condition FIAT PUNTO 1998 176 / 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1998, Model line: PUNTO, Model: FIAT PUNTO 1998 176 / 1.GPages: 225, PDF Size: 18.54 MB
Page 148 of 225
5A»1
Chapters Part A:
Starting and charging systems
Contents
Alternator - brush holder/regulator module renewal 6 Alternator/charging system • testing in vehicle 4 Alternator • removal and refitting 5 Auxiliary drivebelt • removal, refitting and adjustment See Chapter 1A or 1B Battery • condition check See Weekly Checks Battery • removal and refitting 3
Battery - testing and charging 2 Electrical fault finding • general Information See Chapter 12 General Information and precautions 1 Starter motor • removal and refitting 8 Starter motor - testing and overhaul 9 Starting system - testing 7
Degrees of difficulty
Easy, suitable for & novice with Tittle jg experience ^
Fairly easy, suitable ^ for beginner with some experience 3J
Fairly tfifftait, J^ sutable for competent ^ DIYmechanic ^
Difficult, suitable for ^ experienced D!Y mechanic ^
Verydtfficult, jk stitable far expert DfY X or professional ^
Specifications
General System type 12 volt, negative earth
Starter motor Type: Petrol engines Magneti-Marelli pre-engaged Diesel engines Bosch pre-engaged with reduction gear Output: 5A Petrol engines 0.8 kW (1108 cc) or 0.9 kW (1242 cc) Diesel engines 1.7 kW
Battery Capacity: Petrol engines 32 to 50 amp/hr Diesel engines 60 amp/hr Charge condition: Poor 12.5 volts Normal 12.6 volts Good 12.7 volts
Alternator Type Magneti-Marelli Output 65 to 85 amp
Torque wrench settings Nm ibt ft Alternator 60 44 Battery tray 29 21 Oil pressure switch: Petrol engine 32 24 Diesel engine 37 27
Page 149 of 225

5A«2 Starting and charging systems
1 General information and precautions
General information The engine electrical system consists mainly of the charging and starting systems. Because of their engine-related functions, these components are covered separately from the body electrical devices such as the Ilght3, Instalments, etc (which are covered In Chapter 12). On petrol engine models refer to Part B for information on the ignition system, and on diesel models refer to Part C for information on the preheating system. The electncal system Is of 12-volt negative earth type. The battery fitted as original equipment is of maintenance* free (sealed for life} type and Is charged by the alternator, which is belt-driven from the crankshaft pulley. If a non-original battery is fitted It may be of standard or low maintenance type. The starter motor is of the pre-engaged type Incorporating an integral solenoid. On starting, the solenoid moves the drive pinion into engagement with the flywheel ring gear before the starter motor is energised. Once the engine has started, a one-way clutch prevents the motor armature being driven by the engine until the pinion disengages from the flywheel.
Precautions Further details of the various systems are given In the relevant Sections of this Chapter. While some repair procedures are given, the usual course of action is to renew the component concerned. The owner whose interest extends beyond mere component renewal should obtain a copy of the Automobile Electrical & Electronic Systems Manual, available from the publishers of this manual It Is necessary to take extra care when working on the electrical system to avoid damage to semiconductor devices (diodes and transistors), and to avoid the risk of personal injury. In addition to the precautions given in Safety first! at the beginning of this manual, observe the following when working on the system: Always remove rings, watches, etc before working on the electrical system. Even with the battery disconnected, capacitlve discharge could occur If a component's live terminal is earthed through a metal object. This could cause a shock or nasty bum. Do not reverse the battery connections. Components such as the alternator, electronic control units, or any other components having semi-conductor circuitry could be irreparably damaged. If the engine is being started using jump leads and a slave battery, connect the batteries positive-to-posibve and negative-to-
negative (see Jump starting). This also applies when connecting a battery charger but In this case both of the battery terminals should first be disconnected. Never disconnect the battery terminals, the alternator, any electrical wiring or any test Instalments when the engine Is running. Do not allow the engine to turn the alter-nator when the alternator Is not connected. Never test for alternator output by flashing the output lead to earth. Never use an ohmmeter ot the type Incorporating a hand-cranked generator for circuit or continuity testing. Always ensure that the battery negative lead is disconnected when working on the electrical system. Before using electric-arc welding equipment on the car, disconnect the battery, alternator and components such as the fuel Injection/ignition electronic control unit to protect them from the risk of damage. Several systems fitted to the vehicle require battery power to be available at all times, either to ensure their continued operation (such as the clock) or to maintain control unit memories or security codos which would be wiped if the battery were to be disconnected. To ensure that there are no unforeseen consequences of this action. Refer to Disconnecting the battery In the Reference Section of this manual for further Information.
2 Battery- % testing and charging
Standard and tow maintenance battery - testing 1 If the vehicle covers a small annual mileage, it is worthwhile checking the specific gravity of the electrolyte every three months to determine the state of charge of the battery. Use a hydrometer to make the check and compare the results with the following table, Note that the specific gravity readings assume an electrolyte temperature of 15*C (60'F); for every 10*C (18°f) below 158C (60aF) subtract 0.007, For every 108C (16'F) above 15"C (60'F) add 0.007. Ambient temperature Above 26"C Below 25DC Charged 1,210 to 1£30 1,270 to 1.290 70% charged 1.170to1.l90 1.230to1.250 Discharged 1.050toJ.070 1.110 to 1.130 2 If the battery condition is suspect, first check the specific gravity of electrolyte In each cell. A variation of 0.040 or more between any cells indicates loss of electrolyte or deterioration of the internal plates. 3 If the specific gravity variation is 0.040 or more, the battery should be renewed. If the cell variation Is satisfactory but the battery is discharged, it should be charged as described later in this Section.
Maintenance-free battery -testing 4 In cases where a sealed tor life maintenance-free battery is fitted, topplng-up and testing of the electrolyte in each cell Is not possible. The condition of the battery can therefore only be tested using a battery condition Indicator or a voltmeter. 5 Certain models may be fitted with a maintenance-free battery with a built-in charge condition Indicator. The indicator Is located in the top of the battery casing, and indicates the condition of the battery from its colour. If the Indicator shows green, then the battery is In a good state of charge. If the Indicator turns darker, eventually to black, then the battery requires charging, as described later in this Section. If Ihe indicator shows clear/yellow, then the electrolyte level in Ihe battery is too low to allow further use, and tho battery should be renewed. Do not attempt to charge, load or Jump start a battery when the indicator shows dear/yellow. 6 If testing the battery using a voltmeter, connect the voltmeter across the battery and compare the result with those given In the Specifications under 'charge condition'. The test is only accurate if the battery has not been subjected to any kind of charge for the previous six hours. If this is not the esse, switch on the headlights for 30 seconds, then wait four to five minutes baforo testing the battery after switching off the headlights. All other electrical circuits must be switched off, so check that the doors and tailgate are fully shut when making the test, 7 It the voltage reading Is less than 12.2 voHs, then the battery Is discharged, whilst a reading of 12.2 to 12.4 volts indicates 8 partially discharged condition. 6 If the battery Is to be charged, remove It from the vehicle (Section 3) and charge it as described later In this Section.
Standard and low maintenance battery - charging Note: The following is Intended as a guide only. Always refer to the manufacturer's recommendations (often printed on a label attached to the battery) before charging a battery. 9 Charge the battery at a rate of 3.5 to 4 amps and continue to charge the battery at this rate until no further rise In specific gravity Is noted over a four hour period. 10 Alternatively, a trickle charger charging at the rate of 1.5 amps can safely be used overnight. 11 Specially rapid boost charges which are claimed to restore the power of the battery in t to 2 hours are not recommended, as they can cause serious damage to the battery plates through overheating, 12 While charging the battery, note that the temperature of the electrolyte should never exceed 37.8*C(100°F),
Page 150 of 225

5A«2 Starting and charging systems
Maintenance-free battery -charging Note: The following is intended as a guide only. Always refer to the manufacturer's recommendations (often printed on a label attached to the battery) before charging a battery. 13 This battery type takes considerably longer lo fully recharge than the standard type, the time taken being dependent on the extent of discharge, but it can take anything
up
to three days. 14 A constant voltage type charger is required, tooe set, when connected, to 13.9 to 14.9 votts wth a charger current below 25 amps. Using
mis
method, the battery should be usable within three hours, giving a voltage reading of 12.5 vofts. but this Is for a partially discharged battery and, as mentioned, full charging can
take
considerably longer. 15 If Ihe battery is to be charged from a fully discharged state {condition reading loss lhan 12.2 volts), have it recharged by your FIAT dealer or local automotive electrician, as Ihe charge rate is higher and constant super-vision during charging Is necessary.
3 Battery -removal and refitting
Note: Refer to Disconnecting the battery in ifte Reference Section of this manual before proceeding.
Removal 1 Slacken the clamp bolts and disconnect the ctamp from the battery negative (earth) terminal. 2 Remove the insulation cover (where fitted)
and
disconnect the positive terminal lead(s) in
Die same
way. 3 At the base of the battery, unscrew the bolt from the battery holding clamp plate and remove the clamp plate (see Illustration). A Remove the battery from Ihe engine compartment. 5 II necessary the mounting tray may be removed by unscrewing the bolts. On diesel models it will be necessary to remove the relay guard bolts as well.
Refitting 6 Refitting is a reversal of removal but make sure that the positive terminal is connected first followed by the negative terminal.
4 Alternator/charging system - >%•> testing in vehicle
Note: Refer to the warnings given in Safety first! and in Section 1 of this Chapter before starting work. 1 If the ignition warning light fails to Illuminate when the ignition is switched on, first check the alternator wiring connections for security. If satisfactory, check that the warning light bulb has not blown, and that the bulbholder is secure in its location in the instrument panel. If the light still fails to illuminate, check the continuity of the warning light feed wire from the alternator to the bulbholder. If all is satisfactory, the alternator is at fault and should be renewed or taken to an auto-electrician for testing and repair. 2 If the ignition warning light Illuminates when the engine Is running, stop the engine and check that the drivebelt is correctly tensioned (see Chapter 1A or 18) and that the alternator connections are secure. If all is so far satisfactory, have the alternator checked by an auto-electrician. 3 If the alternator output is suspect even though the warning light functions correctly, the regulated voltage may be checked as follows. 4 Connect a voltmeter across the battery terminals and start the engine. 5 Increase the engine speed until the voltmeter reading remains steady; the reading should be approximately 12 to 13 volts, and no more than 14 volts. 6 Switch on as many electrical accessories (eg. the headlights, heated rear window and heater blower) as possible, and check that the alternator maintains the regulated voltage at around 13 to 14 volts. 7 If ihe regulated voltage is not as stated, the fault may be due to worn brushes, weak brush springs, e faulty voltage regulator, a faulty diode, a severed phase winding or worn or damaged slip rings. The alternator should be renewed or taken to an auto-electrician for testing and repair.
3.3 Removing the battery clamp plate
5 Alternator -removal and refitting
Removal 1 Disconnect the battery negative terminal {refer to Disconnecting the battery In the Reference Section of this manual). 2 Firmly apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of the car and support it securely on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). Remove tho right-hand front roadwheel. 3 Remove Ihe Inner cover from under the right-hand wheelarch for access to tho right-hand side of the engine. 4 Disconnect the cables from the rear Of the alternator (see illustration).
Petrol models 5 Loosen the pivot and adjustment bolts then swivel the alternator towards the engine and slip off the drivebelt. Note that the position of the rpm sensor will prevent complete removal of the drivebelt from the crankshaft puiley. 6 Unscrew and remove the pivot and adjustment bolts then unscrew the upper slot-mounted bolt. Withdraw the alternator from the engine (see illustrations).
Diesel models 7 For additional working room, unclip and remove the upper timing belt cover then unbolt and remove the lower timing belt cover.
5.4 Cable connections on the rear of the alternator
5.6a Alternator adjustment and pivot bolts (petrol engine) B Adjuster bolt C Pivot bolt 5.6b Removing the alternator (petrol engine)
Page 151 of 225

5A«2 Starting and charging systems
5.9a Unbolting the alternator upper bracket from the rear of the coolant pump
fl Loosen the pivot bolt and adjustment locknut then unscrew the adjustment bolt and swivel the alternator towards the engine so that the drivebefi may be slipped off the alternator pulley. 9 Unscrew and remove the pivot and adjustment bolts and withdraw the alternator Irom the engine compartment. If preferred the upper alternator bracket may bo unbolted from the rear of the coolant pump {see illustrations).
Refitting 10 Refitting is a reversal ot removal. Refer to Chapter tA or 1B as applicable for details of tensioning the auxiliary drivebeit. On completion lighten the pivot and adjustment botts/nut to the specified torque.
6 Alternator -brush holder/regulator module renewal
%
1 Remove the alternator as described in Section 5. 2 Extract the two small bolts and withdraw the brush box. Note the small plastic grille on the Marelli alternator (see illustrations), 3 Using a steol rule chock the length of the brushes. If less than 5.0 mm the complete brush holder assembly should be renewed. Note: On Bosch alternators it may be possible to obtain the brushes separate//, in which case the brush ieads should be unsoldered
5.9b Removing the pivot bolt and alternator from the engine
from ihe terminals and the new brush leads soldered onto the terminals. 4 Check the slip rings for excessive wear and clean them with a rag soaked in fuel. 5 Pit the new holder using a reversal of the removal procedure but make sure that each brush moves freely.
7 Starting system • & testing
Note: Refer to Ihe precautions given In Safety firstI and in Section I of this Chapter before stoning work. 1 If the starter motor falls to operate when the Ignition key Is turned to the appropriate position, the following possible causes may be to blame. aj The battery is faulty. b) The electrical connections between the switch, solenoid, battery and starter motor are somewhere failing to pass the necessary current from the battery through the starter to earth. c) 77:© solenoid is faulty. d) The starter motor is mechanically or electrically defective. 2 To check the battery, switch on the headlights. If they dim after a few seconds, this indicates that the battery is discharged -recharge (see Section 2) or renew the battery. If the headlights glow brightly, operate the ignition switch and observe the lights. If they
dim, then this indicates that current it reaching the starter motor, therefore the iao8 must lie In the starter motor. If the lights continue to glow brightly (and no clicking sound can be heard from the starter motor solenoid), this indicates that there is a lairt
In
the circuit or solenoid - see following paragraphs, if the starter motor turns siowfy when operated, but the battery is In good condition, then this indicates that either lae starter motor is faulty, or there is considers resistance somewhere in the circuit. 3 If a fault in the circuit is suspected, disconnect the battery ieads (including ihe earth connection to the body), lt» starter/solenoid wiring and tne engine/transmission earth strap. ThoroygWy clean the connections, and reconnect the leads and wiring, ihen use a voltmeter or J«i lamp to check that full battery voltage is available at the battery positive lead connection to the solenoid, and that the earth is sound. Smear petroleum jelly around ttie battory terminals to prevent corrosion > corroded connections are amongst the most frequent causes of electrical system faults. 4 If the battery and all connections are in good condition, check the circuit disconnecting the wire from the solenod blade terminal. Connect a voltmeter or less lamp between the wire end and a good earth (such as the battery negative terminal), ais check that the wire is live when tne ignition switch is turned to the start position. If It is. then the circuit is sound - if not. the circut wiring can be checked as described Chapter 12. Section 2. 5 The solenoid contacts can be checked
Oy
connecting a voltmeter or test lamp across Ihe solenoid. When the ignition switch is turned to the start position, there should b»a reading or lighted bulb, as applicable. II thars is no reading or lighted bulb, the solenoid is faulty and should be renewed. 6 If the circuit and solenoid are proves sound, the fault must lie in the starter motor. In this event, it may be possible to have tre starter motor overhauled by a specialist, but check on the cost of spares before proceeding, as It may prove more economical to obtain a new or exchange motor
Page 154 of 225
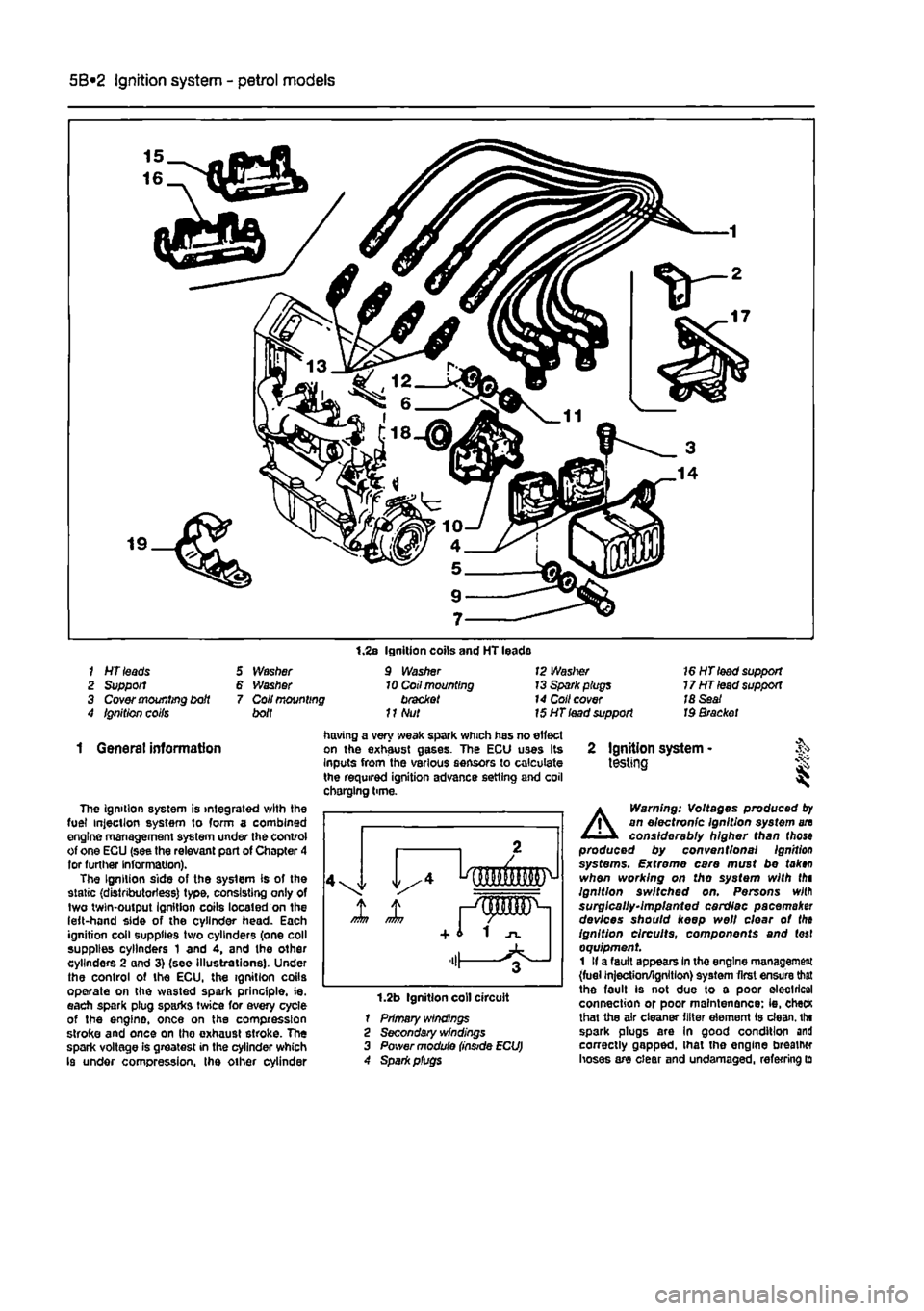
5B*2 Ignition system - petrol models
1 HT leads 2 Support 3 Cover mounting bdt 4 Ignition coifs
5 Washer 6 Washer 7 Coil mounting bolt
1.2s Ignition coils and HT leads 9 Washer 10 Coil mounting bracket
11
Nut
12 Waslrer 13 Spark plugs 14 Coll cover 15 HT lead support
16 HT lead support 17HTlead support 18 Seat Id Bracket
1 General information
The ignition system is integrated with the fuel injection system to form a combined engine management system under the control of one ECU (see the relevant part of Chapter 4 lor further Information). The Ignition side of the system is of the static (distributorless) type, consisting only of two twin-output Ignition coils located on the left-hand side of the cylinder head. Each ignition coil supplies two cylinders (one coll supplies cylinders 1 and 4, and the other cylinders 2 and 3) (see Illustrations). Under the control of the ECU, the ignition coils operate on the wasted spark principle, ie. each spark plug sparks twice for every cycle of the engine, once on the compression stroke and once on tho exhaust stroke. The spark voltage is greatest in the cylinder which Is under compression, the other cylinder
having a very weak spark which has no effect on the exhaust gases. The ECU uses Its Inputs from the various sensors to calculate the required ignition advance setting and coil chorging time.
1.2b Ignition coll circuit 1 Primary windings 2 Secondary windings 3 Power module
2 Ignition system -testing i
A
Warning: Voltages produced
by
an electronic Ignition system an considerably higher than (hose produced by conventional Ignition systems. Extreme care must be tak»n when working on tho system with thi Ignition switched on. Persons wilfl surgically-implanted cardiac pacemaker devices should keep well clear ot the ignition circuits, components and (oaf equipment 1 If a fault appears In the engine management (fuel injection/ignition) system first ensure that the fault is not due to a poor electrical connection or poor maintenance: ie, checK lhat the air cleaner filter element is clean, tht spark plugs are In good condition and correctly gapped, lhat the engine breather hoses are clear and undamaged, referring to
Page 156 of 225
501
Chapter 5 PartC:
Preheating system - diesel models
Contents
Glow plugs - removal, inspection and refitting 2 Preheating system - description and testing 1 Preheating system control unit - removal and refitting 3
Degrees of difficulty
Ea3y, suitable
for &
novice with little
|| experience ^
Fairty easy,
suitable for beginner with
some experience
jQ
Fairty diffctit, ^
suitable
for competent
DIY
mechanic
Difficult, suitable for
experienced DIY JR mechanic ^
Very difficult, ^ suitable fbrexpertDfY JR or professional ^
Specifications
Torque wrench setting Nm ibf ft Heater glow plugs 15 11
1 Preheating system -description and testing
Description 1 Each swirl chamber has a heater plug (commonly called a glow plug) screwed into it. The plugs are electrically-operated before and during start-up when the engine is cold. 2 Electrical feed to the glow plugs Is controlled by a relay/timer unit. The coolant temperature determines the period of heating that takes place. 3 A warning light in the instnjment panel tells the driver that preheating is taking place. When the light goes out, the engine is ready to be started. The voltags supply to the glow plugs continues for several seconds after the light goes out, If no attempt is made to start, the timer then cuts off the supply, In order to avoid draining the battery and overheating the glow plugs.
Testing 4 If the system malfunctions, testing is ultimately by substitution of known good units, but some preliminary checks may be made as follows. 5 Connect a voltmeter or 12-volt test lamp between the glow plug supply cable and earth (engine or vehicle metal). Make sure that the live connection is kept clear of the engine and bodywork. 6 Have an assistant switch on the ignition, and check that vottage is applied to the glow plugs. Note the time for which the warning light Is lit. and the total time for which voltage Is applied before the system cuts out. Switch off the ignition. 7 At an under-bonnet temperature of 20°C. typical times noted should be 5 or 6 seconds for warning light operation, followed by a further 10 seconds supply after the light goes out. Warning light time will increase with lower temperatures and decrease with higher temp-eratures.
8 If there Is no supply at all, the relay or associated winng is at fault. 9 To locate a defective glow plug, disconnect the main supply cable and the interconnecting strap from the top of the glow plugs. Be careful not to drop the nuts and washers. 10 Use a continuity tester, or a 12-voH test lamp connected to the battery positive terminal, to check for continuity between each glow plug terminal and earth. The resistance of a glow plug in good condition is very low (less than 1 ohm), so if the test lamp does not light or the continuity tester shows a high resistance, the glow plug is certainly defective. 11 If an ammeter is available, the current draw of each glow plug can be checked. After an initial surge of 15 to 20 amps, each plug should draw approximately 12 amps. Any plug which draws much more or less than this is probably defective. 12 As a final check, the glow plugs can be removed and Inspected as described in the following Section.
Page 157 of 225

5C«2 Preheating system - diesel models
2.3 No 4 glow plug showing the main supply lead end the interconnecting strap 2.5 Removing a glow plug
2 Glow plugs -removal, Inspection and refitting
Removal Caution: If the preheating system has just been energised, or If tho engine has been running, the glow plugs will be very hot
1 Disconnect the battery negative terminal (refer to Disconnecting the battery in the Reference Section of this manual), 2 Remove Ihe air Inlet ducting from the front of the engine with reference to Chapter 4C, Section 2. 3 Unscrew the nut from the relevant glow plug lerminai(s). and recover the washer(s). Note that tho main supply cable is connected to Number 4 cylinder glow plug and an interconnecting strap lis fitted between the four plugs (see Illustration). 4 Where applicable, carefully move any obstructing pipes or wires lo one side to enable access to the relevant glow plug(s). 5 Unscrew the glow plug(s) and remove from the cylinder head (see illustration).
Inspection 8 Inspect each glow plug for physical damage. Burnt or eroded glow plug tips can bo caused by a bad Injector spray pattern. Have the Injectors checked if this sort of damage is found. 7 If Ihe glow plugs are In good physical condition, check them electrically using a 12 volt test lamp or continuity tester as described in the previous Section. 8 The glow plugs can be energised by applying 12 volts to them to verity that they heat up evenly and In the required time. Observe the following precautions. a) Support the glow plug by clamping it carefully in a vice or selNocking pliers. Remember it will become red-hot. b) Make sura that the power supply or test lead incorporates a fuse or overload trip to protect against damage from a short-circuit. c) After testing, allow the glow plug to cool for several minutes before attempting to handle it. 9 A glow plug In good condition will start to glow red at the tip after drawing current for 5 seconds or so. Any plug which takes much longer to start glowing, or which starts
glowing in the middle instead of at the lip, « defective. Refitting 10 Refit by reversing the removal operations. Apply a smear of copper-based anti-seize compound to the plug threads and tighten Ihe glow plugs to Ihe specified torque. Do not overtighten, as this can damage the glow plug element.
3 Preheating system control unit -removal
and
refitting I
Removal 1 Disconnect the battery negative terminal (refer to Disconnecting the baffery In Ihe Reference Section of this manual). 2 Unscrew the screws and remove the relay cover located at the left-hand end of the engine. 3 Disconnect the wiring then remove the control unit from the bracket. Refitting 4 Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Page 160 of 225

Clutch 6*3
6 WorWng inside the vehicle, extract the split pin and remove the washer securing the master cylinder pushrod to the clutch pedal. Dsoonnect the pushrod from the pivot. 7 Have an assistant support the master cylinder In the engine compartment, then unscrew the mounting bolts. Withdraw the master cylinder from the engine compartment, 8 II is not possible to obtain an overhaul kit from Flat however some motor factors may be abls to supply one. Follow the Instructions with the repair kit if obtained.
Refitting 9 Refit the clutch master cylinder by following ihe removal procedure In reverse, noting the following. a) Apply a
Utile
high-melting point grease to the clutch pedal pivot. b) Tighten the mounting bolts and union nut securely. cj Fit a new split pin to the pushrod. d) Where removed, refit the alternator
as
described In Chapter 5A e) On completion bleed the clutch hydraulic system as descnbed in Section
A.
7 Clutch assembly -
removal,
inspection
and
refitting
S Clutch slave cylinder-removal and refitting
Note: This procedure applies to models fitted
ivrth
the hydraulically-operated clutch release mechanism. Note: Refer to the warning at the beginning
of
Section A regarding the hazards of working
with
hydraulic fluid.
Removal 1 Remove the battery and battery tray as described in Chapter 5A. 2 Fit a brake hose clamp to tha hose leading to the clutch slave cylinder. 3 Unscrew the union nut and disconnect the hydraulic pipe from the slave cylinder. Be prepared for some fluid loss by placing rags beneath the cylinder. 4 Unscrew the mounting bolts and release the slave cylinder pushrod from the release am on the transmission, then remove the unit from the engine compartment (see Illustration). 5 It is not possible to obtain an overhaul kit from Flat however some motor factors may be able to supply one. Follow tha instructions with the repair kit if obtained.
Refitting 6 Refit the clutch slave cylinder by following the removal procedure In reverse, noting the following. a) Apply a little high-melting point grease to the tip of the slave cylinder pushrod. b) Tighten the mounting bolts and union nut securely. c) On completion bleed the dutch hydraulic system as described in Section A.
A
Warning: Dust created by clutch wear and deposited on the clutch components may contain asbestos, which Is a health hazard. DO NOT blow it out with compressed air, or inhale any of it. DO NOT use petrol or petroleum-based solvents to clean off the dust. Brake system cleaner or methylated spirit should be used to flush the dust Into a suitable receptacle. After the clutch components are wiped clean with rags, dispose of the confam/nafed rags and cleaner In a sealed, marked container. Note: Although some friction materials may no longer contain asbestos, it is safest to assume that they DO. and to take precautions accordingly.
Removal 1 Unless the complete engine/transmission is to be removed from the car and separated for major overhaul (see Chapter 2D), Ihe clutch can be reached by removing the transmission as descnbed in Chapter 7A, 2 Before disturbing the clutch, use chalk or a marker pen to mark the relationship of the pressure plate assembly to the flywheel. 3 Working In a diagonal sequence, slacken the pressure plate bolts by half a turn at a time, until spring pressure Is released and the bolls can be unscrewed by hand (see Illustration). 4 Prise the pressure piate assembly off its locating dowels, and collect the friction plate, noting which way round the friction plate is fitted (see Illustration).
Inspection Note: Due to the amount of work necessary to remove and refit clutch components, It is usually considered good practice to renew the clutch friction plate, pressure plate assembly and release bearing as a matched set. even if only one of these is actually worn enough to require renewal. It Is also worth considering the renewal of the clutch components on a preventative basis if the engine and/or
6.4 Removing the clutch slave cylinder from the transmission fransmj'ss/on have been removed for some other reason. 5 Separate the pressure plate and friction plate and place them on the bench. 6 When cleaning clutch components, read first the warning at the beginning of this Section; remove dust using a clean, dry cloth, and working in a well-ventilated atmosphere. 7 Check the friction plats facings for signs Of wear, damage or oil contamination. If the friction material is cracked, burnt, scored or damaged, or if It is contaminated with oil or grease (shown by shiny black patches), the friction plate must be renewed. 8 If tho friction material Is still serviceable, check that the centre boss splines are unworn, that the torsion springs are In good condition and securely fastened, and that all the rivets are tight. If any wear or damage is found, the friction plate must be renewed. 9 If the friction material is fouled with oil, this must be duo to an oil leak from the crankshaft rear (left-hand) oil seal, from the sump-to-cytinder block joint, or from the transmission Input shaft. Renew tha soal or repair the Joint, as appropriate, before Installing the new friction plate. 10 Check tha pressure plate assembly for obvious signs of wear or damage; shake it to check for looss rivets or worn or damaged fulcrum rings, and check thai the drive straps securing the pressure plate to the cover do not show signs (such as a deep yellow or blue discoloration) of overheating. If the diaphragm spring is worn or damaged, or if its pressure is In any way suspect, the pressure plate assembly should be renewed.
7.3 Removing the clutch pressure plate bolts 7.4 Removing the clutch pressure plate and friction plate
expert22 {
a http://rutracker.org
Page 161 of 225

6*4 Clutch
7.17 Using a clutch friction plate centralising toot 11 Examine the machined beanng surfaces of the pressure plate and of the flywheel; they should be clean, completely flat, and free from scratches or scoring. If either is discoloured from excessive heat, or shows signs of cracks, it should be renewed - although minor damage of this nature can sometimes be polished away using emery paper 12 Check that the release bearing contact surface rotates smoothly and easily, with no sign of noise or roughness. Also check that the surface itself is smooth and unworn, with no signs of cracks, pitting or scoring. If there Is any doubt about its condition, the bearing must be renewed.
Refitting 13 On reassembly, onsure that the bearing surfaces of the flywheel and pressure plate are completely clean, smoolh. and tree from oil or grease. Use solvent to remove any protective grease from new components. 14 Fit the friction plate so that its spring hub assembly faces away from the flywheel; there may also be a marking showing which way round the plate Is to be refitted. 15 Refit the pressure plate assembly, aligning the marks made on dismantling (If the original pressure plate Is re-used), and locating the pressure plate on Its three
locating dowels. Fit the pressure plate bolts, but tighten them only finger-tight, so thai the friction plate can skill be moved. 16 The friction plate must now be centralised, so that when the transmission Is refitted, Its Input shaft will pass through the splines at the centre of the friction plate. 17 Centralisation can be achieved by passing a screwdriver or other long bar through the friction plate and into the holo in the crankshaft; the friction plate can then be moved around until it is centred on the crankshaft hole. Alternatively, a clutch-aligning tool can be used to eliminate the guesswork; these can be obtained from most accessory shops (see illustration). A home-made aligning tool can be fabricated from a length of metal rod or wooden dowel which fits closely Inside the crankshaft hole, and has insulating tape wound around it to match Ihe diameter of the friction plate splined hole. 18 When the friction plate is centralised, tighten tho pressure plate bolts evenly and In a diagonal sequence to the specified torque setting. 19 Apply a Ihin smear of molybdenum dlsulphide grease to the splines of the friction plate and the transmission input shaft, and also to the release bearing bore and release fork shaft. 20 Refit the transmission as described In Chapter 7A.
8 Clutch release mechanism - & removal, inspection J and refitting ^
Removal 1 Unless the complete engine/transmission is to be removed from the car and separated lor major overhaul (see Chapter 2D), the clutch release mechanism can be reached by removing the transmission as described In Chapter 7A.
2 Unhook the release bearing from the fork and slide it off Ihe guide tubo (see illustration). 3 Using circlip pliers extract the circllp Irom the top of the release fork shaft. 4 Note the position of the arm then slide it
oW
the splines. 5 Using a small drift, tap out the upper release shaft bush from the transmission casing (see illustration). 6 Lift the release shaft from Ihe lower bush then remove it Irom inside Ihe transmission casing.
7 Extract the lower bush from 1he casing.
inspection 8 Check (he release mechanism, renewing any worn or damaged parts. Carofully checH all bearing surfaces and points of contact. 9 When checking the release bearing ilsell. note that it Is often considered worthwhile to renew it as a matter of course. Check thai the contact surface rotates smoothly and easily, with no sign of roughness, and that Ihe surface itself is smooth and unworn, with no signs of cracks, pitting or sconng. If there is any doubt about Its condition, the bearing must be renewed, Refitting 10 Apply a smear of molybdenum dlsulphide grease to the shaft pivot bushes and the contact surfaces of the release fork. 11 Tap the lower bush into the casing and refit the release fork and shaft. 12 Slide the upper bush down the shaft and tap it into the casing making sure lhat the ridge engages with the cut-out. then slide the arm on the splines the correct way round. 13 Refit the circlip in the shaft groove. 14 Slide the release bearing onto the guide tube and engage it with the fork. 15 Refil the transmission as described in Chapter 7A.
8.2 Removing the release bearing from the fork and guide lube 8.5 Clutch release shaft (1) and upper shaft bush (2)
Page 165 of 225

7A«4 Manual transmission
33 Remove lha air cleaner front section and air ducting with reference to Chapter 4C. Also disconnect the injection pump vacuum pipe from the clips on the left-hand end of the cylinder head. This work is necessary in order to fit the engine hoist 34 Support the weight of the engine using a hoist attached to the engine lifting eyes, or alternatively use a trolley Jack and block of wood beneath the engine. 35 Unscrew the nuts securing the downpipe to the exhaust manifold, then lower it and support on an axle stand. Recover the gasket. 36 Unscrew the starter motor mounting bolts and support the starter motor to one side. 37 Disconnect the wiring from the reversing light switch on the front of the transmission. 38 Unscrew the nut and disconnect the earth cable from its stud. 39 Trace the wiring back from the electronic speedometer sensor and disconnect the connector located on the left-hand side ot the engine. If a mechanical speedometer Is fitted unscrew the knurled collar and disconnect the cabte from the transmission. 40 Unbolt and remove the transmission lower cover. 41 Using an Allen key unscrew the bolts securing the inner end of the left-hand driveshaft to the transmission flange. Remove the bolts and recover the spacer plates. Support the driveshaft on an axle stand. 42 Unscrew and remove the bolts securing the left-hand swivel hub assembly to the front suspension strut, then separate the components and support the swivel hub on an axle stand. 43 Move the swrvel hub assembly outwards and support the driveshaft away from Ihe transmission. 44 Using an Allen key unscrew the bolts securing the Inner end of the right-hand driveshaft to the intermediate shaft flange. Remove the bolts and recover the spacer plates. Support the driveshaft on an axle stand. 45 Remove the intermediate driveshaft with reference to Chapter 8. 46 Working beneath the vehicle, unscrew the bolts securing the rear engine mounting to the underbody then unscrew the bolts securing the mounting to the transmission and withdraw the mounting assembly from under the vehicle.
47 Unscrew the bolts securing the left-hand engine/transmission mounting to the body then unscrew Ihe bolts from the transmission and remove the mounting. 48 Support the weight of the transmission on a trolley jack then unscrew the remaining nut and bolts from the bellhousing and pull the transmission away from the engine.
A
Warning: Support the trans-mission to ensure that It remains steady o/i the jack head. Keep the transmission level until the Input shaft
1$
fully withdrawn from the clutch friction plate.
Refitting 48 Refitting is a reversal of the removal procedure, but note the following points. a) Appiy a smear* of high-meiting-point grease to the clutch friction piate splines; take care to avoid contaminating the friction surfaces. b) Tighten all bolts to the specified torque. c) Fit new clips to secure the driveshaft gaiters to the transmission output shafts. d) Adjust the clutch cable (where applicable) as described In Chapter 6.
4 Manual transmission overhaul -general Infomtatlon
Overhauling a manual transmission is a difficult and Involved Job for the DIY home mechanic. In addition to dismantling and reassembling many small parts, clearances must be precisely measured and, if necessary, changed by selecting shims and spacers. Internal transmission components are also often difficult to obtain, and in many Instances, extremely expensive. Because of this, If the transmission develops a fault or becomes noisy. Ihe best course of action is to have the unit overhauled by a specialist repairer, or to obtain an exchange reconditioned unit. Nevertheless, it is not impossible for the more experienced mechanic to overhaul the transmission, provided the special tools are available, and the Job is done in a deliberate step-by-step manner, so that nothing is overlooked.
The tools necessary for an overhaul include internal and external clrclip pliers, bearing pullers, a slide hammer, a sat of pin punches, a dial test Indicator, and possibly a hydraulic press. In addition, a large, sturdy workbench 8od a vice will be required. During dismantling o1 the transmission, make careful notes of how each component
1$
fitted, to make reassembly easier and more accurate. Before dismantling the transmission, it will help if you have some idea what area is malfunctioning. Certain problems can be closely related to specific areas In the transmission, which can make component examination and replacement easier. Refer to the Fault Finding Section at the end of this manual for more Information.
5 Reversing light switch -testing, removal and refitting ||
Testing 1 The reversing light circuit is controlled by a plunger-type switch screwed into the front of the transmission casing. If a fault develops, first ensure that Ihe circuit fuse has not blown. 2 To test the switch, disconnect the wiring connector, and use a multimeter (set to the resistance function) or a battery-and-bulb test circuit to check that there is continuity between the switch terminals only when reverse gear is selected. If this is not the case, and there are no obvious breaks or other damage to the wires, the switch is faulty, and must be renewed.
Removal 3 Access to the reversing light switch Is best achieved from under the vehicle. Apply the handbrake then jack up Ihe front of the vehicle and support on axle stands (see Jacking and vehicle support). 4 Disconnect the wiring connector, then unscrew It from the transmission casing.
Refitting 5 Refit the switch and tighten securely. 6 Reconnect the wiring then lower the vehicle to the ground.