ESP FIAT PUNTO 1998 176 / 1.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1998, Model line: PUNTO, Model: FIAT PUNTO 1998 176 / 1.GPages: 225, PDF Size: 18.54 MB
Page 84 of 225

2C*2 Diesel engine in-car repair procedures
10.2 Locking the flywheel using a homo* made tool
10 Flywheel - £ removal, inspection § and refitting ^
Removal 1 Remove the transmission and clutch as described in Chapter 7A and 6, 2 Lock the tlywheei in position using a home-made locking tool, fabricated from a piece of scrap metal. Boll it to one of the transmission belihousing mounting holes (see illustration). Mark the position of the flywheel with respect to the crankshaft using a dab of paint. Note that although there is only one location dowel on the flywheel, there are two holes In the end ol the crankshaft and it Is therefore possible to locate tne flywheel 180v out resulting in the timing mark being In Ihe incorrect position. 3 Unscrew and remove the flywheol mounting bolts then lift olf the llywheel. Recover the spacer piate (see illustrations). Discard the flywheol retaining bolts: new ones must be used on refitting,
Inspection 4 If the flywheel's clutch mating surface >s deeply scored, cracked or otherwise damaged, the flywhoel must be renewed. However, H may be possible to have It surface-ground: seek the advice of a Fiat dealer or engine reconditioning specialist, 5 If the ring gear Is bsdly worn or has missing teeth, the flywheel must be renewed.
Refitting 6 Clean the mating surfaces of the flywheel and crankshaft. Remove any remaining locking compound from the threads of the crankshaft holes, using the correct-size tap, if available.
HBTiffSrl If a suitable tap Is not
Wijlilfil
available, cut two slots down HlNTi threads of one of the old 1 J flywheel bolts with a hacksaw, and use the bolt to removo the locking compound form tho threads.
7 If the now flywheel retaining bous are not
10.8a Location dowel on the flywheel
supplied with their threads already pre* coated, apply a suitable thread-locking compound to the threads of each bolt. 8 Otter up the flywheel to the crankshaft, using the abgnment marks made during removal, and fit the new retaining oolts together with the spacer plate (see Illustrations). 9 Lock the flywheel using Ihe method employed on dismantling, and tighten the retaining bolts to the specified torque. 10 Refit the clutch as described in Chapter 6. Remove the locking tool and refit the transmission as described in Chapter 7A,
11 Engine mountings -inspection and renewal
Inspection 1 Firmly apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of the car and support it securely on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). 2 Check the mounting rubbers to see if they are cracked, hardened or separated from the metal ai any point; renew Ihe mounting if any such damage or deterioration is evident. 3 Check that all the mounting's fasteners are securely tightened, 4 Using a large screwdriver or a crowbar, check for wear In the mounting by carefully levering against il to check for free ploy. Where this is not possible enlist the aid of an assistant to move the onglno/transmission back and forlh. or from side lo side, while you watch the mounting While some free play is to be
10.8b Inserting tho flywheel bolts
expected even from new components, axcessive wear should be obvious. II excessive free play Is found, check first that the fasteners are correctly secured, then renew any worn components as described below.
Renewal Right-hand mounting 5 If not already done, firmly apply the handbrake, then jack up the front ot tho car and support it securely on axle stands (see Jacking and vohicle support), 6 Place a trolley lack beneath the right-hand side of the engine, with a block of wood on Ihe jack head. Raise the jack until it is supporting the weight of the engine. 7 Unscrew the bolts securing the nght-hand mounting to the body (see illustration). 8 Unscrew the special long nut securing the mounting to Ihe engine and recover the washers.
11.7 Right-hand engine mounting viewed from below
Page 91 of 225

2D*10 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
1 General information
Included In (his Part of Chapter 2 are details of removing the engine/transmission from the car and general overhaul procedures for tho cylinder head, cylinder block/crankca9e and all other engine internal components. The information given ranges from advice concerning preparation for an overhaul and the purchase of replacement parts, to detailed step-by-step procedures covering removal, inspection, renovation and refitting of engine Internal components. After Section 5, all instructions are based on the assumption that the engine has been removed from the car. For Information concerning in-car engine repair, as well as the removal and refitting of those external components necessary for full overhaul, refer to Part A, 8 or C of this Chapter (as applicable) and to Section 5. Ignore any preliminary dismantling operations described in Part A. B or C that are no longer relevant onca the engine has been removed from ihe car.
2 Engine overhaul -general information
1 It Is not always easy to determine when, or if, an engine should be completely overhauled, as a number of lectors must be considered. 2 High mileage Is not necessarily an Indication that an overhaul Is needed, while low mileage does not preclude the need for an overhaul. Frequency of servicing Is probably the most important consideration. An engine which has had regular and frequent oil and filter changes, as well as other required maintenance, should give many thousands of miles of reliable service. Conversely, a neglected engine may require an overhaul very early In its life. 3 Excessive oil consumption Is an Indication that piston rings, vaivo seals and/or valve guides are in need of attention. Make sure that oil leaks are not responsible before deciding that the rings and/or guides are worn Perform a compression test, as described In Parts A or B (petrol engines) or C (diesel engines) of this Chapter, to determine the likely cause of the problem. 4 Check the oil pressure with a gauge fitted In place of the oil pressure switch. If it Is extremely low. the main and big-end bearings, and/or the oil pump, are probably worn out. 5 Loss of power, rough running, knocking or metallic engine noises, excessive valve gear noise, and high fuel consumption may also point to Ihe need for an overhaul, especially if
they are all present at the same time. If a complete service does not remedy the situation, major mechanical work is the only solution. 6 An engine overhaul involves restoring ell Internal parts to the specification of a new engine. During an overhaul, the cylinders are rebored (where applicable), the pistons and the piston rings are renewed. New main and big-end bearings are generally fitted; If necessary, the crankshaft may be reground. to restore the journals. 7 The valves are also servrced as well, since they are usually In less-than-perfect condition at this point. While the engine is being overhauled, other components, such as the starter and alternator, can be overhauled as well. The end result should be an as-new engine that will give many trouble-free miles. Note: Critical cooling system components such as the hoses, thermostat and coolant pump should be renewed when an engine is overhauled. The radiator should be checked carefully, to ensure that it is not clogged or leaking. A/so. it Is a good Idea to renew the ofI pump whenever the engine i$ overhauled.
8 Before beginning the engine overhaul, read through tho entire procedure, to familiarise yourself with the scope and requirements of the job. Overhauling an engine is not difficult If you follow carefully all of the instructions, have the necessary tools and equipment, and pay close attention to all specifications. It can, however, be time-consuming. Plan on the car being off the road for a minimum of two weeks, especially If pans must be taken to an engineering wo'kd for repair or reconditioning.
9 Check on the availability of parts and make sure that any necessary special tools and equipment are obtained in advance. Most work can be done with typical hand lools, although a number of precision measuring tools are required (or Inspecting parts to determine if they must be renewed. Often the engineering works will handle the inspection of parts and offer advice concerning reconditioning and renewal, Note: Always wait unt'l the engine has been completely dismantled, and until all components (especially the cylinder block/crankcase and the crankshaft) have been inspected, before deciding what service and repair operations must be performed by an engineering works. The condition of these components will be the major factor to consider when determining whether to overhaul the original engine, or to buy a reconditioned unit. Do not. fh ere tore, purchase parts or have overhaul work done on other components until they have been thoroughly Inspected. As a general rule, time is the primary cost of an overhaul, so it does not pay to fit worn or sub-standard parts.
10 As a final note, to ensure maximum life and minimum trouble from a reconditioned engine, everything must be assembled wilh care, in a spotlessly-clean environment.
3 Engine and transmission removal -methods
and
precautions
1 If you have decided that the engine must be removed for overhaul or major repair work, several preliminary steps should be taken. 2 Locating a suitable place to work is extremely important. Adequate work space, along with storage space for the car, will be needed. If a workshop or garage Is not available, at the very least, a flat, level, clean work surface Is required. 3 Cleaning the engine compartment and engine/transmission before beginning the removal procedure wilt help keep tools clean and organised. 4 An engine hoist or A-frame will also be necessary. Make sure the equipment is rated In excess of the combined weight of the engine and transmission, Safety Ib of primary Importance, considering the potential hazards involved in lifting the engine/transmission out of the car. 5 If this is Ihe first time you have removed
an
engine, an assistant Bhould Ideally be available. Advice and aid from someone more experienced would also be helpful. There are many instances when one person cannot simultaneously perform all of the operations required when lifting the engine out of Ihe vehicle. 6 Plan the operation ahead of time. Before starting work, arrange for the hire of or obtain all of the tools and equipment you will need. Some of the equipment necessary to perform engine/transmission removal and Installation safely and wilh relative ease On addition to an engine hoist) Is as follows: a heavy duly trolley jack, complete sets of spanners and sockets as described in the reference section of this manual, wooden blocks, and plenty of rags and cleaning solvent for mopping up spitted oil, coolant and fuel. If the hoist must be hired, make sure that you arrange for it In advance, and perform all of the operations possible without it beforehand. This will save you money and time.
7 Plan for the car to be out of use for quite a while. An engineering works will be required to perform some of the work which the do-it-yourselfer cannot accomplish without special equipment. These places often have a busy schedule, so it would be a good idea to consul! them before removing the engine, in order to accurately estimate the amount of time required to rebuild or repair components that may need work, 9 Always be extremely careful when removing and refitting the engine/transmission. Serious injury can result from careless actions. Plan ahead and take your time, and a job of this nature, although major, can be accomplished successfully.
Page 103 of 225

2D*10 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
Valves and associated components 35 Examine the head of each vaive for pitting, burning, cracks, and general wear. Check the valve stem for scoring and wear ridges. Rotate the valve, and check lor any obvious indication that it Is bent. Look tor pits or excessive wear on the tip of each valve stem. Renew any valve that shows any such signs of wear or damage. 36 if the valve appears satisfactory at this stage, measure the vaive stem diameter at several points using a micrometer. Any significant difference in the readings obtained Indicates wear of the valve stem. Should any of these conditions be apparent, the valve(s) must be renewed. 37 If the valves are In satisfactory condition, they should be ground (lapped) into their respective seats, to ensure a smooth, gas-tight seal. If the seat is only tightly pitted, or if it has been re-cut, fine grinding compound only should be used to produce the required finish. Coarse valve-grinding compound should nor be used, unless a seat is badly bumed or deeply pitted, If this is the case, the cylinder head and valves should be Inspected by an expert, to decldo whether seat re-cutting, or even the renewal of the valve or seat insert (where possible) is required. 38 Valve grinding Is carried out as follows. Place the cylinder head upside-down on blocks on a bench. 39 Smear a trace of (the appropriate grade of) valve-gnndtng compound on the seat face, and press a suction grinding tool onto the valve head. With a semi-rotary action, grind
6.48 Compressing the vaive spring and fitting the split collets
them
the valve head to its seat, lifting the valve occasionally to redistribute tho grinding compound (see Illustration). A light spring placed under the valve head will greatly ease this operation 40 If coarse grinding compound Is being used, v/ork only until a dull, matt even surface Is produced on both the valve seal and the valve, then wipe off tho used compound, and repeat the process with fine compound. When a smooth unbroken ring ol light grey malt finish Is produced on both the valve and seat, the grinding operation is complete. Do not grind-In the valves any further than absolutely necessary, or the seat will be prematurely sunk into the cylinder head. 41 When all the valves have been ground-m, carefully wash off all traces of grinding compound using paraffin or a suitable solvent, before reassembling the cylinder head. 42 Examine the valve springs for signs of damage ano discoloration, If possible compare the length of the springs with new ones and renew them if necessary. 43 Stand each spring on a flat surface, and check ft tor squareness. If any of the springs are damaged, distorted or have lost mar tension, obtain a complete new set of springs. It Is normal to renew the valve springs as a matter of course if a major overhaul is being earned out. 44 Renew (he valve stem oil seals regardless of their apparent condition.
Reassembly 45 Lubricate the stems of the valves, and insert the valves into their original locations
6.53 Tightening the camshaft bearing cap nuts (diesel engines)
6.46 Using a socket to press the valve stem seals onto the guides
(see illustration). If new valves are being fitted, insert them Into the locations to which they have been ground. 46 Refit the spring sea( then, working on the first valve, dip the new valve stem sesl in fresh engine oil. Carefully locate it over the valve and onto the guide. Take care not to damage the seal as it Is passed over the valve stem. Use a suitable socket or metal tube to press the seal firmly onto the guide (sea Illustration). 47 Locate the valve spring on top of its seat, then refit the spring retainer. 48 Compress the valve spring, and locate the split collets in the recess in the valve stem. Release the compressor, then repeat the procedure on the remaining valves (see illustration)
Use a dab o) grease to hold Uiejitts* the collets In position on the HlNT valve stem while the spring compressor is released.
49 With ail the valves Installed, place the cylinder head on blocks on the bench and, using a hammer and Interposed block ol wood, top the end of each valve stem to settle the components. 50 On diesel engines, refit the swirl chambers together with their washers and tighten the retaining collars to the specified torque. 51 Oil the cam followers and locate them In their correct positions in the cylinder head. Locate the shims In the cam followers making sure they are in their original positions. 52 Oil the journals then locate the camshaft m the cylinder head with the cam lobes of No 1 cylinder facing upwards (ie No 1 cylinder at TDC). 53 Refit the bearing caps In their correct positions and progressively tighten the nuts/bolts to the specified torque (sea illustration). On petrol engines locate the lubrication pipe on Ihe head and press in the oil feed stub before refitting the bolts. 54 On diesel engines fit a new oil sea) to the right-hand side mount, then refit both side mounts together with new gaskets, Tighten the right-hand mount bolts. Also refit the coolant cover and thermostat housing together with new gaskets (see illustrations).
Page 104 of 225

2D*10 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
65 On diesel engines. (It new O-ring seals to the vacuum pump then refit it to the left-hand end of the cylinder head and tighten the nuts (see illustrations). 96 Refit the camshaft sprocket with reference to Chapter 2A or 2C. 57 Refit the spark plugs, glow plugs and nfectors as applicable. 58 If required, refit the inlet and exhaust manifolds at this point. The valve clearances can also be checked now. The cylinder head is now ready for refitting as described In Part A, B or C of this Chapter (as applicable).
7 Pistons and connecting rods -removal, Inspection, and big- ^ end running clearance check ^
7.6a Unscrew the bolts.
8.54a Fitting a new oil seal to the right-hand side mount 6.54b Coolant cover gasket
Removal 1 Remove the sump and gasket with reference to Chapter 2A, 2B or 2C. 2 Unbolt and remove the oil pump pick-up/lilter screen assembly. On 16-valve engines, unbolt ond remove the anti-vibration ptate from the main bearing caps. 3 The big-end bearing shells can be renewed without having to remove the cylinder head, If the caps are unbolted and the piston/ connecting rod pushed gently up the bore slightly (the crankpin being at Its lowest point). It ihe3e shells are worn, however, the main bearing shells will almost certainly be worn as well. In this case. Ihe crankshaft should be removed for inspection. 4 To remove the pistons and connecting
6.55a Fitting a now large O-ring on the vacuum pump rods, remove the cylinder head first with reference to Chapter 2A, 2B or 2C. 5 Check to see if the big-end caps and connecting rods are numbered. If no numbers are visible, use a hammer and centre-punch, paint or similar, to mark each connecting rod and big-end cap with its respective cylinder number on the flat machined surface provided. 6 Turn the crankshaft as necessary to bring the first crankpin to its lowest point, then unscrew the bolts and remove the big-end cap and shell bearing (see illustrations). 7 Push the piston/rod assembly up the bore and out of the cylinder block. There is one reservation; if a wear ndge has developed at the top of the bores, remove this by careful scraping before trying to remove the piston/rod assemblies. Tho ridge will otherwise prevent removal, or wilt broak the piston nngs during the attempt.
.55b Fitting the vacuum pump • note the small O-ring on the end of the shaft 6 Remove the remaining pistons/rods In a similar way. If the boaring shells are to be used again, tape them to their respective caps or rods (see illustrations).
Inspection 9 Before the inspection process can begin, the piston/connecting rod assemblies must be cleaned, and the original piston rings removed from the pistons. 10 Carefully expand the old rings over the top of the pistons. The use of two or three old feeler blades will be helpful In preventing the rings dropping into empty grooves. Be careful not to scratch the piston with the ends of the nng. The rings are brittle, and will snap if they are spread too tar. They are also very sharp -protect your hands and fingers. Always remove the rings from the top of the piston. Keep each set of nngs with its piston If the old rings are to be re-used.
.. and remove the big-end cap and shell bearing
7.8a Connecting rod and cap (diesel engine) showing cylindor numbering (A) and shell location tags (B) 7.8b Connecting rod and cap numbers (petrol engine)
Page 105 of 225
2D*10 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
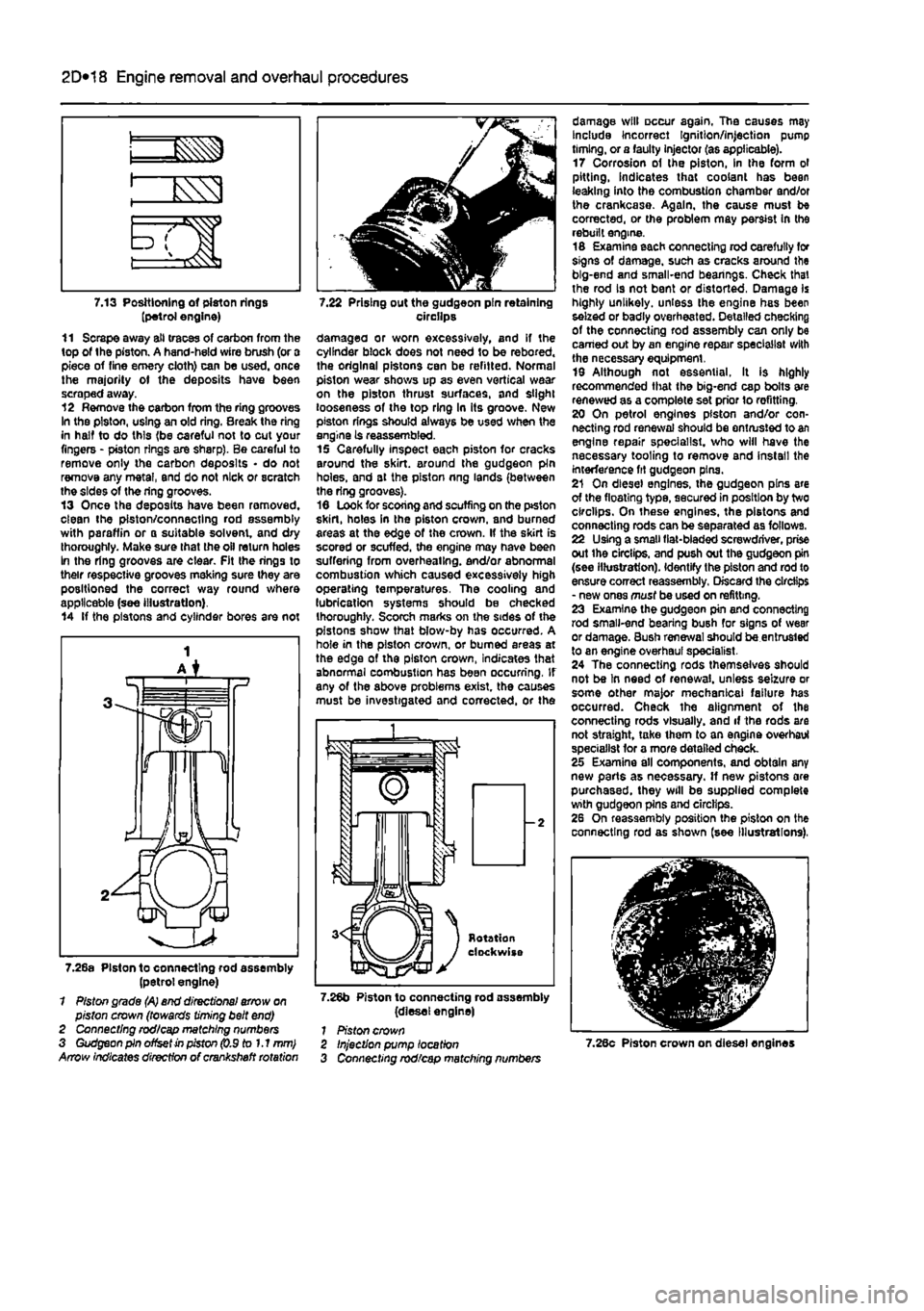
7.13 Positioning of piston rings (petrol engine) 11 Scrape away all traces of carbon from the top of the piston. A hand-held wire brush (or a piece of fine emery cloth) can be used, once the majority ot the deposits have been scraped away. 12 Remove the carbon from the ring grooves In the piston, using an old ring. Break the ring in half to do this (be careful not to cut your fingers - piston rings are sharp). Be careful to remove only the carbon deposits • do not remove any metal, end do not nick or scratch the sides of the ring grooves. 13 Once the deposits have been removed, clean the piston/connecting rod assembly with paraffin or o suitable solvent, and dry thoroughly. Make sure that the oil return holes In the ring grooves are clear. Fit the rings to their respective grooves meking sure they are positioned the correct way round where applicable (see illustration). 14 If the pistons and cylinder bores are not
7.22 Prising out the gudgeon pin retaining circilps damagea or worn excessively, and if the cylinder block does not need to be rebored. the original pistons can be refitted. Normal piston wear shows up as even vertical wear on the piston thrust surfaces, and slight looseness of the top ring In its groove. New piston rings should always be used when the engine is reassembled. 15 Carefully inspect each piston for cracks around the skirt, around the gudgeon pin holes, and at the piston nng lands (between the ring grooves). 16 Look for scoring and scuffing on the ptston skirt, holes in the piston crown, and burned areas at the edge of the crown. If the skirt is scored or scuffed, the engine may have been suffering from overheating, end/or abnormal combustion which caused excessively high operating temperatures. The cooling and lubrication systems should be checked thoroughly. Scorch marks on the sides of the pistons show that blow-by has occurred. A hole in the piston crown, or burned areas at the edge of the piston crown, Indicates that abnormal combustion has been occurring. If any of the above problems exist, the causes must be investigated and corrected, or the
7.26a Piston to connecting rod assembly (petrol engine) 1 Piston grade (A) end directional arrow on piston crown (towards timing belt end) 2 Connecting rod/cap matching numbers 3 Gudgeon pin offset in piston (0.9 to 1.1 mm) Arrow indicates direction of crankshaft rotation
7.26b Piston to connecting rod assembly (diesel engine) 1 Piston crown
damage will occur again. The causes may Include Incorrect Ignition/injection pump timing, or a faulty injector (as applicable). 17 Corrosion of the piston, in the form ol pitting, indicates that coolant has been leaking into the combustion chamber and/or the crankcase. Again, the cause must be corrected, or the problem may persist In the rebuilt engine. 16 Examine each connecting rod carefully for signs of damage, such as cracks around the big-end and small-end bearings. Check that the rod is not bent or distorted, Damage is highly unlikely, unless the engine has been seized or badly overheated. Detailed checking of the connecting rod assembly can only be earned out by an engine repair specialist with the necessary equipment. 19 Although not essential. It is highly recommended that the big-end cap bolts are renewed as a complete set prior lo refitting. 20 On petrol engines piston and/or con-necting rod renewal should be entrusted to an engine repair specialist, who will have the necessary tooling to remove and install the interference fit gudgeon pins. 21 On diesel engines, the gudgeon pins are of the floating type, secured in position by two circlips. On these engines, the pistons and connecting rods can be separated as follows. 22 Using a small fiat-bladed screwdriver, prise out ihe circlips, and push out the gudgeon pin (see illustration). Identify the piston and rod to ensure correct reassembly. Discard the circlips - new ones must be used on refitting. 23 Examine the gudgeon pin and connecting rod small-end bearing bush for signs of wear or damage. Bush renewal should be entrusted to an engine overhaul specialist. 24 The connecting rods themselves should not be In need of renewal, unless seizure or some other major mechanical failure has occurred. Check the alignment of the connecting rods visually, and if the rods are not straight, take ihem to an engine overhaul specialist for a more detailed check. 25 Examine all components, and obtain any new parts as necessary. If new pistons are purchased, they will be supplied complete with gudgeon pins and circlips. 26 On reassembly position the piston on the connecting rod as shown (see Illustrations),
Injection pump location Connecting rod/cap matching numbers 7.28c Piston crown on diesel engines
Page 106 of 225

Apply a smear of clean engine oil to the gudgeon pin. Slide it Into the piston and through the connecting rod small-end. Check that the piston pivots freely on the rod. then secure the gudgeon pin in position with two new circlips. Ensure that each circlip is correctly located In Its groove in the piston.
Refitting and big-end bearing running ciearance check 27 Prior to refitting the piston/connecting rod assemblies, it Is recommended that the big-end bearing running clearance is checked as follows. Big-end bearing running clearance check 28 Clean the backs of the bearing shells, and the bearing locations in both the connecting rod and bearing cap. 29 Press the bearing shells into their locations, ensuring that the tab on each shell engages in the notch In the connecting rod and cap. Take care not to touch any shell's bearing surface with your fingers. If the onginal bearing shells are being used for the check, ensure that they are refitted in their original locations. The clearance can be checked in either of two ways. 30 One method is to refit the big-end bearing cap to Ihe connecting rod, ensuring that they are litted the correct way around, with the bearing shells in place. Wilh the cap retaining bolls correctly tightened, use an internal micrometer or vernier caliper to measure the internal diameter of each assembled pair of bearing shells. If the diameter of each corresponding crankshaft journal is measured and Ihen subtracted from the bearing internal diameter, the result will be the big-end beanng running clearance. 31 The second, and more accurate method is to use a product called Plasligauge. Ensure that the bearing shells are correctly fitted then place a strand of Plastlgauge on each (cleaned) crankpin journal. 32 Refit the (clean) piston/connecting rod assemblies to the crankshaft, and refit the bg-end bearing caps, using the marks made or noted on removal to ensure that they are fitted the correct way around. 33 Tighten the beanng cap bolts taking care not to disturb the Plastlgauge or rotate the connecting rod dunng the tightening sequence. 34 Dismantle the assemblies without rotating the connecting rods. Use the scale pnnted on the Plastigauge envelope to obtain the big-end bearing running clearance. 35 If the clearance is significantly different from that expected, the bearing shells may be Ihe wrong size (or excessively worn. If the original shells are being re-used). Make sure mat no dirt or oil was trapped between Ihe bearing shells and the caps or block when the clearance was measured. If the Plastigauge was wider al one end than at the other, the crankshaft journal may be tapered.
2D*10 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
7.40a The arrow on the piston crown must point towards the timing belt end of the engine (petrol engine) 36 On completion, carefully scrape away all traces of the Plastigauge material from the crankshaft and bearing shells. Use your fingernail, or some other object which is unlikely to score the beanng surfaces.
Final piston/connecting rod refitting 37 Ensure that the bearing shells are correctly fitted. If new shells are being fitted, ensure that alt traces of the protective grease are cleaned off using paraffin. Wipe dry the shells and connecting rods with a lint-free cloth. 38 Lubricate the cylinder bores, the pistons, and piston rings, then lay out each piston/con-necting rod assembly in its respective position. 39 Start with assembly No 1. Position the piston ring gaps 120° apart, then clamp them in position with a piston nng compressor. 40 Insert Ihe piston/connecting rod assembly into the top of cylinder making sure it is Ihe correct way round. On petrol engines, ensure that the arrow on the piston crown is pointing towards the timing belt end of the engine and on diesel engines, ensure that the cloverleaf-shaped cut-out on the piston crown is towards the front (oil filter side) of the cylinder block. Using a block of wood or hammer handle against the piston crown, tap the assembly into the cylinder until the piston crown is Hush with the top of the cylinder (sea illustrations). 41 Ensure that the bearing shell is still correctly Installed. Liberally lubricate the crankpin and both bearing shells. Taking care not to mark the cylinder bores, pull the piston/connecting rod assembly down the bore and onto the crankpin.
7.40b Inserting the piston/connecting rod assembly into the cylinder bore using a hammer handle (diesel englno) 42 Refit the big-end beanng cap, tightening Its retaining bolts finger-tight at first, Note that Ihe faces with the identification marks must match (which means that the bearing shell locating tabs abut each other). 43 Tighten the bearing cap retaining bolts evenly and progressively to the specified torque setting. On diesel engines tighten the bolts to the Stage 1 torque then angle-tighten them to the specified Stage 2 angle using an angle-measuring gauge, (see illustrations) 44 Once the bearing cap retaining bolts have been correctly tightened, rotate the crankshaft. Check that il turns freely; some stiffness is to be expected if new components have been fitted, but there should be no signs of binding or tight spots. 45 Refit the remaining three piston/ connecting rod assemblies in the same way. 46 Refit the cylinder head, anti-vibration plate (16-valve engines), oil pump pick-up/filter screen assembly and sump with reference to Chapter 2A, 2B or 2C.
8 Crankshaft -removal and inspection 35
Removal 1 Remove the
sump,
oil pump and pick-up tube, and flywheel/driveplate with reference to the relevant Sections of Chapter 2 Parts A, 8 or C. On 16-valve engines, unbolt and remove the anti-vibration plate from the main bearing caps.
7.43a Torque-tightening the big-end bearing cap bolls (diesel engine) 7.43b Angle-tightening the big-end bearing cap bolts (diesel engine)
Page 107 of 225

2D*10 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
8.4 Using a dial gauge to check the crankshaft endfloat 2 Remove the pistons and connecting rods, as described in Section 7. However, If no work fs to be done on the pistons and connecting rods there is no need to remove the cylinder head, or to push the pistons out of the cylinder bores. The pistons should just be pushed far enough up the bores that they are positioned clear of the crankshaft Journals. 3 Unbolt the crankshaft rear oil seal housing from the cylinder block and recover the gasket where fitted. 4 Before removing the crankshaft, check the endfloat using a dial gauge. Push the crankshaft fully one way, and then zero Ihe gauge. Push the crankshaft fully the other way, and check tho endfloat (see Illustration). The result can be compared with the specified amount, and will give an indication as to whether new thrustwashers are required. 6 If a dial gauge is not available, feeler blades can be used. First push the crankshaft fully towards the flywheel end of the engine, then use feeler blades to measure the gap - on petrol engines measure between the centre main bearing thrust washer and the crankshaft web. and on diesel engines measure between the rear main bearing and tha crankshaft web. 6 Note the markings on the main bearing caps which vary according to type. On 8-valve petrol engines there is one line on Ihe cap nearest the timing belt end, two on the second cap, C on the centre cap, then three and four lines on the remaining caps (soo illustration). On 16-valve petrol engines, the caps are marked one to five with a series of lines (one line for the cap nearest the timing
8.6 Main bearing markings (petrol engine)
belt end, two for tho next cap and so on). On diesel engines the caps are marked one to live In the same way but with notches instead ol lines. Note also that on some diesel engines the cap nearest the timing belt end Is not marked and the notches therefore start with No 2 cap. 7 Loosen and remove the main bearing cop retaining bolts, and lift off each bearing cap. Recover the lower bearing shells, and tape them to their respective caps for safe-keeping. On some diesel engines note that the centre main bearing cap botts are longer than the other bolls. 8 Lift the crankshaft Irom the crankcase and remove the upper bearing shells from the crankcase. If the shells are 1o be used again, keep them identified for position. Also remove the thrustwashers from their position either side of the centre main bearing (petrol engines) or rear main bearing (diesel engines) (see illustrations)
Inspection 9 Wash the crankshaft in a suitable solvent and allow It to dry. Flush the oil holes thoroughly, to ensure that ihey are not blocked - use a pipe cleaner or a needle brush il necessary. Remove any sharp edges from the edge of the holes which may damage the new bearings when they are installed. 10 Inspect the main searing and crankpin journals carefully; if uneven wear, cracking, scoring or pitting are evident then the crankshaft should be reground by an engineering workshop, and refitted to the engine with underslze bearings.
11 Use a micrometer to measure the diameter of each main bearing journal. Taking a number of measurements on the surface of each journal will reveal if it Is worn unevenly. Differences in diameter measured at 90" intervals Indicate that the journal is out of round. Differences In diameter measured aiong the length of the journal, indicate that the journal is tapered. Again. If wear is detected, the crankshaft can be reground by an engineering workshop and refitted with undersize bearings. 12 Check the oil seal journals at either end of the crankshaft. If they appear excessively scored or damaged, they may cause the new seals to leak when the engine is reassembled. It may be possible to repair the |ournal; seek the advice of an engmeenng workshop. 13 Measure the crankshaft runoul by setting up a DTI gauge on the centre main bearing journal and rotating the shaft In V - blocks. The maximum deflection of the gauge will indicate Ihe runout. Take precautions to protect the bearing journals and oil seal mating surfaces from damage during this procedure. A maximum runout figure Is not quoted by the manufacturer, but use the figure of 0.05 mm
a»
a rough guido. If the runoul exceeds this figure, crankshaft renewal should be considered • consult your Flat dealer or an engine rebuilding specialist for advico. 14 Refer to Section 10 for details of main and big-end bearing inspection.
9 Cylinder block/crankcase - % cleaning and inspection Sk
Cleaning 1 Remove all external components, brackets and electrical switches/sensors from the block Including the rear engine plate, injection pump/oil filter bracket and gasket, Intermediate shaft bracket, oH vapour breather casing, and coolant pump. Also unboit and remove the ol return tube from the crankcase (see illustrations). For complete cleaning, the core plugs should Ideally be removed. Drill a small hole in the plugs, then insert a self-tapping screw into the hole. Pull out the plugs by
8.8a Removing the thrustwashers.. ... and upper bearing shells (diesel engine) 8.8o Thrustwashers located on the centre main bearing (petrol engine)
Page 109 of 225

2D*10 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
failure, (he cause must be corrected (where applicable) before the engine is reassembled, to prevent it from happening again. 3 When examining the bearing shells, remove them from the cylinder block/crankcase, Ihe main bearing caps, the connecting rods and the connecting rod big-end bearing caps. Lay them out on a clean surface in the same general position as their location in the engine. This will enable you to match any bearing problems with the corresponding crankshaft journal. Do not touch any shell's bearing surface with your fingers while checking it. 4 Din and other foreign matter gets into the engine in a variety of ways. It may be left in the engine during assembly, or It may pass through fillers or the crankcase ventilation system. It may get into the oil, and from there into the bearings. Metal chips from machining operations and normal engine wear are often present. Abrasives are sometimes left In engine components after reconditioning, especially when parts are not thoroughly cleaned using the proper cleaning methods. Whatever the source, these foreign objects often end up embedded In the soft bearing material, and are easily recognised. Large particles will not embed in the bearing, and will score or gouge the bearing and journal. The best prevention for this cause of bearing failure Is to clean all parts thoroughly, and keep everything spotlessly-clean during engine assembly. Frequent and regular engine oil and filter changes are also recommended. 5 Lack of lubrication (or lubrication breakdown) has a number of interrelated causes. Excessive heat (which thins the oil), overloading (which squeezes the oil from the bearing face) and oil leakage (from excessive bearing clearances, worn oil pump or high engine speeds) all contribute to lubrication
breakdown. Blocked oil passages, which can be the result of misaligned oil holes in a bearing shell, will also oil-starve a bearing, and destroy it. When lack of lubrication is the cause of bearing failure, the bearing materiel is wiped or extruded from the steel backing of Ihe bearing. Temperatures may increase to the point where the steel backing turns blue from overheating. 6 Driving habits can have a definite effect on bearing life. Full-throttle, low-speed operation (labouring ihe engine) puts very high loads on bearings, tending to squeeze out the oil film. These loads cause the beanngs to flex, which produces fine cracks in the bearing face (fatigue failure). Eventually, the bearing material will loosen in pieces, and tear away from Ihe steel backing. 7 Short-distance driving leads to corrosion of bearings, because insufficient engine heat is produced to drive off the condensed water and corrosive gases. These products collect in the engine oil, forming acid and sludge. As the oil Is carried to the engine bearings, the acid attacks and corrodes the bearing material. 8 Incorrect bearing installation during engine assembly will lead to bearing failure as well. Tight-fitting bearings leave insufficient bearing running clearance, and will result in oil starvation. Dirt or foreign particles trapped behind a bearing shell result in high spots on the bearing, which lead to failure. 9 Do not touch any shell's bearing surface with your fingers during reassembly: there is a risk of scratching the delicate surface, or of depositing particles of dirt on ft. 10 As mentioned at the beginning of this Section, the bearing shells should be renewed as a matter of course during engine overhaul; to do otherwise is false economy.
Selection 11 Main and big-end bearings are available in standard sizes and a range of undersizes to suit reground crankshafts • refer to the Specifications for details. The engine reconditioner will select the correct bearing shells for a machined crankshaft. 12 The running clearances can be checked when the crankshaft is refitted with its new bearings.
11 Engine overhaul -reassembly sequence
1 Before reassembly begins, ensure that all new parts have been obtained, and that all necessary tools are available. Read through the entire procedure to familiariss yourself with the work Involved, and to ensure that ail items necessary for reassembly of the engine are at hand. In addition to all normal tools and materials, thread-locking compound will be needed. A tube of sealant will also be required for the joint faces that are fitted without gaskets.
2 In order to save time and avoid problems, engine reassembly can be carried out in the following order: a) Crankshaft (Section 12). b) Piston/connecting rod assemblies (Section 7). c) Oil pump (see Part A, B or C - as applicable). d) Sump (see Pan A, BorC-as applicable). e) Flywheel/driveplate (see Part A, B or C • as applicable). 1) Cylinder head (see Part A B or C - as applicable). g) Coolant pump (see Chapter
3)
h) Timing belt tensioner and sprockets, and timing belt (See Part A, B or C- as applicable). I) Engine external components, 3 At this stage, ail engine components should be absolutely clean and dry, with all faults repaired. The components should be laid out on a completely clean work surface.
12 Crankshaft- % refitting and main bearing S running clearance check ^
Crankshaft - initial refitting 1 Crankshaft refitting Is the first stage ol engine reassembly following overhaul. At this point, it is assumed that the crankshaft, cylinder block/crankcase and beanngs have been cleaned, inspected and reconditioned or renewed. 2 Place the cylinder block on a clean, level work surface, with the crankcase facing upwards. Where necessary, unbolt the bearing caps and lay them out in order to ensure correct reassembly. If they are still in place, remove the bearing shells from the caps and the crankcase and wipe out the inner surfaces wilh a clean rag - they musl be kept spotlessly clean. 3 Clean the rear surface of the new bearing shells with a rag and fit ihem on Ihe bearing saddles. Ensure that the orientation lugs on the shells engage with the recesses in the saddles and lhat the oil holes are correctly aligned. Do not hammer or otherwise force the bearing shells into place. It Is critically important that the surfaces of the bearings ore kept free from damage and contamination. 4 Give the newly fitted bearing shells and the crankshaft journals a final clean with a rag. Check that the oil holes In the crankshaft are free from dirt, as any left here will become embedded In the new bearings when Ihe engine is first started. 5 Carefully lay the crankshaft In the crankcase, taking care not to dislodge the bearing shells (see illustration}.
Main bearing running clearance check 8 When Ihe crankshaft and bearings are refitted, a clearance must exist between them
Page 110 of 225

2D*10 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
12.5 Lowering the crankshaft into the crankcase
12.9 Fit tho main bearing caps...
to allow lubricant to circulate. This clearance is impossible to check using feeler blades, however Plastlgauge can be used. This consists of a thin strip of soft plastic that is crushed between the bearing shells and journals when the beanng caps are tightened up. Its width then indicates the size of the clearance gap. 7 Cut off five pieces of Plastlgauge. just shorter than the length of the crankshaft journal. Lay a piece on each journal, in line with its axis (see Illustration). 8 Wipe off the rear surfaces of the new lower half main bearing shells and fit them to the main beanng caps, again ensuring that the locating lugs engage correctly (see illustration). 9 Fit the caps in their correct locations on the bearing saddles, using the manufacturers markings as a guide (see illustration). Ensure lhat Ihey are correctly orientated • the caps should be fitted such that the recesses (or the bearing shell locating lugs are on the same side as those in the bearing saddle. 10 Insert and tighten the bolls until they are
811
correctly torqued (see illustrations). Do not allow the crankshaft to rotate at all whilst ihe Plastlgauge is in place. Progressively unbolt the bearing caps and remove them, taking care not to dislodge the Plastlgauge. 11 The width of the crushed Plastigauge can now be measured, using the scale provided (see illustration). Use the correct scale, as both Imperial and metric are printed. This measurement Indicates the running clearance • compare it with that listed in the Specifications.
21 \ „ 12.7 Lay the Plastigauge on the main bearing journals
t
12.10a ... Insert the bolts...
If tho clearance is outside ihe tolerance, it may be due to dirt or debns trapped under the bearing surface; try cleaning them again and repeat the clearance check. If the results are still unacceptable, re-check Ihe journal diameters and the bearing sizes. Note that if the Plastigauge is thicker at one end. the loumals may be tapered and as such, will require regrinding. 12 When you are satisfied that the clearances are correct, carefully remove the remains of the Plastigauge from the journals and bearings faces. Use a soft, plastic or wooden scraper as anything metallic is likely to damage the surfaces.
Crankshaft • final refitting 13 Lift the crankshaft out of the crankcase. Wipe off the surfaces of the bearings in the crankcase and the bearing caps. Fit the thrust beanngs using grease to hold them in
12.11 Use the special scale card to determine the main bearing running clearance
shell In its cap
12.10b ... and torque-tighten them
position, Ensure they are seated correctly in the machined recesses, with tho oil grooves facing outwards 14 Liberally coat the bearing shells in the crankcase with dean engine oil (see Illustration). 15 Lower the crankshaft into position in the crankcase. 16 Lubricate the lower bearing shells in the main bearing caps with clean engine oil. Make sure that the locating lugs on the shells are still engaged with the corresponding recesses in the caps. 17 Fit the main bearing caps in the correct order and orientation. Insert the bearing cap bolts and hand tighten them only. 18 Working from the centre bearing cap outwards, tighten the retaining bolts to their specified torque. On petrol engines, tighten all the bolts to the first stage, then angle-tighten them to the Stage 2 anglo (see illustration)
12.14 Lubricate the main bearing shells before final assembly
Page 118 of 225

3*2 Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
12 If tho pump is stuck, tap It gently using a soft-faced mallet • do not lever between the pump and cylinder block mating faces.
Inspection 13 Check the pump body and impeller for signs of excessive corrosion. Turn the impeller, and check for stiffness due to corrosion, or roughness due to excessive end play. 14 Check the clearance between the pump Impeller and the casing using a feeler blade (see Illustration). If the clearance is different to that given In the Specifications, the pump must be renewed. No spare components are available; the pump can only be renewed as a complete assembly. 15 On diesel engine models, remove the O-rlng at the end ol the transfer pipe, which runs behind Ihe cylinder block and fits Into the rear of the coolant pump. A new O-rlng should be fitted as a matter of course.
Refitting
Petrol engine models 16 Commence refitting by thoroughly cleaning all traces of sealant from the mating faces of the pump and cylinder block/pump housing. 17 Apply a continuous bead of sealant {liquid gasket) to the cylinder block mating face of the pump, taking care not to apply excessive sealant, which may enter the pump itself (see Illustration). 18 Place the pump In position In Its housing, then refit and lighten the bolts/nuts to the specified torque. 19 Refit the liming belt as described In Chapter 2A or 28. 20 Refit the auxiliary drivebeltfs) and refill the cooling system as described in Chapter
t
A. 21 Reconnect Ihe battery negative terminal. Diesel engine models 22 Commence refitting by thoroughly cleaning all traces of old gasket from the mating faces of the pump housing and cylinder block. 23 Place a new gasket in position on (he cylinder block, locate the pump in position, then refit and tighten the bolts (see
7.17 On petrol engine models, apply a continuous bead of sealant (liquid gasket) to the pump mating face
pump Impeller and the casing using a feeler blode (diesel engine) illustration). Ensure that the end of the coolant transfer pipe seats firmly In tho port at the rear of the coolant pump, without displacing the O-ring seal. 24 Refit Ihe pump pulley, then refit the securing bolts and tighten to the specified torque. Counterhofd the pulley using the same method employed during removal. 25 Where applicable, refit the power steering pump with reference to Chapter 10. 26 Refit and tension the auxiliary drivebelt(s) as described in Chapter 18. 27 Refill (he cooling system as desenbed in Chapter 1B. 28 Reconnect the battery negative terminal.
8 Heater/ventilation components - § removal and refitting
Complete heater assembly
A
Warning: On mode's fitted with air conditioning, do not attempt to remove the cooling unit, which Is located between the heater blower motor casing and the main heater assembly. Romovat of the cooling unit entails disconnection of refrigerant lines - refer to Section 10 for precautions to be observed.
rfJS
8.3 Slacken the clips (arrowed) and detach the heater unit coolant hoses from the ports at the bulkhead