engine FIAT UNO 1983 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1983, Model line: UNO, Model: FIAT UNO 1983Pages: 303, PDF Size: 10.36 MB
Page 206 of 303

33Detach the vacuum pick-up pipes from
the points indicated in Fig. 13.57.
34Detach the wiring connector from the
throttle position switch.
35Unscrew and remove the inlet manifold
mounting bracket-to-cylinder head retaining
bolt shown in Fig. 13.58.
36Unscrew and remove the injector cable
shield retaining screws. Detach the cables
from the injectors.
37Disconnect the earth leads and the air
intake sensor lead shown in Fig. 13.59.
38Release and withdraw the injector cable
shield from the left-hand underside of the
throttle housing.
39Unscrew and detach the injector fuel
supply pipe and disconnect the fuel pressure
regulator pipe from its inlet manifold union.
40Disconnect the injector cooling fan
thermostatic switch lead.
41Unscrew the securing bolts and remove
the fuel pressure regulator.
42Unscrew and remove the heat
shield-to-exhaust manifold retaining bolts.
Unscrew the retaining bolts at the rear and
withdraw the heat shield.
43Undo the inlet manifold retaining
bolts/nuts and carefully withdraw the
manifold/throttle housing. Remove the gasket
from the mating face.
Injectors and fuel rail
44Depressurise the system as described
previously. 45Disconnect the fuel supply line from the
fuel rail.
46Disconnect the fuel return line from the
base of the fuel pressure regulator. Unbolt
and remove the pressure regulator from the
fuel rail.
47Unscrew and remove the injector cable
shield retaining screws. Detach the cables
from the injectors.
48Disconnect the fuel rail/injector unit and
withdraw the fuel rail, together with the
injectors, from the engine.
49With the injectors and the fuel rail
removed, one or more injectors can be
removed and renewed as described below.
Note that the connecting hoses will be
destroyed during removal and these together
with the injector seals will therefore need to be
renewed.
Injector(s) and connecting hoses
50Remove the injectors and the injector fuel
rail as described in the previous sub-Section
and secure the fuel rail in a vice, but do not
overtighten.
51Cut free the hose between the fuel rail and
the injector. Make the cut in-line with the hose
and cut the hose as close as possible to the
fuel rail connection, then pull the hose free
from its retaining cap. Once the hose is
detached, the retaining cap is released.
52Repeat the procedure and release the
hose and its retaining cap from the injector.
53Whether or not the injector unit itself is tobe renewed, the injector O-ring seals must
always be renewed when disturbed.
54Check that the connections of the fuel rail
and the injector are clean, then push the new
injector with retaining cap onto the new hose.
Ensure that the hose is fully located in the
retaining cap.
55Check that the fuel rail-to-hose retaining
cap is located on the connector, then push
the other end of the injector hose over the fuel
rail connector. Ensure that the hose is fully
located in the retaining cap.
56The interconnecting hose between the
fuel rail sections can be removed and
renewed in the same manner as that
described above for the injector hoses.
Electronic control unit (ECU)
57The ECU is mounted on the top face of
the airflow meter. Ensure that the ignition is
switched off before disconnecting the
multiplug from the ECU. Disconnect the wiring
multiplug connector by compressing the tag
and pulling the connector free from the unit.
Undo the retaining screws and remove the
ECU from the airflow meter. Handle the unit
with care and if removed for an extensive
period, store it in a safe place where it will not
get knocked or damaged.
Fuel pump - removal and refitting
58Depressurise the fuel system as
described previously.
59Raise the car at the rear and support it on
axle stands. Detach and remove the
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•81
Fig. 13.59 Disconnecting the earth leads
(arrowed) on the 1372 cc Turbo ie engine
(Sec 9E)
Fig. 13.58 removing the inlet manifold
mounting bracket from the cylinder head
on the 1372 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 9E)Fig. 13.57 Detach the vacuum pick-up
pipes from the points arrowed on the
1372 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 9E)
Fig. 13.62 ECU (1) wiring multiplug (2) and
tag (3) - 1372 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 9E)Fig. 13.61 Cutting free the hose from an
injector on the 1372 cc Turbo ie engine
(Sec 9E)Fig. 13.60 Disconnecting the injector fuel
supply pipe and fuel pressure regulator pipe
on the 1372 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 9E)
13
2
3
3
1
Page 207 of 303

protective shield to gain access to the pump
which is located forward of the fuel tank.
60Disconnect the fuel hoses and the wiring
connector, release the retaining clamp and
withdraw the pump unit.
Refitting all components
61Refitting of all components is a reversal of
the removal procedure, but note the following
specific points.
62Ensure that all components are clean prior
to refitting and where applicable, use new
seals and gaskets. Ensure that all connectionsare securely and correctly made.
63Do not reconnect the battery until all the
refitting procedures are complete.
64When the engine is restarted, check
around the fuel injection system for any signs
of leakage from the fuel supply and return
components.
Lambda sensor - general
65The sensor is screwed into the exhaust in
front of the catalytic converter.
66A faulty sensor can damage the converter,
therefore it must be checked regularly (see
Maintenance schedule, Section 3) by a dealer
using special equipment.
67Use of leaded fuel will also damage this
sensor, as well the converter.
PART F:
TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM
Description
1A turbocharger is fitted to certain 1301 and
1372 cc ie engines. The accompanying
photographs are all taken from a 1301 cc
engine, but the system is much the same for
both engine types.
2The turbocharger is basically a shaft with an
exhaust gas-driven turbine at one end, and a
compressor located at the other end which
draws in outside air and forces it into the inlet
manifold. By compressing the incoming air, a
larger charge can be let into each cylinder,
and greater power output is achieved than
with normal aspiration.3Lubrication of the turbocharger shaft
bearings is provided by pressurised engine
oil, and the unit is cooled by the coolant from
the engine cooling system.
4A wastegate valve is incorporated in the
turbocharger to divert excessive exhaust gas
pressure from the turbine into the exhaust
pipe at a predetermined pressure level.
5A maximum air pressure switch is located in
the inlet manifold. Its purpose is to cut the
ignition system off when the turbocharger
system pressure continues to increase
beyond 0.86 bars (12.5 lbf/in
2). This would
otherwise damage the engine, due to high
combustion temperatures and pressures
(photo).
6An intercooler (heat exchanger) is located
between the turbocharger and the inlet
manifold. Its function is to cool the inlet
charge, thus increasing its density, to provide
greater power output.
7A mechanical bypass valve is located
between the low-pressure pipe (downstream)
and the high-pressure pipe (upstream), which
reduces the inherent noise from the
turbocharger when the accelerator pedal is
released (photo).
8None of the components of the
turbocharger system can be repaired and
parts are not available. Any fault will therefore
mean that the turbocharger or associated
assemblies will have to be renewed complete.
Precautions
9The following precautions should be
observed when using a turbocharged vehicle.
a) Never operate the engine without the air
cleaner fitted.
b) Never switch off the engine before its
speed has dropped to idling. If the car
has been driven hard, allow it to idle for a
few minutes before switching off. Failure
to observe these recommendations can
cause damage to the turbocharger due to
lack of lubrication.
10Always keep the fuel injection system
well-maintained and tuned. Operating on a
weak mixture can cause overheating of the
turbocharger.
Turbocharger
(1301 cc ie engine) -
removal and refitting
Á
11Disconnect and remove the airflow meter
as described in Section 9C.
12Disconnect the spiral-wound hose from
the fuel injector cooling duct.
13Remove the turbocharger air hoses from
within the left-hand side of the engine
compartment. Note particularly their routing.
14Remove the throttle housing/inlet
manifold as described in Section 9C, also the
fuel rail, injectors and inlet manifold branch
pipe stubs. Remove the alternator heat shield
(photo).
15Remove the exhaust heat shield.
16Unscrew the turbocharger-to-exhaust
pipe flange nuts (photos).
13•82 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
9F.16A Turbocharger-to-exhaust flange
nut (arrowed)9F.14 Alternator heat shield
9F.7 Bypass valve9F.5 Maximum air pressure switch
(arrowed)
Fig. 13.63 Fuel pump and sender unit
location on the 1372 cc Turbo ie engine
(Sec 9E)
1 Fuel level gauge sender connector
2 Fuel pump connector
3 Fuel return hose
4 Fuel supply hose
Page 208 of 303

17Disconnect the air hoses from the
turbocharger (photo).
18Drain the cooling system, and then
disconnect the coolant hoses from the
turbocharger (photos).
19Disconnect the oil feed pipe, which has a
banjo-type union (photo).
20Disconnect the oil return pipe which runs
to the engine sump pan (photo).
21Working underneath the car, disconnect
the exhaust manifold support bracket (photo).
22Unbolt the exhaust manifold and lift it out
of the engine compartment, complete with
turbocharger.
23The turbocharger may now be unbolted
from the exhaust manifold (photo).
24Refitting is a reversal of removal, but use
new gaskets and seals throughout.Turbocharger
(1372 cc ie engine) -
removal and refitting
Á
25Refer to Part E of this Section for details
and remove the inlet manifold.
26Drain the cooling system as described in
Section 8 of this Chapter.
27Unscrew the union bolt and disconnect
the oil supply pipe from the turbocharger.
28Loosen off the securing clip and detach
the air hose from the turbocharger filter.
29Raise and support the car at the front end
on axle stands.
30Working from underneath the car, unscrew
the downpipe-to-exhaust system joint nuts
then unscrew the retaining nuts and detach
the exhaust downpipe from the turbocharger
outlet flange. Remove the downpipe.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•83
9F.18A Releasing turbocharger coolant
inlet union (arrowed)9F.17 Releasing turbocharger air hose clip9F.16B Unscrewing turbocharger-to-
exhaust manifold nut
Fig. 13.64 Turbocharger oil supply pipe
connection (arrowed) (Sec 9F)9F.23 Exhaust manifold bolts
9F.21 Exhaust manifold support bracket9F.20 Turbocharger oil return pipe at sump9F.19 Turbocharging oil feed pipe
9F.18B Turbocharger connections
1 Exhaust connecting nut
2 Oil return hose 3 Coolant pipe union
13
Fig. 13.65 Detach the air hose from the
Turbocharger (arrowed) (Sec 9F)
Page 209 of 303

31Unscrew and remove the two
turbocharger mounting bracket bolts.
32Referring to Fig. 13.67, loosen off the
retaining clip and detach the air hose from the
heat exchanger and the oil return pipe from
the turbocharger (to sump).
33Working from above, undo the
turbocharger mounting bracket bolts.
34Unscrew and remove the coolant
pipe-to-pump retaining bolts. The
turbocharger can now be removed from above
by withdrawing it together with the exhaust
manifold from the engine compartment.
35Locate and support the exhaust manifold
in a vice. Fit protector clamps to the jaws of the
vice to avoid possible damage to the manifold.
36Note the orientation and fitted position of
the turbocharger mounting bracket, then
unscrew the retaining nuts and detach the
bracket.
37Undo the retaining nuts, separate andremove the exhaust manifold from the
turbocharger.
38The turbocharger and wastegate valve are
not repairable and must therefore be renewed
as a complete unit. This being the case,
remove the following ancillary items from the
turbocharger unit before renewing it.
a) Loosen off the retaining clip and remove
the air outlet hose from turbocharger.
b) Undo the two retaining bolts and remove
the oil return hose union.
c) Unscrew the union and bolt and coolant
inlet pipe.
d) Undo the retaining nuts and remove the
turbocharger-to-exhaust manifold
connector.
39Where applicable, always use new
gaskets and ensure that the mating faces are
clean before refitting the ancillary components
to the turbocharger.Intercooler -
removal and refitting Á
40The intercooler is mounted behind the
left-hand side of the front bumper/spoiler (photo).
41Disconnect the air ducts from the intercooler.
42Unscrew the mounting bolts and lift the
intercooler from the car.
43Refitting is a reversal of removal (photo).
Injector cooling fan -
removal and refitting Á
44This unit is located on the left-hand side at
the front of the car. It can be accessed for
removal from above, in the engine compartment.
45Detach and remove the air intake duct
from the air cleaner unit to the ECU/airflow
meter.
46Disconnect and remove the air duct from
the air blower unit.
47Undo the air blower retaining nuts, withdraw
the unit and detach its wiring connector.
13•84 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
9F.43 Intercooler mounting bolt (arrowed)
on 1301 cc engine9F.40 Intercooler location (1301 cc engine)Fig. 13.69 Turbocharger coolant pipe-to-
pump bolt location (arrowed) (Sec 9F)
Fig. 13.68 Turbocharger mounting bracket
bolts removal (Sec 9F)Fig. 13.67 Disconnect the heat exchanger
air hose and the oil return pipe
(turbocharger-to-sump) (Sec 9F)Fig. 13.66 Turbocharger mounting bracket
bolts (arrowed) (Sec 9F)
Fault finding - fuel injection system
Difficult starting from cold
m mFuel pump fault
m mBlocked fuel pipe or filter
m mSupplementary air valve fault
m mCoolant temperature sensor fault
Excessive fuel consumption
m
mIncorrect mixture setting
m mDirty air cleaner element
m mCoolant temperature sensor fault
m mAirflow sensor fault
Difficult to start when hot
m
mChoked air cleaner element
m mFuel pump fault
Uneven idling
m
mIncorrect mixture setting
m mIntake system air leak
m mThrottle position switch out of adjustment
m mLoose ECU connector
Page 210 of 303

Fault finding - turbocharger system
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•85
13
Noise or vibration
m mWorn shaft bearings
m mLack of lubrication
m mInlet or exhaust manifold leaking
m mOut-of-balance impeller shaft
Engine “pinking”
m
mHigh boost pressure, caused by faulty wastegate valve
m mFuel octane rating too low
m mFaulty TDC sensor (ignition advanced)
m mIncorrect spark plugs or plug gaps, or spark plugs worn
Indicated boost pressure too high
m
mFaulty wastegate valve
m mIce forming in exhaust pipe (during very cold weather)
Power loss/indicated boost pressure too low
m
mTurbocharger leaking, or leak at turbocharger mounting
m mIncorrectly adjusted wastegate valve/wastegate valve not closing
m mBlocked exhaust pipe
m mClogged air cleaner element
m mFaulty TDC sensor (ignition retarded)
m mTurbo/intercooler connecting hose leaking
Oil leaks from shaft oil seals, with blue exhaust
fumes
m mOil return pipe blocked
m mAir cleaner element clogged
m mWorn oil seals
10 Ignition system
General
1The ignition systems dealt with in this
Section are all fully electronic and are referred
to individually according to type as the
“breakerless”, Microplex and Digiplex 2
system. The Microplex system is used on the
1301 and 1372 cc Turbo ie engines, the
Digiplex 2 on the 1372 cc ie engine and the
“breakerless” system on all other models.
Ignition timing
(all later models)#
2The ignition timing check on all systems
covered in this Section is made using a
stroboscope, connected up in accordance with
the manufacturer’s instructions and pointed at
one of the two positions given below (photos).
a) The timing marks on the crankshaft pulley
and the timing cover. The right-hand
underwing shield will need to be
detached and removed to allow access to
view these marks (see photos 7B.27 and
7B.30B in this Chapter).
b) The timing marks on the flywheel and the
clutch housing. The rubber plug will need
to be extracted for access to these marks.
3A dwell angle check is not possible on any
of these systems.
4When making the stroboscopic ignition
timing check it is necessary to disconnect the
vacuum hose from the distributor or inlet
manifold to module (as applicable) and plug it.
The engine must be at its normal operating
temperature and running at the normal
specified idle speed when making the check.
Refer to the appropriate part of the Specifica-
tions at the start of this Chapter for the idle
speed and ignition settings.
Breakerless ignition system -
description
5On 903 cc engines, the distributor is driven
from an extension of the oil pump driveshaft
which is geared to the camshaft.
10.2B Flywheel timing marks
(1372 cc ie engine)10.2A Flywheel timing marks
(999 cc engine)
Fig. 13.70 Breakerless ignition system - 999 and 1108 cc engines (Sec 10)
1 Battery
2 Ignition switch
3 Ignition coil
4 Coil HT lead5 Distributor
6 ECU
7 LT cables
8 Vacuum advance unit9 Spark plug HT leads
10 Spark plugs
11 Vacuum hose
Page 211 of 303

6On 999, 1108 and 1372 cc engines, the
distributor is driven from the rear end of the
camshaft.
7On the 1116 and 1299/1301 cc engines, the
distributor is driven from an extension of the
oil pump driveshaft which is geared to the
auxiliary shaft.
8The distributor contains a reluctor mounted
on its shaft, and a magnet and stator fixed to
the baseplate.
9Ignition advance is controlled in the
conventional way mechanically by centrifugal
weights and a diaphragm unit for vacuum
advance.
10Instead of the conventional method of
interrupting the low tension circuit to generate
high tension voltage in the coil by means of a
mechanical contact breaker, when the
electronic ignition is switched on, the
switching of the transistors in the electronic
control unit (ECU) prevents current flow in the
coil primary windings.
11Once the crankshaft rotates, the reluctor
moves through the magnetic field created by
the stator and when the reluctor teeth are in
alignment with the stator projections a small
AC voltage is created. The ECU amplifies this
voltage and applies it to switch the transistors
and so provide an earth path for the primary
circuit.
12As the reluctor teeth move out of
alignment with the stator projections the AC
voltage changes, the transistors in the ECU
are switched again to interrupt the primary
circuit earth path. This causes a high voltage
to be induced in the secondary winding.
Distributor
(breakerless type) -
removal and refitting
#
13Removal of the distributor on the 903,1116, 1299 and 1301 cc engines is as
described in Chapter 4, Section 6.
14On 999, 1108 and 1372 cc engines, mark
the position of the distributor clamp plate in
relation to the cylinder head surface.
15Unclip the distributor cap and move it to
one side with the HT leads attached.
16Disconnect the LT lead plug and, where
applicable, the vacuum hose (photo).
17Unscrew the distributor fixing nuts and
withdraw the unit.
18The distributor drive is by means of an
offset dog no special procedure is required to
refit it. Providing the dog engages in its slot
and the distributor body is turned to align the
marks made before removal, the timing will
automatically be correct.
19If a new distributor is being fitted (body
unmarked), set No. 4 piston at TDC (0º) by
turning the crankshaft pulley bolt until the
timing marks on the crankshaft pulley and
engine front cover are in alignment.
20Align the drive dog and fit the distributor
then turn the distributor body until the contact
end of the rotor is aligned with the arrow on
the distributor dust shield.
21Tighten the distributor clamp nuts. Refit the
cap and disconnected components and then
check ignition timing using a stroboscope.
Distributor (breakerless
type) - overhaul#
22It is recommended that a worn out or
faulty distributor is renewed. However,
individual components such as the cap, rotor,
reluctor, magnet/stator/baseplate assembly,
vacuum diaphragm unit, and drive gear or dog
are available separately.
Breakerless
ignition system
components - testing
ª
23A voltmeter and an ohmmeter will be
required for this work.
Primary circuit voltage
24Turn on the ignition, and using a voltmeter
check the voltage at the ignition coil LT
terminals. Any deviation from battery voltage
will indicate a faulty connection, or if these are
satisfactory, then the coil is unserviceable.
Magnetic impulse generator winding
25Remove the distributor and ECU and
disconnect their connecting leads.
26Connect an ohmmeter to the impulse
generator terminals and note the reading. The
resistance should be as given in the Specifi-
cations at the beginning of this Chapter.
27Now check between one of the impulse
generator terminals and the metal body of the
distributor. Infinity should be indicated on the
ohmmeter. If it is not, renew the impulse
generator carrier plate. Note: When carrying out
this test it is imperative that the connections are
remade as originally observed. Also ensure that
there is no possibility of the ECU supply (red)
cable and earth cable making contact in service.
Ignition coil winding resistance
28Check the resistance using an ohmmeter
between the coil LT terminals. Refer to the
Specifications for the expected coil resistance.
29Check the resistance between the LT lead
socket on the coil and each of the LT
terminals. Refer to the Specifications for the
expected coil resistance.
30The rotor arm resistance should be
approximately 5000 ohms.
Microplex ignition system -
description
31This system is fitted to the 1301 and
1372 cc Turbo ie models, and comprises the
following components.
Electro-magnetic sensors
32Two sensors are used to pick up engine
speed and TDC position directly from the
crankshaft.
Pressure and vacuum sensor
33This converts inlet manifold vacuum
pressure into an electrical signal for use by
the electronic control unit (ECU).
Anti-knock sensor
34This converts “pinking” detonations which
occur within the combustion chambers into
an electrical signal for use by the ECU (photo).
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
35This computes the optimum ignition
advance angle from the sensor signals
received, and controls the action of the
ignition unit (photo).
13•86 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.72 Rotor aligned with arrow on
distributor dust shield - 999 and 1108 cc
engines (Sec 10)
1 ECU
2 Ignition coil
3 Distributor
4 Vacuum advance
unit5 Pick-up filter with
calibrated opening
for atmospheric
pressure
Fig. 13.71 Location of electronic ignition
components on early models with
breakerless ignition (Sec 10)
10.16 Distributor LT lead connecting plug
Page 212 of 303
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•87
13
10.35 Ignition ECU on rear bulkhead
(1301 cc Turbo ie engine)
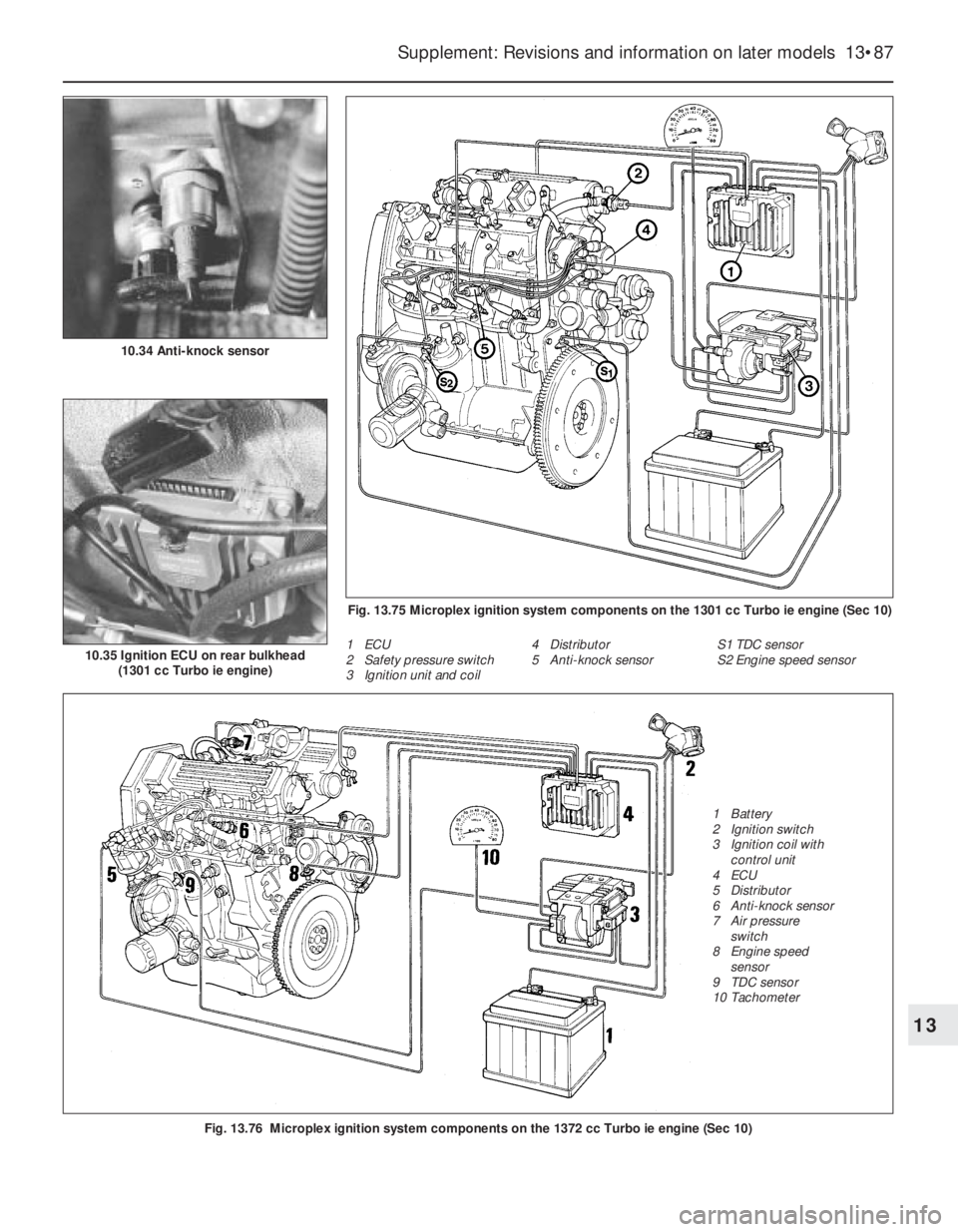
Fig. 13.76 Microplex ignition system components on the 1372 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 10)
Fig. 13.75 Microplex ignition system components on the 1301 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 10)
1 ECU
2 Safety pressure switch
3 Ignition unit and coil4 Distributor
5 Anti-knock sensorS1 TDC sensor
S2 Engine speed sensor
1 Battery
2 Ignition switch
3 Ignition coil with
control unit
4 ECU
5 Distributor
6 Anti-knock sensor
7 Air pressure
switch
8 Engine speed
sensor
9 TDC sensor
10 Tachometer 10.34 Anti-knock sensor
Page 213 of 303

13•88 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.73 Wiring diagram of the Microplex ignition system on the 1301 cc Turbo ie
engine (Sec 10)Fig. 13.74 Wiring diagram of the Microplex ignition system on the 1372 cc Turbo ie
engine (Sec 10)1 ECU
2 Safety pressure switch
3 Ignition unit with coil
4 Distributor
5 Anti-knock sensor
6 Vacuum/pressure pick-up in engine inlet
manifold
7 Socket for diagnostic equipment8 Tachometer
9 Spark plugs
10 Switch to earth (to retard advance
curve if necessary)
11 Turbocharger operation warning light
12 Anti-theft relay (where fitted)
13 Hidden anti-theft switch (where fitted)1 ECU
2 Pipe (pressure/vacuum
in inlet manifold to
control unit)
3 Spark plug
4 Distributor
5 Ignition coil (with
control unit)6 Tachometer
7 Ignition switch
8 Connector
9 TDC sensor
10 Engine speed
11 Anti-knock sensor
12 Air pressure safety
switch13 Speedometer signal
for electronic injection
14 Connector
15 Diagnostic socket
a Crankshaft pulley
b Flywheel
Page 214 of 303

Ignition unit
36This comprises four elements (photo).
a) Power module - receives the ignition
advance command and controls the
conduction angle of the primary current
and energy stored in the coil.
b) Dissipater plate - eliminates the heat
which is generated by the high volume of
current.
c) Ignition coil with low primary resistance.
d) Distributor - a means of distributing high
tension to the spark plugs. The rotor is
driven in an anti-clockwise direction
(viewed from transmission) by a dog on
the end of the camshaft.
37The system incorporates a safety
pressure switch, which cuts out the ignition if
the turbocharging pressure exceeds a value
of between 0.84 and 0.93 bars (12.2 and
13.5 lbf/in
2) above atmospheric pressure.
Distributor (Microplex) -
removal and refitting#
38Remove the distributor cap and place it to
one side, complete with spark plug leads
(photo).
39Turn the crankshaft by means of the
pulley nut, or by raising and turning a front
wheel with top gear engaged, until No. 4
piston is on its firing stroke. This will be
indicated when the contact end of the rotorarm is aligned with the mark on the distributor
body rim, and the lug on the crankshaft pulley
is aligned with the timing pointer on the
engine. The right-hand underwing shield will
have to be removed in order to see the marks
(photo).
40Unscrew the distributor fixing nuts and
withdraw the distributor.
41When fitting the distributor, the offset
drive dog will automatically locate the
distributor rotor in its correct position, but the
distributor body may require rotating in order
to align the rim mark with the rotor. The
elongated slots for the fixing studs are to
permit initial alignment, not for subsequent
adjustment, as advance angle alterations are
carried out automatically by the system ECU
(photos).
42Tighten the nuts and refit the cap with
leads.
43Unless a stroboscope and a vacuum
pressure gauge are available, it will not be
possible to check the advance values with the
engine running. Where these instruments are
available, connect the vacuum gauge to the
inlet manifold, and the stroboscope in
accordance with the equipment manufac-
turer’s instructions. Refer to Fig. 13.79
according to the inlet manifold vacuum
pressure indicated.
Microplex ignition system
components - testing ª
44An ohmmeter and a voltmeter will be
required for these tests.
45Remove the multipin plug from the ECU.
Engine speed sensor
46Insert the probes of an ohmmeter
between terminals 3 and 16 of the multipin
connector; 618 to 748 ohms (1301 cc) or
578 to 782 ohms (1372 cc) should be
indicated.
47If necessary, carry out a check of the gap
between the sensor and flywheel teeth as
described in Chapter 4, Section 10.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•89
10.39 Crankshaft pulley timing marks
(arrowed)10.38 Removing the distributor cap10.36 Ignition coil (1) and power module (2)
on 1301 cc Turbo ie engine
Fig. 13.78 Rotor aligned with distributor
body rim mark - Microplex ignition system
(Sec 10)
10.41A Distributor body showing elongated
slots in the mounting lugs
Fig. 13.77 Crankshaft pulley timing mark
aligned with timing pointer - Microplex
ignition system (Sec 10)
1 TDC sensor10.41B Distributor drive dog
13
Page 215 of 303

TDC sensor
48Insert the probes of the ohmmeter
between terminals 1 and 2 of the multipin
connector; 618 to 748 ohms (1301 cc) or 578
to 782 ohms (1372 cc) should be indicated.
49If necessary, carry out a check of the gap
between the sensor and the crankshaft pulley,
as described in Chapter 4, Section 10.
ECU supply
50Switch on the ignition, and then insert the
probes of a voltmeter between terminals 13
and 11 of the multipin connector. Battery
voltage should be indicated. If not, check the
battery earth, ignition switch or intermediate
connector plug for security.
Power module supply (1301 cc)
51Pull the multipin plug from the powermodule, and connect the probes of a
voltmeter between terminal 4 of the connector
and earth. If the reading is less than battery
voltage, check the security of all connections
between the ignition switch and terminal + 15
of the ignition coil.
52Reconnect the multipin connector to the
ECU, but have the one from the power
module disconnected, and then switch on the
ignition.
53Connect the voltmeter between terminals
4 and 2 of the power module multipin
connector. If the indicated voltage is less than
battery voltage, check the security of all
connections between the ignition switch and
terminal + 15 of the ignition coil, and the
battery earth. If all are satisfactory, check for
continuity between terminals 11 and 12. If
continuity is broken, renew the ECU.
Power module (1372 cc)
54Proceed as described in paragraph 53.
Anti-knock sensor
55If “pinking” occurs, or loss of power is
noticed, test the sensor by substitution of a
new one.
Ignition coil
56Disconnect the leads from terminals 1
and 15 on the coil before testing.
57Using the ohmmeter, check the resistance
of the primary winding. This should be
between 0.31 and 0.37 ohms (1301 cc) or
0.40 to 0.49 ohms (1372 cc), at an ambient
temperature of 20ºC (68ºF).
58The secondary winding resistance should
be between 3330 and 4070 ohms (1301 cc) or
4320 to 5280 ohms (1372 cc), at an ambient
temperature of 20ºC (68ºF).
Distributor
59Check the resistance of the rotor arm,
which should be between 800 and
1200 ohms.
60Where all the foregoing tests have proved
satisfactory, then any problem must be due to
a fault in either the power module or the ECU.
These components can only be checked by
the substitution of a new unit - power module
first, then the ECU.
Safety pressure switch
61The device protects the engine from
excessive turbocharging pressure, cutting off
the ignition by earthing the Microplex ECU.
Testing is not possible without a special
pressure pump, so the easiest way to check a
suspected fault is to fit a new unit.
Digiplex 2 ignition system -
description
62This system operates in a similar manner
to that of the earlier type described in Chap-
ter 4, but the circuit layout differs to suit the
Mono Jetronic fuel injection system. In
operation, the main difference is that the
Digiplex 2 system has a greater number of
13•90 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.81 Microplex ignition system
control unit connection (Sec 10)
For colour code, see main wiring diagramsFig. 13.80 Microplex ignition system ECU multipin connector (Sec 10)
For colour code, see main wiring diagrams
Fig. 13.79 Ignition advance curves - Microplex ignition system on the 1301 cc Turbo ie
(Sec 10)