checking oil FORD FESTIVA 1991 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1991, Model line: FESTIVA, Model: FORD FESTIVA 1991Pages: 454, PDF Size: 9.53 MB
Page 283 of 454

Circuits with external injector resistors. Used predominately on some Asian & European systems, they are used to reduce the available
voltage to an injector in order to limit the current flow. This lower voltage can cause a dim flash on a noid light designed for full voltage.
Circuits with current controlled injector drivers (e.g. "Peak and Hold"). Basically, this type of driver allows a quick burst of
voltage/current to flow and then throttles it back significantly for the remainder of the pulse width duration. If a noid light was designed
for the other type of driver (voltage controlled, e.g. "Saturated"), it will appear dim because it is expecting full voltage/current to flow
for the entire duration of the pulse width.
Let's move to the other situation where a noid light flashes normally when it should be dim. This could occur if a more sensitive n o id l igh t is
used on a higher voltage/amperage circuit that was weakened enough to cause problems (but not outright broken). A circuit with an actual
problem would thus appear normal.
Let's look at why. A noid light does not come close to consuming as much amperage as an injector solenoid. If there is a partial driver failure
or a minor voltage drop in the injector circuit, there can be adequate amperage to fully operate the noid light BUT NOT ENOUGH TO
OPERATE THE INJECTOR.
If this is not clear, picture a battery with a lot of corrosion on the terminals. Say there is enough corrosion that the starter motor will not
operate; it only clicks. Now imagine turning on the headlights (with the ignition in the RUN position). You find they light normally and are
fully bright. This is the same idea as noid light: There is a problem, but enough amp flow exists to operate the headlights ("noid light"), but not
the starter motor ("injector").
How do you identify and avoid all these situations? By using the correct type of noid light. This requires that you understanding the types of
injector circuits that your noid lights are designed for. There are three. They are:
Systems with a voltage controlled injector driver. Another way to say it: The noid light is designed for a circuit with a "high" resistance
injector (generally 12 ohms or above).
Systems with a current controlled injector driver. Another way to say it: The noid light is designed for a circuit with a low resistance
injector (generally less than 12 ohms) without an external injector resistor.
Systems with a voltage controlled injector driver and an external injector resistor. Another way of saying it: The noid light is designed
for a circuit with a low resistance injector (generally less than 12 ohms) and an external injector resistor.
If you are not sure which type of circuit your noid light is designed for, plug it into a known good car and check out the results. If it flashes
normally during cranking, determine the circuit type by finding out injector resistance and if an external injector resistor is used. You now
know enough to identify the type of injector circuit. Label the noid light appropriately.
Next time you need to use a noid light for diagnosis, determine what type of injector circuit you are dealing with and select the appropriate
noid light.
Of course, if you suspect a no-pulse condition you could plug in any one whose connector fit without fear of misdiagnosis. This is because it is
unimportant if the flashing light is dim or bright. It is only important that it flashes.
In any cases of doubt regarding the use of a noid light, a lab scope will overcome all inherent weaknesses.
OVERVIEW OF DVOM
A DVOM is typically used to check injector resistance and available voltage at the injector. Some techs also use it check injector on-time
either with a built-in feature or by using the dwell/duty function.
There are situations where the DVOM performs these checks dependably, and other situations where it can deceive you. It is important to be
aware of these strengths and weaknesses. We will cover the topics above in the following text.
Checking Injector Resistance
If a short in an injector coil winding is constant, an ohmmeter will accurately identify the lower resistance. The same is true with an open
winding. Unfortunately, an intermittent short is an exception. A faulty injector with an intermittent short will show "good" if the ohmmeter
cannot force the short to occur during testing.
Alcohol in fuel typically causes an intermittent short, happening only when the injector coil is hot and loaded by a current high e n o u gh t o
jump the air gap between two bare windings or to break down any oxides that may have formed between them.
When you measure resistance with an ohmmeter, you are only applying a small current of a few milliamps. This is nowhere near enough to
load the coil sufficiently to detect most problems. As a result, most resistance checks identify intermittently shorted injectors as being normal.
There are two methods to get around this limitation. The first is to purchase an tool that checks injector coil windings under full load. The
Kent-Moore J-39021 is such a tool, though there are others. The Kent-Moore costs around $240 at the time of this writing and works on many
different manufacturer's systems.
The second method is to use a lab scope. Remember, a lab scope allows you to see the regular operation of a circuit in real time. If an injector
is having an short or intermittent short, the lab scope will show it.
Checking Available Voltage At the Injector
Verifying a fuel injector has the proper voltage to operate correctly is good diagnostic technique. Finding an open circuit on the feed circuit
like a broken wire or connector is an accurate check with a DVOM. Unfortunately, finding an intermittent or excessive resistance problem with
a DVOM is unreliable.
Let's explore this drawback. Remember that a voltage drop due to excessive resistance will only occur when a circuit is operating? Since the
injector circuit is only operating for a few milliseconds at a time, a DVOM will only see a potential fault for a few milliseconds. The remaining
90+% of the time the unloaded injector circuit will show normal battery voltage. NOTE:Som e noid lights can m eet both the second and third categories sim ultaneously.
Page 2 of 19 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Waveforms - Injector Pattern Tutorial
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 306 of 454

Back To Article
1991 GENERAL SERVICING
A/C Com pressor Refrigerant Oil Checking
ISOLATING COMPRESSOR
1. Connect service gauge set to the compressor service valves and open compressor valves slightly (turn in clockwise). Start engine and
operate air conditioning. Slowly turn compressor suction valve clockwise toward closed (front-seated) position.
2. When suction pressure is reduced to zero or less, turn off engine and compressor and quickly turn suction valve stem in to full front-
seated position. Suction pressure should be slightly above zero. Turn discharge valve into front-seated position.
3. To check oil level, slowly open compressor crankcase plug to relieve any remaining pressure. After oil level is corrected, cap service
gauge ports on both valves. Back-seat suction service valve to allow refrigerant to enter compressor. Open discharge valve halfway.
4. Loosen discharge service valve cap, allowing refrigerant pressure to force air out of compressor. Back-seat service valve and tighten cap.
Compressor is now ready for operation.
REFRIGERANT OIL
Only new, pure, moisture-free refrigerant oil should be used in the air conditioning system. This oil is highly refined and dehydrated to a point
where moisture content is less than 10 parts per million. The oil container must be tightly closed at all times when not in use, or moisture will
be absorbed into the refrigerant oil from the air.
SERVICING PRECAUTIONS
DISCHARGING SYSTEM PRECAUTIONS
If compressor has stem-type service valves, it can be isolated and removed without discharging entire system. See ISOLATING
COMPRESSOR at the beginning of this article. Otherwise, discharge system completely before loosening any fittings.
DISCONNECTING LINES & FITTINGS TEST
After system is discharged, carefully clean area around all fittings to be opened. Always use 2 wrenches when tightening or loosening fittings
to avoid twisting or distorting lines. Cap or plug all openings as soon as lines are removed. DO NOT remove caps until immediately before
connections are made. This will keep entry of air and moisture to a minimum.
CONNECTING LINES AND FITTINGS
A new gasket or "O" ring should be used in all instances when connecting lines or fittings. Dip "O" ring in new refrigerant oil and ensure it is
not twisted during installation. Always use 2 wrenches to prevent damage to lines and fittings.
PLACING SYSTEM IN OPERATION
After component service or replacement has been completed and all connections have been made, evacuate system thoroughly with a vacuum
pump. Charge system with proper amount of refrigerant and perform a leak test. See REFRIGERANT OIL & R-12 SPECIFICATIONS chart in
this section for system capacities. Be sure to check all fittings that have been opened. After system has been leak tested, make a system
performance check.
ATSUGI ROTARY VANE DRAIN & REFILL
1. Before checking and adjusting oil level, operate compressor at engine idling speed, with controls set for maximum cooling and high
blower speed, for 20 to 30 minutes to return oil to compressor.
2. Stop engine, discharge refrigerant and remove compressor from vehicle. See SERVICING PRECAUTIONS at beginning of article. Drain
compressor oil from compressor discharge port and measure the amount. Oil is sometimes hard to drain when compressor is cool.
Remove oil while compressor is warm.
3. If the amount drained is less than 3 ounces, conduct leak tests at system connections, and if necessary, repair or replace faulty parts.
Check purity of oil and adjust oil level as follows.
4. If amount drained was above 3 ounces, oil level is right. Pour in same amount as was drained. If amount drained was below 3 ounces,
pour in 3 ounces of new refrigerant oil.
BOSCH 6-CYL DRAIN & REFILL
1. Before checking and adjusting oil level, operate compressor at engine idling speed, with controls set for maximum cooling and high
blower speed, for 20 to 30 minutes to return oil to compressor.
2. Stop engine and discharge refrigerant. Remove refrigerant oil level inspection plug on side of compressor. Oil should be at lower lip of
threaded hole. Add necessary new refrigerant oil (if low). Replace inspection plug and tighten to 10-12 ft. lbs. (14-16 N.m). NOTE:Only com pressors with stem -type service valves can be isolated.
NOTE:Recent findings by the EPA indicate that refrigerant is harm ful to the earth's protective Ozone layer.
When discharging refrigerant, DO NOT allow refrigerant to enter the atm osphere. If available, use
refrigerant recovery/recycle system s when discharging system . Always follow m anufacturer's
instructions.
NOTE:Air conditioning system s will not norm ally need addition of refrigerant oil unless definite oil loss has
occurred due to ruptured lines, leaking com pressor seals, com pressor overhaul or com ponent
replacem ent.
Page 1 of 4 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - 1991 GENERAL SERVICING A/C Compressor Refrigerant Oil Checking
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 307 of 454

CALSONIC V5 5-CYLINDER
1. Before checking and adjusting oil level, operate compressor at 1000-1500 engine RPM, and set controls at maximum cooling and
blowing speed for 20-30 minutes to return oil to compressor.
2. Stop engine. Discharge refrigerant and remove compressor from vehicle. See SERVICING PRECAUTIONS at the beginning of this
article. Drain compressor oil from compressor discharge port and measure oil amount. Oil may be hard to drain if compressor is cool.
Drain oil while compressor is warm.
3. If amount drained is less than 3.2 ounces, conduct leak tests at system connections. Repair or replace faulty parts as necessary. Check
purity of oil and oil level as follows.
4. If amount drained is more than 3.2 ounces, oil level is okay; fill with same amount drained using new oil. If amount drained is less than
3.2 ounces, pour in 3.2 ounces of new refrigerant oil.
DIESEL KIKI ROTARY VANE DRAIN & REFILL
1. Before checking and adjusting oil level, operate compressor at engine idling speed, with controls set for maximum cooling and high
blower speed, for 20 to 30 minutes to return oil to compressor.
2. Stop engine, discharge refrigerant and remove compressor from vehicle. See SERVICING PRECAUTIONS at the beginning of this
article. Drain compressor oil from compressor discharge port and measure the amount. Oil is sometimes hard to drain when compressor
is cool. Remove oil while compressor is warm.
3. If the amount is less than 2.4 ounces, conduct leak tests at system connections, and if necessary, repair or replace faulty parts. Check
purity of oil and adjust oil level as follows.
4. If amount drained was above 2.4 ounces, oil level is right. Pour in same amount as was drained. If amount drained was below 2.4
ounces, pour in 2.4 ounces of new refrigerant oil.
DIESEL KIKI 6-CYL DRAIN & REFILL
1. Before checking and adjusting oil level, operate compressor at engine idling speed, with controls set for maximum cooling and high
blower speed, for 20 to 30 minutes to return oil to compressor.
2. Stop engine, discharge refrigerant and remove compressor from vehicle. See SERVICING PRECAUTIONS at the beginning of this
article. Remove oil drain plug and drain oil. Measure amount of oil drained. Install drain plug with new "O" ring.
3. If amount drained was more than 2 ounces (4.4 ounces for Infinity), refill with same amount of new oil. If amount drained was less than
2 ounces (4.4 ounces for Infinity), refill with 2 ounces (4.4 ounces for Infinity). Install filler plug and recharge system.
FORD FX-15 6-CYLINDER DRAIN & REFILL
1. Slowly discharge system. Remove A/C compressor. Drain compressor oil from suction and discharge ports. Measure amount drained and
discard oil.
2. If amount drained from removed (old) compressor is between 3 and 5 ounces, add drained amount of new SUNINSO 5GS refrigerant oil
into the NEW compressor through suction port.
3. If amount drained is less than 3 ounces, add 3 ounces to the NEW compressor. If amount drained is more than 5 ounces, add 5 ounces.
Use new "O" rings on refrigerant lines. Install A/C compressor. Evacuate and recharge system. Perform leak test.
HARRISON 4-CYL DRAIN & REFILL
The Harrison 4-cyl compressor is charged (new) with 6 ounces of refrigerant oil. Because compressor does not have an oil sump, it should not
have to be removed for oil measurement (it retains very little oil). Note the following situations for checking and adding oil to this compressor.
NO OIL LEAK; REPLACING COMPONENTS
If only the compressor is to be replaced, remove, drain oil, measure and reinstall an equal amount of new oil. If evaporator is being replaced,
add 3 ounces of new oil. If condenser is being replaced, add one ounce.
LOSS OF REFRIGERANT OVER EXTENDED PERIOD
When a loss of refrigerant has occurred over an extended period of time and a component is being replaced to correct the leak, add an
appropriate amount of refrigerant oil to the component.
SIGNS OF EXCESSIVE OIL LEAKAGE
If system has lost excessive oil, remove accumulator. Drain and measure oil. If more than 3 ounces is measured, replace the same amount of
new oil as was drained. If less than 3 ounces is measured, add 3 ounces of new oil. Add and additional 2 ounces of new oil to compensate for
that lost by replacing the accumulator (held in desiccant).
HARRISON V5 5-CYLINDER DRAIN & REFILL
1. If system is operable, run for several minutes to stabilize system before performing repairs. Turn off engine. Discharge system and
remove compressor. See SERVICING PRECAUTIONS at the beginning of this article. Remove drain plug. Drain and measure oil. NOTE:Replacem ent FX-15 com pressors contain 7 ounces of refrigerant oil. Prior to installing com pressor,
drain refrigerant oil and determ ine proper am ount of refrigerant oil to be added.
NOTE:T he Harrison com pressor DOES NOT have an oil sum p. It's crucial that the com pressor rem ains well
oiled. It takes very little tim e to destroy this com pressor if it runs dry.
NOTE:If the exact oil charge is in doubt, drain and flush system . Add a new 6-ounce charge of refrigerant oil to
the system .
Page 2 of 4 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - 1991 GENERAL SERVICING A/C Compressor Refrigerant Oil Checking
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 308 of 454

2. If more than one ounce is drained, add same amount. If less than one ounce is drained, add 2 ounces of new refrigerant oil to
compressor.
3. If A/C components are replaced, add refrigerant oil to system. Add one ounce if condenser is replaced. Add 3.5 ounces if accumu l at o r is
replaced.
4. When replacing a component which has caused a large refrigerant leak, add 3 ounces of new oil plus the required amount for the part
being replaced. Add oil directly to part being replaced if possible. If oil can not be easily added to part, add oil to accumulator.
HITACHI 5-CYL DRAIN & REFILL
1. Before checking and adjusting oil level, operate compressor at 1000-1500 engine RPM, and set controls at maximum cooling and high
blowing speed for about 10 minutes to return oil to compressor.
2. Stop engine. Discharge refrigerant and remove compressor from vehicle. See SERVICING PRECAUTIONS at the beginning of this
article. Drain oil from compressor through suction port. Measure amount of oil drained.
3. If amount drained is more than 2.4 ounces, fill with same amount using new oil. If amount drained is less than 2.4 ounces, fill with 2.4
ounces. Install compressor and recharge.
4. If A/C components are replaced. add refrigerant oil to system. Add 1.7 ounces if condenser is replaced. Add 2.4 ounces if evaporator is
replaced. oil does not need to be added if receiver-drier is replaced.
HITACHI 6-CYL DRAIN & REFILL
1. Before checking and adjusting oil level, operate compressor at engine idling speed, with controls set for maximum cooling and high
blower speed, for 10 minutes to return oil to compressor.
2. Stop engine, discharge refrigerant and remove compressor from vehicle. See SERVICING PRECAUTIONS at the beginning of this
article. Drain oil from compressor suction port. Measure amount of oil drained. If amount drained was more than 2.4 ounces, refill with
same amount of new oil. If amount drained was less than 2.4 ounces, refill with 2.4 ounces. Install compressor and recharge.
MATSUSHITA ROTARY VANE DRAIN & REFILL
Discharge system. Remove compressor from vehicle. Drain oil from compressor through inlet and outlet holes. Refill compressor with 3.4-4.7
ounces of oil through suction port. When replacing evaporator, add 2 ounces. When replacing other A/C components, add 1.4 ounces per
component replaced.
NIPPONDENSO ROTARY VANE DRAIN & REFILL
1. Before checking and adjusting oil level, operate compressor at engine idle speed, and set controls at maximum cooling and high blowing
speed for 20-30 minutes to return oil to compressor.
2. Stop engine. Discharge refrigerant and remove compressor from vehicle. See SERVICING PRECAUTIONS at the beginning of this
article. Drain compressor oil through compressor intake and discharge ports. Measure amount drained. Oil may be hard to drain if
compressor cool. Drain compressor while compressor is warm.
3. If amount drained is less than 2.4 ounces, conduct leak tests at system connections. If necessary, repair or replace faulty parts. Check
purity of oil level and adjust oil level as follows.
4. If amount drained is more than 2.4 ounces, oil level is okay; fill with same amount drained using new oil. If amount drained is less than
2.4 ounces, pour 2.4 ounces of new refrigerant oil.
5. When replacing condenser, add one ounce. when replacing other A/C components, add .33 ounce per container replaced.
NIPPONDENSO 6 & 10-CYL DRAIN & REFILL
When inspecting system for oil loss, look for signs of leaking (shiny, wet spots on components or underside of hood). If oil leak is noted or
component replacement is required, use the following procedure as indicated:
NO OIL LEAK
Discharge system and change components as necessary. See SERVICING PRECAUTIONS at the beginning of this article. Add refrigerant oil
to components as necessary.
OIL LEAK
1. Slowly discharge system. Repair or replace faulty components. If equipped with a drain plug, remove plug, drain and discard oil. If not
equipped with a drain plug, remove compressor from vehicle and pour oil out suction and discharge ports.
2. Replace drain plug (if equipped). Add 1.5 ounces of new refrigerant oil through suction port. Use new gaskets or "O" rings when
replacing suction and discharge lines.
COMPRESSOR FAILURE OR SYSTEM CONTAMINATED
If either situation exists, discharge system and remove compressor, receiver-drier and expansion valve. Clean expansion valve screen. Flush
entire system. Install new compressor and receiver-drier. New compressors contain correct amount of oil. If installing overhauled compressor,
add 1.5 ounces of new refrigerant oil through suction port.
PANASONIC ROTARY VANE DRAIN & REFILL
1. Before checking and adjusting oil level, operate compressor at 1000-1500 engine RPM, and set controls at maximum cooling and high
blowing speed for about 10 minutes to return oil to compressor.
2. Stop engine. Discharge refrigerant and remove compressor from vehicle. See SERVICING PRECAUTIONS at the beginning of this NOTE:If oil drained contains m etal chips or other debris, replace receiver-drier. Flush out system before
evacuating and recharging.
Page 3 of 4 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - 1991 GENERAL SERVICING A/C Compressor Refrigerant Oil Checking
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 309 of 454
article. Drain oil from compressor through suction and discharge ports. Measure amount of oil drained. If amount drained is more than
2.4 ounces, fill with same amount using new oil. If amount drained is less than 2.4 ounces, fill with 2.4 ounces. Install compressor and
recharge.
3. If A/C components are replaced, add refrigerant oil to system. Add 1.4 ounces if condenser is replaced. Add 2 ounces if the evaporator
is replaced. Oil does not need to be added if receiver-drier is replaced.
SANDEN SCROLL DRAIN & REFILL
Discharge system. Remove compressor from vehicle. Drain oil from compressor through inlet and outlet holes. Refill compressor with 2.8
ounces of oil through suction port. When replacing condenser, add .5 ounce. When replacing evaporator, add 1.7 ounces. When replacing
other A/C components, add .5 ounce per component replaced.
SANDEN 5-CYL DRAIN & REFILL
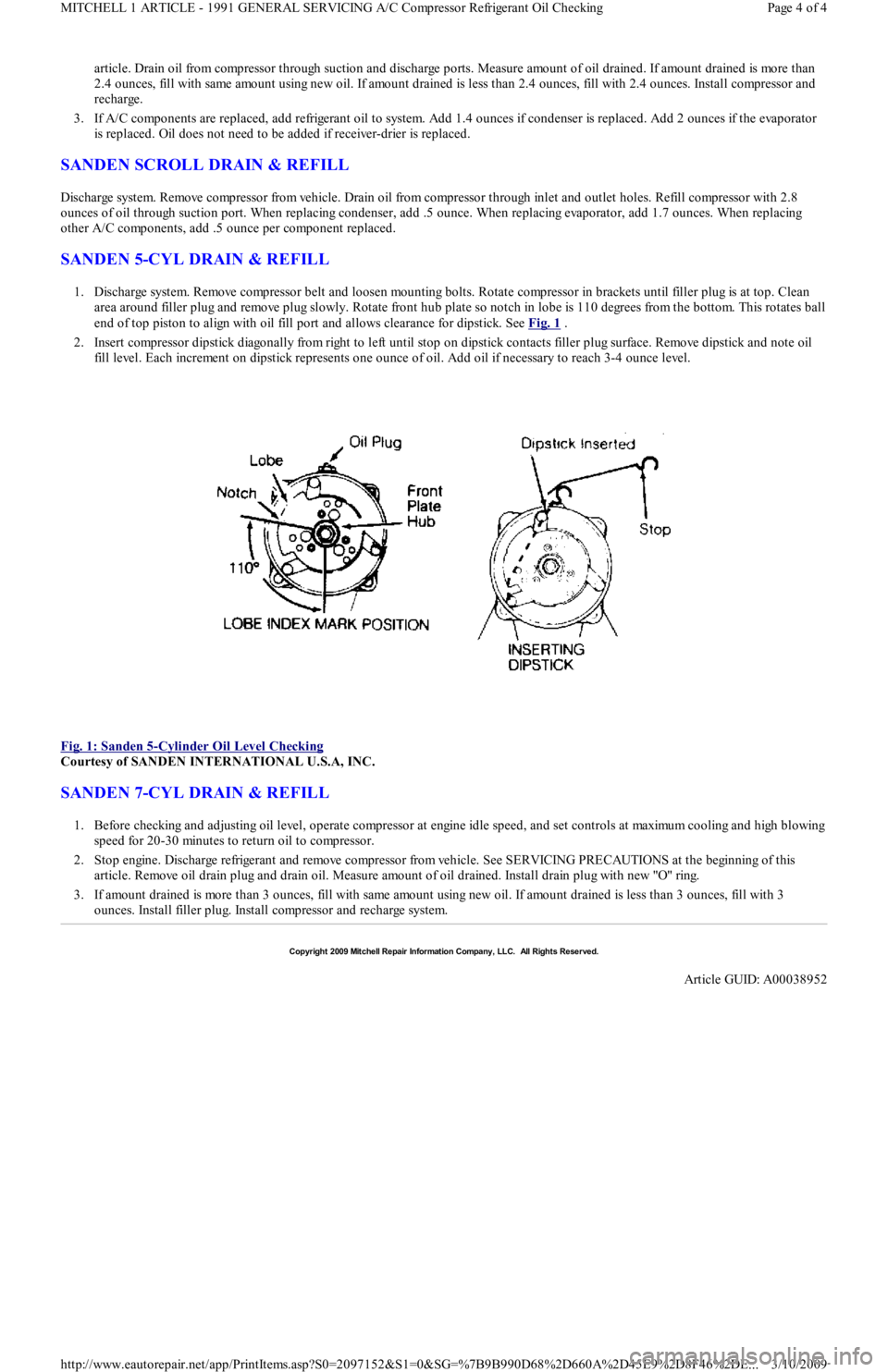
1. Discharge system. Remove compressor belt and loosen mounting bolts. Rotate compressor in brackets until filler plug is at top. Clean
area around filler plug and remove plug slowly. Rotate front hub plate so notch in lobe is 110 degrees from the bottom. This rotates ball
end of top piston to align with oil fill port and allows clearance for dipstick. See Fig. 1
.
2. Insert compressor dipstick diagonally from right to left until stop on dipstick contacts filler plug surface. Remove dipstick and note oil
fill level. Each increment on dipstick represents one ounce of oil. Add oil if necessary to reach 3-4 ounce level.
Fig. 1: Sanden 5
-Cylinder Oil Level Checking
Courtesy of SANDEN INTERNATIONAL U.S.A, INC.
SANDEN 7-CYL DRAIN & REFILL
1. Before checking and adjusting oil level, operate compressor at engine idle speed, and set controls at maximum cooling and high blowing
speed for 20-30 minutes to return oil to compressor.
2. Stop engine. Discharge refrigerant and remove compressor from vehicle. See SERVICING PRECAUTIONS at the beginning of this
article. Remove oil drain plug and drain oil. Measure amount of oil drained. Install drain plug with new "O" ring.
3. If amount drained is more than 3 ounces, fill with same amount using new oil. If amount drained is less than 3 ounces, fill with 3
ounces. Install filler plug. Install compressor and recharge system.
Copyr ight 2009 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Article GUID: A00038952
Page 4 of 4 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - 1991 GENERAL SERVICING A/C Compressor Refrigerant Oil Checking
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 326 of 454
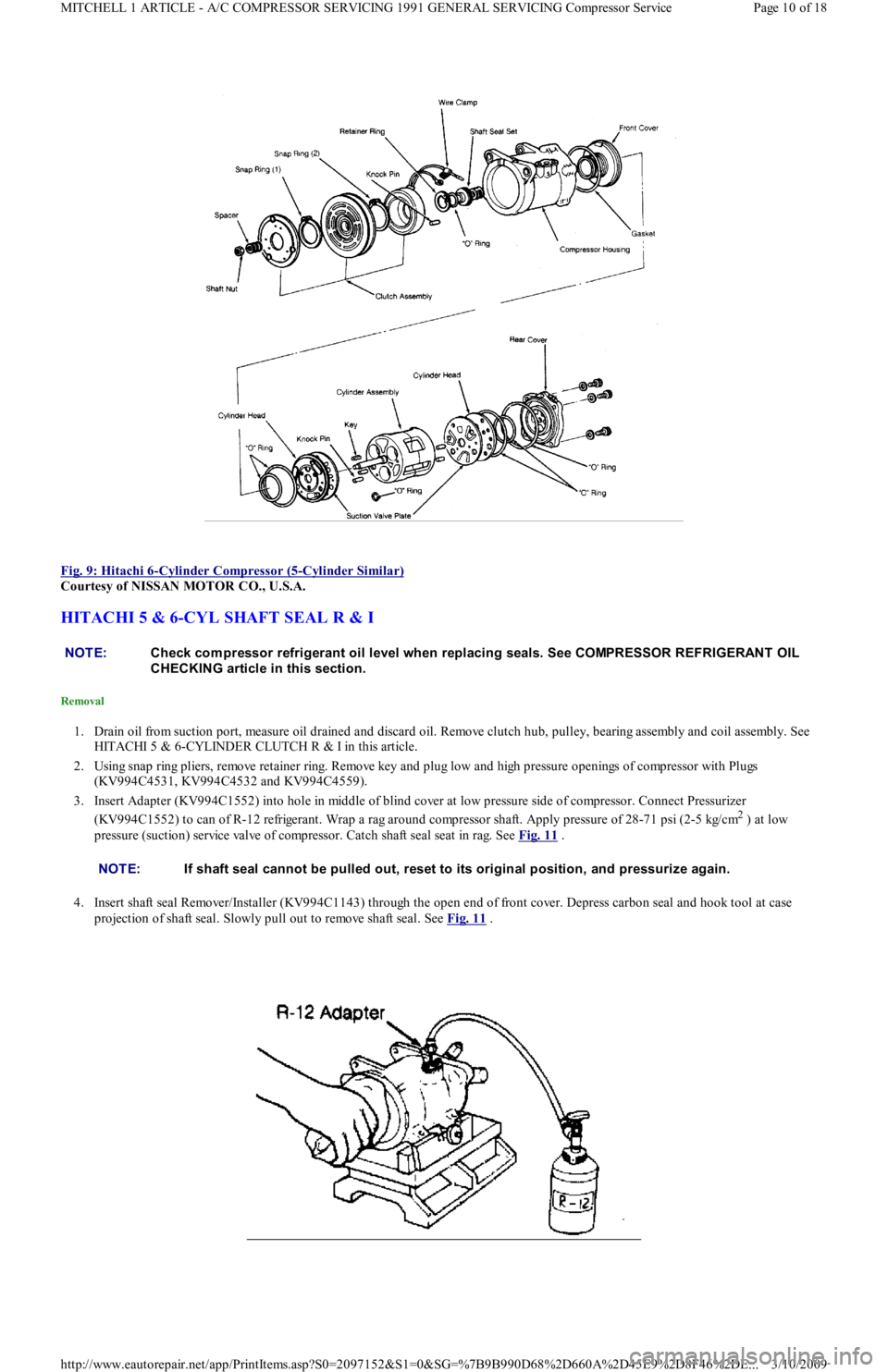
Fig. 9: Hitachi 6
-Cylinder Compressor (5-Cylinder Similar)
Courtesy of NISSAN MOTOR CO., U.S.A.
HITACHI 5 & 6-CYL SHAFT SEAL R & I
Removal
1. Drain oil from suction port, measure oil drained and discard oil. Remove clutch hub, pulley, bearing assembly and coil assembly. See
HITACHI 5 & 6-CYLINDER CLUTCH R & I in this article.
2. Using snap ring pliers, remove retainer ring. Remove key and plug low and high pressure openings of compressor with Plugs
(KV994C4531, KV994C4532 and KV994C4559).
3. Insert Adapter (KV994C1552) into hole in middle of blind cover at low pressure side of compressor. Connect Pressurizer
(KV994C1552) to can of R-12 refrigerant. Wrap a rag around compressor shaft. Apply pressure of 28-71 psi (2-5 kg/cm
2 ) at low
pressure (suction) service valve of compressor. Catch shaft seal seat in rag. See Fig. 11
.
4. Insert shaft seal Remover/Installer (KV994C1143) through the open end of front cover. Depress carbon seal and hook tool at case
projection of shaft seal. Slowly pull out to remove shaft seal. See Fig. 11
.
NOTE:Check com pressor refrigerant oil level when replacing seals. See COMPRESSOR REFRIGERANT OIL
CHECKING article in this section.
NOTE:If shaft seal cannot be pulled out, reset to its original position, and pressurize again.
Page 10 of 18 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - A/C COMPRESSOR SERVICING 1991 GENERAL SERVICING Compressor Service
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 329 of 454

Courtesy of MAZDA MOTORS CO., U.S.A.
NIPPONDENSO 6 & 10-CYL CLUTCH R & I
Removal
1. Remove A/C compressor. Remove pressure plate shaft bolt using socket wrench and Clutch Stopper (07112-76060). Install Clutch
Remover (07112-66040) on pressure plate. Using clutch stopper and socket wrench, rotate clutch remover to remove pressure plate.
2. Remove shims from pressure plate. Remove snap ring from compressor. Tap rotor off shaft with plastic hammer. Disconnect stator wire
from housing. Remove snap ring from inside stator. Remove stator. See Fig. 12
.
Installation
To install, reverse removal procedure. Ensure snap rings are installed with beveled side up. tighten shaft bolt to 10 ft. lbs. 14 N.m). Ensure
clutch clearance is .014-.026" (.36-66 mm). adjust clearance by adding or subtracting shims as necessary.
NIPPONDENSO 6 & 10-CYL SHAFT SEAL R & I
Removal
1. Hold clutch hub stationary and remove center nut. Screw remover into center of hub. Turn center bolt to remove pressure plate.
2. Remove shims from shaft. Remove snap ring from inside of pulley. Tap pulley off of shaft with plastic mallet. Be careful not to distort
pulley while removing.
3. Disconnect clutch coil wires from compressor housing. remove snap ring inside coil and lift coil off compressor. Pry dust seal out from
around compressor shaft (if equipped).
4. Place shaft key remover on shaft and turn to remove key. Remove drain plug (if equipped). Remove service valves-to-compressor body
bolts. Remove valves. Discard "O" rings. Drain oil out of compressor.
5. Remove 6 through bolts from front head of compressor and discard washers. Tap head loose from compressor; be careful not to scratch
sealing surfaces. remove snap ring (if equipped) from front housing. Press seal plate out. Remove seal from shaft. See Fig. 14
.
Installation
1. Lubricate shaft seal with clean refrigerant oil and place on compressor shaft. Lubricate seal plate and "O" ring (if equipped) and install
in front housing. Install snap ring (if equipped).
2. Place front housing on compressor body. Install through bolts with new washers. Tighten bolts evenly and alternately to 18 ft. lbs. (24
N.m). Install shaft key using installer and plastic mallet. Insert dust seal into front of compressor.
3. Install drain plug with new gasket. Add correct amount of refrigerant oil to compressor. If service valves were removed, coat n ew "O"
rings with refrigerant oil and install service valves.
4. Place clutch coil on compressor and install snap ring. Install shims on shaft to adjust pressure plate-to-rotor clearance to .016-
.028" (.41-.71 mm). Tighten shaft nut to 12 ft. lbs. (16 N.m). CAUTION: DO NOT dam age pulley when tapping on rotor.
NOTE:Check com pressor refrigerant oil level when replacing seals. See COMPRESSOR OIL CHECKING article
in the AIR CONDIT IONING & HEAT section.
Page 13 of 18 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - A/C COMPRESSOR SERVICING 1991 GENERAL SERVICING Compressor Service
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 376 of 454
the WHEEL ALIGNMENT section.
OVERHAUL
STEERING GEAR
Disassembly
1. With steering gear removed from vehicle, place steering gear in a soft-jawed vise. Mark threaded portion of tie rod for reassembly.
Remove tie rod ends. Remove tie rod boots. Remove lock pins from both ends of rack. See Fig. 1
.
2. Remove tie rod ball socket from end of rack. Remove both tie rods. Remove lock nut from yoke plug. Remove yoke plug, spring and
yoke support. Use a small screwdriver to remove pinion oil seal from pinion shaft. Remove pinion bearing snap ring.
3. Remove pinion and bearing assembly. If necessary use Valve Body Puller (T78P-3504-B) to remove pinion and bearing assembly.
Remove rack from pinion side of housing. If lower pinion bearing needs replacing, use Blind Hole Bearing Puller (D80L-100-L) and
Slide Hammer (T50T-100-A) to remove.
4. Press bushing lock tabs into the 3 slots located at end of rack housing. Use Blind Hole Bearing Puller (D80L-100-L), to remove rack
support bushing from right end of rack housing.
Inspection
1. Check rubber boots, ball bearings and tooth surface of rack for wear or damage. Using a dial indicator and "V" blocks, check rack for
straightness. Maximum allowable runout is 0.012" (0.3 mm). If rack support bushings are worn, use a screwdriver to release the tab lock
on the side opposite the pinion. Use blind hole Bearing Puller (D80L-100R) with slide hammer to remove bushing.
2. Check tie rod ball joints for smooth operation. Replace parts as necessary. Check sliding surface of rack support and gear housing for
cracks or damage. Check rack bushing for excessive wear. Replace entire gear housing assembly if any of these parts are worn or
damaged.
Reassembly
1. Apply lithium grease to ball bearing, roller bearing, inside of gear housing, lip of oil seal, sliding surface and back of rack support,
sliding surface of rack bushing, rack pinion teeth and ball joints. Install rack support bushing into right end of rack housing. Ensure lock
tabs engage with slots in housing.
2. If previously removed, install a new lower pinion bearing using a bushing installer or a piece of wooden dowel stock. Carefully insert
non-toothed side of rack into left end of rack housing, with rack teeth facing pinion bore. Position rack in housing so rack protrudes
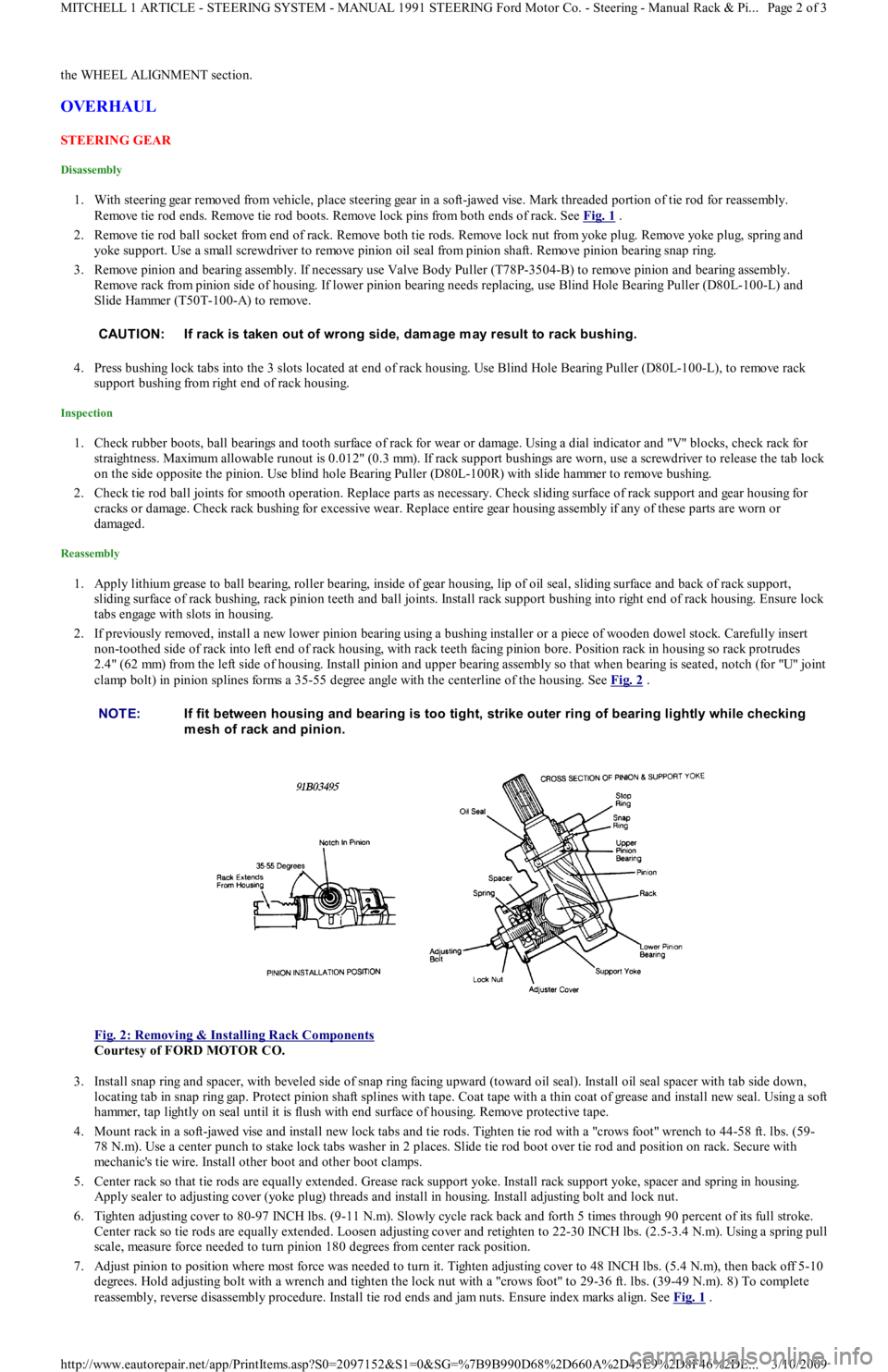
2.4" (62 mm) from the left side of housing. Install pinion and upper bearing assembly so that when bearing is seated, notch (for "U" joint
clamp bolt) in pinion splines forms a 35-55 degree angle with the centerline of the housing. See Fig. 2
.
Fig. 2: Removing & Installing Rack Components
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
3. Install snap ring and spacer, with beveled side of snap ring facing upward (toward oil seal). Install oil seal spacer with tab side down,
locating tab in snap ring gap. Protect pinion shaft splines with tape. Coat tape with a thin coat of grease and install new seal. Using a soft
hammer, tap lightly on seal until it is flush with end surface of housing. Remove protective tape.
4. Mount rack in a soft-jawed vise and install new lock tabs and tie rods. Tighten tie rod with a "crows foot" wrench to 44-58 ft. lbs. (59-
78 N.m). Use a center punch to stake lock tabs washer in 2 places. Slide tie rod boot over tie rod and position on rack. Secure with
mechanic's tie wire. Install other boot and other boot clamps.
5. Center rack so that tie rods are equally extended. Grease rack support yoke. Install rack support yoke, spacer and spring in housing.
Apply sealer to adjusting cover (yoke plug) threads and install in housing. Install adjusting bolt and lock nut.
6. Tighten adjusting cover to 80-97 INCH lbs. (9-11 N.m). Slowly cycle rack back and forth 5 times through 90 percent of its full stroke.
Center rack so tie rods are equally extended. Loosen adjusting cover and retighten to 22-30 INCH lbs. (2.5-3.4 N.m). Using a spring pull
scale, measure force needed to turn pinion 180 degrees from center rack position.
7. Adjust pinion to position where most force was needed to turn it. Tighten adjusting cover to 48 INCH lbs. (5.4 N.m), then back off 5-10
degrees. Hold adjusting bolt with a wrench and tighten the lock nut with a "crows foot" to 29-36 ft. lbs. (39-49 N.m). 8) To comp l et e
reassembly, reverse disassembly procedure. Install tie rod ends and jam nuts. Ensure index marks align. See Fig. 1
. CAUT ION: If rack is taken out of wrong side, dam age m ay result to rack bushing.
NOTE:If fit between housing and bearing is too tight, strike outer ring of bearing lightly while checking
m esh of rack and pinion.
Page 2 of 3 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - STEERING SYSTEM - MANUAL 1991 STEERING Ford Motor Co. - Steering - Manual Rack & Pi
...
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 392 of 454

WHEEL BEARINGS
Wheel bearing preload is maintained by a selective spacer in the steering knuckle, between the inner and outer hub bearings. For adjustment
procedures and inspection, see WHEEL BEARING under REMOVAL & INSTALLATION.
BALL JOINT CHECKING
Raise and support vehicle until tire is just off ground. Move wheel vertically and check for play. If play is noticed between steering knuckle
and control arm, control arm assembly should be replaced. If play is present but ball joint is okay, wheel bearings should be checked for wear
and replaced if necessary.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
STABILIZER BAR
Removal & Installation (Festiva)
1. Remove stabilizer mounting bracket nuts and brackets. Remove split bushings from stabilizer bar. Remove stabilizer bushing nuts at
lower control arms. Remove rear dished washers and bushings.
2. To loosen stabilizer bar, pull forward from control arms. Remove front bushings and washers. Install control arm bushing washers on
ends of stabilizer and install control arm front bushings. Insert ends of stabilizer bar into control arm bushings and install rear bushings
and washers on stabilizer bar ends.
3. Install retaining nuts finger tight. Install split bushings on stabilizer cross bar with split side forward. Position split bushings next to
White locating marks on bar. Install stabilizer mounting brackets. Tighten all bolts and nuts to specification.
STRUT ASSEMBLY & COIL SPRING
Removal
1. Raise and support front of vehicle so struts are fully extended. Remove front wheels. Remove brake line clip from strut lower mounting
bracket and remove brake line.
2. Remove 2 bolts retaining strut lower bracket to steering knuckle. Working inside engine compartment, remove 2 nuts retaining strut
mounting block in strut tower. Disengage strut lower bracket from steering knuckle and lower strut from vehicle.
Disassembly & Reassembly
1. Using spring compressor, compress spring to unload strut. Pry out mounting block cap and remove strut upper nut and lock washer.
2. Remove strut mounting block and spacer plate. Remove washer, bearing seal and bearing from strut rod. Remove spring upper seat, seat
insulator and coil spring. Remove jounce bumper and dust shield from strut. Reverse disassembly procedure to install coil spring a n d
reassemble strut.
Installation
1. Position strut, with spacer plate installed, in strut tower with White alignment mark facing outward. Install and tighten nuts on upper
mounting block studs.
2. Install steering knuckle in strut lower bracket. To complete installation, reverse removal procedure. Tighten all bolts and nuts to
specification.
HUB & KNUCKLE ASSEMBLY
Removal
1. Raise and support vehicle. Remove wheel. Straighten staked edge of drive axle lock nut flange. DO NOT damage groove or threads in
end of drive axle. Apply brakes to prevent hub assembly from turning. Remove and discard drive axle lock nut.
2. Remove clip which secures brake hose to strut bracket. Remove cotter pin and tie rod end attaching nut. Using Tie Rod End Separator
(T85M-3395A), remove tie rod end from steering knuckle.
3. Remove brake caliper attaching bolts and remove assembly from steering knuckle. Do not allow caliper to hang by brake hose. Remove
clamp bolt and nut where lower control arm ball joint connects to steering knuckle.
4. Using a pry bar, pull down on lower control arm and release ball joint from steering knuckle. Remove 2 bolts which attach steering
knuckle between flanges of MacPherson strut bracket. Slide hub/knuckle assembly off end of drive axle. If binding is present or drive
hub is rusted to half-shaft, use a hub puller to push axle from drive hub.
Installation
1. Apply a thin coat of SAE 30 weight oil to drive axle splines. Slide steering knuckle/rotor/hub assembly onto drive axle. Stop at area
where uppermost arm of steering knuckle seats into MacPherson strut bracket.
2. To complete installation, reverse removal procedure. Install NEW drive axle lock nut. Tighten all bolts and nuts to specification. Stake
axle lock nut into shaft groove.
WHEEL BEARING NOTE:Inform ation for stabilizer bar rem oval and installation on Capri is not available from m anufacturer.
NOTE:Always use a new drive axle lock nut when servicing drive hub or drive axle.
CAUT ION: DO NOT use a pointed tool to stake nut. If lock nut flange cracks, even slightly, during staking process,
it m ust be replaced.
Page 2 of 5 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - SUSPENSION - FRONT 1991-92 SUSPENSION Front
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 411 of 454
Fig. 3: Identifying Vacuum Diaphragm Rod Gauge
Courtesy of FORD MOTOR CO.
VALVE BODY R & I
Removal & Installation
Disconnect battery ground cable. Raise and support vehicle. Remove front fender splash shield and front splash shield. Drain transaxle fluid.
Unbolt and remove oil pan. Remove 9 valve body bolts. Remove valve body. Ensure care is used not to loose check ball and detent spring. To
install, reverse removal procedure. Fill transaxle with fluid. Check for leaks.
TROUBLESHOOTING
PRELIMINARY INSPECTION
1. Ensure vehicle is thoroughly road tested to verify driver's complaint. Determine if problem occurs during upshift, downshift, coasting or
engagement. If noise is diagnosed, check if noise is affected by RPM, vehicle speed, gear selection or temperature. Ensure vehicle is at
normal operating temperature when checking.
2. Inspect fluid level and condition. Visually inspect for vehicle modifications, electronic add-ons, fluid leaks and/or incorrect linkage
adjustment. See applicable symptom diagnosis.
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
Engine Starts in "D", "2", "1" OR "R", or will not Start in "N" OR "P"
Check ignition and starter circuit. Shift linkage faulty or installed improperly. Park/Neutral switch and/or wiring faulty.
No Movement In Any Gear
Incorrect fluid level. Shift linkage faulty or out of adjustment. Incorrect oil pressure. Manual control valve faulty. Faulty oil pump. Leak in
hydraulic system. Parking linkage improperly adjusted.
No Movement In "D", Okay In Other Gears
Shift linkage faulty, out of adjustment or improperly installed. Incorrect oil pressure. Manual control valve faulty. Faulty one-way clutch.
No Movement In "D", "2" Or "1", Okay In "R"
Incorrect fluid level. Shift linkage faulty, out of adjustment or incorrectly installed. Incorrect oil pressure. Manual control valve faulty. Engine
performance poor or brakes improperly adjusted. Rear clutch faulty. Leak in hydraulic system.
No Movement In "R", Okay In Other Gears
Incorrect fluid level. Shift linkage faulty, out of adjustment or incorrectly installed. Incorrect oil pressure. Manual control valve faulty. Faulty
rear clutch, front clutch or low-reverse brake. Leak in hydraulic system.
Slippage
Page 3 of 26 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - 1988-94 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS Ford ATX Overhaul
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...