wheel FORD EXPLORER SPORT TRAC 2002 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2002, Model line: EXPLORER SPORT TRAC, Model: FORD EXPLORER SPORT TRAC 2002Pages: 200, PDF Size: 3.34 MB
Page 112 of 200

vehicle is moving; this is normal and should be no reason for concern.
Refer toShifting to/from 4X4 LOWfor proper operation.
Shifting between 2WD and 4X4 HIGH
•Move the 4WD control between 2WD and 4X4 HIGH at any forward
speed.
Note:Do not perform this operation if the rear wheels are slipping.
Shifting to/from 4X4 LOW
1. Bring the vehicle to a complete stop
2. Depress the brake
3. On vehicles equipped with an automatic transmission, place the
transmission in N (Neutral); on vehicles equipped with a manual
transmission, depress the clutch.
4. Move the 4WD control to the desired position.
•If shifting into 4WD LOW, wait for the 4X4 LOW light in the
instrument cluster to turnonindicating the shift is complete.
•If shifting out of 4WD LOW, wait for the 4X4 LOW light in the
instrument cluster turn turnoffindicating the shift is complete.
Driving off-road with truck and utility vehicles
Basic operating principles
Maintain steering wheel control at all times, especially in rough terrain;
sudden changes in terrain can result in abrupt steering wheel motion. Do
not use 4WD on dry, hard surfaced roads (except models equipped with
Auto 4WD).
If your vehicle goes off the edge of the pavement
Slow down and don’t slam on the brakes. Ease the vehicle back onto the
pavement only after reducing your speed.
Do not turn the steering wheel sharply while returning to the
road as this may cause you to lose control of the vehicle.
It may be safer to stay on the shoulder of the road and slow down before
returning to the pavement.
If your vehicle gets stuck
The vehicle may be rocked out by shifting from forward and reverse
gears, stopping between shifts, in a steady pattern. Press lightly on the
Driving
112
Page 113 of 200

accelerator in each gear.Do not rock the vehicle for more than a
few minutes or damage to the transmission and tires may occur
or the engine may overheat.
Do not spin the wheels at over 56 km/h (35 mph). The tires may
fail and injure a passenger or bystander.
Emergency maneuvers
In an emergency situation where a sudden sharp turn must be made,
turn the steering wheel only as rapidly and as far as required to avoid
the emergency. Excessive steering will result in less vehicle control. Also
avoid abrupt braking. In the event of an emergency stop, do not attempt
any sharp steering wheel movements. If the vehicle goes from one type
of surface to another (i.e., from concrete to gravel) there will be a
change in the way the vehicle responds to a maneuver (steering,
acceleration or braking).
Parking
On some 4WD vehicles, when the transfer case is in the N (Neutral)
position, the engine and transmission are disconnected from the rest of
the driveline. Therefore, the vehicle is free to roll even if the automatic
transmission is in P (Park) or the manual transmission is in gear. Do not
leave the vehicle unattended with the transfer case in N (Neutral)
position. Always set the parking brake fully and turn off the ignition
when leaving the vehicle.
Normal characteristics
On some 4WD vehicles, the initial shift from two-wheel drive to
four–wheel drive while the vehicle is moving can cause some momentary
clunk and ratcheting sounds. This is normal and should be no cause for
concern.
Driving on sand, mud and water
When driving over sand, avoid reducing the tire pressures; instead, shift
to a lower gear. Apply the accelerator slowly and avoid spinning the
wheels. If you must reduce the tire pressure, make sure you re-inflate
the tires as soon as possible. Avoid excessive speed because vehicle
momentum can work against your vehicle and cause it to become stuck.
Driving
113
Page 114 of 200

If you must drive through high
water, drive slowly. Traction or
braking ability may be reduced.
Also, if the ignition system gets wet,
the vehicle may stall.
Once you’re through the water, always dry the brakes by moving your
vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal. Wet
brakes do not stop the vehicle as quickly as dry brakes.
When driving through mud, be cautious of sudden changes in vehicle
speed or direction. Even 4WD vehicles can lose traction in slick mud.
Apply the accelerator slowly and avoid spinning your wheels. If the
vehicle does slide, steer in the direction of the slide until you regain
control of the vehicle. If the transmission, transfer case or either axle
become submerged in mud or water, their fluids should be checked and
changed, if necessary. After driving through mud, clean off residue stuck
to rotating driveshafts and tires. Excess mud stuck on tires and rotating
driveshafts could damage driveline components.
“Tread Lightly”is an educational
program designed to increase public
awareness of land-use regulations
and responsibilities in our nations
wilderness areas. Ford joins the U.S.
Forest Service and the Bureau of Land Management in encouraging you
to help preserve our national forest and other public and private lands by
“treading lightly.”
Driving on hilly or sloping terrain
Avoid driving crosswise or turning on steep slopes or hills. Your vehicle
may lose traction and slip sideways and possibly roll over. Do not drive
in reverse over a hill without the aid of an observer.
Driving
114
Page 115 of 200
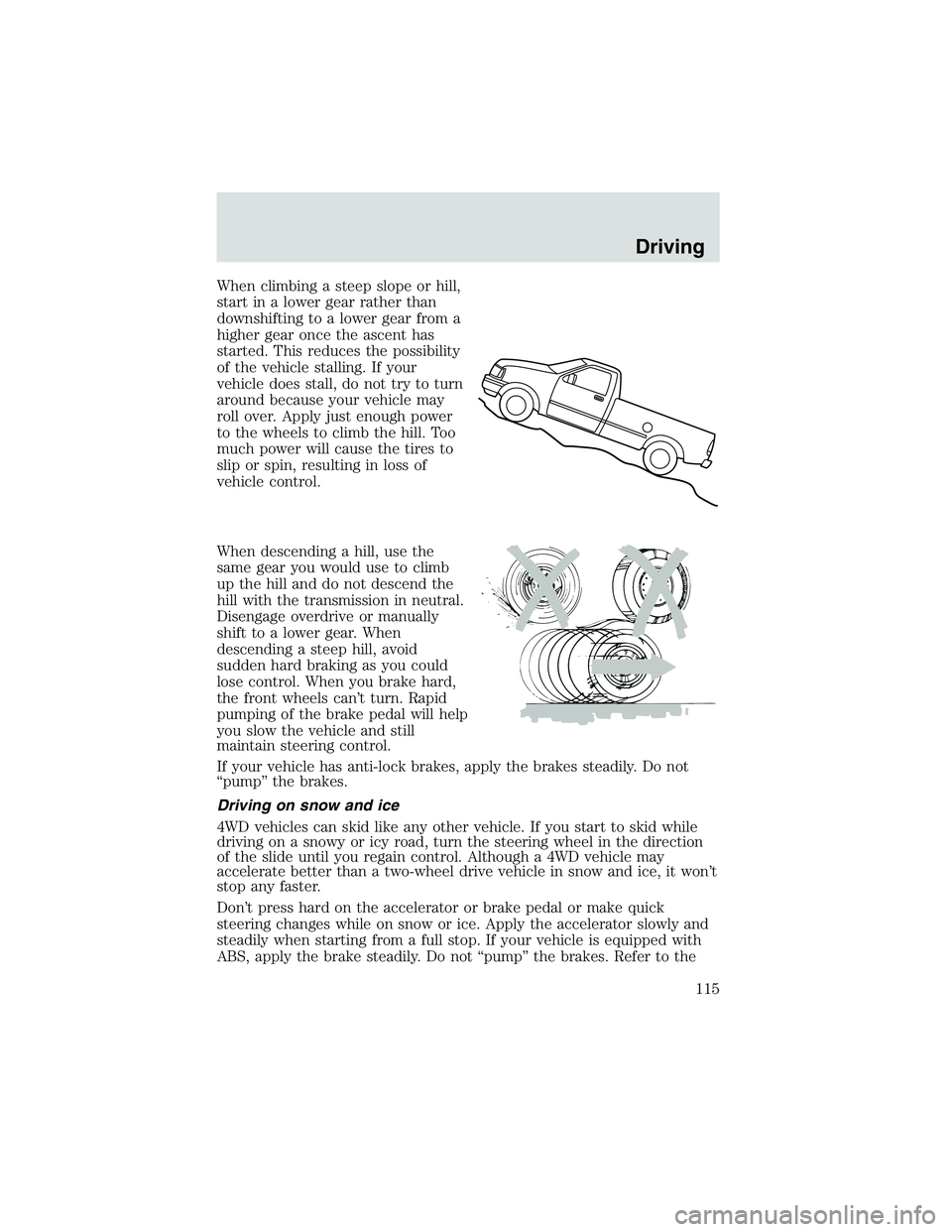
When climbing a steep slope or hill,
start in a lower gear rather than
downshifting to a lower gear from a
higher gear once the ascent has
started. This reduces the possibility
of the vehicle stalling. If your
vehicle does stall, do not try to turn
around because your vehicle may
roll over. Apply just enough power
to the wheels to climb the hill. Too
much power will cause the tires to
slip or spin, resulting in loss of
vehicle control.
When descending a hill, use the
same gear you would use to climb
up the hill and do not descend the
hill with the transmission in neutral.
Disengage overdrive or manually
shift to a lower gear. When
descending a steep hill, avoid
sudden hard braking as you could
lose control. When you brake hard,
the front wheels can’t turn. Rapid
pumping of the brake pedal will help
you slow the vehicle and still
maintain steering control.
If your vehicle has anti-lock brakes, apply the brakes steadily. Do not
“pump”the brakes.
Driving on snow and ice
4WD vehicles can skid like any other vehicle. If you start to skid while
driving on a snowy or icy road, turn the steering wheel in the direction
of the slide until you regain control. Although a 4WD vehicle may
accelerate better than a two-wheel drive vehicle in snow and ice, it won’t
stop any faster.
Don’t press hard on the accelerator or brake pedal or make quick
steering changes while on snow or ice. Apply the accelerator slowly and
steadily when starting from a full stop. If your vehicle is equipped with
ABS, apply the brake steadily. Do not“pump”the brakes. Refer to the
Driving
115
Page 116 of 200

Brakessection of this chapter for additional information on the
operation of the anti-lock brake system. If your vehicle is not equipped
with ABS, use a“squeeze”braking technique. Push on the brake pedal
with a steadily increasing force which allows the wheels to brake yet
continue to roll so that you may steer in the direction you want to travel.
If you lock the wheels, release the brake pedal and repeat the squeeze
technique.
Never drive with chains on the front tires of 4WD vehicles without also
putting them on the rear tires. This could cause the rear to slide and
swing around during braking.
Maintenance and Modifications
Ford strongly recommends that you do not add or removing steering or
suspension parts (such as lift kits or stabilizer bars) or by using
replacement parts not equivalent to the original factory equipment. Do
not use aftermarket“lift kits”or other suspension modifications. These
could adversely affect the vehicle’s handling characteristics, which could
lead to loss of vehicle control or roll over and serious injury. Frequent
inspection of vehicle chassis components is recommended if the vehicle
is subjected to heavy off-road usage.
DRIVING THROUGH WATER
If driving through deep or standing water is unavoidable, proceed very
slowly especially if the depth is not known. Never drive through water
that is higher than the bottom of the hubs (for trucks) or the bottom of
the wheel rims (for cars). Traction or brake capability may be limited
and your vehicle may stall. Water may also enter your engine’s air intake
and severely damage your engine.
Once through the water, always dry the brakes by moving your vehicle
slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal. Wet brakes do
not stop the vehicle as quickly as dry brakes.Driving through deep
water where the transmission vent tube is submerged may allow
water into the transmission and cause internal transmission
damage.
VEHICLE LOADING
Before loading a vehicle, familiarize yourself with the following terms:
•Base Curb Weight:Weight of the vehicle including any standard
equipment, fluids, lubricants, etc. It does not include occupants or
aftermarket equipment.
•Payload:Combined maximum allowable weight of cargo, occupants
and optional equipment. The payload equals the gross vehicle weight
rating minus base curb weight.
Driving
116
Page 123 of 200

Trailer towing tips
•Practice turning, stopping and backing up before starting on a trip to
get the feel of the vehicle/trailer combination. When turning, make
wider turns so the trailer wheels will clear curbs and other obstacles.
•Allow more distance for stopping with a trailer attached.
•The trailer tongue weight should be no more than 10–15% of the
loaded trailer weight.
•After you have traveled 80 km (50 miles), thoroughly check your
hitch, electrical connections and trailer wheel lug nuts.
•When stopped in traffic for long periods of time in hot weather, place
the gearshift in P (Park) (automatic transmissions) or N (Neutral)
(manual transmissions). This aids engine cooling and air conditioner
efficiency.
•Vehicles with trailers should not be parked on a grade. If you must
park on a grade, place wheel chocks under the trailer’s wheels.
Launching or retrieving a boat
When backing down a ramp during boat launching or retrieval:
•do not allow the static water level to rise above the bottom edge of
the rear bumper.
•do not allow waves to break higher than 15 cm (6 inches) above the
bottom edge of the rear bumper.
Exceeding these limits may allow water to enter critical vehicle
components, adversely affecting driveability, emissions, reliability and
causing internal transmission damage. Replace the rear axle lubricant
any time the axle has been submerged in water.
Disconnect the wiring to the trailer before backing the trailer into the
water. Reconnect the wiring to the trailer after the trailer is removed
from the water.
Camper bodies
Your Explorer Sport Trac is not recommended for slide–in camper
bodies.
RECREATIONAL TOWING
An example of recreational towing is towing your vehicle behind a
motorhome. The following recreational towing guidelines are designed to
ensure that your transmission is not damaged.
Driving
123
Page 124 of 200

ALL REAR WHEEL DRIVE (RWD) VEHICLES WITH AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSIONS:
•Place the transmission in N (Neutral).
•Maximum speed is 56 km/h (35 mph).
•Maximum distance is 80 km (50 miles).
If a distance of 80 km (50 miles) or a speed of 56 km/h (35 mph)
must be exceeded, you must disconnect the driveshaft. Ford
recommends the driveshaft be removed/installed only by a
qualified technician. Improper removal/installation of the
driveshaft can cause transmission fluid loss, damage to the
driveshaft and internal transmission components.
In case of a roadside emergency with a disabled vehicle (without access
to wheel dollies, a car hauling trailer or a flatbed transport vehicle), your
vehicle can be flat towed (all wheels on the ground) under the following
conditions:
•Release the parking brake.
•Turn the ignition to the OFF position.
•Place the transmission in N (Neutral).
•Do not exceed a distance of 80 km (50 miles).
•Do not exceed 56 km/h (35 mph) vehicle speed.
RWD VEHICLES WITH 4X4 ELECTRONIC SHIFT TRANSFER CASE
AND AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION:
4x4 vehicles with electronic shift on the fly cannot be towed with any
wheels on the ground (with the exception of moving it as a disabled
vehicle off the road out of traffic).
Driving
124
Page 126 of 200

If you need to arrange roadside assistance for yourself, Ford Motor
Company will reimburse a reasonable amount. To obtain reimbursement
information, U.S. Ford or Mercury vehicles customers call
1-800-241-3673; Lincoln vehicle customers call 1–800–521–4140.
Canadian customers who need to obtain reimbursement information, call
1–800–665–2006.
Roadside coverage beyond basic warranty
In the United States, you may purchase additional roadside assistance
coverage beyond this period through the Ford Auto Club by contacting
your Ford or Lincoln Mercury dealer.
Similarly in Canada, for uninterrupted Roadside Assistance coverage, you
may purchase extended coverage prior to your Basic Warranty’s Roadside
Assistance expiring. For more information and enrollment, contact
1–877–294–2582 or visit our website at www.ford.ca.
HAZARD FLASHER
The hazard flasher is located on the
steering column, just behind the
steering wheel. The hazard flashers
will operate when the ignition is off.
Push in the flasher control and all
front and rear direction signals will
flash. Press the flasher control again
to turn them off. Use it when your
vehicle is disabled and is creating a
safety hazard for other motorists.
Note:With extended use, the flasher may run down your battery.
FUEL PUMP SHUT-OFF SWITCH
FUEL
RESET
This device stops the electric fuel pump from sending fuel to the engine
when your vehicle has had a substantial jolt.
After an accident, if the engine cranks but does not start, this switch
may have been activated.
Roadside Emergencies
126
Page 135 of 200
Fuse/Relay
LocationFuse Amp
RatingPower Distribution Box Description
50A–Not used
50B–Fuel pump relay
51–Not used
52–Not used
53–PCM diode
54–PCM relay
55–Blower relay
56A–A/C clutch solenoid
56B–Horn relay
CHANGING A FLAT TIRE
If you get a flat tire while driving:
•do not brake heavily.
•gradually decrease the vehicle’s speed.
•hold the steering wheel firmly.
•slowly move to a safe place on the side of the road.
The use of tire sealants is not recommended and may compromise the
integrity of your tires. The use of tire sealants may also affect your tire
pressure monitoring system (if equipped).
Spare tire information
The spare tire can be used as a spare or a regular tire.
Location of the spare tire and tools
The spare tire and tools for your vehicle are stowed in the following
locations:
Tool Location
Spare tire Under the vehicle, just in front of
the rear bumper
Jack, Jack handle, jack handle
extension, wheel lug nut wrenchIn the passenger side rear cab
compartment behind the access
door in trim panel
Roadside Emergencies
135
Page 136 of 200
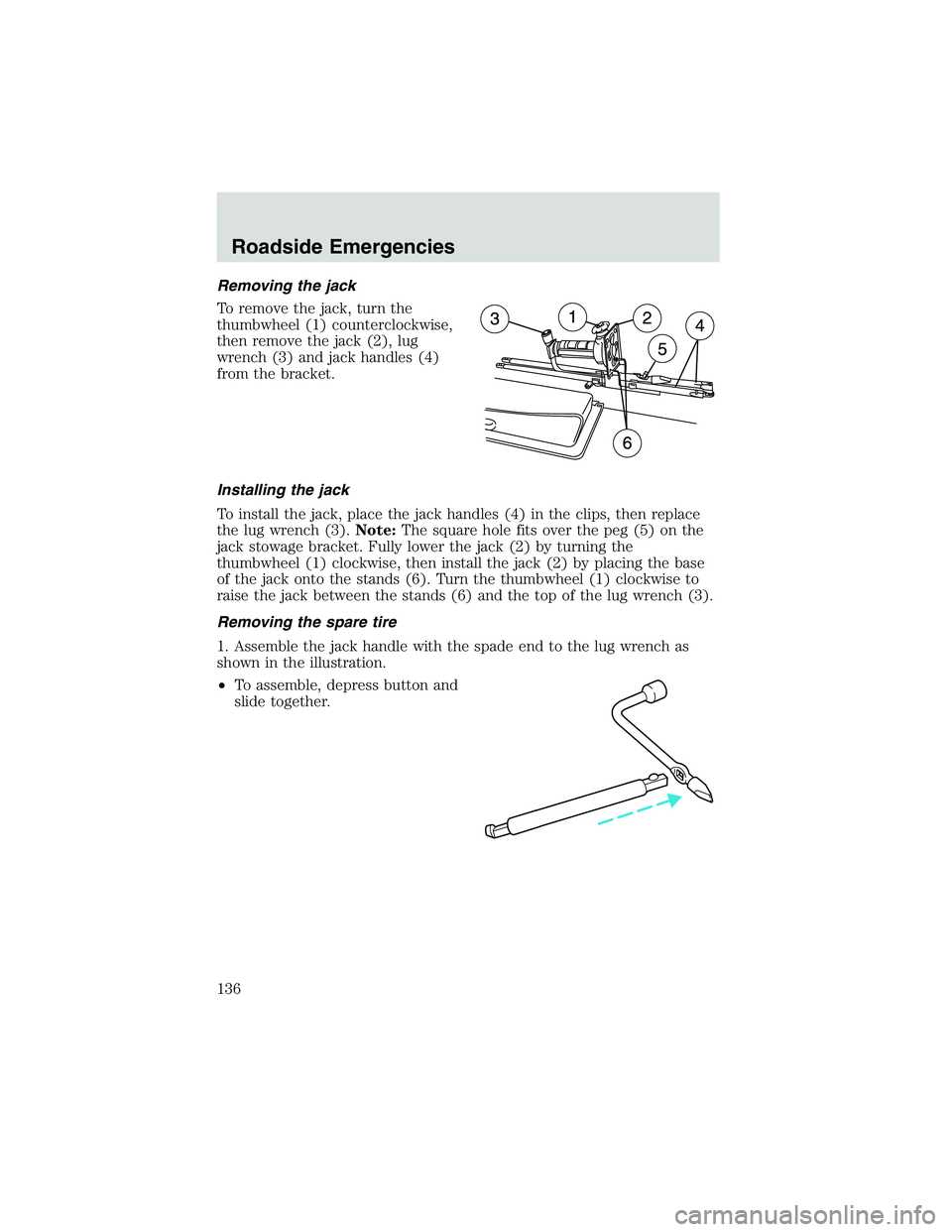
Removing the jack
To remove the jack, turn the
thumbwheel (1) counterclockwise,
then remove the jack (2), lug
wrench (3) and jack handles (4)
from the bracket.
Installing the jack
To install the jack, place the jack handles (4) in the clips, then replace
the lug wrench (3).Note:The square hole fits over the peg (5) on the
jack stowage bracket. Fully lower the jack (2) by turning the
thumbwheel (1) clockwise, then install the jack (2) by placing the base
of the jack onto the stands (6). Turn the thumbwheel (1) clockwise to
raise the jack between the stands (6) and the top of the lug wrench (3).
Removing the spare tire
1. Assemble the jack handle with the spade end to the lug wrench as
shown in the illustration.
•To assemble, depress button and
slide together.
Roadside Emergencies
136