child restraint FIAT PALIO 2003 178 / 1.G India Version Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 2003, Model line: PALIO, Model: FIAT PALIO 2003 178 / 1.GPages: 156, PDF Size: 6.27 MB
Page 30 of 156

29
TRANSPORTING
CHILDREN
IN SAFETY
For optimal protection in the event
of a crash, all passengers must be seat-
ed and wearing adequate restraint sys-
tems.
This is especially relevant for chil-
dren.
A child’s head is larger and heavier
than an adult’s head with respect to
their body weight. Moreover, a child’s
muscular and bone structure is not ful-
ly developed. For these reasons, chil-
dren require specific restraint systems,
different from those required by adult
passengers.
Child’s restraint systems are classi-
fied into the following four weight
groups,
fig. 16:
Group 0 weight 0-10 kg
Group 0 weight 9-18 kg
Group 0 weight 15-25 kg
Group 3 22-36 weight kg.
The groups partially overlap. This is
because there are systems which cov-
er more than one weight group.
Children weighing more than 36 kg
or taller than 1.5 m are, with reference
to restraint systems, considered adults
and can wear normal seat belts.
fig. 16
P4E00197
The seat shown in fig. 16 is suitable
for children weighing between 18-36
kgs.
20-63 03/03/2003 06:02 PM Page 29
Page 31 of 156
30
There are child re-
straints for groups 0 and
1 which are fastened with
the car seat belts by means of an
attachment on the seat back. The
child is then secured to the seat
with specific straps. Due to their
weight, child seats can be dan-
gerous if they are fitted incor-
rectly with a cushion placed be-
tween the seat and the car seat
belts. Always attain carefully to
the specific installation instruc-
tions attached. We recommend seating
children on the rear seat.
This is the most protect-
ed position in the event of a
crash.
GROUP 0
Babies up to 10 Kg are to be seated
in a cot type seat supporting the child’s
head, facing backwards. This ensures
there is no stress on the child’s neck
in sudden decelerations.
The cot is secured with the seat
belts, as shown in
fig. 17. The child
must be strapped to the carrier with
its incorporated straps.
GROUP 1
Children from 9 kg are to be seated
facing forward in child seats with front
cushions. The seat belt secures both
seat and child
fig. 18.
fig. 17
P4E00198
fig. 18
P4E00199
The figure is only an ex-
ample. Follow the in-
structions for fastening
the specific child restraint
system you are using.
The figure is only an ex-
ample. Follow the in-
structions for fastening
the specific child restraint system
you are using.
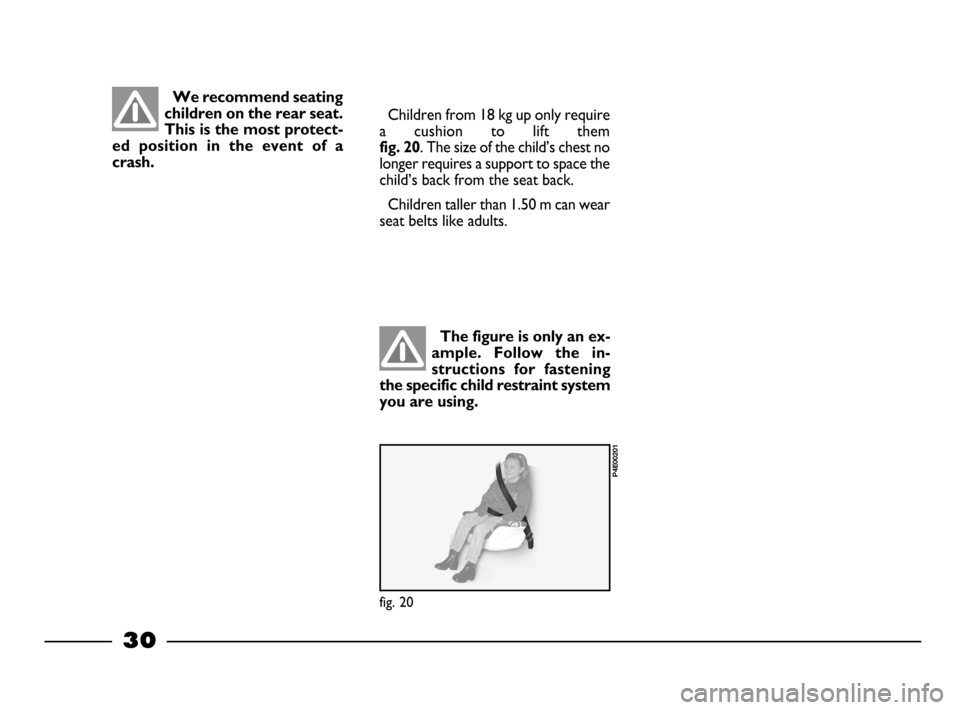
Children from 18 kg up only require
a cushion to lift them
fig. 20. The size of the child’s chest no
longer requires a support to space the
child’s back from the seat back.
Children taller than 1.50 m can wear
seat belts like adults.
fig. 20
P4E00201
The figure is only an ex-
ample. Follow the in-
structions for fastening
the specific child restraint system
you are using.
20-63 03/03/2003 06:02 PM Page 30
Page 32 of 156

The figure is only an ex-
ample. Follow the in-
structions for fastening
the specific child restraint system
you are using.
31
GROUP 2
Children from 15 kg can be secured
directly with the car seat belts. The
child seat has the purpose of posi-
tioning the child correctly with respect
to the seat belt, so that the diagonal
section crosses the child’s chest and
never the throat, and that the hori-
zontal section fits snugly on the child’s
hips and not to the abdomen
fig. 19.
fig. 19
P4E00200
5) Always check the seat belts do
not fit around the child’s throat.
6) While travelling, do not let the
child sit incorrectly or release the
belts.
7) Passengers should never carry
children on their laps. No-one, how-
ever strong they are, can hold a child
in the event of a crash.
8)Replace the child restraint system
after an accident.
A summary of safety precau-
tions to follow when transport-
ing children.
1)
Child restraint systems should be
installed on the rear seat as this is the
most protected area in the car in the
event of a crash.
2)Adhere to the instructions for fas-
tening the specific child restraint which
you are using. These instructions must
be provided by the manufacturer.
Keep the child restraint system instal-
lation instructions with the car docu-
ments and this Handbook. Never use
a child restraint system without in-
stallation instructions.
3) Always check the seat belt is well
fastened by pulling the webbing.
4)Only one child is to be strapped
to each restraint system.
20-63 03/03/2003 06:02 PM Page 31
Page 70 of 156

69
Water, ice or salt sprin-
kled on the road can de-
posit on the brake discs
and reduce efficiency of the first
braking.
Consider that fitting ex-
tra spoilers, alloy rims or
non standard wheel caps
can reduce ventilation of the
brakes and reduce their efficien-
cy under conditions of violent or
repeated braking or long down-
hill travel.
BEFORE GETTING BEHIND
THE WHEEL
– Make sure all lights including the
headlights are working properly.
– Adjust the position of the seats, the
steering wheel and the rearview mir-
rors properly for the best driving po-
sition.
– Carefully adjust the head restraints
so the back of the head and not the
nape of the neck is supported.
– Make sure that nothing (mats etc.)
gets in the way of the pedals when
they are pushed down.
– Do not drive using the clutch ped-
al as a foot rest. Such behaviour can
cause a premature wear of the clutch.
– Make sure that any child restraint
systems (child seats, carriers, etc.) are
properly fixed preferably on the back
seat. Follow the precautions listed in
the “Transporting children in safety”
paragraph in the “Getting to know the
car” chapter.
– Arrange the load in the boot in such
a way that it cannot be thrown for-
wards in the event of an accident.– Do not place clear objects or
sheets of paper on the dashboard that
reflect on the windscreen.
– Do not eat a heavy meal before
travelling. Light eating will help keep
your reflexes prompt. Above all, do
not have anything alcoholic to drink.
The use of some medicines can reduce
the driving capability: carefully read the
relevant use warnings.
Remember to periodically carry out
the checks specified in the “Repeated
checks before long trips” paragraph
given in this section.
64-79 03/03/2003 06:45 PM Page 69
Page 71 of 156

70
WHEN TRAVELLING
– The first rule of safe driving is pru-
dence.
– Prudence also means putting your-
self into a position where you can pre-
dict wrong or imprudent behaviour
from other drivers.
– Stick closely to the rules of the
road in the particular country where
the car is being driven and, above all,
do not exceed speed limits.
– Ensure that, besides yourself, all the
other passengers in the car have their
seat belts fastened, that children are
sitting in the appropriate child seats
and any animals in the car are placed
in suitable compartments.
Driving under the influ-
ence of drugs or certain
medicines is dangerous
for both you and other road
users.
Always fasten both front
and back seat belts, in-
cluding the child restraint
systems. Travelling with the seat
belts unfastened increases the
risk of injury or death in an acci-
dent.
Do not drive with ob-
jects on the floor in front
of the driver’s seat: they
could get caught under the ped-
als making braking or accelerat-
ing impossible.
Pay attention to the
measurements of car-
pets. Any hinderance,
even modest, to the braking sys-
tem could necessiate a longer
than normal pedal run.
You should be physically fit and men-
tally alert before setting out on long
journeys.
– Do not drive too many hours at a
time but stop at intervals to stretch
your legs and recoup your energy.
– Constantly change the air in the
passenger compartment.
– Never coast downhill (i.e. with the
engine off): if you do, you lose the aid
of engine braking and the brake boost-
er so that braking requires greater ef-
fort.
64-79 03/03/2003 06:45 PM Page 70