fuel FIAT 500 1973 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1973, Model line: 500, Model: FIAT 500 1973 1.GPages: 128, PDF Size: 9.01 MB
Page 31 of 128
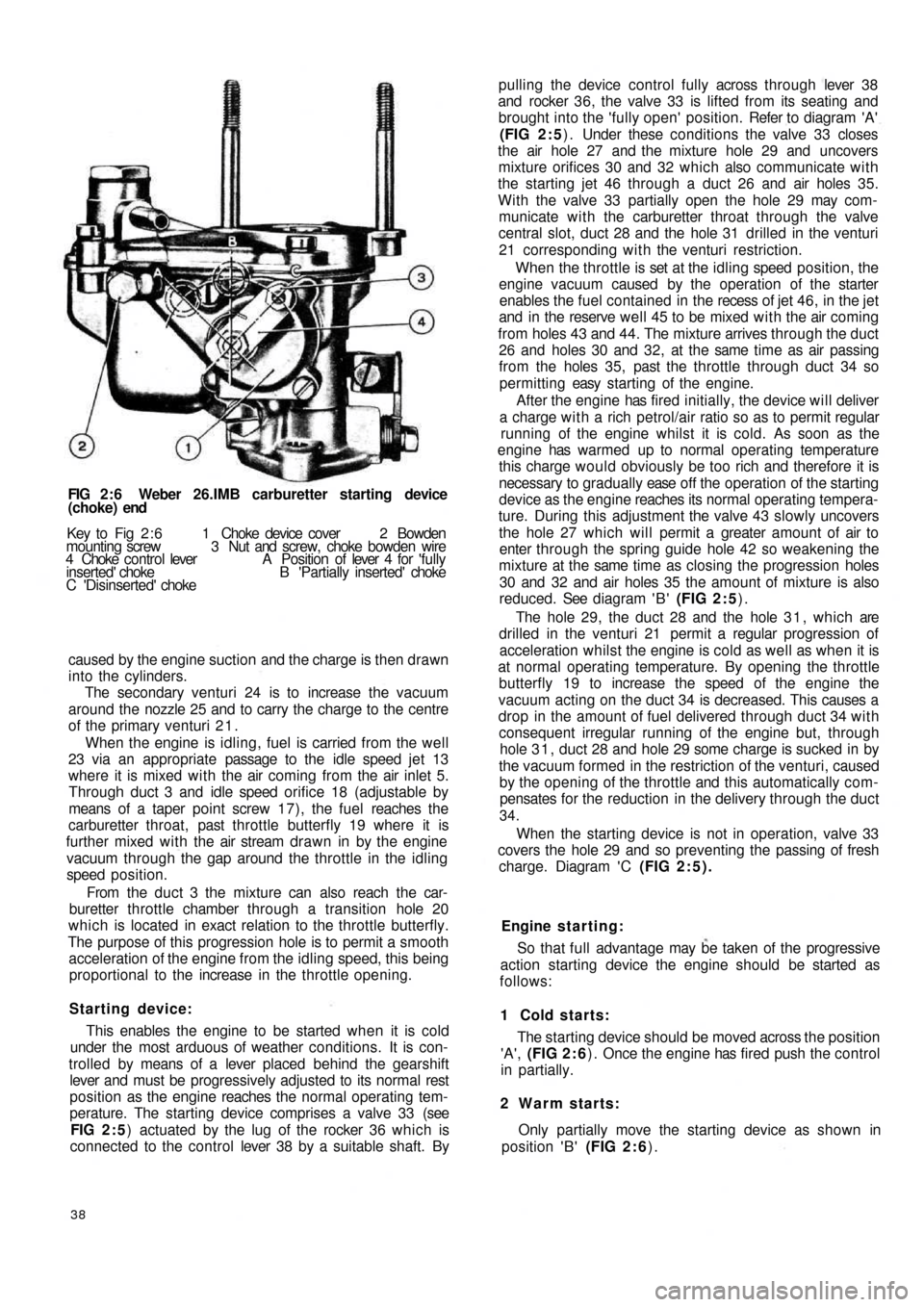
FIG 2 : 6 Weber 26.IMB carburetter starting device
(choke) end
Key to Fig 2 : 6 1 Choke device cover 2 Bowden
mounting screw 3 Nut and screw, choke bowden wire
4 Choke control lever A Position of lever 4 for 'fully
inserted' choke B 'Partially inserted' choke
C 'Disinserted' choke
caused by the engine suction and the charge is then drawn
into the cylinders.
The secondary venturi 24 is to increase the vacuum
around the nozzle 25 and to carry the charge to the centre
of the primary venturi 2 1 .
When the engine is idling, fuel is carried from the well
23 via an appropriate passage to the idle speed jet 13
where it is mixed with the air coming from the air inlet 5.
Through duct 3 and idle speed orifice 18 (adjustable by
means of a taper point screw 17), the fuel reaches the
carburetter throat, past throttle butterfly 19 where it is
further mixed with the air stream drawn in by the engine
vacuum through the gap around the throttle in the idling
speed position.
From the d u c t 3 the mixture can also reach the car-
buretter throttle chamber through a transition hole 20
which is located in exact relation to the throttle butterfly.
The purpose of this progression hole is to permit a smooth
acceleration of the engine from the idling speed, this being
proportional to the increase in the throttle opening.
Starting device:
This enables the engine to be started when it is cold
under the most arduous of weather conditions. It is con-
trolled by means of a lever placed behind the gearshift
lever and must be progressively adjusted to its normal
rest
position as the engine reaches the normal operating tem-
perature. The starting device comprises a valve 33 (see
FIG 2 : 5) actuated by the lug of the rocker 36 which is
connected to the control lever 38 by a suitable shaft. By
38
pulling the device control fully across through lever 38
and rocker 36, the valve 33 is lifted from its seating and
brought into the 'fully open' position. Refer to diagram 'A'
(FIG 2 : 5) . Under these conditions the valve 33 closes
the air hole 27 and the mixture hole 29 and uncovers
mixture orifices 30 and 32 which also communicate with
the starting jet 46 through a duct 26 and air holes 35.
With the valve 33 partially open the hole 29 may com-
municate with the carburetter throat through the valve
central slot, duct 28 and the hole 31 drilled in the venturi
21 corresponding with the venturi restriction.
When the throttle is set at the idling speed position, the
engine vacuum caused by the operation of the starter
enables the fuel contained in the recess of jet 4 6 , in the jet
and in the reserve well 45 to be mixed w i t h the air coming
from holes 43 and 44. The mixture arrives through the duct
26 and holes 30 and 32, at the same time as air passing
from the holes 35, past the throttle through duct 34 so
permitting easy starting of the engine.
After the engine has fired initially, the device will deliver
a charge with a rich petrol/air ratio so as to permit regular
running of the engine whilst it is cold. As soon as the
engine has warmed up to normal operating temperature
this charge would obviously be too rich and therefore it is
necessary to gradually ease o f f the operation of the starting
device as the engine reaches its normal operating tempera-
ture. During this adjustment the valve 43 slowly uncovers
the hole 27 which will permit a greater amount of air to
enter through the spring guide hole 42 so weakening the
mixture at the same time as closing the progression holes
30 and 32 and air holes 35 the amount of mixture is also
reduced. See diagram ' B ' (FIG 2 : 5).
The hole 29, the duct 28 and the hole 3 1 , which are
drilled in the venturi 21 permit a regular progression of
acceleration whilst the engine is cold as well as when it is
at normal operating temperature. By opening the throttle
butterfly 19 to increase the speed of the engine the
vacuum acting on the duct 34 is decreased. This causes a
drop in the amount of fuel delivered through duct 34 with
consequent irregular running of the engine but, through
hole 3 1 , duct 28 and hole 29 some charge is sucked in by
the vacuum formed in the restriction of the venturi, caused
by the opening of the throttle and this automatically com-
pensates for the reduction in the delivery through the duct
34.
When the starting device is not in operation, valve 33
covers the hole 29 and so preventing the passing of fresh
charge. Diagram ' C (FIG 2:5).
Engine s t a rting:
So that full advantage may be taken of the progressive
action starting device the engine should be started as
follows:
1 Cold starts:
The starting device should be moved across the position
'A', (FIG 2 : 6) . Once the engine has fired push the control
in partially.
2 Warm starts:
Only partially move the starting device as shown in
position 'B' (FIG 2 : 6).
Page 32 of 128
3 Engine warm-up:
As the engine begins to warm up to its normal operating
temperature, gradually push home the starting device
lever so as only to supply the engine with the richened
charge enabling the cold engine operation to be smooth
and regular. Position ' B ' (FIG 2:6).
4 Normal car driving:
Once the engine has reached its normal operating
temperature the starting device should be completely
brought out of operation by bringing the control lever to
the position 'C (FIG 2:6).
Idle speed adjustment:
The idling speed of the engine is adjusted by means of a
throttle setscrew and the mixture setscrew, the position of
which are shown in FIG 2:7. The throttle screw allows for
the adjustment of the throttle butterfly opening, the coni-
cal mixture setscrew meters the amount of charge issuing
from the idling speed passage which causes the mixture
to blend with the air flowing past the throttle that leaves a
gap between its edges and the throat walls. This ensures
a correct petrol/air mixture ratio best suited to the engine
requirements giving smooth operation.
The engine idling speed must always be adjusted when
the engine is at its normal operating temperature and then
setting the throttle butterfly position to its minimum open-
ing position by adjusting the throttle setscrew so giving a
steady engine speed. Turn the mixture screw in or out so
as to set the mixture richness to the most suitable ratio for
the selected throttle opening. This will accomplish a fast
but steady idling. Reduce the minimum throttle opening
slightly by adjusting the throttle setscrew until the best
idling speed is obtained.
Adjustment of fuel level in float chamber:
The needle valve, seating and float are easily accessible
for inspection by removing the carburetter top cover. Before
checking the petrol level in the float chamber, ensure that
the needle valve seat is screwed well home and that the
gasket is in place. Also check that the calibrated orifice in
the valve seat is unobstructed and not worn and finally
check that the needle slides freely in its guide. Should the
valve and seating be leaking, then the valve assembly must
be renewed. Check that the float is not distorted or punc-
tured and that it moves on its pivot without resistance or
excessive play. Again renew the float assembly if there is
any doubt. To check the level proceed as follows:
1 Check that the needle valve 3 (see FIG 2 : 8) is screwed
tight on its seat.
2 Keep the carburetter cover 1 upright or else the weight
of the float 9 will lower the ball 8 fitted on the needle 4.
Check that with the cover held in the vertical position
and the float arm 6 in slight contact with the ball 8 of the
needle 4, the float is 5/16 inch away from the cover with
its gasket 2
fitted flat against the cover face.
3 Check that the float travel is 5/16 inch and if necessary
bend the lug 5 to give the required settings.
4 If the float 9 is not correctly positioned, bend the float
arms 7 until the correct adjustment is obtained. Ensure
that the arm 6 is perpendicular to the needle axis and
F50039
does not show any rough spots or indentations which
might impair free movement of the needle. Check that
the float 9 freely moves about its pivot pin.
Every time a new float or needle valve assembly is fitted
the above detailed adjustment operations must be com-
pleted to ensure correct fuel levels. FIG 2 : 8 Float adjustment data
Key to Fig 2: 8 1 Carburetter cover 2 Cover gasket
3 Needle valve seat 4 Needle 5 Lug 6, 7 Arms
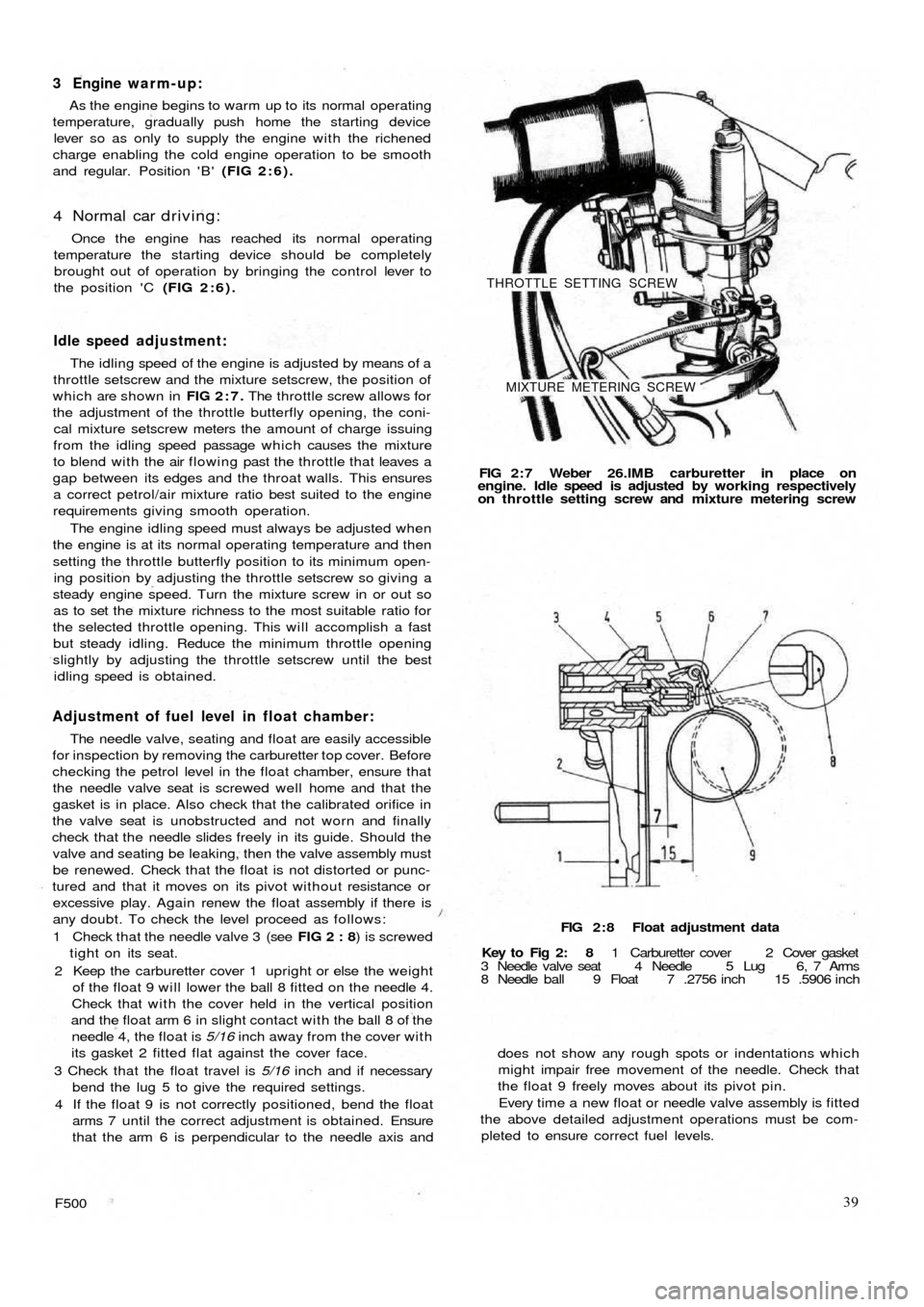
8 Needle ball 9 Float 7 .2756 inch 15 .5906 inch FIG 2 : 7 Weber 26.IMB carburetter in place on
engine. Idle speed is adjusted by working respectively
on throttle setting screw and mixture metering screw
THROTTLE SETTING SCREW
MIXTURE METERING SCREW
Page 33 of 128
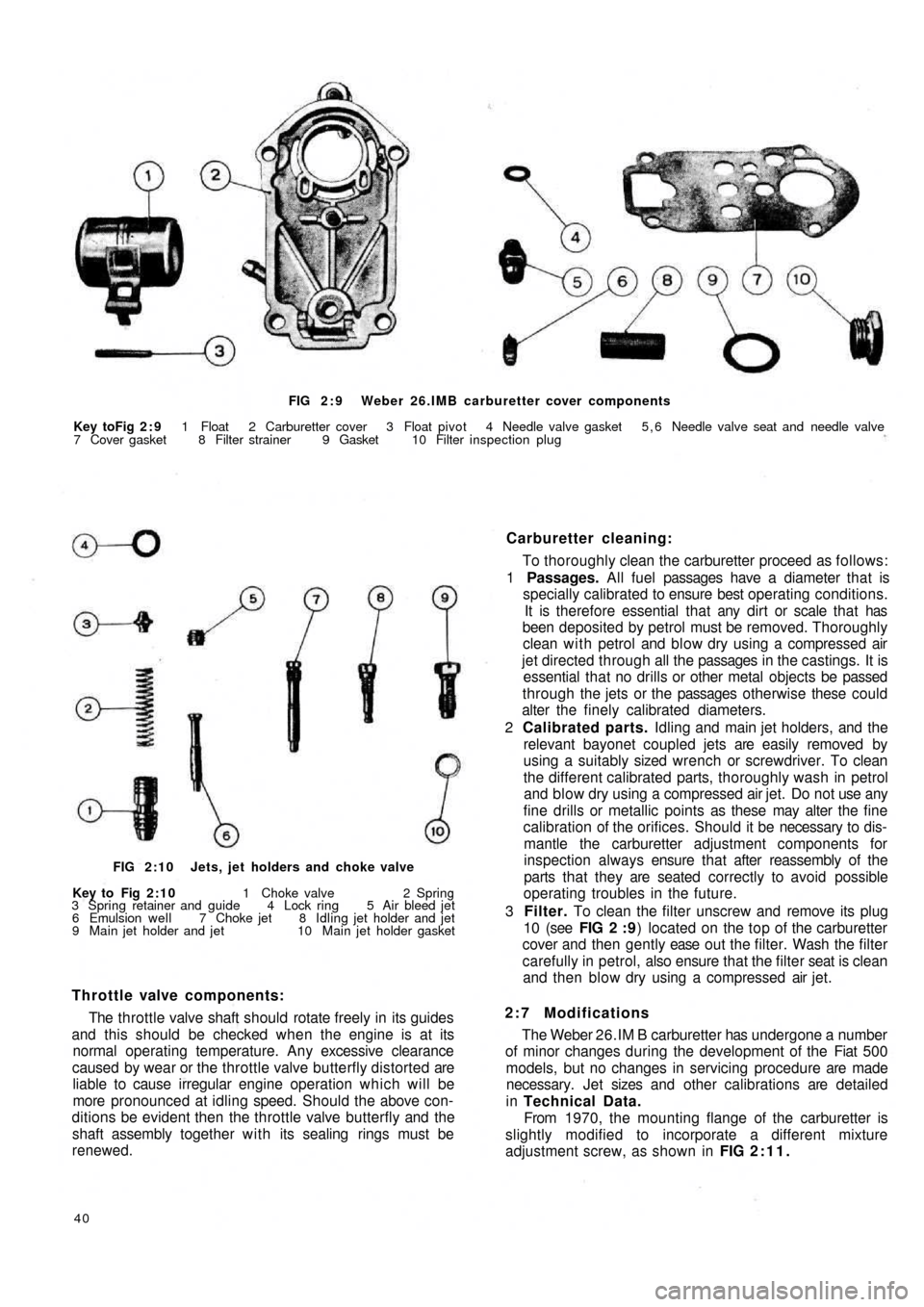
FIG 2 : 9 Weber 26.IMB carburetter cover components
Key toFig 2 : 9 1 Float 2 Carburetter cover 3 Float pivot 4 Needle valve gasket 5 , 6 Needle valve seat and needle valve
7 Cover gasket 8 Filter strainer 9 Gasket 10 Filter inspection plug
Carburetter cleaning:
To thoroughly clean the carburetter proceed as follows:
1 Passages. All fuel passages have a diameter that is
specially calibrated to ensure best operating conditions.
It is therefore essential that any dirt or scale that has
been deposited by petrol must be removed. Thoroughly
clean with petrol and blow dry using a compressed air
jet directed through all the passages in the castings. It is
essential that no drills or other metal objects be passed
through the jets or the passages otherwise these could
alter the finely calibrated diameters.
2 Calibrated parts. Idling and main jet holders, and the
relevant bayonet coupled jets are easily removed by
using a suitably sized wrench or screwdriver. To clean
the different calibrated parts, thoroughly wash in petrol
and blow dry using a compressed air jet. Do not use any
fine drills or metallic points as these may alter the fine
calibration of the orifices. Should it be necessary to dis-
mantle the carburetter adjustment components for
inspection always ensure that after reassembly of the
parts that they are seated correctly to avoid possible
operating troubles in the future.
3 Filter. To clean the filter unscrew and remove its plug
10 (see FIG 2 : 9) located on the top of the carburetter
cover and then gently ease o u t t h e filter. Wash the filter
carefully in petrol, also ensure that the filter seat is clean
and then blow dry using a compressed air jet.
2:7 Modifications
The Weber 26.IM B carburetter has undergone a number
of minor changes during the development of the Fiat 500
models, but no changes in servicing procedure are made
necessary. Jet sizes and other calibrations are detailed
in Technical Data.
From 1970, the mounting flange of the carburetter is
slightly modified to incorporate a different mixture
adjustment screw, as shown in FIG 2:11.
40
Throttle valve components:
The throttle valve shaft should rotate freely in its guides
and this should be checked when the engine is at its
normal operating temperature. Any excessive clearance
caused by wear or the throttle valve butterfly distorted are
liable to cause irregular engine operation which will be
more pronounced at idling speed. Should the above con-
ditions be evident then the throttle valve butterfly and the
shaft assembly together with its sealing rings must be
renewed.
FIG 2:10 Jets, jet holders and choke valve
Key to Fig 2:10 1 Choke valve 2 Spring
3 Spring retainer and guide 4 Lock ring 5 Air bleed jet
6 Emulsion well 7 Choke jet 8 Idling jet holder and jet
9 Main jet holder and jet 10 Main jet holder gasket
Page 34 of 128
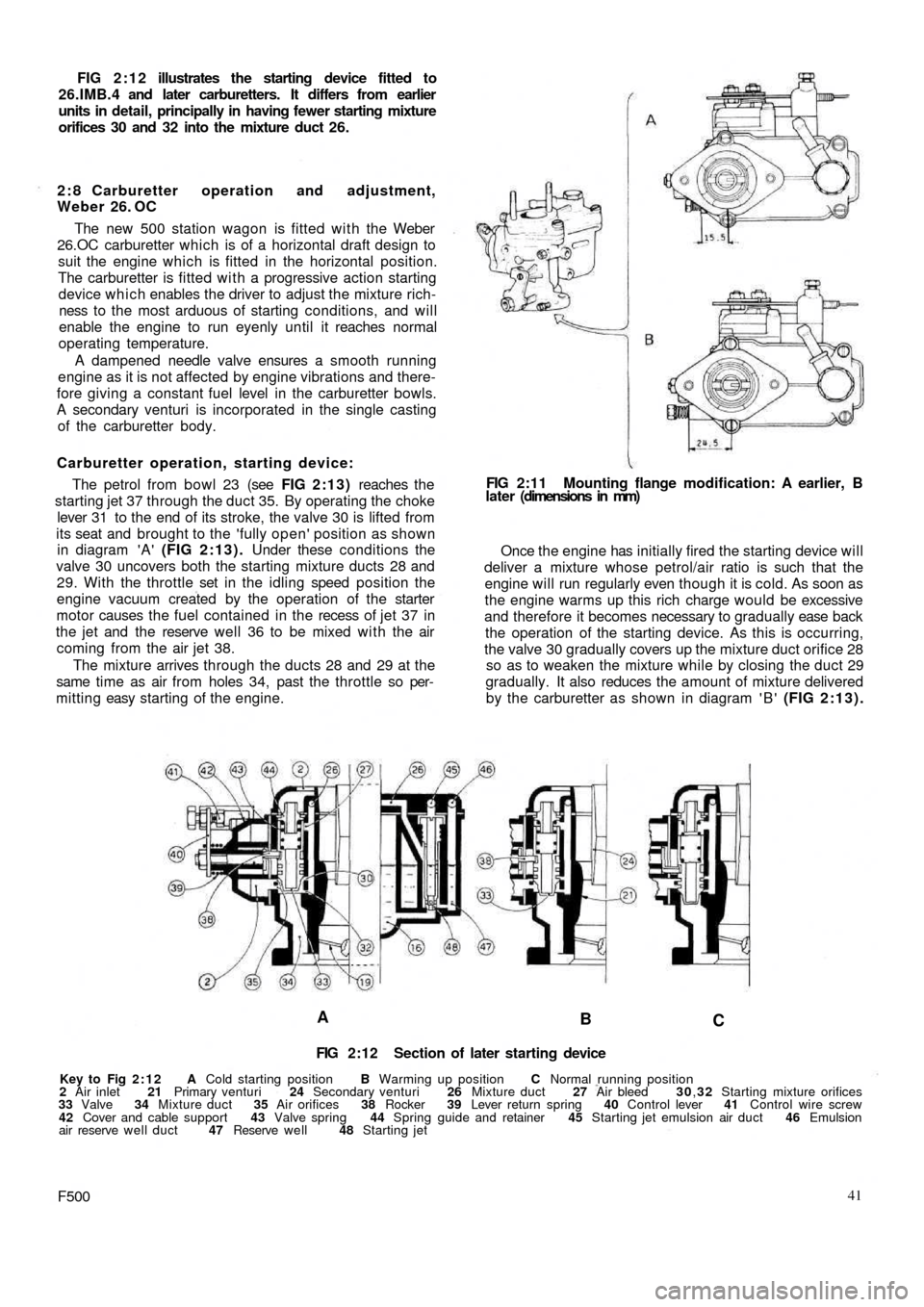
FIG 2:12 illustrates the starting device fitted to
26.IMB.4 and later carburetters. It differs from earlier
units in detail, principally in having fewer starting mixture
orifices 30 and 32 into the mixture duct 26.
2 : 8 Carburetter operation and adjustment,
Weber 26. OC
The new 500 station wagon is fitted with the Weber
26.OC carburetter which is of a horizontal draft design to
suit the engine which is fitted in the horizontal position.
The carburetter is fitted with a progressive action starting
device which enables the driver to adjust the mixture rich-
ness to the most arduous of starting conditions, and will
enable the engine to run eyenly until it reaches normal
operating temperature.
A dampened needle valve ensures a smooth running
engine as it is not affected by engine vibrations and there-
fore giving a constant fuel level in the carburetter bowls.
A secondary venturi is incorporated in the single casting
of the carburetter body.
Carburetter operation, starting device:
The petrol from bowl 23 (see FIG 2:13) reaches the
starting jet 37 through the duct 35. By operating the choke
lever 31 to the end of its stroke, the valve 30 is lifted from
its seat and brought to the 'fully open' position as shown
in diagram 'A' (FIG 2:13). Under these conditions the
valve 30 uncovers both the starting mixture ducts 28 and
29. With the throttle set in the idling speed position the
engine vacuum created by the operation of the starter
motor causes the fuel contained in the recess of j e t 37 in
the jet and the reserve
well 36 to be mixed with the air
coming from the air jet 38.
The mixture arrives through the ducts 28 and 29 at the
same time as air from holes 34, past the throttle so per-
mitting easy starting of the engine.
A
B
C
FIG 2:12 Section of later starting device
Key to Fig 2:12 A Cold starting position B Warming up position C Normal running position
2 Air inlet 21 Primary venturi 24 Secondary venturi 26 Mixture duct 27 Air bleed 30,32 Starting mixture orifices
33 Valve 34 Mixture duct 35 Air orifices 38 Rocker 39 Lever return spring 40 Control lever 41 Control wire screw
42 Cover and cable support 43 Valve spring 44 Spring guide and retainer 45 Starting jet emulsion air duct 46 Emulsion
air reserve well duct 47 Reserve well 48 Starting jet
F50041 Once the engine has initially fired the starting device will
deliver a mixture whose petrol/air ratio is such that the
engine will run regularly even though it is cold. As soon as
the engine warms up this rich charge would be excessive
and therefore it becomes necessary to gradually ease back
the operation of the starting device. As this is occurring,
the valve 30 gradually covers up the mixture duct orifice 28
so as to weaken the mixture while by closing the duct 29
gradually. It also reduces the amount of mixture delivered
by the carburetter as shown in diagram ' B ' (FIG 2:13). FIG 2:11 Mounting flange modification: A earlier, B
later (dimensions in mm)
Page 35 of 128
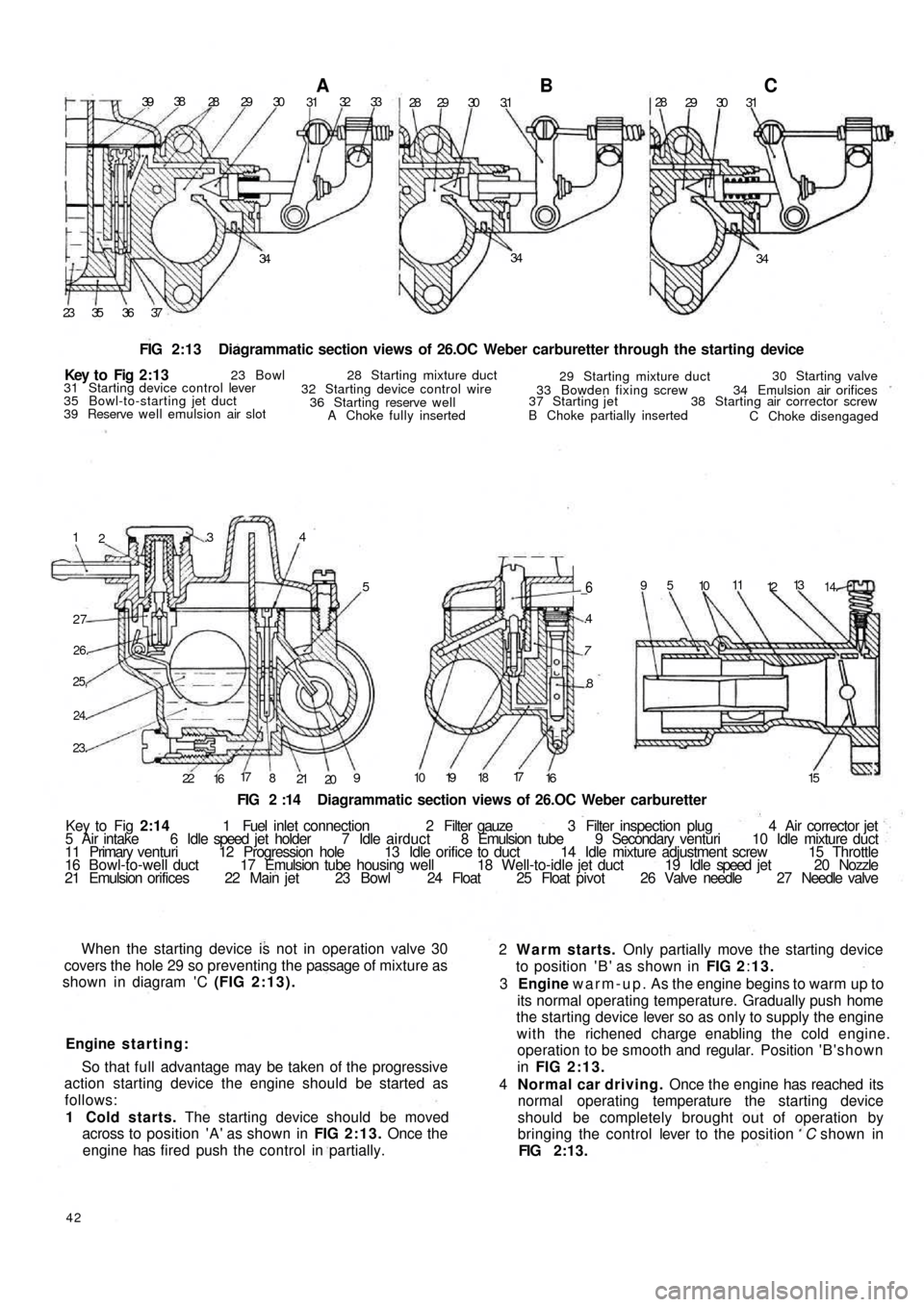
3938
28 29 30A3132 33
28 29 30 3.1B28
29 30 31C
34 34
34
37 36 35 23
FIG 2:13 Diagrammatic section views of 26.OC Weber carburetter through the starting device
1
2.34
5
27
26.
25,
24.
23.
22
1617
8
21
209
_6
.4
7
.8
10 19 1817
16 1595
1011
1213
14.
FIG 2 :14 Diagrammatic section views of 26.OC Weber carburetter
Key to Fig 2:14 1 Fuel inlet connection 2 Filter gauze 3 Filter inspection plug 4 Air corrector jet
5 Air intake 6 Idle speed jet holder 7 Idle airduct 8 Emulsion tube 9 Secondary venturi 10 Idle mixture duct
11 Primary venturi 12 Progression hole 13 Idle orifice to duct 14 Idle mixture adjustment screw 15 Throttle
16 B o w l - t o - w e l l duct 17 Emulsion tube housing well 18 Well-to-idle jet duct 19 Idle speed jet 20 Nozzle
21 Emulsion orifices 22 Main jet 23 Bowl 24 Float 25 Float pivot 26 Valve needle 27 Needle valve
When the starting device is not in operation valve 30
covers the hole 29 so preventing the passage of mixture as
shown in diagram 'C (FIG 2:13).
Engine starting:
So that full advantage may be taken of the progressive
action starting device the engine should be started as
follows:
1 Cold starts. The starting device should be moved
across to position 'A' as shown in FIG 2:13. Once the
engine has fired push the control in partially.
42
2 Warm starts. Only partially move the starting device
to position ' B ' as shown in FIG 2:13.
3 Engine warm-up. As the engine begins to warm up to
its normal operating temperature. Gradually push home
the starting device lever so as only to supply the engine
with the richened charge enabling the cold engine.
operation to be smooth and regular. Position ' B ' s h o w n
in FIG 2:13.
4 Normal car driving. Once the engine has reached its
normal operating temperature the starting device
should be completely brought out of operation by
bringing the control lever to the position C shown in
FIG 2:13. Key t o Fig 2 : 1 3
23 Bowl 28 Starting mixture duct
29 Starting mixture duct30 Starting valve
34 Emulsion air orifices
38 Starting air corrector screw
C Choke disengaged B Choke partially inserted 37 Starting jet33 Bowden fixing screw
A Choke fully inserted 36 Starting reserve well 32 Starting device control wire 31 Starting device control lever
35 Bowl-to-starting jet duct
39 Reserve well emulsion air slot
Page 36 of 128
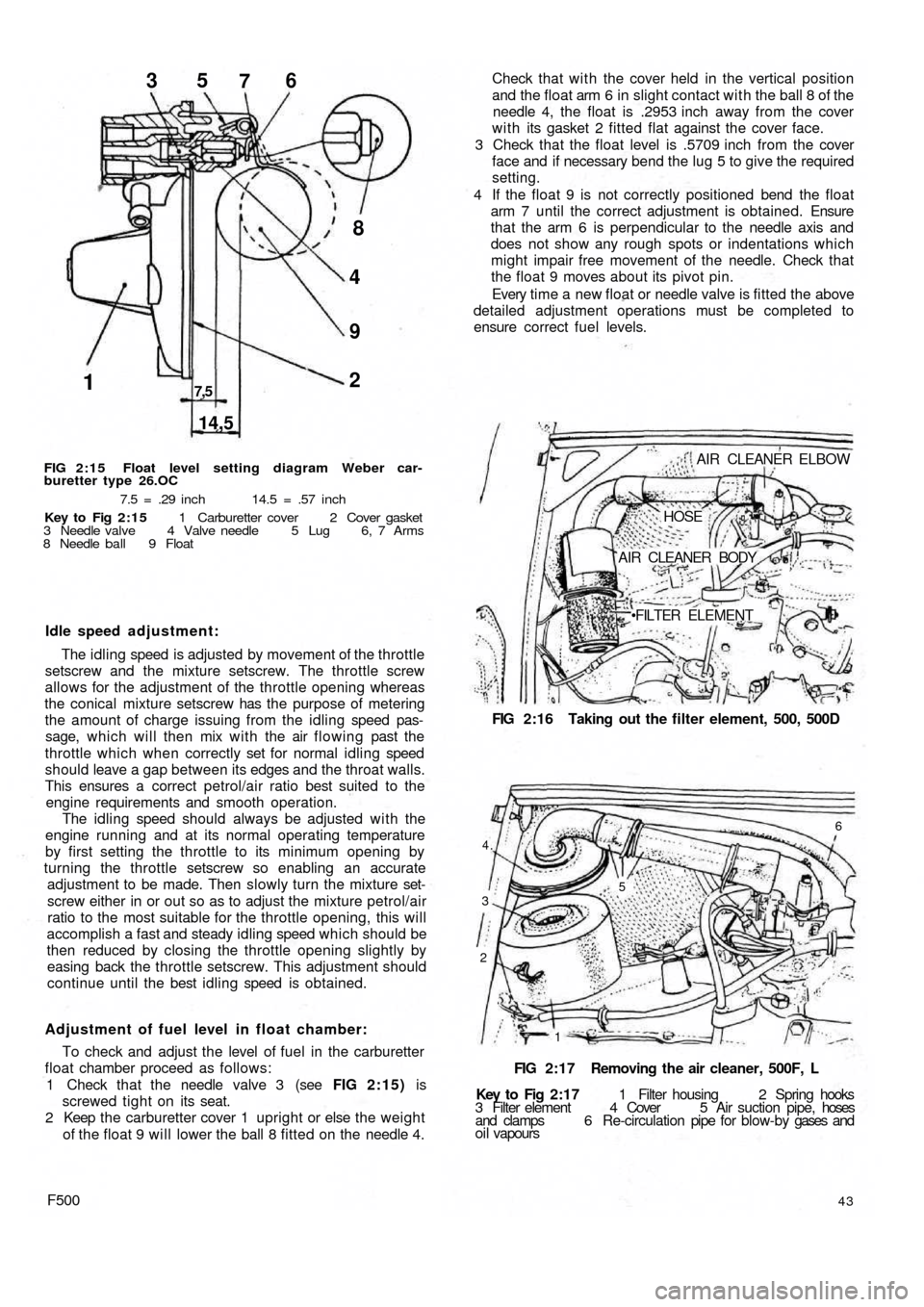
1
14,5
7,52 9 48 35
76
FIG 2:15 Float level setting diagram Weber car-
buretter type 26.OC
7.5 = .29 inch 14.5 = .57 inch
Key to Fig 2:15 1 Carburetter cover 2 Cover gasket
3 Needle valve 4 Valve needle 5 Lug 6, 7 Arms
8 Needle ball 9 Float
Idle speed adjustment:
The idling speed is adjusted by movement of the throttle
setscrew and the mixture setscrew. The throttle screw
allows for the adjustment of the throttle opening whereas
the conical mixture setscrew has the purpose of metering
the amount of charge issuing from the idling speed pas-
sage, which will then mix with the air flowing past the
throttle which when correctly set for normal idling speed
should leave a gap between its edges and the throat walls.
This ensures a correct petrol/air ratio best suited to the
engine requirements and smooth operation.
The idling speed should always be adjusted with the
engine running and at its normal operating temperature
by first setting the throttle to its minimum opening by
turning the throttle setscrew so enabling an accurate
adjustment to be made. Then slowly turn the mixture set-
screw either in or out so as to adjust the mixture petrol/air
ratio to the most suitable for the throttle opening, this will
accomplish a fast and steady idling speed which should be
then reduced by closing the throttle opening slightly by
easing back the throttle setscrew. This adjustment should
continue until the best idling speed is obtained.
Adjustment of fuel level in float chamber:
To check and adjust the level of fuel in the carburetter
float chamber proceed as follows:
1 Check that the needle valve 3 (see FIG 2:15) is
screwed tight on its seat.
2 Keep the carburetter cover 1 upright or else the weight
of the float 9 will lower the ball 8 fitted on the needle 4.
F50043
Key to Fig 2:17 1 Filter housing 2 Spring hooks
3 Filter element 4 Cover 5 Air suction pipe, hoses
and clamps 6 Re-circulation pipe for blow-by gases and
oil vapoursFIG 2:17 Removing the air cleaner, 500F, L
2
1 3
4.
6
5
FIG 2:16 Taking out the filter element, 500, 500D AIR CLEANER ELBOW
HOSE
AIR CLEANER BODY
FILTER ELEMENT Check that with the cover held in the vertical position
and the float arm 6 in slight contact with the ball 8 of the
needle 4, the float is .2953 inch away from the cover
w i t h its gasket 2 fitted flat against the cover face.
3 Check that the float level is .5709 inch from the cover
face and if necessary bend the lug 5 to give the required
setting.
4 If the float 9 is not correctly positioned bend the float
arm 7 until the correct adjustment is obtained. Ensure
that the arm 6 is perpendicular to the needle axis and
does not show any rough spots or indentations which
might impair free movement of the needle. Check that
the float 9 moves about its pivot pin.
Every time a new float or needle valve is fitted the above
detailed adjustment operations must be completed to
ensure correct fuel levels.
Page 38 of 128
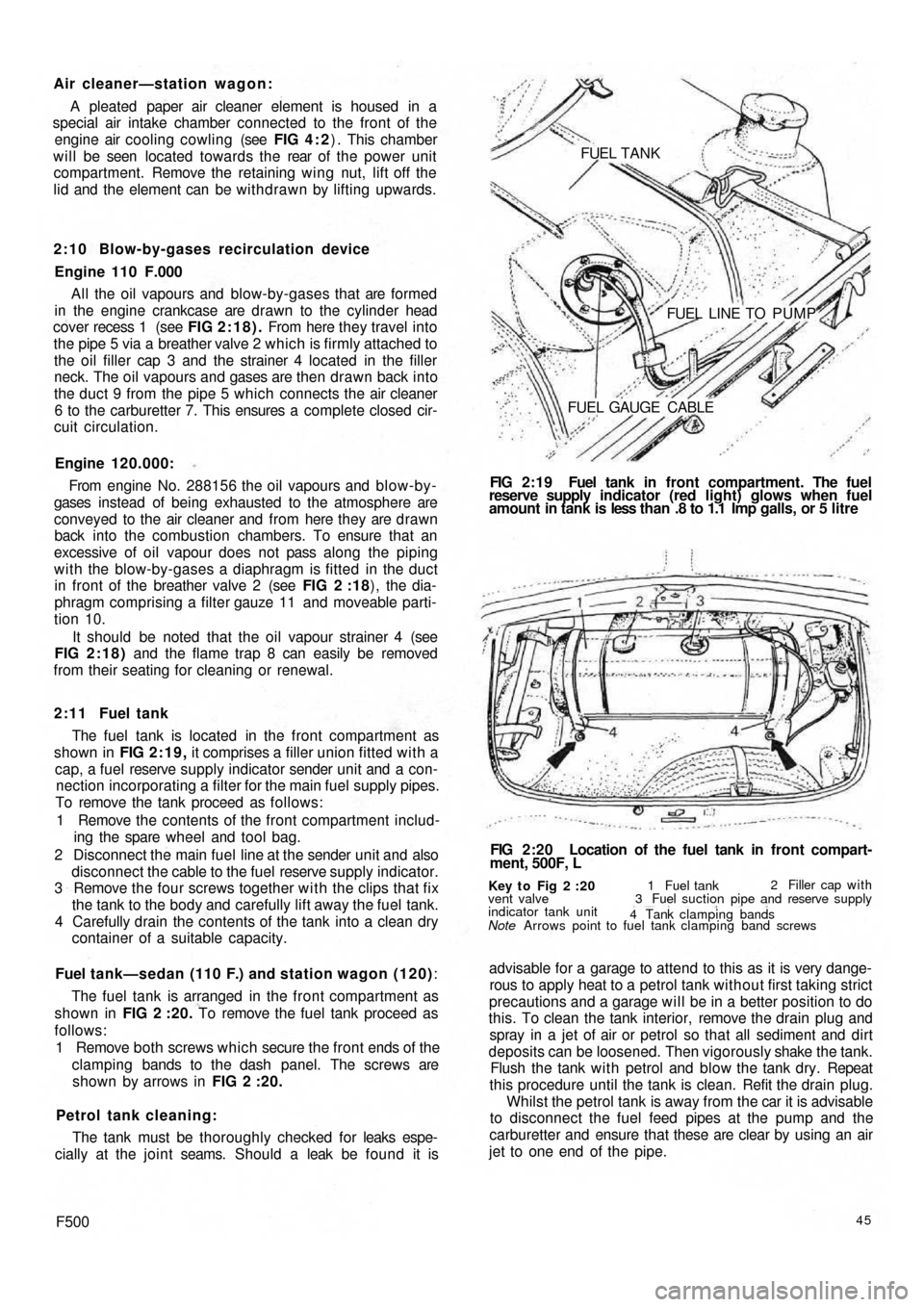
Air cleaner—station wagon:
A pleated paper air cleaner element is housed in a
special air intake chamber connected to the front of the
engine air cooling cowling (see FIG 4 : 2) . This chamber
will be seen located towards the rear of t h e power unit
compartment. Remove the retaining wing nut, lift off the
lid and the element can be withdrawn by lifting upwards.
2:10 Blow-by-gases recirculation device
Engine 110 F.000
All the oil vapours and blow-by-gases that are formed
in the engine crankcase are drawn to the cylinder head
cover recess 1 (see FIG 2:18). From here they travel into
the pipe 5 via a breather valve 2 which is firmly attached to
the oil filler cap 3 and the strainer 4 located in the filler
neck. The oil vapours and gases are then d r a w n back into
the duct 9 from the pipe 5 which connects the air cleaner
6 to the carburetter 7. This ensures a complete closed cir-
cuit circulation.
Engine 120.000:
From engine No. 288156 the oil vapours and blow-by-
gases instead of being exhausted to the atmosphere are
conveyed to the air cleaner and from here they are drawn
back into the combustion chambers. To ensure that an
excessive of oil vapour does not pass along the piping
with the blow-by-gases a diaphragm is fitted in the duct
in front of the breather valve 2 (see FIG 2 :18), the dia-
phragm comprising a filter gauze 11 and moveable parti-
tion 10.
It should be noted that the oil vapour strainer 4 (see
FIG 2:18) and the flame trap 8 can easily be removed
from their seating for cleaning or renewal.
2 : 1 1 Fuel tank
The fuel tank is located in the front compartment as
shown in FIG 2:19, it comprises a filler union fitted with a
cap, a fuel reserve supply indicator sender unit and a con-
nection incorporating a filter for the main fuel supply pipes.
To remove the tank proceed as follows:
1 Remove the contents of the front compartment includ-
ing the spare wheel and tool bag.
2 Disconnect the main fuel line at the sender unit and also
disconnect the cable to the fuel reserve supply indicator.
3 Remove the four screws together w i t h the clips that fix
the tank to the body and carefully lift away the fuel tank.
4 Carefully drain the contents of the tank into a clean dry
container of a suitable capacity.
Fuel tank—sedan (110 F.) and station wagon (120):
The fuel tank is arranged in the front compartment as
shown in FIG 2 :20. To remove the fuel tank proceed as
follows:
1 Remove both screws which secure the front ends of the
clamping bands to the dash panel. The screws are
shown by arrows in FIG 2 :20.
Petrol tank cleaning:
The tank must be thoroughly checked for leaks espe-
cially at the joint seams. Should a leak be found it is
F50045
advisable for a garage to attend to this as it is very dange-
rous to apply heat to a petrol tank without first taking strict
precautions and a garage will be in a better position to do
this. To clean the tank interior, remove the drain plug and
spray in a jet of air or petrol so that all sediment and dirt
deposits can be loosened. Then vigorously shake the tank.
Flush the tank w i t h petrol and blow the tank dry. Repeat
this procedure until the tank is clean. Refit the drain plug.
Whilst the petrol tank is away from the car it is advisable
to disconnect the fuel feed pipes at the pump and the
carburetter and ensure that these are clear by using an air
jet to one end of the pipe.
Key t o Fig 2 :20
Note Arrows point to fuel tank clamping band screws vent valve
indicator tank unit1 Fuel tank2 Filler cap with
3 Fuel suction pipe and reserve supply
4 Tank clamping bands
FIG 2:20 Location of the fuel tank in front compart-
ment, 500F, L FIG 2:19 Fuel tank in front compartment. The fuel
reserve supply indicator (red light) glows when fuel
amount in tank is less than .8 to 1.1 Imp galls, or 5 litre FUEL TANK
FUEL LINE TO PUMP
FUEL GAUGE CABLE
Page 39 of 128

2:12 Fault diagnosis
(a) Leakage or insufficient fuel delivered
1 Air vent in tank restricted
2 Petrol pipes blocked
3 Air leaks at pipe connections
4 Pump or carburetter filters blocked
5 Pump gaskets faulty
6 Pump diaphragm defective
7 Pump valves sticking or seating badly
8 Fuel vapourizing in pipelines due to heat
(b) Excessive fuel consumption
1 Carburetter needs adjusting
2 Fuel leakage
3 Sticking controls or choke device
4 Dirty air cleaner
5 Excessive engine temperature
6 Brakes binding
7 Tyres under-inflated
8 Idling speed too high
9 Car overloaded(c) Idling speed too high
1 Rich fuel mixture
2 Carburetter controls sticking
3 Slow-running screws incorrectly adjusted
4 Worn carburetter butterfly valve
(d) Noisy fuel pump
1 Loose mountings
2 Air leaks on suction side and at diaphragm
3 Obstruction in fuel pipe
4 Clogged pump filter
(e) No fuel delivery
1 Float needle stuck
2 Vent in tank blocked
3 Pipeline obstructed
4 Pump diaphragm stiff or damaged
5 Inlet valve in pump stuck open
6 Bad air leak on suction side of pump
46
Page 102 of 128
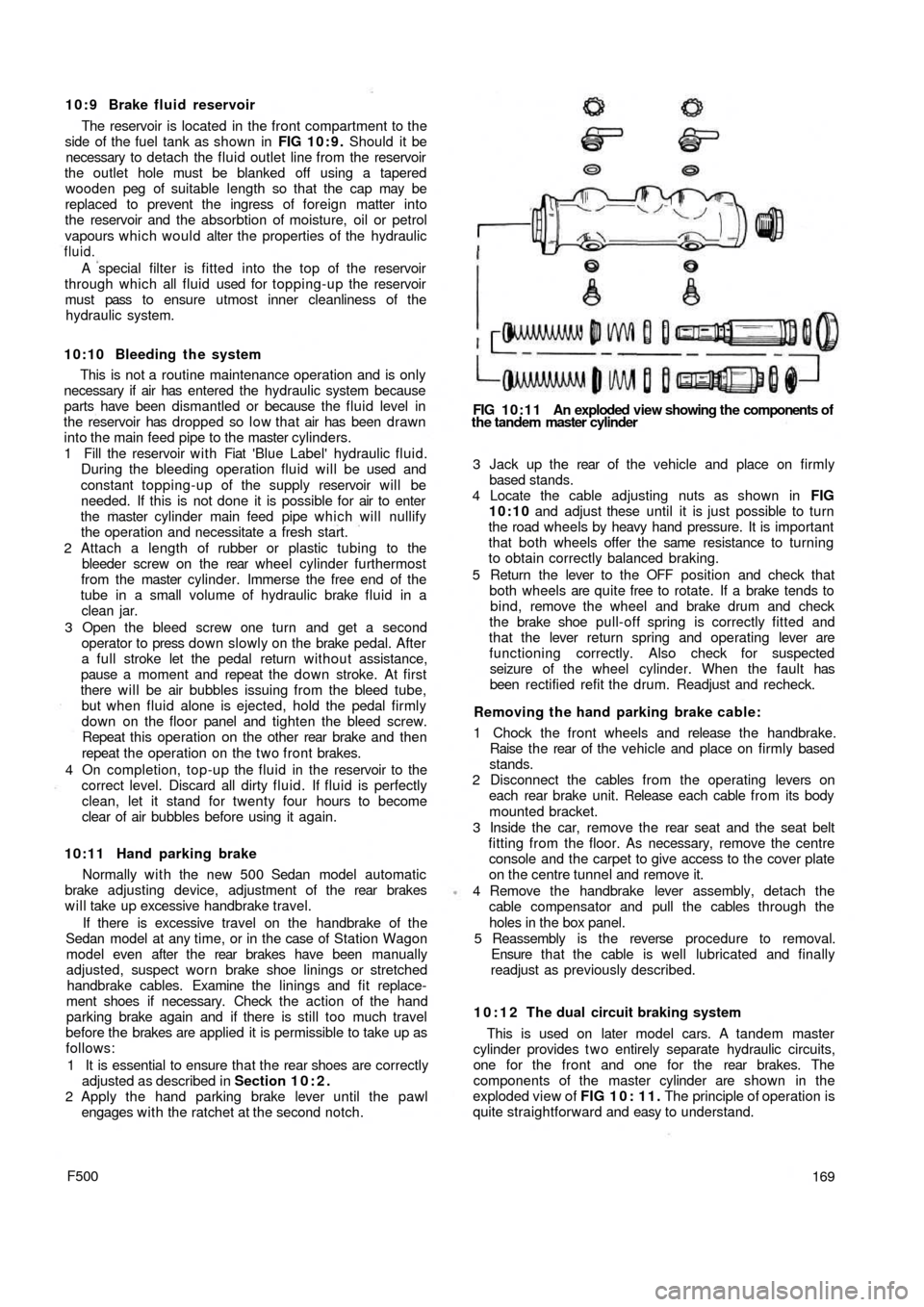
10:9 Brake fluid reservoir
The reservoir is located in the front compartment to the
side of the fuel tank as shown in FIG 10:9. Should it be
necessary to detach the fluid outlet line from the reservoir
the outlet hole must be blanked off using a tapered
wooden peg of suitable length so that the cap may be
replaced to prevent the ingress of foreign matter into
the reservoir and the absorbtion of moisture, oil or petrol
vapours which would alter the properties of the hydraulic
fluid.
A special filter is fitted into the top of the reservoir
through which all fluid used for topping-up the reservoir
must pass to ensure utmost inner cleanliness of the
hydraulic system.
10:10 Bleeding the system
This is not a routine maintenance operation and is only
necessary if air has entered the hydraulic system because
parts have been dismantled or because the f l u i d level in
the reservoir has dropped so low that air has been drawn
into the main feed pipe to the master cylinders.
1 Fill the reservoir w i t h Fiat 'Blue Label' hydraulic fluid.
During the bleeding operation fluid will be used and
constant topping-up of the supply reservoir will be
needed. If this is not done it is possible for air to enter
the master cylinder main feed pipe which will nullify
the operation and necessitate a fresh start.
2 Attach a length of rubber or plastic tubing to the
bleeder screw on the rear wheel cylinder furthermost
from the master cylinder. Immerse the free end of the
tube in a small volume of hydraulic brake fluid in a
clean jar.
3 Open the bleed screw one turn and get a second
operator to press down slowly on the brake pedal. After
a full stroke let the pedal return without assistance,
pause a moment and repeat the d o w n stroke. At first
there will be air bubbles issuing from the bleed tube,
but when fluid alone is ejected, hold the pedal firmly
down on the floor panel and tighten the bleed screw.
Repeat this operation on the other rear brake and then
repeat the operation on the two front brakes.
4 On completion, top-up the fluid in the reservoir to the
correct level. Discard all dirty fluid. If fluid is perfectly
clean, let it stand for twenty four hours to become
clear of air bubbles before using it again.
10:11 Hand parking brake
Normally with the new 500 Sedan model automatic
brake adjusting device, adjustment of the rear brakes
will take up excessive handbrake travel.
If there is excessive travel on the handbrake of the
Sedan model at any time, or in the case of Station Wagon
model even after the rear brakes have been manually
adjusted, suspect worn brake shoe linings or stretched
handbrake cables. Examine the linings and fit replace-
ment shoes if necessary. Check the action of the hand
parking brake again and if there is still too much travel
before the brakes are applied it is permissible to take up as
follows:
1 It is essential to ensure that the rear shoes are correctly
adjusted as described in Section 10:2.
2 Apply the hand parking brake lever until the pawl
engages with the ratchet at the second notch.
F500
FIG 10:11 An exploded view showing the components of
the tandem master cylinder
3 Jack up the rear of t h e vehicle and place on firmly
based stands.
4 Locate the cable adjusting nuts as shown in FIG
10:10 and adjust these until it is just possible to turn
the road wheels by heavy hand pressure. It is important
that both wheels offer the same resistance to turning
to obtain correctly balanced braking.
5 Return the lever to the OFF position and check that
both wheels are quite free to rotate. If a brake tends to
bind, remove the wheel and brake drum and check
the brake shoe pull-off spring is correctly fitted and
that the lever return spring and operating lever are
functioning correctly. Also check for suspected
seizure of the wheel cylinder. When the fault has
been rectified refit the drum. Readjust and recheck.
Removing the hand parking brake cable:
1 Chock the front wheels and release the handbrake.
Raise t h e rear of the vehicle and place on firmly based
stands.
2 Disconnect the cables from the operating levers on
each rear brake unit. Release each cable from its body
mounted bracket.
3 Inside the car, remove the rear seat and the seat belt
fitting from the floor. As necessary, remove the centre
console and the carpet to give access to the cover plate
on the centre tunnel and remove it.
4 Remove the handbrake lever assembly, detach the
cable compensator and pull the cables through the
holes in the box panel.
5 Reassembly is the reverse procedure to removal.
Ensure t h a t the cable is well lubricated and finally
readjust as previously described.
10:12 The dual circuit braking system
This is used on later model cars. A tandem master
cylinder provides t w o entirely separate hydraulic circuits,
one for the front and one for the rear brakes. The
components of the master cylinder are shown in the
exploded view of FIG 1 0 : 1 1 . The principle of operation is
quite straightforward and easy to understand.
169
Page 116 of 128
Lamp brilliance varies w i t h the speed of t h e car:
Check the condition of the battery. Examine the battery
connections. Make sure they are tight and renew faulty
cables.
11:10 Panel and warning lights:
All the gauges are clustered in a single instrument
mounted on the dashboard above the steering column.
Incorporated in this cluster is the parking light pilot light,
generator charge indicator, fuel reserve supply indicator,
low oil pressure indicator, and the speedometer w i t h
mileage recorder.
The parking lamp indicator glows green when the
ignition lock switch key is in either position 1 or 2 once
the toggle switch on the instrument panel has been
operated.
The generator charge indicator shows red only when
the ignition is turned on. It should be extinguished when
the generator output is sufficient for battery charge
(12.6 ± 0.2 volts) with the engine running at a speed
of 1100 rev/min and the headlights switched off.
The fuel reserve supply indicator shows red only when
the ignition is turned on and the amount of fuel in the
petrol tank has dropped to approximately .8 to 1.1
Imp. gallons.
The low oil pressure indicator shows red only when the
ignition is turned on and should be extinguished when
the oil pressure reaches 7.1 to 21.3 Ib/sq in, and opens
the sending unit contacts. Once the engine is at normal
operating temperature but at a speed below 1000 rev/
min the indicator might light up even the pressure is under
control and with normal operation.
All the bulbs fitted to the above described units are of
the tubular 2.5W type and to renew a bulb extract the
bulb holder from the rear of t h e instrument cluster and
release the bulb which is attached by a normal bayonet
coupling.
Fuel reserve supply indicator sender u n i t:
The fuel reserve supply indicator should be checked for
correct indication by allowing the fuel tank to empty and
then inserting .8 to 1.1 Imp. gallons at which stage the
light should extinguish. Any failure to do so should be
checked as follows:
1 Ensure that the indicator bulb operates correctly.
2 Check for complete circuit between the sender unit and
the indicator bulb.
3 If the sender unit float bracket is distorted the bulb
will
indicate a reserve supply of fuel greater or smaller than
specified. The bracket should be adjusted to give
correct indication of fuel level.
4 The sender unit could have been inadvertantly
damaged in which case the unit must be renewed.
11 :11 The horn
The horn circuit comprises the horn, push button at the
centre of the steering wheel and normal earth return
electrical circuit through the car body. One terminal is
connected to the battery whilst the other to the push
button on the steering wheel which when the button is
depressed the circuit will be closed so causing the horn
to operate.
F500
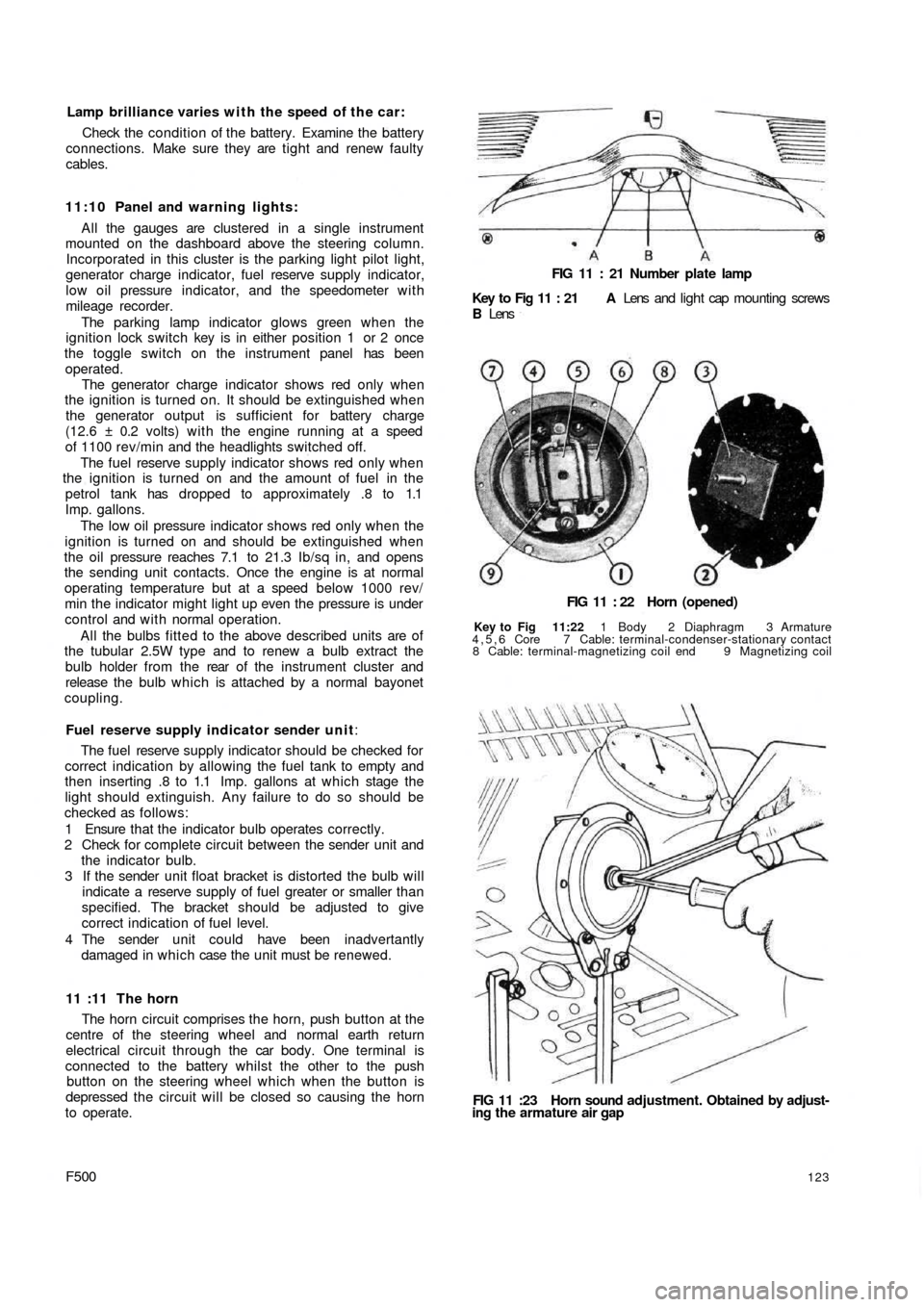
FIG 11 : 21 Number plate lamp
Key to Fig 11 : 21 A Lens and light cap mounting screws
B Lens
FIG 11 : 22 Horn (opened)
Key to Fig 11:22 1 Body 2 Diaphragm 3 Armature
4,5,6 Core 7 Cable: terminal-condenser-stationary contact
8 Cable: terminal-magnetizing coil end 9 Magnetizing coil
FIG 11 :23 Horn sound adjustment. Obtained by adjust-
ing the armature air gap
123