transmission FORD EXPEDITION 2002 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2002, Model line: EXPEDITION, Model: FORD EXPEDITION 2002 1.GPages: 280, PDF Size: 2.32 MB
Page 167 of 280

FOUR-WHEEL DRIVE (4WD) OPERATION (IF EQUIPPED)
For important information regarding safe operation of this type
of vehicle, seePreparing to drive your vehiclein this chapter.
When Four±wheel drive (4WD) is engaged, power is supplied to all four
wheels through a transfer case. 4WD power can be selected when
additional driving power is desired.
If equipped with the Electronic Shift 4WD System, and the
instrument panel control is moved to 4WD Low while the vehicle
is moving, the system will not engage and no damage will occur to
the 4WD system. Before 4WD Low can be engaged, the vehicle
must be at a complete stop with the brake pedal depressed and
the transmission in N (Neutral).
4H or 4L operation is not recommended on dry pavement. Doing
so could result in difficult disengagement of the transfer case,
damage to the transfer case, increased tire wear, decreased fuel
economy and difficulty turning.
Control-Trac automatic four-wheel drive system (if equipped)
Your 4x4 features the heavy-duty Control-Trac system which includes a
computer-operated transfer case. This unique system is interactive with
the road, continually monitoring and adjusting torque delivery to the
front and rear wheels to optimize vehicle control.
Positions of the Control-Trac system
The Control-Trac A4WD system
functions in three modes:
²A4WDposition delivers power to
the rear axle. If the rear wheels
lose traction, power will be
automatically delivered to the
front axle to maintain traction
throughout the slippery condition.
²4Hposition provides
mechanically locked four-wheel
drive power delivery to front and rear axles.
²4Lposition provides mechanically locked four-wheel drive when above
average power at reduced speeds is required.
4HA4WD4L
Driving
167
Page 170 of 280

²Drive slower in strong crosswinds which can affect the normal steering
characteristics of your vehicle.
²Be extremely careful when driving on pavement made slippery by
loose sand, water, gravel, snow or ice.
If your vehicle goes off the edge of the pavement
²If your vehicle goes off the edge of the pavement, slow down, but
avoid severe brake application, Ease the vehicle back onto the
pavement only after reducing your speed. Do not turn the steering
wheel too sharply while returning to the road surface.
²It may be safer to stay on the apron or shoulder of the road and slow
down gradually before returning to the pavement. You may loose
control if you do not slow down or if you turn the steering wheel too
sharply or abruptly.
²It often may be less risky to strike small inanimate objects, such as
highway reflectors, with minor damage to your vehicle rather than
attempt a sudden return to the pavement which could cause the
vehicle to slide sideways out of control or roll over. Remember, your
safety and the safety of others should be your primary concern.
If your vehicle gets stuck
If the vehicle is stuck it may be rocked out by shifting from forward and
reverse gears, stopping between shifts, in a steady pattern. Press lightly
on the accelerator in each gear.
Do not rock the vehicle for more than a few minutes or damage to
the transmission and tires may occur or the engine may overheat.
Do not spin the wheels at over 56 km/h (35 mph). The tires may
fail and injure a passenger or bystander.
Emergency maneuvers
²In an unavoidable emergency situation where a sudden sharp turn must
be made, remember to avoid ªover-drivingº your vehicle, i.e., turn the
steering wheel only as rapidly and as far as required to avoid the
emergency. Excessive steering will result in less vehicle control, not
more. Additionally, smooth variations of the accelerator and/or brake
pedal pressure should be utilized if changes in vehicle speed are called
for. Avoid abrupt steering, acceleration or braking. Use all available road
surface to return the vehicle to a safe direction of travel.
Driving
170
Page 171 of 280
²In the event of an emergency stop, avoid skidding the tires and do not
attempt any sharp steering wheel movements.
²If the vehicle goes from one type of surface to another (i.e., from
concrete to gravel) there will be a change in the way the vehicle
responds to a maneuver (steering, acceleration or barking). Again,
avoid these abrupt inputs.
Parking
On some 4WD vehicles, when the transfer case is in the N (Neutral)
position, the engine and transmission are disconnected from the rest of
the driveline. Therefore, the vehicle is free to roll even if the automatic
transmission is in P (Park) or the manual transmission is in gear. Do not
leave the vehicle unattended with the transfer case in N (Neutral)
position. Always set the parking brake fully and turn off the ignition
when leaving the vehicle.
4WD Systems (if equipped)
4WD (when you select the 4WD mode), uses all four wheels to power
itself. This increases traction, enabling you to drive over terrain and road
conditions that a conventional two-wheel drive vehicle can't.
Power is supplied to all four wheels
through a transfer case. On 4WD
vehicles, the transfer case allows
you to select 4WD when necessary.
Information on transfer case
operation and shifting procedures
can be found in theDriving
chapter. Information on transfer
case maintenance can be found in theMaintenance and specifications
chapter. You should become thoroughly familiar with this information
before you operate your vehicle.
Normal characteristics
On some 4WD models, the initial shift from two-wheel drive to 4x4 while
the vehicle is moving can cause some momentary clunk and ratcheting
sounds. This is the front drivetrain coming up to speed and the
automatic locking hubs engaging and is not cause for concern.
Driving
171
Page 172 of 280

Sand
When driving over sand, try to keep all four wheels on the most solid
area of the trail. Avoid reducing the tire pressures but shift to a lower
gear and drive steadily through the terrain. Apply the accelerator slowly
and avoid spinning the wheels.
If you must reduce the tire pressure for whatever reason in sand, make
sure you re-inflate the tires as soon as possible.
Avoid excessive speed because vehicle momentum can work against you
and cause the vehicle to become stuck to the point that assistance may
be required from another vehicle. Remember, you may be able to back
out the way you came if you proceed with caution.
Mud and water
If you must drive through high
water, drive slowly. Traction or
brake capability may be limited.
When driving through water,
determine the depth; avoid water
higher than the bottom of the hubs
(if possible) and proceed slowly. If
the ignition system gets wet, the
vehicle may stall.
Once through water, always try the brakes. Wet brakes do not stop the
vehicle as effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be improved by moving
your vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal.
Be cautious of sudden changes in vehicle speed or direction when you
are driving in mud. Even 4WD vehicles can lose traction in slick mud. As
when you are driving over sand, apply the accelerator slowly and avoid
spinning your wheels. If the vehicle does slide, steer in the direction of
the slide until you regain control of the vehicle.
If the transmission, transfer case or front axle are submerged in water,
their fluids should be checked and changed, if necessary.
Water intrusion into the transmission may damage the transmission.
If the front or rear axle is submerged in water, the axle lubricant should
be replaced.
After driving through mud, clean off residue stuck to rotating driveshafts
and tires. Excess mud stuck on tires and rotating driveshafts causes an
imbalance that could damage drive components.
Driving
172
Page 177 of 280

system gets wet, your engine may stall. Water may also enter your
engine's air intake and severely damage your engine.
If driving through deep or standing water is unavoidable, proceed very
slowly. Never drive through water that is higher than the bottom of the
hubs (for trucks) or the bottom of the wheel rims (for cars).
Once through the water, always try the brakes. Wet brakes do not stop
the vehicle as effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be improved by
moving your vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake
pedal.
Driving through deep water where the transmission vent tube is
submerged may allow water into the transmission and cause
internal transmission damage.
VEHICLE LOADING
Before loading a vehicle, familiarize yourself with the following terms:
²Base Curb Weight:Weight of the vehicle including any standard
equipment, fluids, lubricants, etc. It does not include occupants or
aftermarket equipment.
²Payload:Combined maximum allowable weight of cargo, occupants
and optional equipment. The payload equals the gross vehicle weight
rating minus base curb weight.
²GVW (Gross Vehicle Weight):Base curb weight plus payload
weight. The GVW is not a limit or a specification.
²GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating):Maximum permissable total
weight of the base vehicle, occupants, optional equipment and cargo.
The GVWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the Safety
Certification Label on the driver's door pillar.
²GAWR (Gross Axle Weight Rating):Carrying capacity for each axle
system. The GAWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the
Safety Certification Label on the driver's door pillar.
²GCW (Gross Combined Weight):The combined weight of the
towing vehicle (including occupants and cargo) and the loaded trailer.
²GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating):Maximum permissable
combined weight of towing vehicle (including occupants and cargo)
and the loaded trailer
²Maximum Trailer Weight Rating:Maximum weight of a trailer the
vehicle is permitted to tow. The maximum trailer weight rating is
Driving
177
Page 178 of 280

determined by subtracting the vehicle curb weight for each
engine/transmission combination, any required option weight for trailer
towing and the weight of the driver from the GCWR for the towing
vehicle.
²Maximum Trailer Weight:Maximum weight of a trailer the loaded
vehicle (including occupants and cargo) is permitted to tow. It is
determined by subtracting the weight of the loaded trailer towing
vehicle from the GCWR for the towing vehicle.
²Trailer Weight Range:Specified weight range that the trailer must
fall within that ranges from zero to the maximum trailer weight rating.
Remember to figure in the tongue load of your loaded trailer when
figuring the total weight.
Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the
certification label.
Do not use replacement tires with lower load carrying capacities than the
originals because they may lower the vehicle's GVWR and GAWR
limitations. Replacement tires with a higher limit than the originals do
not increase the GVWR and GAWR limitations.
The Safety Certification Label, found on the driver's door pillar, lists
several important vehicle weight rating limitations. Before adding any
additional equipment, refer to these limitations. If you are adding weight
to the front of your vehicle, (potentially including weight added to the
cab), the weight added should not exceed the front axle reserve capacity
(FARC). Additional frontal weight may be added to the front axle reserve
capacity provided you limit your payload in other ways (i.e. restrict the
number of occupants or amount of cargo carried).
Always ensure that the weight of occupants, cargo and equipment being
carried is within the weight limitations that have been established for
your vehicle including both gross vehicle weight and front and rear gross
axle weight rating limits. Under no circumstance should these limitations
be exceeded.
Exceeding any vehicle weight rating limitation could result in
serious damage to the vehicle and/or personal injury.
Driving
178
Page 180 of 280

TRAILER TOWING
Trailer towing with your vehicle may
require the use of a trailer tow
option package.
Trailer towing puts additional loads
on your vehicle's engine,
transmission, axle, brakes, tires, and
suspension. For your safety and to
maximize vehicle performance, be
sure to use the proper equipment
while towing.
Follow these guidelines to ensure safe towing procedure:
²Stay within your vehicle's load limits. If exceeded, cargo should be
removed from the trailer and/or the vehicle until all weights are within
specified limits.
²Thoroughly prepare your vehicle for towing. Refer toPreparing to
towin this chapter.
²Use extra caution when driving while trailer towing. Refer toDriving
while you towin this chapter.
²Service your vehicle more frequently if you tow a trailer. Refer to the
severe duty schedule in the scheduled maintenance guide.
²Do not tow a trailer until your vehicle has been driven at least 800 km
(500 miles).
²Refer to the instructions included with towing accessories for the
proper installation and adjustment specifications.
If your vehicle is equipped with the optional heavy duty trailer tow
wiring, it is pre-wired for trailer towing. An electrical connector is
provided under the instrument panel for installing a customer-supplied
electric brake controller. Another electrical connector is provided at the
hitch. This connector provides power to the trailer for taillamps, stop
and turn lamps, back up lamps, battery charge, electric brakes (when a
customer provided controller is installed) and ground. The kit included
with your vehicle provides you with adaptors to attach the brake
controller and convert the hitch connector for Class I trailer usage.
Driving
180
Page 181 of 280
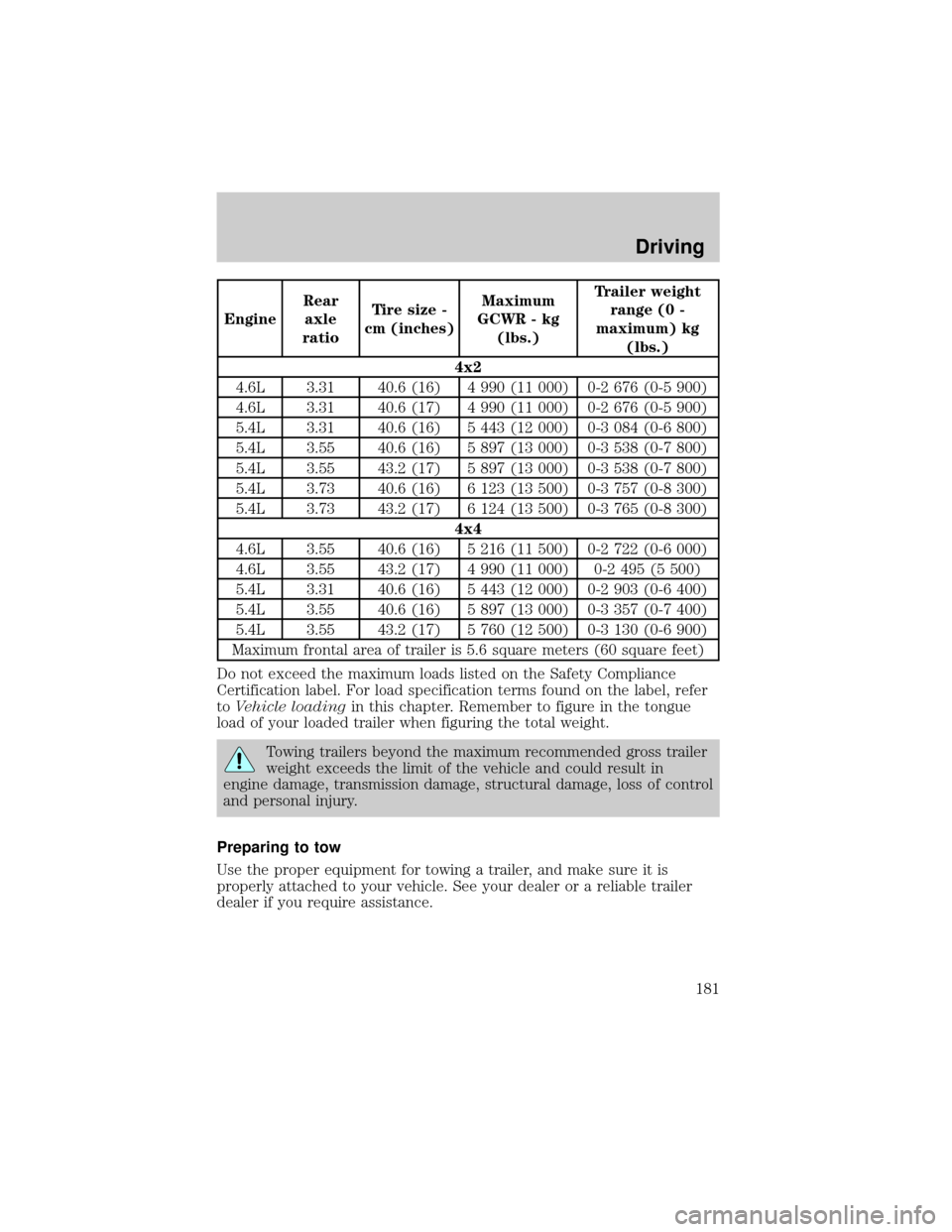
EngineRear
axle
ratioTire size -
cm (inches)Maximum
GCWR - kg
(lbs.)Trailer weight
range (0 -
maximum) kg
(lbs.)
4x2
4.6L 3.31 40.6 (16) 4 990 (11 000) 0-2 676 (0-5 900)
4.6L 3.31 40.6 (17) 4 990 (11 000) 0-2 676 (0-5 900)
5.4L 3.31 40.6 (16) 5 443 (12 000) 0-3 084 (0-6 800)
5.4L 3.55 40.6 (16) 5 897 (13 000) 0-3 538 (0-7 800)
5.4L 3.55 43.2 (17) 5 897 (13 000) 0-3 538 (0-7 800)
5.4L 3.73 40.6 (16) 6 123 (13 500) 0-3 757 (0-8 300)
5.4L 3.73 43.2 (17) 6 124 (13 500) 0-3 765 (0-8 300)
4x4
4.6L 3.55 40.6 (16) 5 216 (11 500) 0-2 722 (0-6 000)
4.6L 3.55 43.2 (17) 4 990 (11 000) 0-2 495 (5 500)
5.4L 3.31 40.6 (16) 5 443 (12 000) 0-2 903 (0-6 400)
5.4L 3.55 40.6 (16) 5 897 (13 000) 0-3 357 (0-7 400)
5.4L 3.55 43.2 (17) 5 760 (12 500) 0-3 130 (0-6 900)
Maximum frontal area of trailer is 5.6 square meters (60 square feet)
Do not exceed the maximum loads listed on the Safety Compliance
Certification label. For load specification terms found on the label, refer
toVehicle loadingin this chapter. Remember to figure in the tongue
load of your loaded trailer when figuring the total weight.
Towing trailers beyond the maximum recommended gross trailer
weight exceeds the limit of the vehicle and could result in
engine damage, transmission damage, structural damage, loss of control
and personal injury.
Preparing to tow
Use the proper equipment for towing a trailer, and make sure it is
properly attached to your vehicle. See your dealer or a reliable trailer
dealer if you require assistance.
Driving
181
Page 182 of 280

If your vehicle is not equipped with the factory heavy duty trailer tow
option, auxiliary coolers are recommended for the automatic
transmission system if you are planning on:
²traveling farther than 80 km (50 miles)
²towing in hilly terrain
²towing frequently
Hitches
Do not use hitches that clamp onto the vehicle's bumper or attach to the
axle. You must distribute the load in your trailer so that 10%±15% of the
total weight of the trailer is on the tongue.
Load equalizing hitch
When hooking up a trailer using a load equalizing hitch, always use the
following procedure:
1. Park the unloaded vehicle on a level surface. With the ignition on and
all doors closed, allow the vehicle to stand for several minutes so that it
can level.
2. Turn the air suspension (if equipped) control to OFF.
3. Measure the height of a reference point on the front and rear bumpers
at the center of the vehicle.
4. Attach the trailer to the vehicle and adjust the hitch equalizers so that
the front bumper height is within 0±13 mm (0.5 in) of the reference
point. After proper adjustment, the rear bumper should be no higher
than in Step 3.
5. Turn the air suspension (if equipped) control to ON.
Adjusting an equalizing hitch so the rear bumper of the vehicle
is lower or higher than it was unloaded will defeat the function
of the load equalizing hitch and may cause unpredictable handling.
Safety chains
Always connect the trailer's safety chains to the frame or hook retainers
of the vehicle hitch. To connect the trailer's safety chains, cross the
chains under the trailer tongue and allow slack for turning corners.
If you use a rental trailer, follow the instructions that the rental agency
gives to you.
Do not attach safety chains to the bumper.
Driving
182
Page 183 of 280

Trailer brakes
Electric brakes and manual, automatic or surge-type trailer brakes are
safe if installed properly and adjusted to the manufacturer's
specifications. The trailer brakes must meet local and Federal
regulations.
Do not connect a trailer's hydraulic brake system directly to your
vehicle's brake system. Your vehicle may not have enough
braking power and your chances of having a collision greatly increase.
The braking system of the tow vehicle is rated for operation at the
GVWR not GCWR.
Trailer lamps
Trailer lamps are required on most towed vehicles. Make sure your
trailer lamps conform to local and Federal regulations. See your dealer or
trailer rental agency for proper instructions and equipment for hooking
up trailer lamps.
Using a step bumper
The rear bumper is equipped with an integral hitch and requires only a
ball with a 25.4 mm (one inch) shank diameter. The bumper hasa1814
kg (4 000 lb.) trailer weight and 181 kg (400 lb.) tongue weight
capability.
Use a frame-mounted weight distributing hitch for trailers over 1 814 kg
(4 000 lb).
Driving while you tow
When towing a trailer:
²Ensure that you turn off your speed control. The speed control may
shut off automatically when you are towing on long, steep grades.
²Consult your local motor vehicle speed regulations for towing a trailer.
²Use a lower gear when towing up or down steep hills. This will
eliminate excessive downshifting and upshifting for optimum fuel
economy and transmission cooling.
²Anticipate stops and brake gradually.
Exceeding the GCWR rating may cause internal transmission
damage and void your warranty coverage.
Driving
183