radiator FIAT UNO 1983 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1983, Model line: UNO, Model: FIAT UNO 1983Pages: 303, PDF Size: 10.36 MB
Page 151 of 303
99Tighten the big-end bolts to the specified
torque (photo). The correct torque is
important as the bolts have no locking
arrangement. After tightening each big-end,
check that the crankshaft rotates smoothly.
100Repeat the operations on the remaining
piston/rod assemblies.
101Refit the oil pump pick-up assembly
using a new sealing ring.
102Refit the sump pan and the cylinder head
as described in earlier sub-Sections.
103Fill the engine with oil and coolant.
Pistons/connecting rods -
separation and piston
ring renewal
ª
104If the piston/connecting rods have been
removed in order to renew the piston rings,
refer to Chapter 1, Section 18, but note thatthe piston rings should be fitted so that the
word TOP is uppermost.
105If new pistons are to be fitted, it is
recommended that the gudgeon pins are
removed and refitted by a FIAT dealer as the
connecting rods must be carefully heated in
order to be able to push the gudgeon pin out
of the rod small-end, change the piston and
push the pin back into position. Locating the
gudgeon pin will require a special tool. The
gudgeon pin is a sliding fit in the piston but an
interference fit in the connecting rod.
106Refer to Fig. 13.6 for the correct
assembly of the piston and connecting rod.
Engine/transmission mountings
- renewal
107Refer to Chapter 1, Section 33. Three
mountings are used (photos).
PART C: ENGINE REMOVAL
AND DISMANTLING
Method of removal - general
1The engine, complete with transmission,
should be removed upwards out of the engine
compartment.
Engine/transmission -
removal and separation #
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of Section 9 before starting any
work.
2Mark the position of the hinges on the
underside of the bonnet and then, with the
help of an assistant, unscrew the hinge bolts
and lift the bonnet to a safe storage area.
3Drain the coolant; a cylinder block drain
plug is not fitted.
4Drain the engine and transmission oils.
5Disconnect the battery, negative lead first.
6Remove the air filter.
7Disconnect the radiator hoses from the
engine (photos).
13•26 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
5C.7B Radiator hose at thermostat
housing5C.7A Radiator hose connection to coolant
distribution tube5B.107C Right-hand engine mounting
5B.107B Left-hand rear
engine/transmission mounting5B.107A Left-hand front
engine/transmission mounting
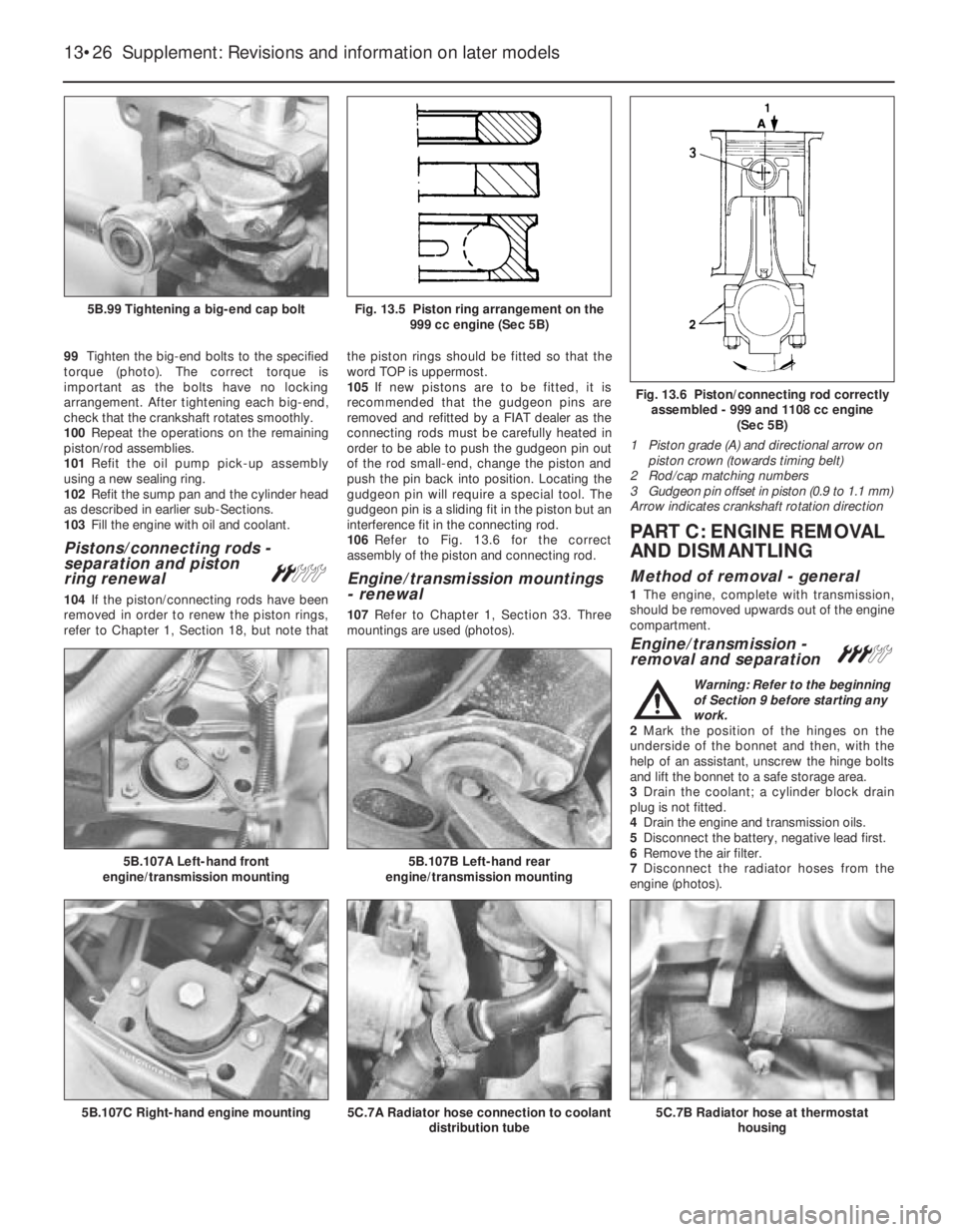
Fig. 13.6 Piston/connecting rod correctly
assembled - 999 and 1108 cc engine
(Sec 5B)
1 Piston grade (A) and directional arrow on
piston crown (towards timing belt)
2 Rod/cap matching numbers
3 Gudgeon pin offset in piston (0.9 to 1.1 mm)
Arrow indicates crankshaft rotation direction
Fig. 13.5 Piston ring arrangement on the
999 cc engine (Sec 5B)5B.99 Tightening a big-end cap bolt
Page 152 of 303
8Disconnect the heater hose from the inlet
manifold.
9On fuel injection models, depressurize the
fuel system (refer to Section 9D). Disconnect
the fuel inlet and return hoses from the fuel
pump (photo) or throttle body, as applicable.
10Disconnect the brake servo vacuum hose
from the inlet manifold.
11Disconnect the throttle cable from the
carburettor, or throttle body as applicable.
12Disconnect the choke cable, if applicable
(photo).
13Disconnect the leads from the alternator.
14Disconnect the battery earth lead from the
transmission casing.15Disconnect the leads from the starter
motor and the HT lead from the ignition coil
(photo).
16Disconnect the coolant temperature
switch lead and the HT leads from the
distributor (photo).
17Disconnect the lead from the carburettor
fuel cut-off (anti-diesel) solenoid valve, where
applicable.
18Disconnect the lead from the oil pressure
switch (photo).
19Although not essential, removal of the
radiator is recommended as a precaution
against its damage during removal of the
power unit. Disconnect the wiring plugs from the fan and thermostatic switches
(photos).
20Disconnect the leads from the reversing
lamp switch on the transmission.
21Disconnect the clutch cable from the
release lever on the transmission.
22Disconnect the speedometer cable from
the transmission by unscrewing the knurled
ring.
23Working under the car, disconnect the
exhaust downpipes from the manifold and the
lower support bracket (photos).
24Disconnect the gearchange rods from the
levers on the transmission. One rod is
retained by a spring clip, the other by a
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•27
5C.15 Ignition coil HT lead connection5C.12 Choke cable connection at
carburettor5C.9 Fuel hose identification at pump; inlet
hose (1), hose to carburettor (2), return
hose (3)
5C.19D Removing the radiator/fan
assembly5C.19C Radiator fan cut-out thermostatic
switch5C.19B Radiator fan motor wiring
connector
5C.19A Radiator retaining clip5C.18 Oil pressure switch5C.16 Coolant temperature switch
13
Page 180 of 303

Coolant pump -
removal and refitting#
11The coolant pump is located on the
crankshaft pulley end of the engine and is
driven by the timing belt.
12The pump cannot be repaired and must
be regarded as disposable.
13Drain the cooling system.
14Remove the timing belt cover and then set
No. 1 piston to TDC. To achieve this, turn the
crankshaft pulley bolt until the camshaft
sprocket timing mark is aligned with the one
on the cylinder head.
15Release the belt tensioner and slip the
timing belt off the camshaft and coolant pump
sprockets.
16Unbolt and remove the coolant pump and
clean the mounting face of all old gasket
material.
17Apply a continuous bead of RTV silicone
sealant (instant gasket) to the mounting face
of the coolant pump and bolt it into position
(photos).
18Check that the camshaft sprocket and the
crankshaft have not been moved and fit the
timing belt to the camshaft and coolant pump
sprockets. The pump sprocket does not
require setting in any particular position
before connecting the timing belt.
19Tension the belt as described in Sec-
tion 5B of this Chapter.
20Fit the timing belt cover.
21After allowing one hour for the gasket
material to cure, refill and bleed the cooling
system.
PART B:
1301 CC TURBO IE ENGINE
Description
1The cooling system on this model has flow
and return connections to the turbocharger,
and is an essential means of cooling the
turbocharger.
2The radiator cooling fan is of two-speed
type, being controlled by a two-stage
thermostatic switch screwed into the radiator
side tank.
3According to the coolant temperature level,
the fan speed is regulated to provide the most
effective cooling.
4The remote cooling system expansion tank
is mounted in the left-hand rear corner of the
engine compartment (photo).
PART C:
1372 CC IE AND 1372 CC
TURBO IE ENGINES
Description
1The cooling system layout and components
for the 1372 cc engines is shown in
Figs. 13.29 and 13.30.
2The system on each engine operates in
essentially the same manner as that
described for the other models in Chapter 2,
but the location of components and the
coolant hose routings differ according to
model. The cooling system expansion tank
location differs according to model, being
either located on the side of the radiator ormounted separately on the side of the inner
wing panel.
3On Turbo models, the cooling system also
assists in cooling the turbocharger.
Maintenance
4The maintenance procedures are
essentially the same as those described for
the other models in Chapter 2.
Cooling system - draining,
flushing and refillingÁ
Warning: Wait until the engine is
cold before starting this
procedure. Do not allow
antifreeze to come into contact
with your skin or painted surfaces of the
vehicle. Rinse off spills immediately with
plenty of water. Never leave antifreeze
lying around in an open container or in a
puddle in the driveway or on the garage
floor. Children and pets are attracted by its
sweet smell. Antifreeze is fatal if ingested.
5Disconnect the battery negative lead.
6Working inside the vehicle, turn the heater
temperature control knob fully to the right,
which will fully open the heater coolant valve.
7With the expansion tank cap removed,
place a suitable container beneath the
radiator bottom hose.
8Loosen the clip and ease the bottom hose
away from the radiator outlet (photo). Allow
the coolant to drain into the container.
9Reposition the container under the front of
the cylinder block, and unscrew the cylinder
block drain plug (photo). Allow the coolant to
drain into the container.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•55
8A.17B Tightening the coolant pump bolts8A.17A Fitting the coolant pump to the
999 cc engineFig. 13.28 Sectional view of the coolant
pump on the 999 and 1108 cc engines
(Sec 8A)
8C.9 Cylinder block drain plug8C.8 Bottom hose connection to the
radiator8B.4 Topping up the expansion tank with
antifreeze on the 1301 cc engine
13
Page 181 of 303

1 Electric fan
2 Radiator
3 Thermostat
4 Coolant supply hose (inlet
manifold to heater matrix)
5 Heater matrix6 Coolant return hose (heater
matrix to the manifold pipe)
7 Coolant pump
8 Coolant manifold pipe
9 Coolant supply hose (cylinder
block/crankcase to the
turbocharger)10 Coolant return hose
(turbocharger to the expansion
tank)
11 Coolant supply hose (expansion
tank to the manifold pipe)
12 Expansion tank13 Coolant return hose (radiator to
the manifold pipe)
14 Fan thermostatic switch
15 Coolant supply hose
(thermostat to the radiator)
16 Coolant return hose (radiator to
the expansion tank)
13•56 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.29 Cooling system circuit - 1372 cc ie engine (Sec 8C)
Fig. 13.30 Cooling system circuit - 1372 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 8C)
1 Expansion tank
2 Radiator
3 Electric fan
4 Coolant supply hose (thermostat
to radiator)
5 Coolant manifold pipe
6 Coolant pump
7 Coolant supply hose (thermostat
to heater matrix)
8 Coolant return hose (heater
radiator to manifold pipe)
9 Heater matrix10 Coolant return hose (inlet manifold
to manifold pipe)
11 Coolant return hose (radiator to
manifold pipe)
12 Thermostat
13 Fan thermostatic switch
Page 182 of 303

10Apply suitable sealant to the threads of
the drain plug, then refit and tighten the plug.
11Dispose of the drained coolant safely, or
keep it in a covered container if it is to be
re-used.
12If required, the system can be flushed
through as described in Section 2 of Chap-
ter 2.
13Before attempting to refill the cooling
system, make sure that all hoses have been
reconnected, that the hoses and clips are in
good condition, and that the clips are tight.
Also ensure that the cylinder block drain plug
has been refitted and tightened. Note that an
antifreeze mixture must be used all year round
to prevent corrosion of the engine
components - refer to Section 3, Chapter 2.
14Open the bleed screw in the top of the
expansion tank (photo).
15Remove the expansion tank cap, and fill
the system by slowly pouring the coolant into
the expansion tank to prevent air locks from
forming.
16Top up the coolant until liquid free from air
bubbles emerges from the radiator bleed
screw orifice, then close the bleed screw.
17Continue topping up until the coolant
reaches the Maximum mark on the expansion
tank.
18Start the engine and run it until it reaches
normal operating temperature, then stop the
engine and allow it to cool. Normal operating
temperature is reached when the cooling fancuts into operation. Feel the radiator top hose
to ensure that it is hot. If cool, it indicates an
air lock in the system.
19Check for leaks, particularly around
disturbed components. Check the coolant
level in the expansion tank, and top up if
necessary. Note that the system must be cold
before an accurate level is indicated. There is
a risk of scalding if the expansion tank cap is
removed whilst the system is hot.
Radiator (and cooling fan)
- removal and refitting Á
20Disconnect the battery negative lead.
21Detach the wiring connectors from the
cooling fan and the fan switch located in the
radiator (photos).
22If preferred, the cooling fan unit can be
removed separately from the radiator, by
undoing the attachment bolts and carefully
withdrawing the unit upwards from the
vehicle. Take care not to damage the radiator
core as it is lifted clear (photo).
23Drain the cooling system as described
earlier in this part of the Section, but note that
it will not be necessary to remove the cylinder
block drain plug.
24Undo the retaining screws and remove
the front grille panel.
25Loosen off the retaining clips and detach
the upper coolant hose and the expansion
hose from the radiator.26Note their direction of fitting, then prise
free the radiator retaining clips. Carefully lift
the radiator from the car.
27Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure. Ensure that as the radiator is
lowered into position, it engages in the two
rubber location grommets.
28With the radiator (and cooling fan) refitted,
top up the cooling system as described earlier
in this Section (photo).
Thermostat -
removal and refitting Á
Note: A new thermostat cover gasket must be
used on refitting.
29Drain the cooling system as described
earlier in this Section, but note that there is no
need to drain the cylinder block.
30Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
thermostat cover (situated at the gearbox end
of the cylinder head).
31Unscrew the two thermostat cover
securing bolts, noting that the left-hand bolt
may also secure the HT lead bracket, and
remove the thermostat/cover assembly.
Recover the gasket (photo).
32If faulty, the thermostat must be renewed
complete with the housing as an assembly.
33If desired the thermostat can be tested as
described in Chapter 2.
34Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•57
8C.21B Cooling fan switch wiring
connector8C.21A Cooling fan and wiring connector8C.14 Bleed screw location on top of the
expansion tank (arrowed)
8C.31 Thermostat unit removal on the
1372 cc ie engine (distributor removed for
clarity)8C.28 Topping up the radiator coolant level
on the 1372 cc ie engine. Note orientation
of radiator retaining clip (arrowed)8C.22 Cooling fan to radiator securing bolt
13
Page 194 of 303

39Now use the ohmmeter to check the
resistance of the following components.
Supplementary air valve
40Resistance between the terminals should
be between 40 and 60 ohms at 20ºC (68ºF).
Airflow meter
41Resistance between terminals 5 and 8 of
the potentiometer should be between 330 and
360 ohms at 20ºC (68ºF).
42Resistance between terminals 8 and 9 of
the internal circuit should be between 190 and
210 ohms at 20ºC (68ºF) and between 170
and 190 ohms at 60ºC (140ºF).
Coolant temperature sensor
43At 20ºC (68ºF) the resistance should be
between 2 and 4 k ohms. At 50ºC (122ºF) the
resistance should be between 600 and
900 ohms. At 90ºC (194ºF) the resistance
should be between 100 and 300 ohms.
Fuel injectors
44The winding resistance should be
between 15 and 17 ohms at 20ºC (68ºF).
Throttle position switch
45With the throttle butterfly valve closed,
there should be continuity between ter-
minals 18 and 2, and with the valve fully open,
there should be no continuity between
terminals 18 and 3.
46The throttle position switch should not be
disturbed unless absolutely necessary. If it
has to be removed, then refit it so that themicroswitch is heard to click immediately the
throttle butterfly is opened.
Fuel injection system -
mechanical tests ª
Fuel pump
47To test the pressure of the fuel pump, a
pressure gauge will be required, connected
into the fuel delivery hose.
48Remove the multipin plug from the system
control relay and bridge terminals 87b and 30.
49Turn the ignition switch on. The pump
should operate and indicate a pressure of
between 2.8 and 3.0 bars (40 and 44 lbf/in
2).
50To check the operation of the peak
pressure regulator, pinch the fuel return hose.
If the fuel pressure increases, the regulator
must be faulty, and should be renewed.
51Check that the fuel pressure increases
when, with the engine idling, the accelerator is
depressed sharply.
Supplementary air valve
52With the engine at normal operating
temperature and idling, pinch the
supplementary air valve hose using a pair of
pliers. The engine speed should not drop by
more than 50 rpm. If it does, renew the valve.
Fuel injection system
components -
removal and refitting
ª
53Disconnect the battery before carrying out
any of the following operations.
Air cleaner
54Remove the cover and filter element as
previously described.
55Disconnect the duct from the air cleaner
casing, and then unbolt and remove the
casing. Note that the lower bracket bolt need
not be completely removed, only unscrewed,
due to the design of the bracket. The air
cleaner metal duct is routed over the top of
the radiator (photos).
Airflow meter
56Release the securing clip and disconnect
the air intake duct (photo).
57Release the securing clip and disconnect
the air outlet duct (photo).
58Disconnect the wiring plug.
59Unscrew the fixing screws and remove
the airflow meter from its mounting bracket.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•69
9C.55B Removing the air cleaner casing
upper bracket9C.55A Disconnecting the duct from the air
cleanerFig. 13.43 System control relay connector
plug terminals 1301 cc Turbo ie engine
(Sec 9C)
9C.57 Air outlet duct securing clip removal
from airflow meter
9C.55C Air cleaner casing lower bracket
and bolt (arrowed)
9C.56 Air intake duct at airflow meter
(securing clip arrowed)9C.55D Air cleaner metal duct over
radiator
13
Page 196 of 303

80The injector retaining plate socket-headed
screws may now be removed using an Allen
key. Withdraw the fuel injectors and insulators
(photos).
81New injectors, complete with the fuel rail,
must be purchased as an assembly. Always
use new seals when refitting the injectors and
the insulators (photos).
Electronic control unit (ECU)
82The ECU is located under the right-hand
side of the facia panel.
83Pull off the multipin connector plug and
extract the fixing screws (photo).
System control relay
84This is located adjacent to the airflow
meter. Pull off the multipin connector and
release the relay fixing (photo).
Fuel injector cooling fan
85This is located low down on the left-hand
side of the radiator (photo).
86Remove the spiral-wire-wound hose
which connects with the injector cooling duct.
87Pull off the wiring plug, and unbolt and
remove the fan.
Supplementary air valve
88Disconnect the hoses and wiring plug
from the valve, which is located on the front
face of the engine (photos).
89Unscrew the mounting bracket screws
and withdraw the valve.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•71
9C.80A Extracting a fuel injector screw9C.79 Fan thermostatic switch on
underside of injector cooling air duct (duct
removed for clarity)
9C.85 Fuel injector cooling fan9C.84 Fuel injector system relay9C.83 ECU multipin plug
9C.81C Injector wiring plug refitting9C.81B Fuel injector cooling air duct
refitting
9C.81A Fuel injectors attached to fuel rail9C.80B Fuel injector removal
13
9C.78 Throttle valve housing support
bracket
Page 203 of 303

c) If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the car at all (or at least as little as
possible) until the fault is cured - the
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in its
overheating, as noted above.
d) DO NOT push- or tow-start the car - this
will soak the catalytic converter in
unburned fuel, causing it to overheat
when the engine does start - see b)
above.
e) DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds - if the ignition is switched
off at anything above idle speed,
unburned fuel will enter the (very hot)
catalytic converter, with the possible risk
of its igniting on the element and
damaging the converter.
f) DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives -
these may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter.
g) DO NOT continue to use the car if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke - the unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages and reduce its efficiency; in
severe cases the element will overheat.
h) Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures and
the casing will become hot enough to
ignite combustible materials which brush
against it. DO NOT, therefore, park the car
in dry undergrowth, over long grass or
piles of dead leaves.
i) Remember that the catalytic converter is
FRAGILE - do not strike it with tools
during servicing work, take great care
when working on the exhaust system,
ensure that the converter is well clear of
any jacks or other lifting gear used to raise
the car and do not drive the car over
rough ground road humps, etc., in such a
way as to ground the exhaust system.
j) In some cases, particularly when the car is
new and/or is used for stop/start driving, a
sulphurous smell (like that of rotten eggs)
may be noticed from the exhaust. This is
common to many catalytic
converter-equipped cars and seems to be
due to the small amount of sulphur found
in some petrols reacting with hydrogen in
the exhaust to produce hydrogen sulphide
(H
2S) gas; while this gas is toxic, it is not
produced in sufficient amounts to be a
problem. Once the car has covered a few
thousand miles the problem should
disappear - in the meanwhile a change of
driving style or of the brand of petrol used
may effect a solution.
k) The catalytic converter, used on a
well-maintained and well driven car,
should last for at least 50 000 miles
(80 000 km) or five years - from this point
on, careful checks should be made at all
specified service intervals on the CO level
to ensure that the converter is still
operating efficiently - if the converter is no
longer effective it must be renewed.
Fuel evaporation control system
- general
76As mentioned earlier, fuel evaporation is
contained within the system. In high outdoor
temperatures, when the vehicle is parked for a
period of time, the fuel in the tank evaporates,
building up pressure. When the pressure builds
up to a predetermined level a vent valve opens
to allow the vapours to pass on to and absorbed
by a carbon filter. However, if extreme pressure
or vacuum should build up, a two way safety
valve opens to allow external venting.
77If the safety valve needs replacing, note
that it must be fitted correctly. The black end
should be connected to the fuel tank and the
blue to the carbon filter.
78The vapours in the carbon filter are
flushed by warm air passing through the filter
on to a ECU controlled vapour cut-off
solenoid.
79The cut-off solenoid is closed when
starting the engine and opens to allow
vapours to be drawn into the inlet manifold,
through a second solenoid. If the cut-off
solenoid needs replacing ensure that the
black arrow on the casing is pointing towards
the inlet manifold.
80The second solenoid, known as an Elbi
solenoid, is closed when the engine is turned
off, thus preventing engine run-on. The side
facing connection is for the inlet manifold
pipe.
PART E:
BOSCH L3.1/2 JETRONIC
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEMS
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of this Section before starting
any work.
Description
1A Bosch L3.1 (or L3.2, as fitted from 1992)
Jetronic fuel injection system is fitted to the
1372 cc Turbo ie engine. The system circuit
and main component locations are shown in
Figs. 13.48 and 13.49.
2The L3.1/2 Jetronic system is a multi-point
fuel injection (MPi) system. It operates in a
similar manner to that of the LE2-Jetronic
system fitted to the 1301 cc Turbo ie engine
described in Part C of this Section. The L3.1/2
system is more sophisticated and has the
ability to provide reasonably efficient engine
operation when system sensors malfunction.
As with the LE2 system, the fuel and air
supply mixture circuits are regulated in
accordance with the electronic control unit
(ECU), but on the L3.1/2 system the control
unit is attached to the upper part of the
airflow meter.
3The ECU analyses the information passed
to it from the system sensors. These signals
are then processed and the air/fuel mixture is
constantly adjusted as required to provide the
13•78 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.48 Bosch L3.1 Jetronic fuel injection system - 1372 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 9E)
1 ECU
1A Diagnostic socket
2 Injection system relay and
fuel pump relay
3 Ignition switch
4 Battery
5 Fuel tank
6 Fuel pump
6A Primary fuel filter7 Coolant temperature
sensor
8 Intake air cooling radiator
(intercooler)
9 Air cleaner
10 Supplementary air valve
11 Throttle position switch
11A Throttle housing
12 Airflow meter12A Intake air temperature
sensor
13 Fuel pressure regulator
14 Fuel rail (to injectors)
15 Secondary fuel filter
16 Injectors
17 Injector cooling fan
18 Thermostatic switch (to
engage injector cooling fan)
Page 230 of 303

Starter motor brushes
(later models) - renewal#
25When renewing the starter motor brushes
on later models, the old brushes will need to
be crushed (in a vice or with a hammer) and
their leads then soldered to the new brushes.
Fuses - later models
26The fuse arrangement is slightly different
on later models, but the circuits protected are
still identified by a symbol. Refer to the
Specifications Section for full details. Note
also the terminal block with plastic cover,
which can be used to isolate the battery from
the electrical system by disconnecting the
leads from the terminals (photos).
Relays (Turbo ie models) -
general
27On Turbo ie models, the relays mounted
in the fuse block are as shown in Fig. 13.103.
Additional relays are located as follows:
Headlamp relay - on lead under main fuse
blockFuel injection system main control relay -
adjacent to airflow meter
Headlamps later models
28The headlamp units fitted on later models
differ according to model, but the bulb and
unit replacement details are generally the
same as described for previous models in
Chapter 9. Note that the rubber cover can
only be fitted with the tab to the top as shown
(photo).
Headlamp beam adjusters for
load compensation - later
models
29Some later models are fitted with
headlamp beam adjusters which allowtemporary resetting to be made (such as
when the car is fully loaded). Access to these
adjusters is made by lifting the bonnet (photo).
30Turn the adjusters anti-clockwise to lower
the beam to the normal level or clockwise to
raise the beam (when the car is unloaded).
Repeat the procedure on the opposite
headlamp unit an equal amount.
31Other later models have separate
horizontal and vertical beam adjusters,
positioned as shown (photos). A load
compensating lever is attached to the
adjusters to enable temporary resetting of the
headlamp beams, without changing the
normal adjustment. Turn the lever to the
appropriate side (right or left) to make the
adjustment as required. The normal setting
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•105
15.26B Battery lead terminal block on the
1301 cc Turbo ie model15.23B Starter motor and wiring
connections on the 1372 cc ie engine
15.31B Headlamp vertical beam alignment
adjuster screw on a 1372 cc ie model. Note
the load compensator lever which is set in
the “O” (normal load) setting position15.31A Headlamp horizontal beam
alignment adjuster screw on a 1372 cc ie
model
15.29 Headlamp beam adjuster on the
999 cc Turbo ie model15.28 Headlamp unit fitted to the 1372 cc ie
model
15.26A Fuse block on the 1301 cc Turbo ie
model
13
Fig. 13.103 Auxiliary fuses and relays on
1301 cc Turbo ie models (Sec 15)
1 Horn relay
2 Heated rear screen relay
3 Foglamps relay
4 Radiator fan relay
5 Electric windows relay
6 Foglamps fuse
7 Radiator fan second speed fuse
8 Fuel injector fan fuse
9 Electric windows fuse
10 Electric fuel pump fuse
Page 238 of 303

18Refitting of all components is a reversal of
removal.
Radiator grille (1301 cc
Turbo ie model) -
removal and refitting
Á
19The grille is secured by a central screw
and two upper clips. Use a screwdriver to
prise the tabs on the upper clips downwards
(photos).
20Lift the grille upwards and forwards to
disengage its lower mountings (photo).
21Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Radiator grille (1372 cc ie
and 1372 cc Turbo ie
models) - removal
and refitting
Á
22The radiator grille on these models is
secured by screws at the top edge (photo).
Raise and support the bonnet. Undo the
retaining screws, then lift the grille clear.
23Refit in the reverse order of removal.
Bumpers (1301 cc Turbo ie,
1372 cc ie and 1372 cc
Turbo ie models) -
removal and refitting
Á
Removal - front
24Remove the radiator grille as previously
described, to provide access to the bumper
upper mounting screws (photo).
25The ends of the bumpers are secured withbolts and captive nuts but to reach them, the
underwing shields must be released and
pulled away.
26Disconnect the leads from the auxiliary
lamps which are mounted in the spoiler, and
then lift the bumper/spoiler from the car.
Removal - rear
27Open the tailgate to provide access to the
bumper upper mounting screws.
28Disconnect the leads from the rear
number plate lamp. Unscrew the lower
mounting nuts (photo).
29Disconnect the bumper end fixings, which
are accessible under the rear wing edges
(photo).
Refitting - front and rear
30Refitting either front or rear bumpers is a
reversal of removal.
Rear hinged windows -
removal and refittingª
31These have toggle-type catches and
hinges bolted directly through the glass
(photo).
32To remove the window glass, have an
assistant support it, and then unscrew the
cross-head hinge screws and the toggle catch
anchor plate screws. Lift the glass away. If the
toggle catch must be removed from the glass,
first drive out the handle pivot pin and then,
using a pin wrench or circlip pliers, unscrew
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•113
17.20 Removing the radiator grille from a
1301 cc Turbo ie model17.19B Prising down a radiator grille clip17.19A Extracting a radiator grille screw
17.31 Rear window toggle-type catch17.29 Unscrewing a bumper end fixing nut
17.24 Front bumper upper mounting screw
(arrowed)17.22 Radiator grille screw removal on a
1372 cc SX ie model
17.28 Rear bumper lower mounting nut
13