temperature FIAT MAREA 2001 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 2001, Model line: MAREA, Model: FIAT MAREA 2001 1.GPages: 330
Page 86 of 330

Marea- Marea Weekend 9 \) JTD
2000 range O
Engine
Index
FUEL SYSTEM
- Introduction
- System management strategies
- Fuel system functional diagram
- Diagram showing information ente
ring/leaving the control unit and
sensors/actuators
INJECTION SYSTEM WIRING DIA
GRAM
- Injection electronic control unit
- Rpm sensor
- Timing sensor
- Air flow meter
- Injectors
- Engine coolant temperature sensor
- Fuel temperature sensor
- Fuel pressure sensor
- Heater plugs control unit
- Accelerator pedal potentiometer
- Brake pedal switch
- Clutch pedal switch
- Excess pressure sensor
- Atmospheric pressure sensor
page
1
1
1
2
8
10
12
13
13
14
15
15
15
16
16
17
17
17
17
THROTTLE CASING
- Removing-refitting
E.G.R. VALVE
- Removing-refitting
E.G.R. VALVE SELF-ADJUSTMENT
MOTOR
- Removing-refitting
E.G.R. VALVE HEAT EXCHANGER
- Removing-refitting
SOLENOID VALVE ON VACUUM
RESERVOIR FOR THROTTLE CA
SING PNEUMATIC VALVE
- Removing-refitting
VACUUM RESERVOIR
- Removing-refitting
10.
page
30
31
32
32
34
34
FUEL SUPPLY CIRCUIT 18
- Immersed (auxiliary) pump and fuel
gauge assembly 19
- Fuel filter 19
- Pressure pump 20
- Fuel pressure regulator 20
- Multifunction valve 21
- Supply manifold (rail) 21
- Inertia safety switch 22
AIR SUPPLY CIRCUIT 23
- Throttle case 24
- Turbocharger 25
SUPERCHARGING PRESSURE
CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE
- Removing-refitting 35
FUEL FILTER
- Removing-refitting 35
PRESSURE REGULATOR
- Removing-refitting 36
EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES 27
- Oxidizing catalytic converter 27
- Exhaust gas recirculation circuit
(EGR) 27
- Recirculation circuit for crankcase
vapours (blow-by) 29
Copyright by Fiat Auto VI 01 Cancels anil replaces
Page 87 of 330

Marea- Marea Weekend © ™ Engine
2000 range Q Fuel feed system
10.
FUEL SYSTEM
INTRODUCTION
Marea and Marea Weekend 1.9 JTD cars are equipped with a 4 cylinder in line, 1910 cc turbodiesel en
gine with two valves per cylinder, an overhead camshaft, turbocharger and intercooler and electronic in
jection.
The fuel system ensures correct engine operation and can be divided into the following subsystems:
- Fuel feed circuit with common rail injection;
- air feed circuit;
- exhaust circuit;
- blow by vapour recirculation circuit;
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) circuit
Operation of the various circuits making up the fuel system is optimised by an electronic control system
managed by a special control unit.
The main feature of the fuel system is common rail fuel injection. Common rail is a higher pressure elec
tronic injection system for fast direct injection diesel engines.
The main features of the common rail system are as follows:
- availability of high injection pressures (up to 1350 bars);
- possibility of modulating these pressures (from a minimum of 150 bars to a maximum of 1350 bars)
independently of engine speed (rpm) and engine load;
- ability to operate at high engine speeds (up to 6000 rpm);
- precise injection control (injection advance and duration);
- reduced fuel consumption;
- reduced emissions.
FUEL SYSTEM MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES
The management program (software) is stored inside the control unit memory and consists of a series of
strategies, each of which manages a precise system control function.
Through the use of information providd by the various sensors (input), each strategy processes a set of
parameters based on data stored in special control unit memory areas. It then controls system actuators
(output), i.e. the devices that allow the engine to operate.
The main purpose of these management strategies is to determine the exact amount of fuel to be injected
into the cylinders with timing (injection advance) and pressure designed to achieve the best possible en
gine performance in terms of power, fuel consumption, fumes, emissions and handling.
The main system management strategies are essentially as follows:
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
contro
of injected fuel quantity;
of injection advance;
of injection pressure;
of auxiliary fuel pump;
of injection during over-run (cut-off);
of idle speed;
of maximum speed limitation;
of maximum torque limitation;
of fuel temperature;
of engine coolant temperature;
of air turbocharging pressure;
of glow plugs;
of exhaust fumes;
of exhaust gas recirculation (EGR);
of climate control system activation;
control of engine immobiliser operation (Fiat
CODE);
self-diagnosis
Copyright by Fiat Auto 1
Page 88 of 330
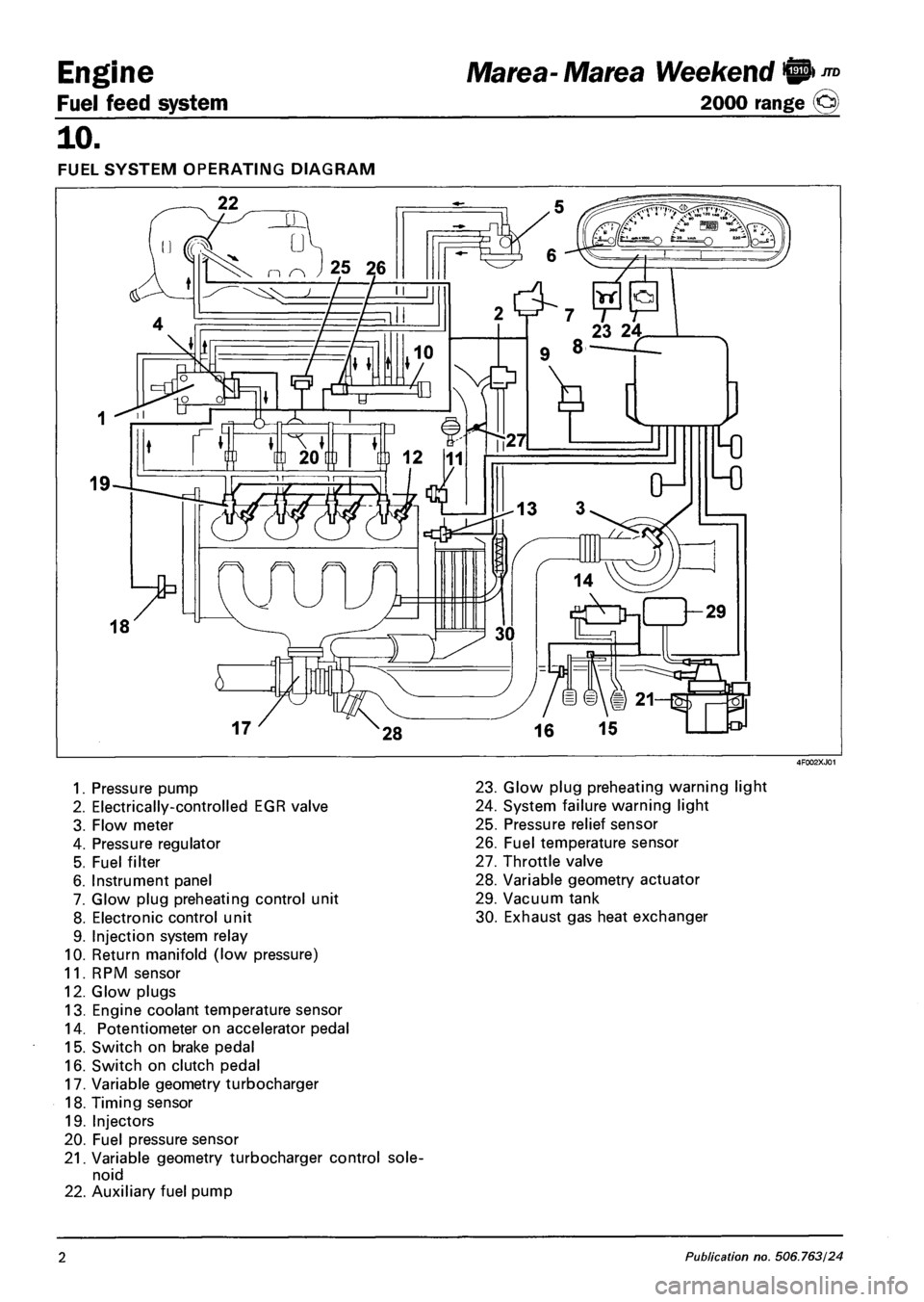
Engine
Fuel feed system
Marea- Marea Weekend © ™
2000 range ©
10.
FUEL SYSTEM OPERATING DIAGRAM
1. Pressure pump
2. Electrically-controlled EGR valve
3. Flow meter
4. Pressure regulator
5. Fuel filter
6. Instrument panel
7. Glow plug preheating control unit
8. Electronic control unit
9. Injection system relay
10. Return manifold (low pressure)
11. RPM sensor
12. Glow plugs
13. Engine coolant temperature sensor
14. Potentiometer on accelerator pedal
15. Switch on brake pedal
16. Switch on clutch pedal
17. Variable geometry turbocharger
18. Timing sensor
19. Injectors
20. Fuel pressure sensor
21. Variable geometry turbocharger control sole
noid
22. Auxiliary fuel pump
23. Glow plug preheating warning light
24. System failure warning light
25. Pressure relief sensor
26. Fuel temperature sensor
27. Throttle valve
28. Variable geometry actuator
29. Vacuum tank
30. Exhaust gas heat exchanger
2 Publication no. 506.763/24
Page 89 of 330

Ma tea- Marea Weekend 9 ™
2000 range (Q) Fuel feed system
Engine
10.
Control of injected fuel quantity
The control unit controls the fuel pressure regulator and injectors on the basis of output signals from the
accelerator pedal potentiometer, flow meter and rpm sensor.
The timing and thus the injection sequence are determined when the engine is started up using signals
from the rpm and timing sensor (synchronisation stage); injection timing is then implemented using the
rpm sensor signal alone and considering a injection sequence of 1 -3-4-2.
The control unit inhibits injection in the following cases:
- fuel pressure level greater than 1500 bars;
- fuel pressure level lower than 120 bars;
- engine speed higher than 6000 rpm.
When the engine has warmed up, maximum injection duration (injector opening time) is 1500 ns, but it
can reach 3000 ns during the start-up stage.
Control of injection advance
The electronic control unit determines injection advance mainly on the basis of the quantity of fuel to be
injected.
The injection advance is then corrected on the basis of coolant temperature and speed in order to com
pensate for ignition delays due to low temperatures in the combustion chamber during warm-up.
The optimum injection point is also processed to ensure driving comfort and emission limits laid down by
Euro 3 legislation.
Control of injection pressure
This control is of particular importance because injection pressure influences the following parameters:
- amount of fuel taken into the cylinders for the same injection time duration;
- injected fuel nebulation;
- spray penetration;
- lag between electrical control to injection and actual injection start and end times.
The above parameters engine behaviour significantly, particularly in terms of power output, exhaust emis
sions, noise levels and handling.
The injection control unit controls the pressure governor on the basis of engine load to obtain an optimal
line pressure at all times.
When the engine is cold, injection pressure is corrected on the basis of engine speed and engine coolant
temperature to meet engine needs at different operating temperatures.
Control of auxiliary fuel pump
The auxiliary fuel pump submerged in the tank is supplied by the injection control unit by means of a relay
when the ignition key is turned on.
Fuel supply to the pump is inhibited when one of the following condition occurs:
- when the ignition has been turned on for a certain length of time without the engine running;
- if the inertia switch cuts in.
Control of injection during over-run (cut-off)
The fuel cut-off strategy is implemented when the injection control unit receives information that the ac
celerator pedal has been released from the potentiometer.
Under these conditions, the control unit cuts off the fuel supply to the injectors and restores it before idle
speed is reached.
Copyright by Fiat Auto 3
Page 90 of 330

Fuel feed system
Engine Marea- Marea Weekend 9 ™
2000 range (Q)
10.
Control of idle speed
On the basis of signals from the rpm sensor and engine coolant temperature sensor, the injection control
unit controls the pressure governor and alters the injector control times to maintain idle speed stable at all
times.
Under certain conditions, the idle speed control unit also considers battery voltage.
Control of maximum speed limitation
According to rpm level, the injection control unit limits maximum speed by means of two types of inter
vention:
- as maximum speed approaches, it reduces the amount of fuel injected to reduce line pressure;
- when maximum speed is exceeded, it inhibits operation of the auxiliary pump and injectors.
Control of maximum torque limitation
On the basis of rpm level, the injection control unit computes limit torque and maximum permitted fume
index parameters on the basis of predefined, stored maps.
It then corrects the above parameters using engine coolant temperature and car speed data. The resulting
values are then used to modulate the amount of fuel to be injected by adjusting the pressure regulator and
injectors.
Control of fuel temperature
The injection control uint is kept constantly informed of fuel temperature by a sensor on the return mani
fold.
If fuel temperature exceeds a set value (about 110 °C), the control unit reduces line pressure by adjusting
the pressure governor, leaving injection times unaltered.
Control of coolant temperature
The injection control unit is constantly informed of coolant temperature by a sensor on the thermostat.
If engine coolant temperature or air conditioning fluid pressure exceeds certain levels, the control unit
performs the following actions:
- It reduces the amount of fuel injected by adjusting the pressure governor and injectors (power reduc
tion);
- it controls the engine radiator cooling fan.
Control of glow plugs
The injection control unit controls operation of the glow plug preheating control unit to bring the tem
perature in the combution chambers up to levels that promote fuel self-ignition and thus make start-up
easier.
The control unit controls the operation of the glow plug control unit for a certain time both before (pre
heating) and after (postheating) engine start-up and also controls activation of the warning light on the
control panel.
Preheating, postheating and glow plug warning light activation times vary according to engine coolant
temperature.
4 Publication no. 506.763/24
Page 93 of 330
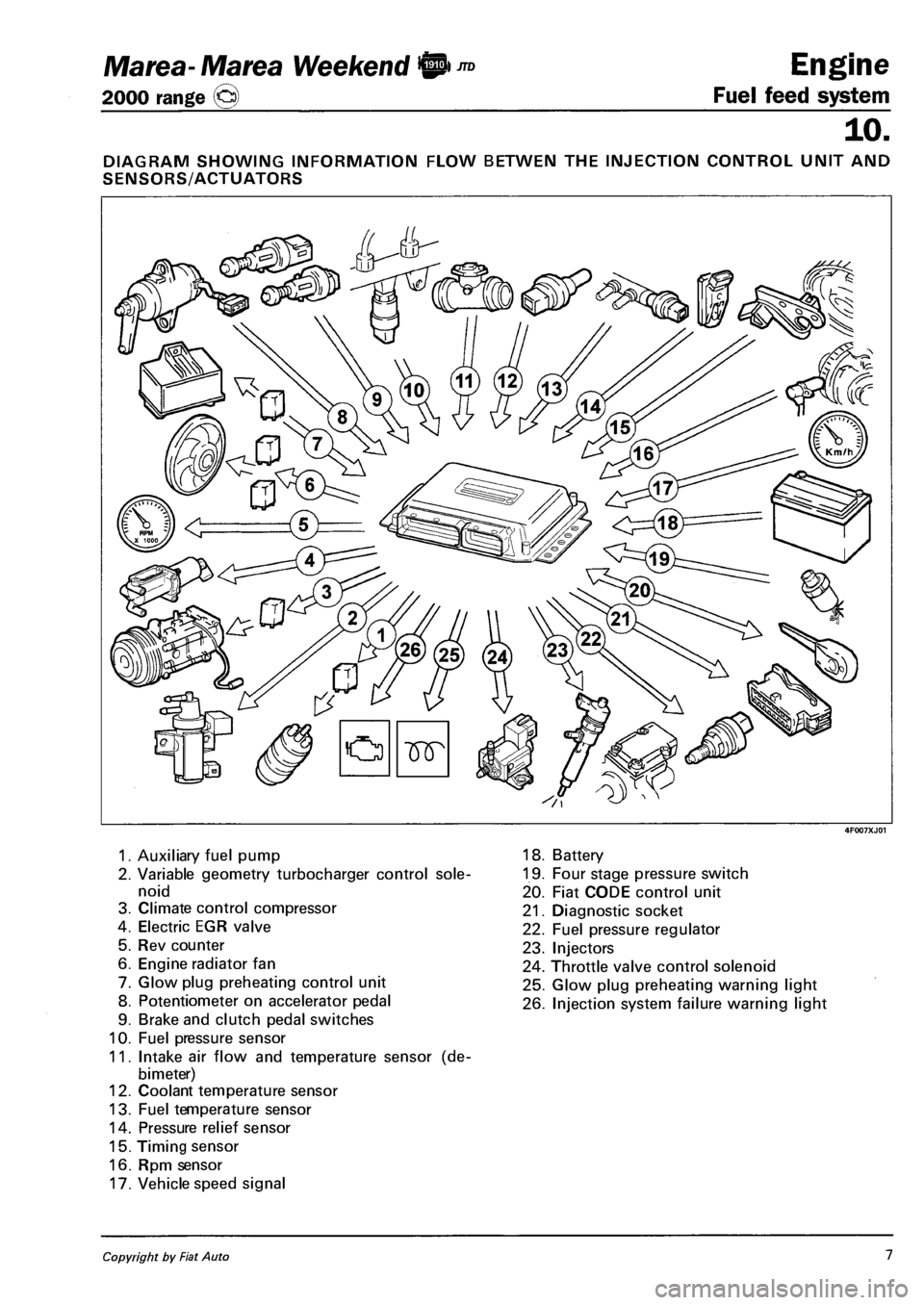
Marea- Marea Weekend 9 ™
2000 range ©
Engine
Fuel feed system
10.
DIAGRAM SHOWING INFORMATION FLOW BETWEN THE INJECTION CONTROL UNIT AND
SENSORS/ACTUATORS
1. Auxiliary fuel pump
2. Variable geometry turbocharger control sole
noid
3. Climate control compressor
4. Electric EGR valve
5. Rev counter
6. Engine radiator fan
7. Glow plug preheating control unit
8. Potentiometer on accelerator pedal
9. Brake and clutch pedal switches
10. Fuel pressure sensor
11. Intake air flow and temperature sensor (de-
bimeter)
12. Coolant temperature sensor
13. Fuel temperature sensor
14. Pressure relief sensor
15. Timing sensor
16. Rpm sensor
17. Vehicle speed signal
18. Battery
19. Four stage pressure switch
20. Fiat CODE control unit
21. Diagnostic socket
22. Fuel pressure regulator
23. Injectors
24. Throttle valve control solenoid
25. Glow plug preheating warning light
26. Injection system failure warning light
Copyright by Fiat Auto 1
Page 95 of 330

Marea- Marea Weekend 9 ™
2000 range ©) Fuel feed system
Engine
10.
Compents of injection system wiring diagram
1. Vehicle speepd
2. Rev counter
3. Engine radiator fan low speed relay
4. Radiator fan high speed activation relay
5. Potentiometer on accelerator pedal
6. Timing sensor
7. Fuel pressure sensor
8. EGR system modulator solenoid
9. Fuel pressure regulator
10. Glow plug preheating warning light on control panel
11. Injection system failure warning light
12. Air conditioning system relay
13. Coolant temperature sensor
14. Rpm sensor
15. Fuel temperature sensor
16. Diagnostic socket
17. Fiat CODE control unit
18. Four stage pressure switch
19. Injection electronic control unit
20. Pressure relief sensor
21. 7.5A fuse protecting electronic injection system ( + 15 power supply from ignition switch)
22. 7.5A fuse protecting electronic injection system ( + 30 power supply from ignition switch)
23. Main injection system relay
24. 30A fuse protecting injection system
25. Auxiliary fuel pump relay
26. Glow plug preheating control unit
27. Intake air flow and temperature sensor (debimeter)
28. Brake pedal switch
29. Clutch pedal switch
30. Ignition switch
31. Battery
32. Inertia switch
33. Auxiliary fuel pump (submerged in tank)
34. 60A fuse protecting glow plug control unit
35. Cylinder no. 1 glow plug
36. Cylinder no. 2 glow plug
37. Cylinder no. 3 glow plug
38. Cylinder no. 4 glow plug
39. Cylinder no. 1 injector
40. Cylinder no. 2 injector
41. Cylinder no. 3 injector
42. Cylinder no. 4 injector
43. Throttle valve control solenoid
44. Variable geometry turbocharger control solenoid
45. Diesel filter heater relay
Copyright by Fiat Auto 9
Page 97 of 330

Ma tea- Ma tea Weekend !@ ™
2000 range ©
Engine
Fuel feed system
10.
37 Not connected
38 Not connected
39 Not connected
40 Not connected
41 Not connected
42 Not connected
43 Not connected
44 Not connected
45 Not connected
46 Not connected
47 Engine rpm signal output
48 Diagnostic line k
49 Vehicle speed signal input
50 Not connected
51 Activation signal from 4-stage pressure switch
52 Activation signal from 3-stage pressure switch
53 Not connected
54 Not connected
55 Not connected
56 Not connected
57 Not connected
58 Key ON signal
59 Brake switch
60 Air conditioner activation request
61 Clutch switch
62 Glow plug diagnosis
63 Not connected
64 Not connected
65 Not connected
66 Not connected
67 Not connected
68 Not connected
69 Not connected
70 Not connected
71 Not connected
72 Not connected
73 Not connected
74 Not connected
75 Not connected
76 Accelerator pedal 1 earth
77 Accelerator pedal 1 signal
78 Accelerator pedal 1 power supply
79 Accelerator pedal 2 earth
80 Accelerator pedal 2 signal
81 Accelerator pedal 2 power supply
82 Diesel temperature sensor (pin 1)
83 Diesel temperature sensor (pin 2)
84 Coolant temperature sensor (pin 1)
85 Coolant temperature sensor (pin 2)
86 Air flow meter (pin 1)
87 Not connected
88 Air flow meter (pin 3)
89 Air flow meter (pin 5)
90 Fuel pressure sensor (pin 3)
91 Fuel pressure sensor (pin 2)
92 Fuel pressure sensor (pin 1)
93 Turbo pressure sensor (pin 1)
94 Turbo pressure sensor (pin 3)
95 Turbo pressure sensor (pin 2)
96 Not connected
97 Air flow meter (pin 4)
98 Not connected
99 RPM sensor (pin 1)
100 RPM sensor (pin 2)
101 RPM sensor (pin 3)
102 RPM sensor (pin 1)
103 Timing sensor (pin 2)
104 Timing sensor (pin 3)
105 Not connected
106 Not connected
107 Not connected
108 Fuel pressure regulator
109 Fuel pressure regulator
110 Not connected
111 Heater relay control Fuel filter
112 Not connected
113 Not connected
114 Cylinder 4 injector control
115 Not connected
116 Not connected
117 Cylinder 1 and 2 injector power supply
118 Cylinder 3 and 4 injector power supply
119 Cylinder 1 injector control
120 Cylinder 2 injector control
121 Cylinder 3 injector control
Copyright by Fiat Auto 11
Page 99 of 330
Marea- Marea Weekend 9"°
2000 range ©
Engine
Fuel feed system
10.
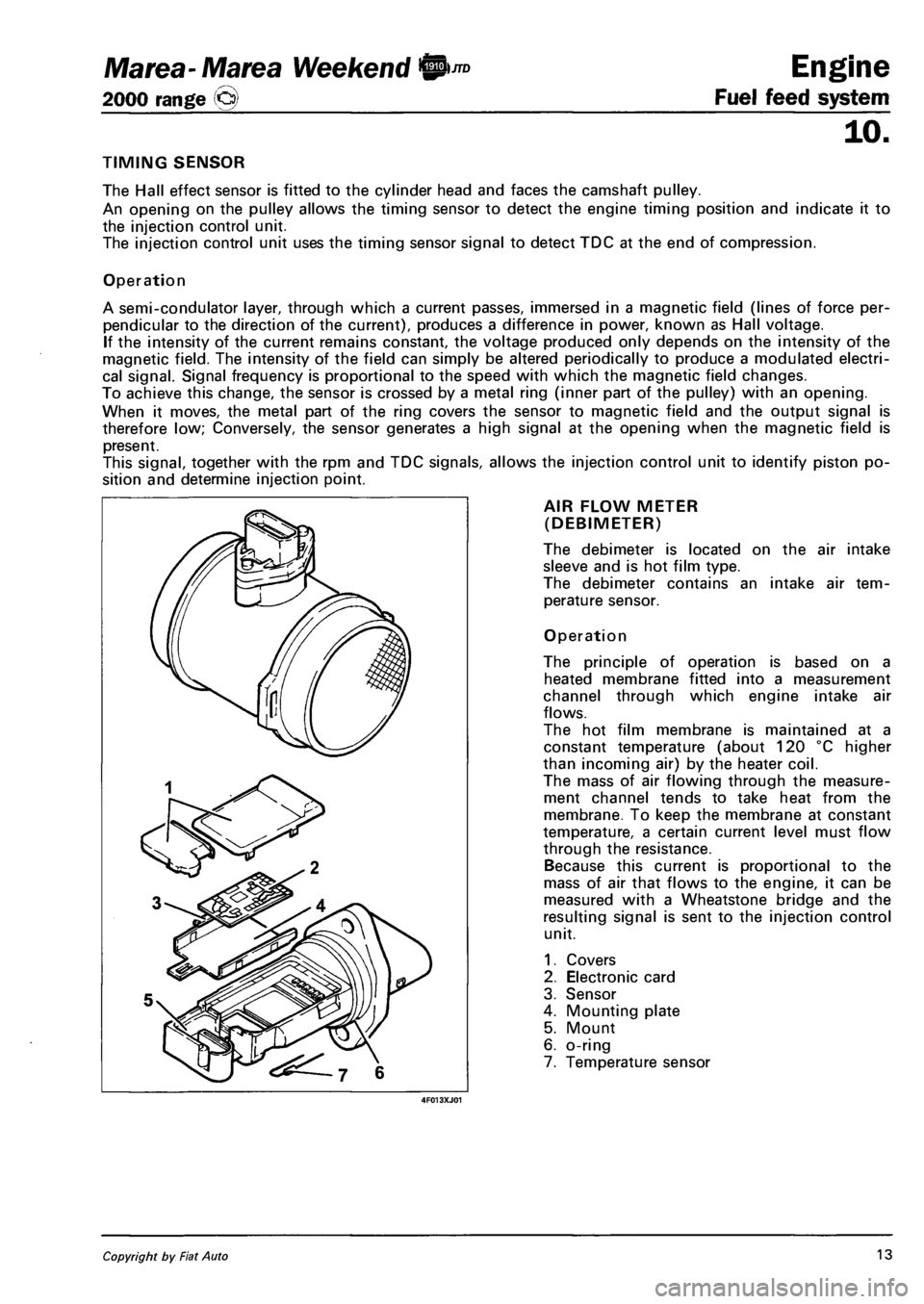
TIMING SENSOR
The Hall effect sensor is fitted to the cylinder head and faces the camshaft pulley.
An opening on the pulley allows the timing sensor to detect the engine timing position and indicate it to
the injection control unit.
The injection control unit uses the timing sensor signal to detect TDC at the end of compression.
Operation
A semi-condulator layer, through which a current passes, immersed in a magnetic field (lines of force per
pendicular to the direction of the current), produces a difference in power, known as Hall voltage.
If the intensity of the current remains constant, the voltage produced only depends on the intensity of the
magnetic field. The intensity of the field can simply be altered periodically to produce a modulated electri
cal signal. Signal frequency is proportional to the speed with which the magnetic field changes.
To achieve this change, the sensor is crossed by a metal ring (inner part of the pulley) with an opening.
When it moves, the metal part of the ring covers the sensor to magnetic field and the output signal is
therefore low; Conversely, the sensor generates a high signal at the opening when the magnetic field is
present.
This signal, together with the rpm and TDC signals, allows the injection control unit to identify piston po
sition and determine injection point.
AIR FLOW METER
(DEBIMETER)
The debimeter is located on the air intake
sleeve and is hot film type.
The debimeter contains an intake air tem
perature sensor.
Operation
The principle of operation is based on a
heated membrane fitted into a measurement
channel through which engine intake air
flows.
The hot film membrane is maintained at a
constant temperature (about 120 °C higher
than incoming air) by the heater coil.
The mass of air flowing through the measure
ment channel tends to take heat from the
membrane. To keep the membrane at constant
temperature, a certain current level must flow
through the resistance.
Because this current is proportional to the
mass of air that flows to the engine, it can be
measured with a Wheatstone bridge and the
resulting signal is sent to the injection control
unit.
1. Covers
2. Electronic card
3. Sensor
4. Mounting plate
5. Mount
6. o-ring
7. Temperature sensor
Copyright by Fiat Auto 13
Page 101 of 330
Marea- Marea Weekend 9™
2000 range (§)
4F015XJ03
Engine
Fuel feed system
ijo.
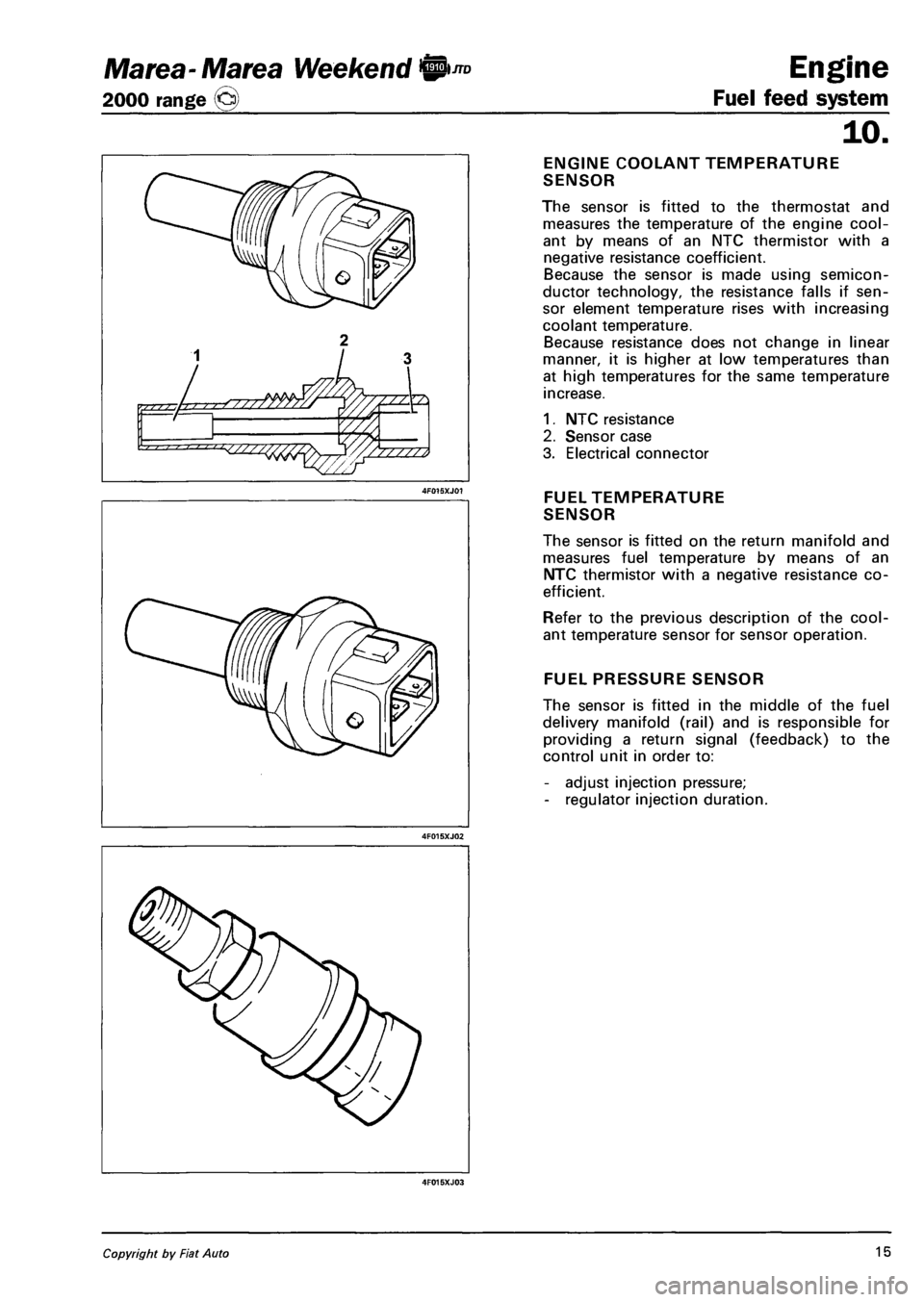
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
The sensor is fitted to the thermostat and
measures the temperature of the engine cool
ant by means of an NTC thermistor with a
negative resistance coefficient.
Because the sensor is made using semicon
ductor technology, the resistance falls if sen
sor element temperature rises with increasing
coolant temperature.
Because resistance does not change in linear
manner, it is higher at low temperatures than
at high temperatures for the same temperature
increase.
1. NTC resistance
2. Sensor case
3. Electrical connector
FUEL TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
The sensor is fitted on the return manifold and
measures fuel temperature by means of an
NTC thermistor with a negative resistance co
efficient.
Refer to the previous description of the cool
ant temperature sensor for sensor operation.
FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
The sensor is fitted in the middle of the fuel
delivery manifold (rail) and is responsible for
providing a return signal (feedback) to the
control unit in order to:
- adjust injection pressure;
- regulator injection duration.
Copyright by Fiat Auto 15