wheel bolt torque FORD FIESTA 1989 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1989, Model line: FIESTA, Model: FORD FIESTA 1989Pages: 296, PDF Size: 10.65 MB
Page 4 of 296

Ignition system
Firing order:HCS engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 1-2-4-3 (No 1 cylinder at timing chain end of engine)
All other engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . 1-3-4-2 (No 1 cylinder at timing belt end of engine)
Spark plugs*:
HCS engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . Champion RS9YCC or RS9YC
1.4 and 1.6 litre CVH (carburettor) engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion RC7YCC or RC7YC
1.6 litre CVH (EFi fuel injection) and PTE engines Non-turbo models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . Champion RC7YCC4 or RC7YC4
Turbo models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . Champion C61YC
1.6 and 1.8 litre Zetec engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion RE7YCC
Electrode gap*:
HCS engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 1.0 mm
1.4 litre CVH (carburettor) engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.8 mm
1.4 litre CVH (CFi fuel injection) and PTE engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 mm
1.6 litre CVH (carburettor) engines: With Champion RC7YCC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.8 mmWith Champion RC7YC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.7 mm
1.6 litre CVH (EFi fuel injection) engines: Non-turbo models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 1.0 mm
Turbo models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . 0.7 mm
1.6 and 1.8 litre Zetec engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.3 mm
Spark plug (HT) leads: HCS engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . Champion LS-28
1.4 and 1.6 litre CVH (carburettor) engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion LS-14
1.4 litre CVH (CFi fuel injection) and PTE engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion LS-14
1.6 litre CVH (EFi fuel injection) engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion LS-26
1.6 and 1.8 litre Zetec engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion type not available
Maximum resistance per lead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 000 ohms * Information on spark plug types and electrode gaps is as recommended b\
y Champion Spark Plug. Where alternative types are used, refer to their
manufacturer’s recommendations.
Braking system
Minimum front brake pad lining thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.5 mm
Minimum rear brake shoe lining thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 mm
Tyres
Tyre pressures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . See “Weekly Checks”
Wiper blades
Windscreen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . Champion X-4803Tailgate/rear window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . Champion X-4103
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Auxiliary drivebelt cover fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 6
Auxiliary drivebelt adjustment: Adjusting bolt (sliding arm) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2216
Central (locking) bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 2216
Pinion (adjuster) nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 129
Alternator mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2418
Tensioner pulley centre bolt (HCS engines) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2015
Engine oil drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . 2418
Manual transmission filler/level plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2015
Spark plugs: HCS engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 1813
CVH and PTE engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
2418
Zetec engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 1511
Roadwheel nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 71 to 100 52 to 74
Servicing Specifications1•3
1
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 13 of 296

V-belt and flat “polyvee” type
drivebelt with rack-and-pinion type
adjuster
12Loosen off the alternator mounting bolts
and the adjusting arm mounting bolt. Slacken
the pinion central locking bolt, and turn the
pinion nut as required to take up the tension
of the drivebelt. Hold it at the required setting,
and tighten the central bolt securely to lock
the adjuster arm and set the tension (see
illustrations) .
13 Tighten the alternator mounting and
adjusting arm bolts securely.
14 Refit the auxiliary drivebelt cover (where
applicable) and roadwheel, then lower the
vehicle to the ground.
15 Run the engine for about five minutes,
then recheck the tension.
Flat “polyvee” type drivebelt with
tensioner pulley adjuster (HCS engine
power steering pump drivebelt)
16 Slacken the tensioner pulley centre bolt
then turn the adjuster bolt at the base of the
tensioner pulley bracket, as required, to take
up the tension of the drivebelt. When the belt
deflection is correct, tighten the adjuster
pulley centre retaining bolt.
17 Refit the auxiliary drivebelt cover (where
applicable) and roadwheel, then lower the
vehicle to the ground.
18 Run the engine for about five minutes,
then recheck the tension.
Flat “polyvee” type drivebelt with
automatic adjuster
19 As mentioned above, this type of drivebelt
is tensioned by an automatic tensioner;
regular checks are not required, and manual
“adjustment” is not possible.
20 If you suspect that the drivebelt is slipping
and/or running slack, or that the tensioner is
otherwise faulty, it must be renewed. To do
this, remove the drivebelt as described below,
then unbolt and remove the tensioner. On
fitting the new tensioner, ensure that it is
aligned correctly on its mountings, and
tightened to the specified torque wrench
setting.
Renewal
21 Open the bonnet. Jack up the front right-
hand side of the vehicle, and support it
securely on an axle stand. Remove the
roadwheel, then remove the auxiliary drivebelt
lower cover (where fitted) from inside the
wheel arch.
22 The routing of the drivebelt around the
pulleys is dependent on the drivebelt type,
and on whether power steering is fitted.
Before removing the drivebelt, it’s a good idea
to sketch the belt run around the pulleys; this
will save a lot of frustration when it comes to
refitting. Note that on HCS engines with
power steering, to renew the alternator/
water pump drivebelt it will be necessary to
remove the power steering pump drivebelt
first.
23 If the existing drivebelt is to be refitted,
mark it, or note the maker’s markings on its
flat surface, so that it can be installed the
same way round.
24 To renew a drivebelt with manual
adjustment, slacken the belt tension fully as
described above, according to type. Slip the
belt off the pulleys, then fit the new belt,
ensuring that it is routed correctly. If fitting a
flat “polyvee” type drivebelt, arrange it on the
grooved pulleys so that it is centred in
their grooves, and not overlapping their raised
sides. With the belt in position, adjust the
tension as previously described.
25 To renew the flat, “polyvee” type drivebelt
with automatic adjuster, reach up between
the body and the engine (above the
crankshaft pulley), and apply a spanner to the
hexagon in the centre of the automatic
tensioner’s pulley. Rotate the tensioner pulley
clockwise to release its pressure on the
drivebelt, then slip the drivebelt off the
crankshaft pulley, and release the tensioner
again (see illustration) . Note that on certain
models, a self-cocking tensioner is fitted, and
that this will remain in the released position.
Working from the wheel arch or engine
compartment as necessary, and noting its
routing, slip the drivebelt off the remaining
pulleys and withdraw it.
26 Check all the pulleys, ensuring that their
grooves are clean, and removing all traces of oil and grease. Check that the tensioner
works properly, with strong spring pressure
being felt when its pulley is rotated clockwise,
and a smooth return to the limit of its travel
when released.
27
If the original drivebelt is being refitted,
use the marks or notes made on removal, to
ensure that it is installed to run in the same
direction as it was previously. To fit the
drivebelt, arrange it on the grooved pulleys so
that it is centred in their grooves, and not
overlapping their raised sides, and is routed
correctly. Start at the top, and work down to
finish at the crankshaft pulley; rotate the
tensioner pulley clockwise, slip the drivebelt
onto the crankshaft pulley, then release the
tensioner again.
28 Using a spanner applied to the crankshaft
pulley bolt, rotate the crankshaft through at
least two full turns clockwise to settle the
drivebelt on the pulleys, then check that
the drivebelt is properly installed.
29 Refit the auxiliary drivebelt cover (where
applicable) and roadwheel, then lower the
vehicle to the ground.
5 Underbonnet check for fluid leaks and hose condition
1
General
1High temperatures in the engine
compartment can cause the deterioration of
the rubber and plastic hoses used for engine,
accessory and emissions systems operation.
Periodic inspection should be made for
cracks, loose clamps, material hardening and
leaks.
2 Carefully check the large top and bottom
radiator hoses, along with the other smaller-
diameter cooling system hoses and metal
pipes; do not forget the heater hoses/pipes
which run from the engine to the bulkhead.
Inspect each hose along its entire length,
replacing any that is cracked, swollen or
shows signs of deterioration. Cracks may
become more apparent if the hose is
1•12Every 10 000 miles or 12 months
4.25 Automatic drivebelt tensioner - “polyvee” type drivebelt
Turn tensioner clockwise to release tension4.12b When the tension is correct, hold
the adjuster nut, and tighten the central bolt securely to lock the adjuster arm4.12a Rack-and-pinion type auxiliary drivebelt adjuster
A Adjuster arm
B Pinion (adjuster) nut
C Central (locking) bolt
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 19 of 296

3Check that the roadwheel nuts are tightened
to the specified torque wrench setting.
4 Refit the wheel covers.
16 Door, tailgate and bonnet
check and lubrication
1
1Check that the doors and tailgate/boot lid
close securely. Check that the bonnet safety
catch operates correctly. Check the operation
of the door check straps.
2 Lubricate the hinges, door check straps,
the striker plates and the bonnet catch
sparingly with a little oil or grease.
17 Seat belt check
1
1 Check the seat belts for satisfactory
operation and condition. Inspect the webbing
for fraying and cuts. Check that they retract
smoothly and without binding into their reels.
2 Check that the seat belt mounting bolts are
tight, and if necessary tighten them to the
specified torque wrench settings as given in
Chapter 11.
18 Bodywork, paint and exterior trim check
1
1The best time to carry out this check is after
the car has been washed so that any surface
blemish or scratch will be clearly evident and
not hidden by a film of dirt.
2 Starting at one front corner check the
paintwork all around the car, looking for minor
scratches or more serious dents. Check all
the trim and make sure that it is securely
attached over its entire length.
3 Check the security of all door locks, door
mirrors, badges, bumpers, front grille and
wheel trim. Anything found loose, or in need of
further attention should be done with reference
to the relevant Chapters of this manual.
4 Rectify any problems noticed with the
paintwork or body panels as described in
Chapter 11.
19 Road test
1
Check the operation and
performance of the braking
system
1 Make sure that the vehicle does not pull to
one side when braking, and that the wheels
do not lock prematurely when braking hard.
2 Check that there is no vibration through the
steering when braking. 3
Check that the handbrake operates
correctly, without excessive movement of the
lever, and that it holds the vehicle stationary
on a slope.
4 Test the operation of the brake servo unit
as follows. With the engine switched off,
depress the footbrake four or five times to
exhaust the vacuum, then hold the pedal
depressed. Start the engine, and there should
be a noticeable “give” in the brake pedal as
vacuum builds up. Allow the engine to run for
at least two minutes, and then switch it off. If
the brake pedal is depressed again, it should
be possible to detect a hiss from the servo as
the pedal is depressed. After about four or five
applications, no further hissing should be
heard, and the pedal should feel considerably
firmer.
Steering and suspension
5 Check for any abnormalities in the steering,
suspension, handling or road “feel”.
6 Drive the vehicle, and check that there are
no unusual vibrations or noises.
7 Check that the steering feels positive, with
no excessive sloppiness or roughness, and
check for any suspension noises when
cornering and driving over bumps.
Drivetrain
8 Check the performance of the engine,
transmission and driveshafts.
9 Check that the engine starts correctly, both
when cold and when hot.
10 Listen for any unusual noises from the
engine and transmission.
11 Make sure that the engine runs smoothly
when idling, and that there is no hesitation
when accelerating.
12 On manual transmission models, check
that all gears can be engaged smoothly
without noise, and that the gear lever action is
not abnormally vague or “notchy”.
13 On automatic transmission models, make
sure that the drive seems smooth without
jerks or engine speed “flare-ups”. Check that
all the gear positions can be selected with the
vehicle at rest. If any problems are found, they
should be referred to a Ford dealer.
14 Listen for a metallic clicking sound from
the front of the vehicle, as the vehicle is driven
slowly in a circle with the steering on full-lock.
Carry out this check in both directions. If a
clicking noise is heard, this indicates wear in a
driveshaft joint, in which case renew the joint
if necessary.
Clutch
15 Check that the clutch pedal moves
smoothly and easily through its full travel, and
that the clutch itself functions correctly, with
no trace of slip or drag. If the movement is
uneven or stiff in places, check that the cable
is routed correctly, with no sharp turns.
16 Inspect both ends of the clutch inner
cable, both at the transmission end and inside
the car, for signs of wear and fraying.
Instruments and electrical
equipment
17 Check the operation of all instruments
and electrical equipment.
18 Make sure that all instruments read
correctly, and switch on all electrical equipment
in turn, to check that it functions properly.
20 Automatic transmission fluid level check
1
1The level of the automatic transmission fluid
should be carefully maintained. Low fluid level
can lead to slipping or loss of drive, while
overfilling can cause foaming, loss of fluid and
transmission damage.
2 The transmission fluid level should only be
checked when the transmission is hot (at its
normal operating temperature). If the vehicle
has just been driven over 10 miles (15 miles in
a cold climate), and the fluid temperature is 60
to 70ºC, the transmission is hot.
Caution: If the vehicle has just been driven
for a long time at high speed or in city
traffic in hot weather, or if it has been
pulling a trailer, an accurate fluid level
reading cannot be obtained. In these
circumstances, allow the fluid to cool
down for about 30 minutes.
3 Park the vehicle on level ground, apply the
handbrake, and start the engine. While the
engine is idling, depress the brake pedal and
move the selector lever through all the gear
positions three times, beginning and ending in
“P”.
4 Allow the engine to idle for one minute, then
(with the engine still idling) remove the
dipstick from its tube. Note the condition and
colour of the fluid on the dipstick.
5 Wipe the fluid from the dipstick with a clean
rag, and re-insert it into the filler tube until the
cap seats.
6 Pull the dipstick out again, and note the
fluid level. The level should be between
the “MIN” and “MAX” marks. If the level is
on the “MIN” mark, stop the engine, and add
the specified automatic transmission fluid
through the dipstick tube, using a clean funnel
if necessary. It is important not to introduce
dirt into the transmission when topping-up.
7 Add the fluid a little at a time, and keep
checking the level as previously described
until it is correct. The difference between the
“MIN” and “MAX” marks on the dipstick is
approximately 0.4 litres.
8 The need for regular topping-up of the
transmission fluid indicates a leak, which
should be found and rectified without delay.
9 The condition of the fluid should also be
checked along with the level. If the fluid on the
dipstick is black or a dark reddish-brown
colour, or if it has a burned smell, the fluid
should be changed. If you are in doubt about
the condition of the fluid, purchase some new
fluid, and compare the two for colour and smell.
1•18Every 10 000 miles or 12 months
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 29 of 296

Lubrication
Engine oil type/specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See “Lubricants, fluids and tyre pressures”
Engine oil capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . See “Lubricants, fluids and tyre pressures”
Oil pressure: At idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 0.60 barsAt 2000 rpm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 1.50 bars
Oil pump clearances: Outer rotor-to-body . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 0.14 to 0.26 mm
Inner rotor-to-outer rotor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.051 to 0.127 mm
Rotor endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . 0.025 to 0.06 mm
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Camshaft thrust plate bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 4
Camshaft sprocket bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. 1813
Crankshaft pulley bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . 115 85
Rocker shaft pedestal bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4332
Flywheel bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . 6749
Sump: Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . 7 5
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . 9 7
Stage 3 (with engine warm) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 7
Oil pressure switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . 1410
Cylinder head bolts (may be re-used once only): Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . 3022
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten a further 90º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten a further 90º
Timing chain tensioner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . 8 6
Timing chain cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . 9 7
Crankshaft rear oil seal housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1813
Rocker cover bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . 5 4
Oil pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 1813
Oil pump cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 9 7
Engine mountings: Engine mounting (right-hand):Bolt to body (in wheel arch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 to 58 30 to 43
Nut to body (by suspension strut) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 to 58 30 to 43
Bracket to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54 to 72 40 to 53
Rubber insulator to bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71 to 95 52 to 70
Transmission mounting fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Refer to Chapter 7A or 7B
Note: Refer to Part D of this Chapter for remaining torque wrench settings.
2A•2 HCS engine in-car repair procedures
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
1 General information
How to use this Chapter
This Part of Chapter 2 is devoted to repair
procedures possible while the engine is still
installed in the vehicle, and includes only the
Specifications relevant to those procedures.
Similar information concerning the 1.4 and
1.6 litre CVH and PTE engines, and the 1.6
and 1.8 litre Zetec engines, will be found in
Parts B and C of this Chapter respectively.
Since these procedures are based on the
assumption that the engine is installed in the
vehicle, if the engine has been removed from
the vehicle and mounted on a stand, some
of the preliminary dismantling steps outlined
will not apply. Information concerning engine/transmission
removal and refitting, and engine overhaul, can
be found in Part D of this Chapter, which also
includes the Specifications relevant to those
procedures.
Engine description
The engine is an overhead valve, water-
cooled, four cylinder in-line design,
designated HCS (High Compression Swirl).
The engine is mounted transversely at the
front of the vehicle together with the
transmission to form a combined power unit. The crankshaft is supported in three or five
shell-type main bearings. The connecting rod
big-end bearings are also split shell-type, and
are attached to the pistons by interference-fit
gudgeon pins. Each piston is fitted with two
compression rings and one oil control ring. The camshaft, which runs on bearings
within the cylinder block, is chain-driven from
the crankshaft, and operates the valves via
pushrods and rocker arms. The valves are
each closed by a single valve spring, and
operate in guides integral in the cylinder head. The oil pump is mounted externally on the
crankcase, incorporates a full-flow oil filter,
and is driven by a skew gear on the camshaft.
On carburettor versions, the fuel pump is also
driven from the camshaft, via an eccentric
lobe.
Repair operations possible with
the engine in the car
The following work can be carried out with
the engine in the car:
a) Compression pressure - testing.
b) Cylinder head rocker cover - removal
and refitting.
c) Valve clearances - adjustment.
d) Rocker shaft assembly - removal,
inspection and refitting.
e) Cylinder head - removal and refitting
f) Cylinder head and pistons - decarbonising.
g) Crankshaft pulley - removal and refitting.
h) Crankshaft oil seals - renewal.
i) Timing chain, sprockets and tensioner -
removal, inspection and refitting.
j) Oil filter renewal.
k) Oil pump - removal and refitting.
l) Sump - removal and refitting.
m) Flywheel - removal, inspection and
refitting.
n) Engine/transmission mountings -
inspection and renewal.
Note: It is possible to remove the pistons and
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 32 of 296

8Reassemble in the reverse order of
dismantling. Make sure that the “flat” on the
rear end of the rocker shaft is to the same side
as the rocker arm adjusting screws (closest to
the thermostat end of the cylinder head when
fitted) (see illustration) . This is essential for
the correct lubrication of the cylinder head
components.
9 Refit the rocker shaft assembly. As it is
fitted, ensure that the rocker adjuster screws
engage with their corresponding pushrods.
10 Refit the rocker shaft retaining bolts,
hand-tighten them and then tighten them to
the specified torque wrench setting. As they
are tightened, some of the rocker arms will
apply pressure to the ends of the valve stems,
and some of the rocker pedestals will not
initially be in contact with the cylinder head -
these should pull down as the bolts are
tightened to their specified torque. If for any
reason they do not, avoid the temptation to
overtighten in order to pull them into position;
loosen off the bolts, and check the cause of
the problem. It may be that the rocker adjuster
screws require loosening off in order to allow
the assembly to be tightened down as
required.
11 Adjust the valve clearances as described
in Section 5.
7 Cylinder head -
removal and refitting
3
Removal
Note: The following procedure describes
removal and refitting of the cylinder head
complete with inlet and exhaust manifolds. If
wished, the manifolds may be removed first,
as described in the relevant Part of Chapter 4,
and the cylinder head then removed on its
own.
1 On fuel injection engines, depressurise the
fuel system as described in Chapter 4, Part B.
2 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
3 Refer to Chapter 4A or 4B as applicable
and remove the air cleaner.
4 Refer to Section 4 and remove the rocker
cover. 5
Refer to Chapter 1 and drain the cooling
system.
6 Disconnect the hoses from the thermostat
housing.
7 Disconnect the heater (coolant) hoses from
the inlet manifold and CFi unit, where
applicable.
8 Disconnect the accelerator and choke
cables as applicable (see Chapter 4A or 4B).
9 Disconnect the vacuum and breather hoses
from the carburettor/CFi unit, and inlet
manifold as applicable.
10 Disconnect the fuel feed and return lines
at the carburettor, or at the quick-release
couplings, then unclip the fuel hoses from the
inlet manifold; use rag to soak up any spilt
fuel.
11 Disconnect the HT leads from the spark
plugs and the support bracket. Unscrew and
remove the spark plugs.
12 Disconnect the electrical leads from the
temperature gauge sender, radiator cooling
fan, the engine coolant temperature sender,
and the anti-run-on (anti-dieselling) valve at
the carburettor.
13 Disconnect the remaining wiring multi-
plugs from the engine sensors at the inlet
manifold and from the oxygen sensor (where
fitted) in the exhaust manifold or downpipe.
14 On vehicles equipped with a pulse-air
system, remove the pulse-air piping and filter
assembly as described in Chapter 4E.
15 Chock the rear wheels then jack up the
front of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support” ).
16 Undo the retaining nuts and bolts, and
disconnect the exhaust downpipe from the
manifold. Remove the flange gasket. (Note
that both the gasket and the joint self-locking
nuts must be renewed.) To prevent the
exhaust system from being strained, tie the
downpipe up using strong wire or a length of
cord to support it. Lower the vehicle.
17 Undo the four retaining bolts and lift clear
the rocker gear assembly from the cylinder
head.
18 Lift out the pushrods. Keep them in order
of fitting by labelling them 1 to 8, starting from
the thermostat end of the cylinder head.
Alternatively, push them through a piece of
card in their fitted sequence.
19 Progressively unscrew and loosen off the
cylinder head retaining bolts in the reverse
sequence to that shown for tightening (see
illustration 7.27a). When they are all loosened off, remove the bolts, then lift the
cylinder head clear and remove the gasket. If
it is stuck, tap it upwards using a hammer and
block of wood. Do not try to turn it, as it is
located by dowels; make no attempt
whatsoever to prise it free using a screwdriver
inserted between the block and head faces.
The gasket must always be renewed; it should
be noted that the cylinder head retaining bolts
may be re-used, but only once. They should
be marked accordingly with a punch or paint
mark. If there is any doubt as to how many
times the bolts have been used, they must be
renewed.
20
To dismantle/overhaul the cylinder head,
refer to Part D of this Chapter. It is normal for
the cylinder head to be decarbonised and the
valves to be reground whenever the head is
removed.
Preparation for refitting
21 The mating faces of the cylinder head and
cylinder block must be perfectly clean before
refitting the head. Use a hard plastic or wood
scraper to remove all traces of gasket and
carbon; also clean the piston crowns. Take
particular care during the cleaning operations,
as aluminium alloy is easily damaged. Also,
make sure that the carbon is not allowed to
enter the oil and water passages - this is
particularly important for the lubrication
system, as carbon could block the oil supply
to the engine’s components. Using adhesive
tape and paper, seal the water, oil and bolt
holes in the cylinder block.
22 Check the mating surfaces of the cylinder
block and the cylinder head for nicks, deep
scratches and other damage. If slight, they
may be removed carefully with a file, but if
excessive, machining may be the only
alternative to renewal.
23 If warpage of the cylinder head gasket
surface is suspected, use a straight-edge to
check it for distortion. Refer to Part D of this
Chapter if necessary.
24 Clean the threads of the cylinder head
bolts or fit new ones (as applicable) and clean
out the bolt holes in the block. Screwing a bolt
into an oil-filled hole can (in extreme cases)
cause the block to fracture, due to the
hydraulic pressure.
Refitting
25 Check that the new cylinder head gasket
is the same type as the original, and that the
“TOP” (or “OBEN”) marking is facing
upwards. Locate the new cylinder head
HCS engine in-car repair procedures 2A•5
6.8 Flat on the rocker shaft (arrowed) to
same side as rocker arm adjusting screws
2A
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
Whenever you disconnect
any vacuum lines, coolant or
emissions hoses, wiring
connectors and fuel lines,
always label them clearly, so that they
can be correctly reassembled. Masking
tape and/or a touch-up paint applicator
work well for marking items. Take
instant photos, or sketch the locations
of components and brackets.
To prevent carbon entering
the gap between the pistons
and bores, smear a little
grease in the gap. After
cleaning each piston, use a small brush
to remove all traces of grease and
carbon from the gap, then wipe away
the remainder with a clean rag.
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 33 of 296

gasket onto the top face of the cylinder block
and over the dowels. Ensure that it is correctly
aligned with the coolant passages and
oilways (see illustration) .
26 Lower the cylinder head carefully into
position, then insert the retaining bolts and
hand-tighten them.
27 Tightening of the cylinder head bolts must
done in three stages, and in the correct
sequence (see illustration) . First tighten all of
the bolts in the sequence shown to the
Stage 1 torque setting (see illustration).
When all of the bolts are tightened to the
Stage 1 setting, further tighten each bolt (in
sequence) through the Stage 2 specified
angle of rotation. When the second stage
tightening is completed on all of the bolts,
further tighten them to the Stage 3 angle
setting (in sequence) to complete. Where
possible, use an angular torque setting gauge
attachment tool for accurate tightening of
stages two and three (see illustration).
28 Lubricate the pushrods with clean engine
oil, and then insert them into their original
locations in the engine.
29 Refit the rocker shaft assembly. As it is
fitted, ensure that the rocker adjuster screws
engage with their corresponding pushrods.
30 Refit the rocker shaft retaining bolts,
hand-tighten them and then tighten them
to the specified torque wrench setting. As
they are tightened, some of the rocker arms
will apply pressure to the ends of the valve
stems, and some of the rocker pedestals will
not initially be in contact with the cylinder head - these should pull down as the bolts are
tightened. If for any reason they do not, avoid
the temptation to overtighten in order to pull
them into position; loosen off the bolts, and
check the cause of the problem. It may be
that the rocker adjuster screws require
loosening off in order to allow the assembly to
be tightened down as required.
31
Adjust the valve clearances as described
in Section 5.
32 Refit the rocker cover as described in
Section 4.
33 The remainder of the refitting procedure is
a reversal of the removal process. Tighten all
fastenings to their specified torque setting
(where given). Refer to the appropriate Parts
of Chapter 4 for details on reconnecting the
fuel and exhaust system components. Ensure
that all coolant, fuel, vacuum and electrical
connections are securely made.
34 On completion, refill the cooling system
and top-up the engine oil (see Chapter 1 and
“Weekly Checks” ). When the engine is
restarted, check for any sign of fuel, oil and/or
coolant leakages from the various cylinder
head joints.
8 Crankshaft pulley -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
2 Chock the rear wheels then jack up the
front of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support” ). Remove
the right-hand front roadwheel.
3 Remove the auxiliary drivebelt as described
in Chapter 1.
4 Loosen off the crankshaft pulley retaining
bolt. To prevent the crankshaft from turning,
unbolt and remove the clutch housing cover
plate. Lock the starter ring gear on the
flywheel using a large screwdriver or similar
tool inserted through the cover plate aperture.
Alternatively, remove the starter motor
(Chapter 5A) and lock the ring gear through
the starter motor aperture. 5
Fully unscrew the crankshaft pulley bolt,
and withdraw the pulley from the front end of
the crankshaft. If it does not pull off by hand,
lever it free using a pair of suitable levers
positioned diagonally opposite each other
behind the pulley.
6 If required, the crankshaft front oil seal can
be renewed at this stage, as described in
Section 14.
Refitting
7 Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure ensuring that the pulley retaining
bolt is tightened to the specified torque
setting.
8 Refit the auxiliary drivebelt as described in
Chapter 1, and lower the vehicle to complete.
9 Timing chain cover -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1 Remove the sump as described in Sec-
tion 11.
2 Remove the crankshaft pulley as described
in the previous Section.
3 A combined timing cover and water pump
gasket is fitted during production; if this is still
in position, it will be necessary to drain the
cooling system and remove the water pump
as described in Chapter 3. If the water pump
and/or the timing cover have been removed at
any time, the single gasket used originally will
have been replaced by an individual gasket
for each component, in which case the water
pump can remain in position.
4 Unscrew the retaining bolts, and carefully
prise free the timing chain cover.
5 Clean the mating faces of the timing chain
cover, and the engine.
6 If necessary, renew the crankshaft front oil
seal in the timing cover prior to refitting the
cover (see Section 14).
Refitting
7 Lightly lubricate the front end of the
crankshaft and the radial lip of the timing
chain cover oil seal (already installed in the
2A•6 HCS engine in-car repair procedures
7.27c Cylinder head bolt tightening
(Stages 2 and 3) using an angle gauge
7.27b Tightening the cylinder head bolts (Stage 1)7.27a Cylinder head bolt tighteningsequence7.25 Cylinder head gasket top-facemarking (“OBEN”)
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 34 of 296
cover). Using a new gasket, fit the timing
chain cover, centring it with the aid of the
crankshaft pulley - lubricate the seal contact
surfaces beforehand. Refit and tighten the
retaining bolts but, where applicable, leave
out the timing cover bolt which also secures
the water pump at this stage.
8Where applicable, refit the water pump as
described in Chapter 3.
9 Refit the crankshaft pulley as described in
the previous Section.
10 Refit the sump as described in Section 11.
10Timing chain, sprockets and
tensioner - removal,
inspection and refitting
3
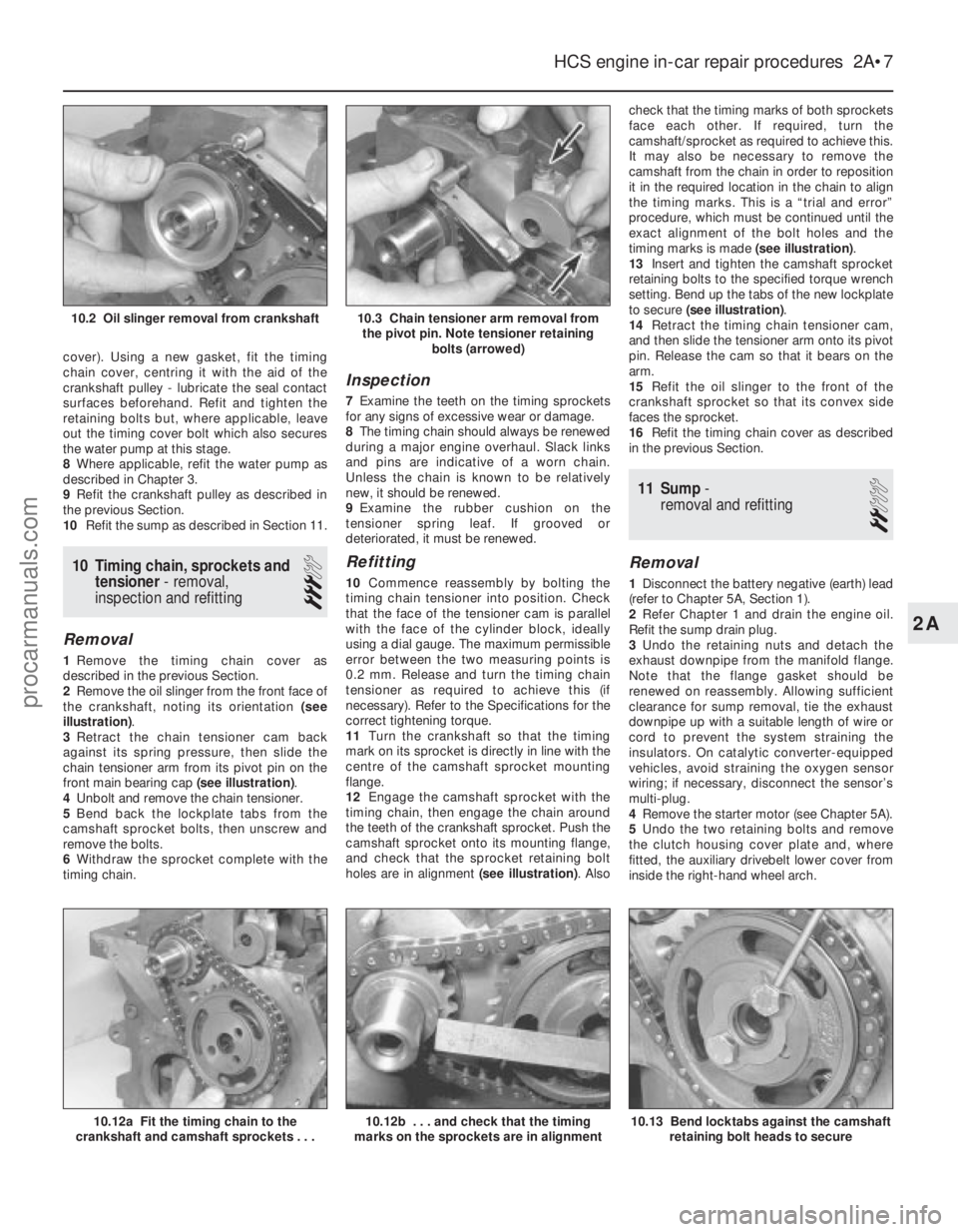
Removal
1 Remove the timing chain cover as
described in the previous Section.
2 Remove the oil slinger from the front face of
the crankshaft, noting its orientation (see
illustration) .
3 Retract the chain tensioner cam back
against its spring pressure, then slide the
chain tensioner arm from its pivot pin on the
front main bearing cap (see illustration).
4 Unbolt and remove the chain tensioner.
5 Bend back the lockplate tabs from the
camshaft sprocket bolts, then unscrew and
remove the bolts.
6 Withdraw the sprocket complete with the
timing chain.
Inspection
7 Examine the teeth on the timing sprockets
for any signs of excessive wear or damage.
8 The timing chain should always be renewed
during a major engine overhaul. Slack links
and pins are indicative of a worn chain.
Unless the chain is known to be relatively
new, it should be renewed.
9 Examine the rubber cushion on the
tensioner spring leaf. If grooved or
deteriorated, it must be renewed.
Refitting
10 Commence reassembly by bolting the
timing chain tensioner into position. Check
that the face of the tensioner cam is parallel
with the face of the cylinder block, ideally
using a dial gauge. The maximum permissible
error between the two measuring points is
0.2 mm. Release and turn the timing chain
tensioner as required to achieve this (if
necessary). Refer to the Specifications for the
correct tightening torque.
11 Turn the crankshaft so that the timing
mark on its sprocket is directly in line with the
centre of the camshaft sprocket mounting
flange.
12 Engage the camshaft sprocket with the
timing chain, then engage the chain around
the teeth of the crankshaft sprocket. Push the
camshaft sprocket onto its mounting flange,
and check that the sprocket retaining bolt
holes are in alignment (see illustration). Alsocheck that the timing marks of both sprockets
face each other. If required, turn the
camshaft/sprocket as required to achieve this.
It may also be necessary to remove the
camshaft from the chain in order to reposition
it in the required location in the chain to align
the timing marks. This is a “trial and error”
procedure, which must be continued until the
exact alignment of the bolt holes and the
timing marks is made
(see illustration).
13 Insert and tighten the camshaft sprocket
retaining bolts to the specified torque wrench
setting. Bend up the tabs of the new lockplate
to secure (see illustration) .
14 Retract the timing chain tensioner cam,
and then slide the tensioner arm onto its pivot
pin. Release the cam so that it bears on the
arm.
15 Refit the oil slinger to the front of the
crankshaft sprocket so that its convex side
faces the sprocket.
16 Refit the timing chain cover as described
in the previous Section.
11 Sump -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
2 Refer Chapter 1 and drain the engine oil.
Refit the sump drain plug.
3 Undo the retaining nuts and detach the
exhaust downpipe from the manifold flange.
Note that the flange gasket should be
renewed on reassembly. Allowing sufficient
clearance for sump removal, tie the exhaust
downpipe up with a suitable length of wire or
cord to prevent the system straining the
insulators. On catalytic converter-equipped
vehicles, avoid straining the oxygen sensor
wiring; if necessary, disconnect the sensor’s
multi-plug.
4 Remove the starter motor (see Chapter 5A).
5 Undo the two retaining bolts and remove
the clutch housing cover plate and, where
fitted, the auxiliary drivebelt lower cover from
inside the right-hand wheel arch.
HCS engine in-car repair procedures 2A•7
10.12a Fit the timing chain to the
crankshaft and camshaft sprockets . . .
10.3 Chain tensioner arm removal from the pivot pin. Note tensioner retaining bolts (arrowed)10.2 Oil slinger removal from crankshaft
10.13 Bend locktabs against the camshaftretaining bolt heads to secure10.12b . . . and check that the timing
marks on the sprockets are in alignment
2A
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 35 of 296

6Undo the eighteen bolts securing the sump
to the base of the engine crankcase, then
prise free and lower the sump. If the sump is
stuck tight to the engine, cut around the
flange gasket with a sharp knife, then lightly
tap and prise it free. Keep the sump upright as
it is lowered, to prevent spillage of any
remaining oil in it. Also be prepared for oil
drips from the crankcase when the sump is
removed.
7 Remove any dirt and old gasket from the
contact faces of the sump and crankcase, and
wash the sump out thoroughly before refitting.
Check that the mating faces of the sump are
not distorted. Check that the oil pick-up
strainer is clear, cleaning it if necessary.
Refitting
8 Clean the gasket location faces. Apply a
dab of sealing compound to the mating faces
where the ends of each cork half-gasket are
to be fitted (see illustration) . Stick the new
cork gaskets into position on the block face,
using clean thick grease to retain them, then
locate the new rubber gaskets into their slots
in the timing chain cover and rear oil seal
carrier. The lugs of the cork gasket halves fit
under the cut-outs in the rubber gaskets (see
illustration) .
9 Before offering up the sump, check that the
gap between the sump and the oil baffle is
between 2.0 and 3.8 mm (see illustration).Do not use a dented or damaged sump, as
the indicated dimension is important for
correct engine lubrication.
10
Fit the sump into position, and fit the
retaining bolts. Initially tighten them all finger-
tight, then further tighten them in the sequence
shown through Stages 1 and 2, to the torque
wrench settings specified (see illustration).
Note that different tightening sequences are
specified for the tightening stages. Final
(Stage 3) tightening is carried out after the
engine has been started and warmed up.
11 Refit the lower plate to the front face of
the clutch housing and refit the auxiliary
drivebelt lower cover.
12 Refit the starter motor.
13 Check that the downpipe and manifold
mating faces are clean, then locate a new
gasket and reconnect the exhaust downpipe
to the manifold. Where applicable, use new
self-locking nuts, and tighten securely.
14 Check that the sump drain plug is fitted
and tightened to the specified torque, then
lower the vehicle to the ground.
15 Refill the engine with oil as described in
Chapter 1.
16 Reconnect the battery, then start the
engine and run it up to its normal operating
temperature. Check that no oil leaks are
evident around the sump joint.
17 After the engine has warmed up for
approximately 15 minutes, switch it off.
Tighten the sump bolts to the Stage 3 torque
wrench setting given in the Specifications, in
the sequence shown in illustration 11.10.
12 Oil pump -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1 The oil pump is externally-mounted, on the
rear-facing side of the crankcase.
2 Chock the rear wheels then jack up the
front of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support” ).
3 Unscrew and remove the oil filter cartridge.
It should unscrew by hand, but will probably
be tight. Use a strap wrench to loosen it off, if
required. Catch any oil spillage in a suitable
container.
4 Undo the three retaining bolts and withdraw
the oil pump from the engine (see
illustration) .
5 Clean all traces of the old gasket from the
mating surfaces of the pump and engine.
Refitting
6 If the original oil pump has been dismantled
and reassembled and is to be re-used, or if a
new pump is to be fitted, it must first be
primed with engine oil prior to fitting. To do
this, turn its driveshaft and simultaneously
inject clean engine oil into it.
7 Locate a new gasket into position on the
pump mounting flange, then insert the pump,
engaging the drivegear as it is fitted (see
illustration) . Fit the retaining bolts, and
tighten to the specified torque wrench setting.
2A•8 HCS engine in-car repair procedures
12.7 Refitting the oil pump. Note the new gasket12.4 Unscrewing the oil pump retaining bolts
11.10 Sump bolt tightening sequence -
arrow indicates crankshaft pulley end of
engine
See Specifications for torque wrench settings
Stage 1 - Tighten in alphabetical order
Stage 2 - Tighten in numerical order
Stage 3 - Tighten in alphabetical order
11.9 Sump (A) and oil baffle (B) clearance details11.8b Lugs of cork gasket halves to fit
under the cut-outs in the rubber gaskets11.8a Sump gasket fitting details at the
timing chain cover end (A) and the flywheel end (B)
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 36 of 296

8Fit a new oil filter into position on
the oil pump body, as described in Chap-
ter 1.
9 Lower the vehicle to the ground, and top-
up the engine oil as described in “Weekly
Checks”.
13 Oil pump - dismantling,
inspection and reassembly
3
Dismantling
1 To inspect the oil pump components for
excessive wear, undo the retaining bolts and
remove the cover plate from the pump body.
Remove the O-ring seal from the cover face
(see illustration) .
2 Wipe the exterior of the pump housing
clean housing.
Inspection
3 Noting their orientation, extract and clean
the rotors and the inner body of the pump
housing. Inspect them for signs of severe
scoring or excessive wear, which if evident
will necessitate renewal of the complete
pump.
4 Using feeler gauges, check the clearances
between the pump body and the outer rotor,
the inner-to-outer rotor clearance, and the
amount of rotor endfloat (see illustrations).5
Check the drivegear for signs of excessive
wear or damage.
6 If the clearances measured are outside the
specified maximum clearances and/or the
drivegear is in poor condition, the complete
pump unit must be renewed.
Reassembly
7 Refit the rotors into the pump (in their
original orientation), lubricate the rotors and
the new O-ring seal with clean engine oil, and
refit the cover. Tighten the retaining bolts to
the specified torque wrench setting.
14 Crankshaft oil seals -
renewal
3
Front oil seal
1 Remove the crankshaft pulley as described
in Section 8.
2 Using a suitable claw tool, extract the oil
seal from the timing chain cover, but take care
not to damage the seal housing. As it is
removed, note the fitted orientation of the seal
in the cover.
3 Clean the oil seal housing in the timing
chain cover. Lubricate the sealing lips of the
new seal and the crankshaft stub with clean
engine oil.
4 Locate the new seal into position so that it is squarely located on the crankshaft stub and
in the housing, and is correctly orientated.
Drift it into position using a large socket,
another suitable tool, or the old seal, until the
new seal is flush with the edge of the timing
chain cover.
5
Lightly lubricate the rubbing surface of the
crankshaft pulley, then refit the pulley as
described in Section 8.
Rear oil seal
6 Remove the flywheel as described in
Section 16.
7 Using a suitable claw tool, lever the seal
from the rear seal housing (taking care not to
damage the housing). As it is removed, note
the fitted orientation of the seal.
8 Clean the seal housing, the crankshaft
rear flange face and the flywheel mating
surface.
9 One of two possible methods may be used
to insert the new oil seal, depending on the
tools available.
10 If Ford service tool No 21-011 is available,
lubricate the crankshaft flange and the oil seal
inner lip with clean engine oil. Position the
seal onto the service tool (ensuring correct
orientation), then press the seal into its
housing.
11 If the service tool is not available, remove
the engine sump (Section 11), then unscrew
the Torx-head bolts retaining the rear seal
housing in position, and remove the
seal housing from the rear face of the cylinder
block. New gaskets will be required for both
the seal housing and the sump when refitting.
Clean the seal housing seat and the mating
surfaces of the sump and the crankcase. To fit
the seal squarely into its housing without
damaging either component, place a flat
block of wood across the seal, then carefully
tap the seal into position in the housing (see
illustration) . Do not allow the seal to tilt as it
is being fitted. Lubricate the crankshaft flange
and the oil seal inner lip with clean engine oil,
then with a new gasket located on the seal
housing/crankcase face, fit the housing into
position. Take care not damage the seal lips
as it is passed over the crankshaft rear flange
HCS engine in-car repair procedures 2A•9
13.4b Checking the inner rotor-to-outer rotor clearance13.4a Checking the outer body-to-rotor clearance13.1 Extract the O-ring from the groove inthe oil pump
14.11a Positioning the crankshaft rear oilseal in its housing13.4c Checking the rotor endfloat
2A
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 37 of 296

(see illustration). Centralise the seal on the
shaft, then insert and tighten the housing
retaining bolts to the specified torque setting.
Refit the sump with reference to Section 11.
12 Check that the crankshaft rear flange
and the flywheel mating faces are clean, then
refit the flywheel as described in Section 16.
15 Engine/transmission mountings - inspection and
renewal
2
Inspection
1 The engine/transmission mountings seldom
require attention, but broken or deteriorated
mountings should be renewed immediately, or
the added strain placed on the driveline
components may cause damage or wear.
2 During the check, the engine/transmission
must be raised slightly, to remove its weight
from the mountings.
3 Chock the rear wheels then jack up the
front of the car and support it on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support” ). Position
a jack under the sump, with a large block of
wood between the jack head and the sump,
then carefully raise the engine/transmission
just enough to take the weight off the
mountings.
4 Check the mountings to see if the rubber is
cracked, hardened or separated from the metal components. Sometimes, the rubber
will split right down the centre.
5
Check for relative movement between each
mounting’s brackets and the
engine/transmission or body (use a large
screwdriver or lever to attempt to move the
mountings). If movement is noted, lower the
engine and check-tighten the mounting
fasteners.
Renewal
6 The engine mountings can be removed if
the weight of the engine/transmission is
supported by one of the following alternative
methods.
7 Either support the weight of the assembly
from underneath using a jack and a suitable
piece of wood between the jack saddle and
the sump or transmission (to prevent
damage), or from above by attaching a hoist
to the engine. A third method is to use a
suitable support bar with end pieces which
will engage in the water channel each side of
the bonnet lid aperture. Using an adjustable hook and chain connected to the engine, the
weight of the engine and transmission can
then be taken from the mountings.
Engine right-hand mounting
8
Unscrew and remove the mounting side
bolt from under the right-hand wheel arch
(see illustration) .
9 Unscrew and remove the mounting
retaining nut and washer from the suspension
strut cup retaining plate (see illustration).
10 Undo the three bolts securing the
mounting unit to the cylinder block. The
mounting unit and bracket can then be
lowered from the engine (see illustration).
11 Unbolt and remove the mounting from its
support bracket.
Transmission bearer and mountings
12 Unscrew and remove the two nuts
securing the mountings (front and rear) to the
transmission bearer (see illustration).
13 Support the transmission bearer, then
undo and remove the four retaining bolts from
the floorpan, two at the front and two at the
2A•10 HCS engine in-car repair procedures
15.12 Exploded view of the transmission bearer mountings
15.10 Undo the three bolts securing the
mounting assembly to the cylinder block
and withdraw the mounting
15.9 Unscrew and remove the mountingretaining nut and washer from the
suspension strut cup retaining plate15.8 Unscrew and remove the engine
mounting side bolt (arrowed) from under the wheel arch14.11b Fitting the rear oil seal housing
with a new gasket in position on the rear face of the cylinder block
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su