flowing to the car interior is
heated to higher temperature than that from the standard
version of heater (see FIG 12:19).
Windshield demisting:
As will be seen from FIG 12:18, t w o air hoses w i t h
throttle valves for airflow control are relayed from a casing
F500135
FIG 12:19 Diagram of booster
Key to Fig 12:19 1 Thermostat controlling shutter
2 Car interior heater booster 3 Hand control unit
in front of the centre of the floor tunnel. Flexible hoses
are connected to two air diffusers which are located on
the instrument panel and parallel to the windshield glass.
When the throttle valves 5 (see FIG 12:18) are operated
through the two control knobs, warmed air is directed
onto the windshield glass so preventing misting, frosting
or icing in adverse weather conditions.
Inspection:
Ensure that t h e lever, the lever spring and butterfly
valve hinge are not distorted. Check that the ducting to
the tunnel as well as the upper and lower hoses are air-
tight which if not, should be renewed.